Clonal variation and selection for growth and branch traits in young Tectona grandis plantations
-
摘要:目的
研究柚木Tectona grandis无性系生长与分枝性状遗传变异及相关性,综合评价并筛选速生、优良枝型的柚木无性系。
方法调查位于广西凭祥市的19个5年生柚木无性系的生长和分枝性状,进行重复力估算和相关性分析,并通过主成分分析计算每个无性系的综合得分。
结果柚木无性系间树高、胸径和单株材积差异极显著(P<0.001),变异系数28.2%~38.8%,重复力0.821~0.863;不同无性系间平均分枝角度、分枝基径和分枝长度呈极显著差异(P<0.001),变异系数16.3%~57.9%,重复力0.497~0.817;生长和分枝性状之间存在极显著(P < 0.01)或显著(P < 0.05)相关;利用主成分得分值大小和15%的入选率,兼顾生长和分枝性状,选出了3个优良的柚木无性系(7765、6601、7703),其综合得分大于对照,它们的树高、胸径、单株材积的平均值分别为5.68 m、6.20 cm和11.52 dm3,分别比相应均值提高了10.65%、15.39%和31.51%,选择后现实增益分别达到了9.07%、10.69%和30.20%。
结论5年生柚木无性系间生长与枝条性状存在丰富的遗传变异,有较高的改良潜力。生长和分枝性状受中等至较强的遗传控制。通过对5年生柚木无性系综合评价,选出了3个速生且分枝特性优良的柚木无性系,可作为优质柚木无性系材料在桂西南地区推广种植。
Abstract:ObjectiveThis study aims to investigate the genetic variation and correlation of the growth and branch traits of teak clones, and to comprehensively evaluate and select teak clones with rapid growth and excellent branch types.
MethodWe investigated the growth and branch traits of 19 teak clones at 5-year old located in the Pingxiang City of Guangxi, and conducted repeatability estimation and phenotype correlation analysis. The comprehensive score of each clone was calculated through principal component analysis.
ResultThere were significant differences (P<0.001) in tree height (H), diameter at breast height (DBH), and individual volume (V) among the teak clones, with coefficients of variation ranging from 28.2% to 38.8%, and repeatability ranging from 0.821 to 0.863. There were significant differences (P<0.001) in average branch angle (Ang), branch base diameter (BD), and branch length (BL) among different clones, with coefficients of variation ranging from 16.3% to 57.9%, and repeatablity ranging from 0.497 to 0.817. There were significant correlations (P<0.01 or P<0.05) between growth and branch traits. Using the principal component scores and a selection rate of 15%, three excellent teak clones (7765, 6601, 7703) were selected, with their comprehensive scores exceeding the control. Their average values for H, DBH and V were 5.68 m, 6.20 cm and 11.52 dm3 respectively, representing increases of 10.65%, 15.39% and 31.51% compared to the corresponding averages. After selection, the real gains in H, DBH and V were 9.07%, 10.69% and 30.20% respectively.
ConclusionThe growth and branch traits of 5-year-old teak clones exhibit rich genetic variation and high potential for improvement. The growth and branch traits are moderately to strongly controlled by genetic factors. Through comprehensive evaluation of the 5-year-old teak clones, three teak clones with rapid growth and excellent branch characteristics were selected. These clones can serve as high-quality genetic materials for teak clones and can be promoted in the southwest region of Guangxi.
-
Keywords:
- Tectona grandis /
- Clone /
- Branch character /
- Genetic variation /
- Comprehensive evaluation /
- Young tree stage
-
柚木Tectona grandis是马鞭草科柚木属高大乔木,具有生长快、质地美、耐腐防虫、易加工、尺寸稳定性好等优良特点,是世界著名珍贵用材树种[1]。由于其极高的经济价值和国际市场需求,被广泛引种于全球70多个国家,人工林总覆盖面积达435~689万公顷[2],我国大面积种植于上世纪60年代以后,目前柚木人工林覆盖总面积约3.5万公顷,但良种仍然缺乏,大径级无节材无法满足市场需求,主要依靠进口,速生、高效、优质的柚木人工林成为发展的主要目标[3-4]。
前期研究发现,柚木具有较强的萌芽力和成枝力,树冠内平均每20~30 cm基本形成一组对称的枝条[5],枝条作为树冠组成的主要构件[6],与林木生长有着密切关系,枝条的生长和分布特征直接影响森林树木的活力和生产力[6-7]。然而,枝条的生长及无用枝的发育不仅会消耗部分的养分,一定程度上还影响了木材的质量。随着树干的生长,侧枝在树干内部极易形成结疤,严重影响木材的机械性能,特别是自然整枝造成的死枝在树干内形成的节子,其完全愈合需要较长的时间,还极易遭受真菌、害虫的侵蚀,使得木材等级大打折扣[8-9]。因此,开展分枝性状相关研究对于了解树木的生长和提升木材品质具有重要作用。国内外研究者从栽培条件对枝条的影响方面对云杉Picea asperata[10]、夏栎Quercus robur[11]、西南桦Betula alnoides[12-13]、桉树Eucalyptus[14] 等树种进行了研究,为这些林木的培育发挥了重要的指导作用。目前,国内柚木良种选育主要围绕抗性[15-16]、生长[17-19]进行,迄今鲜见柚木分枝及其与生长的关系的报道。开展柚木无性系分枝性状遗传变异研究,有利于了解柚木分枝与生长的关系,减少潜在的节子缺陷,实现木材产量和质量的协同提升。本研究以广西凭祥市柚木无性系大田测定林5年生柚木数据为基础,重点分析柚木无性系生长与分枝性状的遗传变异规律及其相关性,综合选育出一批速生、分枝特性好的柚木无性系,为后续柚木优良无性系选育以及无节材培育提供材料保证。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料与大田试验设计
柚木无性系大田测定林位于广西壮族自治区凭祥市大青山实验场林区(21°57°47″~22°19°27″N,106°39′50″~106°59′30″E)。试验地为高温多雨的亚热带季风型气候,长夏无冬,干湿季节差异明显,光、水、热资源丰富。年平均气温19.5~21.4 ℃,年活动积温7124~7836 ℃,无霜期 > 340 d,作物可全年生长,四季宜耕。年平均降水量为1200~1500 mm,相对湿度为80%~84%。地貌类型为低山丘陵,坡度在25~30°之间。土壤为砖红壤,土层厚度>1 m。
柚木无性系大田测定林于2016年3月营建,参试材料是从印度和缅甸不同种源中选择优树组培繁殖的19个柚木无性系,并以1个柚木嫁接种子园中的优良家系为对照,其中,有15个无性系是原产缅甸的我国次生种源(6601、7514、7544、7549、7552、7559、7663、7703、7765、7772、7773、7886、7551、7813和FS3),1个无性系来自尼日利亚种源(7024),3个无性系来自印度种源(7107、7111和7114)。造林采用完全随机区组设计,每个小区9株(3×3),4次重复。带状造林,三行一带,种植带内柚木株行距2 m×2 m,种植带间距8 m,挖穴规格:60 cm×60 cm×50 cm,基肥:1.0 kg钙镁磷肥(P2O5质量分数为17%)+1.5 kg有机肥(N、P和K的质量分数均≥6%,有机质的质量分数≥48%,腐殖酸的质量分数≥12%)。
1.2 生长和分枝性状测定
2020年,用胸径尺和测高仪对柚木无性系测定林每木检尺测定树高(H)、胸径(DBH),按以下公式计算单株材积[14](V):
$$ {{V}} = 0.478\;7 \times {\text{DB}}{{\text{H}}^2} \times {{H}}。$$ (1) 计算出林分中柚木平均胸径和树高,据此每个无性系每次重复选出1株标准木(树冠完整,树干无分叉、无倾斜),包括对照总计80株标准木,全株测量分枝性状。所有标准木分枝调查最高高度为8 m,用游标卡尺在每个分枝的底部以2个垂直的方向测量分枝基径,用卷尺测量枝长,用角度尺测量除下冠直径小于1.3 cm的枝条外,其余所有枝条的分枝角(近轴角),根据分枝数据计算每株标准木所有分枝的平均分枝角度(Ang)、平均分枝基径(BD)、分枝频率(每米茎的分枝数,BF)、分枝基底面积(通过测量的分枝基径计算每米茎的所有分枝环处的分枝的横截面积之和,BBA)。其中BF和BBA是基于树干的分枝部分,即在每棵树中测量到的最高分枝的高度,而不是总树高。
1.3 数据分析
对生长和分枝指标进行方差分析和Duncan’s法多重比较,其线性混合模型[20] 为:
$$ {Y_{ijk}} = \mu + {B_i} + {C_j} + B{C_{ij}} + {\varepsilon _{ijk}},$$ (2) 式中,Yijk为试验第i重复第j无性系第k单株的观测值,μ为群体总体平均值,Bi为第i重复效应,Cj为第j无性系效应,
$B{C_{ij}} $ 为第j无性系和第i重复的互作效应,εijk为误差效应。$$ 表型变异系数^{[21]}({\rm{PCV}})={{{S}}}/{\bar X}\times 100{\text{%}},$$ (3) 式中,S为无性系表型标准差;
$ \bar X $ 为无性系某一性状的平均值。$$ 无性系重复力^{[18]}(R)=1-1/F,$$ (4) 式中,F为方差分析的F值。
$$ 无性系现实增益^{[17]}(G)= (\bar x - \bar X )/\bar X,$$ (5) 式中,G为现实增益,
$ \bar x $ 为入选无性系的平均值,$ \bar X $ 为所有无性系总均值。$$ 表型相关系数^{[17]}(\mathop r\nolimits_{\text{p}})= {{\mathop \sigma \nolimits_{{\text{p}x{\mathrm{p}}y}} }}\Big/\Big.{{\sqrt {\mathop \sigma \nolimits_{{\text{p}x}}^2 \mathop \sigma \nolimits_{{\text{p}y}}^2 } }},$$ (6) 式中,
$ \mathop \sigma \nolimits_{{\text{p}x{\mathrm{p}}y}} $ 为性状x与性状y的表型协方差;$ \mathop \sigma \nolimits_{\text{p}x} $ 为性状x的表型方差;$ \mathop \sigma \nolimits_{\text{p}y} $ 为性状y的表型方差。采用主成分分析[22],对柚木无性系生长和分枝性状进行综合得分排序。根据柚木优良无性系要求速生、节少、分枝细和分枝角小等特点,先对树高、胸径等正向性状(值越大越好)和分枝角度、分枝基径和分枝频率等负向性状(值越小越好)进行标准化处理[23],再计算不同主成分得分,根据各主成分方差贡献率计算综合得分并进行排序。正向性状标准化处理:(Xi−Xmin)/(Xmax−Xmin)和负向性状标准化处理:(Xmax−Xi)/(Xmax−Xmin),式中,Xi为各性状测量值,Xmax和Xmin分别为该性状不同无性系最大值和最小值。使用Genstat、SPSS26和Origin2023进行数据分析与图形绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 柚木无性系生长和分枝性状变异分析
参试的19个柚木无性系生长和分枝8个性状调查情况(表1)表明:5年生柚木树高、胸径和单株材积平均值为5.37 m、5.13 cm和8.76 dm3;单株材积的变幅最大,最小值仅为0.08 dm3,最大值为64.79 dm3;生长性状的变异系数范围28.2%~38.8%,其中树高为28.2%,胸径为35.1%,单株材积为38.8%。
表 1 柚木无性系各性状均值、变幅和变异系数Table 1. The mean value, amplitude and coefficient of variation of each character in teak clones性状
Trait均值
Mean变幅
Range表型变异系数(PCV)/%
Phenotypic variation coefficient树高/m Tree height 5.37 1.70~9.60 28.2 胸径/cm DBH 5.13 1.00~12.00 35.1 单株材积/dm3 Individual volume 8.76 0.08~64.79 38.8 分枝频率/m−1 Branch frequency 2.36 1.76~2.91 37.7 分枝角度/(°) Branch angle 54.01 33.21~88.00 17.7 分枝基底面积/(cm2·m−1) Branch basal area 28.84 6.87~109.68 57.9 分枝长度/m Branch length 1.39 0.80~2.57 16.3 分枝基径/cm Branch diameter 2.31 1.00~5.80 19.8 从分枝性状看,5年生柚木分枝频率、分枝角度、分枝基底面积、分枝长度和分枝基径的平均值分别为2.36 m−1、54.01°、28.84 cm2/m、1.39 m和2.31 cm;分枝基底面积的变幅最大,为6.87~109.68 cm2/m。分枝性状的变异系数范围16.3%~57.9%,其中分枝频率为37.7%,分枝角度为17.7%,分枝基径为19.8%,分枝长度为16.3%,分枝基底面积为57.9%。
这些结果还表明,分枝长度、分枝角度和分枝基径变异系数最小,胸径和树高中等,分枝基底面积变异系数最大,说明5年生柚木无性系生长和分枝性状之间存在丰富的遗传变异,在无性系水平上有较高的遗传改良潜力。
如表2所示,生长性状中,参试的19个柚木无性系间和无性系×重复间胸径、树高、单株材积均呈极显著差异(P<0.001),重复间树高差异不显著,胸径和单株材积呈显著差异(P<0.01)。生长性状在无性系水平上重复力的范围为0.821~0.863,都在0.8以上,属于高强度重复力,其中胸径的重复力最高,达到了0.863。表明了柚木无性系生长性状遗传变异显著,且遗传控制较强。
表 2 柚木无性系各性状方差分析与重复力Table 2. Analysis of variance and repeatability of various indicators in teak clones性状
TraitF1) 重复力
Repeatability无性系
Clone重复
Repeat无性系×重复
Clone×Repeat树高 Tree height 1.686*** 0.929 5.127*** 0.821 胸径 DBH 1.176*** 2.275** 3.921*** 0.863 单株材积 Individual volume 1.159*** 1.345** 3.269*** 0.846 分枝频率 Branch frequency 1.985 0.749 1.170 0.497 分枝角度 Branch angle 2.126*** 0.928 4.396*** 0.530 分枝基底面积 Branch basal area 2.856 2.827** 1.890*** 0.652 分枝长度 Branch length 3.823*** 0.552 1.517*** 0.739 分枝基径 Branch diameter 5.443*** 0.917 3.174*** 0.817 1)“**”和“***”分别表示在、0.01和0.001水平上差异显著 (F检验)
1) “**” and “***” represent significant differences at 0.01 and 0.001 levels, respectively (F statistics)分枝性状中,参试柚木19个无性系间分枝角度、分枝基径和分枝长度呈极显著差异(P<0.001),其余性状差异不显著,重复间分枝基底面积呈显著差异(P<0.01),其余性状差异不显著,无性系×重复间分枝角度、分枝基底面积、分枝长度、分枝基径呈极显著差异(P<0.001),其余性状差异不显著。分枝性状的重复力范围为0.497~0.817,其中分枝频率和分枝角度重复力较低,分别为0.497和0.530,分枝长度和分枝基径的重复力最高,分别为0.739和0.817。这意味着柚木无性系分枝性状也存在显著的遗传变异,且其遗传控制程度中等偏上,但相比于生长性状,环境因素对柚木分枝性状影响较大。
Duncan’s多重比较结果(表3)显示: 参试柚木19个无性系间胸径平均值为5.13 cm,共有12个无性系的胸径超过总体均值,以无性系7765最高,为6.09 cm,超过相应总体均值的18.70%。树高平均值为5.37 m,共有10个无性系的树高超过总体均值,以无性系7765最高,为6.46 m,超过相应总体均值的20.3%。单株材积平均值为8.76 dm3,共有8个无性系的材积超过总体均值,以无性系7765最高,为14.09 dm3,超过相应总体均值的60.84%。
表 3 柚木无性系生长和分枝性状的多重比较1)Table 3. Multiple comparisons of growth and branch traits of teak clones无性系
Clone胸径/cm
DBH树高/m
Tree
height单株材积/dm3
Individual
volume分枝角度/(°)
Branch
angle分枝基底面积/
(cm2·m−1)
Branch basal area分枝基径/cm
Branch
diameter分枝频率/m−1
Branch
frequency分枝长度/m
Branch
length7765 6.09a 6.46a 14.09a 51.76b 30.02ab 2.25abc 2.43a 1.45ab 7703 5.78a 6.26a 11.38ab 53.54ab 35.51a 2.35abc 1.91a 1.51ab CK 5.72ab 5.87ab 11.52ab 54.53ab 32.49ab 2.23abc 2.28a 1.52a 7559 5.62ab 5.57abc 10.55abc 57.06ab 32.41ab 2.65a 2.05a 1.40ab 7107 5.40bab 4.74bc 7.55bcde 61.08a 41.81a 2.66a 2.91a 1.37b 7514 5.40abc 5.82ab 11.78a 55.95ab 31.01ab 2.30abc 2.11a 1.51a 7111 5.39abc 5.11bc 8.42abcde 53.03ab 19.68b 2.31abc 2.66a 1.24c 7663 5.36abcd 5.63abc 9.35bc 51.98b 29.73ab 2.30abc 2.23a 1.43ab 7773 5.34abcd 5.92ab 10.44abcd 56.07ab 28.30ab 2.36abc 2.18a 1.43ab 7551 5.23abcd 5.52abc 8.66bcd 55.58ab 28.99ab 2.24abc 2.51a 1.34b 7813 5.18bcd 5.51abc 8.62abcde 52.17ab 26.31ab 2.14abc 2.69a 1.30c 6601 5.16bcd 5.87ab 9.09bc 53.05ab 18.51b 2.09bc 1.90a 1.25c 7544 5.04bcd 5.36bc 8.47abcde 54.91ab 32.73ab 2.16abc 1.76a 1.31b FS3 4.75bcd 4.46c 5.66cde 55.97ab 20.62b 2.04c 2.31a 1.30c 7886 4.75bcd 5.27bc 6.73bcde 52.85ab 29.96ab 2.30ab 2.67a 1.39ab 7549 4.38cd 5.04bc 5.36de 49.21b 28.59ab 2.36abc 2.86a 1.45ab 7114 4.37cd 4.41c 6.58bcde 52.32ab 25.21ab 2.36abc 2.62a 1.38b 7772 4.33cd 4.62bc 4.99e 54.19ab 28.96ab 2.47ab 2.55a 1.40ab 7552 4.12cd 4.52bc 5.01de 51.99b 19.87b 2.11bc 2.34a 1.32b 7024 4.11d 4.24c 7.08bcde 55.31ab 43.28a 2.65a 1.93a 1.54a 总计
Total5.13±0.08 5.37±0.06 8.76±0.34 54.01±0.58 28.84±1.27 2.31±0.33 2.36±0.06 1.39±0.23 1) 同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)分枝角度平均值为54.01°,以无性系7549最小,为49.21°。分枝基径平均值为2.31 cm,无性系FS3最低,为2.04 cm。分枝长度平均值为1.39 m,以无性系7024最高,为1.54 m,以无性系7111最低,为1.24 m。分枝基底面积平均值为28.84 cm2/m,无性系6601最低,为18.51 cm2/m。分枝频率平均值为2.36 m−1,无性系7544最低,为1.76 m−1。
2.2 柚木无性系生长与分枝性状相关性分析
生长与分枝性状间的相关性分析结果如表4所示,生长性状两两间呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),相关系数范围为0.78~1.00,胸径和单株材积的相关性最高(0.86),胸径和树高的相关性较低(0.78)。
表 4 柚木无性系生长与分枝性状间的相关性1)Table 4. Correlation between growth and branch traits of teak clones性状Trait BF BA BD BBA BL DBH H V 分枝频率(BF) Branch frequency 1.00 分枝角度(BA) Branch angle 0.11* 1.00 分支基径(BD) Branch diameter 0.09* −0.18** 1.00 分枝基底面积(BBA) Branch basal area 0.19** 0.37 0.81** 1.00 分枝长度(BL) Branch length −0.12* 0.35 0.21** 0.13** 1.00 胸径(DBH) Diameter at breast height 0.10 −0.27 −0.15 0.15* 0.31** 1.00 树高(H) Tree height −0.20* −0.13* −0.16 0.11* 0.28** 0.78** 1.00 单株材积(V) Individual volume −0.15* −0.18 −0.05 0.23** 0.43** 0.86** 0.85** 1.00 1)“*”和“**”分别表示在0.05和0.01水平显著相关 (Pearson法)
1) “*” and “**” represent significant correlations at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively (Pearson method)分枝性状间,分枝频率与分枝基底面积呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),相关系数为0.19,分枝频率与分枝角度和分枝基径呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),相关系数分别为0.11和0.09,分枝频率与分枝长度呈显著负相关(P < 0.05),相关系数为−0.12,分枝角度与分枝基径呈极显著负相关(P < 0.01),相关系数为−0.18,分枝基径与分枝基底面积呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),相关系数达到了0.81,分枝基底面积与分枝长度呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),相关系数为0.13。
生长与分枝性状间,分枝长度与树高、胸径、单株材积均呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),相关系数分别为0.28、0.31和0.43。分枝基底面积与单株材积呈极显著正相关(P < 0.01),相关系数为0.23,分枝基底面积与树高和胸径呈显著正相关(P < 0.05),相关系数分别为0.11和0.15。分枝基径与生长性状相关性不显著。分枝角度与树高呈显著负相关(P < 0.05),相关系数为−0.13,与胸径和单株材积相关性不显著。分枝频率与树高和单株材积呈显著负相关(P < 0.05),相关系数分别为−0.20和−0.15,与胸径相关性不显著。
2.3 参试柚木无性系综合评价与选择
本研究对柚木无性系的8个性状进行主成分分析(表5),共取得4个主成分,第1主成分的特征值(λ)为2.953,贡献率为36.914% ,在对应的特征向量中,数量较大的性状为树高、胸径和单株材积,相关系数分别为0.912、0.942和0.962。第2主成分的λ为1.649,贡献率达到了20.613%,数量较大的性状为分枝角度和分枝基底面积,相关系数分别为0.729和0.857。第3主成分的λ为1.143,贡献率为14.287%,数量较大的性状为分枝基径,相关系数为0.778。第4主成分的λ为0.999,贡献率为12.486%,数量较大的性状为分枝频率,相关系数为0.670。前4个主成分的累计贡献率达到了84.299% 。这样把原来的8个单项性状转换为4个新的相互独立的综合性状,而这4个新的综合性状则代表了原来8个单项性状84.299%的信息。可以用这4个主成分对柚木无性系综合性状进行概括分析。根据计算得到的特征向量,可得出前4个主成分的函数表达式:
表 5 柚木无性系生长与分枝性状主成分分析Table 5. Principal component analysis of growth and branch traits of teak clones成分
Component特征值
Eigenvalue方差百分比/%
Variance percentage累计贡献率/%
Contribution rate1 2.953 36.914 36.914 2 1.649 20.613 57.526 3 1.143 14.287 71.813 4 0.999 12.486 84.299 5 0.650 8.123 92.422 6 0.466 5.830 98.252 7 0.084 1.045 99.296 8 0.056 0.704 100 Y1=0.942X1+0.912X2+0.962X3−0.183X4−0.255X5−0.277X6+0.332X7−0.151X8,
Y2=0.008X1+0.313X2+0.065X3+0.857X4+0.729X5−0.275X6−0.064X7+0.447X8,
Y3=−0.031X1+0.037X2+0.106X3+0.059X4−0.046X5+0.778X6+0.54X7+0.446X8,
Y4=−0.129X1−0.036X2−0.082X3+0.12X4+0.313X5−0.056X6+0.67X7−0.64X8。
以不同主成分贡献率作为权重,计算主成分综合模型得分为:
Y=(36.914Y1+20.613Y2+14.287Y3+12.486Y4)/84.299。
数据标准化处理后,主成分综合模型得分由高到低统计见表6。
表 6 主成分得分和综合分数排名1)Table 6. Main component score and comprehensive score ranking无性系
CloneF1 F2 F3 F4 综合分值
Comprehensive score排名
Ranking7765 1.722 1.288 0.228 −1.367 0.905 1 6601 0.280 1.837 0.942 0.545 0.812 2 7703 1.479 −0.110 0.166 0.545 0.730 3 CK 1.103 −0.017 0.247 −0.576 0.435 4 7514 1.014 −0.389 −0.118 0.386 0.386 5 7544 0.300 −0.421 −0.144 2.381 0.357 6 7773 0.880 −0.311 −0.650 0.717 0.306 7 7559 0.911 −0.608 0.249 −0.127 0.274 8 7663 0.546 0.056 −0.674 0.729 0.246 9 7813 −0.187 0.197 0.634 −0.333 0.024 10 7111 −0.172 0.960 −0.652 −0.421 −0.013 11 7551 0.012 −0.587 0.975 −0.473 −0.043 12 FS3 −1.065 −0.426 1.709 1.043 −0.126 13 7886 −0.531 0.374 −0.613 −0.814 −0.365 14 7552 −1.455 0.990 −0.561 0.620 −0.398 15 7549 −1.273 1.449 −0.113 −1.698 −0.474 16 7024 −1.120 −1.522 2.439 −0.708 −0.554 17 7114 −1.306 0.122 −1.304 0.651 −0.667 18 7772 −1.162 −0.451 −1.120 0.513 −0.733 19 7107 0.026 −2.432 −1.641 −1.614 −1.101 20 1) F1、F2、F3和F4代表各主成分得分值
1) F1, F2, F3 and F4 represent the scores of each principal component综合主成分得分结果(表6)表明,参试材料中,对照CK的综合主成分得分为0.435,居20个参试材料的第4位;优于对照的无性系有3个,无性系7765排名第一,其综合主成分得分为0.905,其次为无性系6601和无性系7703,综合主成分得分依次为0.812和0.730;较对照差的柚木无性系有16个,综合主成分得分在−1.101~0.386。
通过上述分析评价,以15%的入选率选出速生、分枝特性优异的柚木无性系7765、6601和7703。入选无性系的生长性状树高、胸径和单株材积的平均值分别为5.68 m、6.20 cm和11.52 dm3,分别比相应均值提高10.65%、15.39%和31.51%。入选无性系的分枝性状分枝角度、分枝基底面积、分枝基径、分枝频率和分枝长度的平均值分别为52.78°、28.01 cm2/m、2.23 cm、2.08 m−1和1.40 m,分别比总平均值降低2.30%、2.81%、3.47%、11.86%和0.96%。选择后树高、胸径和单株材积的现实增益分别为9.07%、10.69%和30.20%。
3. 讨论与结论
3.1 讨论
本研究通过对广西凭祥市19个柚木无性系大田测定林进行生长和分枝性状研究,发现生长性状在无性系间存在极显著差异,分枝性状中的分枝角度、分枝基径和分枝长度在无性系间存在极显著差异,柚木无性系生长和分枝性状的表型变异系数均在15%以上。生长性状的重复力均在0.8以上(0.821~0.863),属于高度重复力,这和黄桂华等[18]对海南定安试验点3.5年生柚木无性系重复力估算的结果接近(0.852~0.873),大于Callister等[24]对西澳大利亚北部5年生柚木无性系生长性状(0.43~0.46)、Naranjo等[25]对哥斯达黎加北部4年生柚木无性系生长性状(0.36~0.53)和Goh等[26]对马来西亚东部6年生柚木生长性状(0.306~0.564)的重复力估算结果,稍小于付强等[27]对5年生柚木无性系(0.892~0.931)和黄桂华等[17]对11年生柚木无性系生长性状(0.888~0.924)的重复力估算结果,这可能是由于柚木无性系林龄不同,无性系选自种源不同及种植地点气候环境不同所导致,有待深入探究。分枝性状受中等及以上的遗传控制(0.497~0.817),这与王家燚等[28]对木荷Schima superba、凌娟娟等[22]对灰楸Catalpa fargesii、杨孟晴等[23]对赤皮青冈Quercus gilva和罗芊芊等[29]对南方红豆杉Taxus wallichiana var. mairei分枝性状研究结果相似。说明早期综合评价和选出生长和分枝性状优良的柚木无性系具有可行性。
林木不同性状之间存在不同程度的相关,本研究中对柚木无性系各性状间的相关性分析有助于优良无性系的选择。结果表明,生长性状之间存在极显著正相关关系,这与以前有关柚木无性系生长性状相关性的研究结果一致[17-18, 30],分枝性状之间也存在极显著或显著的相关关系,分枝基径与分枝基底面积的相关系数较大(0.81),其余各性状之间相关系数相对较小,其中分枝角度与分枝基径相关系数较小(−0.18),且与分枝长度不相关,说明分枝角度可能独立于其他性状进行遗传,这与凌娟娟等[22]对5年生灰楸、辛娜娜等[31]对5年生木荷和罗芊芊等[29]对5年生南方红豆杉结论相似,他们的研究表明,5年生灰楸分枝角度与其他性状间表型相关不显著,5年生木荷最大分枝角度与最大分枝基径不相关或弱相关,5年生南方红豆杉最大分枝角度与最大分枝基径相关性弱,这有利于选择易自然整枝的(分枝细、分枝角大)木荷和南方红豆杉等。本研究生长与分枝性状间存在极显著或显著的相关关系,相关系数都较小,说明生长和分枝性状相互独立,可单独定向选择[28]。其中分枝长度、分枝基底面积和分枝基径与生长性状呈正相关,分枝角度和分枝频率与与生长性状呈负相关。这与West等[14]对桉树分枝发育的研究结论相似,他的研究表明,拥有较大胸径的树木往往分枝的平均直径也越大。Hein等[10]对挪威云杉的分枝特征的研究也表明,分枝长度及直径的大小与林木胸径显著正相关。本研究说明了生长性状越好的柚木无性系,其分枝越长且越粗,其分枝角度越小(窄冠),分枝数量越少,自然整枝能力越强,这与其他树种得出的结论稍有不同[22, 28-29, 32]。介于本研究试验点只有1个,分枝特性对立地条件是否敏感,有待进一步探究,因此,加强柚木优良无性系多点测定,明确各无性系在所有潜在种植区域的相对表现,可选出适合不同地区的速生、分枝特性优异的无性系。
通过上述分析可知,柚木无性系各性状具有相互关联的作用,可以开展基于速生、分枝特性优异的无性系选育。根据付强等[27]报道的5年生可作为柚木无性系早期选择的年龄,并以此年龄按20%选择强度预选11年生柚木最优无性系,其选准率达80%。本研究采用5年生无性系的8个生长和分枝性状开展综合评价和筛选,为桂西南地区选择出速生、分枝特性优异的柚木无性系7765、6601、7703的结果是可信的,并且入选的3个无性系无论是从生长性状和分枝性状单独看亦或综合看,均在19个无性系中排名靠前,可作为后续遗传改良、良种选育和推广应用的基础。据前人研究,入选的柚木无性系7765在广东清远地区生长较好,无性系7703在广州苗圃中生长较好,无性系6601在潮州、湛江、清远大田和广州苗圃4个试验点中生长均表现优异[33],表明这3个无性系在华南的两广地区均有良好表现且推广应用潜力较大。尽管如此,由于柚木被定为25年长轮伐期树种[18],现仍处于幼林期,今后还需进一步进行跟踪观测和评价,验证无性系选择的准确性。
3.2 结论
5年生柚木无性系间生长与分枝性状存在丰富的遗传变异,有较高的改良潜力,生长和分枝性状受中等至较强的遗传控制,重复力变幅为0.497~0.863。可综合评价和选择速生且分枝特性优良的柚木无性系。通过对5年生柚木无性系综合评价,选出了3个优良无性系(7765、6601、7703),其综合得分大于对照,它们的树高、胸径和单株材积的平均值分别为5.68 m、6.20 cm和11.52 dm3,分别比相应均值提高10.65%、15.39%和 31.51%。选择后树高、胸径和单株材积的现实增益为9.07%、10.69%和30.20%。可作为生长和分枝综合优良的柚木无性系遗传材料在桂西南地区推广种植。
-
表 1 柚木无性系各性状均值、变幅和变异系数
Table 1 The mean value, amplitude and coefficient of variation of each character in teak clones
性状
Trait均值
Mean变幅
Range表型变异系数(PCV)/%
Phenotypic variation coefficient树高/m Tree height 5.37 1.70~9.60 28.2 胸径/cm DBH 5.13 1.00~12.00 35.1 单株材积/dm3 Individual volume 8.76 0.08~64.79 38.8 分枝频率/m−1 Branch frequency 2.36 1.76~2.91 37.7 分枝角度/(°) Branch angle 54.01 33.21~88.00 17.7 分枝基底面积/(cm2·m−1) Branch basal area 28.84 6.87~109.68 57.9 分枝长度/m Branch length 1.39 0.80~2.57 16.3 分枝基径/cm Branch diameter 2.31 1.00~5.80 19.8 表 2 柚木无性系各性状方差分析与重复力
Table 2 Analysis of variance and repeatability of various indicators in teak clones
性状
TraitF1) 重复力
Repeatability无性系
Clone重复
Repeat无性系×重复
Clone×Repeat树高 Tree height 1.686*** 0.929 5.127*** 0.821 胸径 DBH 1.176*** 2.275** 3.921*** 0.863 单株材积 Individual volume 1.159*** 1.345** 3.269*** 0.846 分枝频率 Branch frequency 1.985 0.749 1.170 0.497 分枝角度 Branch angle 2.126*** 0.928 4.396*** 0.530 分枝基底面积 Branch basal area 2.856 2.827** 1.890*** 0.652 分枝长度 Branch length 3.823*** 0.552 1.517*** 0.739 分枝基径 Branch diameter 5.443*** 0.917 3.174*** 0.817 1)“**”和“***”分别表示在、0.01和0.001水平上差异显著 (F检验)
1) “**” and “***” represent significant differences at 0.01 and 0.001 levels, respectively (F statistics)表 3 柚木无性系生长和分枝性状的多重比较1)
Table 3 Multiple comparisons of growth and branch traits of teak clones
无性系
Clone胸径/cm
DBH树高/m
Tree
height单株材积/dm3
Individual
volume分枝角度/(°)
Branch
angle分枝基底面积/
(cm2·m−1)
Branch basal area分枝基径/cm
Branch
diameter分枝频率/m−1
Branch
frequency分枝长度/m
Branch
length7765 6.09a 6.46a 14.09a 51.76b 30.02ab 2.25abc 2.43a 1.45ab 7703 5.78a 6.26a 11.38ab 53.54ab 35.51a 2.35abc 1.91a 1.51ab CK 5.72ab 5.87ab 11.52ab 54.53ab 32.49ab 2.23abc 2.28a 1.52a 7559 5.62ab 5.57abc 10.55abc 57.06ab 32.41ab 2.65a 2.05a 1.40ab 7107 5.40bab 4.74bc 7.55bcde 61.08a 41.81a 2.66a 2.91a 1.37b 7514 5.40abc 5.82ab 11.78a 55.95ab 31.01ab 2.30abc 2.11a 1.51a 7111 5.39abc 5.11bc 8.42abcde 53.03ab 19.68b 2.31abc 2.66a 1.24c 7663 5.36abcd 5.63abc 9.35bc 51.98b 29.73ab 2.30abc 2.23a 1.43ab 7773 5.34abcd 5.92ab 10.44abcd 56.07ab 28.30ab 2.36abc 2.18a 1.43ab 7551 5.23abcd 5.52abc 8.66bcd 55.58ab 28.99ab 2.24abc 2.51a 1.34b 7813 5.18bcd 5.51abc 8.62abcde 52.17ab 26.31ab 2.14abc 2.69a 1.30c 6601 5.16bcd 5.87ab 9.09bc 53.05ab 18.51b 2.09bc 1.90a 1.25c 7544 5.04bcd 5.36bc 8.47abcde 54.91ab 32.73ab 2.16abc 1.76a 1.31b FS3 4.75bcd 4.46c 5.66cde 55.97ab 20.62b 2.04c 2.31a 1.30c 7886 4.75bcd 5.27bc 6.73bcde 52.85ab 29.96ab 2.30ab 2.67a 1.39ab 7549 4.38cd 5.04bc 5.36de 49.21b 28.59ab 2.36abc 2.86a 1.45ab 7114 4.37cd 4.41c 6.58bcde 52.32ab 25.21ab 2.36abc 2.62a 1.38b 7772 4.33cd 4.62bc 4.99e 54.19ab 28.96ab 2.47ab 2.55a 1.40ab 7552 4.12cd 4.52bc 5.01de 51.99b 19.87b 2.11bc 2.34a 1.32b 7024 4.11d 4.24c 7.08bcde 55.31ab 43.28a 2.65a 1.93a 1.54a 总计
Total5.13±0.08 5.37±0.06 8.76±0.34 54.01±0.58 28.84±1.27 2.31±0.33 2.36±0.06 1.39±0.23 1) 同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)表 4 柚木无性系生长与分枝性状间的相关性1)
Table 4 Correlation between growth and branch traits of teak clones
性状Trait BF BA BD BBA BL DBH H V 分枝频率(BF) Branch frequency 1.00 分枝角度(BA) Branch angle 0.11* 1.00 分支基径(BD) Branch diameter 0.09* −0.18** 1.00 分枝基底面积(BBA) Branch basal area 0.19** 0.37 0.81** 1.00 分枝长度(BL) Branch length −0.12* 0.35 0.21** 0.13** 1.00 胸径(DBH) Diameter at breast height 0.10 −0.27 −0.15 0.15* 0.31** 1.00 树高(H) Tree height −0.20* −0.13* −0.16 0.11* 0.28** 0.78** 1.00 单株材积(V) Individual volume −0.15* −0.18 −0.05 0.23** 0.43** 0.86** 0.85** 1.00 1)“*”和“**”分别表示在0.05和0.01水平显著相关 (Pearson法)
1) “*” and “**” represent significant correlations at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively (Pearson method)表 5 柚木无性系生长与分枝性状主成分分析
Table 5 Principal component analysis of growth and branch traits of teak clones
成分
Component特征值
Eigenvalue方差百分比/%
Variance percentage累计贡献率/%
Contribution rate1 2.953 36.914 36.914 2 1.649 20.613 57.526 3 1.143 14.287 71.813 4 0.999 12.486 84.299 5 0.650 8.123 92.422 6 0.466 5.830 98.252 7 0.084 1.045 99.296 8 0.056 0.704 100 表 6 主成分得分和综合分数排名1)
Table 6 Main component score and comprehensive score ranking
无性系
CloneF1 F2 F3 F4 综合分值
Comprehensive score排名
Ranking7765 1.722 1.288 0.228 −1.367 0.905 1 6601 0.280 1.837 0.942 0.545 0.812 2 7703 1.479 −0.110 0.166 0.545 0.730 3 CK 1.103 −0.017 0.247 −0.576 0.435 4 7514 1.014 −0.389 −0.118 0.386 0.386 5 7544 0.300 −0.421 −0.144 2.381 0.357 6 7773 0.880 −0.311 −0.650 0.717 0.306 7 7559 0.911 −0.608 0.249 −0.127 0.274 8 7663 0.546 0.056 −0.674 0.729 0.246 9 7813 −0.187 0.197 0.634 −0.333 0.024 10 7111 −0.172 0.960 −0.652 −0.421 −0.013 11 7551 0.012 −0.587 0.975 −0.473 −0.043 12 FS3 −1.065 −0.426 1.709 1.043 −0.126 13 7886 −0.531 0.374 −0.613 −0.814 −0.365 14 7552 −1.455 0.990 −0.561 0.620 −0.398 15 7549 −1.273 1.449 −0.113 −1.698 −0.474 16 7024 −1.120 −1.522 2.439 −0.708 −0.554 17 7114 −1.306 0.122 −1.304 0.651 −0.667 18 7772 −1.162 −0.451 −1.120 0.513 −0.733 19 7107 0.026 −2.432 −1.641 −1.614 −1.101 20 1) F1、F2、F3和F4代表各主成分得分值
1) F1, F2, F3 and F4 represent the scores of each principal component -
[1] YANG B G, JIA H Y, ZHAO Z G, et al. Horizontal and vertical distributions of heartwood for teak plantation[J]. Forests, 2020, 11(2): 225.
[2] PACHAS A N A, SAKANPHET S, MIDGLEY S, et al. Teak (Tectona grandis) silviculture and research: Applications for smallholders in Lao PDR[J]. Australian Forestry, 2019, 82(sup1): 94-105.
[3] 国家林业和草原局. 中国森林资源报告(2014—2018)[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2019. [4] 梁坤南, 周再知, 马华明, 等. 我国珍贵树种柚木人工林发展现状、对策与展望[J]. 福建林业科技, 2011, 38(4): 173-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7351.2011.04.39 [5] 陈天宇. 密度与施肥对柚木无性系生长及枝条发育的影响[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2020. [6] 王志海, 尹光天, 杨锦昌, 等. 不同造林密度对米老排人工林枝条发育的影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(2): 78-86. [7] 王志海. 米老排人工林枝条发育的密度效应[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2019. [8] ALCORN P J, PYTTEL P, BAUHUS J, et al. Effects of initial planting density on branch development in 4-year-old plantation grown Eucalyptus pilularis and Eucalyptus cloeziana trees[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2007, 252(1/2/3): 41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2007.06.021
[9] WANG C S, ZHAO Z Z, HEIN S, et al. Effect of planting density on knot attributes and branch occlusion of Betula alnoides under natural pruning in southern China[J]. Forests, 2015, 6(12): 1343-1361. doi: 10.3390/f6041343
[10] HEIN S, MÄKINEN H, YUE C F, et al. Modelling branch characteristics of Norway spruce from wide spacings in Germany[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2007, 242(2/3): 155-164. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2007.01.014
[11] KINT V, HEIN S, CAMPIOLI M, et al. Modelling self-pruning and branch attributes for young Quercus robur L. and Fagus sylvatica L. trees[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2010, 260(11): 2023-2034. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2010.09.008
[12] WANG C S, TANG C, HEIN S, et al. Branch development of five-year-old Betula alnoides plantations in response to plantation density[J]. Forests, 2018, 9(1): 42.
[13] LIU K L, WANG C S, CHEN B Y, et al. Branch development in monoculture and mixed-species plantations of Betula alnoides, Erythrophleum fordii and Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis in southwestern China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2023, 528: 120643. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2022.120643
[14] WEST P W, RATKOWSKY D A, SMITH R G B. Factors controlling individual branch development during early growth of an experimental plantation of Eucalyptus pilularis in subtropical Australia[J]. Trees, 2021, 35(2): 395-405. doi: 10.1007/s00468-020-02040-4
[15] 黄桂华, 梁坤南, 周再知, 等. 柚木无性系苗期抗寒生理评价与选择[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2015, 43(9): 12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2015.09.003 [16] 黄桂华, 梁坤南, 周再知, 等. 柚木无性系苗期抗旱生理评价与选择的研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(5): 11-17. [17] 黄桂华, 梁坤南, 付强, 等. 11年生柚木无性系遗传变异与优良无性系选择[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(8): 18-22. [18] 黄桂华, 梁坤南, 周再知, 等. 柚木无性系生长性状的遗传变异与选择效应[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(1): 101-106. [19] 梁坤南, 黄桂华, 林明平, 等. 琼西南柚木次生种源/家系多性状综合选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2020, 33(6): 13-22. [20] 王楚彪, 罗建中, 何文亮, 等. 桉树无性系多区域联合测试的G×E分析及选优[J]. 林业科学, 2022, 58(11): 108-117. [21] 王芳, 马茂, 王佳兴, 等. 日本落叶松遗传变异分析及优良家系无性系选择[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39(4): 48-57. [22] 凌娟娟, 肖遥, 杨桂娟, 等. 灰楸无性系生长和形质性状变异与选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2019, 32(5): 149-156. [23] 杨孟晴, 邵慰忠, 徐永宏, 等. 3年生赤皮青冈家系生长和形质性状变异与选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2023, 36(4): 31-40. [24] CALLISTER A N. Genetic parameters and correlations between stem size, forking, and flowering in teak (Tectona grandis)[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 2013, 43(12): 1145-1150. doi: 10.1139/cjfr-2013-0226
[25] NARANJO S S, MOYA R, CHAUHAN S. Early genetic evaluation of morphology and some wood properties of Tectona grandis L. clones[J]. Silvae Genetica, 2012, 61: 58-65. doi: 10.1515/sg-2012-0008
[26] GOH D K S, JAPARUDIN Y, ALWI A, et al. Growth differences and genetic parameter estimates of 15 teak (Tectona grandis L. f.) genotypes of various ages clonally propagated by microcuttings and planted under humid tropical conditions[J]. Silvae Genetica, 2013, 62: 196-206. doi: 10.1515/sg-2013-0024
[27] 付强, 黄桂华, 周强, 等. 柚木无性系早期选择年龄的研究[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 30-38. [28] 王家燚, 陈焕伟, 张蕊, 等. 木荷全同胞家系生长与分枝性状的遗传变异及效应分析[J]. 浙江农林大报, 2023, 40(4): 738-746. [29] 罗芊芊, 楚秀丽, 李峰卿, 等. 5年生南方红豆杉生长和分枝性状家系变异与选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2020, 33(1): 136-143. [30] 黄桂华. 柚木种质资源遗传变异和优良无性系早期选择的研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2015. [31] 辛娜娜, 张蕊, 范辉华, 等. 5年生木荷生长和形质性状的家系变异和选择[J]. 林业科学研究, 2014, 27(3): 316-322. [32] 刘青华, 金国庆, 张蕊, 等. 24年生马尾松生长、形质和木材基本密度的种源变异与种源区划[J]. 林业科学, 2009, 45(10): 55-61. [33] 刘炳妤. 柚木无性系生长、光合与耐寒生理特性的研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2019.
计量
- 文章访问数: 72
- HTML全文浏览量: 11
- PDF下载量: 9





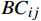










 下载:
下载:
