Design and experiment of rigid-flexible coupling rod tooth threshing device of harvester for ratooning rice
-
摘要:目的
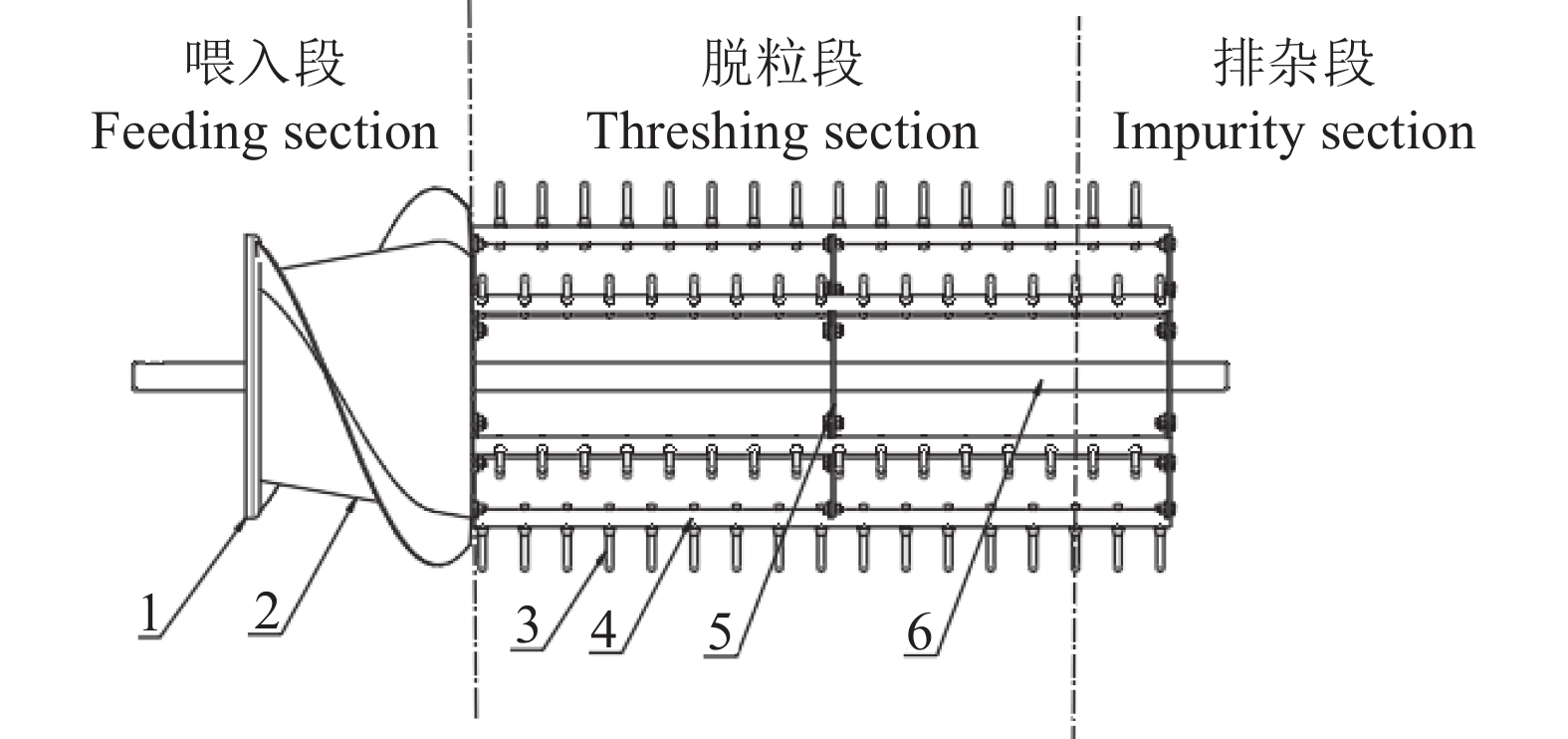
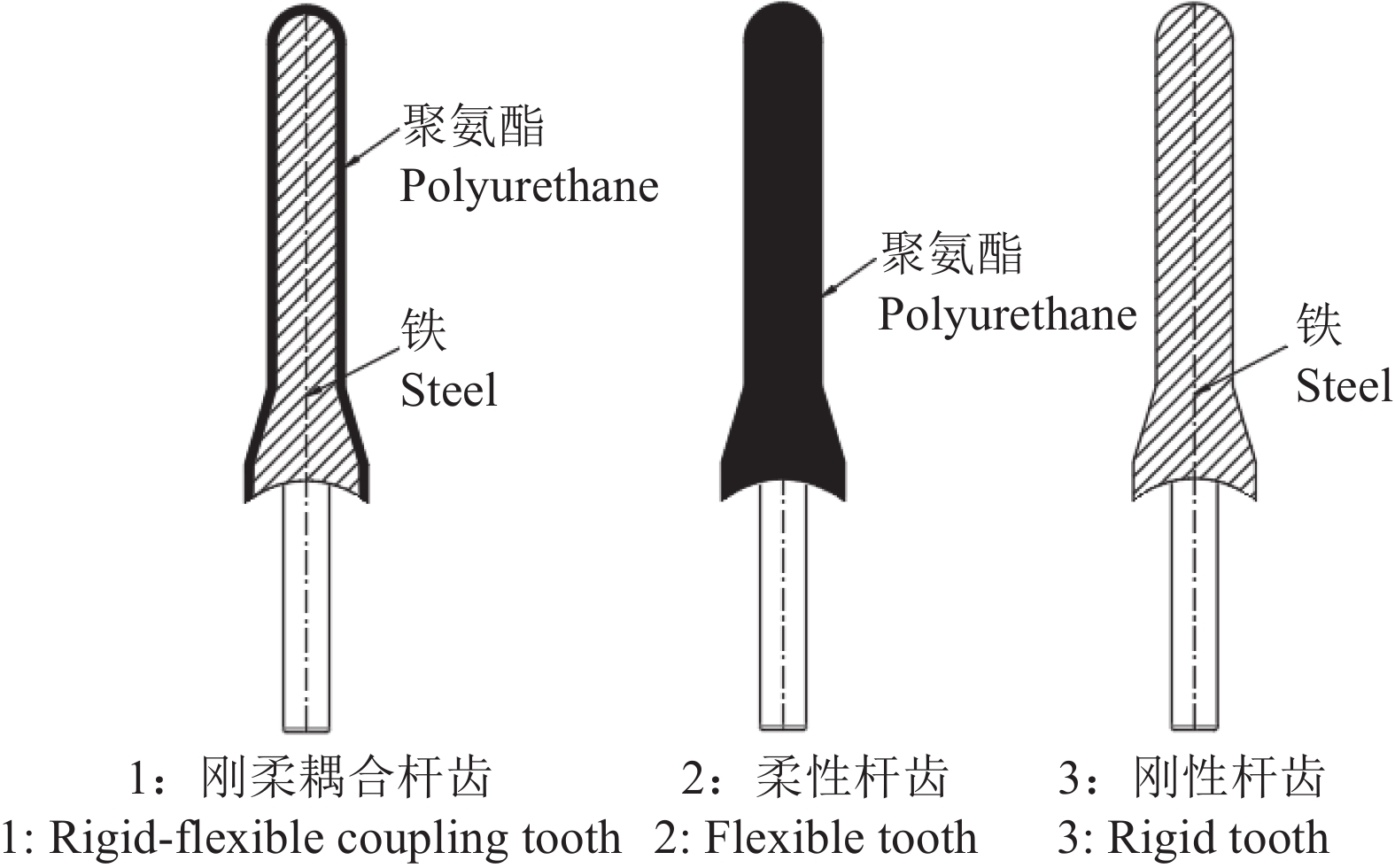
针对再生稻头季收获时籽粒和秸秆含水率较高,籽粒与稻穗的黏结力较大,采用传统刚性杆齿脱粒装置的收割机收获时会导致大量籽粒破碎的问题,在轴流式脱粒滚筒的基础上设计了一种刚柔耦合杆齿的脱粒滚筒。
方法采用EDEM仿真软件对脱粒过程进行仿真模拟,通过后处理获得3种不同杆齿(刚性、柔性、刚柔耦合)对籽粒的平均法向打击力和切向揉搓力;以夹带损失率、破碎率和未脱净率为评价指标,分别以不同滚筒转速下的单因素和以滚筒转速、水稻籽粒含水率、杆齿种类为因素的三因素三水平进行不同杆齿的正交台架验证试验。
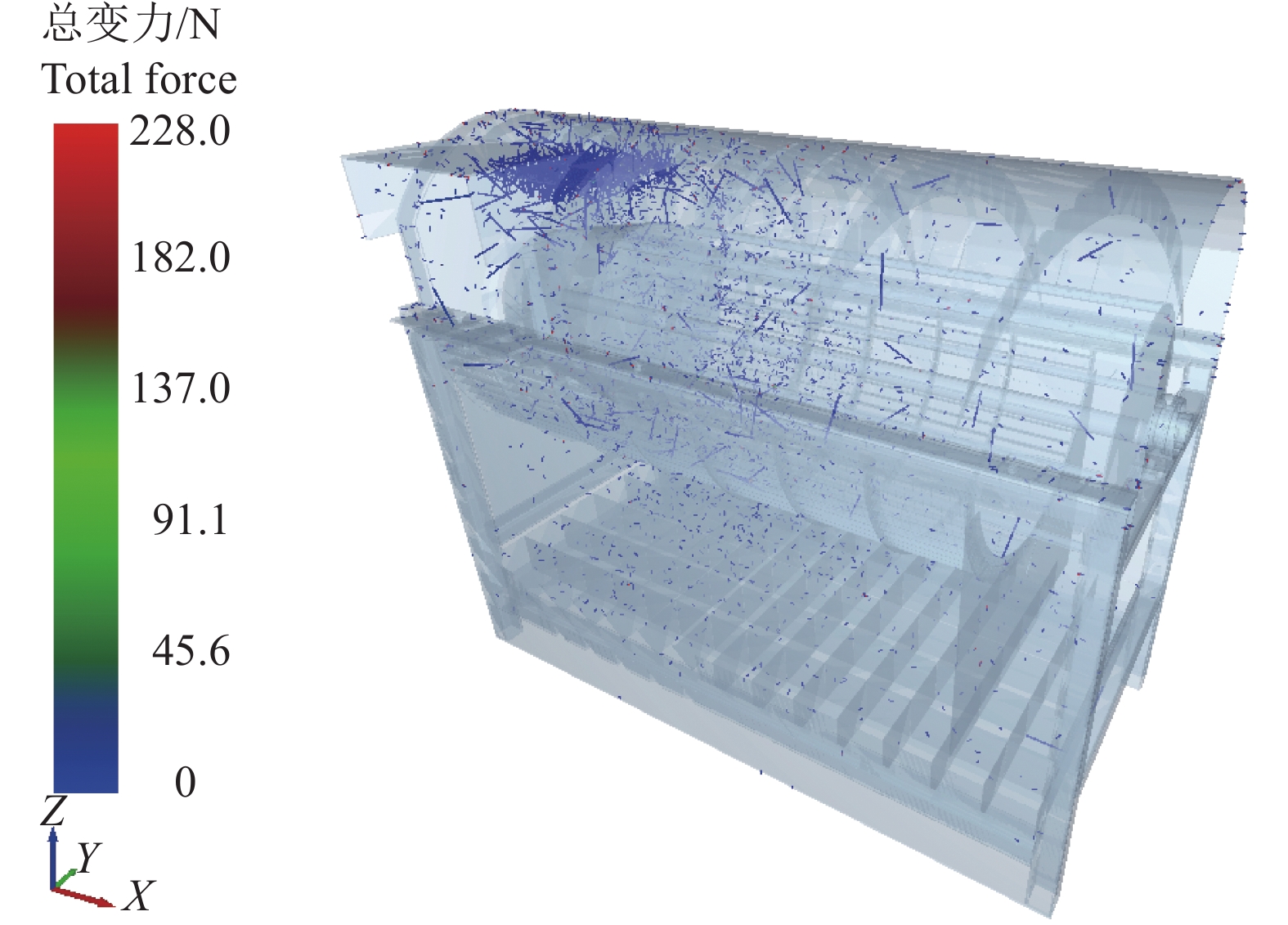
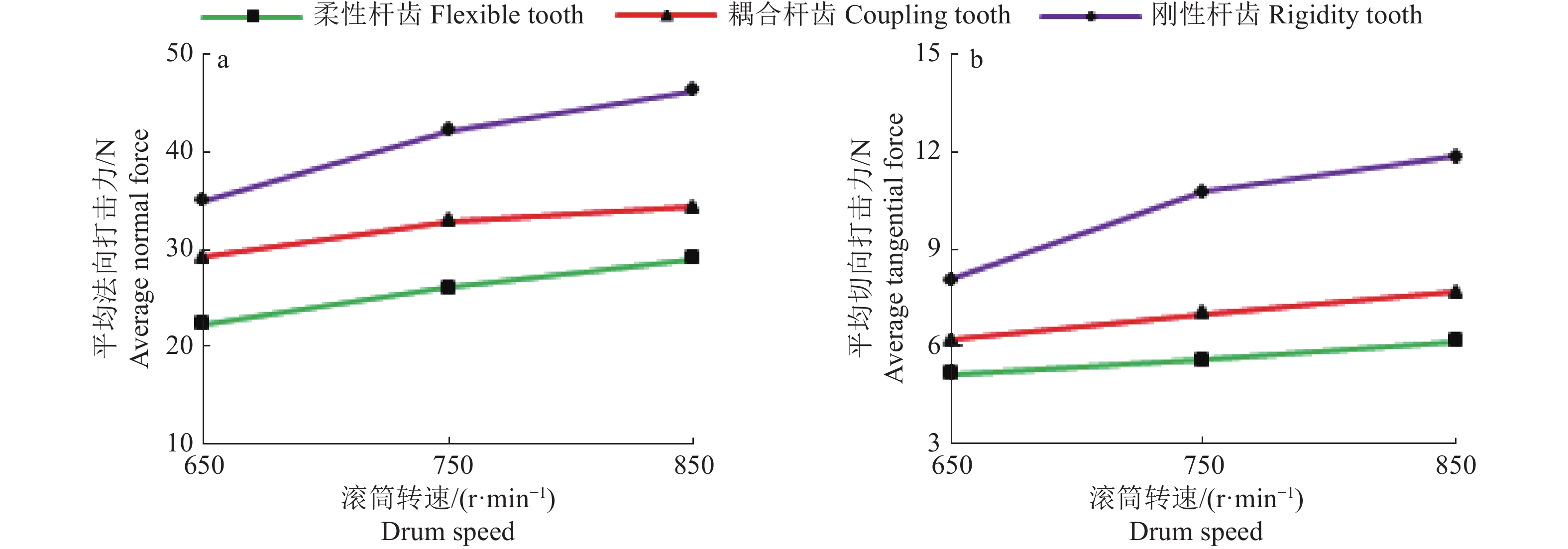
结果EDEM仿真结果表明,在滚筒转速分别为650、750和850 r/min时,3种杆齿对籽粒的平均法向打击力和切向揉搓力均表现为刚性杆齿最大、柔性杆齿最小。单因素试验结果表明,刚性杆齿脱粒装置的籽粒破碎率明显高于柔性杆齿脱粒装置和刚柔耦合脱粒装置,在滚筒转速为900 r/min时,柔性杆齿、刚性杆齿和刚柔耦合杆齿的破碎率均很高,分别为1.632%、1.925%和2.564%;柔性杆齿脱粒装置的未脱净率和夹带损失率明显高于刚性杆齿脱粒装置和刚柔耦合脱粒装置,在滚筒转速为900 r/min时,柔性杆齿、刚性杆齿和刚柔耦合杆齿的未脱净率均很低,分别为0.286%、0.071%和0.240%,在滚筒转速为850 r/min时,柔性杆齿、刚性杆齿和刚柔耦合杆齿的夹带损失率均很低,分别为1.595%、0.729%和1.341%。正交试验结果表明,影响籽粒夹带损失率和破碎率的因素顺序依次为杆齿种类 > 滚筒转速 > 籽粒含水率,影响未脱净率因素的顺序依次为杆齿种类 > 籽粒含水率 > 滚筒转速。
结论相同条件下,刚柔耦合脱粒装置能够在保证籽粒脱净率的前提下,降低籽粒破碎率。研究结果可为再生稻收割机脱粒装置的设计与田间应用提供参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn response to the problem of high moisture content of seed and straw, high bonding force between seed and rice spike at the first harvest season of ratooning rice, there will lead to large amount of broken seeds when harvested by harvesters with traditional rigid rod-tooth threshing device, a rigid-flexible coupled rod-tooth threshing drum based on the axial flow threshing drum was designed.
MethodThe EDEM discrete element simulation software was used to simulate the threshing process, and the average normal striking force and tangential kneading force of three different rod teeth (rigid, flexible, and rigid-flexible coupling) on seeds were obtained through post-processing. Using entrapment loss, breakage rate and unclean rate as the evaluation indexes, the orthogonal bench validation tests were carried out with different drum speed as single factor, and three factors (drum speed, seed moisture content, and rod teeth type) and three levels.
ResultThe EDEM simulation results showed that the average normal striking force and tangential kneading force of the three types of rod teeth on seeds were the largest for the rigid rod teeth and the smallest for the flexible rod teeth at the drum speeds of 650, 750 and 850 r/min, respectively. The results of single-factor test showed that the broken rate of seeds threshed by the rigid rod tooth threshing device was significantly higher than those of the flexible rod tooth and the rigid-flexible coupling threshing devices. The broken rates of the flexible rod tooth, rigid rod tooth and rigid-flexible coupling rod tooth were very high at 900 r/min, with the broken rates of 1.632%, 1.925% and 2.564%, respectively. The unthawed rate and the entrained loss rate of the flexible rod tooth threshing device were significantly higher than those of the rigid rod tooth and the rigid-flexible coupling threshing devices. The unthreshing rates of the flexible rod tooth, rigid rod tooth and rigid-flexible coupling rod tooth were very low at 900 r/min, with the unthreshing rates of 0.286%, 0.071% and 0.240%, respectively. The entrainment loss rate of the flexible rod tooth, rigid rod tooth and rigid-flexible coupling rod tooth were very low at 850 r/min, with the entrainment loss rates of 1.595%, 0.729% and 1.341%, respectively. The results of orthogonal test showed that the order of factor affecting seed entrainment loss and broken rate was rod tooth type > drum speed > seed moisture content, and the order of factor affecting the uncleaned rate was rod tooth type > seed moisture content > drum speed.
ConclusionUnder the same conditions, the rigid-flexible coupling threshing device can reduce the rice breaking rate while ensuring the seed removal rate. The results can provide a reference for design and application of threshing device of harvester for ratooning rice.
-
Keywords:
- Ratoon rice /
- Harvester /
- Threshing device /
- Rigid-flexible coupling /
- Rod tooth /
- EDEM simulation
-
-
图 3 水稻植株质点 Q 在螺旋喂入装置上的受力分析
T:螺旋叶片对水稻植株的法向推力;${F_f}$:螺旋叶片与水稻植株之间的摩擦力;F :${F_f}$与T形成的合力;α:水稻植株与螺旋叶片之间的摩擦角;β:螺旋叶片螺旋角;d:前段直径;L: 螺旋喂入头长度;D:后端直径;$ {v}_{x} $:水稻植株轴向喂入速度;$ {T_x} $:轴向推力
Figure 3. Force analysis of rice plant point Q on screw feeding device
T:Normal thrust of spiral blades on rice plant ears;${F_f}$:Friction between spiral blade and rice plant; F : a combined force of ${F_f}$ and T ; α: Friction angle between rice plant and spiral blad; β:Spiral blade helix angle; d:Front section diameter; L: Screw feed head length; D:Rear end diameter; $ {v}_{x} $:Axial feeding rate of rice plants; $ {T_x} $ :Axial thrust
表 1 脱粒装置及籽粒力学参数
Table 1 Threshing device and grain mechanical parameters
项目
Item泊松比
Poisson’s
ratio剪切模量/
MPa
Shear modulus密度/
(kg· $ {\mathrm{m}}^{-2} $)
Density籽粒 Grain 0.30 26 1300 短秸秆 Short straw 0.40 10 100 聚氨酯 Polyurethane 0.28 0.028 1072 脱粒装置 Threshing device 0.30 70000 7800 表 2 在EDEM中的各接触系数
Table 2 Contact coefficients in EDEM
接触物
Contact substances恢复系数
Restitution coefficient静摩擦系数
Static friction coefficient滚动摩擦系数
Rolling friction coefficient籽粒−籽粒 Grain-grain 0.20 1.00 0.01 籽粒−短秸秆 Grain- short straw 0.20 0.80 0.01 籽粒−脱粒装置 Grain-threshing device 0.50 0.58 0.01 短秸秆−短秸秆 Short straw - short straw 0.20 0.90 0.01 短秸秆−脱粒装置 Short straw- threshing device 0.20 0.80 0.01 籽粒−聚氨酯 Grain- polyurethane 0.40 0.50 0.01 短秸秆−聚氨酯 Short straw- polyurethane 0.35 0.40 0.01 表 3 正交试验的因素和水平
Table 3 Factors and levels of orthogonal test
水平
Level滚筒转速/(r·min−1)
Drum speed
(A)籽粒含水率/%
Grain moisture content
(B)杆齿
Rod tooth
(C)1 650 25.62 刚性齿 2 750 28.26 耦合齿 3 850 31.31 柔性齿 表 4 脱粒装置性能单因素试验结果
Table 4 Single factor test results of threshing device performance
% 滚筒转速/(r·min−1)
Drum speed夹带损失率 Entrainment loss rate 破碎率 Breakage rate 未脱净率 Unclean rate 刚性
Rigidity柔性
Flexible耦合
Coupling刚性
Rigidity柔性
Flexible耦合
Coupling刚性
Rigidity柔性
Flexible耦合
Coupling650 1.097 2.312 1.261 1.741 1.026 1.165 0.169 0.351 0.379 700 1.164 2.113 1.368 1.864 1.107 1.198 0.157 0.543 0.402 750 1.315 1.908 1.634 1.955 1.149 1.214 0.149 0.615 0.435 800 1.172 1.732 1.606 2.143 1.156 1.568 0.133 0.434 0.349 850 0.729 1.595 1.341 2.189 1.571 1.621 0.101 0.335 0.273 900 0.933 1.012 1.453 2.564 1.632 1.925 0.071 0.286 0.240 表 5 脱粒装置性能正交试验结果和极差分析
Table 5 Orthogonal test result and range analysis of threshing device performance
% 试验编号
No.of test
因素水平 Factor level 指标 Index 滚筒转速
Drum speed (A)籽粒含水率
Grain moisture content (B)杆齿
Rod tooth (C)夹带损失率
Entrainment loss rate破碎率
Breakage rate未脱净率
Unclean rate1 1 1 1 1.370 1.658 0.315 2 1 2 3 1.970 0.786 0.462 3 1 3 2 1.850 0.972 0.577 4 2 1 3 1.860 0.876 0.434 5 2 2 2 1.170 1.275 0.374 6 2 3 1 0.910 2.132 0.249 7 3 1 2 0.980 1.161 0.312 8 3 2 1 0.160 2.564 0.097 9 3 3 3 1.530 1.324 0.563 指标 Index 因素 Factor $ {K}_{1} $ $ {K}_{2} $ $ {K}_{3} $ $ {{\bar K}_{1}} $ $ {{\bar K}_{2}} $ $ {{\bar K}_{3}} $ R 夹带损失率
Entrainment loss rateA 5.190 3.940 2.670 1.730 1.310 0.890 0.840 B 4.210 3.300 4.290 1.400 1.100 1.430 0.330 C 2.440 4.000 5.360 0.810 1.330 1.790 0.980 破碎率
Breakage rateA 3.416 4.283 5.049 1.138 1.428 1.683 0.545 B 5.370 4.625 4.428 1.074 1.542 1.476 0.468 C 6.354 3.390 2.986 2.118 1.130 0.995 1.123 未脱净率
Unclean rateA 1.354 1.173 0.972 0.451 0.391 0.324 0.127 B 1.061 0.933 1.356 0.354 0.311 0.452 0.141 C 0.661 1.263 1.459 0.220 0.421 0.486 0.286 -
[1] 王飞, 彭少兵. 水稻绿色高产栽培技术研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2018, 30(10): 1129-1136. [2] 徐富贤, 熊洪, 张林, 等. 再生稻产量形成特点与关键调控技术研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(9): 1702-1717. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2015.09.04 [3] 刘伟健, 罗锡文, 曾山, 等. 履带式再生稻收获机田间转弯机理研究与性能试验[J/OL]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), [2022-02-27]. https://doi.org/10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211178. [4] 卢康, 张国忠, 彭少兵, 等. 双割台双滚筒全履带式再生稻收割机的设计与性能试验[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2017, 36(5): 108-114. [5] 徐立章, 李耀明, 丁林峰. 水稻谷粒与脱粒元件碰撞过程的接触力学分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008, 25(6): 146-149. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2008.06.029 [6] 徐立章, 李耀明. 水稻谷粒冲击损伤临界速度分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2009, 40(8): 54-57. [7] 常光宝. 水稻谷粒的力学性能及脱粒损伤机理研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2009. [8] 李佳圣, 李耀明, 徐立章, 等. 再生稻联合收获机脱粒分离装置的设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究, 2022, 44(2): 85-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2022.02.015 [9] 王显仁, 李耀明, 徐立章. 水稻谷粒的机械损伤机理及试验[J]. 农机化研究, 2007, 29(12): 141-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2007.12.044 [10] 王显仁, 李耀明, 徐立章. 水稻脱粒破碎率与脱粒元件速度关系研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(8): 16-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.08.003 [11] 谢方平, 罗锡文, 卢向阳, 等. 柔性杆齿滚筒脱粒机理[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(8): 110-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2009.08.020 [12] 谢方平, 罗锡文, 苏爱华, 等. 刚性弓齿与杆齿及柔性齿的脱粒对比试验[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 31(6): 648-651. [13] 师清翔, 刘师多, 姬江涛, 等. 控速喂入柔性脱粒机理研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 1996, 12(2): 177-180. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.1996.02.036 [14] 师清翔, 刘师多, 姬江涛, 等. 水稻的控速喂入柔性脱粒试验研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 1996, 27(1): 41-46. [15] 付君, 张屹晨, 程超, 等. 刚柔耦合式小麦脱粒弓齿设计及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 730-738. [16] 任述光, 谢方平, 罗锡文, 等. 柔性齿与刚性齿脱粒水稻功耗比较分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(5): 12-18. [17] 钱震杰, 金诚谦, 袁文胜, 等. 柔性脱粒齿杆与谷物含摩擦打击动力学模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1121-1130. [18] 林文雄, 陈鸿飞, 张志兴, 等. 再生稻产量形成的生理生态特性与关键栽培技术的研究与展望[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2015, 23(4): 392-401. [19] 康艳, 金诚谦, 陈艳普, 等. 谷物籽粒损伤研究现状[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2020, 41(7): 94-104. [20] MIU P I, KUTZBACH H D. Modeling and simulation of rain threshing and separation in threshing units: Part I[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2008, 60(1): 96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2007.07.003
[21] 中国农业机械化科学研究院. 农业机械设计手册(上、下册)[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2007: 928-933. [22] 王立军, 彭博, 宋慧强. 玉米收获机聚氨酯橡胶筛筛分性能仿真与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(7): 90-96. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.07.011 [23] ZHAN S, LI Y M, DONG Y H, et al. Simulation of rice threshing performance with concentric and non-concentric threshing gaps[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2020, 197: 270-284. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2020.05.020
[24] LI X, DU Y, LIU L, et al. Research on the constitutive model of low-damage corn threshing based on DEM[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2022, 194: 106722. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2022.106722
[25] 谢干, 张国忠, 付建伟, 等. 鼓形与圆柱形杆齿式纵轴流脱粒滚筒功耗对比试验[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2021, 40(1): 202-209. [26] 陈艳普, 康艳, 王廷恩, 等. 大豆收获机纵轴流柔性脱粒装置脱出物分布规律[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2020, 25(9): 104-111. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2020.09.11 [27] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督监督检验检疫局. 农业机械试验条件测定方法的一般规定: GB/T 5256—2008 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. [28] 农业部农业机械试验鉴定总站. 水稻联合收割机作业质量: GB/T 8097—2008[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008.




 下载:
下载: