Effects of Clostridium butyricum spores on growth performance, biochemical parameters in serum, intestinal flora and short-chain fatty acid content ofPaneaus vannamei
-
摘要:目的
研究饲用丁酸梭菌Clostridium butyricum (CB)芽孢对凡纳滨对虾幼虾生长性能、血清生化指标、肠道菌群组成及5种短链脂肪酸含量的影响。
方法分别将质量分数为0(对照)、0.050%、0.075%和0.100%的丁酸梭菌芽孢制剂添加到基础饲料中(饲料中的活菌数分别为0、2.50×105、3.75×105、5.00×105 CFU/g),饲喂初始体质量为(1.42±0.02) g的凡纳滨对虾幼虾30 d,然后检测生长性能、血清生化指标、肠道菌群组成以及短链脂肪酸含量。
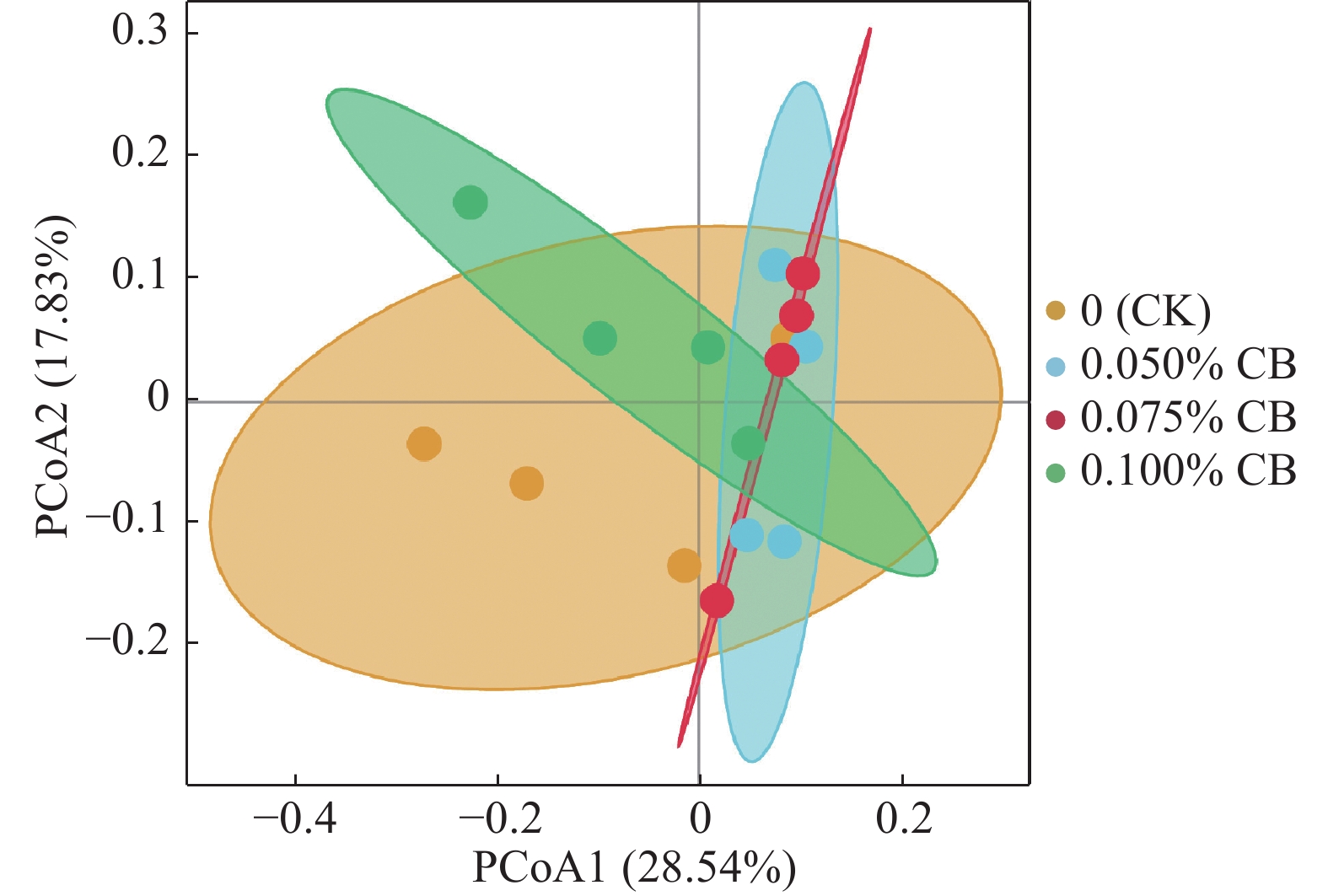
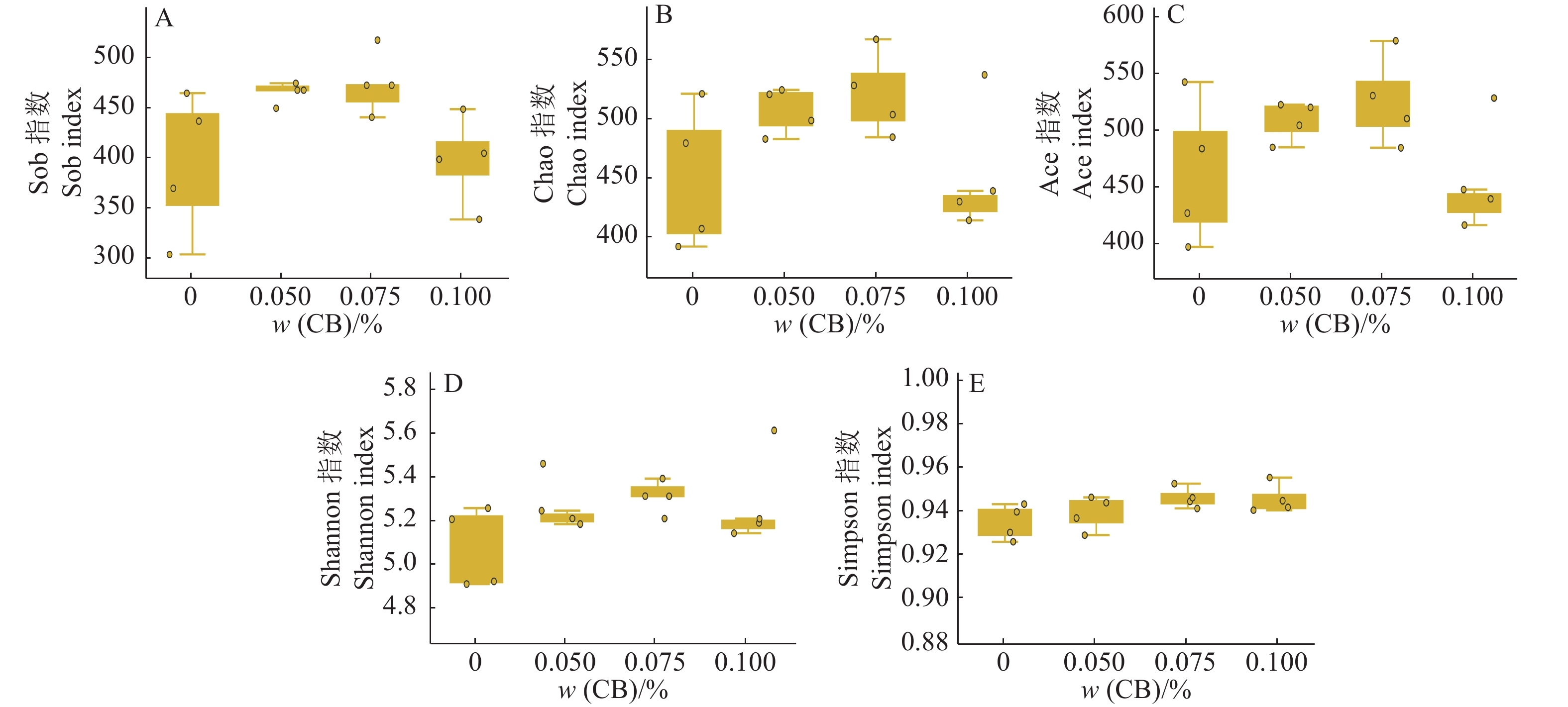
结果与对照组相比,饲喂30 d后对虾的体质量在0.050%和0.075% CB组显著提高(P<0.05),质量增加率则在0.050% CB组显著提高(P<0.05);0.075% CB组对虾的血清葡萄糖、0.100% CB组的血清尿素氮浓度显著降低(P<0.05),0.050% CB组血清磷浓度显著上升(P<0.05)。与对照组相比,0.050% CB组浮霉菌门Planctomycetes和髌骨菌门Patescibacteria丰度显著提高(P<0.05);0.050%和0.075% CB组弧菌属Vibrio的丰度显著降低(P<0.05)。多样性分析表明,0.050%和0.075% CB组的肠道菌群组成相似度更高,且明显不同于对照组和0.100% CB组。肠道内容物中5种短链脂肪酸的含量均随丁酸梭菌添加量的升高而增加。
结论饲料中添加CB芽孢制剂可能通过抑制肠道内潜在病原菌丰度、提高肠道短链脂肪酸的含量,改善营养物质的利用,从而提高凡纳滨对虾的生长性能。本研究中CB芽孢制剂在饲料中的适宜添加量为2.50×105或3.75×105 CFU/g。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of feeding Clostridium butyricum (CB) spores on the growth performance, biochemical parameters in serum, intestinal flora composition and contents of five short-chain fatty acids of Paneaus vannamei juvenile.
MethodBasic diets were supplemented with CB spore product of 0, 0.050%, 0.075% and 0.100% mass fraction (The viable counts of bacteria in the diets were 0, 2.50×105, 3.75×105 and 5.00×105 CFU/g respectively). The P. vannamei juveniles with (1.42 ± 0.02) g initial body weight of each were fed for 30 days, and growth performance, serum biochemical indicators, intestinal flora composition and short chain fatty acid contents were detected.
ResultCompared to the control group, the final body weights of the shrimps after 30 days feeding trial in the 0.050% and 0.075% CB groups significantly increased (P<0.05), and the weight gain rate significantly increased in the 0.050% CB group (P<0.05). The glucose concentration in serum of the 0.075% CB group and urea nitrogen concentration in serum of the 0.100% CB group significantly reduced (P<0.05), while the phosphorus concentration in serum of the 0.050% CB group significantly increased (P<0.05). Compared to the control group, the relative abundance of Planctomycetes and Patescibacteria significantly increased in the 0.050% CB group (P<0.05), while the relative abundance ofVibrio significantly reduced in the 0.050% and 0.075% CB groups (P<0.05). The diversity analysis indicated that the intestinal flora compositions were similar between the 0.050% and 0.075% CB groups, which were quite different from those of the control and 0.100% CB group. The intestinal contents of five short-chain fatty acids increased with dietary CB addition.
ConclusionThe supplementation of CB spore in diets helps to inhibit the proliferation of intestinal pathogens and increase the contents of intestinal short chain fatty acids, thus may enhance the nutrients utilization and growth performance of P. vannamei juvenile. In this study, the appropriate amount of Clostridium butyricum spore in diet is 2.50×105 or 3.75×105 CFU/g.
-
-
表 1 基础饲料配方及营养组成(风干基础)
Table 1 Feed formulation and nutrient composition of the basal diet (air-dry basis)
项目 Item 成分 Ingredient w/% 原料 Ingredient 鱼粉 Fish meal 36.0 小麦粉 Wheat flour 25.5 去皮豆粕 Soybean meal 15.0 花生粕 Peanut meal 8.0 菜籽粕 Rapeseed meal 10.0 鱼油 Fish oil 1.0 大豆卵磷脂 Soybean lecithin 1.0 磷酸二氢钙 Ca(H2PO4)2 1.5 预混料1) Premix 2.0 合计 Total 100.0 实测营养成分 Measured nutrient 粗蛋白 Crude protein 41.5 粗脂肪 Crude lipid 6.5 粗灰分 Crude ash 9.5 水分 Mositure 10.0 1)每千克预混料含有:VA 4 000 000 IU,VD3 1 500 000 IU,VE 100 000 IU,硫胺素 10 g,核黄素30 g,B6 30 g,泛酸 60 g,烟酸 80 g,B12 0.04 g,生物素 0.2 g,叶酸 6 g,肌醇120 g,VC 150 g,MgSO4·7H2O 102.45 g,KI 0.08 g,ZnSO4·7H2O 4.05 g,MnSO4·5H2O 2.19 g,CoCl2·6H2O 0.5 g,FeSO4·7H2O 16.55 g,Na2SeO4 0. 004 g,Ca(H2PO4)2 251.67 g 1)The premix per kilogram provides the following: VA 4 000 000 IU, VD3 1 500 000 IU, VE 100 000 IU, thiamine 10 g, riboflavin 30 g, B6 30 g, pantothenic acid 60 g, nicotinic acid 80 g, B12 0.04 g, biotin 0.2 g, folic acid 6 g, inositol 120 g, VC 150 g, MgSO4·7H2O 102.45 g, KI 0.08 g,ZnSO4·7H2O 4.05 g, MnSO4·5H2O 2.19 g,CoCl2·6H2O 0.5 g, FeSO4·7H2O 16.55 g,Na2SeO4 0. 004 g, Ca(H2PO4)2 251.67 g 表 2 饲料中添加丁酸梭菌(CB)对凡纳滨对虾生长性能的影响1)
Table 2 Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum (CB) on growth performance of Paneaus vannamei
w(CB)/% 初质量/g Initial body weight 末质量/g Final body weight 存活率/% Survival rate 质量增加率/% Weight gain rate 饲料系数 Feed conversion rate 0(CK) 1.42±0.00a 7.03±0.14a 96.66±3.85a 394.53±9.51a 1.50±0.04a 0.050 1.41±0.00a 7.37±0.08b 97.50±1.67a 421.00±5.31b 1.44±0.04a 0.075 1.44±0.03a 7.37±0.03b 99.17±1.67a 410.43±8.65ab 1.45±0.08a 0.100 1.42±0.01a 7.31±0.07ab 100.00±0.00a 412.99±5.84ab 1.43±0.03a 1) 同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s 法) 1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05, Duncan’s method) 表 3 饲料中添加丁酸梭菌(CB)对凡纳滨对虾营养组成的影响1)
Table 3 Effects of dietaryClostridium butyricum (CB) on nutrient compositions ofPaneaus vannamei
w/% w(CB)/% 水分 Mositure 粗蛋白 Crude protein 粗脂肪 Crude lipid 粗灰分 Crude ash 0(CK) 272.93±14.82a 70.57±0.80a 7.33±0.20a 12.87±0.99a 0.050 261.06±7.97a 70.63±0.12a 7.28±0.11a 12.73±0.23a 0.075 280.64±2.11a 70.24±0.37a 7.12±0.36a 13.10±0.60a 0.100 285.98±12.38a 70.56±0.18a 6.36±0.90a 13.60±0.67a 1)同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s 法) 1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05,Duncan’s method) 表 4 饲料中添加丁酸梭菌(CB)对凡纳滨对虾血清生化指标的影响1)
Table 4 Effects of dietaryClostridium butyricum (CB) on biochemical parameters in serum of Paneaus vannamei
w(CB)/% c/(mmol·L−1) 总蛋白/ (U·L−1) Total protein 葡萄糖 Glucose 胆固醇 Cholesterol 甘油三酯 Triglyceride 尿素氮 Urea nitrogen 磷 Phosphorus 0(CK) 1.69±0.15b 2.21±0.23a 2.05±0.15a 1.23±0.17b 1.44±0.32a 64.38±3.13a 0.050 1.62±0.29ab 2.28±0.18a 2.09±0.16a 1.04±0.06ab 1.93±0.31b 66.43±2.94a 0.075 1.39±0.13a 1.83±0.18a 1.97±0.21a 1.11±0.14ab 1.79±0.24ab 66.53±3.83a 0.100 1.55±0.10ab 2.05±0.23a 2.03±0.19a 0.95±0.06a 1.80±0.26ab 65.47±3.72a 1) 同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s 法) 1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05, Duncan’s method) 表 5 饲料中添加丁酸梭菌(CB) 对凡纳滨对虾肠道菌群组成(门水平)的影响1)
Table 5 Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum (CB) on intestinal flora composition (phylum level) of Paneaus vannamei
w(CB)/% 变形菌门 Proteobacteria 拟杆菌门 Bacteroidetes 疣微菌门 Verrucomicrobia 浮霉菌门 Planctomycetes 厚壁菌门 Firmicutes 0(CK) 43.9±3.9a 41.9±3.2a 6.8±1.3a 2.8±0.4a 1.5±0.8a 0.050 36.0±2.0a 46.3±1.7a 6.7±0.7a 5.7±0.6b 0.5±0.2a 0.075 36.5±1.5a 43.0±3.5a 8.1±1.8a 7.1±0.5b 0.4±0.1a 0.100 43.2±4.3a 42.4±3.5a 5.7±1.2a 4.6±0.8b 0.7±0.3a w(CB)/% 放线菌 Actinobacteria 衣原体 Chlamydiae 髌骨菌门 Patescibacteria 埃普西隆杆菌门 Epsilonbacteraeota 柔膜菌门 Tenericutes 0(CK) 1.1±0.1a 0.8±0.4a 0.4±0.0a 0.2±0.1a 0.2±0.0a 0.050 1.9±0.7a 1.3±0.2a 1.1±0.3b 0.0±0.0a 0.0±0.0a 0.075 2.1±1.1a 1.7±0.7a 0.5±0.1a 0.0±0.0a 0.1±0.0a 0.100 0.8±0.1a 1.1±0.6a 0.3±0.0a 0.0±0.0a 0.2±0.1a 1)同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s 法) 1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05, Duncan’s method) 表 6 饲料中添加丁酸梭菌(CB)对凡纳滨对虾肠道菌群组成(属水平)的影响1)
Table 6 Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum (CB) on intestinal flora composition (genus level) of Paneaus vannamei
w(CB)/% 弧菌属 Vibrio Motilimonas Haloferula 黏着杆菌属 Tenacibaculum Tamlana 0(CK) 7.8±3.6b 6.4±1.9a 6.3±1.3a 5.9±0.8a 5.3±0.7a 0.050 1.2±0.3a 6.8±3.0a 6.2±0.8a 4.3±0.3a 7.6± 0.7a 0.075 1.1±0.2a 8.5±1.6a 7.7±1.8a 5.1±0.4a 6.1± 0.8a 0.100 3.8±2.5ab 6.4±1.0a 5.0±1.2a 4.1±0.7a 6.7±0.5a w(CB)% 假交替单胞菌属 Pseudoalteromonas 鲁杰氏菌属 Ruegeria Hoppeia 康氏菌属 Kangiella Halocynthiibacter 0(CK) 2.6±0.5ab 2.6±0.3a 2.5±0.8a 2.2±1.5a 1.6±0.5a 0.050 1.5±0.3a 3.4±0.5a 4.1±0.4a 2.0±0.5a 1.1±0.3a 0.075 2.3±0.4a 4.1±0.9a 3.9±0.8a 0.8±0.2a 1.6±0.3a 0.100 3.7±0.6b 2.5±0.5a 4.7±2.1a 1.3±0.6a 1.4±0.1a 1)同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s 法) 1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05, Duncan’s method) 表 7 饲料中添加丁酸梭菌(CB)对凡纳滨对虾肠道内短链脂肪酸含量的影响1)
Table 7 Effects of dietaryClostridium butyricum (CB) on intestinal short-chain fatty acid contents ofPaneaus vannamei
w/(mg·g−1) w(CB)/% 乙酸 Acetic acid 丙酸 Propanoic acid 丁酸 Butyric acid 戊酸 Pentanoic acid 己酸 Hexanoic acid 0(CK) 5.32±0.31a 0.30±0.04a 0.20±0.00a 1.13±0.02a 0.35±0.00a 0.050 6.99±0.24b 0.32±0.03a 0.18±0.01a 1.24±0.07a 0.37±0.01a 0.075 10.54±0.61c 0.42±0.03a 0.33±0.00b 2.21±0.14b 0.59±0.01b 0.100 15.03±0.31d 1.10±0.08b 0.32±0.01b 2.72±0.11c 0.76±0.01b 1)同列数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s 法) 1) Different lowercase letters of the same column indicate significant differences (P<0.05, Duncan’s method) -
[1] 农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站, 中国水产学会. 2021中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021. [2] POOLSAWAT L, LI X, HE M, et al. Clostridium butyricum as probiotic for promoting growth performance, feed utilization, gut health and microbiota community of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus)[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2019, 26(3): 657-670.
[3] HE R P, FENG J, TIAN X L, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of probiotics on the growth, activities of digestive and non-specific immune enzymes in hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂ × Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀)[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2017, 48(12): 5782-5790. doi: 10.1111/are.13401
[4] 兰菲菲. 饲料中添加丁酸梭菌对鳗鲡生长与健康的促进作用[D]. 厦门: 集美大学, 2019. [5] 潘晓东, 吴天星, 宋增幅, 等. 丁酸梭菌对鮸鱼肠粘膜结构及肠内短链脂肪酸的影响[C]//中国畜牧兽医学会, 中国畜牧兽医学会. 第四届第十次全国学术研讨会暨动物微生态企业发展战略论坛论文集(上册). 2010: 147-151. [6] 朱振祥. 丁酸梭菌对鲤生长、免疫及肠道微生态的影响[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学, 2019. [7] 范晨薇. 丁酸梭菌对克氏原螯虾肠道健康的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020. [8] WANGARI M R, GAO Q, SUN C, et al. Effect of dietary Clostridium butyricum and different feeding patterns on growth performance, antioxidant and immune capacity in freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii)[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2020, 52(1): 12-22.
[9] DUAN Y F, DONG H B, WANG Y, et al. Effects of the dietary probiotic Clostridium butyricum on intestine digestive and metabolic capacities, SCFA content and body composition in Marsupenaeus japonicus[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17(3): 690-696. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3464-3
[10] LI H D, TIAN X L, ZHAO K, et al. Effect of Clostridium butyricum in different forms on growth performance, disease resistance, expression of genes involved in immune responses and mTOR signaling pathway of Litopenaeus vannamai[J]. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2019, 87: 13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.12.069
[11] LUO K, TIAN X L, WANG B, et al. Evaluation of paraprobiotic applicability of Clostridium butyricum CBG01 in improving the growth performance, immune responses and disease resistance in Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei[J]. Aquaculture, 2021, 544: 737041. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737041
[12] TADESE D A, SUN C X, LIU B, et al. Combined effects of emodin and Clostridium butyricum on growth and non-specific immunity of giant freshwater prawns, Macrobrachium rosenbergii[J]. Aquaculture, 2020, 525: 735281. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735281
[13] DUAN Y F, ZHANG Y, DONG H B, et al. Effect of the dietary probiotic Clostridium butyricum on growth, intestine antioxidant capacity and resistance to high temperature stress in kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus[J]. Journal of Thermal Biology, 2017, 66: 93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2017.04.004
[14] DUAN Y F, ZHANG J S, HUANG J, et al. Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum on the growth, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant capacity, and resistance to nitrite stress of Penaeus monodon[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 2019, 11(3): 938-945.
[15] 周建民, 付宇, 王伟唯, 等. 饲粮添加果寡糖对产蛋后期蛋鸡生产性能、营养素利用率、血清生化指标和肠道形态结构的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(4): 1806-1815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.04.039 [16] 杨玲, 欧阳富龙, 袁旭鹏, 等. 饲料中添加复合益生菌对断奶仔猪生长性能、粪便微生物及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 中国饲料, 2018(11): 49-54. doi: 10.15906/j.cnki.cn11-2975/s.20181109 [17] 贾聪慧, 杨彩梅, 曾新福, 等. 丁酸梭菌对肉鸡生长性能、抗氧化能力、免疫功能和血清生化指标的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2016, 28(3): 908-915. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2016.03.033 [18] 贾玲玲. 丁酸梭状芽孢杆菌CGMCC0313.1改善糖尿病及相关代谢紊乱[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017. [19] 邢帅, 朱琪, 梁东梅, 等. 丁酸梭菌缓解仔猪应激防御大肠杆菌病[J]. 中国饲料, 2018(7): 54-58. doi: 10.15906/j.cnki.cn11-2975/s.20180711 [20] 何家俊, 吴汉葵, 杨昕涧, 等. 丁酸梭菌对犊牛生长性能和血清生化、抗氧化、免疫指标及粪便微生物数量的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2021, 33(9): 5076-5085. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.09.028 [21] 夏雨, 范荣波, 易华西, 等. 植物乳杆菌对凡纳滨对虾致病菌抑制及其对肠道菌群结构的影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(10): 37-46. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20190127 [22] HUANG Z B, LI X Y, WANG L P, et al. Changes in the intestinal bacterial community during the growth of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2014, 47(6): 1737-1746.
[23] 张盛静, 赵小金, 宋晓玲, 等. 饲料添加益生菌对凡纳滨对虾肠道菌群、Toll受体及溶菌酶基因表达及抗感染的影响[J]. 中国水产科学, 2016, 23(4): 846-854. [24] DELMONT T O, QUINCE C, SHAIBER A, et al. Nitrogen-fixing populations of Planctomycetes and Proteobacteria are abundant in surface ocean metagenomes[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2018, 3(7): 804-813. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0176-9
[25] 郁维娜, 戴文芳, 陶震, 等. 健康与患病凡纳滨对虾肠道菌群结构及功能差异研究[J]. 水产学报, 2018, 42(3): 399-409. [26] XIONG J B, WANG K , Wu J F, et al. Changes in intestinal bacterial communities are closely associated with shrimp disease severity[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(16): 6911-6919.
[27] SUMON M S, AHMMED F, KHUSHI S S, et al. Growth performance, digestive enzyme activity and immune response of Macrobrachium rosenbergii fed with probiotic Clostridium butyricum incorporated diets[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Science, 2018, 30(1): 21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2016.11.003
[28] 宋增福, 吴天星, 潘晓东. 丁酸梭菌对肠道上皮细胞黏附及对鳗弧菌抑制的研究[J]. 中国兽药杂志, 2006, 40(8): 9-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1280.2006.08.003 [29] ZHOU Z G, LIU Y C, HE S X, et al. Effects of dietary potassium diformate (KDF) on growth performance, feed conversion and intestinal bacterial community of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus♀ × O. aureus♂) [J]. Aquaculture, 2009, 291(1/2): 89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.02.043
[30] GAO Q, XIAO C, MIN M, et al. Effects of probiotics dietary supplementation on growth performance, innate immunity and digestive enzymes of silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus[J]. Indian Journal of Animal Research, 2016, 50: 936-941.
[31] 薛永强, 张辉华, 王达, 等. 短链脂肪酸对肠道健康的调控机制及在动物生产中的应用[J]. 饲料工业, 2020, 41(19): 18-22. doi: 10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2020.19.004 [32] SILVA B C D, VIEIRA F D N, MOURINO J L P, et al. Butyrate and propionate improve the growth performance of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Aquaculture Research, 2016, 47: 612-623.
[33] SILVA B C, NOLASCO-SORIA H, MAGALLON-BARAJAS F, et al. Improved digestion and initial performance of whiteleg shrimp using organic salt supplements[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2016, 22(5): 997-1005.
[34] DUAN Y F, ZHANG Y, DONG H B, et al. Effect of dietary poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) on growth performance, intestinal health status and body composition of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931)[J]. Fish and Shellfish Immunology, 2017, 60: 520-528. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.11.020
[35] RINGER E. Effects of dietary lactate and propionate on growth and digesta in Arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus (L.)[J]. Aquaculture, 1991, 96: 321-333.
[36] MCDONALD J A K, MULLISH B H, PECHLIVANIS A, et al. Inhibiting growth of clostridioides difficile by restoring valerate, produced by the intestinal microbiota[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155(5): 1495-1507. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.014
[37] LI Y, DONG J L, XIAO H W, et al. Gut commensal derived-valeric acid protects against radiation injuries[J]. Gut Microbes, 2020, 11(4): 789-806.
[38] 李芳源, 王常安, 刘红柏. 丁酸梭菌对水产动物营养及免疫研究进展[J]. 水产学杂志, 2021, 34(5): 104-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2021.05.016



 下载:
下载: