Responses of maize growth to low phosphorus and phosphorus fertilizer application in different types of soil
-
摘要:目的
通过在酸性和石灰性土壤上种植玉米,探究在不同类型土壤上,缺磷和施用磷肥对玉米生长、磷吸收、根系性状、菌根侵染率以及根际指标的影响。
方法分别利用2种不同来源的酸性土壤(NX和WY)与2种不同来源的石灰性土壤(SP和CP)进行不施磷肥(低磷,LP)与施磷肥(高磷,HP)的玉米盆栽试验,对玉米的植株干质量、磷质量、根系性状(总根长、根表面积、根体积、平均根直径)、菌根侵染率、以及根际指标(根际pH、根际磷酸酶活性、根际羧酸盐含量)进行测定分析。
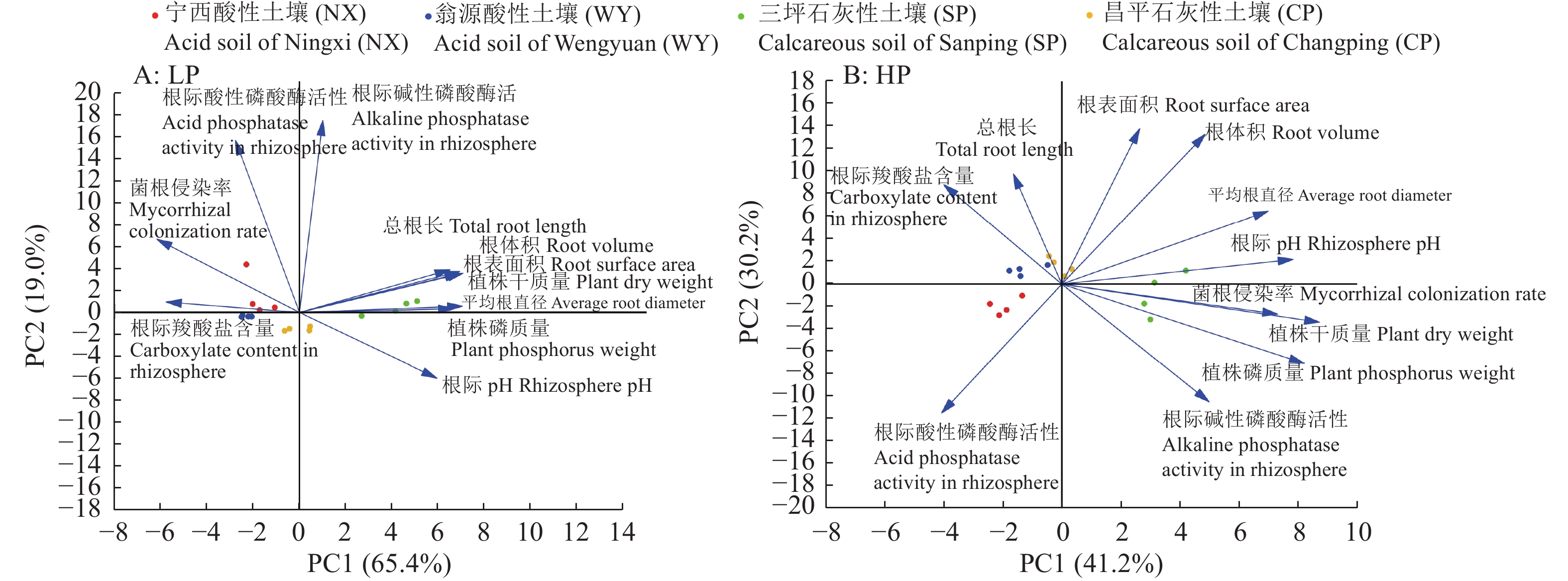
结果缺磷严重影响玉米植株生长,施磷显著增加了酸性和石灰性土壤上玉米植株干质量和磷质量;在2种酸性土壤和CP石灰性土壤中,施磷显著增加了玉米总根长、根表面积、根体积、平均根直径,降低了玉米菌根侵染率和根际羧酸盐含量;施磷显著降低了NX酸性土壤中根际酸性磷酸酶活性和CP石灰性土壤根际pH。主成分分析表明,在低磷条件下,根系性状与植株干质量和磷质量呈正相关关系,根际羧酸盐含量、菌根侵染率与植株干质量和磷质量均呈负相关关系;在高磷条件下,菌根侵染率、碱性磷酸酶活性、根际pH、平均根直径与植株干质量和磷质量均呈正相关关系。
结论施用磷肥可促进不同类型土壤上玉米植株的生长和磷吸收,玉米对施磷的响应很大程度上受到土壤本底养分含量的影响,有效磷含量低的土壤对施用磷肥的响应更加明显。在低磷条件下,玉米主要通过改变根系性状促进磷吸收。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of phosphorus (P) deficiency and P fertilizer application on maize growth, P uptake, root traits, mycorrhizal colonization rate, and rhizosphere indexes in acid or calcareous soil.
MethodTwo different sources of acid soil (NX and WY) and two different sources of calcareous soil (SP and CP) were used in the pot experiment for maize with no P fertilization (low P, LP) or P fertilization (high P, HP) treatment. Maize plant dry weight, P weight, root traits (total root length, root surface area, root volume, average root diameter), mycorrhizal colonization rate, and rhizosphere indexes (rhizosphere pH, rhizosphere phosphatase activity, rhizosphere carboxylate content) were determined.
ResultP deficiency seriously affected plant growth, and P application significantly increased plant dry weight and P weight of maize in acid or calcareous soil. P application significantly increased total root length, root surface area, root volume, and average root diameter, and reduced mycorrhizal colonization rate and rhizosphere carboxylate content of maize in both acid soil and CP calcareous soil. P application also significantly reduced rhizosphere acid phosphatase activity in NX acid soil and rhizosphere pH in CP calcareous soil. Principal component analysis showed that, under low P condition, maize root traits were positively correlated with plant dry weight and P weight, while rhizosphere carboxylate content and mycorrhizal colonization rate were negatively correlated with plant dry weight and P weight. Under high P condition, mycorrhizal colonization rate, alkaline phosphatase activity, rhizosphere pH, and average root diameter of maize were all positively correlated with plant dry weight and P weight.
ConclusionP fertilization can promote plant growth and P uptake of maize in different type of soil. The response of maize to P application is largely influenced by the background nutrient content in soil, and the soil with low P availability is more responsive to P fertilization. Maize mainly alters root traits to promote P uptake under low P condition.
-
Keywords:
- Maize /
- Acid soil /
- Calcareous soil /
- Phosphorus treatment /
- Low phosphorus
-
水稻是全球50%以上人口赖以生存的主要粮食作物[1]。随着温饱问题的解决和生活水平的普遍提高,我国稻米消费结构发生了根本性的变化,已经从吃得饱向吃得好转变,消费者越来越重视稻米品质,尤其是食味品质,导致市场对中高端大米的消费需求日益旺盛[2-4]。尤其是毗邻港澳经济较为发达的广东,历来重视优质稻米产业的发展,是我国籼型水稻优质化育种的先行地,其生产的广东丝苗型优质米畅销港澳、东南亚、欧美、南美和非洲[5]。
米饭食味是一个由稻米及蒸煮营养品质特性共同决定的复杂性状,包括米饭的色、香、味和口感[6]。它不仅受品种自身的遗传基因控制[1,7-9],而且还与其生长期间的光温生态条件和栽培管理措施密切相关,尤其是氮肥的施用量对稻米蒸煮营养与食味品质的影响较大[10-20]。先前研究者们主要是针对影响米饭食味的主要理化指标(蒸煮营养品质)如直链淀粉含量(Amylose content,AC)、胶稠度(Gel consistency,GC)、碱消值(Alklai spreading value, ASV)、蛋白质含量(Protein content, PC)和脂肪酸含量(Fat acid content, FAC)等方面开展了大量研究[6-9,20-21],但同时对稻米蒸煮营养和米饭食味品质的相关研究报道较少,且以往研究所采用的供试材料均以常规稻品种(系)为主[6,21-22],类型比较单一。此外,大量的研究表明,稻米的蒸煮营养与米饭食味品质性状受种植环境(季节)以及施氮水平、施肥方式和插值密度等栽培管理措施的影响较大[10-17,23-29],且不同品种(系)的反应敏感度也不一致[29]。因此,研究不同类型水稻品种(系)的稻米蒸煮营养与米饭食味品质性状对施氮量和种植季节的敏感性,并筛选出食味品质好且对施氮量(即环境条件)和种植季节不敏感的品种/系(基因型),对于进一步培育食味品质优良且品质稳定的水稻新品种,全面提升我国稻米质量、培育稻米品牌、提升农民的种粮效益和优质稻米的国际竞争力,均具有十分重要的意义。
先期的研究多以长江流域中稻或北方粳稻为试材,开展施氮量对稻米品质的影响研究[2,10-15,23-30],而以华南双季籼型水稻品种(系)为研究对象的相关研究较少,且不同品种蒸煮营养与食味品质对环境(种植季节)和施氮量的反应敏感度方面的研究更是鲜有报道。为此,本研究利用华南籼型优质常规稻、优质杂交稻及其亲本、高产杂交稻和高产常规稻品种(系)等3大类型水稻品种(系)作为供试材料,通过在华南早、晚两季4个不同施氮水平下种植,分析华南各类水稻品种的主要蒸煮营养和食味品质受施氮肥量和种植季节的影响情况,为米饭食味优良且稳定的华南水稻优质新品种培育和高产优质配套生产技术的研发提供重要的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
选取各类型水稻品种(系)17份,作为供试材料。其中,广东丝苗米类型优质常规稻品种(系)4份,优质杂交稻及其亲本9份,高产杂交稻及其亲本和高产常规稻4份,其特性如表1所示。由于泰优1002为弱感光迟熟品种,早季不能正常抽穗,因此,该品种不参与早季试验,仅列入晚季试验。
表 1 17个供试材料的品种(系)类型和主要特性Table 1. Types and characteristics of the 17 tested varieties (lines)品种类别
Variety type品种(系)
Variety (line)编号
Code主要特性
Main characteristic优质丝苗米常规品种
High quality inbred variety
of simiao rice美香占2号 MXZ2 广东丝苗米品种,优质常规稻,连续3届获国家优质稻食味鉴评金奖品种 象牙香占 XYXZ 广东丝苗米品种,优质常规稻,国家优质稻食味鉴评金奖品种 客都寿乡1号 KDSX1 广东丝苗米品系,优质常规稻 象竹香丝苗 XZXSM 广东丝苗米优质品种,感温型常规稻 优质杂交稻及其亲本
High quality hybrid rice and their parents泰丰B TFB 杂交稻优质不育系(母本)泰丰A的同核异质保持系,常规稻 泰丰优208 TFY208 感温型三系杂交稻,连续3届获国家优质稻食味鉴评金奖品种 广恢208 R208 优质杂交稻泰丰优208的父本,恢复系 泰优398 TY398 中早熟三系杂交稻,江西、安徽的优质稻食味鉴评金奖品种 广恢398 R398 优质杂交稻泰优398的父本,恢复系 泰优390 TY390 优质三系杂交稻,湘米工程重点推广优质稻品种 广恢390 R390 优质杂交稻泰优390的父本,恢复系 泰优1002 TY1002 弱感光型三系杂交稻,连续2届获国家优质稻食味鉴评金奖品种 广恢1002 R1002 优质杂交稻泰优1002的父本,恢复系 高产常规稻和超级杂交稻品种及其亲本
High yielding inbred and hybrid rice and their parents五丰B WFB 五优308的母本五丰A的同核异质保持系 五优308 WY308 超级杂交稻,感温型三系杂交稻 广恢308 R308 五优308的父本,恢复系 特三矮2号 TSA2 普通高产常规稻品种 1.2 试验方法
本研究的田间试验分别于2021年3—7月(早季)和2021年7—11月(晚季)在广东省农业科学院白云试验基地进行。早、晚两季均在同一块试验田进行,试验开始前采用五点取样法取耕作层(0~20 cm)土壤进行本底养分状况的测定。早造土壤pH为6.01,有机质为28.14 g/kg,有效磷为30.45 mg/kg,速效钾为106.01 mg/kg,碱解氮为82.47 mg/kg;晚造土壤pH为6.10,有机质为31.8 g/kg,有效磷为35.09 mg/kg,速效钾为102.15 mg/kg,全氮(大于碱解氮)为1.66 g/kg。
试验采用裂区设计(主区为施氮量处理,副区为供试品种),主副区完全随机排列,小区面积(13.2 m×6.3 m)83.16 m2,主区组间设置排灌沟,所有小区间筑埂后覆膜。供试材料早季3月8日播种,4月9日移栽;晚季7月23日播种,8月10日移栽。采用人工插秧移栽,插植规格16.7 cm×20.0 cm,双株植。设4个水平的N肥处理,即0(N0)、90(N1)、135(N2)和180 kg/hm2(N3)。早季除N0处理没有设置重复外,其他3个施氮水平处理均设置3次重复;晚季4个施氮处理均设置3次重复。供试肥料氮肥为尿素,磷肥为过磷酸钙,钾肥为氯化钾。其中,氮肥按照基肥︰分蘖肥︰穗肥=5︰2︰3的质量比分3次施入。各处理除氮肥施用量不同外,磷、钾肥的使用量均相同,即过磷酸钙按11 kg/hm2标准在移栽前一次性施入;氯化钾使用量为78 kg/hm2,按基肥︰穗肥=1︰1的质量比分2次施入。其他按常规大田栽培管理。供试材料齐穗后35 d收割,稻谷收获后及时晾晒干。
1.3 品质测定
1.3.1 蒸煮营养品质
碱消值(ASV)参照标准NY/T 83—2017进行测定[31];胶稠度(GC)参照国标GB/T 22294—2008,用米胶延长法进行测定[32];直链淀粉含量(AC)参照标准GB/T 15683—2008/ISO 6647-1:2007进行测定[33];精米的蛋白质含量(PC)参照GB 5009.5—2016进行测定[34],采用全自动凯氏定氮仪测定精米全氮含量,根据以下公式计算精米蛋白质质量分数(PC):
PC=样品全氮量×5.95 ÷ 样品质量×100%。
1.3.2 米饭食味
米饭食味值(Taste value of cooked rice , TV)参照石吕等[23]的方法测定。称取精米样品17 g,用流水洗涤至清澈,按照米︰水质量比为1.0︰1.4的比例,将米和水放进不锈钢罐中,水沸腾后蒸25 min,然后再焖10 min,开盖将米饭翻至松软后冷却15 min,称取7 g米饭制成米饼,利用日本佐竹SATAKE/STAIB米饭食味计测定米饭食味值,正反两面重复测定2次,取平均值。
1.4 数据处理
试验数据利用 Statistic 8.0 软件进行双因素方差分析(Two-way ANOVA)和差异显著性多重比较(LSD),P<0.05 表示差异显著,P<0.01 表示差异达极显著;采用线性模型(Pearson 相关)进行相关性分析;变异系数(CV)计算公式: CV =标准偏差/平均值×100%。
1.5 水稻品种(系)对氮肥敏感度的划分
根据处理间差异显著性,将供试品种(系)的氮肥敏感性划分为3个等级: 1)氮肥钝感型:4个施氮处理间差异不显著;2)中度敏感型:4个施氮处理间差异显著性多重比较结果中,仅标注有a和b两种字母,即仅有a~b之间1个差异等级;3)敏感型:4个施氮处理间差异显著性多重比较结果中,标注有a、b、c 3种字母,即存在有a~b和b~c 2个等级的差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 早、晚季不同施氮量处理下的蒸煮营养与食味品质比较
对早季试验结果进行双因素方差分析,结果(表2)表明,16个供试品种(系)间的胶稠度(GC)、直链淀粉含量(AC)、碱消值(ASV)、蛋白质含量(PC)和米饭食味值(TV)差异均达到极显著水平(P˂0.01);不同施氮量处理间PC差异达到极显著水平(P˂0.01)、米饭TV差异达显著水平(P˂0.05),其他如GC、AC和ASV的差异均未达显著水平;GC在施氮量与品种之间存在极显著的互作效应(P=0.0001),AC、ASV和米饭TV等3个性状则不存在互作效应。说明在早季GC、ASV、AC、精米PC和米饭TV主要由品种的遗传背景决定,但精米PC和米饭TV同时也受施氮量的影响,GC同时受到施氮量与品种之间的互作效应影响。
表 2 早、晚季蒸煮食味品质相关性状的双因素方差分析Table 2. Two-way analysis of variance for cooking and eating quality related traits in early and late seasons性状
Trait变异来源
Source早季 Early season 晚季 Late season 自由度
DF离均差平
方和 SS均方
MSF P 自由度DF 离均差平
方和 SS均方
MSF P 胶稠度
Gel consistency
(GC)施氮量
N application rate2 42.10 21.06 0.58 0.600 9 3 1 490.9 496.97 4.05 0.068 5 品种 Cultivar 15 65 384.80 4 358.99 57.80 0.000 0 16 63 693.3 3 980.83 129.20 0.000 0 施氮量×品种
N application rate×Cultivar30 6 153.70 205.12 2.72 0.000 1 48 3 507.6 73.07 2.37 0.000 1 直链淀粉含量
Amylose content
(AC)施氮量
N application rate2 3.55 1.77 1.46 0.334 1 3 42.60 14.20 9.99 0.009 5 品种 Cultivar 15 2 930.79 195.39 388.33 0.000 0 16 2 347.41 146.71 85.68 0.000 0 施氮量×品种
N application rate×Cultivar30 13.50 0.45 0.89 0.625 2 48 132.93 2.77 1.62 0.017 6 碱消值
Alkali spreading value (ASV)施氮量
N application rate2 0.51 0.25 1.53 0.321 2 3 0.406 0.14 1.39 0.333 6 品种 Cultivar 15 547.79 36.52 99.72 0.000 0 16 890.177 55.64 316.11 0.000 0 施氮量×品种
N application rate×Cultivar30 12.33 0.41 1.12 0.330 4 48 4.251 0.09 0.50 0.996 1 蛋白质含量
Protein content
(PC)施氮量
N application rate2 10.52 5.26 226.10 0.000 1 3 80.364 26.79 81.46 0.000 0 品种 Cultivar 15 31.03 2.07 13.99 0.000 0 16 26.420 1.65 15.81 0.000 0 施氮量×品种
N application rate×Cultivar30 3.52 0.12 0.79 0.7593 48 14.670 0.31 2.93 0.000 0 米饭食味值
Taste value of cooked rice (TV)施氮量
N application rate2 165.30 82.65 7.21 0.047 1 3 820.90 273.63 32.34 0.000 4 品种 Cultivar 15 10 137.40 675.83 101.93 0.000 0 16 6 747.16 421.70 159.09 0.000 0 施氮量×品种
N application rate×Cultivar30 227.60 7.59 1.14 0.306 9 48 387.43 8.07 3.04 0.000 0 对晚季试验结果进行双因素方差分析,结果(表2)表明,17个供试品种(系)间的GC、AC、ASV、PC和米饭TV差异都达到了极显著水平(P˂0.01);不同施氮量处理间AC、PC和TV差异达到极显著水平(P˂0.01),但GC和ASV在不同施氮量处理间差异不显著;施氮量与品种之间互作对AC的影响达显著水平(P˂0.05),对GC、PC和TV的影响达到极显著水平(P˂0.01),仅对ASV影响不显著。说明晚季品种的遗传背景依然是决定GC、ASV、AC、PC和TV的主要因素。施氮量对AC、PC和TV也有极显著影响;施氮量与品种间存在互作,且对AC有显著影响,对GC、PC和TV存在极显著影响。
综上所述,无论早季还是晚季,水稻品种(系)的遗传背景是决定稻米蒸煮营养和食味品质的主要因素,除ASV不受施氮量影响外,其他4个性状都显著地受施氮量影响。此外,晚季GC、AC、PC和TV还显著或极显著地受到施氮量与品种之间互作效应的影响(但早季仅GC存在互作效应),说明晚季施氮水平对GC、AC、PC和TV的影响因品种不同而异。
2.2 早、晚两季不同施氮量处理下各类品种(系)蒸煮营养与食味品质差异比较
2.2.1 丝苗米常规优质稻品种(系)的蒸煮营养与食味品质
表3结果显示,相同施氮量处理条件下,4个丝苗米供试品种(系)的GC、AC和ASV几乎都是晚季高于早季,PC则普遍是晚季低于早季。TV的表现则因施氮量和品种的不同而表现各异。其中,在N0条件下4个品种的TV值都是晚季高于早季,在N1处理中,除美香占2号为晚季高于早季外,其他3个品种均是晚季低于早季;在N2处理条件下,美香占2号和象竹香丝苗都是晚季低于早季,其他2个品种则相反,晚季高于早季;在N3处理条件下,除美香占2号为晚季高于早季外,其他3个品种则均为晚季低于早季。说明优质丝苗米品种(系)的GC、AC、PC和ASV受光温生态条件的影响大,TV则因品种和施氮处理的不同而异。
表 3 丝苗米常规优质品种在不同施氮量处理下的蒸煮营养与食味品质1)Table 3. Cooking, nutritional and eating qualities of fine-quality inbreed varieties of Simiao Rice under different nitrogen application rates品种
Variety处理
Treat-
ment胶稠度/mm
Gel consistency
(GC)w(直链淀粉)/%
Amylose content
(AC)碱消值(级)
Alkali spreading value
(grade) (ASV)w(蛋白质)/%
Protein content
(PC)米饭食味值
Taste value
(TV)ES LS ES LS ES LS ES LS ES LS 美香占2号
MXZ2N0 38.0±0.0* 59.0±8.0a 13.9±0.0* 19.4±0.8a 6.5±0.0* 7.0±0.0a 5.7±0.0* 5.2±0.4b 87.0±0.0* 89.0±1.0a N1 45.7±12.4ab 57.0±5.6a 14.2±0.6a 18.3±0.5ab 6.9±0.1a 7.0±0.0a 6.3±0.3a 5.7±0.4b 84.7±1.5a 87.0±1.7ab N2 42.3±4.9b 61.0±1.0a 14.8±0.7a 19.4±0.2a 5.8±0.8a 7.0±0.0a 6.7±0.3a 6.6±0.1a 86.7±0.6a 86.3±0.6ab N3 66.3±14.3a 54.3±1.5a 13.9±0.0a 17.8±0.7b 6.3±0.7a 7.0±0.0a 7.0±0.5a 7.0±0.1a 83.3±5.5a 84.7±2.5b MV 48.1±7.9 57.8±3.9 14.2±0.3 18.7±0.6 6.4±0.4 7.0±0.0 6.4±0.3 6.1±0.3 85.4±1.9 86.8±1.5 象牙香占
XYXZN0 44.5±0.0* 54.0±3.0ab 15.3±0.0* 17.8±0.6a 6.0±0.0* 7.0±0.0a 5.9±0.0* 5.0±0.5b 84.0±0.0* 87.3±0.6a N1 39.0±4.4b 48.7±3.5b 15.9±0.6a 18.6±0.7a 6.8±0.3a 7.0±0.0a 6.1±0.6a 6.1±0.8a 84.0±6.1a 83.0±2.6b N2 52.7±1.8a 56.0±2.0a 15.3±0.5a 15.9±1.5b 6.9±0.1a 7.0±0.0a 6.4±0.4a 6.8±0.2a 84.0±2.6a 85.0±1.0ab N3 49.0±4.6b 51.0±3.0ab 15.3±0.2a 18.1±0.4a 6.8±0.3a 7.0±0.0a 6.9±0.1a 6.2±0.2a 81.3±1.2a 80.0±0.0c MV 46.3±7.9 52.4±2.9 15.5±0.3 17.6±0.8 6.6±0.2 7.0±0.0 6.3±0.3 6.1±0.4 83.3±2.5 83.8±1.1 客都寿乡1号
KDSX1N0 28.5±0.0* 57.0±1.0a 11.7±0.0* 18.1±1.2a 6.0±0.0* 7.0±0.0a 4.4±0.6b 85.3±0.0* 88.3±1.5a N1 43.7±4.7a 55.0±2.6a 12.3±0.5a 18.1±1.4a 6.4±0.4a 7.0±0.0a 5.3±0.3a 88.3±1.5a 87.0±1.0a N2 47.0±7.9a 54.3±0.6a 12.5±0.6a 16.4±1.9a 6.4±0.4a 7.0±0.0a 5.8±0.1a 83.7±2.5b 85.0±2.0a N3 57.7±8.1a 49.0±2.0b 12.2±0.6a 17.1±1.0a 6.5±0.0a 7.0±0.0a 5.7±0.4a 84.7±2.5ab 81.0±3.0b MV 44.2±5.2 53.8±1.6 12.2±0.4 17.4±1.4 6.3±0.2 7.0±0.0 5.3±0.4 85.5±1.6 85.3±1.9 象竹香丝苗
XZXSMN0 34.0±0.0* 50.7±4.7a 14.3±0.0* 19.0±1.0a 6.0±0.0* 7.0±0.0a 5.0±0.0* 4.4±0.2b 83.8±0.0* 86.7±2.5a N1 60.7±3.5a 53.3±11.2a 15.2±1.2a 19.7±1.3a 6.8±0.0a 7.0±0.0a 5.6±0.3ab 5.0±0.2a 88.0±2.0a 86.3±1.5a N2 45.7±1.5b 49.0±1.0a 14.7±0.5a 20.7±0.7a 6.8±0.1a 7.0±0.0a 5.3±0.4b 5.3±0.2a 85.7±0.6ab 84.0±2.0a N3 36.0±1.7c 43.3±3.5a 15.6±0.4a 19.0±0.3a 6.3±0.7a 7.0±0.0a 6.1±0.2a 5.3±0.1a 83.3±2.5b 79.3±1.5b MV 44.1±1.7 49.1±5.1 15.0±0.5 19.6±0.8 6.5±0.2 7.0±0.0 5.5±0.2 5.0±0.2 85.2±1.3 84.1±1.9 1) ES:早季;LS:晚季;N0、N1、N2和N3:施氮量分别为0、90、135和180 kg/hm2;MV:平均值;同列数据后的不同小写字母表示同一品种不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,LSD法);“*”:早季N0处理未设置重复,未参与差异显著性比较
1) ES: Early season; LS: Late season; N0, N1, N2 and N3: Nitrogen application rates were 0, 90, 135 and 180 kg/hm2, respectively; MV: Mean values of four treatments; Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences among different treatments of the same variety (P < 0.05, LSD method); “*”: No replication was conducted for treatment N0 in the early season, and then it was not involved in LSD analysis早、晚两季4个丝苗米品种(系)施氮处理间的ASV均无显著差异,说明ASV不受施氮量影响,是一个由品种遗传背景决定的稳定性状;其他4个性状均在不同程度上受施氮量的影响。其中,精米PC一般随施氮量的增加而升高,而米饭TV则一般随施氮量的增加而降低。在4个施氮量处理的平均PC方面,象竹香丝苗早、晚季都是最低的,分别为5.5%和5.0%;早季平均PC最高的是美香占2号(6.4%),晚季最高的是象牙香占(6.1%)和美香占2号(6.1%)。在米饭TV方面,早季除美香占2号N0处理的TV最大外,其他3个品种(系)都是N1的TV最大;晚季则都是N0处理的TV最大。说明早季丝苗米适当施用少量氮肥,而晚季则应尽量不施氮肥,这样更有利于米饭的食味品质提升。
美香占2号早季施氮处理间仅GC存在显著差异,晚季AC、PC和TV均存在显著差异。象牙香占早季施氮处理间也仅GC存在显著差异,晚季GC、AC、PC和TV则均存在显著差异。客都寿乡1号早季处理间仅米饭TV差异显著,晚季仅GC和TV的N3与其他3个处理间存在显著差异。象竹香丝苗早季处理间GC、PC和TV有显著差异,晚季处理间多数不存在显著差异。在精米PC方面,早、晚季平均值最低是象竹香丝苗,早季最高的是美香占2号,晚季最高的是美香占2号和象牙香占。在米饭TV方面,美香占2号晚季TV平均值(86.8)大于早季(85.4),说明晚季生产出来的美香占2号稻米食味品质优于早季;象牙香占和客都寿乡1号早季的米饭TV分别为83.3和85.5,晚季的米饭TV分别为83.8和85.3,2个品种基本一致,说明早、晚季生产出来的稻米食味品质相似,受生产季节的影响小;象竹香丝苗早季的平均米饭TV为85.2,稍高于晚季(84.1),尤其是早季N1的米饭TV(88.0)比其晚季最高TV(N0=86.7)还高,说明象竹香丝苗在早季N1条件下种植更能发挥其品质优势。
施氮处理间差异显著性大小,显示供试品种(系)间米饭TV对施氮量的反应敏感程度。早季美香占2号和象牙香占处理间均无显著差异,表现为氮肥钝感型;客都寿乡1号和象竹香丝苗早季处理间差异性多重比较中,差异性标注出现了a和b两种字母,即存在 1个等级的显著性差异,因此,客都寿乡1号和象竹香丝苗早季均为氮肥中度敏感型。晚季除象牙香占施氮处理间差异性多重比较中,差异性标注出现了a、b和c 3种字母,即存在2个等级的显著差异,属于氮肥敏感型外,其他3个丝苗米品种(系)美香占2号、客都寿乡1号和象竹香丝苗晚季处理间多重比较中,仅有1个等级的显著差异,均为氮肥中度敏感型。
2.2.2 优质杂交稻及其亲本的蒸煮食味品质
泰丰优208等4个优质杂交稻是利用优质不育系泰丰A和优质恢复系广恢208、广恢398、广恢390和广恢1002组配育成的。泰丰B是优质不育系泰丰A的同核异质保持系。表4结果表明,泰丰B早季仅精米PC和米饭TV处理间差异显著;晚季的所有5个性状处理间多数都差异显著,其晚季N0的TV高达87.0,4个处理平均值为83.9,与全国优质稻食味鉴评金奖品种象牙香占的晚季TV平均值(83.8)相当,说明泰丰B晚季的米饭食味优良。广恢208早季仅GC处理间差异显著,晚季ASV、PC和TV主要是N0与其他处理间的差异多数达显著水平,其他3个处理间差异一般不显著。泰丰优208早季AC和ASV处理间差异显著,晚季仅PC和TV的N0与其他处理间差异显著,其他处理间差异一般也不显著,与其父本广恢208的表现较为一致。泰丰优208晚季N0的米饭TV高达87.7,且4个施氮量处理的平均TV为85.1,与国家优质稻食味鉴评金奖品种美香占2号早季TV平均值(85.4)和客都寿乡1号晚季TV平均值(85.3)相当,表现出很好的食味品质,这是泰丰优208参加国家优质稻食味鉴评能够连续3届获得金奖的重要原因。
表 4 优质杂交稻及其亲本在不同施氮量处理下的蒸煮食味品质1)Table 4. Cooking and eating qualities of hybrid rice and their parents under different nitrogen application rates品种(系)
Variety (line)处理
Treat-
ment胶稠度/ mm
Gel consistency
(GC)w(直链淀粉)/%
Amylose content
(AC)碱消值(级)
Alkali spreading value
(grade) (ASV)w(蛋白质)/%
Protein content
(PC)米饭食味值
Taste value
(TV)ES LS ES LS ES LS ES LS ES LS 泰丰B
TFBN0 76.0±0.0* 61.3±4.0b 16.5±0.0* 17.1±1.0b 6.0±0.0* 6.7±0.2b 5.5±0.0* 5.0±1.0b 79.5±0.0* 87.0±2.0a N1 60.7±17.8a 69.3±1.5a 16.2±0.1a 17.6±0.8ab 6.7±0.6a 7.0±0.0a 6.1±0.1c 6.2±0.4a 80.7±4.0a 83.3±2.1bc N2 49.3±3.8a 68.3±2.5a 16.2±0.5a 18.2±0.1ab 6.9±0.1a 7.0±0.0a 6.8±0.2b 6.0±0.2ab 73.7±2.5ab 85.0±0.0ab N3 68.0±10.4a 63.3±4.5ab 15.5±0.4a 18.6±0.5a 6.4±0.4a 7.0±0.0a 7.5±0.3a 6.9±0.4a 71.7±4.0b 80.3±1.5c MV 63.5±8.0 65.6±3.1 16.1±0.3 17.9±0.6 6.5±0.3 6.9±0.1 6.5±0.2 6.0±0.5 76.4±2.6 83.9±1.4 泰丰优208
TFY208N0 56.0±0.0* 82.3±10.1a 14.3±0.0* 16.0±0.8a 3.8±0.0* 2.7±0.6a 4.6±0.0* 5.2±0.2b 87.5±0.0* 87.7±1.5a N1 73.3±4.6a 79.7±4.7a 14.5±0.3b 14.4±1.3a 2.0±0.0b 2.3±0.6a 6.2±0.6a 6.5±0.3a 82.7±2.5a 84.7±2.5ab N2 69.3±12.1a 75.0±3.0a 15.2±0.2a 15.1±0.4a 2.8±0.3a 2.3±0.3a 6.6±0.6a 6.6±0.2a 82.7±2.9a 84.0±2.0b N3 71.7±8.3a 74.0±2.0a 15.0±0.1a 14.4±1.5a 2.7±0.6ab 2.0±0.0a 6.8±0.3a 6.5±0.1a 80.0±6.1a 84.0±0.0b MV 67.6±6.25 77.8±5.0 14.8±0.2 15.0±1.0 2.8±0.2 2.3±0.4 6.1±0.4 6.2±0.2 83.2±2.9 85.1±1.5 广恢208
R208N0 80.5±0.0* 84.3±8.7a 12.0±0.0* 13.9±0.8a 3.0±0.0* 2.0±0.0b 4.4±0.0* 5.3±0.2b 83.5±0.0* 88.3±0.6a N1 88.7±6.5ab 77.7±3.5a 12.7±0.3a 15.4±1.4a 2.0±0.0a 3.3±0.6a 5.7±0.4a 5.8±0.3a 83.7±1.5a 85.7±1.5b N2 94.0±13.5a 88.3±9.5a 12.3±0.8a 15.0±0.6a 2.0±0.0a 2.8±0.3a 5.7±0.3a 5.9±0.1a 83.3±2.5a 85.7±0.6b N3 70.7±8.5b 82.7±1.5a 12.8±0.6a 15.6±0.0a 2.3±0.6a 2.0±0.0b 5.9±0.2a 6.0±0.2a 82.3±2.9a 84.3±0.6b MV 83.5±7.1 83.3±5.8 12.5±0.4 15.0±0.7 2.3±0.2 2.5±0.2 5.4±0.2 5.8±0.2 83.2±1.7 86.0±0.8 泰优398
TY398N0 65.0±0.0* 66.7±3.8ab 15.7±0.0* 16.5±1.5ab 6.0±0.0* 6.5±0.5a 5.2±0.0* 4.8±0.6b 82.3±0.0* 87.3±1.2a N1 55.0±7.8a 60.3±2.3b 17.1±0.6a 18.3±1.3a 6.5±0.5a 6.8±0.0a 6.2±0.3b 6.1±0.7a 76.3±3.1a 83.0±3.5b N2 57.3±2.1a 82.7±16.5a 16.3±0.1a 18.1±0.9a 6.7±0.2a 6.9±0.1a 6.9±0.3a 6.3±0.1a 75.3±3.8a 84.0±2.0ab N3 51.3±5.7a 65.3±5.5ab 16.0±0.8a 15.6±0.4b 6.3±0.7a 6.9±0.1a 7.0±0.4a 6.7±0.1a 75.0±1.0a 81.0±1.0b MV 57.2±3.9 68.8±7.0 16.3±0.4 17.1±1.0 6.4±0.4 6.8±0.2 6.3±0.3 6.0±0.4 77.2±2.0 83.8±1.9 广恢398
R398N0 38.0±0.0* 67.7±7.1a 14.8±0.0* 16.5±1.6ab 6.0±0.0* 6.6±0.2a 5.4±0.0 5.0±0.2d 79.5±0.0 88.0±1.0a N1 47.7±8.6a 67.3±4.2a 15.2±0.5a 17.6±1.3a 6.7±0.2a 6.5±0.5a 6.1±0.4a 6.3±0.3c 80.0±2.6a 85.0±2.0a N2 46.3±9.3a 79.7±15.5a 15.1±0.6a 15.7±0.1ab 6.9±0.2a 6.7±0.2a 6.6±0.4a 6.8±0.0b 77.7±3.5a 80.7±3.5b N3 54.3±10.2a 62.0±7.0a 15.2±0.7a 14.9±0.2b 6.5±0.5a 6.8±0.1a 6.8±0.5a 7.3±0.1a 76.0±1.0a 78.7±1.5b MV 46.6±7.0 69.2±8.5 15.1±0.5 16.2±0.8 6.5±0.2 6.7±0.3 6.2±0.3 6.4±0.2 78.3±1.8 83.1±2.0 泰优390
TY390N0 64.5±0.0* 79.0±6.0a 14.6±0.0 15.1±1.5ab 3.0±0.0 2.3±0.6a 5.7±0.0 5.2±0.4b 82.3±0.0 87.7±3.5a N1 64.7±14.2a 73.7±4.5a 13.4±0.5a 15.3±1.0ab 2.5±0.5a 2.7±0.6a 6.3±0.3a 5.7±0.4b 82.3±4.7a 87.3±1.5a N2 76.7±7.1a 85.3±13.5a 13.6±1.1a 16.1±0.1a 2.3±0.6a 2.0±0.0a 6.7±0.3a 6.6±0.1a 79.7±2.1a 86.0±1.0ab N3 75.0±16.8a 79.0±7.0a 13.6±0.9a 14.0±0.5b 3.5±1.8a 2.5±0.5a 7.0±0.5a 7.0±0.1a 79.7±2.1a 82.3±0.6b MV 70.2±9.5 79.3±7.6 13.8±0.6 15.1±0.8 2.8±0.7 2.4±0.4 6.4±0.3 6.1±0.3 81.0±2.2 85.8±1.7 广恢390
R390N0 89.5±0.0* 77.7±2.5a 9.8±0.0 14.7±0.5a 2.0±0.0 2.7±0.6a 5.9±0.0 5.0±0.5b 84.0±0.0 87.3±1.5a N1 97.7±7.6a 78.7±9.2a 9.7±0.3a 12.9±1.2b 2.0±1.0a 3.5±0.5a 6.1±0.6a 6.1±0.8a 84.0±1.7a 84.7±2.1ab N2 96.3±11.2a 91.0±10.0a 9.6±0.7a 12.9±0.2b 2.7±0.6a 3.5±0.5a 6.4±0.4a 6.8±0.2a 80.3±2.3a 82.3±0.6b N3 95.7±6.5a 83.0±2.0a 9.9±0.9a 12.7±0.4b 1.8±0.8a 3.0±0.0a 6.9±0.1a 6.2±0.2a 84.0±4.6a 86.0±2.0a MV 94.8±6.3 82.6±5.9 9.8±0.5 13.3±0.6 2.1±0.6 3.2±0.4 6.3±0.3 6.0±0.4 83.1±2.2 85.1±1.6 泰优1002
TY1002N0 65.7±5.0ab 17.8±1.1a 7.0±0.0a 4.4±0.6b 89.0±1.0a N1 64.7±6.7ab 19.0±2.3a 7.0±0.0a 5.3±0.3a 87.0±1.7ab N2 76.7±6.5a 20.5±1.4a 7.0±0.0a 5.8±0.1a 87.0±0.0ab N3 55.0±8.0b 18.0±2.1a 7.0±0.0a 5.7±0.4a 85.0±1.0b MV 65.5±6.6 18.8±1.7 7.0±0.0 5.3±0.4 87.0±0.9 广恢1002
R1002N0 30.5±0.0* 61.0±4.6ab 12.9±0.0* 16.9±1.6a 6.0±0.0* 7.0±0.0a 5.0±0.0* 4.4±0.2b 84.8±0.0* 88.0±1.0a N1 64.7±3.1a 69.3±10.1a 15.3±0.4a 18.2±3.9a 5.8±0.8a 7.0±0.0a 5.6±0.3ab 5.0±0.2a 86.7±0.6a 87.0±1.0ab N2 57.3±19.7a 58.3±3.5ab 15.2±0.4a 18.7±0.5a 5.0±1.0a 7.0±0.0a 5.3±0.4b 5.3±0.2a 88.3±0.6a 86.0±1.0bc N3 60.0±8.7a 49.3±3.5b 14.5±0.7a 19.9±0.5a 6.3±0.3a 7.0±0.0a 6.1±0.2a 5.3±0.1a 87.7±4.2a 85.0±1.0c MV 53.1±7.9 59.5±5.4 14.5±0.4 18.4±1.6 5.8±0.5 7.0±0.0 5.5±0.2 5.0±0.2 86.9±1.4 86.5±1.0 1) ES:早季;LS:晚季;N0、N1、N2和N3:施氮量分别为0、90、135和180 kg/hm2;MV:平均值;同列数据后的不同小写字母表示同一品种(系)不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,LSD法);“*”:早季N0处理未设置重复,未参与差异显著性比较
1) ES: Early season; LS: Late season; N0, N1, N2 and N3: Nitrogen application rates were 0, 90, 135 and 180 kg/hm2, respectively; MV: Mean values of four treatments; Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences among different treatments of the same variety (line) (P < 0.05, LSD method); “*”: No replication was conducted for tratment N0 in the early season, and then it was not involved in LSD analysis广恢398和广恢390早季所有5个性状处理间均不存在显著差异,仅晚季在AC、PC和TV处理间存在显著差异。由其组配育成的泰优398和泰优390,前者早季仅PC以及二者晚季AC、PC和TV在少数处理间存在显著差异。泰优398晚季平均值TV(83.8)与优质丝苗米象牙香占的83.8相当;泰优390晚季TV平均值(85.8)与客都寿乡1号的85.3相当,显示出很好的米饭食味。
广恢1002早季仅PC处理间差异显著,晚季GC、PC和TV处理间均存在显著差异,由其组配育成的弱感光迟熟杂交稻泰优1002晚季GC、PC和TV处理间也存在显著差异。泰优1002晚季N0的米饭TV最高(89.0),且4个处理TV平均值高达87.0,与优质丝苗米美香占2号晚季的平均TV(86.8)相当,显示出很好的米饭食味。这是泰优1002连续2届参加国家优质稻食味鉴评均能获得金奖的重要原因。
优质杂交稻泰丰优208、泰优398、泰优390和泰优1002的GC、AC、PC和TV多数居于其相应父本与母本之间,但其TV一般偏向高值亲本,表现出部分显性。仅泰优1002的TV平均值高于其高值亲本广恢1002,TV表现出超显性。
在供试材料的米饭TV对施氮敏感性方面,早季泰丰B处理间TV差异性多重比较结果标注了a、b 2种字母(表4),即存在1个等级的显著差异,表现为氮肥中度敏感;其他7个品种(系)广恢208、广恢398、广恢390、泰优390、泰丰优208、泰优398和广恢1002处理间都无显著差异,均为氮肥钝感型。晚季泰丰B和广恢1002处理间TV差异性多重比较中,出现了a、b、c 3种字母(表4),即存在2个等级的显著性差异,属于氮肥敏感型;其他7个品种(系)处理间差异性多重比较结果仅有1个等级的差异,属于氮肥中等敏感型。
2.2.3 高产常规稻和高产杂交稻及其亲本的蒸煮食味品质
试验结果表明,五丰B早季GC、ASV、PC和TV处理间均差异不显著,AC中仅N3与其他处理之间存在显著差异,晚季除ASV处理间无显著差异外,其他4个性状处理间差异显著。五丰B晚季N0的米饭TV达到88.7,4个处理的TV平均值达到86.8,与美香占2号晚季食味平均值(86.8)几乎相同(表3),但其早季TV(73.2)明显差很多。广恢308早、晚季GC和晚季精米PC处理间差异显著,其他性状早、晚季各处理间差异均不显著。超级稻品种五优308晚季AC和早、晚季ASV和PC,以及晚季米饭TV施氮处理间部分差异显著。高AC含量的高产常规稻特三矮2号与广恢308相似,晚季GC、精米PC和米饭TV处理间仅部分差异显著,早季所有性状处理间均无显著差异(表5)。
表 5 高产常规稻和高产杂交稻及其亲本在不同施氮量处理下的蒸煮食味品质1)Table 5. Cooking and eating qualities of high-yielding inbreed and hybrid rice varieties and their parents under different nitrogen application rates品种(系)
Variety (line)处理
Treat-
ment胶稠度/ mm
Gel consistency
(GC)w(直链淀粉)/%
Amylose content
(AC)碱消值(级)
Alkali spreading
value (grade) (ASV)w(蛋白质)/%
Protein content
(PC)米饭食味值
Taste value
(TV)ES LS ES LS ES LS ES LS ES LS 五丰B
WFBN0 103.5±0.0* 93.0±2.0a 12.2±0.0* 14.0±0.8ab 3.0±0.0* 2.0±0.0a 6.7±0.0* 5.2±0.3c 73.0±0.0* 88.7±0.6a N1 90.3±9.3a 87.0±4.4ab 12.4±0.5a 16.5±3.2a 2.3±0.6a 2.0±0.0a 7.2±0.5a 5.7±0.3b 73.7±0.6a 87.7±1.5ab N2 94.3±10.7a 79.3±1.5c 12.4±0.2a 15.5±1.0ab 2.0±1.0a 2.0±0.0a 7.5±0.3a 6.6±0.0a 74.0±2.0a 86.0±2.0bc N3 86.3±8.1a 85.0±5.0bc 10.5±1.5b 12.4±1.2b 2.5±0.5a 2.0±0.0a 7.9±0.4a 6.8±0.2a 72.0±3.0a 84.7±0.6c MV 93.6±7.0 86.1±3.2 11.9±0.6 14.6±1.6 2.5±0.5 2.0±0.0 7.3±0.3 6.1±0.2 73.2±2.2 86.8±1.2 五优308
WY308N0 24.5±0.0* 46.0±6.2a 21.0±0.0* 20.6±1.7b 4.0±0.0* 5.0±0.0a 5.2±0.0* 5.0±0.6c 69.3±0.0* 85.3±1.5a N1 27.3±3.1a 43.7±13.1a 22.8±0.9a 22.4±2.4ab 4.8±0.3ab 2.9±0.8b 6.0±0.4b 5.4±0.8bc 71.3±3.5a 77.0±3.0b N2 27.3±1.5a 40.7±4.5a 22.2±0.3a 22.1±0.7ab 3.5±0.9b 2.3±0.3b 6.0±0.1b 6.1±0.0ab 68.3±2.1a 75.7±2.5b N3 24.3±0.6a 33.7±3.5a 22.8±1.1a 23.7±0.2a 5.8±0.8a 2.8±0.3b 6.8±0.1a 6.5±0.1a 67.7±1.2a 73.3±0.6b MV 25.9±1.3 41.0±6.8 22.2±0.6 22.2±1.3 4.5±0.5 3.3±0.4 6.0±0.2 5.8±0.4 69.2±1.7 77.8±1.9 广恢308
R308N0 20.5±0.0* 26.7±0.6ab 27.6±0.0* 24.8±0.8a 7.0±0.0* 7.0±0.0a 6.3±0.0* 4.7±0.4c 51.3±0.0* 65.7±1.5a N1 20.3±0.6b 25.7±2.1ab 26.8±0.5a 23.9±2.5a 7.0±0.0a 7.0±0.0a 6.8±0.3a 6.4±0.3b 56.7±3.8a 68.0±2.0a N2 23.0±3.0ab 30.0±4.0a 26.0±0.6a 24.5±0.1a 7.0±0.0a 7.0±0.0a 6.7±0.1a 6.5±0.3b 55.0±3.6a 62.7±3.5a N3 26.7±2.9a 25.0±1.0b 25.2±1.2a 24.7±0.8a 6.3±1.2a 6.9±0.1a 7.2±0.6a 7.5±0.1a 57.0±3.5a 65.3±4.5a MV 22.6±1.6 26.9±1.9 26.4±0.6 24.5±1.1 6.8±0.3 7.0±0.0 6.8±0.3 6.3±0.3 55.0±2.7 65.4±2.9 特三矮2号
TSA2N0 24.0±0.0* 36.7±8.5a 26.9±0.0* 25.1±1.0a 7.0±0.0* 7.0±0.0a 5.2±0.0* 5.6±0.2c 66.5±0.0* 75.0±3.0a N1 24.3±3.2a 25.0±2.6b 25.8±0.9a 27.2±2.0a 7.0±0.0a 6.9±0.1a 5.7±0.1a 5.7±0.2bc 66.0±4.4a 72.3±3.1a N2 25.7±5.5a 27.0±0.0b 24.8±1.0a 26.5±0.8a 7.0±0.0a 7.0±0.0a 6.2±0.1a 6.0±0.1b 65.3±1.5a 71.0±2.0ab N3 23.7±2.1a 23.0±1.0b 25.2±1.6a 27.0±0.6a 6.3±1.2a 7.0±0.0a 6.0±0.5a 6.9±0.2a 61.7±1.2a 67.0±0.0b MV 24.4±2.7 27.9±3.0 25.7±0.9 26.5±1.1 6.8±0.3 7.0±0.0 5.8±0.2 6.1±0.2 64.9±1.8 71.3±2.0 1) ES:早季;LS:晚季;N0、N1、N2和N3:施氮量分别为0、90、135和180 kg/hm2;MV:平均值;同列数据后的不同小写字母表示同一品种(系)不同处理间差异显著(P < 0.05,LSD法);“*”:早季N0处理未设置重复,未参与差异显著性比较
1) ES: Early season; LS: Late season; N0, N1, N2 and N3: Nitrogen application rates were 0, 90, 135 and 180 kg/hm2, respectively; MV: Mean values of four treatments; Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences among different treatments of the same variety (line) (P < 0.05, LSD method); “*”: No replication was conducted for tratment N0 in the early season, and then it was not involved in LSD analysis五优308与其母本五丰B、父本广恢308比较,其GC、AC、ASV、精米PC和米饭TV等5个性状的处理平均值基本上均居于双亲之间,且GC偏向低值亲本,即低GC相对高GC呈现部分显性;而AC、TV偏向高值亲本呈部分显性。
从表5中米饭TV处理间差异显著性结果可以看出,早季所有4个高产品种(系)处理间TV均无显著差异,表现为氮肥钝感型。晚季广恢308米饭TV处理间无显著差异,表现为氮肥钝感;五丰B处理间TV差异性多重比较存在a、b、c 3种字母标注,即有2个等级的显著差异,属于氮肥敏感型;五优308和特三矮2号米饭TV处理间差异性多重比较仅有1个等级的显著差异,表现为氮肥中度敏感型。
3. 讨论与结论
3.1 不同施氮量对蒸煮营养与食味品质的影响
本研究结果表明,蒸煮食味品质中,随着施氮量的增加,早、晚季的直链淀粉含量变化趋势并不完全呈规律性的增加或减少,这与王秀芹等[16]和占新春等[17]的研究结果不一致;早、晚季的精米PC基本上都是随施氮量的提高而增加,这与陶进等[18] 和黄元财等[19]的研究结果一致。早、晚季的米饭TV随施氮量的增加呈下降趋势,这与胡雅杰等[14]、赵可等[13]和陈莹莹等[10]的研究结果一致。
3.2 各供试品种(系)的精米PC与米饭TV表现差异及其相互之间的关系
大量的研究结果显示,稻米PC是影响米饭食味最主要的因素之一[22-23]。本研究结果显示,早、晚两季各供试品种(系)随着施氮量的增加,其精米PC也普遍随之增加,而米饭TV则普遍随之降低,说明增加施氮量会降低米饭食味的重要原因可能是提高了PC。此外,在供试的17份材料中,除广恢208、泰丰优208和广恢398之外,其他供试品种(系)精米PC都是早季高于其晚季,从精米PC的早、晚季变化也可以说明,为何同一品种的稻米品质,尤其是食味品质,往往晚季种植生产的稻米要优于其早季。
本研究的各供试水稻品种(系)中,早季精米PC最低的是广恢208,其他较低的依次是象竹香丝苗和广恢1002,其PC平均值为5.4%~5.5%。米饭TV平均值早季最高是广恢1002,其他较高的依次是客都寿乡1号、美香占2号和象竹香丝苗,其平均值介于85.2%~86.9%;晚季精米PC平均值最低的是象竹香丝苗,其他较低的依次是广恢1002、客都寿乡1号和泰优1002,仅为5.0%~5.3%;米饭TV 平均值晚季最高的是泰优1002,其他较高的依次是美香占2号、五丰B、广恢1002和广恢208,TV平均值高达86.0~87.0。由此可见,象竹香丝苗和广恢1002是早、晚两季都表现出较低PC和较高米饭TV的品种(系);美香占2号是早、晚季均具有较高米饭TV的品种,早、晚季食味品质相对稳定是该丝苗米品种能够在全国优质稻品质食味鉴评中连续3届(2018、2019和2020年)获得金奖的主要原因。
值得特别注意的是,晚季精米PC低(5.0%~5.8%)和米饭TV高(86.0~86.5)的恢复系广恢208和广恢1002,与晚季PC中低等(6.0%)和米饭TV中高(83.9)的不育系泰丰A(泰丰B的同核异质不育系)组配育成的杂交稻泰丰优208和泰优1002,二者晚季的PC平均值为中低等水平,分别为6.2%和5.3%,米饭TV平均值达到中高水平(分别为85.1和87.0)。说明利用双亲具有中低PC和中高TV的亲本组配,能够培育出米饭食味优良的杂交稻。这是为什么泰丰优208能够在全国优质稻食味鉴评中连续获得3届(2019、2020和2023年)金奖和泰优1002能够连续2届(2020和2023年)获得金奖的重要原因。
由此可见,要培育食味优良的常规稻和优质杂交稻,可以利用中低PC、中高TV且对氮肥敏感度中低的材料作亲本,这有利于大大提高食味品质优良的水稻新品种的育种效率。
3.3 优质稻米饭食味的氮肥敏感性及其表现的季节差异
优异而稳定的食味品质,是优质稻产业高质量发展和优质稻米品牌打造的关键。然而,在米饭食味方面,不同优质稻品种对氮肥施用量和不同种植生产季节的敏感度是存在明显差异的。本研究根据处理间TV显著性差异程度,将17个供试品种(系)对氮肥敏感性划分为3个等级。其中,广东丝苗米品种美香占2号早季为氮肥钝感型,晚季为氮肥中度敏感型;客都寿乡1号和象竹香丝苗早晚季均属于氮肥中度敏感型;象牙香占早季为氮肥钝感型,晚季为氮肥敏感型。优质杂交稻及其亲本中,母本泰丰A的保持系泰丰B早季为氮肥中度敏感,晚季为氮肥敏感型;优质恢复系广恢208、广恢398、广恢390及其与泰丰A组配育成的优质杂交稻泰优390、泰丰优208、泰优398和泰优1002早季均为氮肥钝感型,晚季均为中等敏感型;广恢1002早季为氮肥钝感型,晚季为氮肥敏感型;由广恢1002与泰丰A组配的杂交稻泰优1002(因其早季感光不能种植)晚季表现为中度敏感型。4个高产品种(系)中,广恢308早、晚季均为氮肥钝感;五丰B早季为钝感型,晚季为氮肥敏感型;五优308和特三矮2号早季为氮肥钝感型,晚季为中度敏感型。
在供试的17份材料中,美香占2号、泰丰优208和泰优1002曾推荐参加全国优质稻食味鉴评,并连续2届或3届获得金奖,这3个品种的共同特点是米饭TV值较高,其晚季处理间TV平均值分别高达86.8、85.1和87.0,且美香占2号和泰丰优208早季表现为氮肥钝感型,而晚季均表现为氮肥中等敏感型。由此可见,选用米饭食味好,且其TV对氮肥用量表现为钝感或中度敏感的优质稻品种,并根据生产季节不同配套合适的施肥技术方案,是高食味优质稻米产业发展的关键。
-
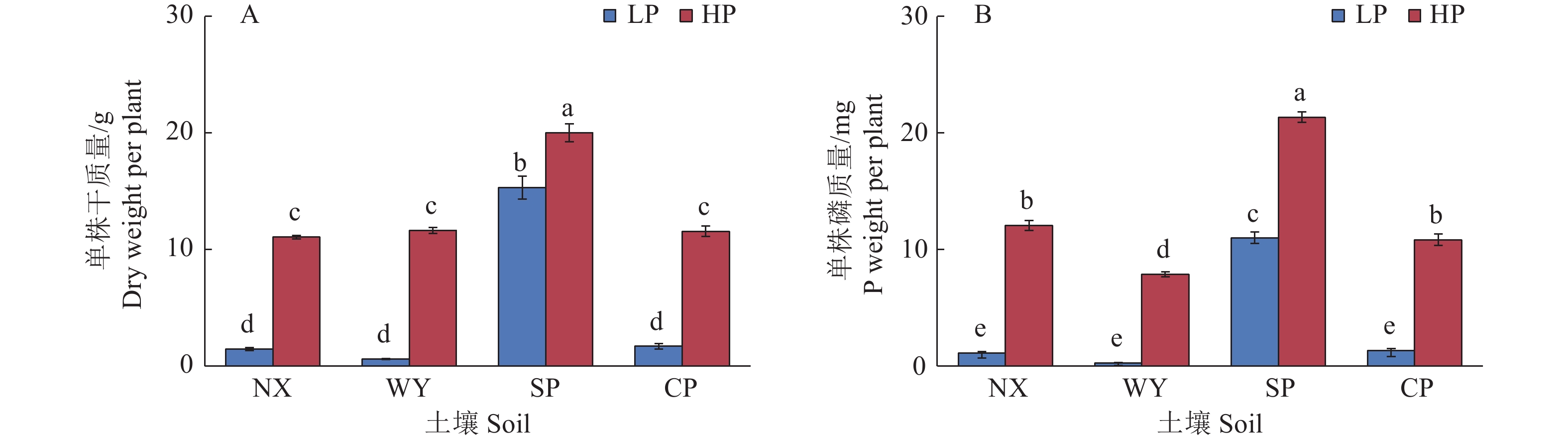
图 1 不同土壤类型和磷处理对玉米植株干质量和磷质量的影响
LP:不施磷;HP:施磷;NX:宁西酸性土壤;WY:翁源酸性土壤;SP:三坪石灰性土壤;CP:昌平石灰性土壤;各图中柱上不同小写字母代表处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 1. Effects of different soil types and phosphorus treatments on plant dry weight and P weight in maize
LP: No P added; HP: P fertilizer added; NX: Acid soil of Ningxi; WY: Acid soil of Wengyuan; SP: Calcareous soil of Sanping; CP: Calcareous soil of Changping; In each figure, different lowercase letters on the column represent significant differences among different treatments (P< 0.05, Duncan’s method)
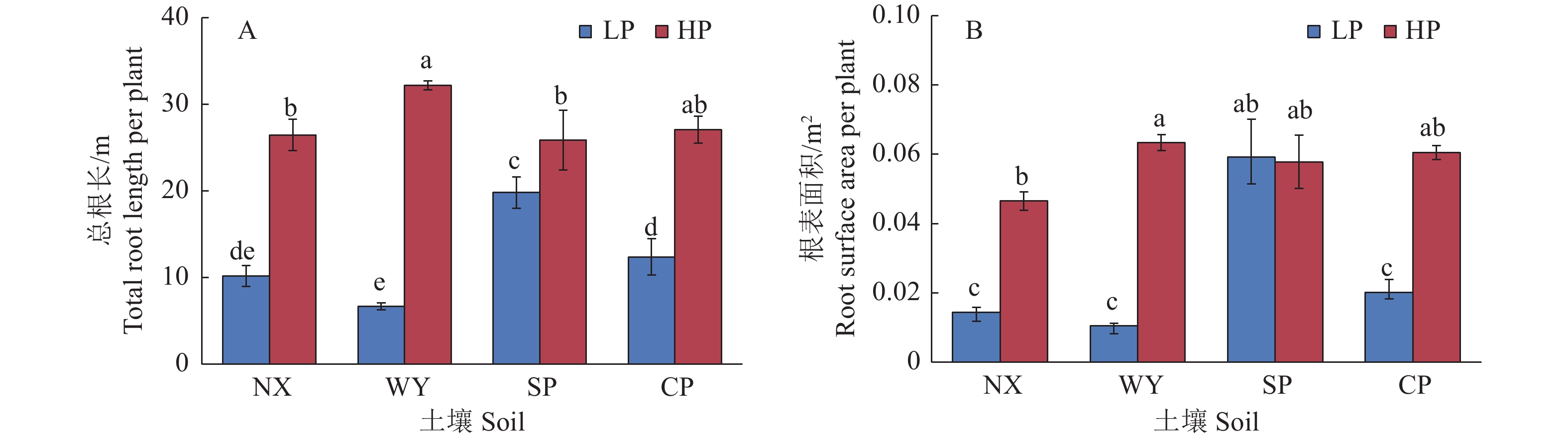
图 2 不同土壤类型和磷处理对玉米总根长和根表面积的影响
LP:不施磷;HP:施磷;NX:宁西酸性土壤;WY:翁源酸性土壤;SP:三坪石灰性土壤;CP:昌平石灰性土壤;各图中柱上不同小写字母代表不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 2. Effects of different soil types and phosphorus treatments on total root length and root surface area in maize
LP: No P added; HP: P fertilizer added; NX: Acid soil of Ningxi; WY: Acid soil of Wengyuan; SP: Calcareous soil of Sanping; CP: Calcareous soil of Changping; In each figure, different lowercase letters on the column represent significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
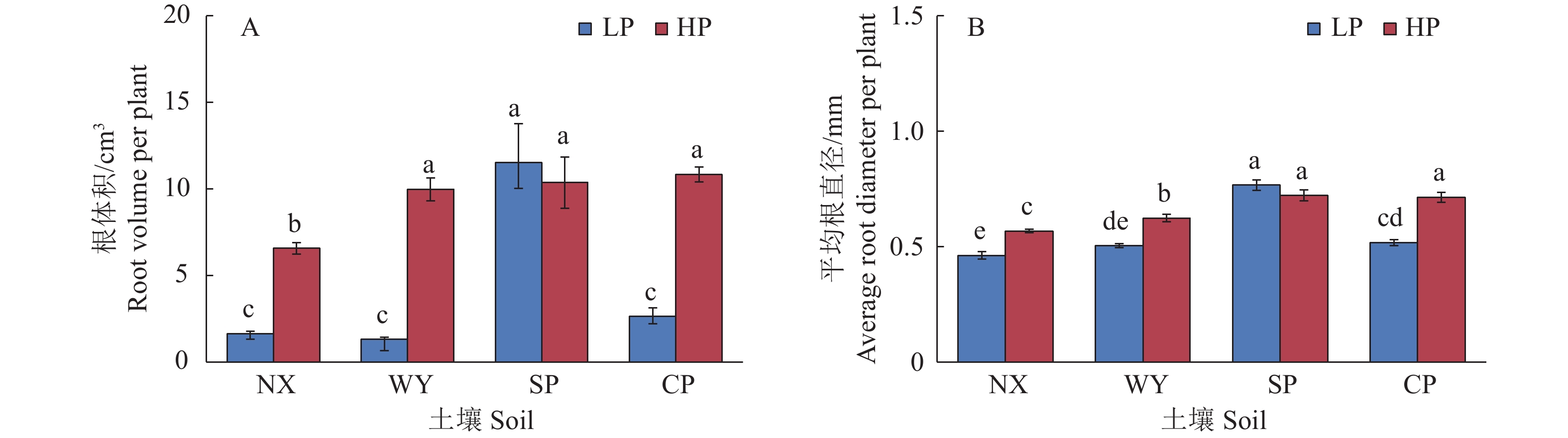
图 3 不同土壤类型和磷处理对玉米单株根体积和平均根直径的影响
LP:不施磷;HP:施磷;NX:宁西酸性土壤;WY:翁源酸性土壤;SP:三坪石灰性土壤;CP:昌平石灰性土壤;各图中柱上不同小写字母代表不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 3. Effects of different soil types and phosphorus treatments on root volume and average root diameter in maize
LP: No P added; HP: P fertilizer added; NX: Acid soil of Ningxi; WY: Acid soil of Wengyuan; SP: Calcareous soil of Sanping; CP: Calcareous soil of Changping; In each figure, different lowercase letters on the column represent significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
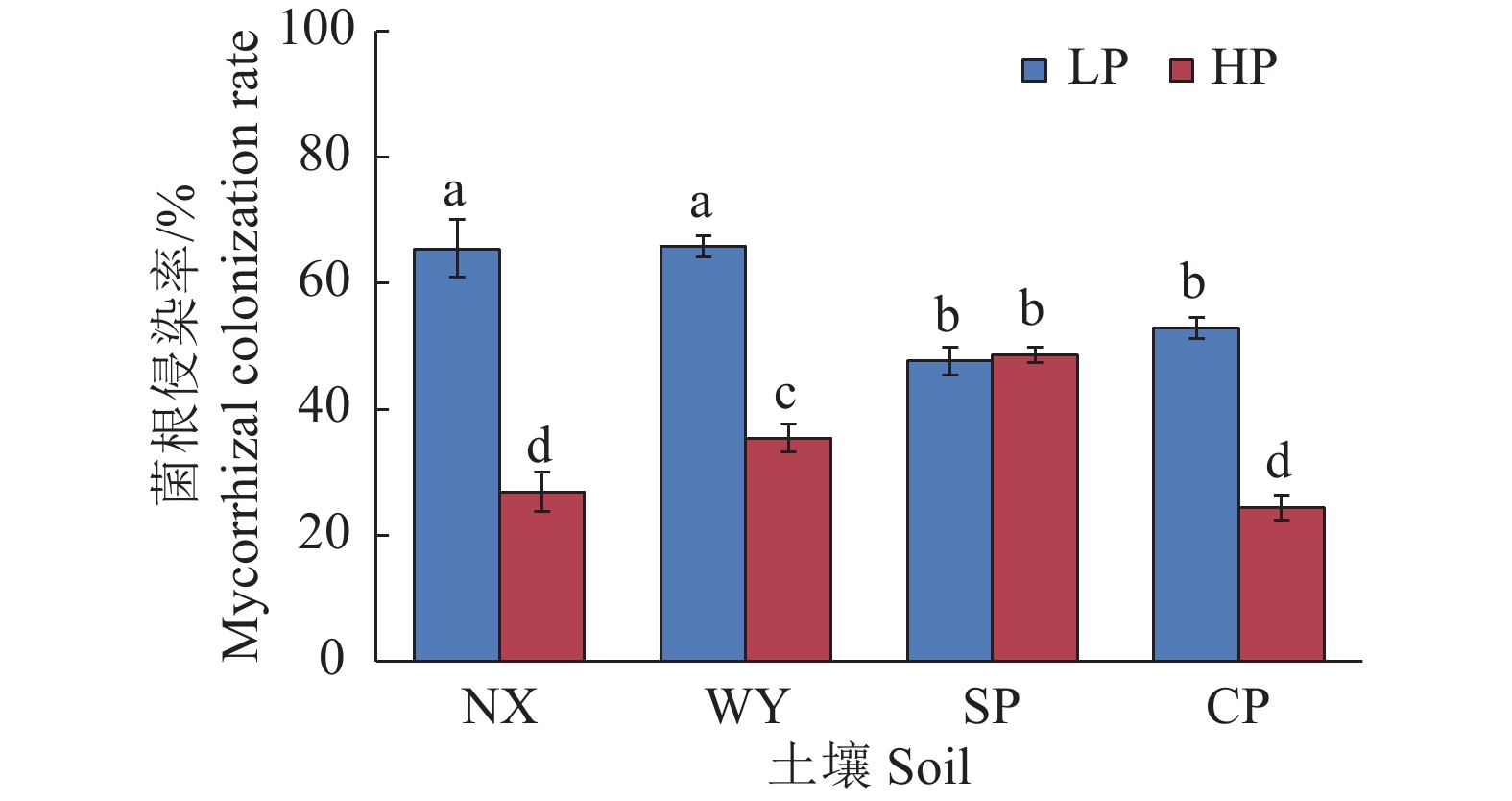
图 4 不同土壤类型和磷处理对玉米菌根侵染率的影响
LP:不施磷;HP:施磷;NX:宁西酸性土壤;WY:翁源酸性土壤;SP:三坪石灰性土壤;CP:昌平石灰性土壤;柱上不同小写字母代表不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 4. Effects of different soil types and phosphorus treatments on mycorrhizal colonization rate in maize
LP: No P added; HP: P fertilizer added; NX: Acid soil of Ningxi; WY: Acid soil of Wengyuan; SP: Calcareous soil of Sanping; CP: Calcareous soil of Changping; Different lowercase letters on the column represent significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
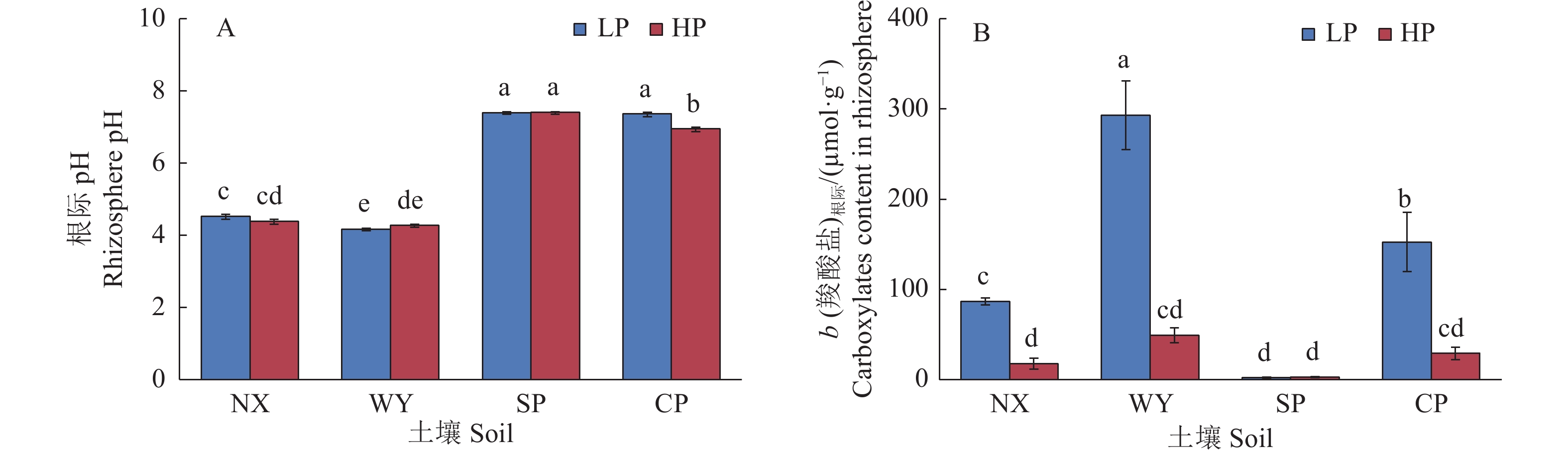
图 5 不同土壤类型和磷处理对玉米根际pH和根际羧酸盐含量的影响
LP:不施磷;HP:施磷;NX:宁西酸性土壤;WY:翁源酸性土壤;SP:三坪石灰性土壤;CP:昌平石灰性土壤;各图中柱上不同小写字母代表不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 5. Effects of different soil types and phosphorus treatments on rhizosphere pH and carboxylate content in maize
LP: No P added; HP: P fertilizer added; NX: Acid soil of Ningxi; WY: Acid soil of Wengyuan; SP: Calcareous soil of Sanping; CP: Calcareous soil of Changping; In each figure, different lowercase letters on the column represent significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
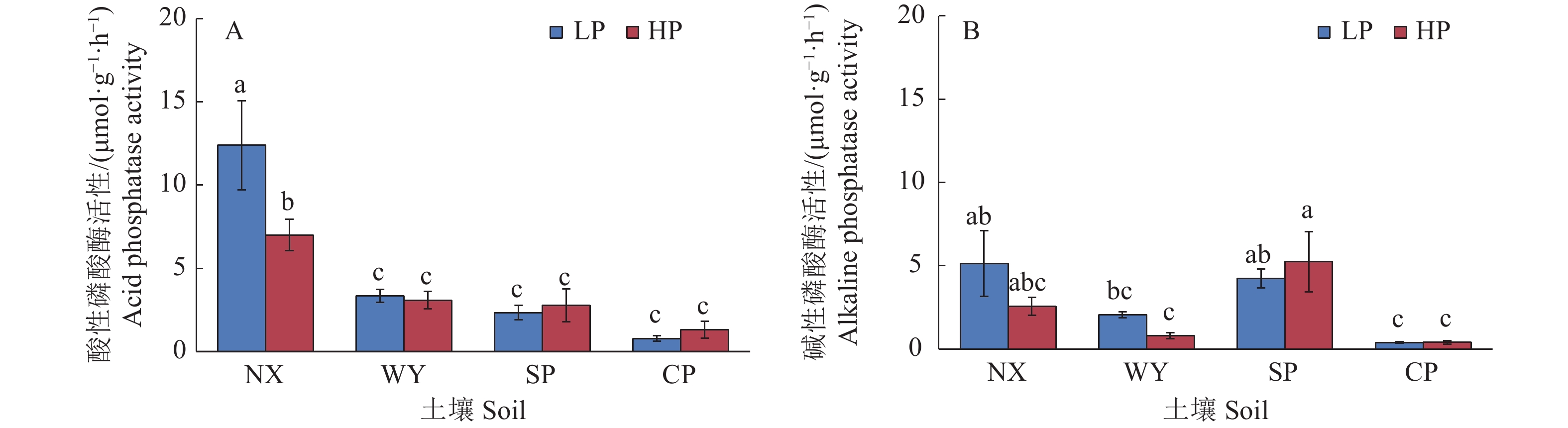
图 6 不同土壤类型和磷处理对玉米根际磷酸酶活性的影响
LP:不施磷;HP:施磷;NX:宁西酸性土壤;WY:翁源酸性土壤;SP:三坪石灰性土壤;CP:昌平石灰性土壤;各图中柱上不同小写字母代表不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 6. Effects of different soil types and phosphorus treatments on rhizosphere phosphatase activities in maize
LP: No P added; HP: P fertilizer added; NX: Acid soil of Ningxi; WY: Acid soil of Wengyuan; SP: Calcareous soil of Sanping; CP: Calcareous soil of Changping; In each figure, different lowercase letters on the column represent significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
表 1 土壤类型(S)和磷处理(P)对玉米植株生长以及根际指标影响的方差分析1)
Table 1 Analysis of variance of effects of soil types (S) and phosphorus treatments (P) on plant growth and rhizosphere indexes in maize
性状(指标) Trait (Indicator) S P S×P 植株干质量 Plant dry weight 261.50*** 632.72*** 16.00*** 植株磷质量 Plant phosphorus weight 16.79*** 632.72*** 1.36*** 总根长 Total root length 2.23ns 145.28*** 9.46*** 根表面积 Root surface area 10.94*** 73.06*** 10.21*** 根体积 Root volume 16.58*** 51.40*** 9.90*** 平均根直径 Average root diameter 64.82*** 59.14*** 16.92*** 菌根侵染率 Mycorrhizal colonization rate 8.25** 181.10*** 23.27*** 根际 pH Rhizosphere pH 1553.68*** 7.54* 5.91** 根际羧酸盐含量 Carboxylate content in rhizosphere 12.57*** 35.30*** 6.56** 根际酸性磷酸酶活性 Acid phosphatase activity in rhizosphere 12.45*** 2.93ns 3.53* 根际碱性磷酸酶活性 Alkaline phosphatase activity in rhizosphere 8.48** 1.01ns 1.25ns 1)“*”:0.01≤P<0.05;“**”:0.001≤P<0.01; “***”:P<0.001; “ns”:不显著
1) “*”: 0.01≤P<0.05; “**”: 0.001≤P<0.01; “***”: P<0.001; “ns”: No significance -
[1] LIU D. Root developmental responses to phosphorus nutrition[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(6): 1065-1090. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13090
[2] 吕春香. 玉米种植现状与新技术应用的效率[J]. 农家参谋, 2021(20): 30-31. [3] 孙军兰. 磷肥用量对玉米产量的影响[J]. 农业工程技术, 2022, 42(8): 17. [4] BARBER S, MACKAY A. Root growth and phosphorus and potassium uptake by two corn genotypes in the field[J]. Fertilizer Research, 1986, 10(3): 217-230. doi: 10.1007/BF01049351
[5] 高文龙, 张赢心, 卢英进, 等. 不同磷素用量对玉米生长及生理生化指标的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2022, 54(4): 90-94. [6] 赵军霞. 土壤酸碱性与植物的生长[J]. 内蒙古农业科技, 2003(6): 33-42. [7] WANG Y, CHEN Y F, WU W H. Potassium and phosphorus transport and signaling in plants[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(1): 34-52. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13053
[8] LYU Y, TANG H, LI H, et al. Major crop species show differential balance between root morphological and physiological responses to variable phosphorus supply[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 1939. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01939
[9] XIA Z, HE Y, ZHU Z, et al. Covariations and trade-offs of phosphorus (P) acquisition strategies in dioecious Populus euphratica as affected by soil water availability[J]. Functional Ecology, 2022, 36(12): 3188-3199. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.14193
[10] MADRID-DELGADO G, OROZCO-MIRANDA M, CRUZ-OSORIO M, et al. Pathways of phosphorus absorption and early signaling between the mycorrhizal fungi and plants[J]. Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, 2021, 90(5): 1321-1338.
[11] 周文利. 不同品种磷肥对土壤有效磷及玉米苗期生长的影响[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2022, 37(11): 45-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6220.2022.11.019 [12] HASHMI Z U H, KHAN M J, AKHTAR M, et al. Enhancing phosphorus uptake and yield of wheat with phosphoric acid application in calcareous soil[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2017, 97(6): 1733-1739. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7921
[13] 习娟, 杨修一, 耿计彪, 等. 不同施磷量对盐渍化土壤玉米磷素吸收及产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022(7): 58-63. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.1673-6257.21233 [14] 王晓锋, 张磊, 袁兴中. 施磷与接种耐酸根瘤菌对酸性黄壤中紫花苜蓿生长、结瘤的影响[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 2018, 3(1): 59-65. [15] 王倩倩, 刘志强, 陈康, 等. 不同土壤施磷和接种根瘤菌对大豆| | 玉米间作系统氮磷吸收的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2022, 30(12): 1913-1924. doi: 10.12357/cjea.20220124 [16] SARDANS J, PEÑUELAS J, ESTIARTE M. Warming and drought alter soil phosphatase activity and soil P availability in a Mediterranean shrubland[J]. Plant and Soil, 2006, 289(1/2): 227-238.
[17] PEARSE S J, VENEKLAAS E J, CAWTHRAY G R, et al. Carboxylate release of wheat, canola and 11 grain legume species as affected by phosphorus status[J]. Plant and Soil, 2006, 288: 127-139. doi: 10.1007/s11104-006-9099-y
[18] HOCKING P J, JEFFERY S. Cluster-root production and organic acid exudation in a group of old-world lupins and a new-world lupin[J]. Plant and Soil, 2004, 258: 135-150. doi: 10.1023/B:PLSO.0000016544.18563.86
[19] 盛萍萍, 刘润进, 李敏. 丛枝菌根观察与侵染率测定方法的比较[J]. 菌物学报, 2011, 30(4): 519-525. [20] QIAO L, WANG X, SMITH P, et al. Soil quality both increases crop production and improves resilience to climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2022, 12(6): 574-580. doi: 10.1038/s41558-022-01376-8
[21] EREL R, BÉRARD A, CAPOWIEZ L, et al. Soil type determines how root and rhizosphere traits relate to phosphorus acquisition in field-grown maize genotypes[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 412: 115-132. doi: 10.1007/s11104-016-3127-3
[22] PEREZ V J C, DE SOUZA J C L, NARRO L A, et al. Genetic effects for maize traits in acid and non-acid soils[J]. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 2008, 31(1): 89-97.
[23] WEN Z H, SHEN J B, BLACKWELL M, et al. Combined applications of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers with manure increase maize yield and nutrient uptake via stimulating root growth in a long-term experiment[J]. Pedosphere, 2016, 26(1): 62-73. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60023-6
[24] JAFARIKOUHINI N, KAZEMEINI S A, SINCLAIR T R. Sweet corn nitrogen accumulation, leaf photosynthesis rate, and radiation use efficiency under variable nitrogen fertility and irrigation[J]. Field Crops Research, 2020, 257: 107913. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2020.107913
[25] RAFAT N, YARNIA M, HASSANPANAH D. Effect of drought stress and potassium humate application on grain yield-related traits of corn (cv. 604)[J]. Journal of Food Agriculture & Environment, 2012, 10(2): 580-584.
[26] NIELSEN K L, ESHEL A, LYNCH J P. The effect of phosphorus availability on the carbon economy of contrasting common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2001, 52: 329-339.
[27] HERMANS C, HAMMOND J P, WHITE P J, et al. How do plants respond to nutrient shortage by biomass allocation?[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2006, 11(12): 610-617. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2006.10.007
[28] KIRCHGESSER J, HAZARIKA M, BACHMANN-PFABE S, et al. Phenotypic variation of root-system architecture under high P and low P conditions in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2023, 23: 68. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04070-9
[29] FITTER A H, HELGASON T, HODGE A. Nutritional exchanges in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: Implications for sustainable agriculture[J]. Fungal Biology Reviews, 2011, 25(1): 68-72. doi: 10.1016/j.fbr.2011.01.002
[30] 刘灵, 廖红, 王秀荣, 等. 磷有效性对大豆菌根侵染的调控及其与根构型、磷效率的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(3): 564-568. [31] FAY P, MITCHELL D T, OSBORNE B A. Photosynthesis and nutrient-use efficiency of barley in response to low arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization and addition of phosphorus[J]. The New Phytologist, 1996, 132(3): 425-433. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1996.tb01862.x
[32] TIAN Y, XU J, LIAN X, et al. Effect of Glomus intraradices on root morphology, biomass production and phosphorous use efficiency of Chinese fir seedlings under low phosphorus stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13: 1095772.
[33] WEN Z H, LI H G, SHEN J B, et al. Maize responds to low shoot P concentration by altering root morphology rather than increasing root exudation[J]. Plant and Soil, 2017, 416: 377-389. doi: 10.1007/s11104-017-3214-0
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王丰,刘迪林,朱满山,廖亦龙,李金华,付崇允,曾学勤,马晓智,霍兴,孔乐,柳武革. 水稻不育系泰丰A创制及其优良品质性状遗传基础研究. 中国稻米. 2024(04): 24-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张兰兰,刘迪林,马晓智,霍兴,孔乐,柳武革,王丰. 施氮水平对华南优质稻产量和食味的影响及适宜施用量探讨. 中国稻米. 2024(05): 96-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: