Development and application of KASP marker for rice blast resistance gene Pi2
-
摘要:目的
水稻稻瘟病抗性基因Pi2对稻瘟病生理小种具有广谱抗性,开发Pi2的KASP分子标记并对其评价,为抗稻瘟病水稻品种分子育种提供简便、可靠的基因分型检测方法。
方法利用593份自然群体中筛选出的不同抗性和亲缘关系的2份材料H-74和H-78,针对Pi2基因核心区域的SNP位点开发成KASP标记Pi2-C3。
结果利用标记Pi2-C3对自然群体中的84份材料进行KASP基因分型,结果表明,该标记可以准确地将不同水稻材料的Pi2位点分为抗病基因型、杂合基因型和感病基因型,是一种高效鉴定抗稻瘟病基因Pi2的方法。利用标记Pi2-C3对阳江市病圃材料进行检测,结合表型调查结果发现,检测到含有Pi2基因的46份材料均表现出不同程度的稻瘟病抗性,表明该标记可以用于检测材料在病圃的发病情况。
结论本研究采用KASP技术,开发了能准确检测Pi2基因的特异性分子标记Pi2-C3,并建立一套水稻Pi2基因的KASP基因分型体系,对提高抗性育种效率,改良抗稻瘟病水稻品种具有重要应用价值。
Abstract:ObjectiveThe rice blast resistance gene Pi2 has broad spectrum resistance to physiological race of rice blast. Developing and evaluating KASP molecular markers for Pi2 will provide a convenient and reliable gene typing method for molecular breeding of rice varieties with blast resistance.
MethodTwo materials H-74 and H-78 with different resistance and genetic relationships selected from 593 natural populations were used to develop KASP marker for the SNP sites in the core region of the Pi2 gene, named Pi2-C3.
ResultUsing the marker Pi2-C3, 84 materials from the natural population were genotyped, and the results showed that the Pi2-C3 marker accurately distinguished the Pi2 loci of different rice materials into resistant, heterozygous, and susceptible genotypes, which was an efficient method for identifying the blast-resistant gene Pi2. The marker Pi2-C3 was used to detect the materials in Yangjiang disease nursery. Combined with the phenotypic investigation, it was found that 46 materials containing Pi2 gene showed different degrees of rice blast resistance, which indicated that the marker could be used to detect the incidence of materials in disease nursery.
ConclusionThis study develops a specific molecular marker Pi2-C3 for accurately detecting the Pi2 gene using the KASP technology, and establishes a KASP genotyping system for rice Pi2 gene. It has important application value for improving the efficiency of resistance breeding and improving blast-resistant rice varieties.
-
Keywords:
- Rice /
- Rice blast /
- Pi2 gene /
- KASP marker /
- Molecular marker /
- Resistance gene /
- Genotyping
-
-
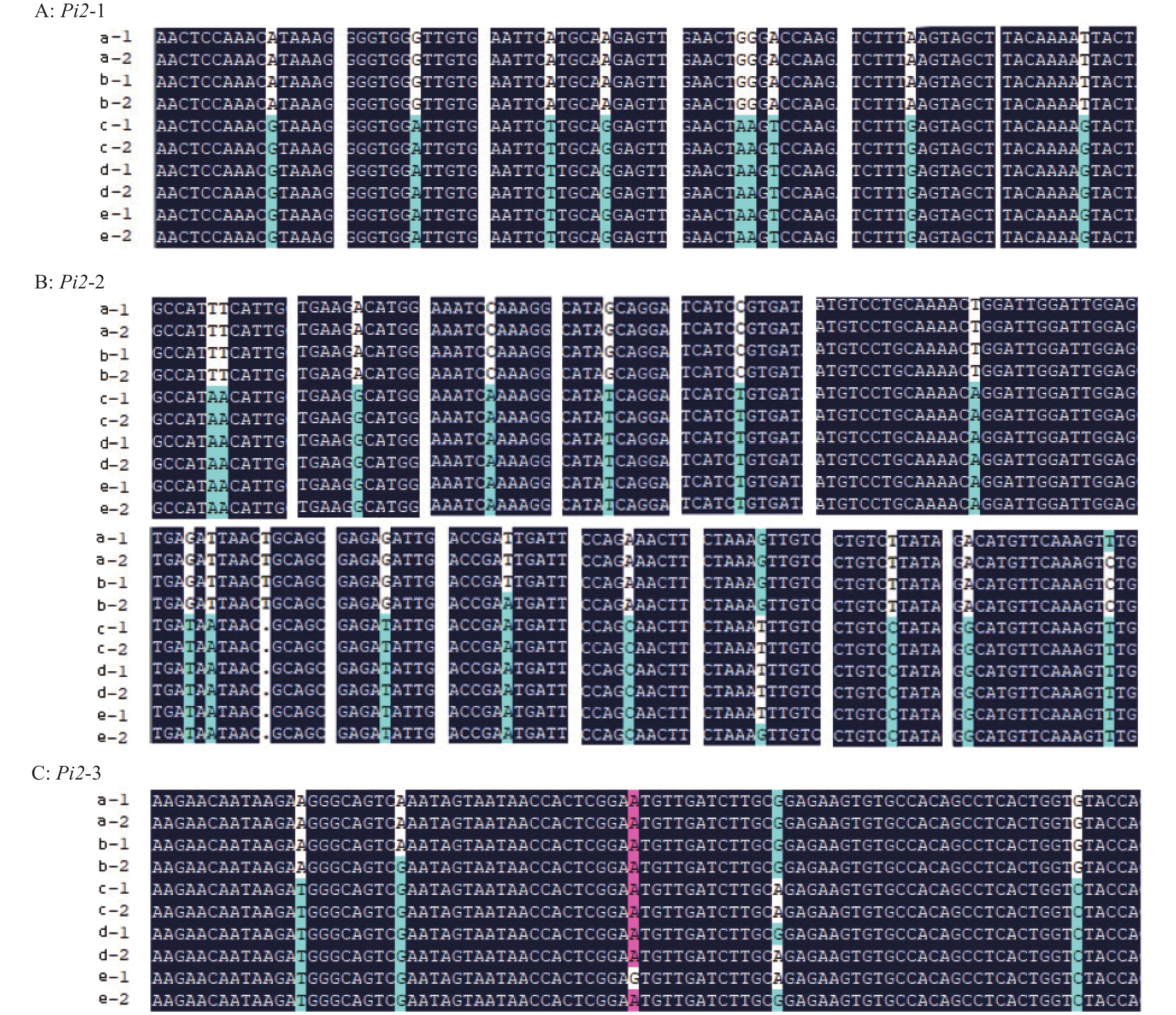
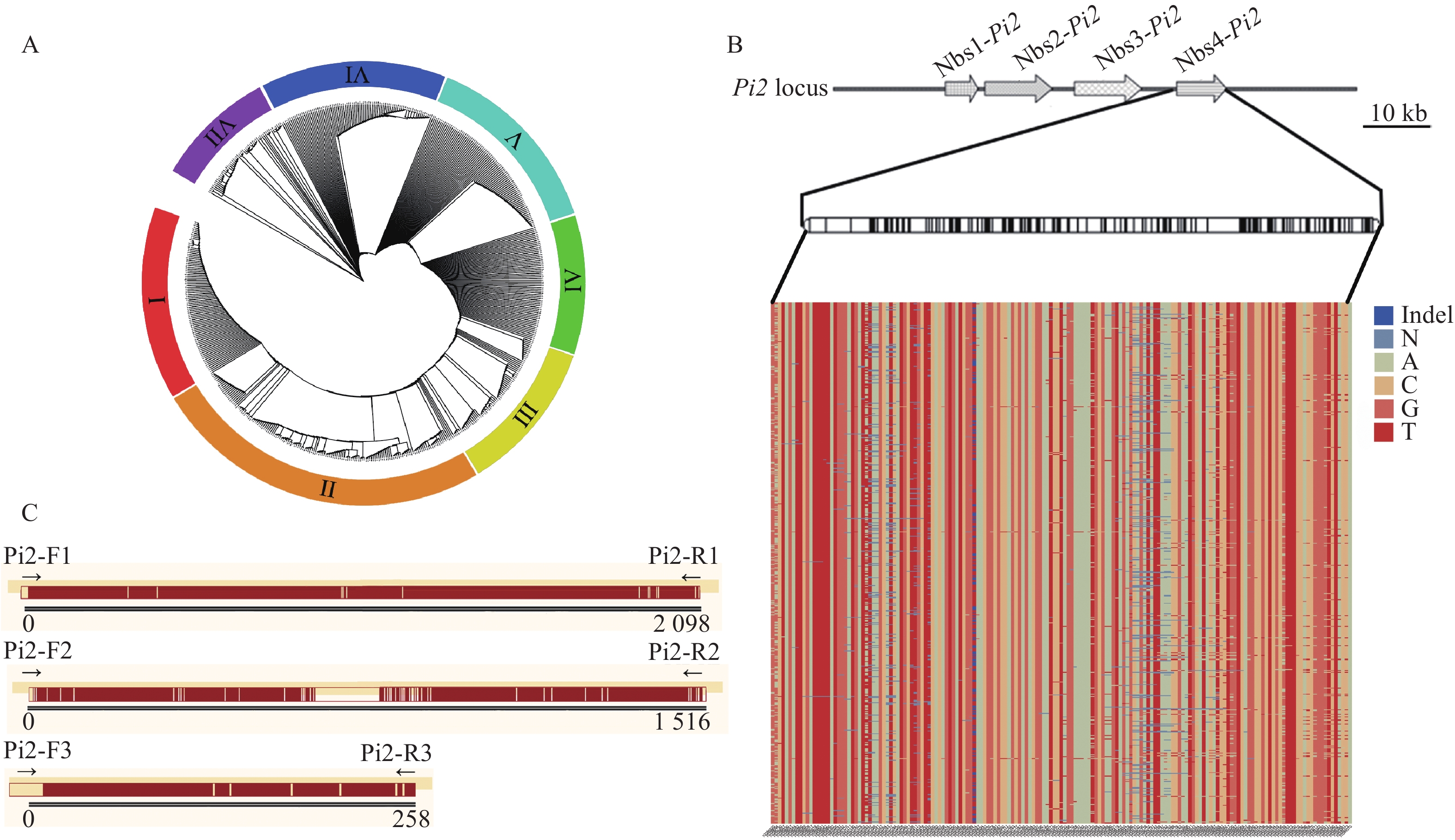
图 1 系统进化树及差异SNP位点分析
A:593份材料系统进化树(Ⅰ~Ⅶ:分布密度不同的7个部分);B:593份材料在Pi2抗性位点核心区域的差异SNP及其碱基分布情况;C:H-74和H-78材料在Pi2抗性位点核心区域差异SNP位点分布(黄色竖线区域表示两者差异SNP位点分布情况)
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree and analysis of different SNP sites
A: Phylogenetic tree of 593 materials (Ⅰ−Ⅶ: Seven parts with different distribution density); B: Distributions of different SNPs and their bases in the core region of the Pi2 resistance locus for the 593 materials; C: Distribution of different SNP sites in the core region of the Pi2 resistance locus for H-74 and H-78 materials (The yellow vertical line area indicates the distribution of SNP sites that are different between them)
图 2 Pi2基因差异位点序列比对
a:H-74材料,b:包含Pi2基因的材料,c:H-78材料,d、e:确定没有Pi2基因的材料;1和2表示材料的2个重复
Figure 2. Sequence alignment analysis of the different sites of Pi2 gene
a: Material H-74, b: Material containing Pi2 gene, c: Material H-78, d and e: Material without Pi2 gene; 1 and 2 represent two repetitions of the material
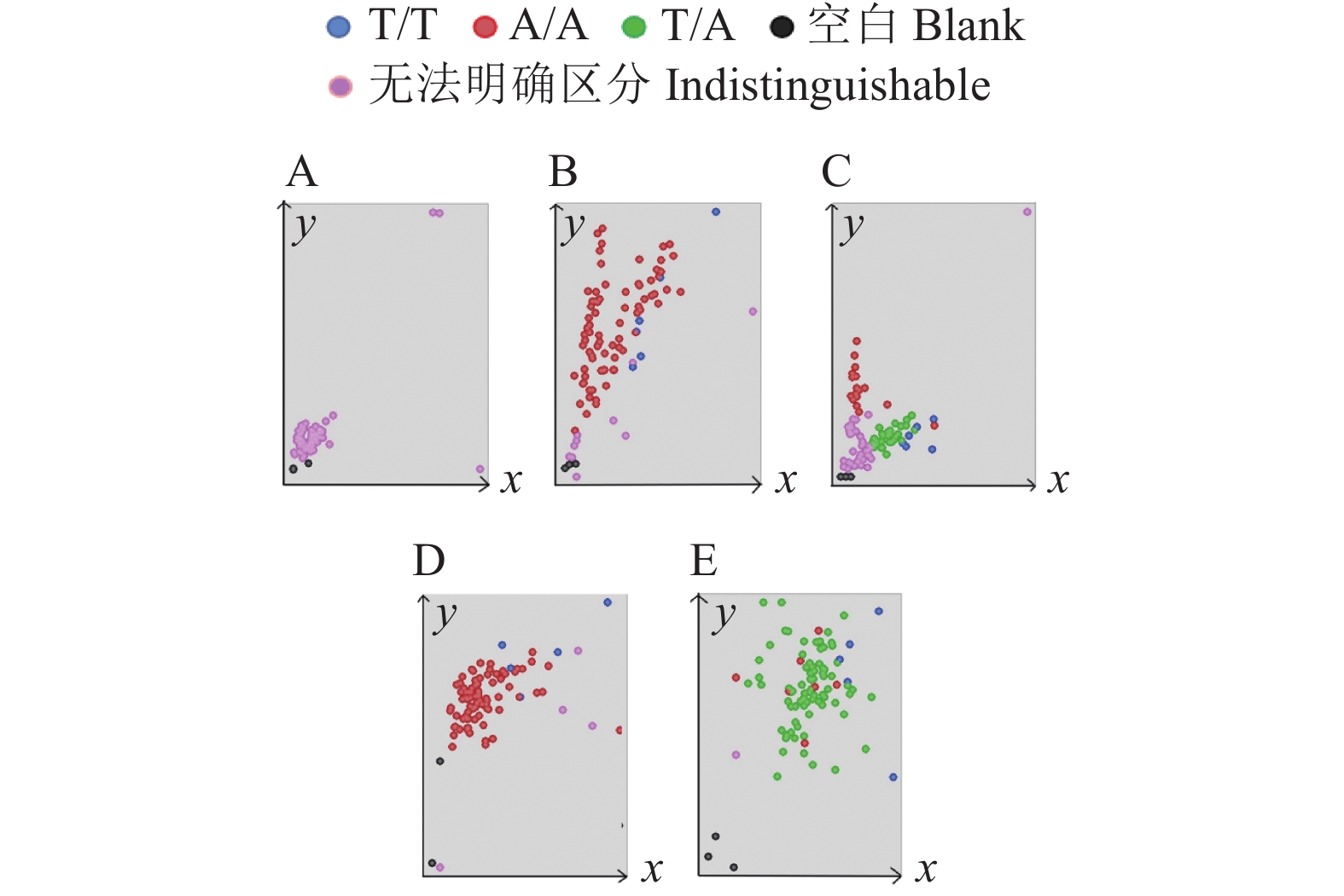
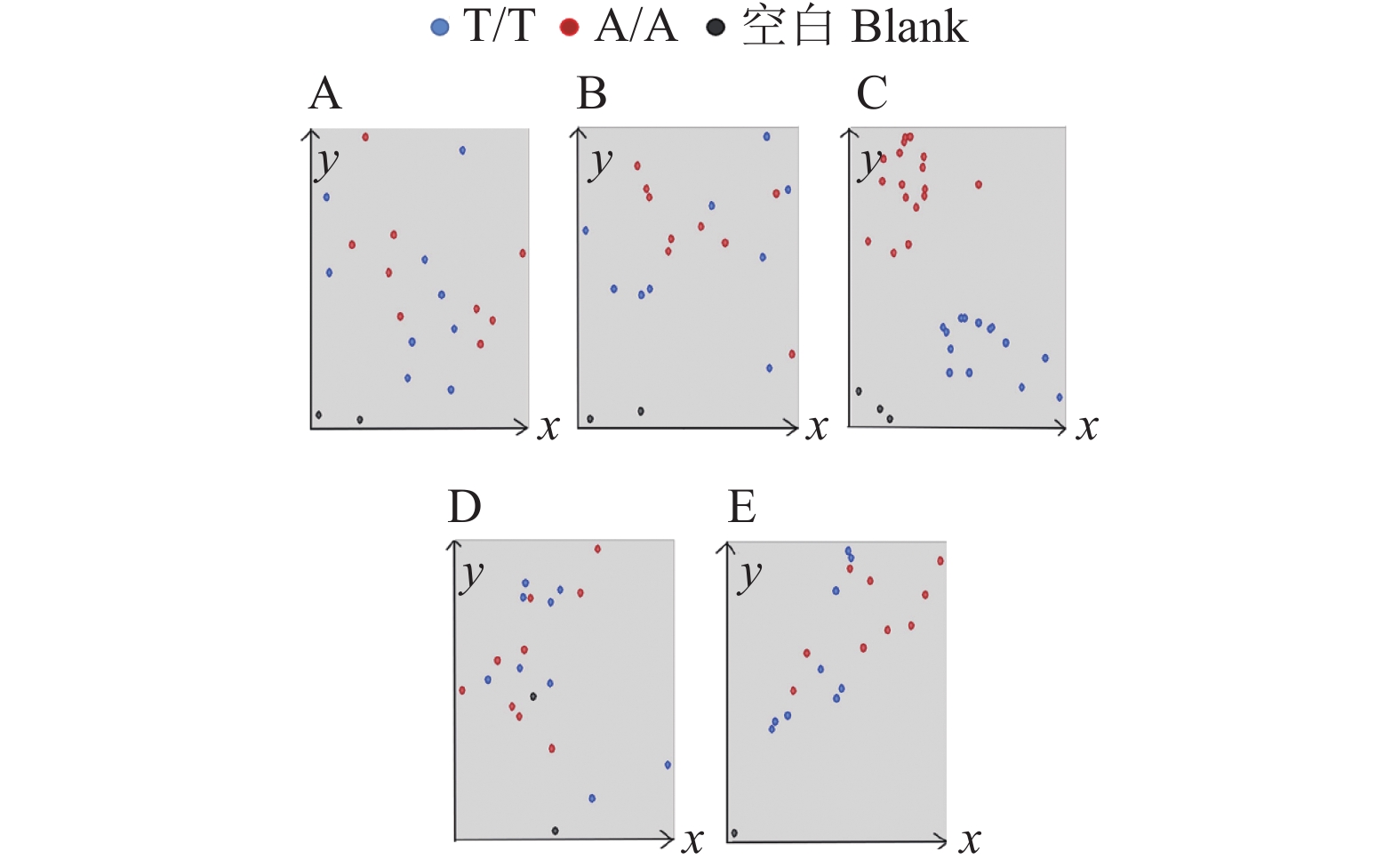
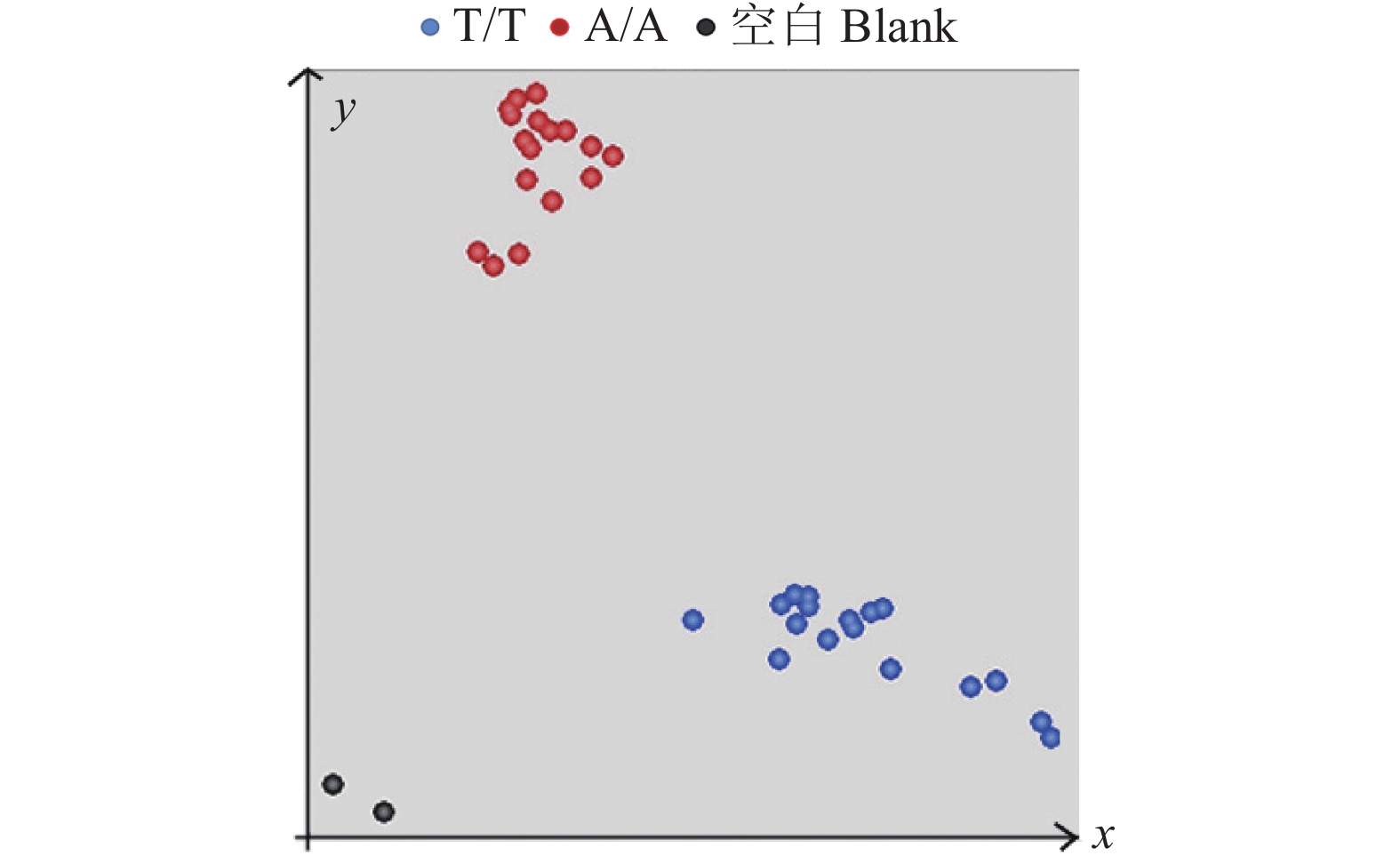
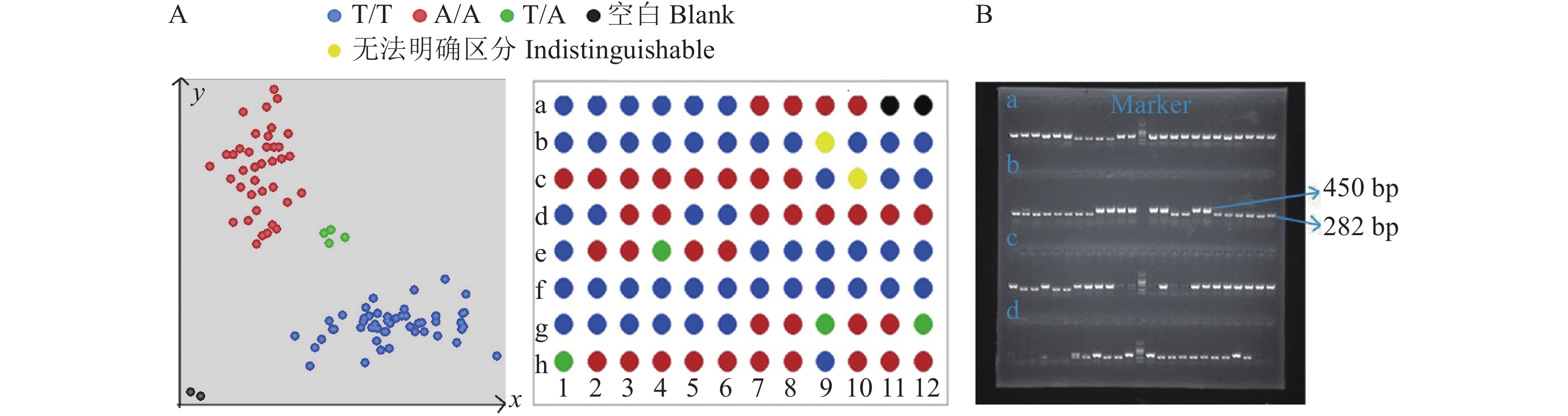
图 6 84个田间材料Pi2-C3 KASP分子标记的验证
A:Pi2 KASP基因分型检测结果;B:SSR标记检测结果(Marker位于胶图中央,大小为2 000 bp,a、 c、 d区域中相应位置片段大小与b区域标示相同)
Figure 6. Verification of Pi2-C3 KASP molecular marker for 84 field samples
A: KASP genotype detection results for Pi2; B: SSR marker detection results (marker is located in the center of the rubber map, with the size of 2 000 bp, and the corresponding fragment sizes in areas a, c and d are the same as that in area b)
表 1 测序引物
Table 1 Sequencing primers
引物
名称
Primer
name序列(5′→3′)
Sequence预期片段
大小/bp
Expected
fragment sizePi2-F1 AAGCCTATGATTGGTTTCT 2 098 Pi2-R1 ACTGCCCTTCTTATTGTTC Pi2-F2 AACAATAAGAAGGGCAGTC 1 516 Pi2-R2 GAGGAGGAGATGAAATAGAAT Pi2-F3 AAGGTGGTGGTGCAAGTAC 258 Pi2-R3 CAATGTTATGGCATCGTTC 表 2 KASP引物
Table 2 KASP primers
引物名称
Primer name检测位点
Detection site序列(5′→3′)
SequencePi2-C1-F1 A GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCAGGTGTCAGAATGGGAGAAATTCTATGAACAA Pi2-C1-F2 C GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTCAGGTGTCAGAATGGGAGAAATTCTATGAACAC Pi2-C1-R A/C TGTCCTTAGTAGGGGAGGAGG Pi2-C2-F1 C GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGTATGATTCAACGATCAAGAGTGGGCAC Pi2-C2-F2 T GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTAGTTATGTATTTAAAACACAGCATGGT Pi2-C2-R C/T CCTGTCTCGAGATTGAAACTGTG Pi2-C3-F1 T GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCATGGGAGTATGTCCTGCAAAACT Pi2-C3-F2 A GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTCATGGGAGTATGTCCTGCAAAACA Pi2-C3-R T/A CAAACTGCATGTGCTAGACTCTTGGGTC Pi2-C4-F1 G GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCATTGGTAAACTACAGGGCCTACAG Pi2-C4-F2 A GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTCATTGGTAAACTACAGGGCCTACAA Pi2-C4-R G/A CACTTGGTAGTGCTGCAATGTATGTGCTC Pi2-C5-F1 A GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCAATGTCTGCATACTCTTCGTTGTATAA Pi2-C5-F2 G GAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTCAATGTCTGCATACTCTTCGTTGTATAG Pi2-C5-R A/G AGGCATATTGTGTTAGTTATGCACTTCATTGGGTG 表 3 广东阳江病圃材料Pi2基因检测结果及抗性评价
Table 3 Pi2 gene detection results and resistance evaluation of materials from the Yangjiang disease nursery in Guangdong
编号
NumberPi2基因检测
Pi2 gene detection抗性评价
Resistance evaluation编号
NumberPi2基因检测
Pi2 gene detection抗性评价
Resistance evaluationJ-201 − 中感 J-217 + 抗 J-202 + 抗 J-218 + 抗 J-203 + 抗 J-219 − 抗 J-204 + 抗 J-220 + 中抗 J-205 + 抗 J-221 − 中抗 J-206 − 抗 J-222 − 中抗 J-207 + 抗 J-223 − 中抗 J-208 + 抗 J-224 + 抗 J-209 + 高抗 J-225 + 抗 J-210 + 高抗 J-226 − 中抗 J-211 + 抗 J-227 − 中抗 J-212 − 中感 J-228 − 中感 J-213 + 抗 J-229 − 中抗 J-214 − 抗 J-230 − 中抗 J-215 + 抗 J-231 − 中抗 J-216 + 高抗 J-232 − 中感 J-233 + 抗 J-259 + 高抗 J-234 + 抗 J-260 + 高抗 J-235 − 抗 J-261 + 抗 J-236 + 高抗 J-262 + 高抗 J-237 + 高抗 J-263 − 中感 J-238 + 中抗 J-264 − 高感 J-239 − 中抗 J-265 + 高抗 J-240 + 抗 J-266 − 高感 J-241 + 高抗 J-267 − 高感 J-242 − 高感 J-268 + 抗 J-243 + 抗 J-269 + 抗 J-244 − 感病 J-270 + 抗 J-245 + 中抗 J-271 − 抗 J-246 + 抗 J-272 + 抗 J-247 − 高感 J-273 + 抗 J-248 − 中抗 J-274 + 高抗 J-249 + 抗 J-275 − 抗 J-250 + 中抗 J-276 − 中抗 J-251 − 抗 J-277 − 中抗 J-252 + 高抗 J-278 − 感病 J-253 + 高抗 J-279 − 感病 J-254 − 中抗 J-280 − 感病 J-255 + 高抗 J-281 − 中抗 J-256 + 高抗 J-282 − 感病 J-257 + 高抗 J-283 + 抗 J-258 − 抗 J-284 − 感病 -
[1] 向聪, 雷东阳, 任西明, 等. 水稻抗稻瘟病遗传育种研究进展[J]. 作物研究, 2017, 31(5): 547-552. [2] 权水清. 水稻稻瘟病菌无毒基因AVR-Pik的共显性标记开发与应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017. [3] 温小红, 谢明杰, 姜健, 等. 水稻稻瘟病防治方法研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(3): 190-195. [4] MENG X L, XIAO G, TELEBANCO-YANORIA M J, et al. The broad-spectrum rice blast resistance (R) gene Pita2 encodes a novel R protein unique from Pita[J]. Rice, 2020, 13(1): 1-15. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0361-3
[5] ZHOU B, QU S H, LIU G F, et al. The eight amino-acid differences within three leucine-rich repeats between Pi2 and Piz-t resistance proteins determine the resistance specificity to Magnaporthe grisea[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2006, 19(11): 1216-1228. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-1216
[6] LIU G, LU G, ZENG L, et al. Two broad-spectrum blast resistance genes, Pi9(t) and Pi2(t), are physically linked on rice chromosome 6[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2002, 267(4): 472-480. doi: 10.1007/s00438-002-0677-2
[7] 朱业宝, 方珊茹, 沈伟峰, 等. 国外引进水稻种质资源的稻瘟病抗性基因检测与评价[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2020, 21(2): 418-430. [8] 陆展华, 付魏魏, 刘维, 等. 广东省主栽水稻品种稻瘟病主效抗性基因的鉴定及分析[J]. 植物病理学报, 2020, 50(6): 711-722. [9] 沈新莲, 张天真. 作物分子标记辅助选择育种研究的进展与展望[J]. 高技术通讯, 2003, 13(2): 105-110. [10] SHABIR G, ASLAM K, KHAN A R, et al. Rice molecular markers and genetic mapping: Current status and prospects[J]. 农业科学学报: 英文, 2017, 16(9): 1879-1891. SHABIR G, ASLAM K, KHAN A R, et al. Rice molecular markers and genetic mapping: Current status and prospects[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(9): 1879-1891.
[11] 何元浩, 胡凤荣. 基于AFLP分子标记的30个风信子品种遗传多样性分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(9): 2955-2963. [12] 李建武. 马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum L. )块茎淀粉含量及植株熟性性状的QTL定位与遗传分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2019. [13] 刘传光, 张桂权. 水稻单核苷酸多态性及其应用[J]. 遗传, 2006, 28(6): 737-744. [14] BEGUM H, SPINDEL J E, LALUSIN A, et al. Genome-wide association mapping for yield and other agronomic traits in an elite breeding population of tropical rice (Oryza sativa)[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0119873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119873.
[15] 王彦云. 基于SNP标记的黄河鲤鱼溯源研究与应用[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. [16] SEMAGN K, BABU R, HEARNE S, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): Overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2014, 33(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s11032-013-9917-x
[17] 练云, 李海朝, 李金英, 等. 利用KASP标记筛选含rhg1和Rhg4位点的大豆抗病资源[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2021, 22(2): 399-406. [18] 王蕊, 施龙建, 田红丽, 等. 玉米杂交种纯度鉴定SNP核心引物的确定及高通量检测方案的建立[J]. 作物学报, 2021, 47(4): 770-779. [19] 张瑞, 王洋, HUSSAIN S, 等. 水培条件下水稻全生育期耐盐筛选鉴定[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2021, 22(6): 1567-1581. [20] 韩美丽, 陆荣生, 霍秀娟, 等. 水稻离体叶抗稻瘟病鉴定方法研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(13): 6037-6039. [21] SU J, WANG W, HAN J, et al. Functional divergence of duplicated genes results in a novel blast resistance gene Pi50 at the Pi2/9 locus[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2015, 128: 2213-2225.
[22] 汪文娟, 周继勇, 汪聪颖, 等. 八个抗稻瘟病基因在华南籼型杂交水稻中的分布[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(3): 299-306. [23] 华丽霞, 汪文娟, 陈深, 等. 抗稻瘟病Pi2/9/z-t基因特异性分子标记的开发[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2015, 29(3): 305-310. [24] 金名捺, 陈竹锋, 丘式浚, 等. 基于HRM体系的稻瘟病抗性基因Pi2特异性分子标记的开发及应用[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2018, 26(3): 365-373. [25] 高利军, 高汉亮, 颜群, 等. 4个抗稻瘟病基因分子标记的建立及在水稻亲本中的分布[J]. 杂交水稻, 2010, 25(S1): 294-298. [26] WU Y, XIAO N, YU L, et al. Combination patterns of major R genes determine the level of resistance to the M. oryzae in Rice (Oryza sativa L. )[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0126130. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126130.
[27] 李潜龙. 水稻抗稻瘟病基因Pi2功能标记的开发及育种应用[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2018. [28] 李冰, 李永聪, 刘芝妤, 等. 水稻抗稻瘟病基因Pi2特异分子标记的开发与应用[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(8): 2638-2643. [29] 杨义强, 朱林峰, 李晓芳, 等. 抗稻瘟病基因Pi2的基因特异性KASP标记开发与应用[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2021, 22(5): 1314-1321. [30] 邓钊, 江南, 符辰建, 等. 隆两优与晶两优系列杂交稻的稻瘟病抗性基因分析[J]. 作物学报, 2022, 48(5): 1071-1080.



 下载:
下载: