Effects of crude protein and energy levels on digestive enzyme activities in duck jejunal fluid
-
摘要:目的
研究日粮蛋白质和能量水平对番鸭空肠液中几种主要消化酶活性的影响。
方法采用3×3双因素完全随机设计,将27只24周龄体质量相近的公番鸭随机分为9组,每组3只鸭,分别饲喂9种不同能量蛋白质配比的日粮,通过实施瘘管手术收集空肠液,并测定肠液中淀粉酶、胰蛋白酶、糜蛋白酶和脂肪酶的活性。
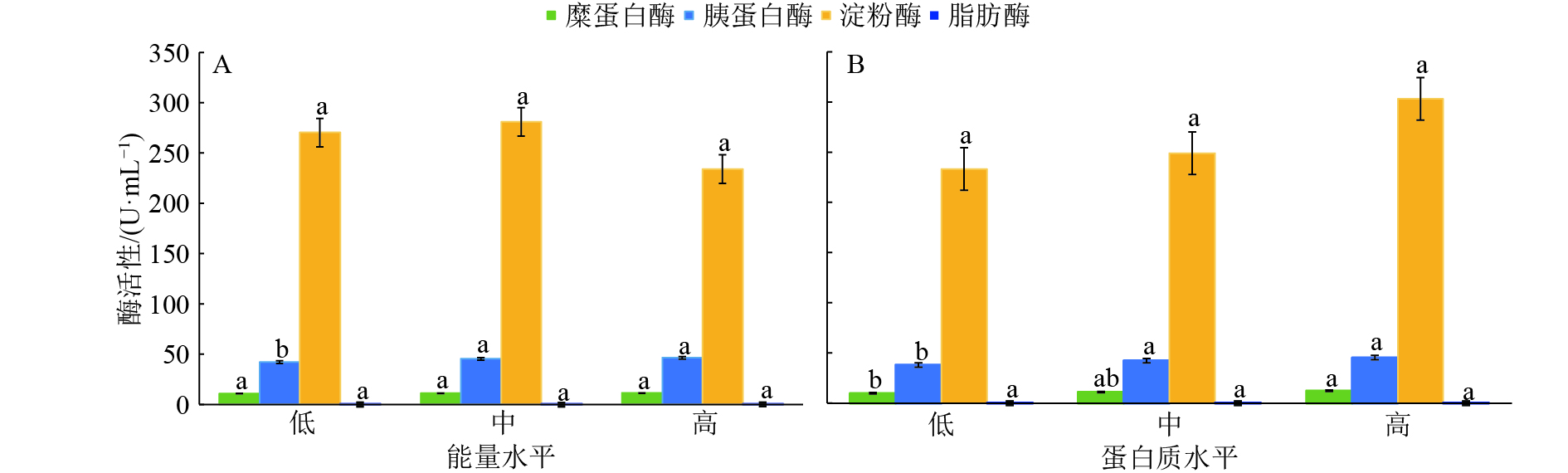
结果随着能量水平的升高,高、中能量组的胰蛋白酶活性显著高于低能量组(P<0.05),糜蛋白酶、淀粉酶和脂肪酶活性差异不显著;随着粗蛋白水平的升高,高、中蛋白质组的胰蛋白酶活性显著高于低蛋白组(P<0.05),高蛋白质组的糜蛋白酶活性显著高于低蛋白质组(P<0.05),淀粉酶和脂肪酶活性差异不显著。蛋白质和能量水平对番鸭空肠液中几种主要的消化酶活性无明显交互效应。
结论本试验条件下,能量水平对胰蛋白酶活性有显著影响,蛋白质水平对胰蛋白酶和糜蛋白酶活性有显著影响,能量和蛋白质水平对淀粉酶和脂肪酶活性均无显著影响。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of dietary protein and energy levels on digestive enzyme activities in the jejunal fluid of Muscovy duck.
MethodA 3×3 factorial and completely randomized design was conducted. Totally 27 male Muscovy ducks were randomly divided into 9 groups with 3 ducks per group, and fed diets with 9 different compositions of energy and protein. Jejunal digesta was collected by fistula surgery and the activities of amylase, trypsin, chymotrypsin and lipase in jejunal fluid were determined.
ResultWith the increase of energy level, trypsin activities in high and medium energy groups were significantly higher compared with low energy group(P<0.05), while chymotrypsin, amylase and lipase activities did not differ significantly. With the increase of crude protein level, trypsin activities in high and medium protein groups were significantly higher compared with low protein group(P<0.05), chymotrypsin activity in high protein group was significantly higher compared with low protein group(P<0.05), while amylase and lipase activities did not differ significantly. Protein and energy levels had no obvious interaction effect on digestive enzyme activities in the jejunal fluid of Muscovy duck.
ConclusionUnder this experimental condition, energy level has a significant effect on trypsin activity, and protein level has a significant effect on trypsin and chymotrypsin activities. Neither energy nor protein level has significant effect on amylase and lipase activities.
-
Keywords:
- protein /
- energy /
- Muscovy duck /
- jejunal fluid /
- digestive enzyme /
- diet
-
三七Panax notoginseng是中国的名贵中药材,在药材市场需求量大,截止2017年云南省三七种植面积已达到3万hm2[1]。三七播种主要依靠人工完成,播种量为270~300万粒/hm2,种植成本高。现有的机械式三七播种机在播种作业前需要对种子进行筛分,播种机对种子大小的适用性不好。其次,由于三七种子的表皮容易破损,在一定程度上机械式清种装置会造成种子的破损,因此研制气力式三七精密排种器很有必要。
与机械式排种器相比,气吹式排种器充种效果好,对种子的外形尺寸适应性好,利用气流清种可以减少对种子的损伤,并且能够在较高速度下作业,播种效率比较高[2]。在国外,英国Ferguson公司研发的MF543型气吹式播种机利用机械式侧充型孔囊种,在清种区多余的种子被低压气流吹掉,可以播种多种作物[3];瑞典Vaderstand公司设计的气力圆盘式排种器通过气流完成种子的充填,效果良好;Kongskilde公司为了减少种子堵塞窝眼,改良了气吹式排种器的结构[4];Zulin等[5]对气力式排种器进行了改进,考察了排种盘速度和气流速度等与排种性能之间的关系。
国内的研究大多借鉴了Aeromat-Ⅱ型气吹式排种器[6-8]。早期马成林等[9]和胡树荣等[10]通过量纲理论的分析,对气吹式排种器的锥孔模型进行了试验研究,设计了一种新的型孔结构;刘佳等[11]和崔涛等[12]仿真分析了清种气嘴截面倾角,通过试验找出了气吹压力的最佳范围,并利用单因素试验考察了气吹压力对于排种效果的影响,设计了一种适用高速作业的机械气力组合式排种器;孙裕晶等[13]采用均匀设计方法进行了大豆的播种,考察了充种角、清种角和排种性能参数的关系;廖庆喜等[14]和雷小龙等[15]对不同条件下的气室流场进行仿真,运用EDEM-CFD耦合仿真方法分析了油麦在输种管道中的迁移规律;李成华等[16]利用三维软件对气吹排种器进行结构设计,找出影响排种器排种性能的主要因素是型孔结构参数;胡靖明等[17]通过对比有无平衡气孔2种模式,设计了一种适用于小粒种子的排种器气室模型。
以上研究表明,现阶段气吹式排种器已经被应用到多种粮食作物的播种过程中,但是将其应用到三七的种植上的研究较少。本文设计一种播种三七的气吹式排种器,通过理论分析与数值模拟,确定排种器的结构和工作参数,利用正交试验方法,进行排种性能试验,寻求可以提高排种性能的最优参数组合。
1. 气吹式排种器总体结构及工作原理
气吹式三七排种器由排种轮、清种气嘴、进种管、排种轴、壳体等组成,其结构如图1所示。
![]() 图 1 三七气吹式排种器结构示意图1:排种轴,2:排种轮,3:壳体,4:型孔,5:清种气嘴,6:风管接口,7:进种管,8:种层高度调节板,9:充种室,10:投种口Figure 1. Structure diagram of air-blowing seed-metering device for Panax notoginseng1:Seeding shaft,2:Seeding wheel,3:Shell,4:Type hole,5:Seed clearing nozzle,6:Duct interface,7:Seed tube,8:Seed height adjustment plate,9:Seed filling room,10:Seeding port
图 1 三七气吹式排种器结构示意图1:排种轴,2:排种轮,3:壳体,4:型孔,5:清种气嘴,6:风管接口,7:进种管,8:种层高度调节板,9:充种室,10:投种口Figure 1. Structure diagram of air-blowing seed-metering device for Panax notoginseng1:Seeding shaft,2:Seeding wheel,3:Shell,4:Type hole,5:Seed clearing nozzle,6:Duct interface,7:Seed tube,8:Seed height adjustment plate,9:Seed filling room,10:Seeding port充种室下端设计成斜面,其角度大于种子的休止角,便于充种时种子流动。充种室内的种层高度调节板,可以随着种子的流动情况进行种层高度的调节。排种器工作时,排种器由地轮带动转动,当充种室内的种子充入到排种轮的型孔时,根据所设计的型孔直径和深度大小,一般在充种过程中会充入2~3粒三七种子。排种轮转动进入清种区,在气流作用下型孔上端多余的种子被吹出,型孔底部的种子在气流压力下会保留在型孔中,完成单粒充种过程。清种气嘴轴线与水平面垂直,竖直向下,气吹压力由风机提供,可以根据需要进行调节。随着排种轮转到护种区,气压消失,由排种器的壳体完成护种,到达投种口上方时,种子在重力的作用下掉落,实现整个排种过程。
2. 排种器关键部件设计与参数分析
2.1 排种轮的直径
排种轮作为排种器的关键部件,其直径会受到排种器的整体结构、型孔数量、制造成本等因素[18-20]的影响。排种轮结构参数如图2所示。
为了研究排种轮直径与型孔充种时间的关系,由公式得:
$$t = \frac{{{l_{\rm{c}}}}}{{{v_{\rm{p}}}}}\text{,}$$ (1) $${l_{\rm{c}}} = \theta \frac{{D{\rm{ - }}h}}{2}\text{,}$$ (2) $${v_{\rm{p}}} = \pi {n_{\rm{p}}}\frac{{D{\rm{ - }}h}}{{60}}\text{,}$$ (3) 式中t为型孔充种时间,s;lc为充种区弧长,mm;vp为排种轮的线速度,m/s;D为排种轮直径,mm;np为排种轮转速,r/min;h为型孔深度,mm;θ为型孔充种区弧度,rad。
由式(1)~(3)得出:
$$t = \frac{{30\theta }}{{\pi {n_{\rm{p}}}}}\text{,}$$ (4) 由式(4)可知,型孔充种时间t只与排种轮转速和型孔充种区弧度有关,但排种轮的直径过小,充种区弧长也会变小,当排种轮上型孔数量一定时,为了保证达到所要求的株距,就必须提高排种轮的转速,这样便不利于充种、清种,会影响排种器的作业质量。根据播种作业速度以及排种器的整体尺寸等因素,选取排种轮直径D=200 mm,材料为聚乳酸(Polylactice acid),简称PLA塑料,利用3D打印制作。
2.2 型孔的结构参数设计
2.2.1 型孔形状及尺寸设计
型孔的形状尺寸会直接影响排种效果。根据已有研究[21],将型孔设计成圆锥形,如图3所示。
为了便于充种,保证良好的充种性能,则型孔上端直径(d1)为:
$${d_1} \geqslant d + \left( {1.0 \sim 1.5} \right)\text{。}$$ (5) 根据文献[22]可知三七种子长度为5.2~7.2 mm,宽度为4.8~6.8 mm,高度为4.0~6.0 mm,种子平均直径(d)为5.6 mm。同时,由于三七种子可能以自身任一状态随机充入型孔,为了保证充种质量,型孔的上端直径应大于2倍的种子直径,从而确定型孔上端直径为12 mm。
加大型孔底部直径可能造成充种易清种难的情况产生,一般选取型孔下端直径(d2)在4~5 mm范围内比较合适。由
$${d_2} < d\text{,}$$ (6) 确定型孔下端直径为4 mm。
由于三七种子大小不均匀,且形状不规则,型孔底部开有宽为2 mm,深为4 mm的环形内槽,正压气流通过内槽形成压差,保证了单粒充种。型孔深度(h)应保证可以将最大粒径的种子囊入,并且当有多余种子充入时,可以利用气流将其清除出来,由
$$d < h \leqslant 1.5d\text{,}$$ (7) 确定型孔深度为8 mm。
2.2.2 排种轮上型孔数量
在相同的作业速度和株距下,同一直径的排种轮,型孔数越多,排种轮线速度越低,型孔的充填性能越好。而型孔数量的多少又受到排种轮直径的制约。根据排种轮上型孔数的计算公式:
$${{Z}} = \frac{{\pi \left( {{{D - }}h} \right){v_{\rm{m}}}}}{{s{v_{\rm{p}}}\left( {1{\rm{ - }}c} \right)}}\text{,}$$ (8) 式中,Z为型孔数;vm为机具的作业速度,取0.5 m/s;s为播种株距,mm;c为滑移系数。
根据三七种植的农艺要求,株距为50 mm左右较为理想,属于密集型播种模式;地轮的滑移系数(c)一般在0.05~0.12之间,取0.1;排种轮转速(np)取20 r/min,联立式(3)、(8),确定型孔数量Z=34。
2.3 清种风压
2.3.1 清种风压力学模型
清种风压的选取直接影响到排种质量。气吹式排种器为了满足种子不分级播种的要求,排种轮上的型孔比一般播种三七种子所用的窝眼轮式排种器上的型孔大。为了达到精密播种的目的,在清种区则需要清除多余的种子。选取适宜的风压,才可以压附接近型孔底部的种子,同时,正压气流在型孔壁面上形成逸出的分流,将型孔上端的种子进行清除[23]。
以型孔上端将被清除的种子作为研究对象,具体的受力如图4所示。
![]() 图 4 清种区种子受力简化模型Fq:种子受到的清种压力,Fl:惯性离心力,FN:型孔侧面对种子的支持力,Ff:种子与型孔侧面的摩擦力,α:压力Fq与x轴的夹角,β:y轴与水平面夹角,δ:摩擦力Ff与y轴的夹角,ε:型孔锥角,ω:排种轮角速度,G:种子的重力,O:排种轮转动中心,1、2:种子Figure 4. Simplified model of force on the seed in seed clearing zoneFq: Air-blowing force on the seed, Fl: Inertial centrifugal force, FN: Supporting force on the side of type hole, Ff: Friction force between the seed and the side of type hole, α: Angle between Fq and x-axis, β: Angle between y-axis and the horizontal plane, δ: Angle between Ff and y-axis, ε: Cone angle of the type hole, ω: Angular velocity of the seeding wheel, G: Seed gravity, O: Rotation center of the seeding wheel, 1 and 2: Seed
图 4 清种区种子受力简化模型Fq:种子受到的清种压力,Fl:惯性离心力,FN:型孔侧面对种子的支持力,Ff:种子与型孔侧面的摩擦力,α:压力Fq与x轴的夹角,β:y轴与水平面夹角,δ:摩擦力Ff与y轴的夹角,ε:型孔锥角,ω:排种轮角速度,G:种子的重力,O:排种轮转动中心,1、2:种子Figure 4. Simplified model of force on the seed in seed clearing zoneFq: Air-blowing force on the seed, Fl: Inertial centrifugal force, FN: Supporting force on the side of type hole, Ff: Friction force between the seed and the side of type hole, α: Angle between Fq and x-axis, β: Angle between y-axis and the horizontal plane, δ: Angle between Ff and y-axis, ε: Cone angle of the type hole, ω: Angular velocity of the seeding wheel, G: Seed gravity, O: Rotation center of the seeding wheel, 1 and 2: Seed为了便于分析,将被清除的种子标记为种子1,型孔底部的种子标记为种子2,并将其简化为刚性小球,其几何中心为种子的质心。假设种子2被压附在型孔底部不发生移动,以种子1在气流作用下即将被吹出的临界状态为条件,沿型孔弧面的切向和法向建立坐标系,型孔中的2粒种子之间没有相互影响,建立受力方程:
$$\left\{ \begin{aligned} & \sum {{{\rm{F}}_x}:{F_{\rm{N}}}\sin \left( {\frac{\pi }{2}{\rm{ - }}\frac{\varepsilon }{2}} \right) + {F_{\rm{f}}}\sin \delta =}\\ &\quad { G\cos \beta +{F_{\rm{q}}}\cos \alpha } \\ & \sum {{F_y}:{F_{\rm{l}}} + {F_{\rm{q}}}\sin \alpha + {F_{\rm{N}}}\cos \left( {\frac{\pi }{2}{\rm{ - }}\frac{\varepsilon }{2}} \right) =}\\ &\quad {G\sin \beta + {F_{\rm{f}}}\cos \delta } \\ & {F_{\rm{l}}} = mr{\omega ^2} \\ & {F_{\rm{f}}} = \mu {F_{\rm{N}}} \\ &G = m{\rm g} \\ &\omega = \frac{{\pi {n_{\rm{p}}}}}{{30}} \\ \end{aligned} \right.\text{,}$$ (9) 式中,Fl为惯性离心力,N;Fq为种子受到的清种压力,N;FN为型孔侧面对种子的支持力,N;Ff为种子与型孔侧面的摩擦力,N;α为压力Fq与x轴的夹角,(°);β为y轴与水平面夹角,(°);δ为摩擦力Ff与y轴的夹角,(°);μ为排种轮与种子间的摩擦系数,μ=0.3;ε为型孔锥角,(°);m为单粒三七种子质量,kg;r为种子质心与传动轴中心间距离,mm;ω为排种轮的角速度,rad/s;g为重力加速度,m/s2。
根据图3和型孔的结构参数,可以得到:
$$\delta = \frac{\varepsilon }{2}\text{,}$$ (10) 由型孔的结构参数计算可得型孔锥角ε为52°。联立式(9)、(10),得出种子被吹出型孔的临界条件为:
$$\begin{split}&{F_{\rm{q}}} \geqslant\left\{ {{\sqrt 2 m{\rm g}\sin \left( {\beta + \frac{\pi }{4}} \right) + m{\rm g}\cos \beta \cos \frac{\varepsilon }{2}}}\right.\\ &\quad\left.\left.{{\left[ {\left( {\mu {\rm{ - }}1} \right)\cos \frac{\varepsilon }{2}{\rm{ - }}\left( {\mu + 1} \right)\sin \frac{\varepsilon }{2}} \right]{{ - mr}}{\omega ^2}}}\right\}\right/{{\sqrt 2 \sin \left( {\alpha {\rm{ - }}\frac{\pi }{4}} \right)}}\text{。} \end{split} $$ (11) 在清种过程中,根据力的相互作用原理,可知作用在种子上的清种压力与种子在清种过程中受到的绕流阻力相等,根据流体力学中绕流阻力公式:
$${F_{\rm{q}}} = kA\frac{{\rho v_0^2}}{2}\text{,}$$ (12) 式中,k为与种子形状和雷诺数有关的无因次系数;A为种子在垂直气流方向的投影面积,mm2;ρ为空气密度,常态下ρ=1.21 kg/m3;v0为气流的流速,m/s。
假设种子为刚性球体,可得:
$$A = \frac{{\pi {d^2}}}{4}\text{。}$$ (13) 气嘴出口处清种风压与流速的关系有:
$${{P}} = \frac{1}{2}\rho v_0^2\text{,}$$ (14) 式中,P为清种风压,kPa。联立式(12)~(14),可得:
$${F_{\rm{q}}} = \frac{{k\pi {d^2}{{P}}}}{4}\text{。}$$ (15) 将式(15)代入式(11),可得:
$$\begin{split}&\frac{{k\pi {d^2}{{P}}}}{4} \geqslant \left\{{{\sqrt 2 m{\rm g}\sin \left( {\beta + \displaystyle\frac{\pi }{4}} \right) + m{\rm g}\cos \beta \cos \displaystyle\frac{\varepsilon }{2}}}\right.\\ &\quad\left.\left.{{\left[ {\left( {\mu {\rm{ - }}1} \right)\cos \frac{\varepsilon }{2}{\rm{ - }}\left( {\mu + 1} \right)\sin \frac{\varepsilon }{2}} \right]{{ - mr}}{\omega ^2}}}\right\}\right/{{\sqrt 2 \sin \left( {\alpha {\rm{ - }}\displaystyle\frac{\pi }{4}} \right)}}\text{,}\end{split}$$ (16) 由式(16)得出:型孔中多余种子能否被吹出与型孔的锥角ε,排种轮转速np,清种风压P等诸多因素有关。经过前期试验,选取清种风压P应大于0.4 kPa。
2.3.2 清种风压数值模拟
1)假设及初始条件:为了确定清种风压的最佳范围,减少试验次数,对清种风压进行了仿真分析。将排种器模型简化为排种轮、外壳、气嘴和挡种板4个部分,利用ICEM对排种器壳体划分网格,并导入Fluent中进行压力模拟。假设流场气体为不可压缩气体,排种器壳体边界不漏气,进气口压力均匀。设置流体为空气,密度为1.205 kg/m3,黏度为1.83×10–5 Pa·s,模拟过程采用
$\kappa - \varepsilon $ 模型,将气嘴风压出口设为速度入口,投种口为压力出口边界条件,压力值为0。选择进入气嘴风压分别为0.4、0.5、0.6、0.7 kPa,对排种器内压力分布云图进行分析。图5为不同风压条件下排种器内部压力云图。2)仿真结果与分析:在排种过程中,气体与种子彼此会产生相互作用力,气流较高的速度将会对种子产生曳力,而种子又会对气流产生阻力[24]。由图5中可以看出,充种区内气流形成的旋涡会在一定程度上扰动种子,提高了排种器的充种性能。沿排种轮轮廓外部分布的气流可以清除多余的种子,轮廓内的气流形成压差,对型孔内的种子进行压附,防止种子被气流吹出,造成漏播。
如图5a所示,当清种风压为0.4 kPa时,由于气嘴出口处压力较小,气流自气嘴流出分散到排种器腔体与排种轮的清种区域,型孔上端由于气流作用,在排种轮轮廓边缘形成的高速气流对于多余的种子可以进行及时清除,同时,型孔下端泄出的压力又可以保留住单粒种子;如图5b所示,当清种风压为0.5 kPa时,气流作用较之前更为明显,排种器腔体内部的流场对于充种更为有利,在充种区形成的涡流可以增大对于种子的扰动,提高充种性能;如图5c所示,当清种风压为0.6 kPa时,排种器内部流场情况与0.5 kPa时类似。如图5d所示,当清种风压为0.7 kPa时,在型孔边缘形成较大涡流,排种器内部气流回流较大,对于充入的种子作用力较大,可能将型孔内部的种子全部吹出,增大了漏播的可能性,在一定程度上会影响充种。实际工作过程中,考虑到振动、排种器壳体泄气等因素影响,实际所需要的风压应大于0.4 kPa。结合仿真结果,选取清种风压为0.4~0.7 kPa。
3. 气吹式排种器排种性能试验
3.1 试验条件
利用台架试验验证气吹式排种器的排种性能[25],以便得到较优的工作参数组合。试验装置由气吹式三七精密排种器、气力管道、KANOMAX6036型热式风速风压测试仪和JPS-12计算机视觉排种器性能检测试验台组成。KANOMAX6036型热式风速风压测试仪的风压测量范围为0~5 kPa,精度为读数的±3%。排种器的作业速度可以通过试验台上的控制柜进行调控;清种风压的调节由控制柜对试验台上配套风机的控制来完成,利用风速风压测试仪测定压力值。试验装置组成如图6所示。
3.2 试验方法
根据国家标准GB/T6973—2005[26],选用正交表L16(43)进行正交试验。选用云南文山优质三七种子作为试验对象,选取粒距的合格指数、漏播指数、重播指数为试验指标,在JPS-12排种器性能检测试验台上进行排种性能试验。排种器在试验时保持不动,种床带进行移动,通过将三七种子排落在涂有油层的种床带上,完成近似于田间播种的过程。通过图像采集处理系统完成实时检测种子的粒距情况[27],每次试验测量200粒种子,并重复5次取平均值。根据前期试验,选取作业速度范围为0.4~1.0 m/s,种层高度记为H,范围为50~110 mm,清种风压为0.4~0.7 kPa,因素水平表如表1所示。
表 1 排种性能试验因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of seeding performance test水平
Level作业速度/(m·s–1)
Operating
speed种层高度/mm
Seed layer
height清种风压/kPa
Air-blowing pressure1 0.4 50 0.4 2 0.6 70 0.5 3 0.8 90 0.6 4 1.0 110 0.7 3.3 试验结果与分析
因素在不同水平下极差大小与该因素对试验指标的影响程度有直接关系。根据表2,对试验结果进行极差分析,通过表3试验结果分析表明,影响合格指数的因素主次顺序为B、A、C,较优的因素组合为B3A2C2;影响漏播指数的因素主次顺序为B、C、A,较优的因素组合为B3C2A2;影响重播指数的因素主次顺序为B、A、C,较优的因素组合为B2A2C3。
表 2 排种性能试验设计与结果Table 2. Design and result of seeding performance test试验序号
Test No.因素 Factor 指标 Index 作业速度
Operating speed (A)种层高度
Seed layer height (B)清种风压
Air-blowing pressure (C)合格指数
Eligible index漏播指数
Leakage sowing index重播指数
Repeat sowing index1 1 1 1 57.23 37.03 5.74 2 1 2 2 76.49 18.52 4.99 3 1 3 3 87.91 3.42 8.67 4 1 4 4 68.63 12.16 19.21 5 2 1 2 79.37 13.56 7.07 6 2 2 1 79.43 14.74 5.83 7 2 3 4 89.34 4.24 6.42 8 2 4 3 82.52 3.53 13.95 9 3 1 3 66.71 28.16 5.13 10 3 2 4 70.45 27.32 2.23 11 3 3 1 76.37 7.95 15.68 12 3 4 2 69.72 3.34 26.94 13 4 1 4 49.67 36.83 13.5 14 4 2 3 67.52 23.95 8.53 15 4 3 2 79.47 3.39 17.14 16 4 4 1 55.45 8.12 36.43 表 3 排种性能试验结果的极差分析1)Table 3. Range analysis of seeding performance test result指标
Index项目
ItemA B C 合格指数
Eligible
indexk1 72.565 63.245 67.120 k2 82.665 73.472 76.263 k3 70.813 83.273 76.165 k4 63.028 69.080 69.523 R 19.637 20.028 9.143 漏播指数
Leakage
sowing indexk1 17.782 28.895 16.960 k2 9.018 21.133 9.703 k3 16.693 4.750 14.765 k4 18.073 6.787 20.137 R 9.055 24.145 10.434 重播指数
Repeat
sowing indexk1 9.652 7.860 15.920 k2 8.317 5.395 14.035 k3 12.495 11.977 9.070 k4 18.900 24.133 10.340 R 10.583 18.738 6.850 1) A、B 和 C 分别表示作业速度、种层高度和清种风压
1) A, B and C represent operating speed, seed layer height and air blowing pressure, respectively利用Design-Expert 8.061软件对试验结果进行方差分析,进一步分析因素对试验指标影响的显著性。如表4所示。可知作业速度、种层高度和清种风压都能显著影响各项指标。作业速度越小,型孔通过充种区时间越长,种子充入型孔的机会增大,随着作业速度的增大,型孔在充种区的时间变短,漏播指数会增大。种层高度较低时,充种角度小于型孔的锥角,种子不易保留在型孔中,会造成漏播指数增大;种层高度较大时,型孔中会充入多颗种子,增加了清种的难度,一定程度上造成重播指数增大。清种风压较小时,对于充入型孔中多余的种子不能及时清除,会造成重播;清种风压较大时,气流有可能将型孔中的种子全部吹出,从而造成漏播。结合试验结果,发现前期合格指数随清种风压的增大而增大,但是当清种风压增大为0.7 kPa时,合格指数会减小,与之前仿真分析的过程一致,验证了利用Fluent模拟确定清种风压的可行性。综上,为了保证排种器良好的排种性能,便需要对这3个因素选取合适的参数组合。
表 4 排种性能试验结果的方差分析1)Table 4. Variance analysis of seeding performance test result指标
Index变异来源
Variation sourceSS DF F 合格指数
Eligible
indexA 782.77 3 61.151** B 856.51 3 66.912** C 260.73 3 20.369** R 25.60 6 漏播指数
Leakage
sowing indexA 220.90 3 5.959* B 1 610.30 3 43.437** C 230.97 3 6.230* R 74.14 6 重播指数
Repeat
sowing indexA 265.84 3 11.454** B 829.99 3 35.762** C 121.53 3 5.236* R 46.42 6 1) A、B、C 和 R 分别表示作业速度、种层高度、清种风压和残差;“*” 和 “**” 分别影响显著和极显著
1) A, B, C and R represent operating speed, seed layer height, air blowing pressure and residual, respectively; “*” and “**” represent significant effects at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively通过上述分析,综合3个因素对试验指标的影响,在保证合格指数最大,漏播指数和重播指数较小的原则下,确定较优组合为B3A2C2,即种层高度为90 mm、作业速度为0.6 m/s、清种风压为0.5 kPa。对较优组合进行试验验证,在相同的试验条件下重复5次验证试验,得到粒距合格指数为90.48,漏播指数为4.24,重播指数为5.28。
4. 结论
1)根据三七种子的物理机械特性以及种植农艺要求,通过理论计算与分析,确定了主要结构参数,设计出了一种适用于播种三七的气吹式精密排种器。
2)利用Fluent软件模拟不同风压条件下排种器内部流场,对比分析了流场内压力与排种性能参数的关系,确定了清种风压的范围为0.4~0.7 kPa,为后期的试验提供了依据。
3)通过三因素四水平的正交试验,确定了影响排种器排种性能因素的主次顺序,依次为种层高度、作业速度、清种风压。根据试验结果,优化参数组合,在种层高度为90 mm、作业速度为0.6 m/s、清种风压为0.5 kPa时,粒距合格指数为90.48,漏播指数为4.24,重播指数为5.28。
-
表 1 番鸭术后恢复期配方
Table 1 Recovery formula of Muscovy duck after surgery
原料 玉米 豆粕 鱼粉 大豆油 麦麸 石粉 磷酸氢钙 NaCl 赖氨酸
盐酸盐DL–蛋
氨酸1)预混料2) w/% 64.00 16.00 3.45 0.67 13.32 1.10 0.42 0.40 0.06 0.08 0.50 代谢能/(MJ·kg–1) 营养组成及质量分数/% 粗蛋白质 钙 总磷 总赖氨酸 总蛋氨酸 11.80 16.00 0.80 0.63 0.83 0.34 1)该原料的初始质量分数为98%;2)预混料为每千克提供:维生素A 3×107 IU;维生素D3 5×106 IU;维生素K3 15 g;维生素E 40 g;维生素B1 8 g;维生素B2 22 g;维生素B6 15 g;维生素B12 0.1 g;烟酰胺 200 g;叶酸 2 g;D–泛酸 40 g;生物素 0.2 g;Fe 20 g;Cu 10 g;Mn 50 g;Zn 70 g;Co 0.2 g;I 0.3 g;Se 0.2 g 表 2 试验日粮组成及营养成分
Table 2 Composition and nutrient levels of experimental diets
组别 日粮组成及质量分数/% 玉米 豆粕 鱼粉 大豆油 麦麸 石粉 磷酸氢钙 NaCl 赖氨酸
盐酸盐DL–蛋
氨酸1)预混料2) 1 62.00 12.48 3.00 0.76 18.77 1.15 0.48 0.40 0.33 0.13 0.50 2 60.00 15.00 4.36 0.49 17.63 1.05 0.30 0.40 0.19 0.08 0.50 3 58.60 17.20 6.00 0.04 16.15 0.95 0.07 0.40 0.05 0.04 0.50 4 63.00 12.48 3.70 2.00 15.99 1.10 0.40 0.40 0.31 0.12 0.50 5 63.00 16.00 4.60 1.28 12.66 1.03 0.28 0.40 0.17 0.08 0.50 6 61.60 19.00 5.70 0.88 10.78 0.95 0.13 0.40 0.03 0.03 0.50 7 65.00 12.50 4.50 2.98 12.34 1.04 0.33 0.40 0.29 0.12 0.50 8 64.00 17.00 4.63 2.57 9.36 1.02 0.29 0.40 0.16 0.07 0.50 9 63.00 19.00 6.44 2.02 7.66 0.90 0.05 0.40 0.01 0.02 0.50 代谢能/
(MJ·kg–1)营养组成及质量分数/% 粗蛋白质 真蛋白质 淀粉 钙 总磷 总赖氨酸 总蛋氨酸 11.50 15.00 14.69 4.87 0.80 0.62 0.95 0.36 11.50 16.50 15.61 3,91 0.80 0.62 0.95 0.34 11.50 18.00 16.31 4.67 0.80 0.62 0.96 0.33 12.00 15.00 14.45 3.82 0.80 0.60 0.95 0.36 12.00 16.50 15.29 3.63 0.80 0.59 0.96 0.34 12.00 18.00 16.51 4.29 0.80 0.59 0.96 0.33 12.50 15.00 14.81 3.38 0.80 0.59 0.96 0.37 12.50 16.50 15.81 3.85 0.80 0.58 0.96 0.34 12.50 18.00 16.96 3.24 0.80 0.58 0.96 0.33 1)该原料的初始质量分数为98%;2)预混料为每千克提供:维生素A 3×107 IU;维生素D3 5×106 IU;维生素K3 15 g;维生素E 40 g;维生素B1 8 g;维生素B2 22 g;维生素B6 15 g;维生素B12 0.1 g;烟酰胺 200 g;叶酸 2 g;D–泛酸 40 g;生物素 0.2 g;Fe 20 g;Cu 10 g;Mn 50 g;Zn 70 g;Co 0.2 g;I 0.3 g;Se 0.2 g 表 3 日粮能量和粗蛋白水平对番鸭空肠液中消化酶活性的影响
Table 3 Effects of dietary energy and crude protein levels on digestive enzyme activities in jejunal fluid of Muscovy duck
能量
水平蛋白质
水平酶活性/(U·mL–1) 淀粉酶 胰蛋
白酶糜蛋
白酶脂肪酶 低 低 237.07 33.92 9.15 0.058 8 中 261.32 38.92 12.14 0.025 0 高 312.96 41.51 11.58 0.043 8 中 低 316.09 46.70 11.02 0.031 3 中 238.63 48.37 10.46 0.065 6 高 288.70 44.48 12.14 0.088 8 高 低 147.09 46.04 9.90 0.033 8 中 247.24 48.93 10.64 0.040 6 高 308.26 53.38 13.63 0.093 8 平均值 261.93 44.69 11.18 0.053 5 标准误 49.73 2.41 0.86 0.020 1 P 代谢能 0.490 <0.010 0.820 0.449 蛋白质 0.210 0.034 0.005 0.073 代谢能×
蛋白质0.350 0.190 0.140 0.223 -
[1] 曹赞. 代谢能和粗蛋白水平对22~42日龄科宝肉鸡生产性能、养分表观代谢率及肠道消化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2016, 36(5): 839-846. [2] 陈明. 蛋白能量水平在畜禽营养中的研究进展[J]. 畜禽业, 2012(10): 30-32. [3] 赵峰. 用酶法评定鸭饲料代谢能的方法学研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2006. [4] 任立芹. 仿生法评定黄羽肉鸡常用饲料代谢能和可消化氨基酸研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2012. [5] WIRNT R. Methods of enzymatic analysis [M]. Weinheinm: Verlag Chemie, 1974.
[6] DAHLQVIST A. A method for the determination of amylase in intestinal content[J]. Scand J Clin Lab Invest, 1962, 14: 145-151.
[7] 郑卫宽, 赵峰, 张宏福. 日粮类型及肠液储存条件对鸭空肠液组成与特性的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2009, 21(5): 652-658. [8] BRZĘK P, CIMINARI M E, KOHL K D, et al. Effect of age and diet composition on activity of pancreatic enzymes in birds[J]. J Comp Physiol B, 2013, 183(5): 685-697.
[9] SHIH B L, YU B, HSU J C. The development of gastrointestinal tract and pancreatic enzymes in White Roman geese[J]. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci, 2005, 18(6): 841-847.
[10] ZHAO F, HOU S S, ZHANG H F, et al. Effects of dietary metabolizable energy and crude protein content on the activities of digestive enzymes in jejunal fluid of Peking ducks[J]. Poultry Sci, 2007, 86(8): 1690-1695.
[11] 官丽辉, 刘海斌, 张立永, 等. 不同能量、蛋白水平日粮对育雏期塞北乌骨鸡生长发育规律、生化指标和肠道消化酶的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2013, 33(8): 1292-1300. [12] SIDDONS R C. Effect of diet on disaccharidase activity in the chick[J]. Br J Nutr, 1972, 27(2): 343-352.
[13] YANG J, YANG L, WANG Y, et al. Effects of dietary protein and energy levels on digestive enzyme activities and electrolyte composition in the small intestinal fluid of geese[J]. Anim Sci J, 2017, 88(2): 294-299.
[14] 李贵锋, 蒋广震, 刘文斌, 等. 不同蛋白质和能量水平对建鲤幼鱼生长性能、体组成和消化酶活性的影响[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2012, 21(2): 225-232. -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 侯云涛. 精量排种器的研究现状与发展趋势. 现代农业装备. 2023(04): 15-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨文彩,张效伟,仲广远,郑嘉鑫,蒲望,马永敢. 三七育苗播种机导种管设计与试验. 华南农业大学学报. 2022(01): 120-132 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 曾心玥,赖庆辉,赵瑾汶,谢观福,韩晓娟. 内充式三七精密排种器的设计. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(06): 139-154 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 支帅,连政国,王家胜,陈明东,王东伟,姜云鹏. 轴针孔式西洋参气力精密播种机的设计与试验. 农机化研究. 2021(11): 83-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: