Cloning of chicken circSFMBT2 and its effect on proliferation of DF-1 cells
-
摘要:目的
验证鸡circSFMBT2的环形结构,探究其表达规律及功能。
方法以麒麟鸡和DF-1细胞为研究对象,根据反向剪切位点序列特征设计引物,通过PCR和测序验证circSFMBT2的环形结构。通过RNase R和反转录试验分析circSFMBT2的基本特性,利用qRT-PCR探究不同组织、不同时期circSFMBT2的表达水平。通过构建过表达载体,结合qRT-PCR、Edu和CCK-8等试验,探究circSFMBT2对鸡DF-1细胞增殖的影响。
结果鸡circSFMBT2全长827 nt,由SFMBT2基因外显子12~18环化形成。RNase R耐受性试验表明,circSFMBT2不易被RNase R降解,随机引物对circSFMBT2的反转录效率是Oligo-d(T)18引物的8倍。组织表达谱表明,circSFMBT2在麒麟鸡14胚龄以及1周龄的肝脏和脾脏中高表达、在胸肌和腿肌中低表达。circSFMBT2在胸肌和腿肌的时序表达谱表明,circSFMBT2在胚胎时期表达量较高,出生后表达量迅速下降。在DF-1细胞中circSFMBT2过表达48 h后,增殖标记基因PCNA和CCND1的表达量分别较对照组上调85%和92%。Edu和CCK-8细胞增殖试验表明,鸡circSFMBT2可以促进细胞增殖进程。
结论circSFMBT2是鸡SFMBT2基因的一个环状转录本,可以促进DF-1细胞的增殖,研究结果为深入探究鸡circSFMBT2的生物学功能和作用机制奠定了基础。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to verify the circular structure of chicken circSFMBT2 and explore its expression and functions.
MethodKirin chicken and DF-1 cells were used in this study. Primers were designed according to the reverse splicing site, and the circular structure of circSFMBT2 was verified by PCR and sequencing. The characteristics of circSFMBT2 were analyzed by RNase R and reverse transcription experiments. The expression levels of circSFMBT2 in different tissues and periods were explored by qRT-PCR. The effect of circSFMBT2 on proliferation of chicken DF-1 cells was investigated by qRT-PCR, Edu and CCK-8 methods.
ResultThe full length of chicken circSFMBT2 was 827 nt and it was formed by cyclization of exons 12−18 of SFMBT2 gene. RNase R tolerance experiments indicated that circSFMBT2 was not easily degraded by RNase R. The reverse transcription efficiency of random primers on circSFMBT2 was eight times of that of oligo d(T)18 primer. The tissue expression profile exhibited that circSFMBT2 expression was high in liver and spleen of Kirin chickens at the age of 14 embryonic and one week old, and low in the pectoral and leg muscles. The temporal expression profile of circSFMBT2 in the pectoral and leg muscles indicated that circSFMBT2 expression was high in embryonic period and decreased rapidly after birth. When circSFMBT2 was overexpressed in DF-1 cells for 48 h, the expressions of PCNA and CCND1 were up-regulated by 85% and 92% respectively compared with control group. The Edu and CCK-8 cell proliferation tests showed that circSFMBT2 promoted the cell proliferation process.
ConclusionThis study confirms the existence of circSFMBT2 as a circular transcript of chicken SFMBT2 and circSFMBT2 can promote DF-1 cell proliferation, which lays a foundation for further exploring the biological function and working mechanism of circSFMBT2 in chicken.
-
Keywords:
- Chicken /
- SFMBT2 /
- circRNA /
- DF-1 cell /
- Cell proliferation
-
环状RNA(circRNA)是一种共价闭合环状内源性RNA,广泛存在于真核生物中[1]。由于反向剪接效率不高,因此表达水平较低[2]。然而一旦形成circRNA就稳定存在,并且具有高度保守性[3]。与线性RNA相比,circRNA不含5′帽子和3′尾巴,半衰期更长,不易被RNase R降解[4]。此外,circRNA还具有组织、时间和疾病表达特异性等特点[5-6]。近年来的研究发现,circRNA具有多种生物学功能,主要包括调控基因转录,充当miRNA 海绵,与蛋白质结合参与调控和编码蛋白质等生物学功能[7-8]。研究发现,circRNA在肌肉发育过程中发挥作用,如circFUT10可作为miR-133a的海绵,在牛原代成肌细胞增殖分化中发挥功能[9],而circZNF609存在开放阅读框,并能翻译成多肽发挥促进成肌细胞增殖的作用[10]。
SFMBT2(Scm-like with four MBT domains 2)是多梳基因,可以编码具有MBT结构域的染色质调节蛋白,在多种基因的遗传调控中发挥作用[11-12]。鸡SFMBT2基因定位于1号染色体,含有21个外显子。广东海洋大学家禽育种团队的高通量测序(BioProject登录号:PRJNA554754)发现SFMBT2存在环状转录本,本研究通过PCR和测序技术手段验证circSFMBT2的环状结构,分析其结构特征和表达规律,并在DF-1 细胞中初步研究其对细胞增殖的影响,以期为后续深入分析circSFMBT2在鸡骨骼肌发育过程中的作用及机制奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
麒麟鸡种蛋采购于广东省高州市万农种鸡场。DF-1细胞系由华南农业大学家禽遗传育种团队赠送。RNA抽提试剂盒、RNA反转录试剂盒、无内毒素质粒抽提试剂盒购自广州美基生物科技有限公司;荧光定量PCR酶、大肠埃希菌Escherichia coli DH5α感受态细胞购自北京全式金公司;环状RNA过表达载体pCD2.1-ciR购自吉赛生物科技有限公司;Kpn I、BamH I购自TAKARA公司;DMEM高糖培养基、胎牛血清、胰蛋白酶购自Gibco公司。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 样品采集与细胞培养
将麒麟鸡种蛋放在37 ℃、湿度为70%的自动孵化箱中孵化,分别采集14胚龄、16胚龄、18胚龄以及1~6周龄麒麟鸡的心脏、肝脏、脾脏、肺脏、肾脏、胸肌和腿肌等组织,液氮速冻后迅速保存于−80 ℃冰箱中,用于组织表达规律和时序表达规律分析。
DF-1是可以无限增殖的成纤维状细胞系,在完全培养基(DMEM高糖+体积分数为10%的胎牛血清+体积分数为1%的双抗)37 ℃、CO2体积分数为5%的条件下培养。
1.2.2 引物设计与circSFMBT2验证
针对circSFMBT2的成环位置,在接头两端设计特异性引物circSFMBT2-D,用于circSFMBT2环分子的验证,设计全长扩增引物circSFMBT2-full,用于克隆circSFMBT2的全长序列,内参基因选用GAPDH。引物通过primer-BLAST(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast/)设计。为验证circSFMBT2的连接位置,使用RNase R外切酶在37 ℃条件下处理RNA样品30 min,反转录成cDNA,分别使用circSFMBT2-D和circSFMBT2-full引物进行PCR扩增,将扩增产物送生工生物技术有限公司测序。引物信息见表1。
表 1 引物序列及用途Table 1. Sequences and uses of primers引物或基因名称
Primer or gene
name引物序列(5'→3')
Primer
sequence退火温度/ ℃
Anealing
temperature产物长度/bp
Product
length用途
PurposeCircSFMBT2-D F:ACAGAGGGAAGACATACAGG
R:GCAGCGGTGGTTGATGTA56 600 环状验证
Circular verificationCircSFMBT2-full F:GTTTACAGATGCCCTCTCCAGA
R:CTCTGCAGAGCCTGCAGCATT58 827 全长克隆
Full length cloningCircSFMBT2-V F:CGGAATTCTAATACTTTCAG
GTTTACAGATGCCCTCTCCAGA
R:CGGGATCCAGTTGTTCTTAC
CGGAATTCTAATACTTTCAG63 867 构建过表达载体
Construction of overexpression vectorSFMBT2-DL F:TCAGACAGACCTCCTCCT
R:AGTCACAGTCCACTCCAAT60 162 线性基因定量
Linear gene quantificationGAPDH F:AGGACCAGGTTGTCTCCTGT
R:CCATCAAGTCCACAACACGG57 153 内参基因
Reference genePCNA F:CTCTGAGGGCTTCGACACCT
R:ATCCGCATTGTCTTCTGCTCT58 133 增殖标记基因定量
Proliferative marker gene quantificationCCND1 F:AACCCACCTTCCATGATCGC
R:CTGTTCTTGGCAGGCTCGTA58 168 增殖标记基因定量
Proliferative marker gene quantificationCDK2 F:GTACAAGGCCCGGAACAAGG
R:TTCTCCGTGTGGATCACGTC58 159 增殖标记基因定量
Proliferative marker gene quantification1.2.3 组织和细胞RNA提取及qPCR试验
组织和细胞总RNA的提取方法参考HiPureUnivesal RNA Mini Kit 试剂盒说明书。依据PrimeScript RT reagent Kit With gDNA Eraser 试剂盒说明书,使用随机引物(N9)和Oligo-d(T)18将总RNA反转录为cDNA,反应程序为25 ℃,10 min;42 ℃,15 min;85 ℃,30 s。以反转录生成的cDNA为模板进行实时荧光定量PCR,PCR反应体系:cDNA模板1 μL、上、下游引物各0.4 μL、2×SYBR Green qPCR Mix 10 μL、双蒸水8.2 μL。PCR反应条件为94 ℃,3 min;94 ℃,15 s,60 ℃,15 s,72 ℃,20 s,40个循环。溶解曲线程序为95 ℃,15 s;60 ℃ 1 min;95 ℃,1 s。以GAPDH作为内参基因,检测circSFMBT2的表达。
1.2.4 鸡circSFMBT2过表达载体构建
根据circRNA的测序数据,通过PCR扩增circSFMBT2的全长序列,并在其两端加上保护序列和酶切位点,使用Kpn I和BamH I酶切PCR扩增产物和pCD2.1-ciR载体,酶切产物纯化后利用T4DNA酶连接,16 ℃过夜。取连接产物转化至大肠埃希菌感受态细胞中,转化完成后涂板,37 ℃恒温培养14~16 h,挑取单克隆菌落,阳性鉴定后送测序,选取测序结果与circSFMBT2基因序列吻合的单克隆菌液留用。
1.2.5 细胞转染试验
将DF-1细胞系接种于12孔板,使用DMEM完全培养基培养细胞至汇合度达80%时,使用脂质体转染试剂Lipofectamine@3000转染空载体pCD2.1-ciR和过表达载体pCD2.1-circSFMBT2,转染48 h后收获细胞。
1.2.6 Edu和CCK-8检测细胞增殖
转染空载体pCD2.1-ciR和过表达载体pCD2.1-circSFMBT2至48 h,参考Edu试剂盒说明书对细胞进行孵育、固定、通透、染色等处理,最后在荧光显微镜下观察和拍照。
CCK-8试验:将细胞接种于96孔板,转染空载体pCD2.1-ciR和过表达载体pCD2.1-circSFMBT2,分别在0、12、24、36、48和60 h使用CCK-8试剂37 ℃孵育2 h后,检测细胞的D450 nm。
1.2.7 生物信息学分析
利用RNAhybird网站在线预测circSFMBT2中潜在的miRNA结合位点,使用SnapGene软件预测circSFMBT2编码蛋白质的能力。
1.2.8 统计学分析
Edu试验与基因定量检测中每个分组包含4个重复,CCK-8试验中每组包含8个重复,使用GraphPad Prism9软件进行统计学分析,采用t检验分析数据。CircSFMBT2时序表达规律和组织表达规律数据采用LSD多重比较进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 鸡circSFMBT2成环验证
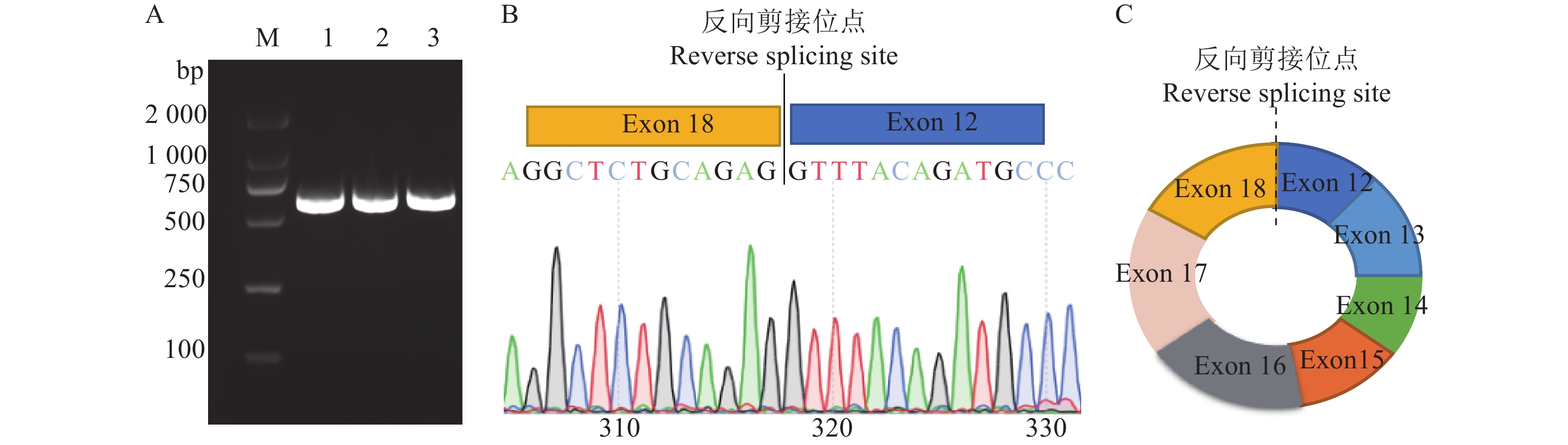
根据华南农业大学家禽遗传育种与繁殖实验室前期高通量测序结果,发现鸡SFMBT2基因可能产生一个环状转录本,为此,本研究首先对circSFMBT2连接成环位置设计发散引物,以1周龄麒麟鸡肝脏组织RNA反转录的cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增。PCR电泳结果产生了预期目的条带(图1A),测序结果显示,circSFMBT2连接成环的片段来源于SFMBT2基因外显子12和外显子18(图1B、1C)。
![]() 图 1 鸡circSFMBT2成环验证A:circSFMBT2环化位置扩增结果,M:DL2000 marker,1~3:以麒麟鸡肝脏组织1日龄cDNA模板扩增circSFMBT2成环位置;B:circSFMBT2成环位置扩增测序结果;C:circSFMBT2结构示意图Figure 1. Validation of the junction of chicken circSFMBT2A: Amplification result of circSFMBT2 junction site, M:DL2000 marker, 1−3: Amplification of circSFMBT2 junction site with one day old cDNA template from Kirin chicken liver tissue; B: Sequencing result of circSFMBT2 junction position; C: Structure diagram of circSFMBT2z
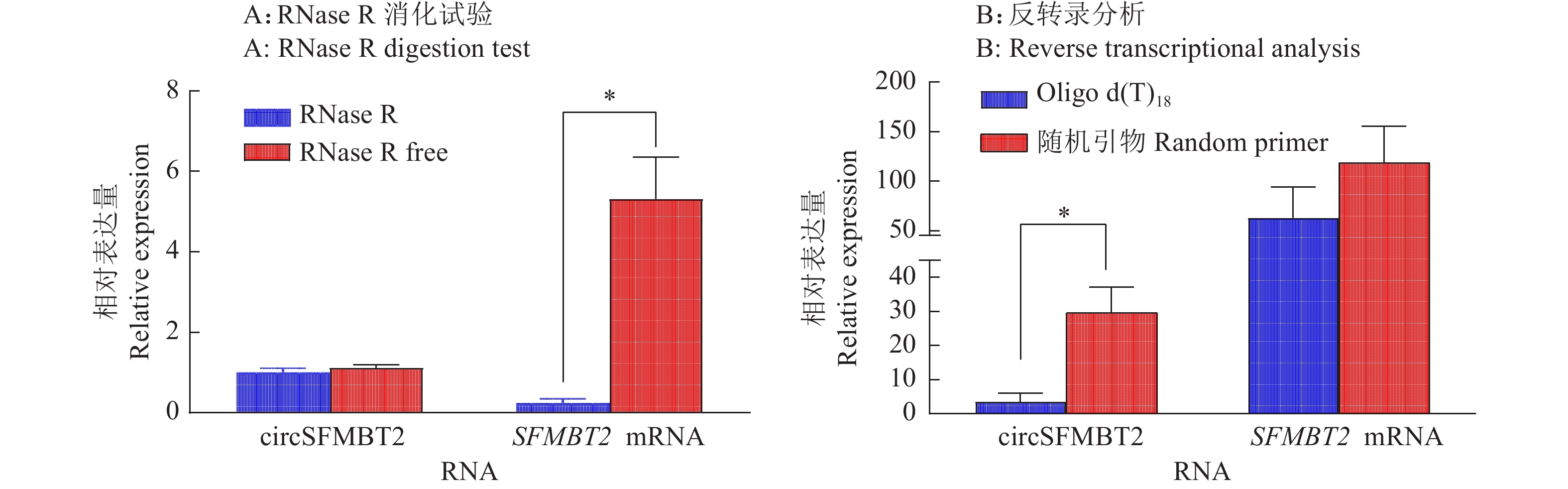
图 1 鸡circSFMBT2成环验证A:circSFMBT2环化位置扩增结果,M:DL2000 marker,1~3:以麒麟鸡肝脏组织1日龄cDNA模板扩增circSFMBT2成环位置;B:circSFMBT2成环位置扩增测序结果;C:circSFMBT2结构示意图Figure 1. Validation of the junction of chicken circSFMBT2A: Amplification result of circSFMBT2 junction site, M:DL2000 marker, 1−3: Amplification of circSFMBT2 junction site with one day old cDNA template from Kirin chicken liver tissue; B: Sequencing result of circSFMBT2 junction position; C: Structure diagram of circSFMBT2z线性RNA在RNase R外切酶的作用下很容易降解,但circRNA具有RNase R耐受性。为了进一步验证circSFMBT2的环形结构,对麒麟鸡肝脏组织的RNA分别以RNase R未处理和处理后,采用实时荧光PCR定量circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA的相对表达量,试验结果表明,使用RNase R处理后,SFMBT2 mRNA的相对表达量显著下降,而circSFMBT2的相对表达量无明显变化(图2A)。另外,分别使用Oligo-d(T)18和随机引物(N9)反转录成cDNA,实时荧光定量PCR结果表明,SFMBT2 mRNA 在Oligo-d(T)18和随机引物组中的表达量无显著变化,而采用Oligo-d(T)18反转录的circSFMBT2的表达量显著低于随机引物组(图2B)。进一步证实circSFMBT2具备环状分子的特点。
2.2 鸡circSFMBT2的组织表达谱
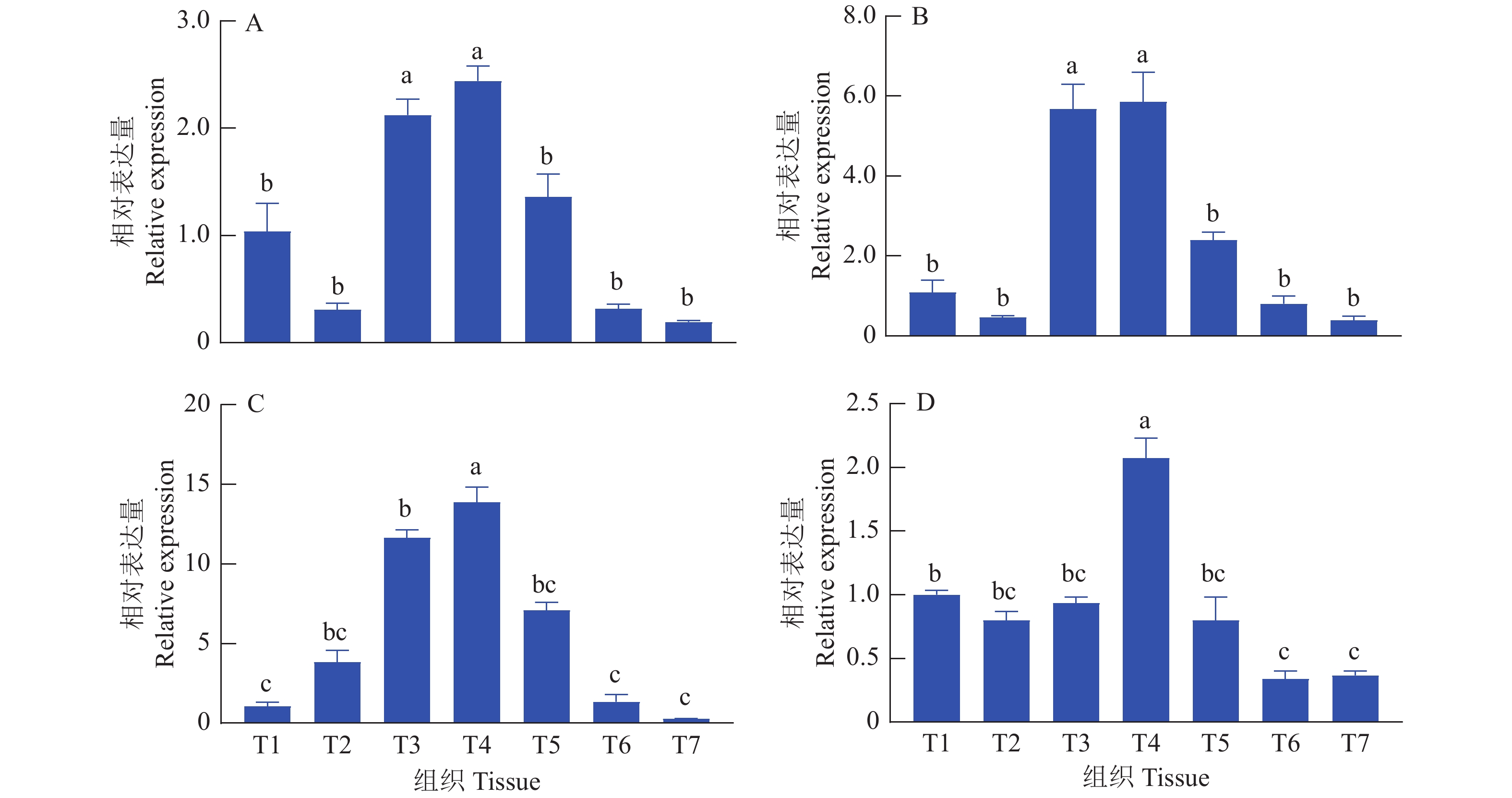
分别提取麒麟鸡14胚龄和1周龄心脏、肝脏、脾脏、肺脏、肾脏、肺脏、胸肌和腿肌等组织RNA,反转录成cDNA后,通过荧光定量PCR对circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA的表达量进行对比分析。发现circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA的组织表达规律存在一定的相似性,两者都在14胚龄和1周龄脾脏和肺脏中高表达,而在胸肌和腿肌中低表达(图3)。
![]() 图 3 麒麟鸡 circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA组织表达谱A:14胚龄circSFMBT2表达;B:14胚龄SFMBT2 mRNA表达;C:1周龄circSFMBT2表达;D:1周龄SFMBT2 mRNA表达;T1:心脏,T2:肝脏,T3:脾脏,T4:肺脏,T5:肾脏,T6:胸肌,T7:腿肌;各组织的RNA表达量为相对于T1的表达量;柱子上方的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05, LSD法)Figure 3. circSFMBT2 and SFMBT2 mRNA expression profiles in tissues of Kirin chickensA: circSFMBT2 expression of 14 embryo age; B: SFMBT2 mRNA expression of 14 embryo age; C: circSFMBT2 expression of one week age; D: SFMBT2 mRNA expression of one week age; T1: Heart, T2: Liver, T3: Spleen, T4: Lung, T5: Kidney, T6: Pectoral, T7: Leg muscle; The RNA expression level in each tissue is relative to the expression level in T1; Different lowercase letters on bars indicate significant differences (P<0.05, LSD test)
图 3 麒麟鸡 circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA组织表达谱A:14胚龄circSFMBT2表达;B:14胚龄SFMBT2 mRNA表达;C:1周龄circSFMBT2表达;D:1周龄SFMBT2 mRNA表达;T1:心脏,T2:肝脏,T3:脾脏,T4:肺脏,T5:肾脏,T6:胸肌,T7:腿肌;各组织的RNA表达量为相对于T1的表达量;柱子上方的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05, LSD法)Figure 3. circSFMBT2 and SFMBT2 mRNA expression profiles in tissues of Kirin chickensA: circSFMBT2 expression of 14 embryo age; B: SFMBT2 mRNA expression of 14 embryo age; C: circSFMBT2 expression of one week age; D: SFMBT2 mRNA expression of one week age; T1: Heart, T2: Liver, T3: Spleen, T4: Lung, T5: Kidney, T6: Pectoral, T7: Leg muscle; The RNA expression level in each tissue is relative to the expression level in T1; Different lowercase letters on bars indicate significant differences (P<0.05, LSD test)2.3 鸡胸肌和腿肌circSFMBT2时序表达规律
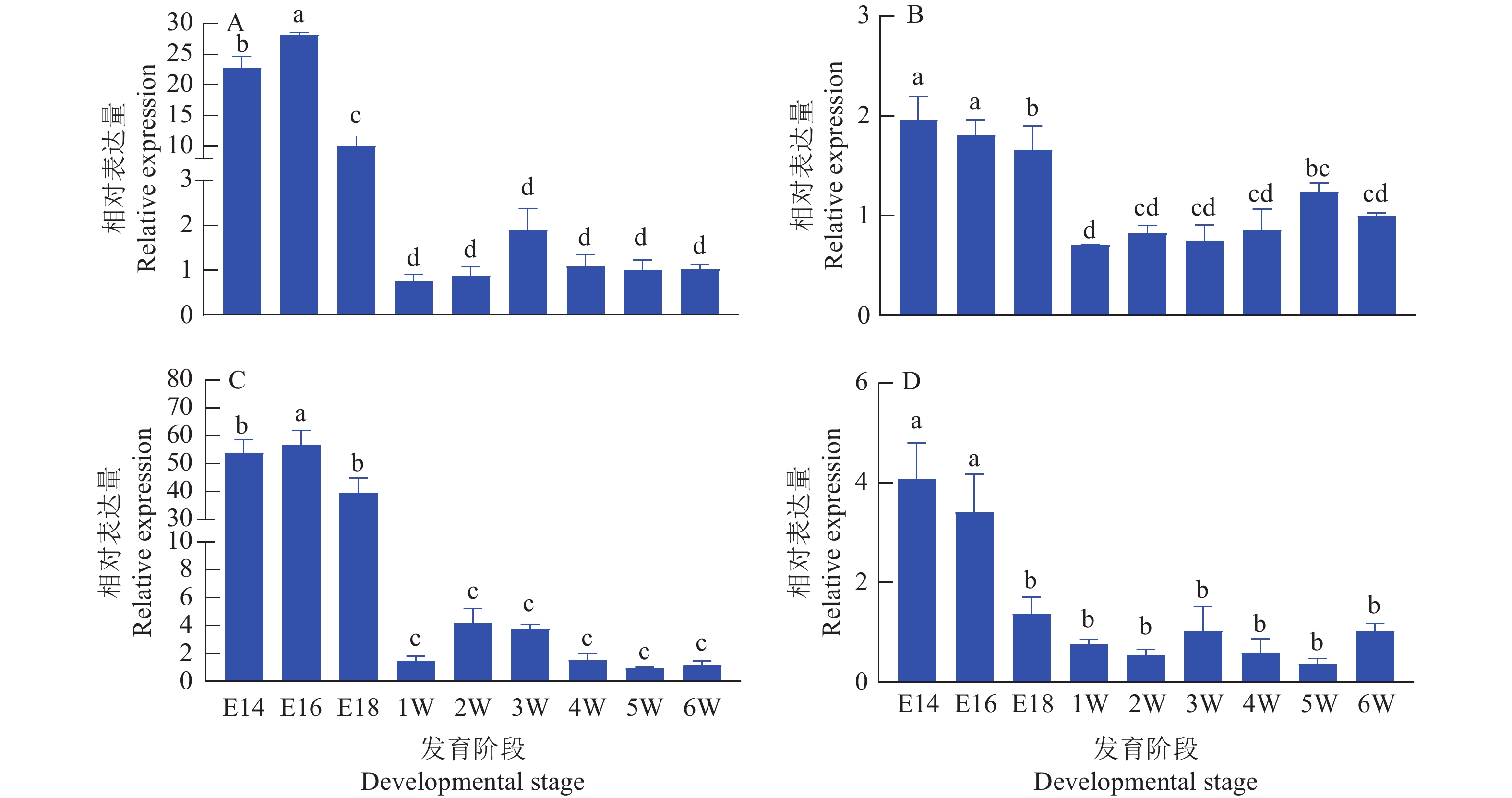
提取麒麟鸡不同发育阶段胸肌和腿肌组织RNA,反转录后定量分析的结果 (图4)表明,circSFMBT2与SFMBT2在胚胎时期的表达量相对较高,而出生后两者的表达量急剧下降,同时circSFMBT2在胸肌的表达量下降趋势更为明显。
![]() 图 4 麒麟鸡circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA的时序表达规律A:胸肌中circSFMBT2表达;B:腿肌中circSFMBT2表达;C:胸肌中SFMBT2 mRNA表达;D:腿肌中SFMBT2 mRNA表达;E14、E16和E18分别表示14、16、18胚龄,1W~6W表示1~6周龄;各阶段的RNA表达量为相对于第6周的表达量;柱子上方的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,LSD法)Figure 4. Temporal expression pattern of circSFMBT2 and SFMBT2 mRNA of Kirin chickensA: circSFMBT2 expression in breast muscle; B: circSFMBT2 expression in leg muscle; C: SFMBT2 mRNA expression in breast muscle; D: SFMBT2 mRNA expression in leg muscle; E14, E16 and E18 indicate 14,16 and 18 embryo ages respectively,1W−6W indicate 1 to 6 week age; The RNA expression level in each stage is relative to the expression level in the 6th week; Different lower case letters on bars indicate significant differences (P<0.05, LSD test)
图 4 麒麟鸡circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA的时序表达规律A:胸肌中circSFMBT2表达;B:腿肌中circSFMBT2表达;C:胸肌中SFMBT2 mRNA表达;D:腿肌中SFMBT2 mRNA表达;E14、E16和E18分别表示14、16、18胚龄,1W~6W表示1~6周龄;各阶段的RNA表达量为相对于第6周的表达量;柱子上方的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,LSD法)Figure 4. Temporal expression pattern of circSFMBT2 and SFMBT2 mRNA of Kirin chickensA: circSFMBT2 expression in breast muscle; B: circSFMBT2 expression in leg muscle; C: SFMBT2 mRNA expression in breast muscle; D: SFMBT2 mRNA expression in leg muscle; E14, E16 and E18 indicate 14,16 and 18 embryo ages respectively,1W−6W indicate 1 to 6 week age; The RNA expression level in each stage is relative to the expression level in the 6th week; Different lower case letters on bars indicate significant differences (P<0.05, LSD test)2.4 鸡circSFMBT2对DF-1细胞增殖的影响
2.4.1 CCK-8试验结果
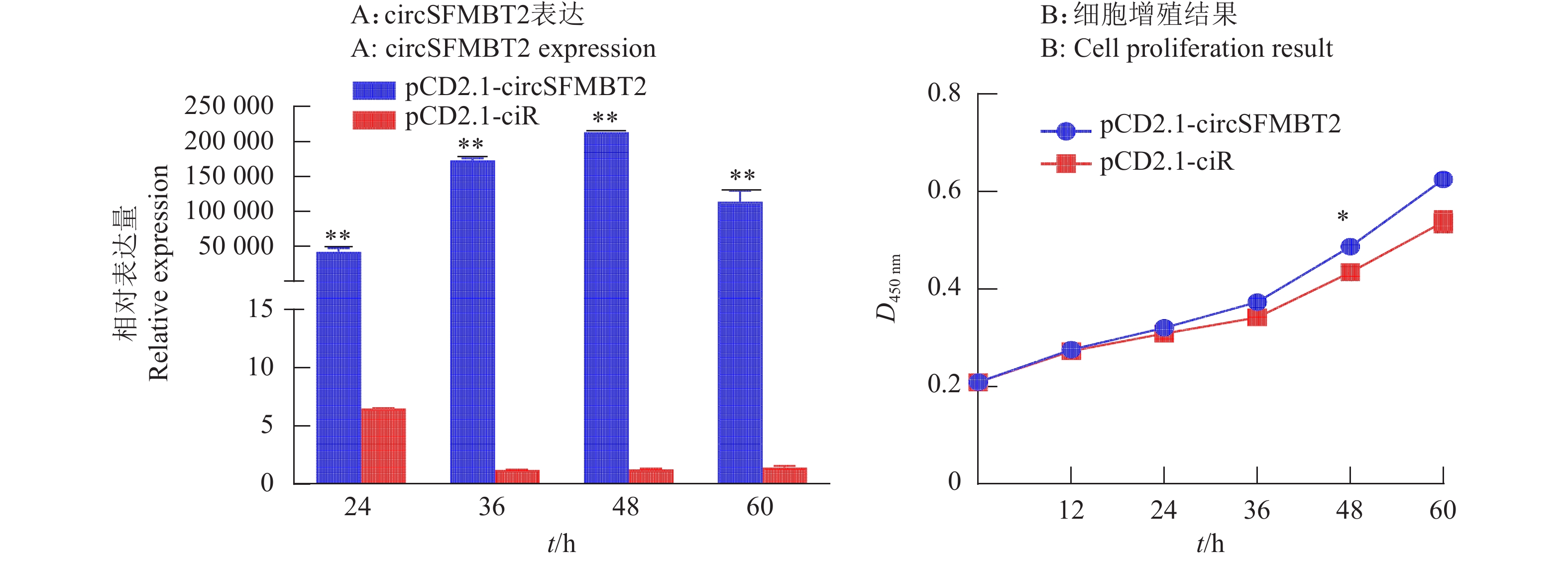
在鸡DF-1细胞中过表达circSFMBT2,荧光定量PCR结果证实过表达效果显著(图5A),pCD2.1-circSFMBT2 过表达质粒可用于后续试验。为了验证过表达后circSFMBT2对细胞增殖的影响,通过转染pCD2.1-circSFMBT2 和 pCD2.1-ciR,收集转染后24、36、48和60 h的细胞,进行CCK-8试验,结果显示,与pCD2.1-ciR组相比,circSFMBT2过表达48 h后,DF-1细胞活力上升(图5B)。
2.4.2 Edu试验结果
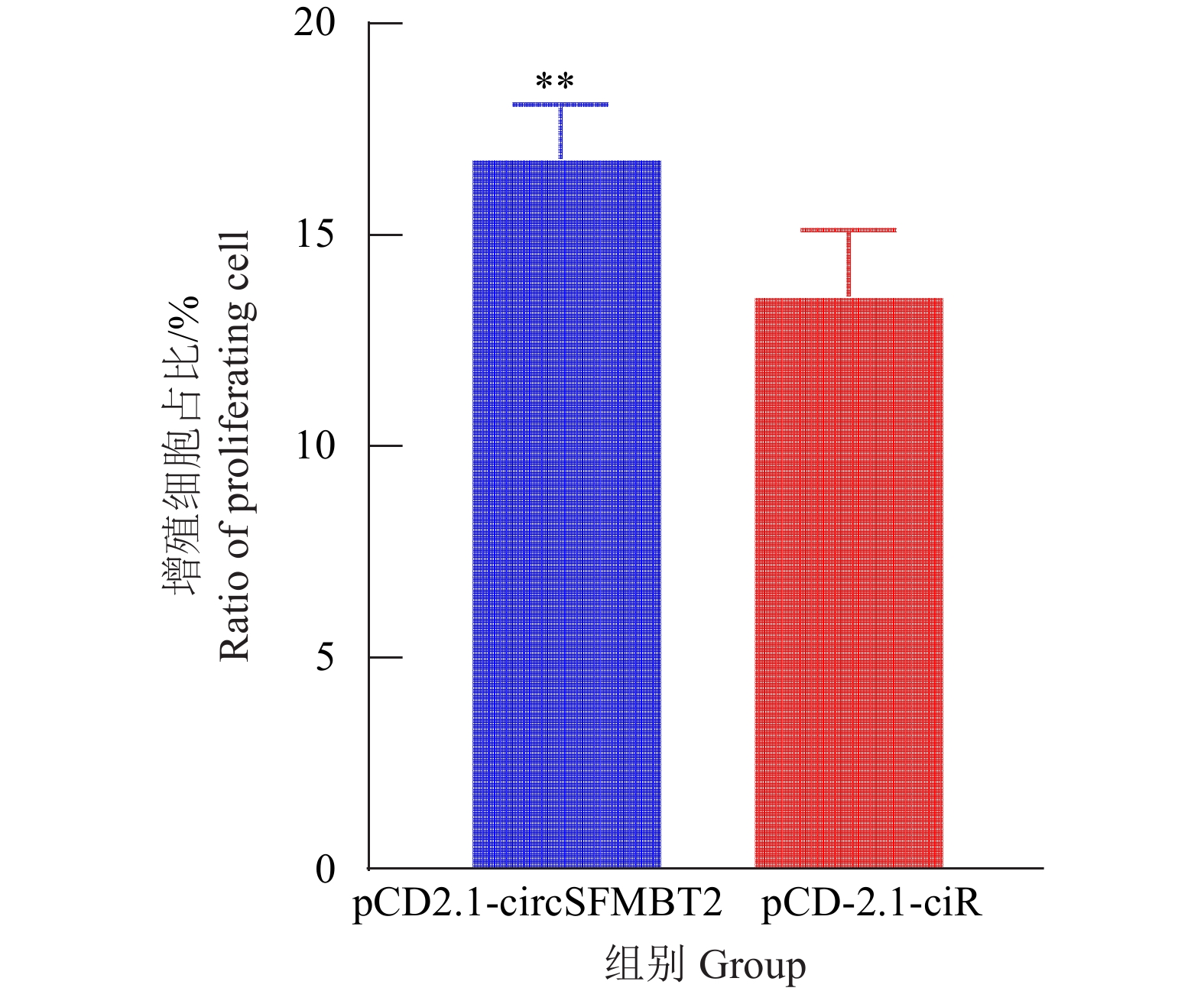
为进一步分析circSFMBT2对细胞增殖的影响,在DF-1细胞中同时转染pCD2.1-ciR和pCD2.1-circSFMBT2质粒,培养48 h后对渗入细胞总数进行分析,结果表明过表达组Edu细胞渗入总数高于对照组(图6、7),circSFMBT2 过表达后可以促进DF-1增殖。
2.4.3 circSFMBT2对细胞增殖标记基因表达的影响
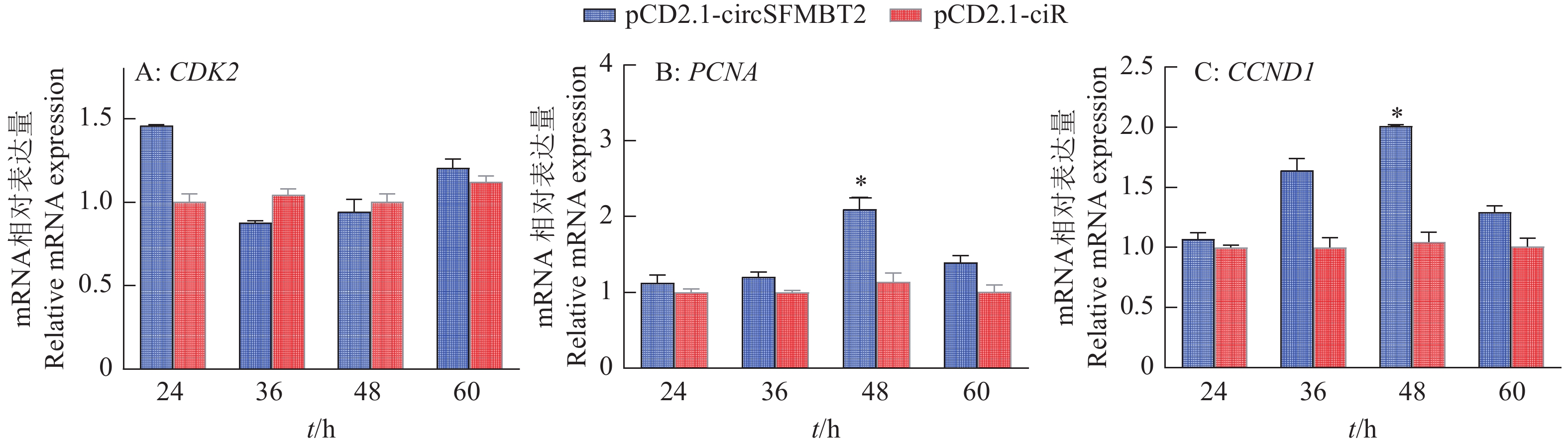
在CCK-8和Edu试验基础上,为了进一步验证circSFMBT2对DF-1细胞增殖的影响,在转染pCD2.1-ciR和pCD2.1-circSFMBT2质粒24、36、48和60 h后,qRT-PCR检测对照组和过表达组增殖标记基因PCNA、CDK2和CCND1表达趋势。结果显示试验组中增殖标记基因CCND1在36和48 h表达量高于对照组,并且CCND1和PCNA的表达量在48 h与对照组差异显著,CDK2的表达量无明显变化(图8)。
2.4.4 circSFMBT2生物学功能预测
利用RNAhybird在线预测 circSFMBT2潜在的靶标位点,发现circSFMBT2存在miR-103、miR-107和let-7b等靶标位点,另外,使用SnapGene软件预测circSFMBT2 存在1个开放阅读框,编码蛋白质能力得分为0.9360,推测其具有较强编码小肽的潜能。
3. 讨论与结论
在华南农业大学家禽遗传育种与繁殖实验室前期研究的基础上,本研究验证了鸡 circSFMBT2 由SFMBT2基因外显子12至外显子18反向剪切形成。查阅circBase(http://www.circbase.org)发现,人SFMBT2也存在环状RNA,人circSFMBT2由亲本基因的外显子5至外显子8组成。研究发现,人circSFMBT2可作为miR-182-5p海绵调控胃癌细胞的增殖[13],也可通过靶向miR-7-5p对肺癌细胞产生影响[14]。
由于环状RNA的闭环结构,不易被RNase R降解,具有较强的稳定性。本研究发现,与线性SFMBT2相比,鸡circSFMBT2具有较强的RNase R耐受性,并且随机引物(N9)相比于Oligo-d(T)18引物具有更高的反转录效率,进一步说明鸡circSFMBT2具备环状分子的基本特征。鸡circSFMBT2还具有时空表达的特异性,本试验通过荧光定量发现,鸡circSFMBT2与线性转录本在胸肌和腿肌时序表达规律相似,其在胚胎时期表达量较高,而出生后(1~6周)表达量迅速下降,推测可能与线性转录本低表达有关。鸡circSFMBT2 在组织中的表达具有差异性,circSFMBT2在14胚龄与1周龄鸡肺脏组织表达量最高,在肌肉组织表达量极低。
目前,已有大量文章报道circRNA在细胞中发挥调控作用,如在牛原代成肌细胞中,发现circLMO7 能抑制成肌细胞分化促进细胞增殖[14]。在家禽中,circSVIL可以通过结合miR-203从而促进成肌细胞的增殖和分化[15]。在细胞增殖试验中,我们发现过表达circSFMBT2 48 h后,增殖标记基因PCNA和CCND1的表达量升高,但CDK2的表达量无明显变化。CCK-8与Edu试验表明,过表达cicrSFMBT2可促进DF-1细胞的增殖。
研究发现,circRNA具有多种生物学功能。一些circRNA含有miRNA应答原件,竞争性与miRNA结合,发挥miRNA海绵作用[16],circRNA也可在转录后调控亲本基因的表达[17-20]。一些定位在细胞核中的circRNA可以与RNA聚合酶 Ⅱ 结合调控亲本基因的转录活性[7],含有内含子序列的circRNA通过RNA-RNA相互作用与U1小核核糖体蛋白结合,进一步与RNA聚合酶 Ⅱ 结合促进亲本基因的转录[21],也可以与DNA结合形成RNA-DNA杂交环,在剪接过程中调控亲本基因的表达[22]。
随着circRNA的研究深入,人们发现有些circRNA具有开放阅读框,能编码蛋白质[23]。circSFMBT2含有8个外显子,利用RNAhybird在线预测发现circSFMBT2存在miR-103和miR-107等靶标位点,另外,使用SnapGene软件预测发现circSFMBT2 存在1个开放阅读框。我们期待更深入的研究,验证circSFMBT2能否作为miRNA的海绵或编码小肽,是否调控线性基因转录,并验证其是否参与调控鸡肌肉生长发育。
-
图 1 鸡circSFMBT2成环验证
A:circSFMBT2环化位置扩增结果,M:DL2000 marker,1~3:以麒麟鸡肝脏组织1日龄cDNA模板扩增circSFMBT2成环位置;B:circSFMBT2成环位置扩增测序结果;C:circSFMBT2结构示意图
Figure 1. Validation of the junction of chicken circSFMBT2
A: Amplification result of circSFMBT2 junction site, M:DL2000 marker, 1−3: Amplification of circSFMBT2 junction site with one day old cDNA template from Kirin chicken liver tissue; B: Sequencing result of circSFMBT2 junction position; C: Structure diagram of circSFMBT2z
图 3 麒麟鸡 circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA组织表达谱
A:14胚龄circSFMBT2表达;B:14胚龄SFMBT2 mRNA表达;C:1周龄circSFMBT2表达;D:1周龄SFMBT2 mRNA表达;T1:心脏,T2:肝脏,T3:脾脏,T4:肺脏,T5:肾脏,T6:胸肌,T7:腿肌;各组织的RNA表达量为相对于T1的表达量;柱子上方的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05, LSD法)
Figure 3. circSFMBT2 and SFMBT2 mRNA expression profiles in tissues of Kirin chickens
A: circSFMBT2 expression of 14 embryo age; B: SFMBT2 mRNA expression of 14 embryo age; C: circSFMBT2 expression of one week age; D: SFMBT2 mRNA expression of one week age; T1: Heart, T2: Liver, T3: Spleen, T4: Lung, T5: Kidney, T6: Pectoral, T7: Leg muscle; The RNA expression level in each tissue is relative to the expression level in T1; Different lowercase letters on bars indicate significant differences (P<0.05, LSD test)
图 4 麒麟鸡circSFMBT2和SFMBT2 mRNA的时序表达规律
A:胸肌中circSFMBT2表达;B:腿肌中circSFMBT2表达;C:胸肌中SFMBT2 mRNA表达;D:腿肌中SFMBT2 mRNA表达;E14、E16和E18分别表示14、16、18胚龄,1W~6W表示1~6周龄;各阶段的RNA表达量为相对于第6周的表达量;柱子上方的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,LSD法)
Figure 4. Temporal expression pattern of circSFMBT2 and SFMBT2 mRNA of Kirin chickens
A: circSFMBT2 expression in breast muscle; B: circSFMBT2 expression in leg muscle; C: SFMBT2 mRNA expression in breast muscle; D: SFMBT2 mRNA expression in leg muscle; E14, E16 and E18 indicate 14,16 and 18 embryo ages respectively,1W−6W indicate 1 to 6 week age; The RNA expression level in each stage is relative to the expression level in the 6th week; Different lower case letters on bars indicate significant differences (P<0.05, LSD test)
表 1 引物序列及用途
Table 1 Sequences and uses of primers
引物或基因名称
Primer or gene
name引物序列(5'→3')
Primer
sequence退火温度/ ℃
Anealing
temperature产物长度/bp
Product
length用途
PurposeCircSFMBT2-D F:ACAGAGGGAAGACATACAGG
R:GCAGCGGTGGTTGATGTA56 600 环状验证
Circular verificationCircSFMBT2-full F:GTTTACAGATGCCCTCTCCAGA
R:CTCTGCAGAGCCTGCAGCATT58 827 全长克隆
Full length cloningCircSFMBT2-V F:CGGAATTCTAATACTTTCAG
GTTTACAGATGCCCTCTCCAGA
R:CGGGATCCAGTTGTTCTTAC
CGGAATTCTAATACTTTCAG63 867 构建过表达载体
Construction of overexpression vectorSFMBT2-DL F:TCAGACAGACCTCCTCCT
R:AGTCACAGTCCACTCCAAT60 162 线性基因定量
Linear gene quantificationGAPDH F:AGGACCAGGTTGTCTCCTGT
R:CCATCAAGTCCACAACACGG57 153 内参基因
Reference genePCNA F:CTCTGAGGGCTTCGACACCT
R:ATCCGCATTGTCTTCTGCTCT58 133 增殖标记基因定量
Proliferative marker gene quantificationCCND1 F:AACCCACCTTCCATGATCGC
R:CTGTTCTTGGCAGGCTCGTA58 168 增殖标记基因定量
Proliferative marker gene quantificationCDK2 F:GTACAAGGCCCGGAACAAGG
R:TTCTCCGTGTGGATCACGTC58 159 增殖标记基因定量
Proliferative marker gene quantification -
[1] MEMCZAK S, JENS M, ELEFSINIOTI A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency[J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 333-338. doi: 10.1038/nature11928
[2] ZHANG Y, XUE W, LI X, et al. The biogenesis of nascent circular RNAs[J]. Cell Reports, 2016, 15(3): 611-624. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.058
[3] JECK W R, SORRENTINO J A, WANG K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats[J]. RNA, 2013, 19(2): 141-157. doi: 10.1261/rna.035667.112
[4] ZHANG C, WU H, WANG Y, et al. Circular RNA of cattle casein genes are highly expressed in bovine mammary gland[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2016, 99(6): 4750-4760. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-10381
[5] SALZMAN J, GAWAD C, WANG P L, et al. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(2): e30733. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030733
[6] HUANG A, ZHENG H, WU Z, et al. Circular RNA-protein interactions: Functions, mechanisms, and identification[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(8): 3503-3517. doi: 10.7150/thno.42174
[7] LI Z, HUANG C, BAO C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2015, 22(3): 256-264.
[8] LI H, YANG J, WEI X, et al. CircFUT10 reduces proliferation and facilitates differentiation of myoblasts by sponging miR-133a[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2018, 233(6): 4643-4651. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26230
[9] LEGNINI I, DI TIMOTEO G, ROSSI F, et al. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular rna that can be translated and functions in myogenesis[J]. Molecular Cell, 2017, 66(1): 22-37. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.017
[10] KLYMENKO T, PAPP B, FISCHLE W, et al. A Polycomb group protein complex with sequence-specific DNA-binding and selective methyl-lysine-binding activities[J]. Genes & Development, 2006, 20(9): 1110-1122.
[11] GRIMM C, MATOSR R, LY-HARTIG N, et al. Molecular recognition of histone lysine methylation by the Polycomb group repressor dSfmbt[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2009, 28(13): 1965-1977. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.147
[12] SUN H, XI P, SUN Z, et al. Circ-SFMBT2 promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells through sponging miR-182-5p to enhance CREB1 expression[J]. Cancer Management and Research, 2018, 10: 5725-5734. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S172592
[13] 李长生, 张莞萍, 任中海. circ-SFMBT2通过靶向miR-7-5p/ADAM10轴对非小细胞肺癌细胞生物学行为的影响[J]. 中华医学遗传学杂志, 2022, 39(2): 162-170. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20201221-00895 [14] WEI X, LI H, YANG J, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circLMO7 that regulates myoblasts differentiation and survival by sponging miR-378a-3p[J]. Cell Death & Disease, 2017, 8(10): e3153.
[15] OUYANG H, CHEN X, LI W, et al. Circular RNA circSVIL promotes myoblast proliferation and differentiation by sponging miR-203 in chicken[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2018, 9: 172. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00172
[16] 骆甲, 王型力, 孙志超, 等. 植物环状 RNA 研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(6): 467-477. [17] RYBAK-WOLF A, STOTTMEISTER C, GLAZAR P, et al. Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed[J]. Molecular Cell, 2015, 58(5): 870-885. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027
[18] CONN V M, HUGOUVIEUX V, NAYAK A, et al. A circRNA from SEPALLATA3 regulates splicing of its cognate mRNA through R-loop formation[J]. Nature Plants, 2017, 3: 17053. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2017.53
[19] LI X, YANG L, CHEN L L. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs[J]. Moleluclar Cell, 2018, 71(3): 428-442. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.034
[20] CHEN X, HAN P, ZHOU T, et al. circRNADb: A comprehensive database for human circular RNAs with protein-coding annotations[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 34985. doi: 10.1038/srep34985
[21] QU S, YANG X, LI X, et al. Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding RNAs[J]. Cancer Letters, 2015, 365(2): 141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.003
[22] ASHWAL-FLUSS R, MEYER M, PAMUDURTI N, et al. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing[J]. Molecular Cell, 2014, 56(1): 55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019
[23] ZHOU B, YANG H, YANG C, et al. Translation of noncoding RNAs and cancer[J]. Cancer Letters, 2021, 497: 89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.002



 下载:
下载: