Path planning method for citrus picking manipulator based on deep reinforcement learning
-
摘要:目的
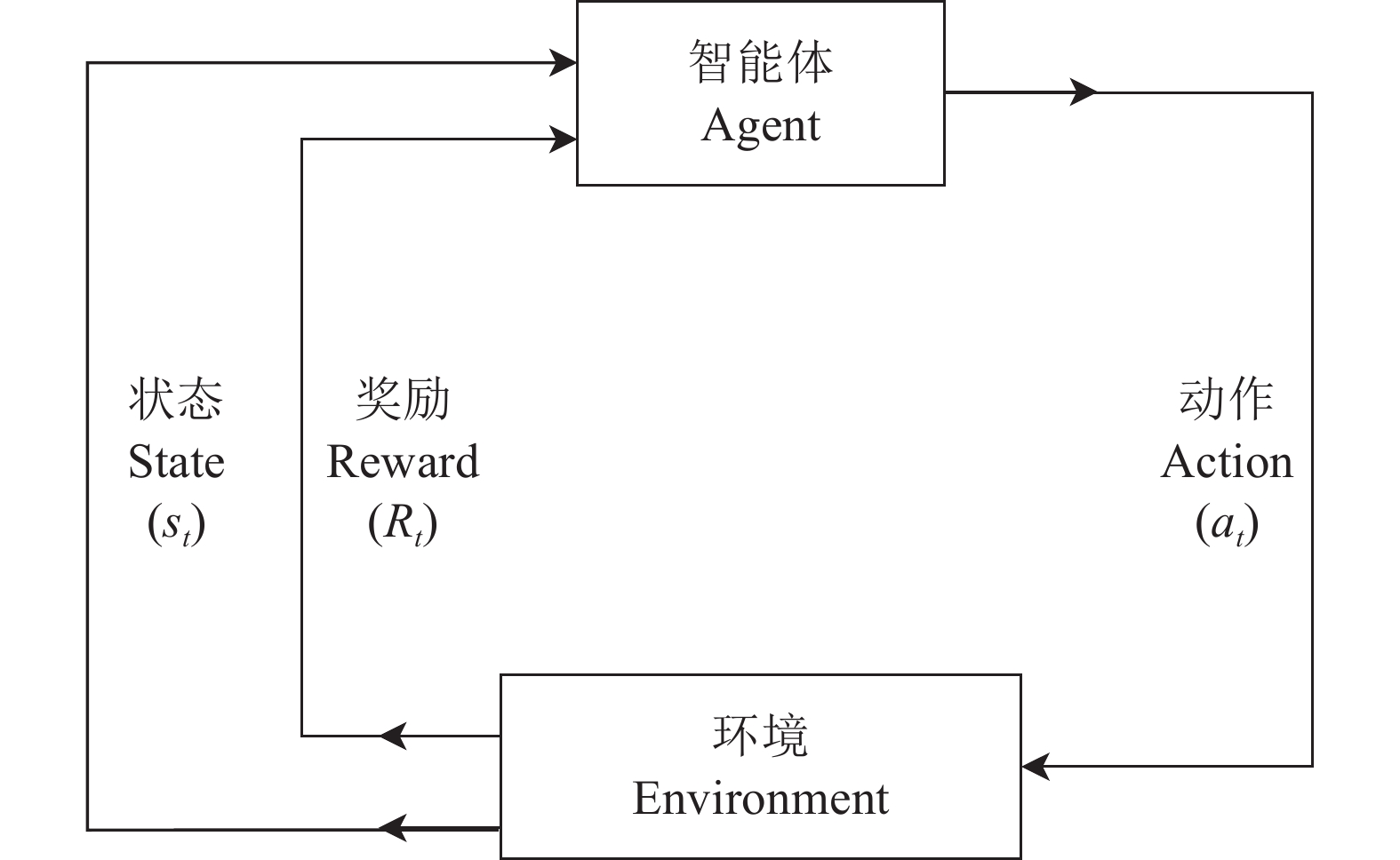
为解决非结构化环境下采用深度强化学习进行采摘机械臂路径规划时存在的效率低、采摘路径规划成功率不佳的问题,提出了一种非结构化环境下基于深度强化学习(Deep reinforcement learning, DRL)和人工势场的柑橘采摘机械臂的路径规划方法。
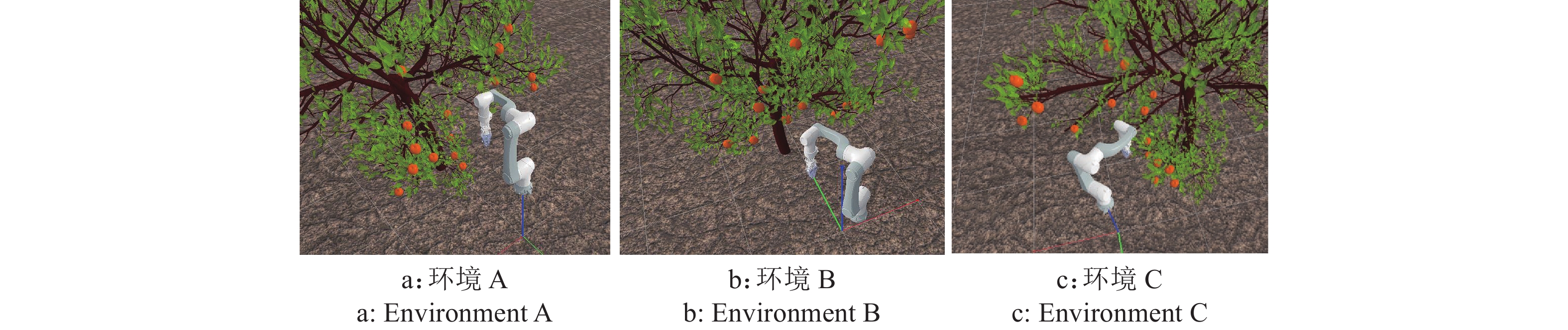
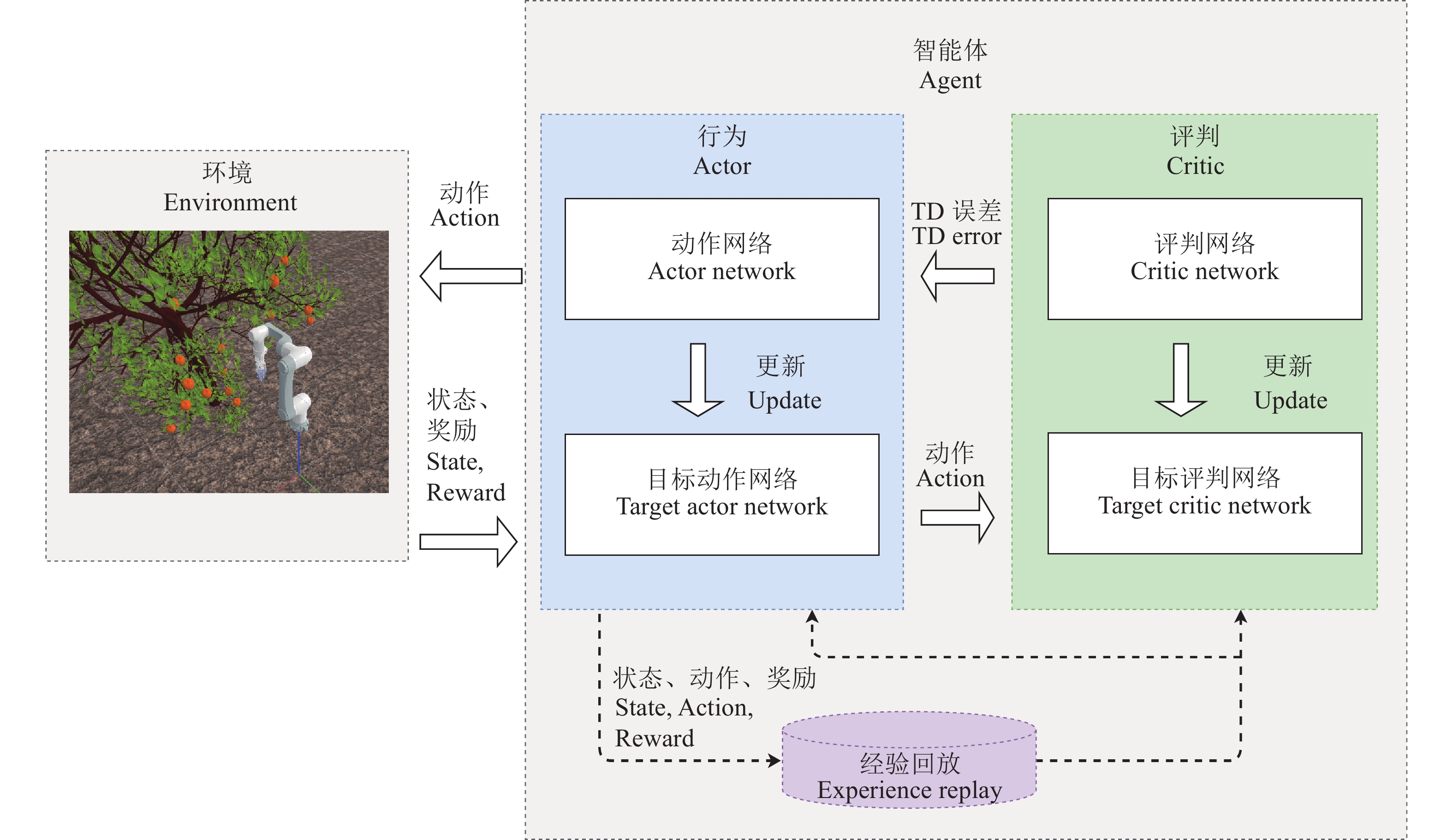
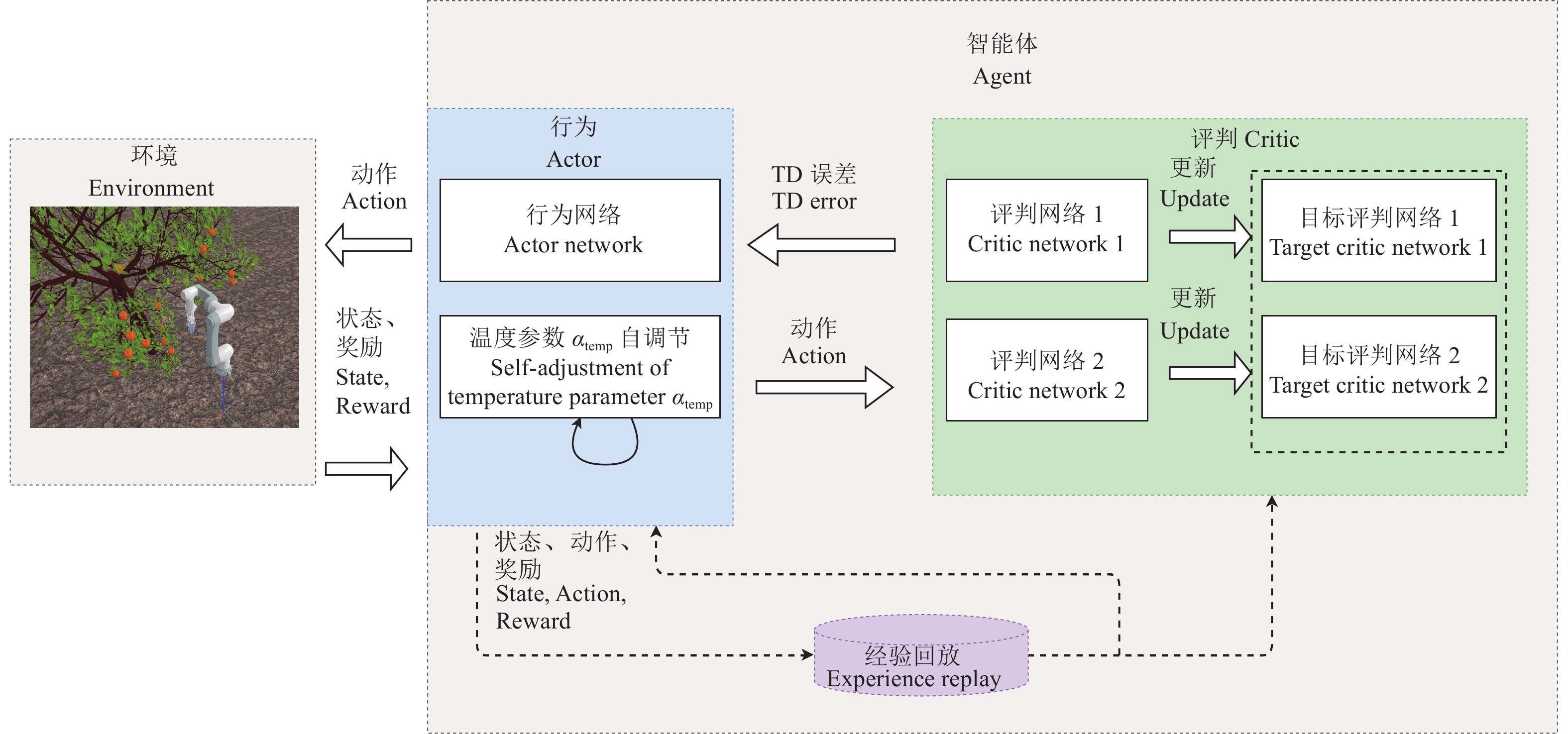
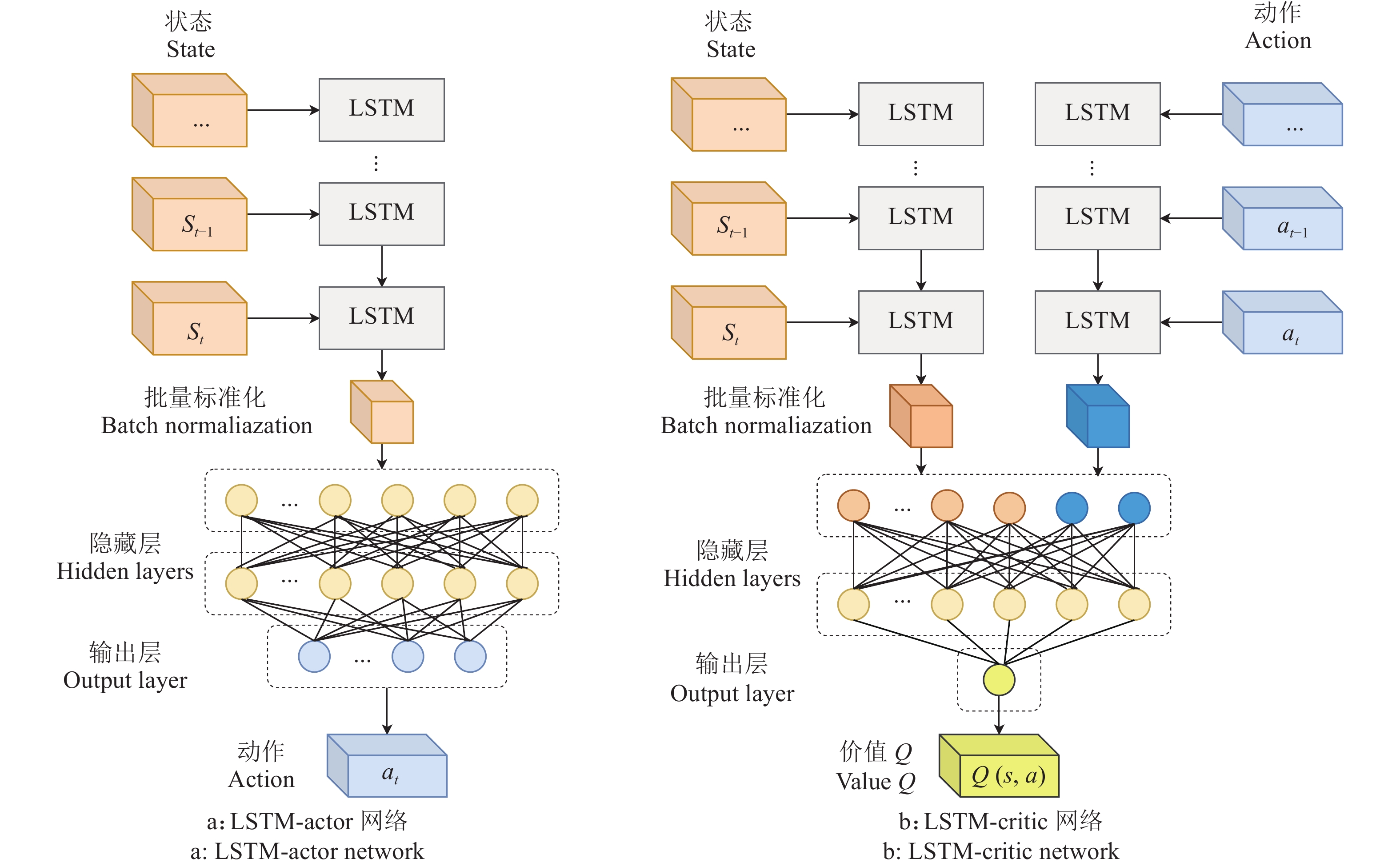
方法首先,通过强化学习方法进行采摘路径规划问题求解,设计了结合人工势场的强化学习方法;其次,引入长短期记忆(Longshort term memory,LSTM)结构对2种DRL算法的Actor网络和Critic网络进行改进;最后,在3种不同的非结构化柑橘果树环境训练DRL算法对采摘机械臂进行路径规划。
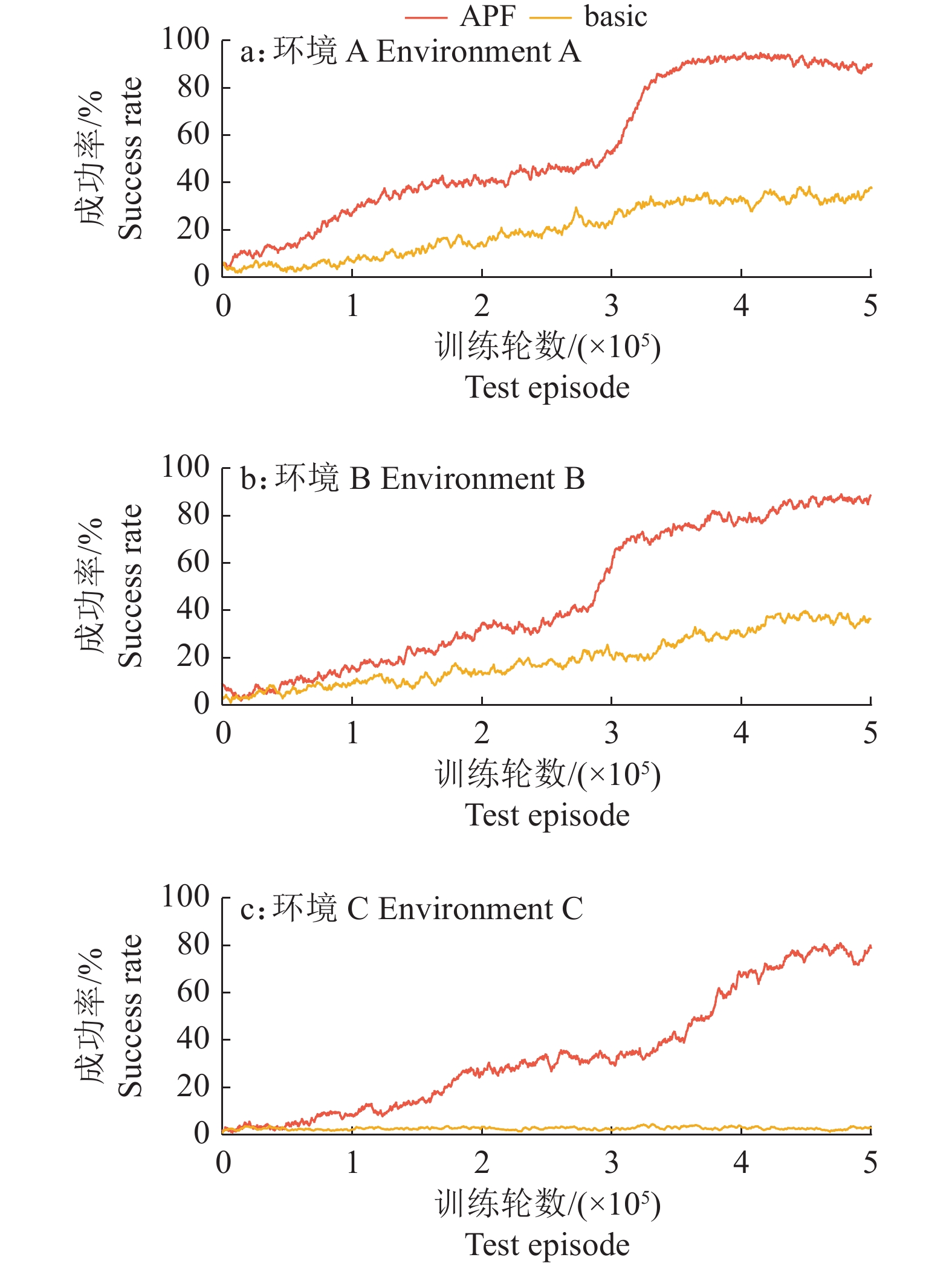
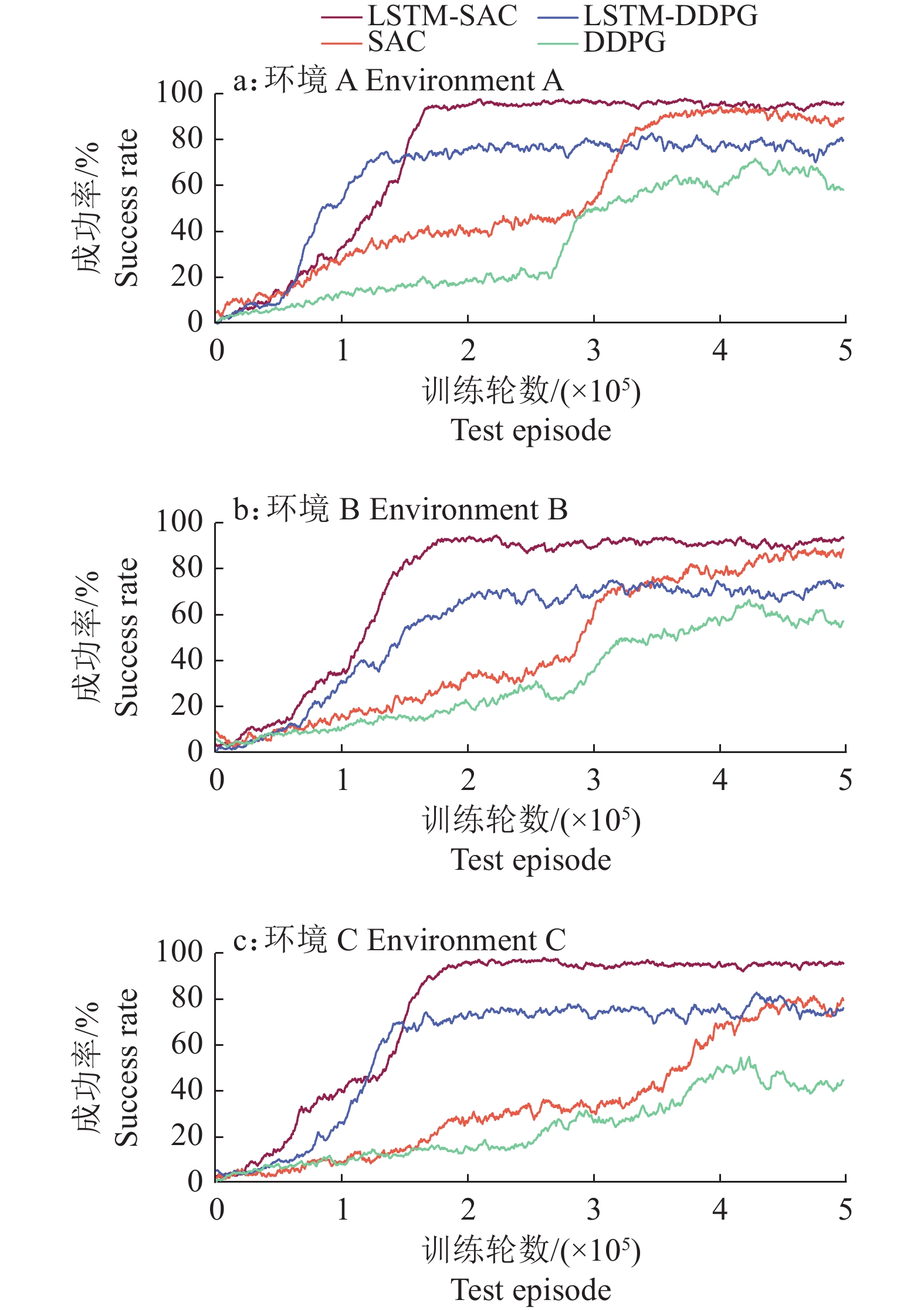
结果仿真对比试验表明:结合人工势场的强化学习方法有效提高了采摘机械臂路径规划的成功率;引入LSTM结构的方法可使深度确定性策略梯度(Deep deterministic policy gradient,DDPG)算法的收敛速度提升57.25%,路径规划成功率提升23.00%;使软行为评判(Soft actor critic,SAC)算法的收敛速度提升53.73%,路径规划成功率提升9.00%;与传统算法RRT-connect(Rapidly exploring random trees connect)对比,引入LSTM结构的SAC算法使规划路径长度缩短了16.20%,路径规划成功率提升了9.67%。
结论所提出的路径规划方法在路径规划长度、路径规划成功率方面存在一定优势,可为解决采摘机器人在非结构化环境下的路径规划问题提供参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to solve the problems of poor training efficiency and low success rate of picking path planning of manipulator using deep reinforcement learning (DRL), this study proposed a path planning method combined with DRL and artificial potential field for citrus picking manipulator in unstructured environments.
MethodFirstly, the picking path planning problem was solved by the DRL with artificial potential field method. Secondly, the longshort term memory (LSTM) structure was introduced to improve the Actor network and Critic network of two DRL algorithms. Finally, the DRL algorithms were trained in three different unstructured citrus growing environments to perform path planning for picking manipulator.
ResultThe comparison of simulation experiments showed that the success rate of path planning was effectively improved by combining DRL with the artificial potential field method, the method with LSTM structure improved the convergence speed of the deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithm by 57.25% and the success rate of path planning by 23.00%. Meanwhile, the method improved the convergence speed of the soft actor critic (SAC) algorithm by 53.73% and the path planning success rate by 9.00%. Compared with the traditional algorithm RRT-connect (Rapidly exploring random trees connect), the SAC algorithm with LSTM structure shortened the planned path length by 16.20% and improved the path planning success rate by 9.67%.
ConclusionThe proposed path planning method has certain advantages for path planning length and path planning success rate, which can provide references for solving path planning problems of picking robots in unstructured environments.
-
Keywords:
- Picking manipulator /
- Citrus /
- Path planning /
- Deep reinforcement learning /
- Unstructured environment /
- LSTM
-
-
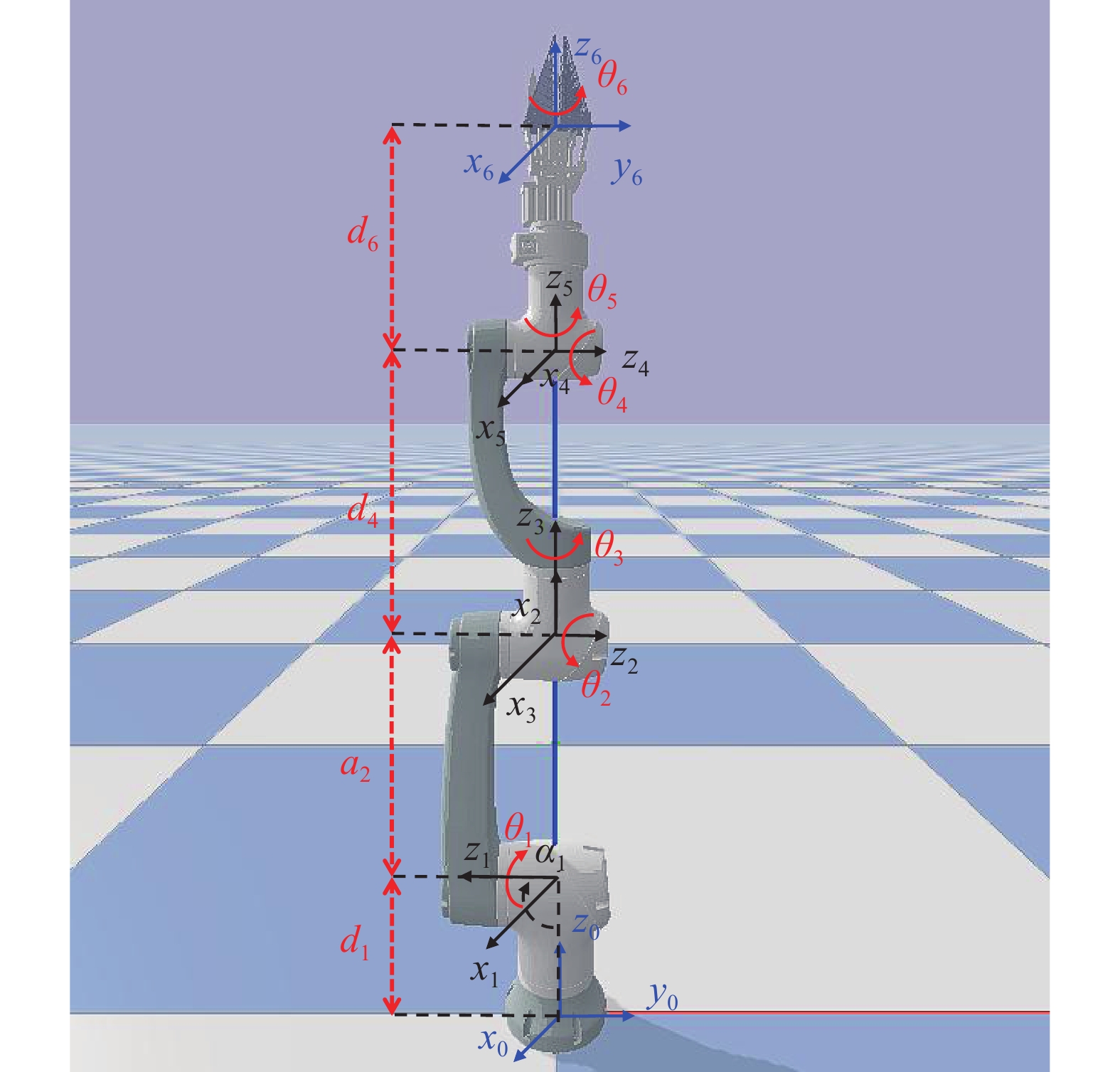
图 1 采摘机械臂
θ:关节角;d:关节偏移量;a:连杆长度;α:连杆扭转角;xyz:机器人坐标系,其中,蓝色坐标系为机械臂的原点和末端坐标系,黑色坐标系为关节坐标系
Figure 1. Picking manipulator
θ: Joint angle; d: Joint distance; a: Link length; α: Link twist angle; xyz: Robot coordinate system, in which the blue coordinate system is the origin and end coordinate system of the manipulator, and the black coordinate system is the joint coordinate system
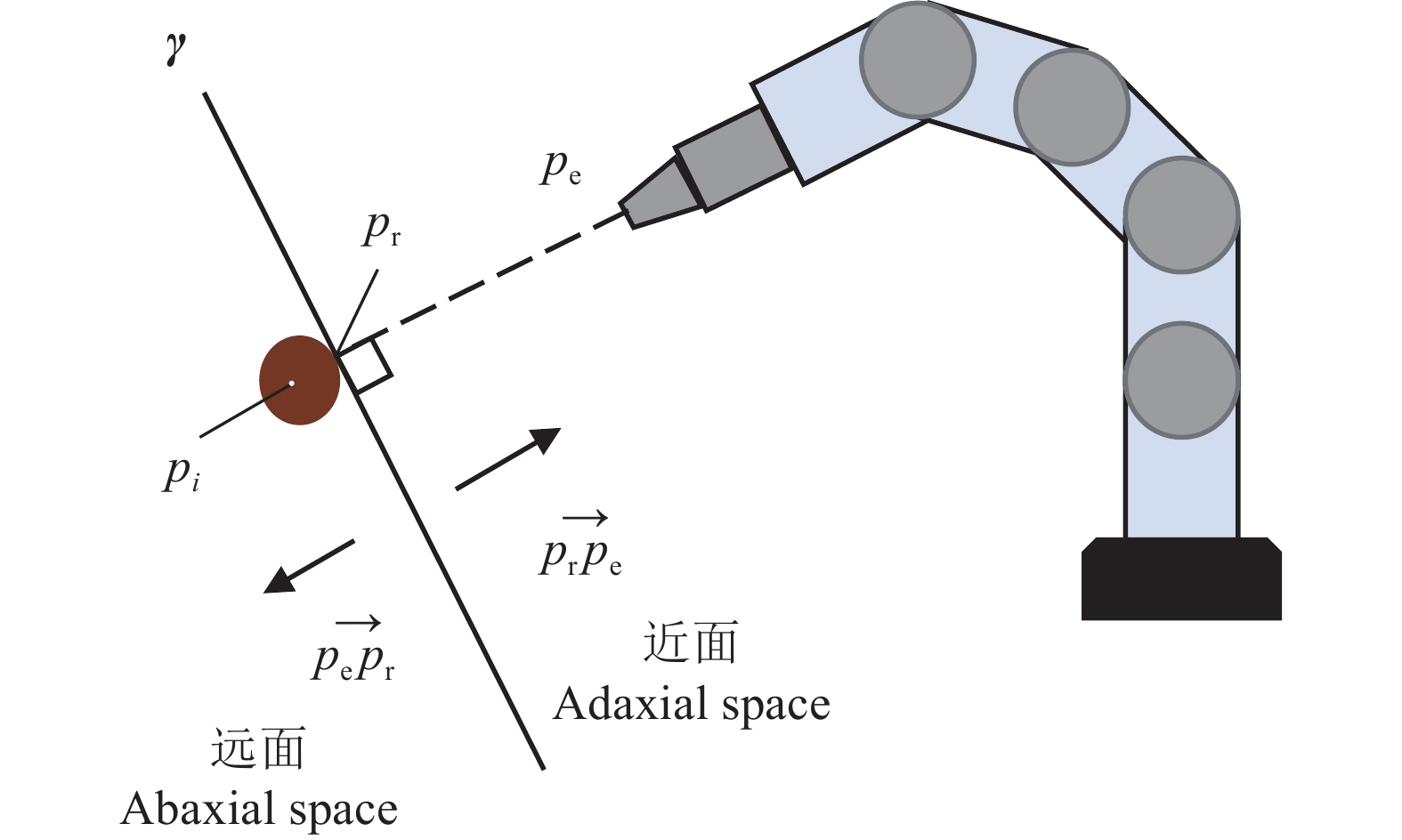
图 4 二维采摘平面
γ:采摘平面,$ {p_i} $:枝干横截面中心点,$ {p_{\rm{e}}} $:末端执行器,$ {p_{\rm{r}}} $:线段$ {p_i}{p_{\rm{e}}} $与横截面的交点,$ \overrightarrow {{p_{\rm{r}}}{p_{\rm{e}}}} $:采摘平面法向量,$ \overrightarrow {{p_{\rm{e}}}{p_{\rm{r}}}} $:采摘平面法向量(方向与$ \overrightarrow {{p_{\rm{r}}}{p_{\rm{e}}}} $相反)
Figure 4. 2D picking plane
γ: Picking plane, $ {p_i} $: Center point of branch cross section, $ {p_{\rm{e}}} $: End effector, $ {p_{\rm{r}}} $: Intersection of line segment $ {p_i}{p_{\rm{e}}} $ and cross section, $ \overrightarrow {{p_{\rm{r}}}{p_{\rm{e}}}} $: Normal vector of picking plane, $ \overrightarrow {{p_{\rm{e}}}{p_{\rm{r}}}} $: Normal vector of picking plane(opposite direction to $ \overrightarrow {{p_{\rm{r}}}{p_{\rm{e}}}} $)
表 1 采摘机械臂D-H参数1)
Table 1 D-H parameters of picking manipulator
关节编号 Joint No. θ d/m a/m α/(°) 1 $ {\theta _1} $ 0.22 0 90 2 $ {\theta _2} $ 0 0.38 180 3 $ {\theta _3} $ 0 0 90 4 $ {\theta _{\text{4}}} $ 0.42 0 −90 5 $ {\theta _{\text{5}}} $ 0 0 90 6 $ {\theta _{\text{6}}} $ 0.4 0 0 1)θ:关节角,d:关节偏移量,a:连杆长度,α:连杆扭转角 1)θ: Joint angle, d: Joint distance, a: Link length, α: Link twist angle 表 2 不同算法在3种环境中的试验结果1)
Table 2 Experiment results of different algorithms in three environments
环境 Environment 算法 Algorithm t/s l/m 成功率/% Success rate A LSTM-SAC 0.03 0.721 96 LSTM-DDPG 0.03 0.764 80 SAC 0.05 1.237 90 DDPG 0.05 1.432 58 RRT-connect 7.28 0.813 90 RRT 11.36 0.896 85 B LSTM-SAC 0.04 1.103 93 LSTM-DDPG 0.04 1.864 72 SAC 0.06 2.034 88 DDPG 0.07 2.339 57 RRT-connect 9.64 1.337 81 RRT 17.32 1.431 77 C LSTM-SAC 0.04 0.793 95 LSTM-DDPG 0.04 0.937 76 SAC 0.06 1.361 79 DDPG 0.07 1.581 44 RRT-connect 8.72 0.973 84 RRT 16.56 1.038 81 1) t:平均规划耗时;l:路径平均长度 1) t: Average planning time; l: Average path length -
[1] 常有宏, 吕晓兰, 蔺经, 等. 我国果园机械化现状与发展思路[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2013, 34(6): 21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5553.2013.06.007 [2] 徐丹琦. 基于kinect相机的自然生长状态下果树枝干的三维构建[D]. 桂林: 广西师范大学, 2021. [3] 崔永杰, 王寅初, 何智, 等. 基于改进RRT算法的猕猴桃采摘机器人全局路径规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(6): 151-158. [4] 张勤, 乐晓亮, 李彬, 等. 基于CTB-RRT~*的果蔬采摘机械臂运动路径规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(10): 129-136. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.10.013 [5] 王怀震, 高明, 王建华, 等. 基于改进RRT~*-Connect算法的机械臂多场景运动规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2022, 53(4): 432-440. [6] 马宇豪, 梁雁冰. 一种基于六次多项式轨迹规划的机械臂避障算法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2020, 38(2): 392-400. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2020.02.021 [7] 贾庆轩, 陈钢, 孙汉旭, 等. 基于A*算法的空间机械臂避障路径规划[J]. 机械工程学报, 2010, 46(13): 109-115. [8] 张敦凤, 赵皓, 徐亮, 等. 基于栅格法的机械臂工作空间解析方法研究[J]. 制造业自动化, 2019, 41(4): 69-70. [9] 张强, 陈兵奎, 刘小雍, 等. 基于改进势场蚁群算法的移动机器人最优路径规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(5): 23-32. [10] 刘可, 李可, 宿磊, 等. 基于蚁群算法与参数迁移的机器人三维路径规划方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(1): 29-36. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.01.003 [11] KHATIB O. Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots[M]// COX I J, WILFONG G T. Autonomous robot vehicles. New York: Springer, 1986: 396-404.
[12] 史亚飞, 张力, 刘子煊, 等. 基于速度场的人工势场法机械臂动态避障研究[J]. 机械传动, 2020, 44(4): 38-44. [13] WANG W, ZHU M, WANG X, et al. An improved artificial potential field method of trajectory planning and obstacle avoidance for redundant manipulators[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2018, 15(5): 1729881418799562.
[14] 谢龙, 刘山. 基于改进势场法的机械臂动态避障规划[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(9): 1239-1249. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.70187 [15] ZHANG N, ZHANG Y, MA C, et al. Path planning of six-DOF serial robots based on improved artificial potential field method[C]// 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Macau: IEEE, 2017.
[16] GU S, HOLLY E, LILLICRAP T, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for robotic manipulation with asynchronous off-policy updates[C]//2017 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Singapore: IEEE, 2017: 3389-3396.
[17] WEN S, CHEN J, WANG S, et al. Path planning of humanoid arm based on deep deterministic policy gradient[C]//2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). Kuala Lumpur: IEEE, 2018: 1755-1760.
[18] KIM M, HAN D, PARK J, et al. Motion planning of robot manipulators for a smoother path using a twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient with hindsight experience replay[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(2): 575. doi: 10.3390/app10020575
[19] LU X, LEE K, ABBEEL P, et al. Dynamics generalization via information bottleneck in deep reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2020: 2008.00614 [2020-08-03]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00614.
[20] BANINO A, BADIA A, WALKER J, et al. CoBERL: Contrastive BERT for reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2021: 2107.05431 [2022-02-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.05431.
[21] LIN G, ZHU L, LI J, et al. Collision-free path planning for a guava-harvesting robot based on recurrent deep reinforcement learning[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2021, 188: 106350. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2021.106350
[22] 毕松, 张潞. 自然环境下的柑橘采摘点识别方法研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(12): 227-231. [23] 杨长辉, 刘艳平, 王毅, 等. 自然环境下柑橘采摘机器人识别定位系统研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(12): 14-22. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.12.002 [24] 尹建军, 武传宇, YANG S, 等. 番茄采摘机器人机械臂避障路径规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2012, 43(12): 171-175. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.12.031 [25] CAO X, ZOU X, JIA C, et al. RRT-based path planning for an intelligent litchi-picking manipulator[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2019, 156: 105-118. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2018.10.031
[26] 郑嫦娥, 高坡, GAN H, 等. 基于分步迁移策略的苹果采摘机械臂轨迹规划方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(12): 15-23. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.12.002 [27] 邓钊. 椪柑省力化疏果和促进果实膨大技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018. [28] 张哲. 柑橘采摘机器人采摘姿态及序列研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2018. [29] 熊俊涛, 李中行, 陈淑绵, 等. 基于深度强化学习的虚拟机器人采摘路径避障规划[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(S2): 1-10. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.S2.001 [30] ZHANG T, ZHANG K, LIN J, et al. Sim2real learning of obstacle avoidance for robotic manipulators in uncertain environments[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 7(1): 65-72.
[31] XIE J, SHAO Z, LI Y, et al. Deep reinforcement learning with optimized reward functions for robotic trajectory planning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 105669-105679. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2932257
[32] DUGULEANA M, BARBUCEANU F, TEIRELBAR A, et al. Obstacle avoidance of redundant manipulators using neural networks based reinforcement learning[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2012, 28(2): 132-146.
[33] LILLICRAP T, HUNT J, PRITZEL A, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2015: 1509.02971 [2019-07-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.02971.
[34] HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, ABBEEL P, et al. Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2018: 1801.01290 [2018-08-08]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.01290.
[35] HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, HARTIKAINEN K, et al. Soft actor-critic algorithms and applications[EB/OL]. arXiv, 2018: 1812.05905 [2019-01-29]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05905.



 下载:
下载: