Research advances in novel DNA base editors
-
摘要:
DNA碱基编辑技术是由CRISPR/Cas系统发展而来,能对基因组碱基进行精准编辑。目前已开发的DNA碱基编辑器包括介导C•G至T•A转换的胞嘧啶单碱基编辑器、介导A•T至G•C转换的腺嘌呤单碱基编辑器、介导C•G至G•C颠换的糖基化酶单碱基编辑器、介导C•G至T•A和A•T至G•C同时转换的双碱基编辑器、介导任意碱基之间转换的引导编辑器以及线粒体DNA编辑器。本文系统总结了上述6种DNA编辑器的原理、优化历程及最新研究进展,着重介绍了应用到植物研究中的碱基编辑器工具及其在作物遗传改良中的应用,并对碱基编辑技术今后的发展进行了展望。
-
关键词:
- CRISPR/Cas9 /
- 碱基编辑技术 /
- DNA碱基编辑器 /
- 线粒体DNA /
- 作物改良
Abstract:The base editing technology is developed from the CRISPR/Cas gene editing systems, which can perform accurate base or gene editing at the DNA level. Recent years, six types of novel DNA base editors have been developed for the editing of nuclear and organellar genomes, including the cytosine base editor (CBE), the adenine base editor (ABE), the glycosylase base editor (GBE), the adenine and cytosine dual base editor (DBE), the prime editor (PE) and the mitochondrial genome editor. In this review, we summarize the principles, optimization processes and current advances of the above six DNA editors and focus on their application in crop genetic improvement. Finally, the future development of base editing technology is prospected.
-
Keywords:
- CRISPR/Cas9 /
- Base editing technology /
- DNA base editor /
- Mitochondrial DNA /
- Crop improvement
-
精准农业是推动农业现代化与信息化发展的关键,其重要的农情数据采集阶段离不开农业物联网(Internet of things in agriculture)的支持[1]。现阶段,农业物联网已在农业生产中得到广泛应用,复杂的传感器网络按时间序列连续地采集温度、湿度、CO2和NH3浓度等大量的环境及作物生长信息。分析和评估采集的信息可为农业精准决策提供保障。因此,农业物联网数据的有效挖掘和利用已成为农业信息化领域的研究热点[2-3]。然而,由于农业作业环境往往较为恶劣,且受制造工艺和网络传输的限制,导致采集到的数据中不可避免地存在异常[4],这些异常可能干扰数据分析并影响农业精准决策。
费欢等[5]以传感器网络多模态数据流之间的相干性为理论基础,利用多维数据和滑动窗口模型对异常数据及其来源进行检测和评估。Zhao等[6]提出一种基于多分类器集成的漂移补偿监督学习算法,利用支持向量机(Support vector machine, SVM)和改进的长短期记忆(Long short term memory, LSTM)构建多分类器模型,通过归一化和加权策略,在每次分类过程中去除精确度最低的基分类器,使模型适应传感器漂移,有效地提高了传感器漂移分类性能。Wang等[7]利用传感器之间的数据相关性,使用信号空间投影和卡尔曼滤波器实现传感器漂移的盲校准。高鹏等[8]利用LSTM和广义回归神经网络(Generalized regression neural network, GRNN)模型对土壤墒情进行建模,实现对柑橘土壤含水量和土壤电导率的预测。
在传统的机器学习任务中,需要用多种信号处理算法检测数据流中的异常,导致效率较低,在数据分析过程中易出现过拟合或欠拟合现象。此外,大多数据异常检测算法泛化能力较弱,不适用于其他类型的异常检测。文献[6]中采用SVM和LSTM的结合模型,获得了理想精确度,但增加了时间复杂度。文献[7]所提信号空间投影和卡尔曼滤波器方法,利用传感器之间的相关性解决传感器漂移问题,但传感器难以密集部署,模型应用场景狭小、泛化能力较弱。
近年来,随着硬件计算能力的显著提升,人工智能(Artificial intelligence)和深度学习(Deep learning)技术已广泛应用于图像识别[9]、自然语言处理[10]、推荐系统[11]和音频识别[12]领域。深度结构的神经网络在传感器数据异常检测领域也得到广泛应用,Bao等[13]提出了一种基于计算机视觉和深度学习的传感器数据异常检测方法,该方法将时间序列信号转换为图像并保存在灰度图像中,通过训练两隐藏层堆叠的自动编码深度神经网络来自动检测未标签的数据。Tang等[14]提出了一种基于卷积神经网络的传感器数据异常检测方法,在图片中融合数据的时域和频域特征,并采用卷积神经网络对图片进行分类,但时域和频域可视化方法无法保存数据的时间数值依赖性。Liu等[15]提出一种动态宽度增量学习算法,通过深度叠加宽度学习系统,解决数据回归和图像分类问题,但在数据预处理中,未采用有效方法增强数据时间依赖性。Wang等[16]提出一种格拉姆角求和域/差分域和马尔科夫过渡域的时间序列数据可视化方法,并采用平铺卷积神经网络学习图像特征,实现时间序列数据分类,但当原始时间序列过长时,重构后的矩阵规模大,增加了运算时间消耗。
针对以上研究现状,本文设计了一种宽度卷积神经网络(Broad convolution neural network, BCNN)的农情数据异常检测方法,并通过滑动窗口机制解决单次输入模型数据量大引起的模型检测耗时长和准确率不足等问题。研究数据预处理与重构方法、滑动窗口尺寸对异常检测性能的影响,对比分析不同异常检测模型的性能差异,以期为精准农业的数据高质量采集提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验数据采用位于安徽省长丰县双墩镇的合肥安谷农业有限公司羊圈监测点传感器的空气湿度、空气温度、土壤湿度和土壤温度数据,时间覆盖范围从2019年12月1日至2019年12月31日,采样间隔3 min,共11355条观测数据。为便于开展检测性能对比分析,在数据中引入一组随机故障率(10%~40%)的异常点[17]。为系统评估所提方法的性能,采用80%的数据集作为训练集、20%的数据集作为测试集。数据集如图1所示,4种数据的周期性和趋势特征存在差异。空气湿度数据值域波动较大,周期性特征不明显。空气温度数据呈周期性变化,波动较小。土壤湿度数据具有明显的周期性特征,值域范围较小。土壤温度数据周期性特征与空气温度数据相似,且值域波动更小。
1.2 异常检测框架
基于宽度学习的农情数据异常检测框架图如图2所示。传感器端负责采集数据并发送至数据中心,数据中心负责存储数据、训练模型和异常检测。模型训练过程如下:部署传感器并采集数据,将数据归一化,基于数据周期和采样间隔等参数确定滑动窗口尺寸l,编码为极坐标表示,并基于滑动窗口尺寸l划分子集,采用格拉姆角求和域(Gramian summation angular field, GASF)方法重构为矩阵,最后训练得到BCNN数据异常检测模型。
在异常数据实时检测过程中,数据中心对采集的最新数据进行归一化处理,编码为极坐标并重构矩阵,最后输入模型检测异常。若模型判断为正常,则将其保存为历史数据,否则,校准异常并保存。校准异常可采用回归模型预测、均值替换等方法[18]。
1.3 数据预处理
设传感器节点在某时刻共采集到n个时间序列数据
$ X = \{ {x_1},{x_2}, \cdots ,{x_n}\} $ ,为降低采样数据取值范围对模型训练效果的影响,将数据归一化至[−1,1]区间内,表示为:$$ x'_i = \frac{{({x_i} - {X_{\max }}) + ({x_i} - {X_{\min }})}}{{{X_{\max }} - {X_{\min }}}},i \in [1,n],x'_i \in {X'}, $$ (1) 式中,xi表示原始时间序列数据,X'
表示归一化后的时间序列数据,Xmax和Xmin分别表示原始时间序列中的最大值和最小值, $ x'_i $ 表示归一化后的数据。归一化将原始数据映射至[−1,1]区间内,将有量纲数据转化为无量纲形式,降低不同量纲对模型的影响,并保留原始数据特征,使不同的数据集处于相同数量级,便于对比分析。模型处理一维时间序列时,无法有效保持数据周期性时间依赖,无法有效提取部分数据之间的相关性,且对于具有不同周期的时间序列数据,模型泛化能力较差。为此,本文通过将时间序列数据编码为极坐标并重构为矩阵,实现模型对时间序列数据时间依赖性的保持和泛化性的增强。
具体的,将归一化后的数据编码为极坐标[16],时间序列数据的数值和时间戳分别编码为极角和极径,表示为:
$$ \begin{array}{l} \theta = \arccos x'_i,x'_i \in {X'} ,\\ r = \dfrac{{{t_i}}}{n},{t_i} \in [1,2,3, \cdots ,n] ,\end{array} $$ (2) 式中,ti表示时间序列数据的时间戳,n表示时间序列数据数量,θ和r分别表示编码后数据的极径和极角。基于极坐标的编码方法是预处理和分析时间序列数据的一种新方法。反余弦函数在[−1,1]区间内是单调的,因此,式(2)在时间序列数据和极坐标之间构建了一个双射。给定一组时间序列数据,可产生唯一的映射关系,且相对笛卡尔坐标系,极坐标可保留绝对时间关系。
滑动窗口控制单次输入模型的数据量,是影响异常检测模型性能的重要参数,选取合适的滑动窗口尺寸可有效提高模型准确率和降低时间消耗。本文设计了基于数据特征的滑动窗口尺寸l的计算方法:
$$ l=\Bigg(\frac{\Delta t}{\beta }+\ln S\Bigg)T{{\text{e}}^{-\beta {{\log }_{2}}\sqrt{{}^{T} \diagup {}_{\Delta t}\;}}}, $$ (3) 式中,β为支持度衰减因子,Δt为农业物联网传感器数据采样间隔,T为农情数据特征周期,S为农情数据的标准差。滑动窗口尺寸对模型准确率和效率存在影响,窗口尺寸过大会增加模型检测耗时,过小则会导致模型无法有效提取数据特征,从而降低准确率。式中T/Δt控制滑动窗口选择函数上升幅度和衰减速度,Δt/β+ln S平衡采样间隔和数据特征的影响,可满足模型异常检测准确率和效率需求。
根据滑动窗口尺寸l,将编码后的数据分为若干个子集
$ \left\{ {\theta' _1, \cdots ,\theta' _l} \right\},\left\{ {\theta' _{l + 1}, \cdots ,\theta' _{2l}} \right\}, \cdots $ ,并将每个子集数据采用GASF方法重构为矩阵,采用类热力图形式可视化:$$ {\boldsymbol{G}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\cos (\theta' _1 + \theta' _1)}& \cdots &{\cos (\theta' _1 + \theta' _l)} \\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ {\cos (\theta' _l + \theta' _1)}& \cdots &{\cos (\theta' _l + \theta' _l)} \end{array}} \right) \text{,} $$ (4) 式中,G为重构后的矩阵,
$ \theta' _1 $ 和$ \theta' _l$ 为编码为极坐标并划分子集后的数据。通过式(2)将归一化后的数据编码为极坐标,采用式(3)重构为矩阵。时间序列数据编码为极坐标后仍保留数据连续性,重构后的矩阵随着位置的变化,时间会增加,可有效保存时间依赖性。此外,矩阵也包含了时间相关性,其中的Gi,j元素叠加了原始数据中第i和第j个数据相关性,主对角线包含了原始数据信息。因此,可采用神经网络提取高维数据特征。
为展示完整的数据预处理方法,以土壤湿度数据为例,完整流程如图3所示。首先,采用式(1)将原始土壤湿度数据归一化至[−1,1]区间内,并通过式(2)编码为极坐标表示(图3B),极坐标数据保留时间依赖性,原始异常数据在极坐标系中仍存在离群特征(即极坐标图中存在显著的异常点),接着,采用式(3)将极坐标数据划分子集,并通过式(4)重构矩阵。图3C展示了部分矩阵,异常数据可在GASF矩阵中显著表示,矩阵中出现颜色突变即表示该点数据存在异常,如矩阵1、2、5、6和7,矩阵中颜色连续变化即表示无异常,如矩阵3、4和8。预处理后的数据特征更为显著,可采用模型更有效地检测异常数据。
1.4 宽度卷积神经网络框架
设计的宽度卷积神经网络结构如图4所示。模型采用宽度学习系统强化传统CNN模型[19]。BCNN的第1层(Layer 1)是输入层,输入矩阵维度为k×k,其中k表示滑动窗口尺寸。第2层(Layer 2)是卷积层,其中卷积核(Filter)数量为20,每个卷积核尺寸为41×41,步长(Stride)为1,采用Relu激活函数。第3层(Layer 3)是Reduction层,其中包含1个池化模块和2个卷积模块,该层采用残差连接。池化模块中,池大小(Pool size)为3×3,步长为3,池化方式为最大池化(Maxpooling)。卷积模块中,第1层卷积采用1×1的卷积核,第2层卷积采用20个3×3大小的卷积核,步长为3。卷积模块和池化模块输出的特征图按其深度连接,并采用Relu函数激活,被平坦化为一维向量输入宽度学习系统。第4层(Layer 4)采用特征提取器代替传统CNN模型中的Softmax分类器,其中包含1000个特征节点。第5层(Layer 5)为特征增强器,其中包含1000个特征增强节点,第4层中特征提取器的输出被特征增强器随机映射输出。最后将特征提取器和特征强化器的输出连接,并加权重构,得到整个模型的输出。
卷积可通过连续地变换提取数据的复杂特征。在卷积层中,利用卷积核对输入数据进行卷积:
$$ x_i^l = {\rm{Relu}}\Bigg(\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {x_n^{l - 1}} f_{n,i}^l\Bigg) \text{,} $$ (5) 式中,
$ x_i^l $ 表示第l层中图片的$ i $ 通道,$ f_{n,i}^l $ 表示位于第l层中第n个卷积核的i通道,N表示l−1层中通道总数,Relu()表示激活函数。池化是一种降采样形式。它将图像划分为若干个区域,每个区域独立地按池化方式输出,减小了数据空间大小,参数数量和模型计算量也随之下降,在一定程度上防止过拟合的发生。本文采用最大池化方式,表示为:
$$ a_{i,n}^l = \max (a_{i,n}^{l - 1}, \cdots ,a_{i,m}^{l - 1}) \text{,} $$ (6) 式中,
$ a_{i,n}^l $ 表示网络l层中图片i通道的第n个位置,$a_{i,n}^{l - 1},\cdots ,a_{i,m}^{l - 1}$ 表示网络l−1层中图片i通道的池化区域对应的第n到m个位置。宽度学习系统[15]是一种通过随机方法将特征扩展到广阔空间的模型,其主要由特征节点和增强节点组成。特征节点将输入随机映射,映射特征由增强节点随机扩展,将最后所有特征加权连接输出。
残差层的输出被平坦化为一维向量X并输入至特征节点,其表示为:
$$ {{\boldsymbol{Z}}_i} = \phi ({\boldsymbol{X}}{{\boldsymbol{W}}_{{z_i}}} + {{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _{{z_i}}}),i = 1,2, \cdots ,n , $$ (7) 式中,权重矩阵
$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_{{z_i}}} $ 和偏置矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _{{z_i}}} $ 随机生成,$ \phi ( ) $ 表示激活函数,Zi表示第i个特征节点的输出,所有特征节点的集合记为$ {{\boldsymbol{Z}}^n} = [{{\boldsymbol{Z}}_1}, \cdots ,{{\boldsymbol{Z}}_n}] $ ,其中n为特征节点数量。类似的,特征增强节点可表示为:$$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}_j} = \xi ({{\boldsymbol{Z}}^n}{{\boldsymbol{W}}_{{h_j}}} + {{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _{{h_j}}}),j = 1,2, \cdots ,m , $$ (8) 式中,权重矩阵
$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_{{h_j}}} $ 和偏置矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _{{h_j}}} $ 随机生成,$ \xi () $ 表示激活函数,Hj表示第j个特征增强节点的输出,所有特征节点的集合记为$ {{\boldsymbol{H}}^m} = [{{\boldsymbol{H}}_1}, \cdots ,{{\boldsymbol{H}}_m}] $ ,其中m为特征增强节点数量。将特征节点和特征增强节点连接加权重构,输出可表示为:
$$ {\boldsymbol{Y}} = \left[ {{{\boldsymbol{Z}}_1}, \cdots ,{{\boldsymbol{Z}}_n}|{{\boldsymbol{H}}_1}, \cdots ,{{\boldsymbol{H}}_m}} \right]{\boldsymbol{W}} = \left[ {{{\boldsymbol{Z}}^n}|{{\boldsymbol{H}}^m}} \right]{\boldsymbol{W}} \text{,} $$ (9) 式中,权重矩阵W可通过伪逆法求解,可表示为:
$$ {\boldsymbol{W}} = {\left[ {{{\boldsymbol{Z}}^n}|{{\boldsymbol{H}}^m}} \right]^\dagger }{\boldsymbol{Y}} = {({{\boldsymbol{A}}^m})^\dagger }{\boldsymbol{Y}} \text{,} $$ (10) 式中,
${{\boldsymbol{A}}^m}$ =$\left[ {{{\boldsymbol{Z}}^n}|{{\boldsymbol{H}}^m}} \right]$ ,${({{\boldsymbol{A}}^m})^\dagger }$ 表示${{\boldsymbol{A}}^m}$ 的伪逆,可通过极限方法求得:$$ {{\boldsymbol{A}}^\dagger } = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{\lambda \to 0} {(\lambda {\boldsymbol{I}} + {\boldsymbol{A}}{{\boldsymbol{A}}^{\rm{T}}})^{ - 1}}{{\boldsymbol{A}}^{\rm{T}}} \text{,} $$ (11) 式中,
${\boldsymbol{A}}$ 表示特征节点和增强节点输出组合成的扩展矩阵,λ表示对权重矩阵W的约束,I表示单位矩阵,AT表示转置矩阵。1.5 检测性能评价指标
本文采用准确率(Accuracy)、F1值和模型检测时间(Time)等指标评估模型的异常检测性能,其表示为:
$$ 准确率=\frac{{T}_{\text{p}}+{T}_{\text{n}}}{{T}_{\text{p}}+{T}_{\text{n}}+{F}_{\text{p}}+{F}_{\text{n}}} \text{,} $$ (12) $$ 精确度=\frac{{T}_{\text{p}}}{{T}_{\text{p}}+{F}_{\text{p}}} \text{,} $$ (13) $$ 召回率=\frac{{T}_{\text{p}}}{{T}_{\text{p}}+{F}_{\text{n}}} \text{,} $$ (14) $$ F1值=\frac{2\times 精确度\times 召回率}{精确度+召回率} \text{,} $$ (15) 式中,Tp表示正确分类至目标类的数量,Fp表示其他类错误分类至目标类的数量,Tn表示其他类正确分类的数量,Fn表示目标类错误分类至其他类的数量。
准确率是正确分类的数据与数据集数据总量的比值,反映模型的正确检测能力。精确度(Precision)和召回率(Recall)分别是正确分类为异常数据的个数与所有分类的异常数据、实际异常数据的比值。F1值同时兼顾了精确度和召回率。除异常检测能力外,模型检测时间也是评估模型是否符合实际应用的重要参数。
2. 试验与分析
2.1 试验环境与参数
试验采用Windows 10操作系统、Intel Core i5 CPU、8GB内存的台式计算机,Python3.6编程语言和Tensor Flow2.0.0框架用于异常检测模型搭建和应用。主要研究滑动窗口尺寸对模型异常检测性能的影响及模型对不同特征数据的异常检测灵敏性,以甄选最优的异常检测方法。在此基础上,对比分析不同异常检测模型性能。
试验将BCNN与当前使用较为广泛的SVM、随机森林(Random forest, RF)和卷积神经网络方法进行比较。SVM模型[20-21]核函数采用径向基函数(Radial basis function, RBF),核函数参数ε为0.2,正则化参数C为1;RF模型[22]聚类数c=2,模糊程度系数m=3,卷积神经网络方法从文献[14]中引用。BCNN模型的特征节点和特征增强节点数量均为1000。对于滑动窗口,传感器监测数据特征周期T为24 h,支持度衰减因子β取0.5[23],采样间隔Δt为3 min,空气湿度、空气温度、土壤湿度和土壤温度的滑动窗口尺寸分别为105、88、76和91。为控制模型参数随机初始化和训练引起的随机性,重复5次试验,以平均数进行结果分析。
2.2 滑动窗口尺寸对检测性能的影响
为评估所提滑动窗口选择方法的有效性,以BCNN模型为例,采用窗口尺寸60~120的数据集进行试验,结果如图5所示。空气湿度数据集中,异常检测准确率在窗口尺寸[60,100]区间内呈上升趋势,在窗口尺寸100时达到峰值;空气温度数据集中,窗口尺寸在[60,90]区间时,异常检测准确率随窗口尺寸增大而增加,窗口尺寸在90时准确率表现最佳,窗口尺寸大于90时准确率无显著变化;土壤湿度数据集中,在窗口尺寸[60,70]区间内准确率呈增加趋势,在[70,120]区间内准确率趋于稳定;土壤温度数据集中,在窗口尺寸[90,100]时准确率最高。值得注意的是,土壤湿度数据集呈最高准确率的窗口尺寸远小于其他数据集,这是由于其数据波动不显著,模型仅需少量数据即可学习其特征。试验所得出的最佳滑动窗口尺寸,与式(3)得出的窗口尺寸基本相符。因此,基于数据特征的滑动窗口选择方法可有效地提高模型异常检测准确率。
模型检测耗时随滑动窗口尺寸变化如图6所示。空气湿度数据集中,滑动窗口尺寸在[90,100]区间时,检测耗时最短。空气温度数据集中,在窗口尺寸[80,100]区间时检测耗时最短,处于理想状态。土壤湿度数据集中,当窗口尺寸变化时,模型检测耗时变化不明显,窗口尺寸80左右时检测耗时最短。土壤温度数据集中,在窗口尺寸[80,90]区间内,检测耗时较短,处于理想水平,其中窗口尺寸90时最优。总体上,窗口尺寸和检测耗时呈二次相关。波动性较强的数据(如空气湿度),窗口尺寸变化时,检测耗时波动更大;而波动小、较为平稳的数据(如土壤湿度),改变滑动窗口尺寸对检测耗时影响较小。
综上,采用滑动窗口机制后,可提升模型对异常数据的检测能力,针对不同特征数据选取合适的滑动窗口尺寸,可提升异常检测准确率和降低检测耗时。
2.3 模型异常检测性能
对比分析SVM、RF、CNN和BCNN模型的数据异常检测性能,各种模型的异常检测准确率和F1值如图7所示。BCNN模型在空气湿度、空气温度、土壤湿度和土壤温度数据集上均表现出良好的异常检测性能,准确率均在97%以上,其中空气湿度数据集的准确率最高,达到99.29%,优于SVM、RF和CNN的95.68%、94.67%和93.31%。相较于CNN模型,BCNN模型在空气湿度、空气温度、土壤湿度和土壤温度数据集上准确率分别提升了5.98%、1.48%、2.19%和2.55%;相较于SVM和RF模型,BCNN模型在空气湿度数据集上的准确率与二者差异最为明显,分别高出3.61%和4.62%。由图1可知,空气湿度数据波动性较大,周期性特征弱于其他数据集,故BCNN在处理波动性大的数据时性能更佳。BCNN模型在空气湿度、空气温度、土壤湿度和土壤温度数据集上的F1值分别为:0.996 4、0.9887、0.9949和0.9920,均优于其他模型。空气温度数据集中,4种模型的F1值差值较小,均小于0.0076。在波动性较大的空气湿度数据集中,BCNN模型的F1值达到0.9964,分别优于SVM、RF和CNN模型0.0188、0.0241和0.0310。因此,BCNN模型异常检测性能优于其他模型,且BCNN模型对波动性大的数据检测能力更优,而其他模型随着数据波动性增大,异常检测能力有所下降。
总之,相较于传统机器学习算法和深度学习模型,BCNN模型对异常数据的检测能力在不同特征的数据集上均得到了一定程度的提升。其中,对波动性较大的数据集的异常检测能力最优。
各种异常检测模型检测耗时如表1所示。BCNN模型检测耗时大幅低于同类的深度模型CNN,仅为其1/6~1/7。相较于SVM和RF传统机器学习算法,BCNN模型虽然需要额外的检测时间,但异常检测准确率和F1值都有明显提升,增强了模型对波动性较大数据的检测能力,同时,BCNN模型的超参数数量较少,有效地降低了超参数选择的复杂度。综上,对于农情数据异常检测,BCNN模型在检测能力和耗时方面优于同类深度学习模型,在检测能力和超参数选择方面优于传统机器学习算法,具有良好的适用性。
表 1 不同模型异常检测耗时Table 1. Anomaly detection time of different modelss 模型
Model空气湿度 Air humidity 空气温度 Air temperature 土壤湿度 Soil humidity 土壤温度 Soil temperature SVM 10.78 14.62 11.58 14.47 RF 12.02 14.39 12.85 13.77 CNN 2 073.04 2 014.88 1 928.76 2 116.24 BCNN 335.74 329.19 283.32 291.96 3. 结论
本研究提出了基于宽度卷积神经网络的农情数据异常检测方法,采用养殖场传感器环境监测数据,综合评估了数据异常检测性能。试验结果表明,基于数据特征的滑动窗口划分子集,可有效地增加模型检测准确率和降低检测耗时。在异常检测模型对比试验中,BCNN模型取得了最高准确率和F1值,对空气和土壤温湿度数据异常检测的平均准确率和F1值分别达到了98.54%和0.993 0,相比于SVM、RF和CNN模型的平均准确率(96.86%、95.79%和95.49%)和F1值(0.983 7、0.978 1和0.9768),表现出良好的检测效果。BCNN模型对波动性较大数据集的检测能力更强,准确率和F1值平均优于其他模型4.74%和0.0246。另一方面,BCNN模型检测时间仅为同类深度学习模型CNN的1/6~1/7,且比传统机器学习模型SVM和RF采用更少的超参数。本研究为农业物联网数据高质量感知及农业信息化提供了一定的参考。考虑到无线传感器网络规模不断扩展,后续研究将更多地关注传感器网络群体异常数据检测,进一步提高农业物联网感知数据质量。
-
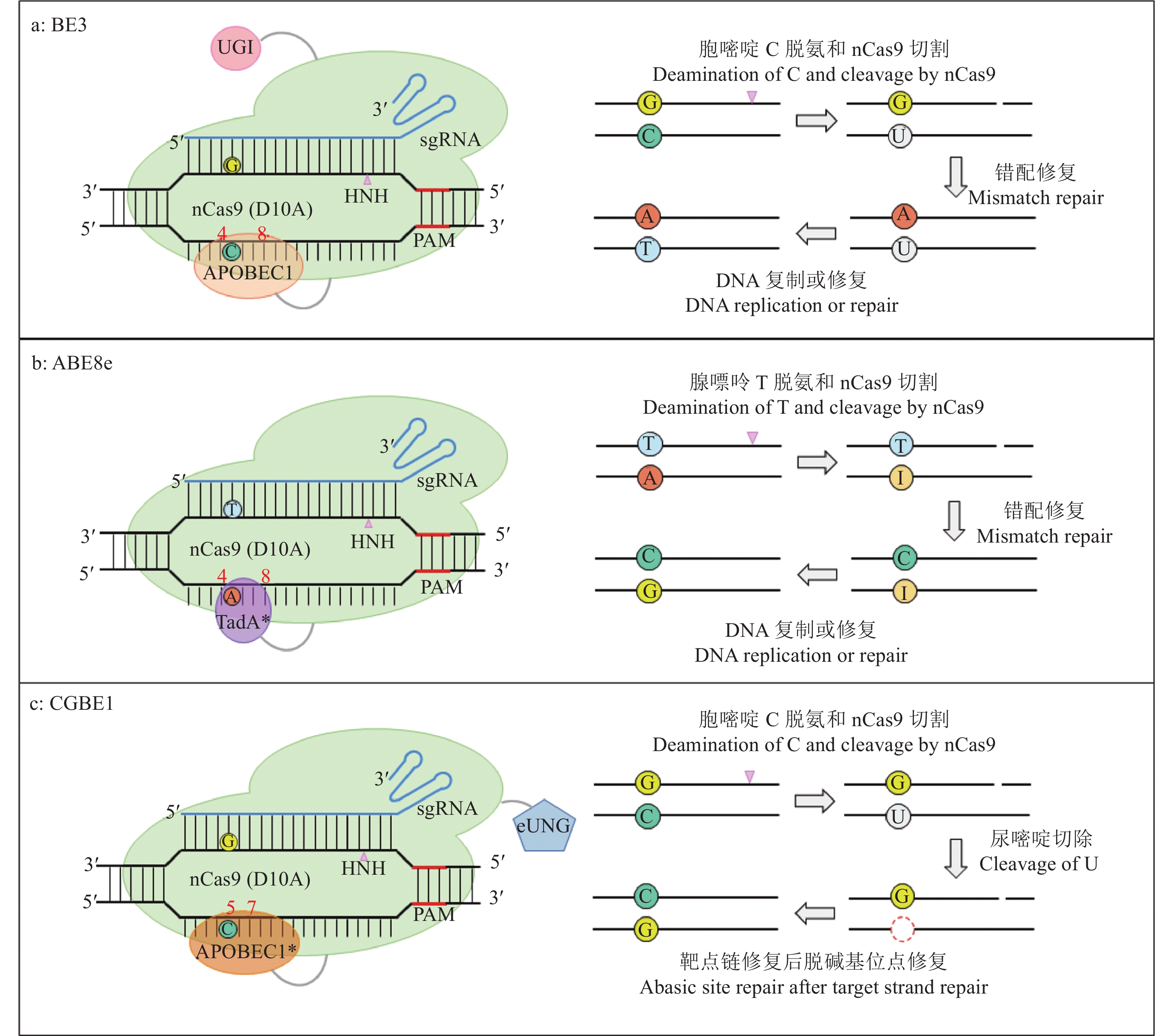
图 1 CBE、ABE和GBE碱基编辑器原理
a:CBE系统,以BE3为例;b:ABE系统,以ABE8e为例;c:GBE系统,以CGBE1为例;染色体单链上红色数字表示该脱氨酶的编辑窗口
Figure 1. Schematic diagrams of CBE, ABE and GBE systems
a: CBE system taking BE3 as an example; b: ABE system taking ABE8e as an example; c: GBE system taking CGBE1 as an example; The numbers in red indicate deamination windows
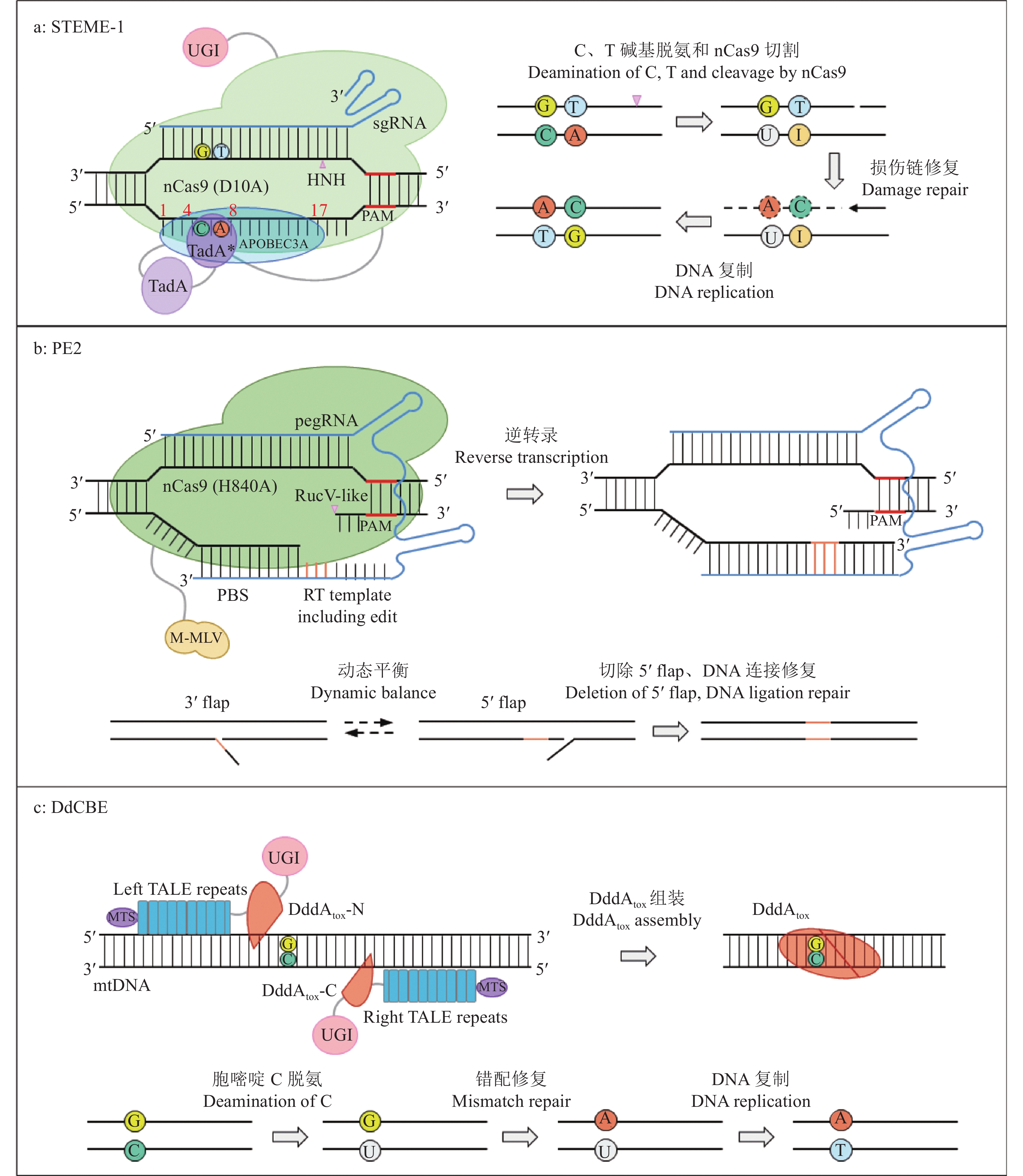
图 2 DBE、PE、线粒体碱基编辑器原理
a:DBE系统,以STEME-1为例;染色体单链上红色数字表示脱氨酶的编辑窗口,其中,APOBEC3A的编辑窗口为C1~C17,TadA的编辑窗口为A4~A8;b:PE系统,以PE2为例;c:线粒体碱基编辑系统,以DdCBE为例
Figure 2. Schematic diagrams of DBE, PE and mitochondrial base editors
a: DBE system taking STEME-1 as an example, the numbers in red indicate deamination windows which are C1−C17 in APOBEC3A and A4−A8 in TadA; b: PE system taking PE2 as an example; c: Mitochondrial base editing system taking DdCBE as an example
-
[1] SMITH J, BIBIKOVA M, WHITBY F G, et al. Requirements for double-strand cleavage by chimeric restriction enzymes with zinc finger DNA-recognition domains[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2000, 28(17): 3361-3369. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.17.3361
[2] BIBIKOVA M, GOLIC M, GOLIC K G, et al. Targeted chromosomal cleavage and mutagenesis in Drosophila using zinc-finger nucleases[J]. Genetics, 2002, 161(3): 1169-1175. doi: 10.1093/genetics/161.3.1169
[3] LLOYD A, PLAISIER C L, CARROLL D, et al. Targeted mutagenesis using zinc-finger nucleases in Arabidopsis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2005, 102(6): 2232-2237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409339102
[4] PETOLINO J F. Genome editing in plants via designed zinc finger nucleases[J]. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology Plant, 2015, 51(1): 1-8.
[5] BOCH J, SCHOLZE H, SCHORNACK S, et al. Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5959): 1509-1512. doi: 10.1126/science.1178811
[6] MOSCOU M J, BOGDANOVE A J. A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5959): 1501. doi: 10.1126/science.1178817
[7] LI T, HUANG S, JIANG W Z, et al. TAL nucleases (TALNs): Hybrid proteins composed of TAL effectors and FokI DNA-cleavage domain[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(1): 359-372. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq704
[8] LEDFORD H. CRISPR, the disruptor[J]. Nature, 2015, 522(7554): 20-24. doi: 10.1038/522020a
[9] GAO C. Genome engineering for crop improvement and future agriculture[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(6): 1621-1635. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.005
[10] HSU P D, LANDER E S, ZHANG F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering[J]. Cell, 2014, 157(6): 1262-1278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010
[11] MA X, ZHU Q, CHEN Y, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 platforms for genome editing in plants: Developments and applications[J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(7): 961-974. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.04.009
[12] REES H A, LIU D R. Base editing: Precision chemistry on the genome and transcriptome of living cells[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2018, 19(12): 770-788. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0059-1
[13] HESS G T, TYCKO J, YAO D, et al. Methods and applications of CRISPR-mediated base editing in eukaryotic genomes[J]. Molecular Cell, 2017, 68(1): 26-43. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.09.029
[14] ZHAO K, TUNG C W, EIZENGA G C, et al. Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2: 467. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1467
[15] LANDRUM M J, LEE J M, BENSON M, et al. ClinVar: Public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, 44(D1): 862-868. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1222
[16] KOMOR A C, KIM Y B, PACKER M S, et al. Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2016, 533(7603): 420-424. doi: 10.1038/nature17946
[17] KOMOR A C, ZHAO K T, PACKER M S, et al. Improved base excision repair inhibition and bacteriophage Mu Gam protein yields C: G-to-T: A base editors with higher efficiency and product purity[J]. Science Advances, 2017, 3(8): eaao4774. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aao4774
[18] WANG L, XUE W, YAN L, et al. Enhanced base editing by co-expression of free uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitor[J]. Cell Research, 2017, 27(10): 1289-1292. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.111
[19] GEHRKE J M, CERVANTES O, CLEMENT M K, et al. An APOBEC3A-Cas9 base editor with minimized bystander and off-target activities[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(10): 977-982. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4199
[20] ZHANG X, CHEN L, ZHU B, et al. Increasing the efficiency and targeting range of cytidine base editors through fusion of a single-stranded DNA-binding protein domain[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2020, 22(6): 740-750. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0518-8
[21] KOBLAN L W, DOMAN J L, WILSON C, et al. Improving cytidine and adenine base editors by expression optimization and ancestral reconstruction[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 843-846. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4172
[22] ZAFRA M P, SCHATOFF E M, KATTI A, et al. Optimized base editors enable efficient editing in cells, organoids and mice[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(9): 888-893. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4194
[23] REES H A, KOMOR A C, YEH W, et al. Improving the DNA specificity and applicability of base editing through protein engineering and protein delivery[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15790. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15790
[24] LEE J K, JEONG E, LEE J, et al. Directed evolution of CRISPR-Cas9 to increase its specificity[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3048. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05477-x
[25] WANG L, XUE W, ZHANG H, et al. Eliminating base-editor-induced genome-wide and transcriptome-wide off-target mutations[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2021, 23(5): 552-563. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00671-4
[26] KIM Y B, KOMOR A C, LEVY J M, et al. Increasing the genome-targeting scope and precision of base editing with engineered Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusions[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(4): 371-376. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3803
[27] HUANG T P, ZHAO K T, MILLER S M, et al. Circularly permuted and PAM-modified Cas9 variants broaden the targeting scope of base editors[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(6): 626-631. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0134-y
[28] NISHIDA K, ARAZOE T, YACHIE N, et al. Targeted nucleotide editing using hybrid prokaryotic and vertebrate adaptive immune systems[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6305): aaf8729.
[29] MA Y, ZHANG J, YIN W, et al. Targeted AID-mediated mutagenesis (TAM) enables efficient genomic diversification in mammalian cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2016, 13(12): 1029-1035. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4027
[30] HU J H, MILLER S M, GEURTS M H, et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity[J]. Nature, 2018, 556(7699): 57-63. doi: 10.1038/nature26155
[31] NISHIMASU H, SHI X, ISHIGURO S, et al. Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease with expanded targeting space[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6408): 1259-1262. doi: 10.1126/science.aas9129
[32] LI X, WANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Base editing with a Cpf1-cytidine deaminase fusion[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(4): 324-327. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4102
[33] LI J, SUN Y, DU J, et al. Generation of targeted point mutations in rice by a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(3): 526-529. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.12.001
[34] LU Y, ZHU J K. Precise editing of a target base in the rice genome using a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(3): 523-525. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.11.013
[35] ZENG D, LI X, HUANG J, et al. Engineered Cas9 variant tools expand targeting scope of genome and base editing in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(6): 1348-1350. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13293
[36] ZHONG Z, SRETENOVIC S, REN Q, et al. Improving plant genome editing with high-fidelity xCas9 and non-canonical PAM-targeting Cas9-NG[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(7): 1027-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.03.011
[37] WANG M, WANG Z, MAO Y, et al. Optimizing base editors for improved efficiency and expanded editing scope in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(9): 1697-1699. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13124
[38] WU Y, XU W, WANG F, et al. Increasing cytosine base editing scope and efficiency with engineered Cas9-PmCDA1 fusions and the modified sgRNA in rice[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2019, 10: 379.
[39] SHIMATANI Z, KASHOJIYA S, TAKAYAMA M, et al. Targeted base editing in rice and tomato using a CRISPR-Cas9 cytidine deaminase fusion[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(5): 441-443. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3833
[40] ZONG Y, SONG Q, LI C, et al. Efficient C-to-T base editing in plants using a fusion of nCas9 and human APOBEC3A[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(10): 950-953. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4261
[41] WANG F, ZHANG C, XU W, et al. Developing high-efficiency base editors by combining optimized synergistic core components with new types of nuclear localization signal peptide[J]. Crop Journal, 2020, 8(3): 408-417. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2020.01.003
[42] XU W, YANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Discriminated sgRNAs-based SurroGate system greatly enhances the screening efficiency of plant base-edited cells[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(1): 169-180. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.10.007
[43] ZENG D, LIU T, TAN J, et al. PhieCBEs: Plant high-efficiency cytidine base editors with expanded target range[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(12): 1666-1669. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.11.001
[44] GAUDELLI N M, KOMOR A C, REES H A, et al. Programmable base editing of A · T to G · C in genomic DNA without DNA cleavage[J]. Nature, 2017, 551(7681): 464-471. doi: 10.1038/nature24644
[45] YANG L, ZHANG X, WANG L, et al. Increasing targeting scope of adenosine base editors in mouse and rat embryos through fusion of TadA deaminase with Cas9 variants[J]. Protein & Cell, 2018, 9(9): 814-819.
[46] CHATTERJEE P, JAKIMO N, JACOBSON J M. Minimal PAM specificity of a highly similar SpCas9 ortholog[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(10): u766.
[47] RICHTER M F, ZHAO K T, ETON E, et al. Phage-assisted evolution of an adenine base editor with improved Cas domain compatibility and activity[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 883-891. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0453-z
[48] LAPINAITE A, KNOTT G J, PALUMBO C M, et al. DNA capture by a CRISPR-Cas9-guided adenine base editor[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6503): 566-571. doi: 10.1126/science.abb1390
[49] LI C, ZONG Y, WANG Y, et al. Expanded base editing in rice and wheat using a Cas9-adenosine deaminase fusion[J]. Genome Biology, 2018, 19: 59. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1443-z
[50] HUA K, TAO X, ZHU J. Expanding the base editing scope in rice by using Cas9 variants[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(2): 499-504. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12993
[51] HUA K, TAO X, YUAN F, et al. Precise A · T to G · C base editing in the rice genome[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(4): 627-630.
[52] HUA K, TAO X, HAN P, et al. Genome engineering in rice using Cas9 variants that recognize NG PAM sequences[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(7): 1003-1014. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.03.009
[53] HUA K, TAO X, LIANG W, et al. Simplified adenine base editors improve adenine base editing efficiency in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(3): 770-778.
[54] KANG B, YUN J, KIM S, et al. Precision genome engineering through adenine base editing in plants[J]. Nature Plants, 2018, 4(7): 427-431. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0178-x
[55] GE Z, ZHENG L, ZHAO Y, et al. Engineered xCas9 and SpCas9-NG variants broaden PAM recognition sites to generate mutations in Arabidopsis plants[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17(10): 1865-1867. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13148
[56] TAN J, ZENG D, ZHAO Y, et al. PhieABEs: A PAM-less/free high-efficiency adenine base editor toolbox with wide target scope in plants[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(5): 934-943. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13774
[57] YAN D, REN B, LIU L, et al. High-efficiency and multiplex adenine base editing in plants using new TadA variants[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(5): 722-731. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.02.007
[58] WEI C, WANG C, JIA M, et al. Efficient generation of homozygous substitutions in rice in one generation utilizing an rABE8e base editor[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(9): 1595-1599. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13089
[59] REN Q, SRETENOVIC S, LIU S, et al. PAM-less plant genome editing using a CRISPR-SpRY toolbox[J]. Nature Plants, 2021, 7(1): 25-33. doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-00827-4
[60] LI J, XU R, QIN R, et al. Genome editing mediated by SpCas9 variants with broad non-canonical PAM compatibility in plants[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(2): 352-360. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.12.017
[61] KURT I C, ZHOU R, IYER S, et al. CRISPR C-to-G base editors for inducing targeted DNA transversions in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(1): 41-46. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0609-x
[62] ZHAO D, LI J, LI S, et al. Glycosylase base editors enable C-to-A and C-to-G base changes[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(1): 35-40. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0592-2
[63] SUN N, ZHAO D, LI S, et al. Reconstructed glycosylase base editors GBE2.0 with enhanced C-to-G base editing efficiency and purity[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2022, 30(7): 2452-2463.
[64] CHEN L, PARK J E, PAA P, et al. Programmable C:G to G:C genome editing with CRISPR-Cas9-directed base excision repair proteins[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1384.
[65] YUAN T, YAN N, FEI T, et al. Optimization of C-to-G base editors with sequence context preference predictable by machine learning methods[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 4902.
[66] KOBLAN L W, ARBAB M, SHEN M W, et al. Efficient C · G-to-G · C base editors developed using CRISPRi screens, target-library analysis, and machine learning[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(11): 1414-1425. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-00938-z
[67] CHEN S, LIU Z, LAI L, et al. Efficient C-to-G base editing with improved target compatibility using engineered deaminase-nCas9 fusions[J]. CRISPR Journal, 2022, 5(3): 389-396. doi: 10.1089/crispr.2021.0124
[68] PARK M, YUN J, KIM H U. C-to-G base editing enhances oleic acid production by generating novel alleles of FATTY ACID DESATURASE 2 in plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 748529. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.748529
[69] SRETENOVIC S, LIU S, LI G, et al. Exploring C-to-G base editing in rice, tomato, and poplar[J]. Frontiers in Genome Editing, 2021, 3: 756766. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2021.756766
[70] TIAN Y, SHEN R, LI Z, et al. Efficient C-to-G editing in rice using an optimized base editor[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2022, 20(7): 1238-1240. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13841
[71] ZENG D, ZHENG Z, LIU Y, et al. Exploring C-to-G and A-to-Y base editing in rice by using new vector tools[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(14): 7990.
[72] LI C, ZHANG R, MENG X, et al. Targeted, random mutagenesis of plant genes with dual cytosine and adenine base editors[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 875-882. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0393-7
[73] ZHANG X, ZHU B, CHEN L, et al. Dual base editor catalyzes both cytosine and adenine base conversions in human cells[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 856-860. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0527-y
[74] SAKATA R C, ISHIGURO S, MORI H, et al. Base editors for simultaneous introduction of C-to-T and A-to-G mutations[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 865-869. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0509-0
[75] GRÜNEWALD J, ZHOU R, LAREAU C A, et al. A dual-deaminase CRISPR base editor enables concurrent adenine and cytosine editing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(7): 861-864. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0535-y
[76] XU R, KONG F, QIN R, et al. Development of an efficient plant dual cytosine and adenine editor[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2021, 63(9): 1600-1605. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13146
[77] XIONG X, LI Z, LIANG J, et al. A cytosine base editor toolkit with varying activity windows and target scopes for versatile gene manipulation in plants[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(6): 3565-3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac166
[78] LIANG Y, XIE J, ZHANG Q, et al. AGBE: A dual deaminase-mediated base editor by fusing CGBE with ABE for creating a saturated mutant population with multiple editing patterns[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(9): 5384-5399. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac353
[79] ANZALONE A V, RANDOLPH P B, DAVIS J R, et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7785): 149-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1711-4
[80] LIN Q, ZONG Y, XUE C, et al. Prime genome editing in rice and wheat[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(5): 582-585. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0455-x
[81] LI H, LI J, CHEN J, et al. Precise modifications of both exogenous and endogenous genes in rice by prime editing[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(5): 671-674. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.03.011
[82] XU W, ZHANG C, YANG Y, et al. Versatile nucleotides substitution in plant using an improved prime editing system[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(5): 675-678. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.03.012
[83] TANG X, SRETENOVIC S, REN Q, et al. Plant prime editors enable precise gene editing in rice cells[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(5): 667-670. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.03.010
[84] HUA K, JIANG Y, TAO X, et al. Precision genome engineering in rice using prime editing system[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(11): 2167-2169. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13395
[85] BUTT H, RAO G S, SEDEEK K, et al. Engineering herbicide resistance via prime editing in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(12): 2370-2372. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13399
[86] LU Y, TIAN Y, SHEN R, et al. Precise genome modification in tomato using an improved prime editing system[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(3): 415-417. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13497
[87] NELSON J W, RANDOLPH P B, SHEN S P, et al. Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(3): 402-410. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01039-7
[88] JIANG Y, CHAI Y, LU M, et al. Prime editing efficiently generates W542L and S621I double mutations in two ALS genes in maize[J]. Genome Biology, 2020, 21(1): 257. doi: 10.1186/s13059-020-02170-5
[89] LIN Q, JIN S, ZONG Y, et al. High-efficiency prime editing with optimized, paired pegRNAs in plants[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(8): 923-927. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-00868-w
[90] JIN S, LIN Q, LUO Y, et al. Genome-wide specificity of prime editors in plants[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(10): 1292-1299. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-00891-x
[91] XU W, YANG Y, YANG B, et al. A design optimized prime editor with expanded scope and capability in plants[J]. Nature Plants, 2022, 8(1): 45-52. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-01043-4
[92] ZONG Y, LIU Y, XUE C, et al. An engineered prime editor with enhanced editing efficiency in plants[J/OL]. Nature Biotechnology, (2022-03-24)[2022-08-10]. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01254-w.
[93] LI H, ZHU Z, LI S, et al. Multiplex precision gene editing by a surrogate prime editor in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2022, 15(7): 1077-1080. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2022.05.009
[94] ZOU J, MENG X, LIU Q, et al. Improving the efficiency of prime editing with epegRNAs and high-temperature treatment in rice[J/OL]. Science China: Life Science, (2022-06-23)[2022-08-10]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2147-2.
[95] JIANG T, ZHANG X, WENG Z, et al. Deletion and replacement of long genomic sequences using prime editing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(2): 227-234. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01026-y
[96] CHOI J, CHEN W, SUITER C C, et al. Precise genomic deletions using paired prime editing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(2): 218-226. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01025-z
[97] ANZALONE A V, GAO X D, PODRACKY C J, et al. Programmable deletion, replacement, integration and inversion of large DNA sequences with twin prime editing[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(5): 731-740. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01133-w
[98] WANG J, HE Z, WANG G, et al. Efficient targeted insertion of large DNA fragments without DNA donors[J]. Nature Methods, 2022, 19(3): 331-340. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01399-1
[99] TAO R, WANG Y, JIAO Y, et al. Bi-PE: Bi-directional priming improves CRISPR/Cas9 prime editing in mammalian cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(11): 6423-6434. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac506
[100] WALLACE D C. A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging, and cancer: A dawn for evolutionary medicine[J]. Annual Review of Genetics, 2005, 39: 359-407. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.39.110304.095751
[101] VAFAI S B, MOOTHA V K. Mitochondrial disorders as windows into an ancient organelle[J]. Nature, 2012, 491(7424): 374-383. doi: 10.1038/nature11707
[102] GAMMAGE P A, RORBACH J, VINCENT A I, et al. Mitochondrially targeted ZFNs for selective degradation of pathogenic mitochondrial genomes bearing large-scale deletions or point mutations[J]. EMBO Molecular Medicine, 2014, 6(4): 458-466.
[103] BACMAN S R, KAUPPILA J H K, PEREIRA C V, et al. MitoTALEN reduces mutant mtDNA load and restores tRNA Ala levels in a mouse model of heteroplasmic mtDNA mutation[J]. Nature Medicine, 2018, 24(11): 1696-1700. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0166-8
[104] BACMAN S R, WILLIAMS S L, PINTO M, et al. Specific elimination of mutant mitochondrial genomes in patient-derived cells by mitoTALENs[J]. Nature Medicine, 2013, 19(9): 1111-1113. doi: 10.1038/nm.3261
[105] FORNER J, KLEINSCHMIDT D, MEYER E H, et al. Targeted introduction of heritable point mutations into the plant mitochondrial genome[J]. Nature Plants, 2022, 8(3): 245-256. doi: 10.1038/s41477-022-01108-y
[106] KAZAMA T, OKUNO M, WATARI Y, et al. Curing cytoplasmic male sterility via TALEN-mediated mitochondrial genome editing[J]. Nature Plants, 2019, 5(7): 722-730. doi: 10.1038/s41477-019-0459-z
[107] MOK B Y, DE MORAES M H, ZENG J, et al. A bacterial cytidine deaminase toxin enables CRISPR-free mitochondrial base editing[J]. Nature, 2020, 583(7817): 631-637. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2477-4
[108] MOK B Y, KOTRYS A V, RAGURAM A, et al. CRISPR-free base editors with enhanced activity and expanded targeting scope in mitochondrial and nuclear DNA[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2022, 40(9): 1378-1387.
[109] CHO S, LEE S, MOK Y G, et al. Targeted A-to-G base editing in human mitochondrial DNA with programmable deaminases[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(10): 1764-1776. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.039
[110] KANG B, BAE S, LEE S, et al. Chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA editing in plants[J]. Nature Plants, 2021, 7(7): 899-905. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00943-9
[111] LI R, CHAR S N, LIU B, et al. High-efficiency plastome base editing in rice with TAL cytosine deaminase[J]. Molecular Plant, 2021, 14(9): 1412-1414. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2021.07.007
[112] HUA K, HAN P, ZHU J. Improvement of base editors and prime editors advances precision genome engineering in plants[J]. Plant Physiology, 2022, 188(4): 1795-1810. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab591
[113] BHARAT S S, LI S, LI J, et al. Base editing in plants: Current status and challenges[J]. Crop Journal, 2020, 8(3): 384-395. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2019.10.002
[114] 李国斌, 艾国, 韦静, 等. 碱基编辑技术及其在作物遗传改良中的应用综述[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(4): 719-732. doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0540 [115] ZONG Y, WANG Y, LI C, et al. Precise base editing in rice, wheat and maize with a Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusion[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2017, 35(5): 438-440. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3811
[116] ZAFAR K, SEDEEK K E M, RAO G S, et al. Genome editing technologies for rice improvement: Progress, prospects, and safety concerns[J]. Frontiers in Genome Editing, 2020, 2: 5.
[117] LI H, QIN R Y, LIU X S, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated adenine base editing in rice genome[J]. Rice Science, 2019, 26(2): 125-128. doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2018.07.002
[118] TIAN S, JIANG L, CUI X, et al. Engineering herbicide-resistant watermelon variety through CRISPR/Cas9-mediated base-editing[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2018, 37(9): 1353-1356. doi: 10.1007/s00299-018-2299-0
[119] VEILLET F, PERROT L, CHAUVIN L, et al. Transgene-free genome editing in tomato and potato plants using Agrobacterium-mediated delivery of a CRISPR/Cas9 cytidine base editor[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2019, 20(2): 402. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020402
[120] ZHANG R, LIU J, CHAI Z, et al. Generation of herbicide tolerance traits and a new selectable marker in wheat using base editing[J]. Nature Plants, 2019, 5(5): 480-485. doi: 10.1038/s41477-019-0405-0
[121] KUANG Y, LI S, REN B, et al. Base-editing-mediated artificial evolution of OsALS1 in planta to develop novel herbicide-tolerant rice germplasms[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(4): 565-572. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.01.010
[122] WU J, CHEN C, XIAN G, et al. Engineering herbicide-resistant oilseed rape by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated cytosine base-editing[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(9): 1857-1859. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13368
[123] VEILLET F, PERROT L, GUYON-DEBAST A, et al. Expanding the CRISPR toolbox in P. patens using SpCas9-NG variant and application for gene and base editing in Solanaceae crops[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(3): 1024. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031024
[124] REN B, YAN F, KUANG Y, et al. Improved base editor for efficiently inducing genetic variations in rice with CRISPR/Cas9-guided hyperactive hAID mutant[J]. Molecular Plant, 2018, 11(4): 623-626. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.01.005
[125] XU Y, LIN Q, LI X, et al. Fine‐tuning the amylose content of rice by precise base editing of the Wx gene[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19(1): 11-13. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13433
[126] XU R, LI J, LIU X, et al. Development of plant prime-editing systems for precise genome editing[J]. Plant Communications, 2020, 1(3): 100043. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100043
[127] 宗媛, 高彩霞. 碱基编辑系统研究进展[J]. 遗传, 2019, 41(9): 777-800. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-205 [128] JIN S, ZONG Y, GAO Q, et al. Cytosine, but not adenine, base editors induce genome-wide off-target mutations in rice[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6437): 292-295. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw7166
[129] ZUO E, SUN Y, WEI W, et al. Cytosine base editor generates substantial off-target single-nucleotide variants in mouse embryos[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6437): 289-292. doi: 10.1126/science.aav9973
[130] GRÜNEWALD J, ZHOU R, GARCIA S P, et al. Transcriptome-wide off-target RNA editing induced by CRISPR-guided DNA base editors[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7756): 433-437. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1161-z
[131] ZHOU C, SUN Y, YAN R, et al. Off-target RNA mutation induced by DNA base editing and its elimination by mutagenesis[J]. Nature, 2019, 571(7764): 275-278. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1314-0
[132] LI S, LIU L, SUN W, et al. A large-scale genome and transcriptome sequencing analysis reveals the mutation landscapes induced by high-activity adenine base editors in plants[J]. Genome Biology, 2022, 23(1): 51. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02618-w
[133] ZUO E, SUN Y, YUAN T, et al. A rationally engineered cytosine base editor retains high on-target activity while reducing both DNA and RNA off-target effects[J]. Nature Methods, 2020, 17(6): 600-604. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-0832-x
[134] DOMAN J L, RAGURAM A, NEWBY G A, et al. Evaluation and minimization of Cas9-independent off-target DNA editing by cytosine base editors[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38(5): 620-628. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0414-6
[135] JIN S, FEI H, ZHU Z, et al. Rationally designed APOBEC3B cytosine base editors with improved specificity[J]. Molecular Cell, 2020, 79(5): 728-740. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.07.005
[136] LIU Y, ZHOU J, LAN T, et al. Elimination of Cas9-dependent off-targeting of adenine base editor by using TALE to separately guide deaminase to target sites[J]. Cell Discovery, 2022, 8(1): 28. doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00384-4
[137] ZHOU J, LIU Y, WEI Y, et al. Eliminating predictable DNA off-target effects of cytosine base editor by using dual guiders including sgRNA and TALE[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2022, 30(7): 2443-2451. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.04.010
[138] JIN S, GAO Q, GAO C. An unbiased method for evaluating the genome-wide specificity of base editors in rice[J]. Nature Protocols, 2021, 16(1): 431-457. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-00423-y
[139] KIM D, KIM D, LEE G, et al. Genome-wide target specificity of CRISPR RNA-guided adenine base editors[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(4): 430-435. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0050-1
[140] MAO Y, BOTELLA J R, LIU Y, et al. Gene editing in plants: Progress and challenges[J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6(3): 421-437. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz005
[141] TANG J, CHEN L, LIU Y G. Off-target effects and the solution[J]. Nature Plants, 2019, 5(4): 341-342. doi: 10.1038/s41477-019-0406-z
[142] WEI Y, LI Z, XU K, et al. Mitochondrial base editor DdCBE causes substantial DNA off-target editing in nuclear genome of embryos[J]. Cell Discovery, 2022, 8(1): 27. doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00391-5
[143] LEI Z, MENG H, LIU L, et al. Mitochondrial base editor induces substantial nuclear off-target mutations[J]. Nature, 2022, 606(7915): 804-811. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04836-5
[144] ZHUANG Y, LIU J, WU H, et al. Increasing the efficiency and precision of prime editing with guide RNA pairs[J]. Nature Chemical Biology, 2022, 18(1): 29-37. doi: 10.1038/s41589-021-00889-1
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 贾鹿,赵磊,凌飞,李广亚. 基于归一化RBFNN的油井动液面测量数据异常辨识. 电子测量技术. 2024(24): 188-194 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李志臣,凌秀军,李鸿秋,李志军. 基于改进ShuffleNet的板栗分级方法. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 299-307 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑显润,郑鹏,王文秀,程亚红,苏宇锋. 基于多尺度特征提取深度残差网络的水稻害虫识别. 华南农业大学学报. 2023(03): 438-446 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 邓雪阳,邓达平,苏万靖. 基于并行深度卷积神经网络的舰船通信异常数据检测研究. 舰船科学技术. 2023(15): 119-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 杨亚琦,李博雄,杨东霞,刘燕. 基于信息熵的异常数据判别方法. 科学技术创新. 2023(24): 194-199 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杜肖鹏,李恺,王春辉,侯永,尹义蕾,潘守江,张凌风. 国内温室空气温湿度检测及传输技术研究进展. 农业工程技术. 2022(34): 28-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: