Finite element analysis of mechanical collision damage during precision seeding of cassava seed stems
-
摘要:目的
明确木薯种茎在播种过程中的碰撞损伤机制,寻求较小损伤的播种方式。
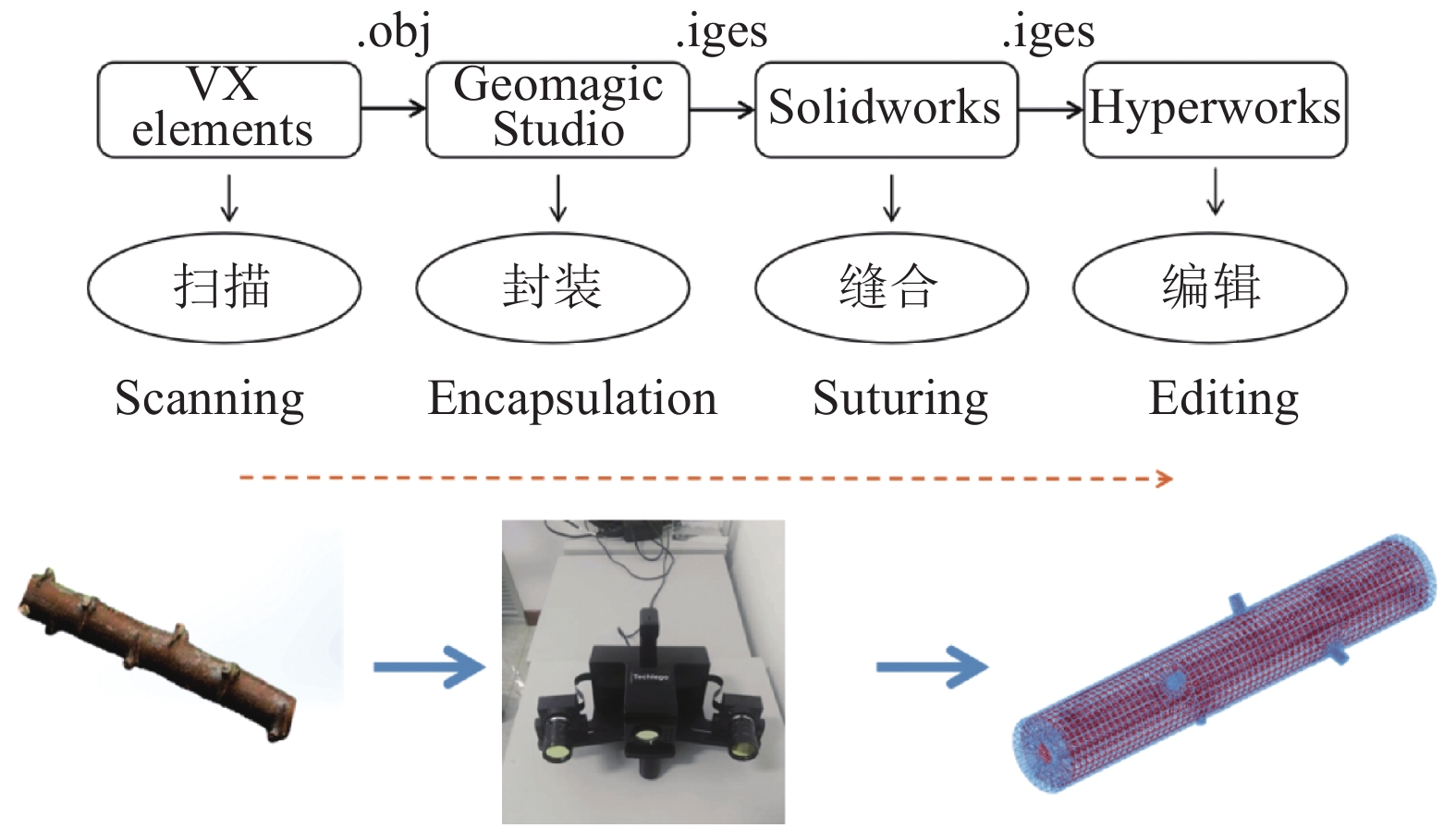
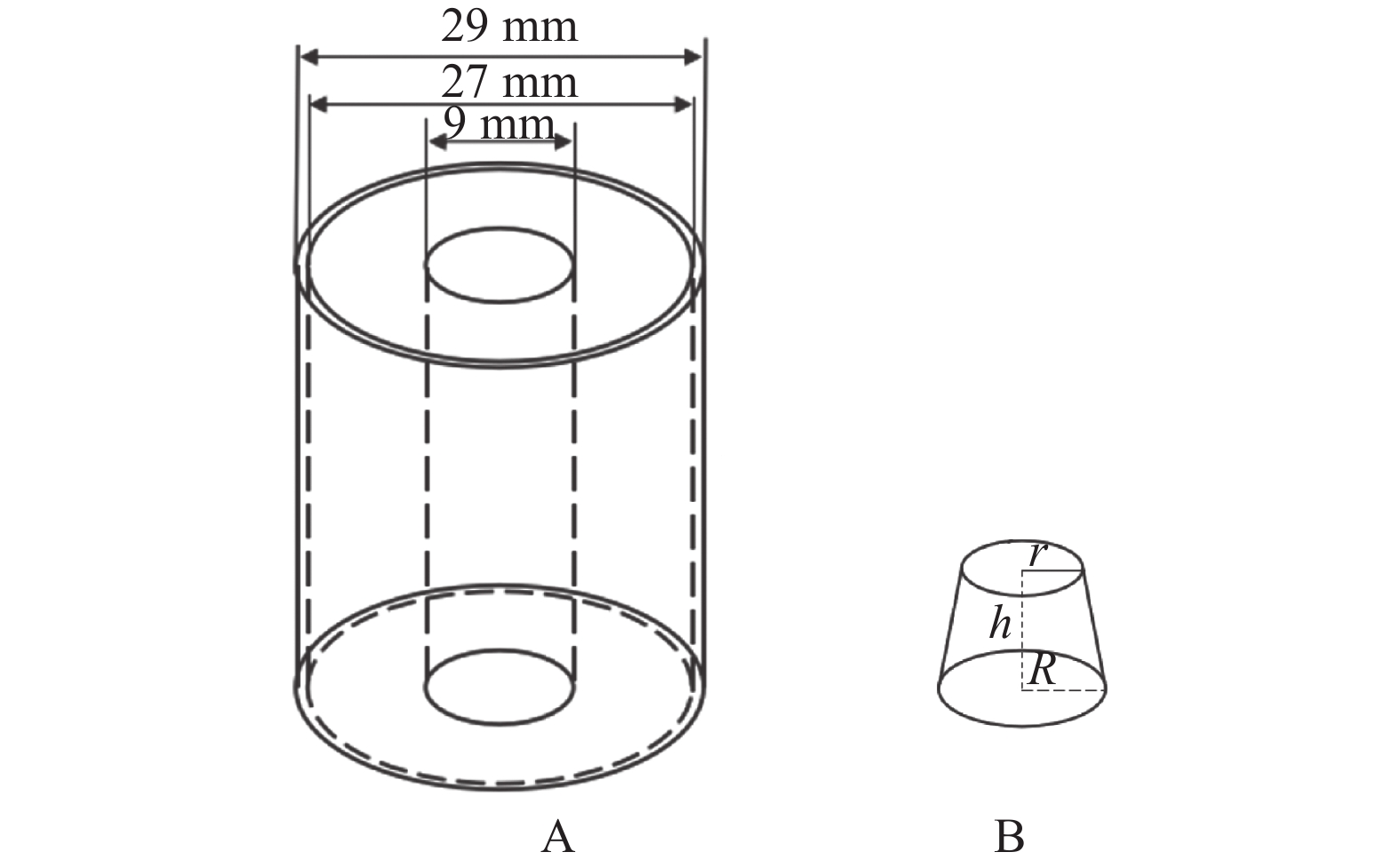
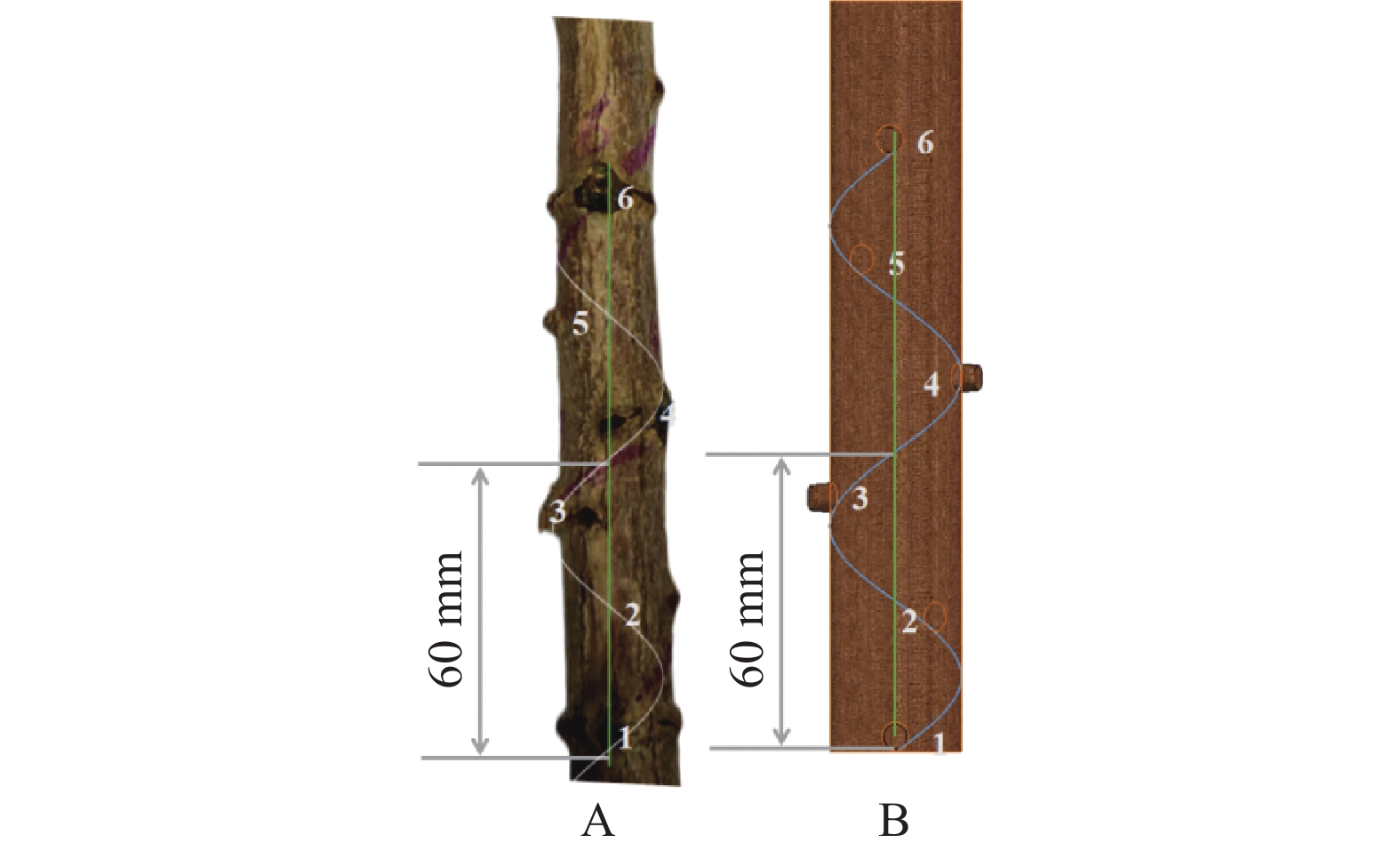
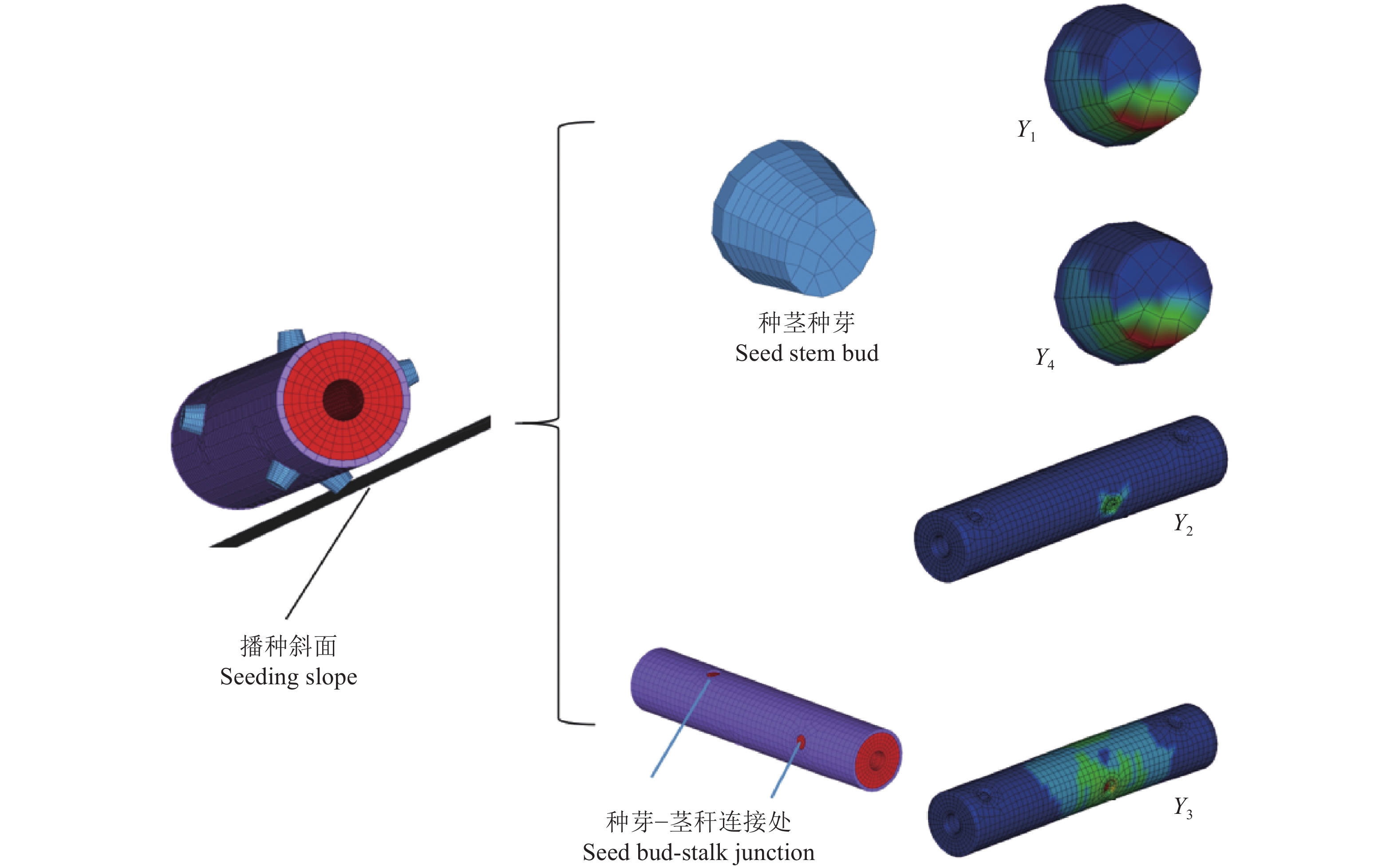
方法利用三维扫描技术逆向建立木薯种茎的三维模型,通过基于Hyper Mesh和LS-DYNA的种茎碰撞有限元分析,研究播种性能的主要影响因素(跌落高度、振动板安装倾斜角度及振动板振动频率)下种茎碰撞损伤过程,明确不同试验因素水平下种茎种芽−播种部件斜面接触等效应力、种芽−茎秆交接处等效应力、种芽−茎秆交接处应变及种芽−播种部件斜面接触应变变化规律;在单因素试验基础上,通过二次旋转正交组合试验研究,结合非线性多目标优化计算方法,对影响因素进行优化,以验证所建立回归模型的合理性。
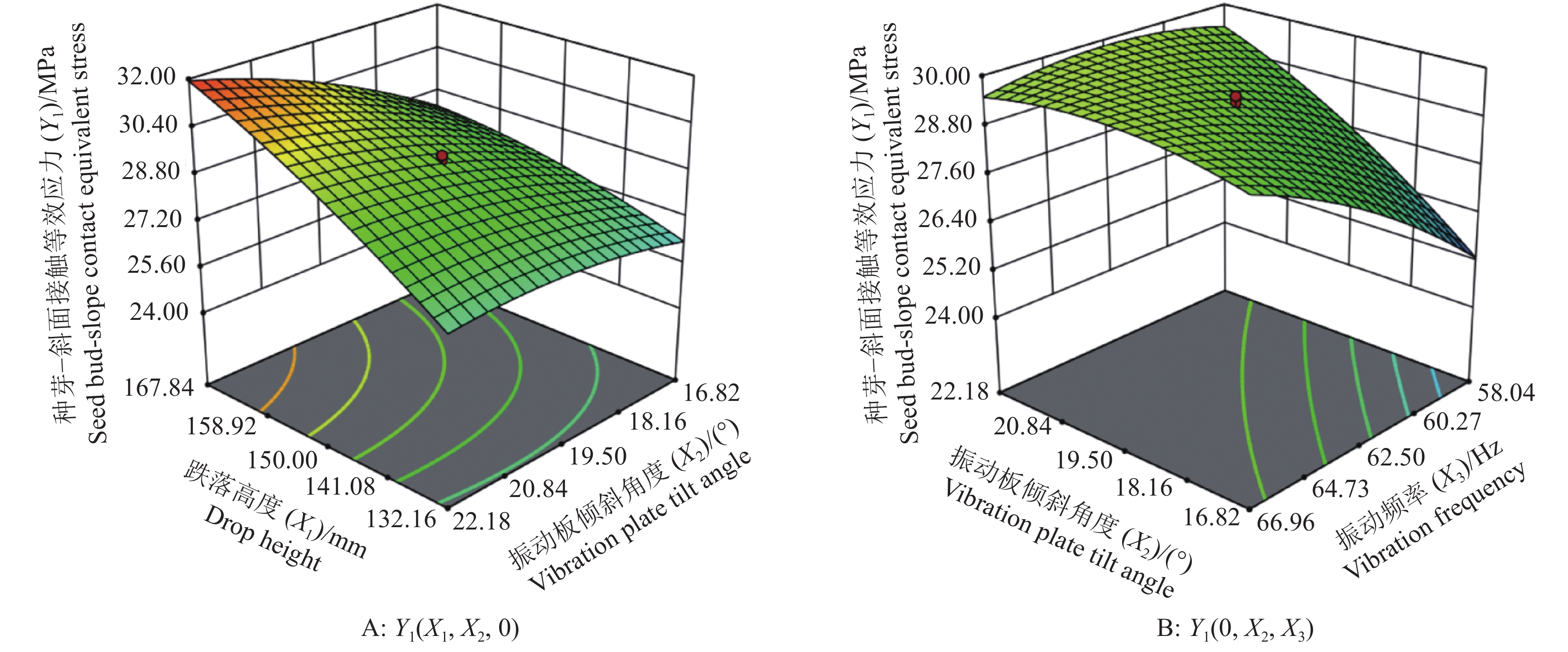
结果当跌落高度为167.83 mm、振动板安装倾斜角度为22.18°、振动频率为66.96 Hz时,种芽−播种部件斜面接触等效应力为32.64 MPa、种芽−茎秆交接处等效应力为17.08 MPa、种芽−茎秆交接处应变为0.094、种芽−播种部件斜面接触应变为1.049,模型预测结果与实际仿真结果相近,证明了回归模型的可靠性。
结论本研究结果为揭示木薯种茎碰撞机制及播种装置优化等提供了理论依据。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo clarify the collision damage mechanism of cassava seed stems during the seeding process and seek a seeding method with less damage.
MethodUsing 3D scanning technology to reversely establish a 3D model of cassava seed stem, and through finite element analysis of seed stem collision based on Hyper Mesh and LS-DYNA, the main influencing factors of seeding performance (drop height, installation inclination angle of vibration plate, and vibration frequency of vibration plate) were studied to investigate the process of seed stem collision damage. The variation law of the equivalent stress of the contact between the seed stem bud and the sowing component slope, the equivalent stress at the junction of seed bud and stalk, the strain at the junction of seed bud and stalk, and the strain of seed bud and sowing components slope contact at different experimental factor levels were clarified. On the basis of single factor experiments, a quadratic rotation orthogonal combination experiment was conducted to study the influencing factors, combined with nonlinear multi-objective optimization calculation methods, in order to verify the rationality of the established regression model.
ResultWhen the drop height was 167.83 mm, the installation inclination angle of the vibration plate was 22.18°, and the vibration frequency was 66.96 Hz, the equivalent stress of the oblique contact between the seed bud and the sowing component was 32.64 MPa, the equivalent stress of the intersection between the seed bud and the stalk was 17.08 MPa, the strain of the intersection between the seed bud and the stalk was 0.094, and the oblique contact strain of the seed bud and the sowing component was 1.049. The predicted results of the model were similar to the actual simulation results, proving the reliability of the regression model.
ConclusionThe results provide a theoretical basis for revealing the collision mechanism of cassava seed stems and optimizing the seeding device.
-
Keywords:
- Cassava /
- Seed stem /
- Collision damage /
- Finite element analysis /
- Seeder /
- Numerical simulation
-
-
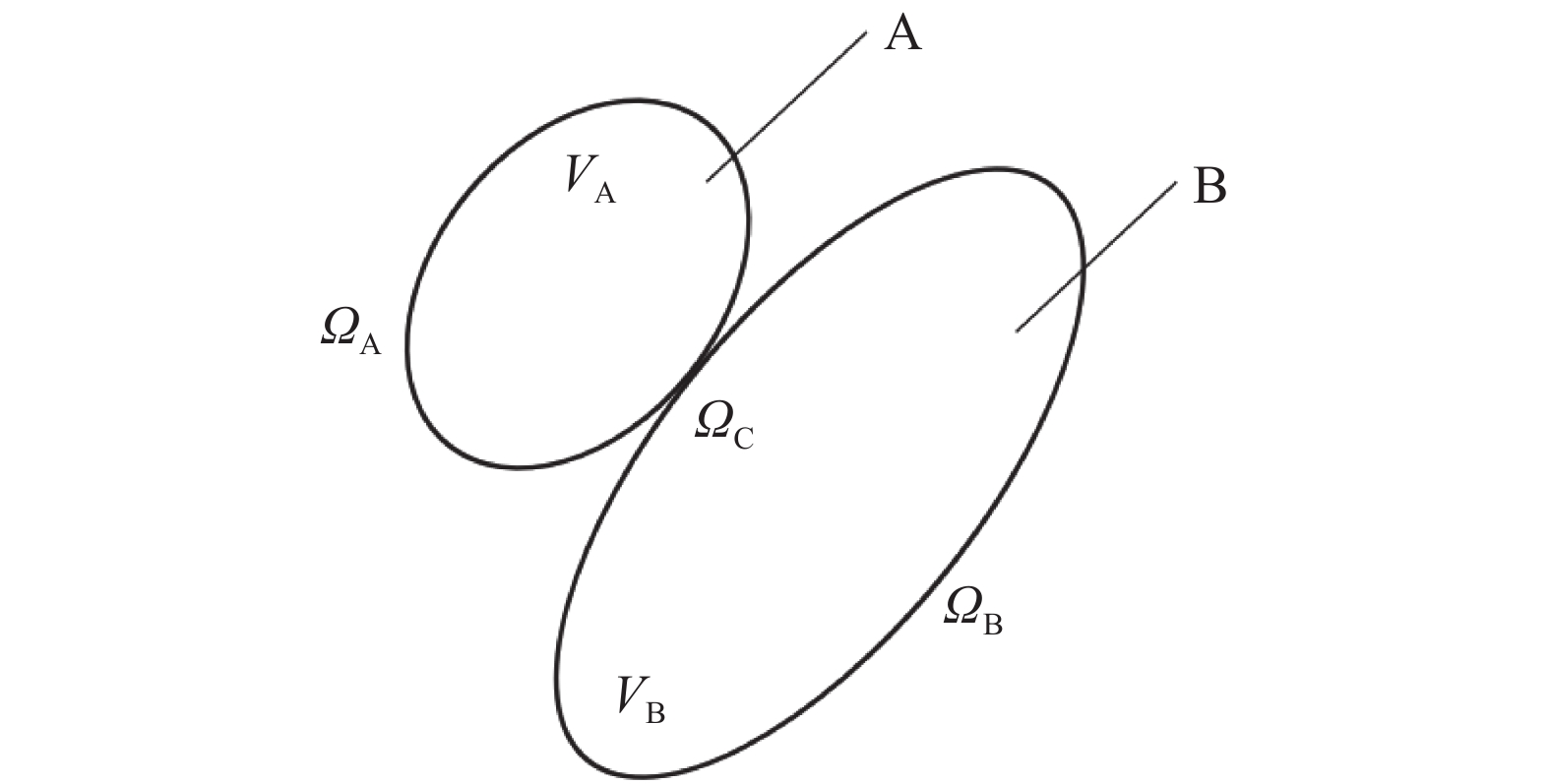
图 6 物体接触面定义
A和B为两物体,$ {V_{\text{A}}} $和$ {V_{\text{B}}} $为构形,$ {\varOmega _{\text{A}}} $和$ {\varOmega _{\text{B}}} $为边界面,$ {\varOmega _{\text{C}}} $为接触面
Figure 6. Definition of object contact surface
A and B are two objects, with conformations of $ {V_{\text{A}}} $ and $ {V_{\text{B}}} $, boundary surfaces of $ {\varOmega _{\text{A}}} $ and $ {\varOmega _{\text{B}}} $, contact surface of $ {\varOmega _{\text{C}}} $
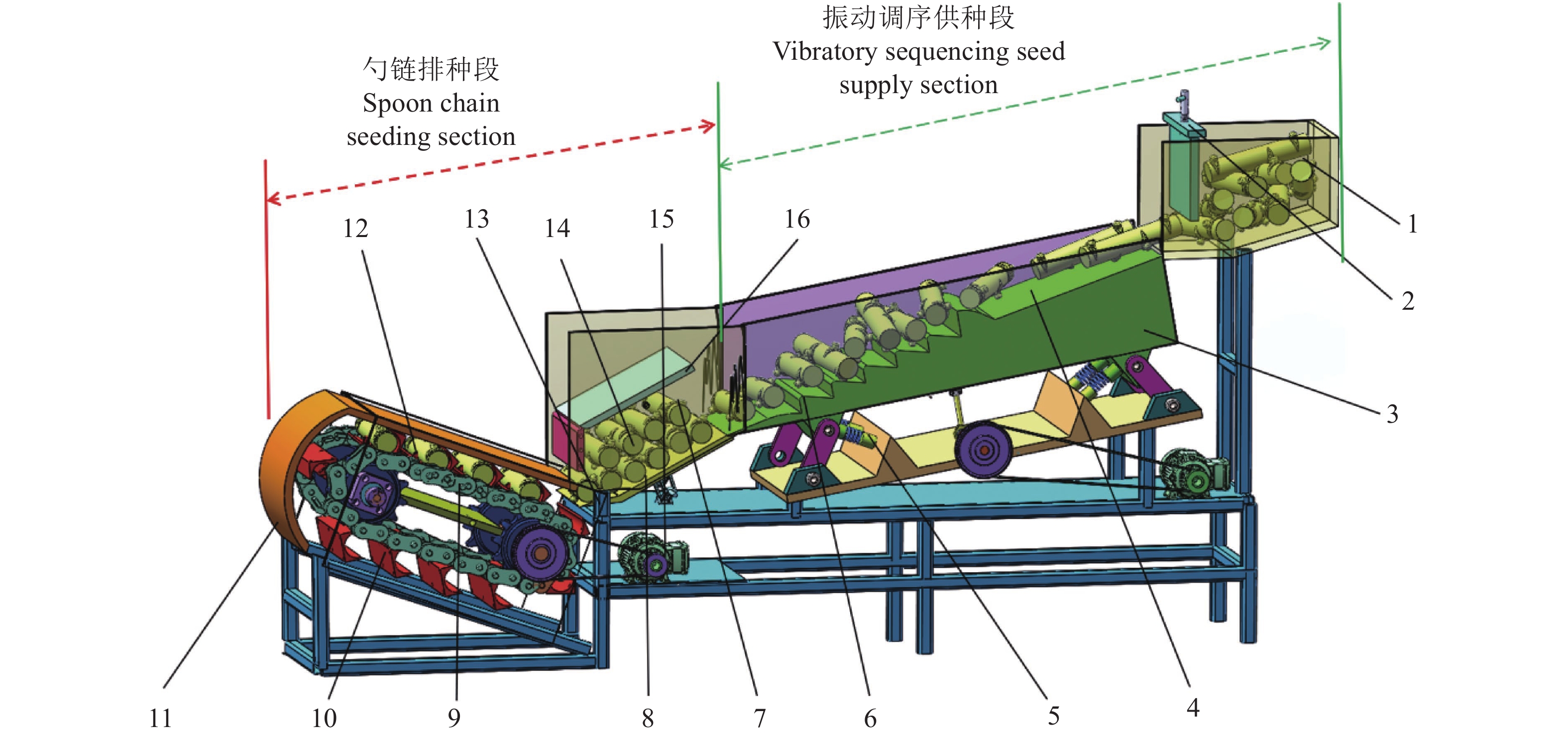
图 8 预切种振动供种式木薯播种器示意图
1:喂种箱,2:种量控制提升板,3:阶梯式振动散种机构,4:振动散种板,5:振动系统,6:阶梯式调姿板,7:充种箱,8:充种板,9:输送链,10:捞种勺,11:护种部件,12:刮种部件,13:机架,14:木薯种茎群,15:电动机,16:种层挡板
Figure 8. Diagram of the whole machine structure of the pre-cut seed vibrating cassava seeder
1: Seed feeding box, 2: Seed volume control lifting plate, 3: Stepped vibration seed dispersal mechanism, 4: Vibration seed dispersal plate, 5: Vibration system, 6: Stepped posturing plate, 7: Seed charging box, 8: Seed charging plate, 9: Conveyor chain, 10: Seed scooping spoon, 11: Seed guarding part, 12: Seed scraping part, 13: Rack, 14: Cassava seed stem cluster, 15: Electric motor, 16: Seed layer baffle plate
表 1 木薯种茎各部位材料参数
Table 1 Material parameters of cassava seed stem
部位
Part密度($ \rho $)/
(×10−10 t·mm−3)
Density径向弹性
模量($ {E_a} $)/MPa
Radial elasticity
modulus轴向弹性
模量($ {E_c} $)/MPa
Axial elasticity
modulus同性平面
泊松比($ {\mu _{ab}} $)
Homogeneous plane
Poisson’s ratio异性平面
泊松比($ {\mu _{ac}} $)
Anisotropic plane
Poisson’s ratio轴向剪切模
量($ {G_{ab}} $)/MPa
Axial shear
modulus径向剪切模量
($ {G_{bc}} $)/MPa
Radial shear
modulus木质部
Xylem8.3 50.01 25.04 0.42 0.35 17.60 92.75 韧皮部
Phloem5.1 1.78 12.24 0.38 0.31 0.68 4.67 种芽
Seed bud7.5 45.00 45.00 0.35 0.35 2.50 2.50 表 2 试验因素与水平
Table 2 Test factor and level
水平
Level种茎跌落高度(X1)/mm
Seed stem drop height振动板安装倾斜角度(X2)/(°)
Vibration plate mounting tilt angle振动板振动频率(X3)/Hz
Vibration plate vibration frequency−1.682 120.00 15.00 55.00 −1 132.16 16.82 58.04 0 150.00 19.50 62.50 1 167.84 22.18 66.96 1.682 180.00 24.00 70.00 表 3 试验方案与结果
Table 3 Test plan and result
序号 X1/mm X2/(°) X3/Hz Y1/MPa Y2/MPa Y3 Y4 1 132.16 16.82 58.04 24.31 8.21 0.045 0.776 2 167.84 16.82 58.04 24.43 8.31 0.046 0.787 3 132.16 22.18 58.04 28.21 11.42 0.063 0.912 4 167.84 22.18 58.04 29.71 12.61 0.069 0.957 5 132.16 16.82 66.96 26.44 10.12 0.056 0.891 6 167.84 16.82 66.96 29.22 16.22 0.091 0.943 7 132.16 22.18 66.96 24.91 9.42 0.052 0.813 8 167.84 22.18 66.96 32.21 17.23 0.095 1.044 9 120.00 19.50 62.50 25.72 8.74 0.048 0.831 10 180.00 19.50 62.50 32.43 16.12 0.087 1.052 11 150.00 15.00 62.50 27.63 10.32 0.057 0.891 12 150.00 24.00 62.50 30.14 11.41 0.063 0.973 13 150.00 19.50 55.00 26.62 8.24 0.045 0.861 14 150.00 19.50 70.00 31.16 14.42 0.081 1.011 15 150.00 19.50 62.50 28.63 10.23 0.056 0.923 16 150.00 19.50 62.50 29.42 11.24 0.062 0.947 17 150.00 19.50 62.50 29.14 10.04 0.055 0.883 18 150.00 19.50 62.50 29.14 10.82 0.061 0.94 19 150.00 19.50 62.50 28.74 10.42 0.057 0.934 20 150.00 19.50 62.50 28.82 10.72 0.059 0.933 21 150.00 19.50 62.50 29.42 11.11 0.061 0.951 22 150.00 19.50 62.50 29.26 10.61 0.058 0.937 23 150.00 19.50 62.50 29.42 11.24 0.062 0.947 -
[1] 薛忠. 木薯茎秆切割力学特性与仿真分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. [2] 陈林涛, 刘兆祥, 牟向伟, 等. 预切种式木薯排种机构设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(13): 1-13. [3] 牟向伟, 陈林涛, 马旭, 等. 预切种振动供种式木薯播种器勺链排种机构设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(2): 20-31. [4] 段洁利, 张汉尧, 付函, 等. 基于高光谱成像技术的青香蕉碰撞损伤检测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(7): 176-184. [5] 闫银发, 赵庆吉, 王瑞雪, 等. 四槽轮配肥器肥料颗粒碰撞掺混离散元分析与优化设计[J]. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54(3): 49-59. [6] 曹明珠, 高学梅, 王建楠, 等. 紫云英种子力学性能与脱粒碰撞损伤机理研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2022, 43(5): 77-84. [7] 张磊, 刘欢, 胡志新, 等. 固体物料造粒碰撞过程有限元仿真研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2022, 45(1): 94-98. [8] 徐立章, 李耀明. 稻谷与钉齿碰撞损伤的有限元分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(10): 27-32. [9] 陈燕, 蔡伟亮, 邹湘军, 等. 荔枝的力学特性测试及其有限元分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(12): 358-363. [10] 张荣荣, 李小昱, 王为, 等. 基于有限元方法的板栗破壳力学特性分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008, 24(9): 84-88. [11] HUSSAIN N N, REGALLA S P, RAO Y V D. Techniques for correlation of drop weight impact testing and numerical simulation for composite GFRP crash boxes using Ls-DYNA[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2022, 27(3): 700-716. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2020.1837478
[12] 袁越锦, 袁月定, 党新安, 等. 板栗真空破壳力学特性有限元分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2011, 42(5): 136-141. [13] 陈林涛, 薛俊祥, 牟向伟, 等. 预切种木薯播种器阶梯式振动散种机构设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(8): 27-37. [14] 王冬, 陈度, 王书茂, 等. 基于有限元方法的整形果树振动收获机理分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(S1): 56-62.




 下载:
下载: