Soil nutrient status and fertility evaluation of typical taro producing areas in Shaoguan City
-
摘要:目的
了解广东省韶关市典型香芋产区的土壤肥力情况,以期为香芋产区土壤养分资源管理提供参考依据。
方法分别于韶关市的3个香芋种植区(桂头镇老均村,廊田镇官坡滩村、农庄村)采集0~30 cm香芋根际土壤样品,测定土壤理化性质,通过主成分分析和相关性分析,筛选出最能代表当地土壤肥力的指标进入最小数据集,通过隶属度函数对所有的指标进行归一化处理,计算土壤质量指数并评价土壤肥力。
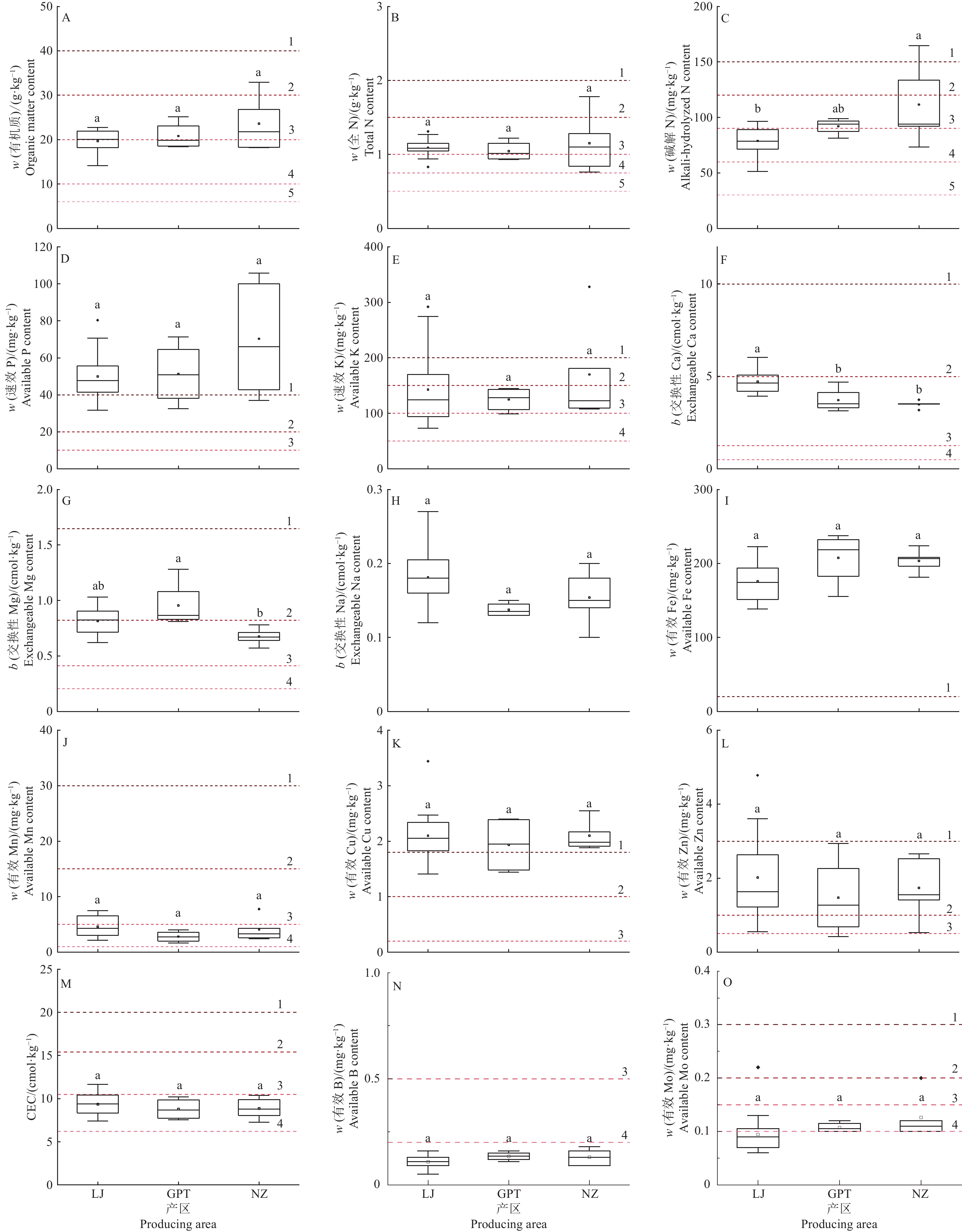
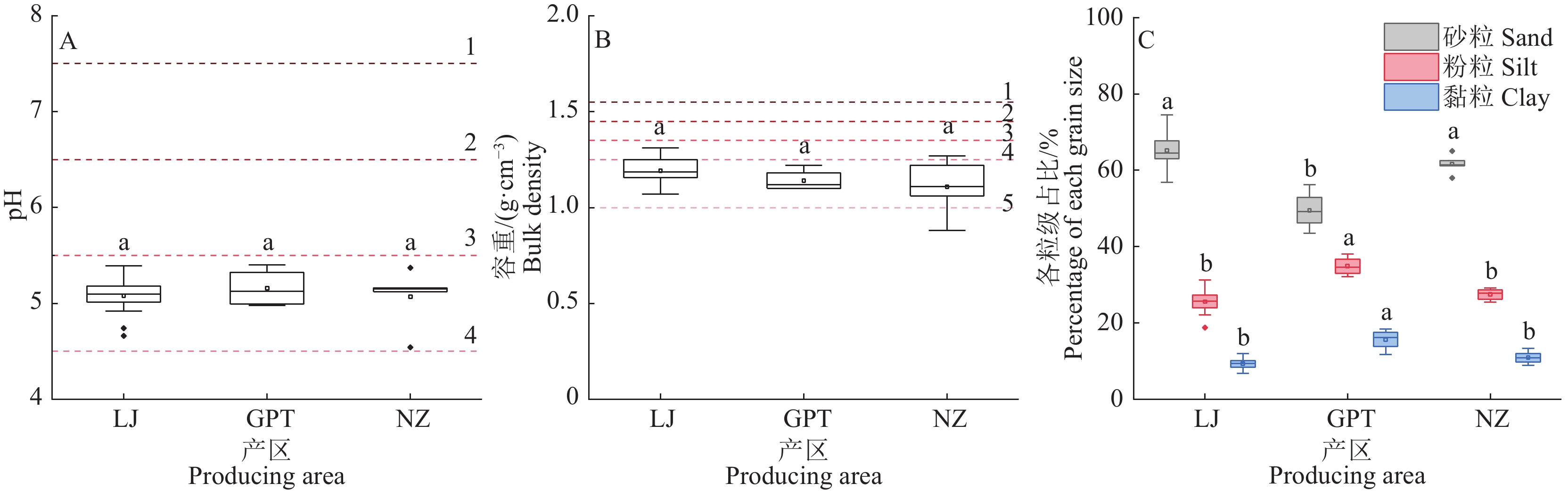
结果3个香芋产区土壤均呈酸性;容重为1.17 g·cm−3,质地适宜;阳离子交换量(Cation exchange capacity,CEC)为9.17 cmol·kg−1,处于较低水平;速效P (54.20 mg·kg−1)、有效Cu (2.07 mg·kg−1)、有效Fe (186.33 mg·kg−1)、有效Zn (1.87 mg·kg−1)丰富,有效Mn (4.21 mg·kg−1)、有效B (0.12 mg·kg−1)、有效Mo (0.10 mg·kg−1)缺乏或极缺乏,其他养分含量处于中等及以上水平。3个香芋产区土壤粒级占比、碱解N、交换性Ca及交换性Mg含量差异显著,其他指标差异均不显著。从20个指标中筛选出7个指标构成土壤质量评价的最小数据集,分别为碱解N、砂粒、黏粒、交换性Ca、有效B和有效Fe含量以及CEC。评价结果表明,3个香芋产区的土壤肥力均处于中等水平,其中,碱解N和交换性Ca含量为肥力水平的主要限制因子。
结论韶关市典型香芋产区的土壤肥力水平整体处于中等水平,土壤保肥能力较差,有效Mn、B、Mo等微量元素缺乏。因此,在香芋种植时,要注重有机肥以及微量元素肥料的施用,平衡施肥,改善土壤理化性质,提高土壤保肥能力。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo better understand the soil fertility status in typical taro producing areas in Shaoguan City, Guangdong Province, and provide suggestions for soil nutrient management in taro producing areas.
MethodThe 0−30 cm soil samples were collected from taro rhizosphere in Laojun Village of Guitou Town, Guanpotan Village and Nongzhuang Village of Langtian Town from Shaoguan City, to determine the physical and chemical properties. Principal component analysis and correlation analysis were conducted to select the key indicators that best represent local soil fertility entering into minimum data set. All indicators were normalized using membership functions, and soil quality indices were calculated for soil fertility evaluation.
ResultThe soils in three taro producing areas were all acidic with suitable bulk density (1.17 g·cm−3) and texture, but with low cation exchange capacity (CEC, 9.17 cmol·kg−1). The contents of available P (54.20 mg·kg−1), Cu (2.07 mg·kg−1), Fe (186.33 mg·kg−1), Zn (1.87 mg·kg−1) were rich, while the contents of available Mn (4.21 mg·kg−1), B (0.12 mg·kg−1), Mo (0.10 mg·kg−1) were deficient or extremely deficient. The contents of other nutrients were at moderate to above-average levels. Among the three taro producing areas, there were significant differences in the percentage of soil grain size, contents of alkali-hydrolyzed N, exchangeable Ca, and exchangeable Mg, whereas the differences in other indicators were not significant. Seven indicators were selected to build the minimum data set for soil fertility evaluation, including alkali-hydrolyzed N, sand, clay, exchangeable Ca, available B, and available Fe contents as well as CEC. The evaluation results indicated that the soil fertilities of the three taro producing areas were at moderate levels, and the contents of alkali-hydrolyzed N and exchangeable Ca were the main limiting factors.
ConclusionThe overall soil fertility level of typical taro producing area in Shaoguan City is moderate, with poor soil nutrient retention capacity and deficiencies in trace elements, such as available Mn, B and Mo. Therefore, it is important to use organic fertilizers and micronutrient fertilizers during taro cultivation. Balanced fertilization shall be practiced to improve soil properties and enhance its nutrient retention capacity.
-
Keywords:
- Taro producing area /
- Nutrient level /
- Minimum data set /
- Soil fertility evaluation
-
《华南农业大学学报》第十届编委会成立暨第一次会议于2025年4月15日下午在广州召开。华南农业大学副校长仇荣亮教授出席会议并致辞,主编薛红卫教授及第十届编委会成员、编辑部工作人员参加会议。
仇荣亮教授在致辞中回顾了《华南农业大学学报》(下简称“学报”)的发展历程,充分肯定了期刊在促进学术交流、引领学科发展方面发挥的重要作用,并提出三点希望:一是坚守质量生命线,立足国家重大战略布局,追踪学科发展前沿动态,着力培育具有原创性的高水平研究成果;二是打造特色新优势,服务学校“双一流”建设,建立“学术-科研-出版”联动机制,重点孵化具有学科引领性的标志性成果;三是推进数字化转型,全方位提升作者和读者的服务体验。他强调,新一届编委会肩负时代赋予的使命,要切实担当起“学科发展引领者、学术规范守护者、期刊品牌建设者”三重重要角色,推动“学报”迈向高质量发展。主编薛红卫教授和仇荣亮教授为第十届编委会成员颁发聘书,标志着新一届编委会正式履职。
主编薛红卫教授主持编委会第一次工作会议。专职副主编周志红编审汇报第九届编委会和编辑部工作情况,“学报”连续入选Q1区中文核心期刊、中国科学引文数据库(CSCD)核心库期刊、高质量科技期刊分级目录和科技期刊世界影响力指数(WJCI)报告(2023)。周志红强调了专题组稿、专家综述对提升期刊影响力的关键作用,同时也提出了期刊发展目前面临的问题,如优质稿源不足、编委会成员作用发挥不够明确等。
薛红卫作《学报发展与定位》专题报告,深入探讨“专家办刊”模式及期刊未来发展方向。薛红卫指出,学术期刊在推动科技创新和学科引领中的作用愈发显著,中国科学技术协会高度重视高质量期刊建设,“学报”应结合学科特色与国情,前瞻性布局学术前沿,构建适应新时代需求的办刊体系。要实现这一目标,需从多维度进行发力:一是优化编委结构和学科板块,推动办刊模式从“编辑部办刊”向“专家办刊”转变;二是突出期刊特色,培育优势学科;三是优化稿件处理流程,明确稿件质量标准,建立“编委荐稿”机制;四是规划专栏策划机制,确定编委宣传义务、激励机制和沟通协作体系,并提出了刊名调整、平衡“综合性”与“特色化”、优化稿源结构、英文刊建设等一系列有待深入讨论的重要议题。
在讨论环节,编委们围绕各项议题积极建言献策,对“学报”高质量发展提出了多项富有建设性的意见:一是进一步明确期刊定位;二是明确服务对象,有针对性地吸引优质稿件;三是依托编委会成员的学术影响力和学科优势,聚焦前沿领域打造特色专题(栏),形成品牌效应;四是通过政策解读、热点专题、科普推广等构建“学者-作者-期刊-编辑”学术生态圈,提升期刊影响力;五是大力建设及完善期刊新媒体平台,充分发挥新媒体的宣传效应;六是完善奖励激励机制,激发学者投稿积极性;七是优化封面设计(故事性封面)及栏目设置,增强期刊辨识度等。
薛红卫对会议进行了总结,他表示,编委专家的真知灼见为“学报”进一步提升学术质量、扩大学术影响力等提供了极具价值的前瞻性思路。后续将进一步明确期刊定位,扎实落实会议讨论内容,齐心协力将《华南农业大学学报》打造成为综合性农业科学学术领域的标杆。
-
图 1 香芋产区土壤理化性质指标评价
LJ:老均村;GPT:官坡滩村,NZ:农庄村;各图中相同指标箱子上方的不同小写字母表示不同产区土壤之间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法);虚线代表土壤理化性质指标分级,参考全国第二次土壤普查的分级标准[30]
Figure 1. Evaluation of soil physicochemical properties in taro producing areas
LJ: Laojun Village, GPT: Guanpotan Village; NZ: Nongzhuang Village; Different lowercase letters on the boxes of the same indicator in each figure indicate significant differences among the soils of different producing areas (P<0.05, Duncan’s method); The dotted line represents the classification of soil physical and chemical properties indices, referring to the classification standard of the second national soil survey[30]
图 2 香芋产区土壤养分指标评价
LJ:老均村,GPT:官坡滩村,NZ:农庄村;各小图中箱子上方的不同小写字母表示不同产区土壤之间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法);虚线代表土壤理化性质指标分级,参考全国第二次土壤普查的分级标准[30]
Figure 2. Evaluation of soil nutrient indices in taro producing areas
LJ: Laojun Village, GPT: Guanpotan Village, NZ: Nongzhuang Village; Different lowercase letters on the boxes in each figure indicate significant differences among the soils of different producing areas (P<0.05, Duncan’s method); The dotted line represents the classification of soil physical and chemical properties indices, referring to the classification standard of the second national soil survey[30]
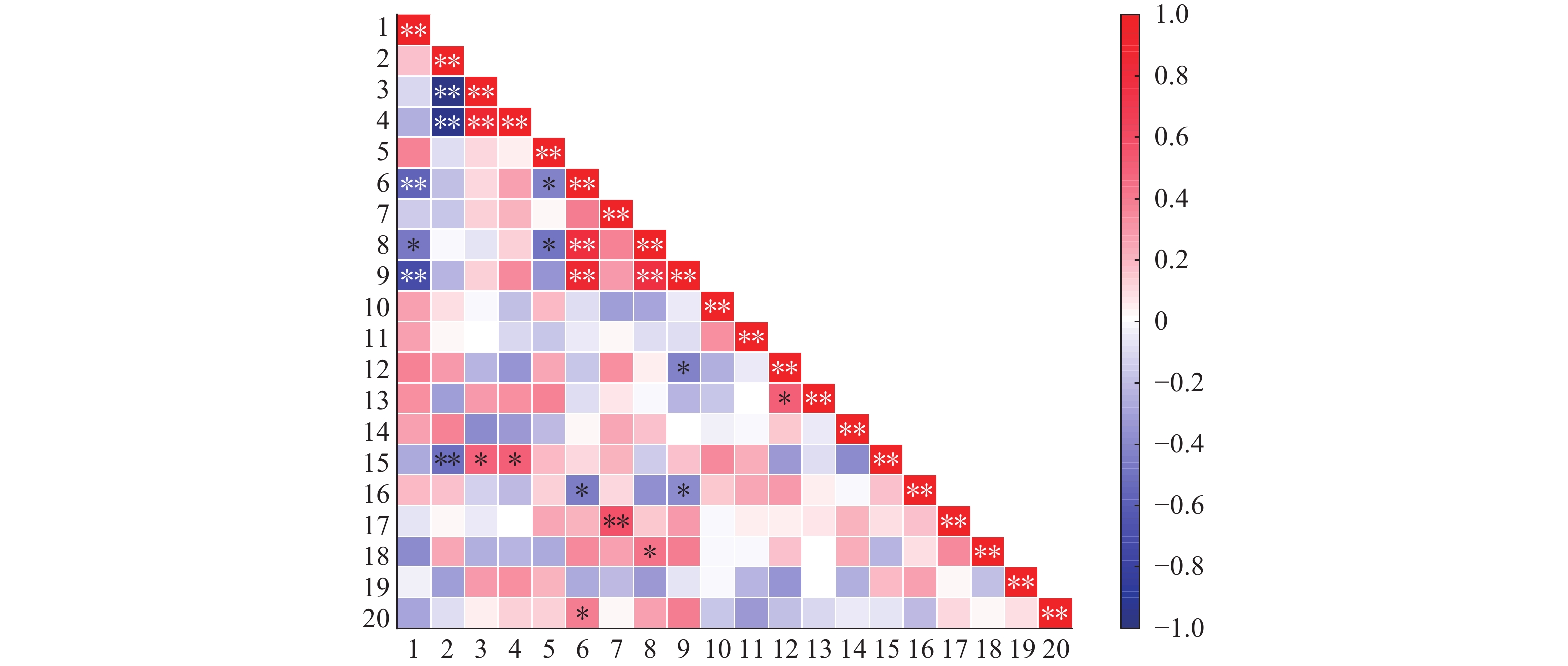
图 3 各土壤指标相关性分析图
“*”和“**”分别表示各土壤指标在0.05和0.01水平显著相关(Pearson法);1:容重,2:砂粒含量,3:粉粒含量,4:黏粒含量,5:pH,6:有机质含量,7:CEC,8:全N含量,9:碱解N含量,10:速效P含量,11:速效K含量,12:交换性Ca含量,13:交换性Mg含量,14:交换性Na含量,15:有效Fe含量,16:有效Mn含量,17:有效Cu含量,18:有效Zn含量,19:有效B含量,20:有效Mo含量
Figure 3. Correlation analysis of soil indices
“*” and “**” indicate that soil indices are significantly correlated at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively (Pearson method); 1: Bulk density, 2: Sand content, 3: Silt content, 4: Clay content, 5: pH, 6: Organic matter content, 7: CEC, 8: Total N content, 9: Alkali-hydrolyzed N content, 10: Available P content, 11: Available K content, 12: Exchangeable Ca content, 13: Exchangeable Mg content, 14: Exchangeable Na content, 15: Available Fe content, 16: Available Mn content, 17: Available Cu content, 18: Available Zn content, 19: Available B content, 20: Available Mo content
表 1 主成分载荷矩阵及Norm值计算结果
Table 1 Calculation results of principal component loading matrix and Norm values
指标
Index主成分载荷值 Principal component loading value Norm 分组
GroupPC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 PC6 碱解N含量 Alkali-hydrolyzed N content 0.886 0.288 −0.111 0.141 0.086 0.118 2.002 1 有机质含量 Organic matter content 0.835 0.368 0.024 0.070 −0.124 0.193 1.948 1 砂粒含量 Sand content −0.562 0.749 −0.208 0.051 0.177 0.032 1.946 1 容重 Bulk density −0.738 −0.173 0.245 −0.041 −0.228 0.345 1.724 1 黏粒含量 Clay content 0.653 −0.666 0.200 −0.099 −0.128 −0.053 1.954 2 粉粒含量 Silt content 0.473 −0.765 0.203 −0.017 −0.201 −0.017 1.861 2 全N含量 Total N content 0.676 0.558 0.147 −0.078 −0.195 0.011 1.851 2 有效Zn含量 Available Zn content 0.237 0.586 0.208 0.253 0.157 −0.213 1.382 2 交换性Na含量 Exchangeable Na content −0.167 0.551 0.191 0.045 −0.057 0.148 1.196 2 交换性Ca含量 Exchangeable Ca content −0.418 0.274 0.708 0.170 0.115 0.087 1.533 3 CEC 0.369 0.195 0.690 0.299 0.070 −0.069 1.439 3 交换性Mg含量 Exchangeable Mg content −0.097 −0.274 0.703 −0.261 −0.218 0.091 1.307 3 有效Fe含量 Available Fe content 0.326 −0.582 −0.047 0.565 0.027 0.024 1.557 4 速效P含量 Available P content −0.234 −0.163 −0.343 0.585 −0.034 0.483 1.249 4 有效B含量 Available B content 0.015 −0.540 −0.148 −0.054 0.541 −0.302 1.329 5 速效K含量 Available K content −0.178 −0.044 −0.010 0.648 −0.502 0.036 1.166 5 pH −0.331 −0.438 0.365 −0.048 0.459 0.470 1.469 有效Mn含量 Available Mn content −0.450 −0.121 0.223 0.479 0.289 −0.458 1.385 有效Cu含量 Available Cu content 0.191 0.190 0.493 0.446 0.471 0.166 1.282 有效Mo含量 Available Mo content 0.419 0.087 −0.070 −0.320 0.485 0.354 1.249 表 2 各指标隶属度
Table 2 Membership of each index
指标
Index老均村
Laojun
Village官坡滩村
Guanpotan
Village农庄村
Nongzhuang
Village碱解N含量
Alkali-hydrolyzed N content0.318 0.423 0.578 黏粒含量 Clay content 0.800 0.314 0.676 交换性Ca含量
Exchangeable Ca content0.589 0.278 0.206 砂粒含量 Sand content 0.372 0.826 0.474 CEC 0.527 0.407 0.427 有效B含量
Available B content0.511 0.679 0.654 有效Fe含量
Available Fe content0.439 0.727 0.690 表 3 各指标公因子方差及权重
Table 3 Common factor variance and weight of each index
指标
Index公因子方差
Common factor
variance权重
Weight碱解N含量
Alkali-hydrolyzed N content0.898 0.164 黏粒含量 Clay content 0.886 0.161 交换性Ca含量
Exchangeable Ca content0.885 0.161 砂粒含量 Sand content 0.874 0.159 CEC 0.801 0.146 有效B含量
Available B content0.629 0.115 有效Fe含量
Available Fe content0.516 0.094 -
[1] 戴修纯, 罗燕羽, 黄绍力, 等. 广东省芋头产业现状与发展对策[J]. 广东农业科学, 2021, 48(6): 126-135. [2] 邓小英. 乳源县桂头镇精准扶贫政策实施效果研究[D]. 广州: 仲恺农业工程学院, 2020. [3] 高琳. 广东乐昌市香芋产区土壤养分特征与香芋品质的相关性[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2014, 42(8): 179-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2014.08.048 [4] 高琳. 基于层次分析法的香芋产区土壤养分肥力评价: 以广东省张溪村为例[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(10): 323-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.10.111 [5] 高琳, 陈晓远, 林昌华, 等. 基于ArcGIS韶关市香芋土壤养分空间变异特征研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2018, 31(5): 1025-1031. [6] 高琳, 卢文婷, 林昌华, 等. 粤北香芋种植区典型土壤剖面发育特征[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(10): 85-91. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0457 [7] 单奇华, 俞元春, 张建锋, 等. 城市森林土壤肥力质量指标筛选: 以南京市为例[J]. 土壤, 2009, 41(5): 777-783. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9829.2009.05.016 [8] BASTIDA F, ZSOLNAY A, HERNANDEZ T, et al. Past, present and future of soil quality indices: A biological perspective[J]. Geoderma, 2008, 147(3/4): 159-171.
[9] 刘引, 颜鸿远, 欧小宏, 等. 基于最小数据集的麻城菊花种植区土壤肥力质量评价[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2019, 44(24): 5382-5389. [10] BÜNEMANN E K, BONGIORNO G, BAI Z, et al. Soil quality: A critical review[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2018, 120: 105-125.
[11] MAURYA S, ABRAHAM J S, SOMASUNDARAM S, et al. Indicators for assessment of soil quality: A mini-review[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2020, 192(9): 604. doi: 10.1007/s10661-020-08556-z
[12] LARSON W E, PIERCE F J. Conservation and enhancement of soil quality[C]//Proceedings of the international workshop on evaluation of sustainable land management in the developing world. Bangkok, Thailand, 1991.
[13] 吴玉红, 田霄鸿, 同延安, 等. 基于主成分分析的土壤肥力综合指数评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(1): 173-180. [14] CHEN S, LIN B, LI Y, et al. Spatial and temporal changes of soil properties and soil fertility evaluation in a large grain-production area of subtropical plain, China[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 357: 113937. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113937
[15] 李鑫, 张文菊, 邬磊, 等. 土壤质量评价指标体系的构建及评价方法[J]. 中国农业科学, 2021, 54(14): 3043-3056. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.14.010 [16] 李鹏飞, 张兴昌, 郝明德, 等. 基于最小数据集的黄土高原矿区复垦土壤质量评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(16): 265-273. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.16.030 [17] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 湖南省土壤肥料工作站, 江西省土壤肥料技术推广站. 土壤检测: 第1部分: 土壤样品的采集、处理和贮存: NY/T 1121.1—2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [18] 中国林业科学研究院林业研究所森林土壤研究室. 森林土壤颗粒组成(机械组成)的测定: LY/T 1225—1999[S]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 1999. [19] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 中国农业科学院农业资源与农业区划研究所, 上海市农业技术推广服务中心. 土壤检测: 第2部分: 土壤pH的测定: NY/T 1121.2—2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [20] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 中国农业科学院农业资源与农业区划研究所, 华中农业大学. 土壤检测: 第6部分: 土壤有机质的测定: NY/T 1121.6—2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [21] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 农业部肥料质量监督检验测试中心(济南), 农业部肥料质量监督检验测试中心(杭州), 等. 土壤检测: 第24部分: 土壤全氮的测定: 自动定氮仪法: NY/T 1121.24—2012[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2012. [22] 中国林业科学研究院林业研究所. 森林土壤氮的测定: LY/T 1228—2015[S]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2015. [23] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 湖南省土壤肥料工作站, 江苏省土壤肥料技术指导站. 土壤检测: 第7部分: 酸性土壤有效磷的测定: NY/T 1121.7—2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [24] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 中国农业大学, 杭州土壤肥料测试中心. 土壤速效钾和缓效钾含量的测定: NY/T 889—2004[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2004. [25] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 湖南省土壤肥料工作站, 湖北省土壤肥料工作站. 土壤检测: 第5部分: 石灰性土壤阳离子交换量的测定: NY/T 1121.5—2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [26] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 湖南省土壤肥料工作站, 江西省土壤肥料技术推广站. 土壤检测: 第13部分: 土壤交换性钙和镁的测定: NY/T 1121.13—2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [27] 中国农业科学院土壤肥料研究所, 农业部肥料质量监督检验测试中心(长沙), 农业部肥料质量监督检验测试中心(成都). 土壤有效态锌、锰、铁、铜含量的测定 二乙三胺五乙酸(DTPA)浸提法: NY/T 890—2004[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2004. [28] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 安徽省土壤肥料总站, 广东省土壤肥料总站. 土壤检测: 第8部分: 土壤有效硼的测定: NY/T 1121.8—2006[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2006. [29] 全国农业技术推广服务中心, 农业部肥料质量监督检验测试中心(济南), 农业部肥料质量监督就由测试中心(成都), 等. 土壤检测: 第9部分: 土壤有效钼的测定: NY/T 1121.9—2012[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2012. [30] 全国土壤普查办公室. 中国土壤[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998. [31] 贡璐, 张雪妮, 冉启洋. 基于最小数据集的塔里木河上游绿洲土壤质量评价[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(3): 682-689. [32] 王英哲, 国坤, 孙云龙, 等. 基于最小数据集的东北地区朝鲜淫羊藿土壤肥力评价[J]. 特产研究, 2021, 43(5): 6-12. [33] 王玲玲, 徐福利, 王渭玲, 等. 不同林龄华北落叶松人工林地土壤肥力评价[J]. 西南林业大学学报, 2016, 36(2): 17-24. [34] 梅楠, 谷岩, 李德忠, 等. 基于最小数据集的吉林省黑土耕层土壤质量评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(12): 91-98. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.12.011 [35] 刘利昆, 赵广举, 穆兴民, 等. 基于最小数据集的青藏公路沿线土壤质量评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2022, 29(2): 125-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2022.2.stbcyj202202020 [36] 张宇恒, 王忠诚, 王亚楠, 等. 基于最小数据集沂蒙山区不同治理模式下的土壤质量评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 2023, 30(1): 241-247. [37] 赵瑾, 鲁瑞洁, 马罗. 青藏高原不同土地利用方式下的土壤质量评价[J]. 地球环境学报, 2023, 14(3): 339-351. doi: 10.7515/JEE222059 [38] 吴克宁, 赵瑞. 土壤质地分类及其在我国应用探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(1): 227-241. doi: 10.11766/trxb201803120129 [39] 黄凯峰. 启东香芋的特征特性及高产栽培技术[J]. 上海蔬菜, 2020(2): 36-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1469.2020.02.017 [40] 田雪, 孙奥博, 陈春羽, 等. 秸秆还田深度对土壤性状及玉米生长的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(11): 2571-2578. [41] YANG S, ZHANG Y, FENG B, et al. Coupling of Hofmeister effect, electrolyte concentration, and mechanical composition in soil loss: Runoff simulation study[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2021, 212: 105073. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2021.105073
[42] WERNEREHL R W, GIVNISH T J. Relative roles of soil moisture, nutrient supply, depth, and mechanical impedance in determining composition and structure of Wisconsin Prairies[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(9): e137963.
[43] 高巨鹏, 何小兰, 廖首发, 等. 荔浦芋生产肥力主因子分析[J]. 土壤通报, 2012, 43(1): 98-101. [44] 黄尚书, 叶川, 钟义军, 等. 不同土地利用方式对红壤坡地土壤阳离子交换量及交换性盐基离子的影响[J]. 土壤与作物, 2016, 5(2): 72-77. [45] 杨树俊, 韩张雄, 王思远, 等. 土壤阳离子交换量与有机质、机械组成的关系[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(7): 2799-2805. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.07.02799 [46] 蒋廷惠, 占新华, 徐阳春, 等. 钙对植物抗逆能力的影响及其生态学意义[J]. 应用生态学报, 2005(5): 971-976. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.05.039 [47] 张亚晨. 简述镁元素对植物的作用[J]. 农业开发与装备, 2018(11): 166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9205.2018.11.112 [48] 胡丽娜. 微量元素对植物的作用[J]. 现代农业, 2014(7): 25. [49] 李桂林, 陈杰, 檀满枝, 等. 基于土地利用变化建立土壤质量评价最小数据集[J]. 土壤学报, 2008(1): 16-25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.01.003



 下载:
下载: