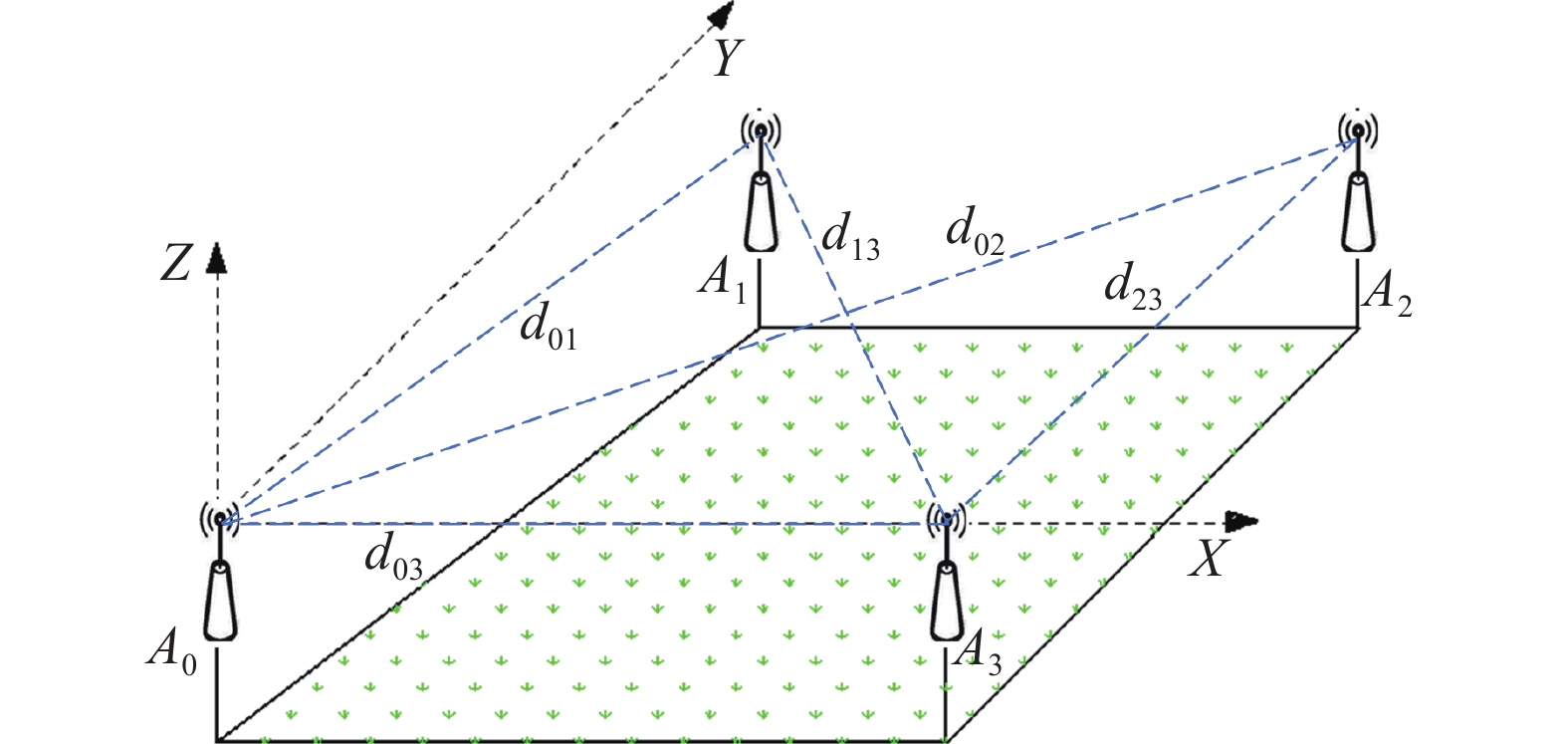
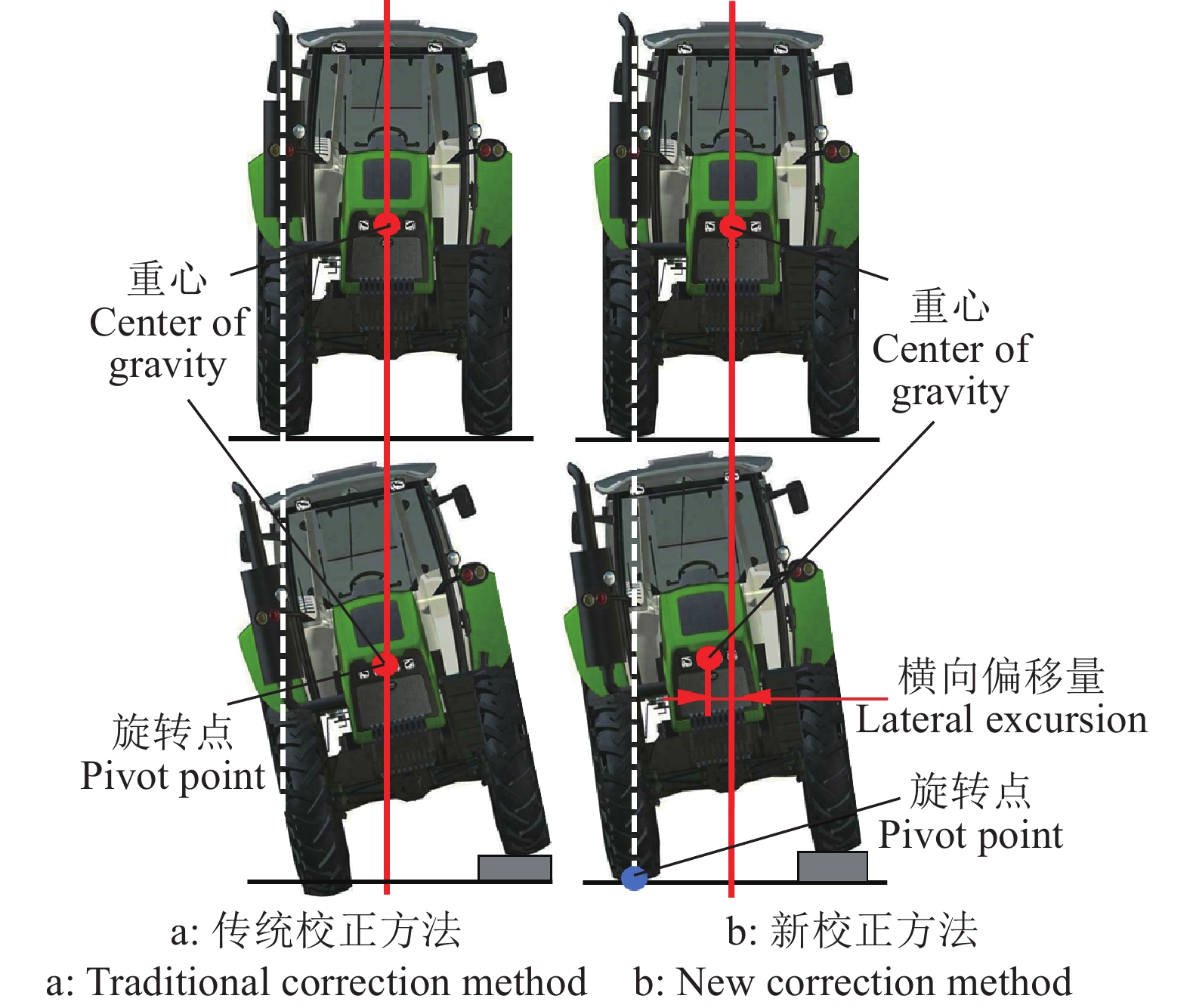
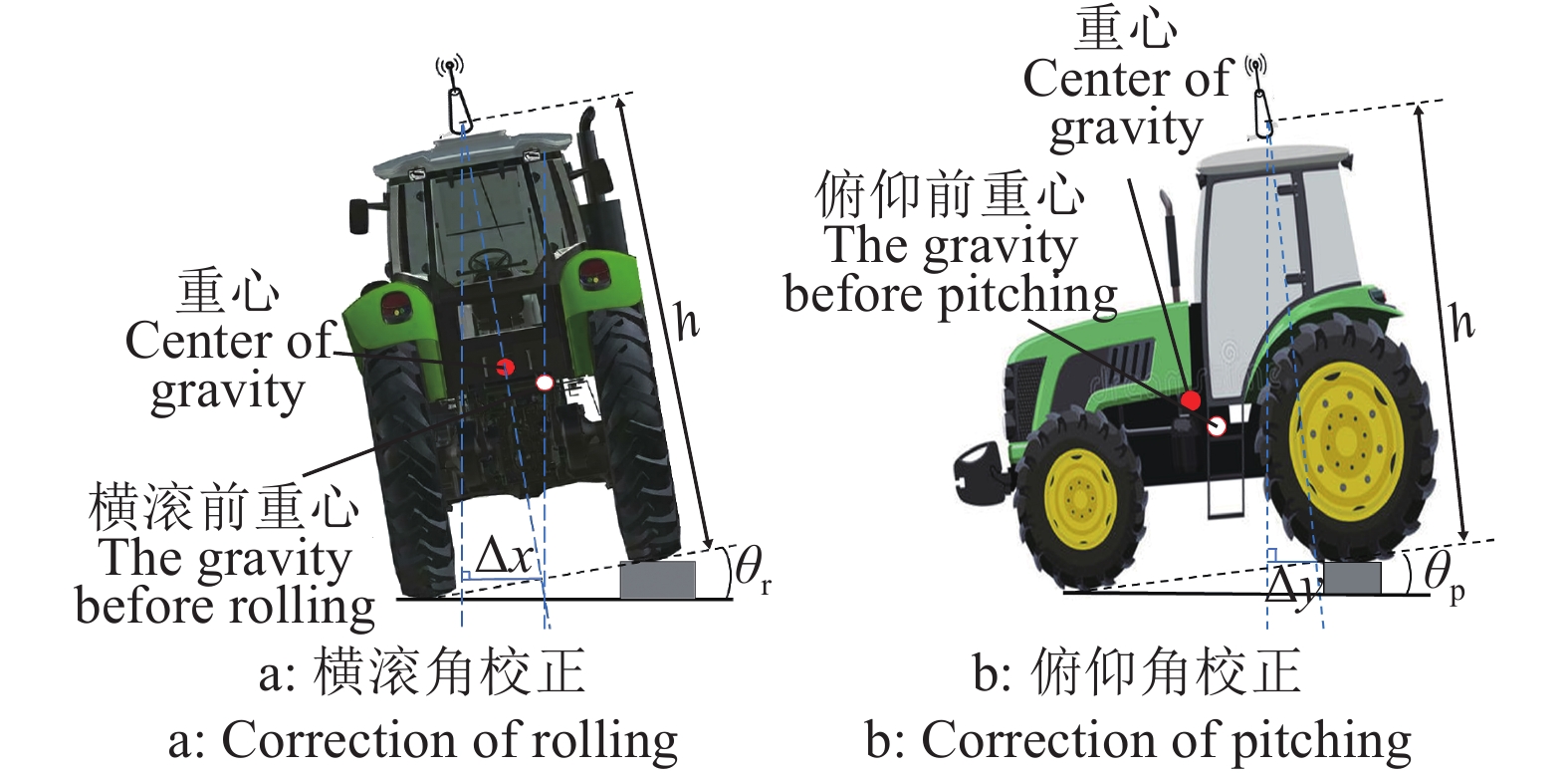
Design and experiment of agricultural machinery auxiliary navigation system based on UWB positioning
-
摘要:目的
低成本实现南方中小型田块中农业机械田间精确定位,降低农机操作人员劳动强度、提高农机作业效率。
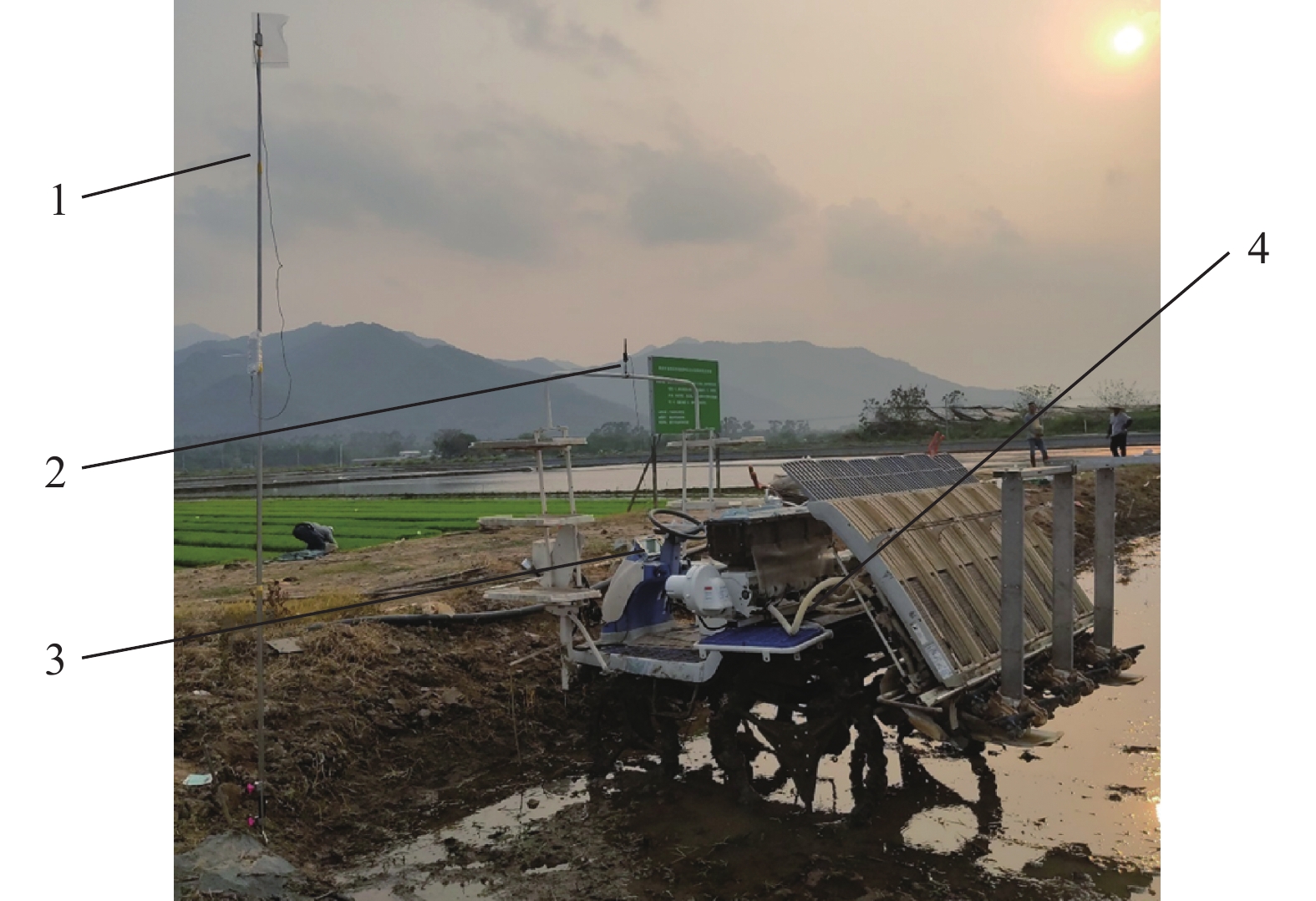
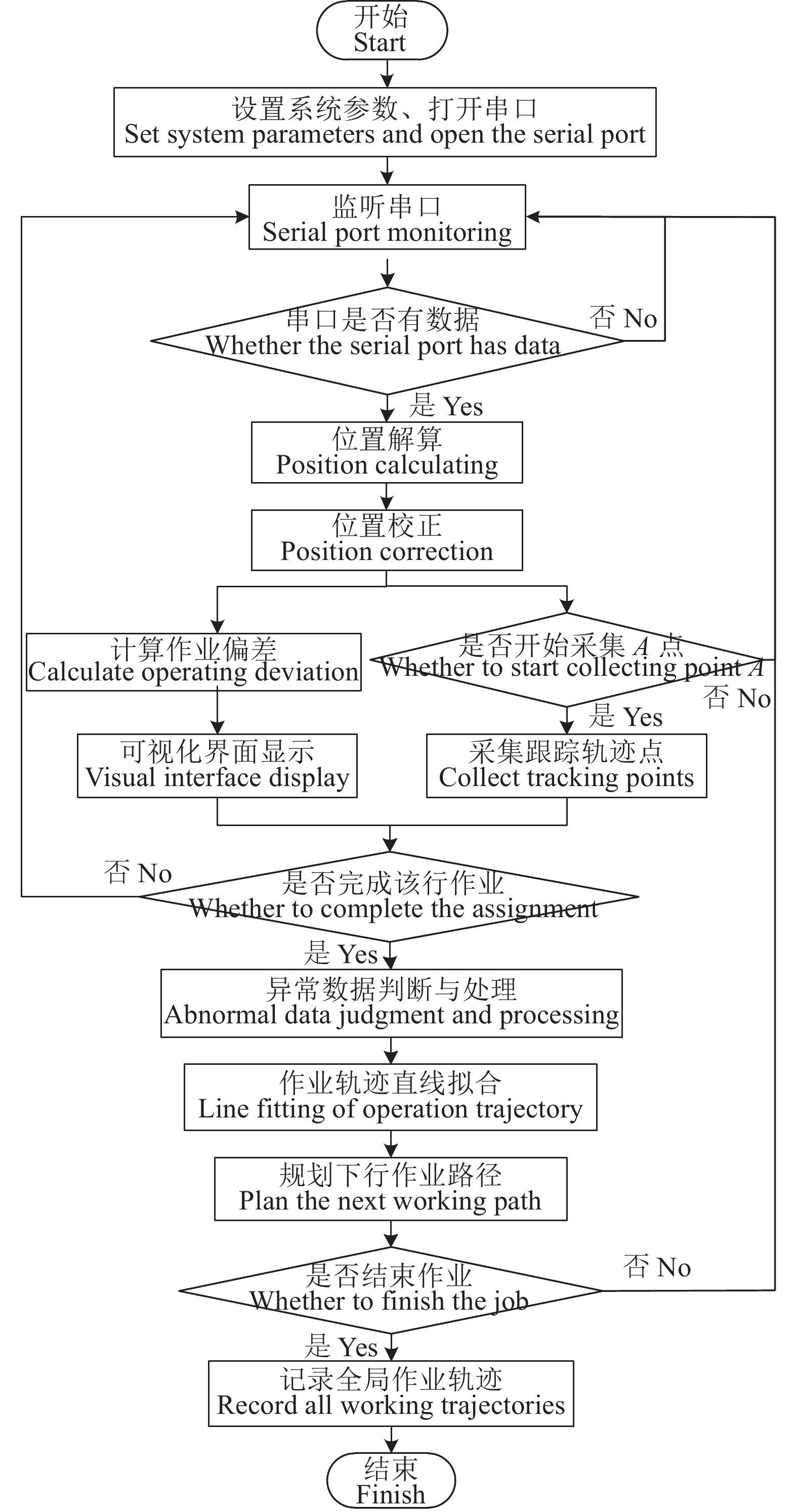
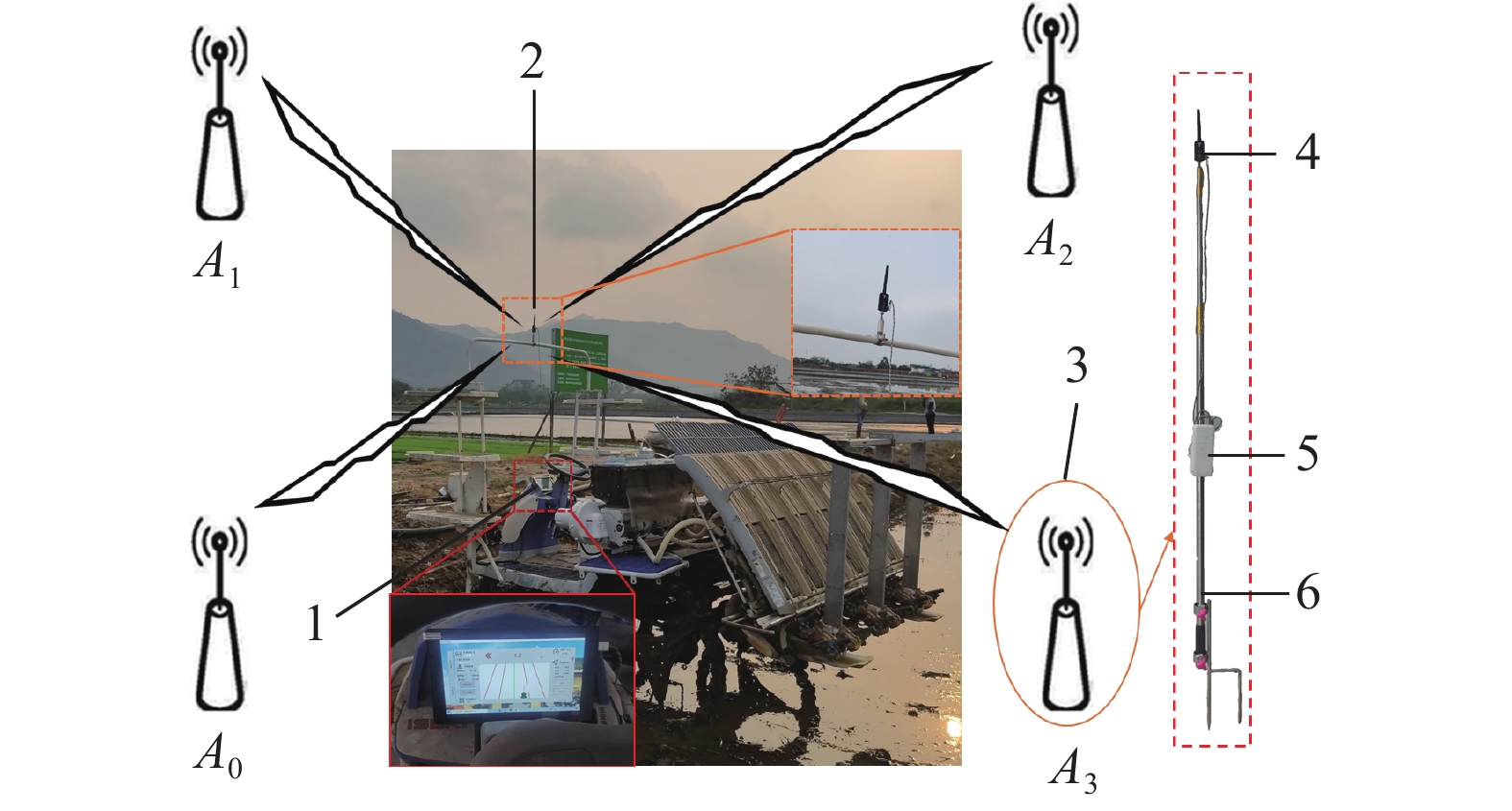
方法采用超宽带(Ultra wide band,UWB)技术对作业机械进行实时定位,通过位置解算算法,得到定位标签的三维精确位置坐标;利用位置校正算法,修正作业机械车身倾斜引起的田间定位误差;设计基于AB线的路径规划算法,实时规划作业路径并计算作业偏差;通过可视化人机交互界面为农机操作人员提供实时辅助驾驶信息。
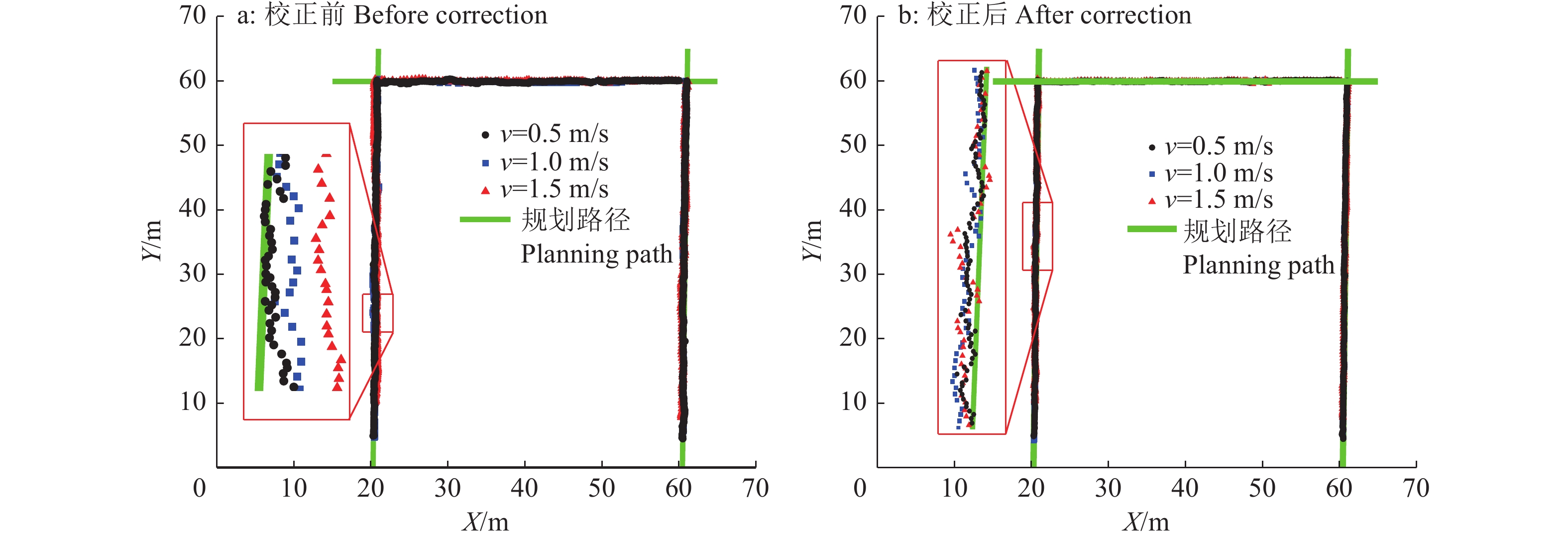
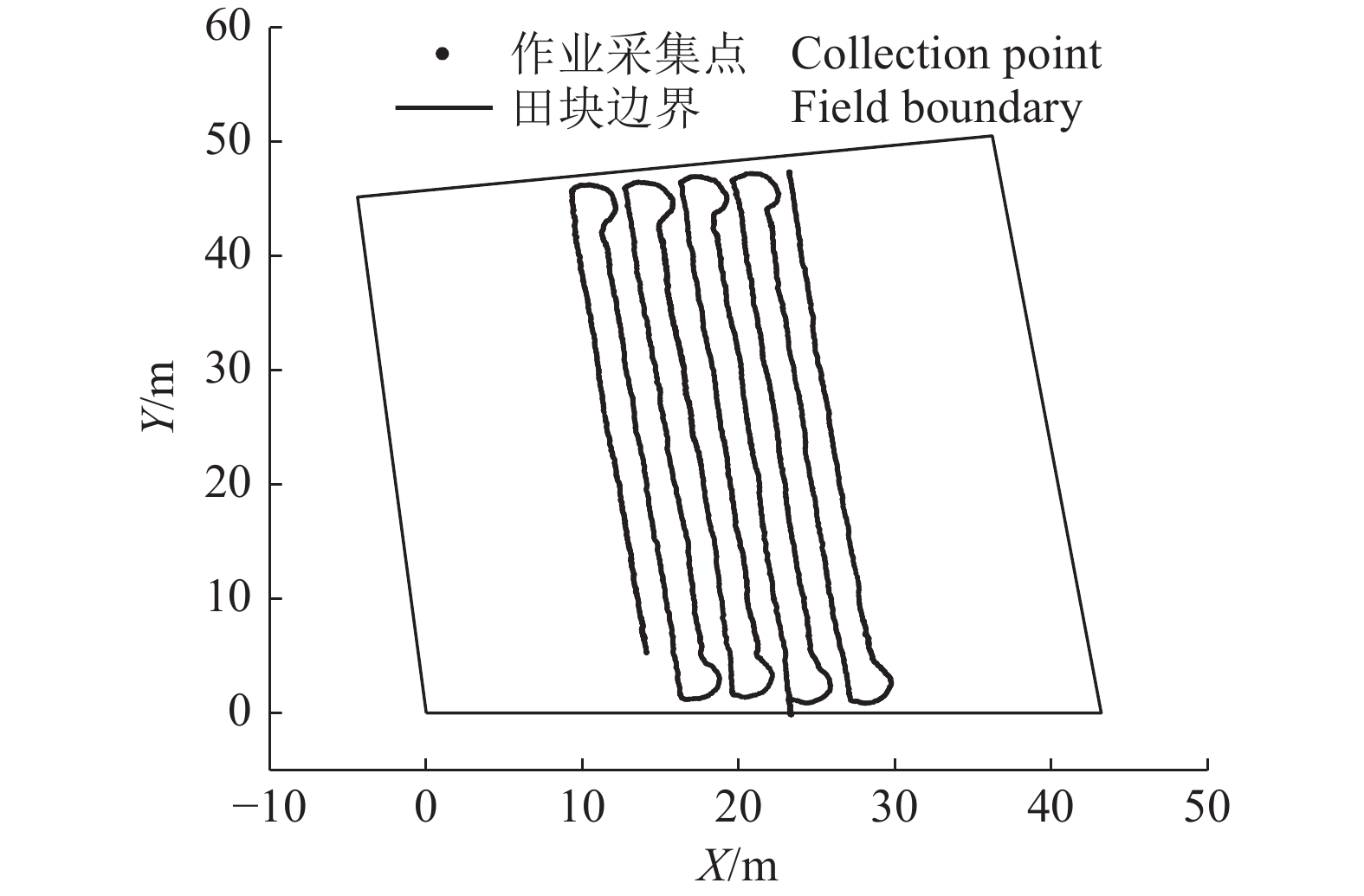
结果水田环境中,分别以0.5、1.0和1.5 m/s的速度沿规划路径行驶时,系统平均横向定位偏差均小于7 cm;当行驶速度大于1.0 m/s时,利用位置校正算法平均横向定位偏差降低了52.79%,标准差降低了49.82%,最大横向定位偏差降低了50.04%。搭载辅助导航系统进行田间插秧试验,各行作业轨迹与自身行拟合直线的平均横向偏差为5.90 cm,标准差为3.64 cm;各行作业轨迹与其规划直线路径的平均横向偏差为6.98 cm,标准差为4.95 cm。
结论辅助导航系统具有较高的定位精度和良好的稳定性,成本低且通用性强,能够满足南方中小型田块中农业机械田间作业要求。研究结果可为农业机械田间精确定位提供参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo achieve low-cost agricultural machinery field positioning for small and medium-size farmland in southern China, so as to reduce labor intensity for machine operator, and improve the working efficiency of agricultural machinery.
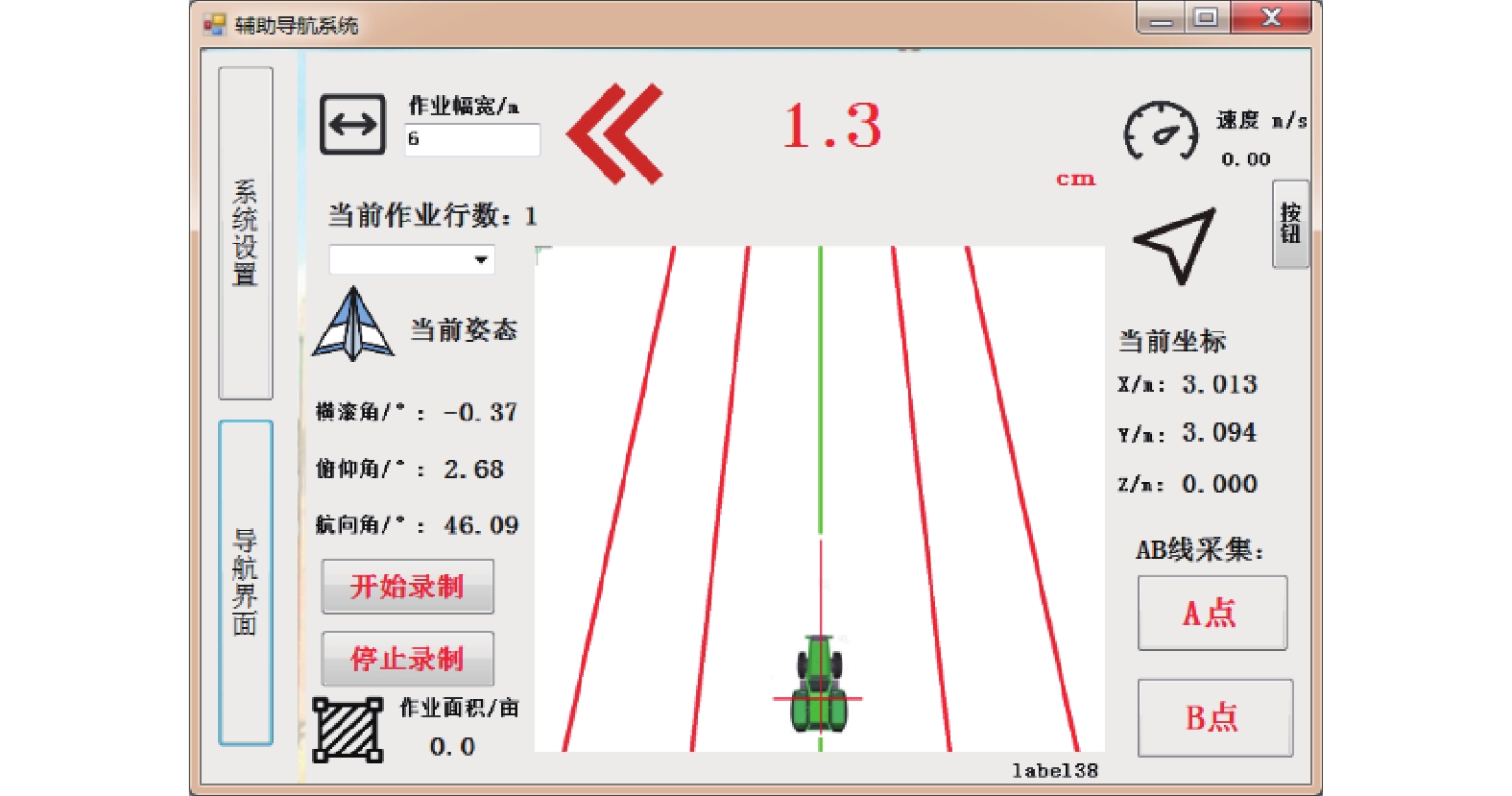
MethodThis system utilized ultra wide band (UWB) technology to accomplish real-time positioning of operating machinery, and the precise three-dimensional coordinates of the positioning labels were calculated using the localization algorithm. The position correction algorithm was then used to correct the field positioning error resulted from the body tilt of working machinery. A path planning algorithm based on AB line was designed to plan the operation path and calculate the operation deviation in a real-time manner. This system provided real-time driving assistance information for agricultural machinery operators through the visual human-computer interaction interface.
ResultIn the paddy field environment, the average lateral deviations were less than 7 cm when agricultural machinery traveled along the planned path at speeds of 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 m/s, respectively. When the travel speed was above 1.0 m/s, the average lateral deviation, the average standard deviation and the maximum lateral deviation were reduced by 52.79%, 49.82% and 50.04% respectively, based on the position correction algorithm. When the agricultural machinery equipped with the auxiliary navigation system was tested in the field transplanting experiment, the average lateral deviation between each operating trajectory and its fitting line was 5.90 cm and the average standard deviation was 3.64 cm. The average lateral deviation between each operating trajectory and its planned path was 6.98 cm and the average standard deviation was 4.95 cm.
ConclusionThe auxiliary navigation system has high positioning accuracy and good stability, as well as low-cost and strong universality, which can address the requirements of agricultural machinery field operation for small and medium-size farmland in southern China. The research results can provide a valuable reference for precise positioning of agricultural machinery in the field.
-
-
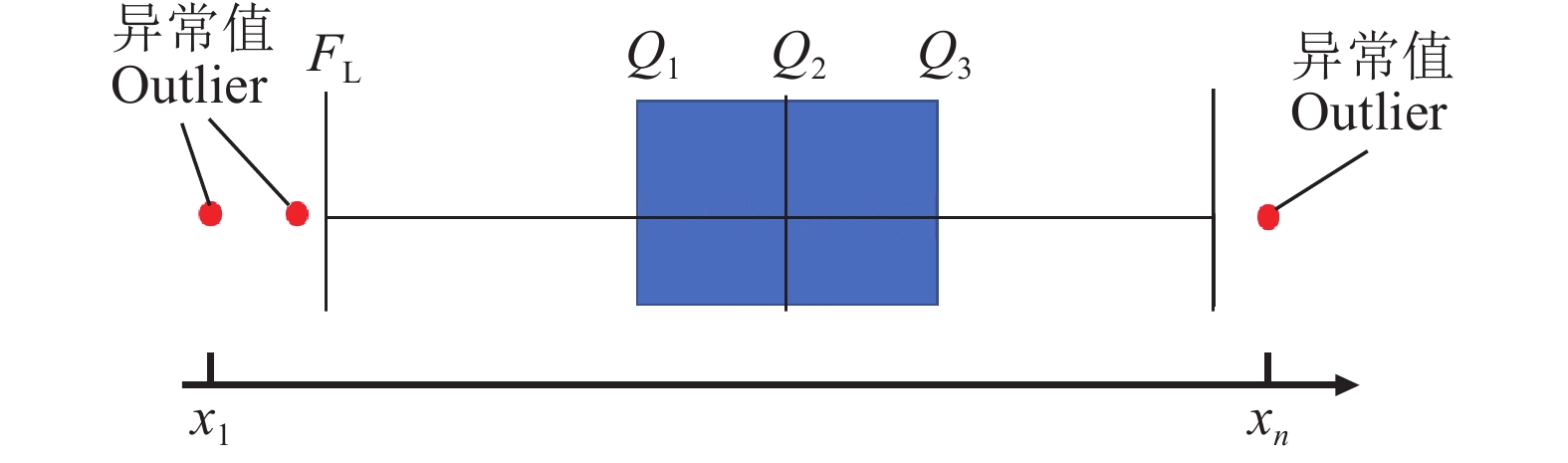
图 5 分位数分布图
FL:下边缘异常值分界点;FU:上边缘异常值分界点;Q1:下四分位数;Q2:中位数;Q3:上四分位数;x1:排序后第1个数据;xn:排序后第n个数据
Figure 5. Quantile distribution
FL: Lower edge outlier cut-off point; FU: Upper edge outlier cut-off point; Q1: Lower quartile; Q2: Median; Q3: Upper quartile; x1: The first data after sorting; xn: The n-th data after sorting
表 1 田间定位横向偏差
Table 1 Lateral deviation of field positioning
cm 行驶速度/
(m·s−1)
Travel speed
校正前 Before correction 校正后 After correction 最大值
Maximum value平均值
Average value标准差
Standard deviation最大值
Maximum value平均值
Average value标准差
Standard deviation0.5 21.10 8.01 4.94 15.93 6.15 4.06 1.0 33.83 13.81 8.57 16.90 6.52 4.30 1.5 45.10 17.30 12.14 17.97 6.61 4.66 表 2 各行作业轨迹与自身拟合直线、规划路径的横向偏差
Table 2 The lateral deviation of each operation track from self-fitting line and the planned path
cm 作业行数
Operation line作业轨迹与自身拟合直线
Between operating trajectory and self-fitting line作业轨迹与规划路径
Between operating trajectory and planned path最大值
Maximum value平均值
Average value标准差
Standard deviation最大值
Maximum value平均值
Average value标准差
Standard deviation1 13.10 8.68 3.54 2 7.80 3.43 2.09 7.87 3.25 2.21 3 13.28 5.23 3.16 16.07 5.41 3.89 4 12.11 4.53 2.95 15.66 5.06 4.00 5 13.20 4.64 3.29 16.52 5.74 4.31 6 18.27 7.54 4.75 31.50 11.30 8.47 7 16.38 6.35 3.98 17.88 7.45 4.04 8 19.27 6.79 4.83 24.28 9.90 6.36 9 16.15 5.88 4.20 24.86 7.73 6.29 -
[1] 姬长英, 周俊. 农业机械导航技术发展分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(9): 44-54. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.09.008 [2] 刘成良, 林洪振, 李彦明, 等. 农业装备智能控制技术研究现状与发展趋势分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(1): 1-18. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.01.001 [3] 胡静涛, 高雷, 白晓平, 等. 农业机械自动导航技术研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(10): 1-10. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.10.001 [4] LI W, XU B, DU Y, et al. Auxiliary navigation system based on Baidu map JavaScript API for high clearance sprayers[C]//2019 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems and Artificial Intelligence (ICUSAI). IEEE, 2019: 160-165.
[5] 刘卉, 孟志军, 付卫强. 基于GPS轨迹的农机垄间作业重叠与遗漏评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(18): 149-154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.18.022 [6] O'CONNOR M, BELL T, ELKAIM G, et al. Automatic steering of farm vehicles using GPS[C]//Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Precision Agriculture, 1996: 767-777.
[7] BAIO F H R. Evaluation of auto-guidance system operating on a sugar cane harvester[J]. Precision Agriculture, 2012(13): 141-147.
[8] 罗锡文, 张智刚, 赵作喜, 等. 东方红X-804拖拉机的DGPS自动导航控制系统[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(11): 139-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.11.025 [9] 刘兆朋, 张智刚, 罗锡文, 等. 雷沃ZP9500高地隙喷雾机的GNSS自动导航作业系统设计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(1): 15-21. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.01.03 [10] HAN S, ZHANG Q, NI B, et al. A guidance directrix approach to vision-based vehicle guidance systems[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2004, 43(3): 179-195. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2004.01.007
[11] 孙元义, 张绍磊, 李伟. 棉田喷药农业机器人的导航路径识别[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 47(2): 206-209. [12] 汪博. 基于机器视觉的农业导航系统[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2016. [13] 张漫, 季宇寒, 李世超, 等. 农业机械导航技术研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(4): 1-18. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.04.001 [14] 陆江林, 张文毅, 金诚谦. 我国水稻育插秧机械化制约因素分析[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2013, 34(2): 30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5553.2013.02.008 [15] 闫银发, 盖顺华, 李法德, 等. 基于北斗的农业机械立体视觉辅助导航系统设计[J]. 农业工程, 2017, 7(5): 36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2017.05.010 [16] 李林, 魏新华, 朱文静, 等. 宽幅施药机械机器视觉辅助导航系统研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2015, 46(9): 28-33. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.09.004 [17] 刘洺辛, 孙建利. 基于能效的WLAN室内定位系统模型设计与实现[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2014, 35(5): 1169-1178. [18] 王沁, 何杰, 张前雄, 等. 测距误差分级的室内TOA定位算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2011, 32(12): 2851-2856. [19] 贾骏超. 超宽带室内定位中NLOS误差抑制方法探讨[J]. 导航定位学报, 2017, 5(2): 60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2017.02.011 [20] 赵书尚, 李会彬, 刘斌. 基于GPS/INS自主耕作拖拉机导航修正研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2018, 40(5): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2018.05.010 [21] HE J, LUO X, ZHANG Z, et al. Positioning correction method for rice transplanters based on the attitude of the implement[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 176: 105598. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105598
[22] RYU J, ROSSETTER E J, GERDES J C. Vehicle sideslip and roll parameter estimation using GPS[C]//Proceedings of the AVEC 2002 6th International, Symposium on Advanced Vehicle Control: Hiroshima, Japan, 2002: 373-380.
[23] OSPINA R, NOGUCHI N. Improved inclination correction method applied to the guidance system of agricultural vehicles[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2020, 13(6): 183-194. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20201306.6012
[24] 孙力帆, 张雅媛, 郑国强, 等. 基于D-S证据理论的智能温室环境控制决策融合方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(1): 268-275. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.01.033



 下载:
下载: