The assessment of litchi flowering growth based on remote sensing image of convolutional neural network
-
摘要:目的
通过无人机获取荔枝冠层的遥感图像,评估每棵荔枝的开花率,以期为后续荔枝花期疏花保果、精准施肥施药提供决策依据。
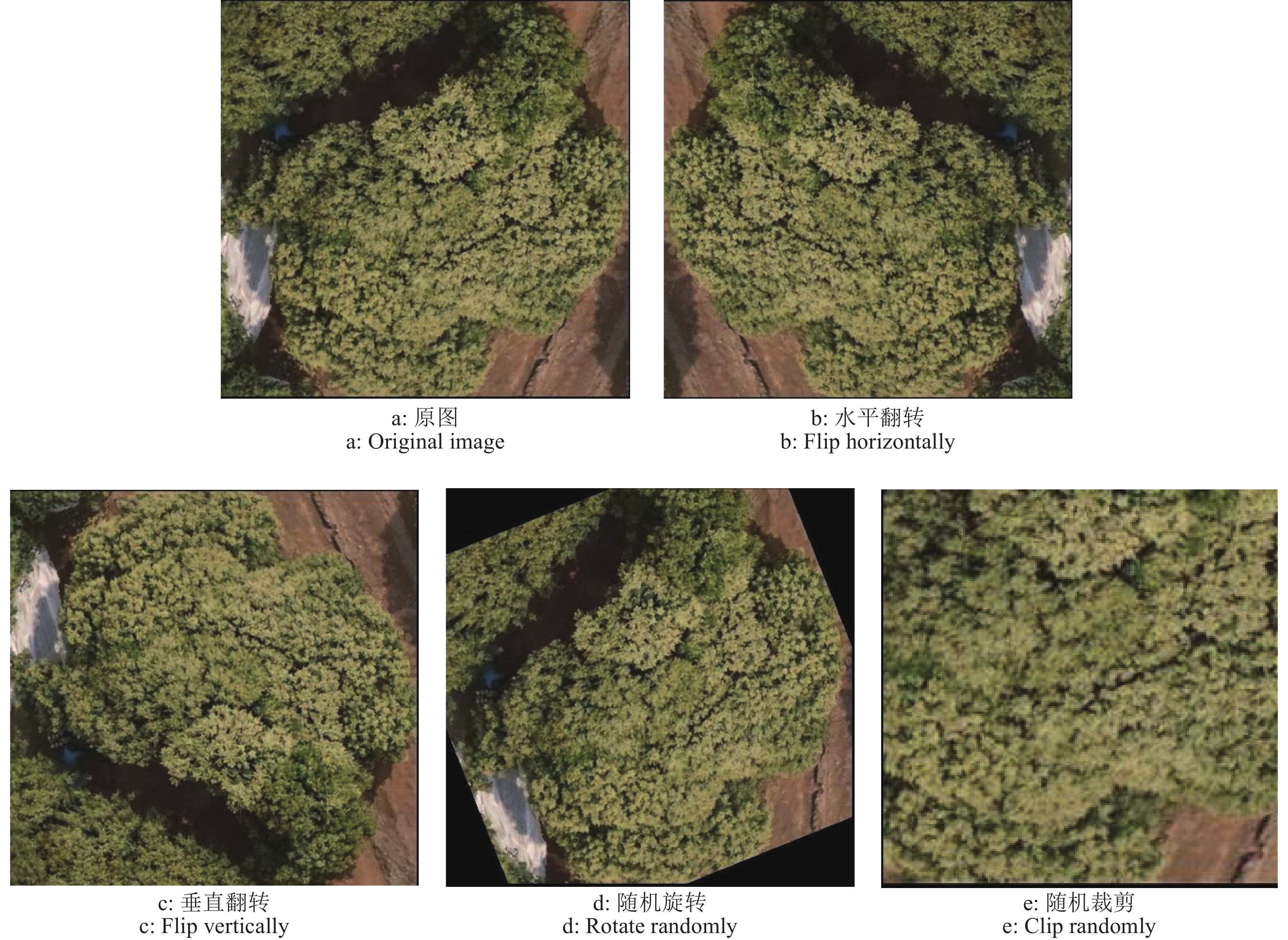
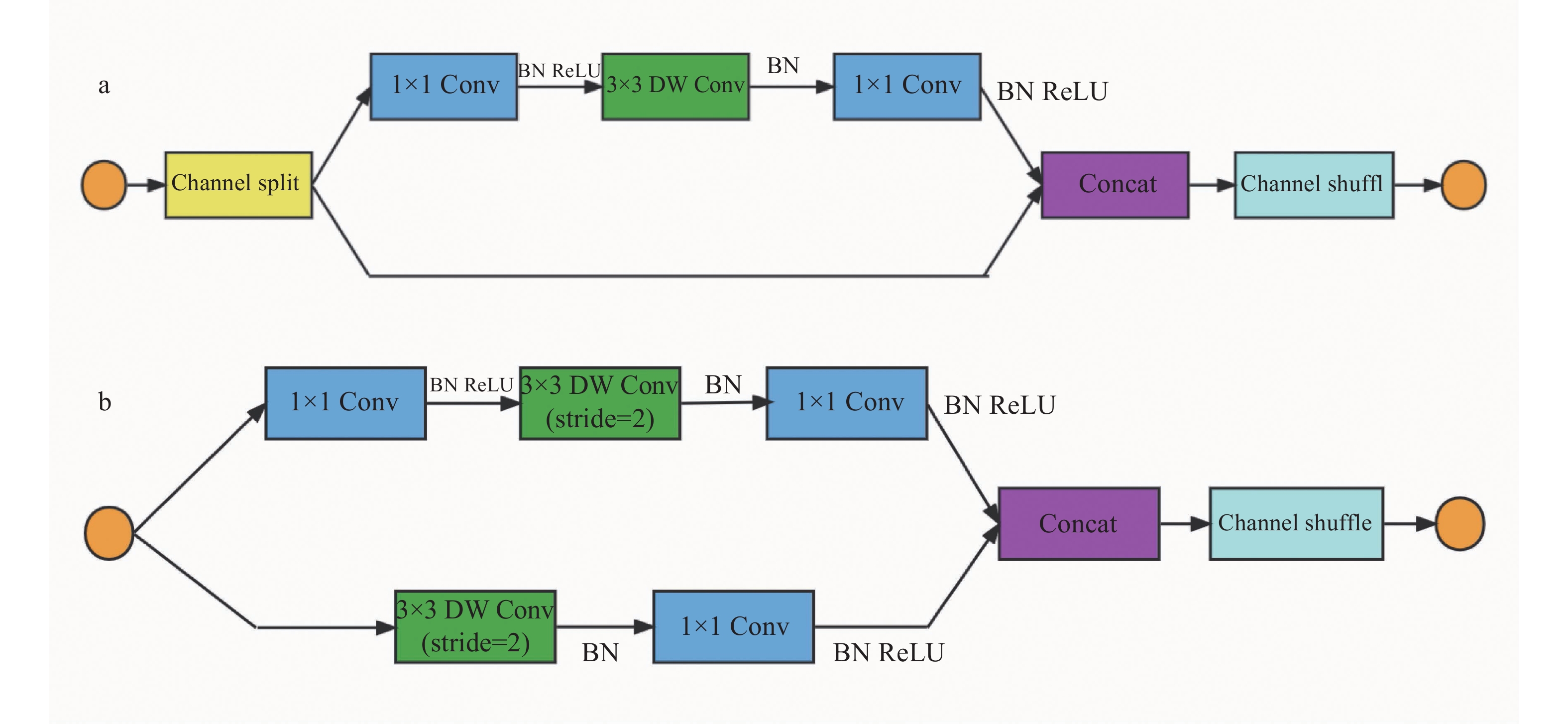
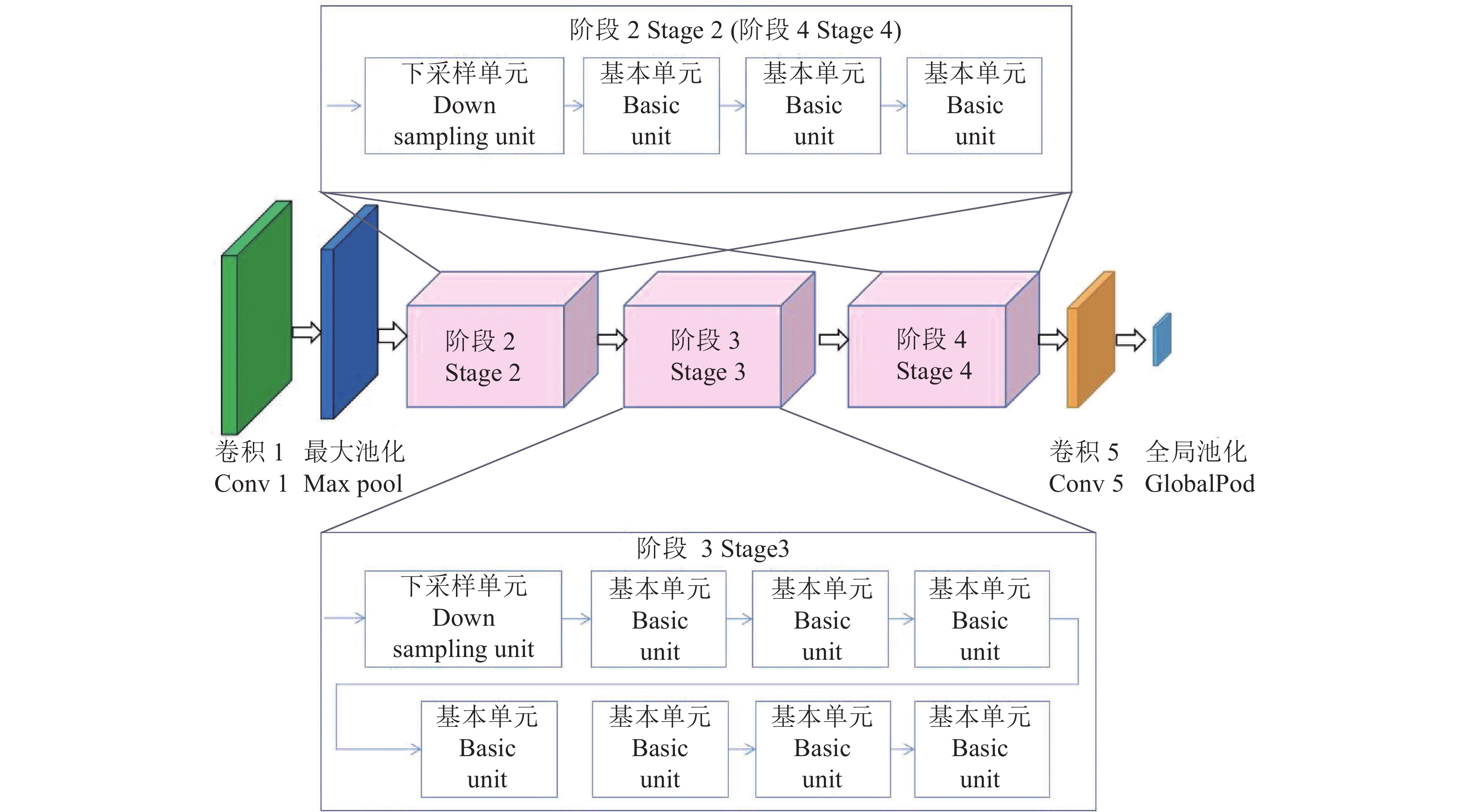
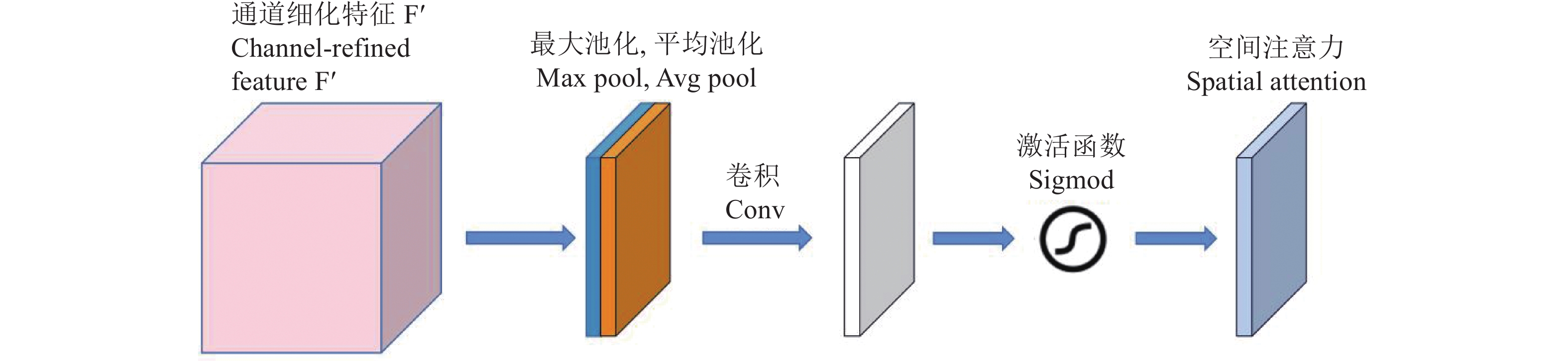
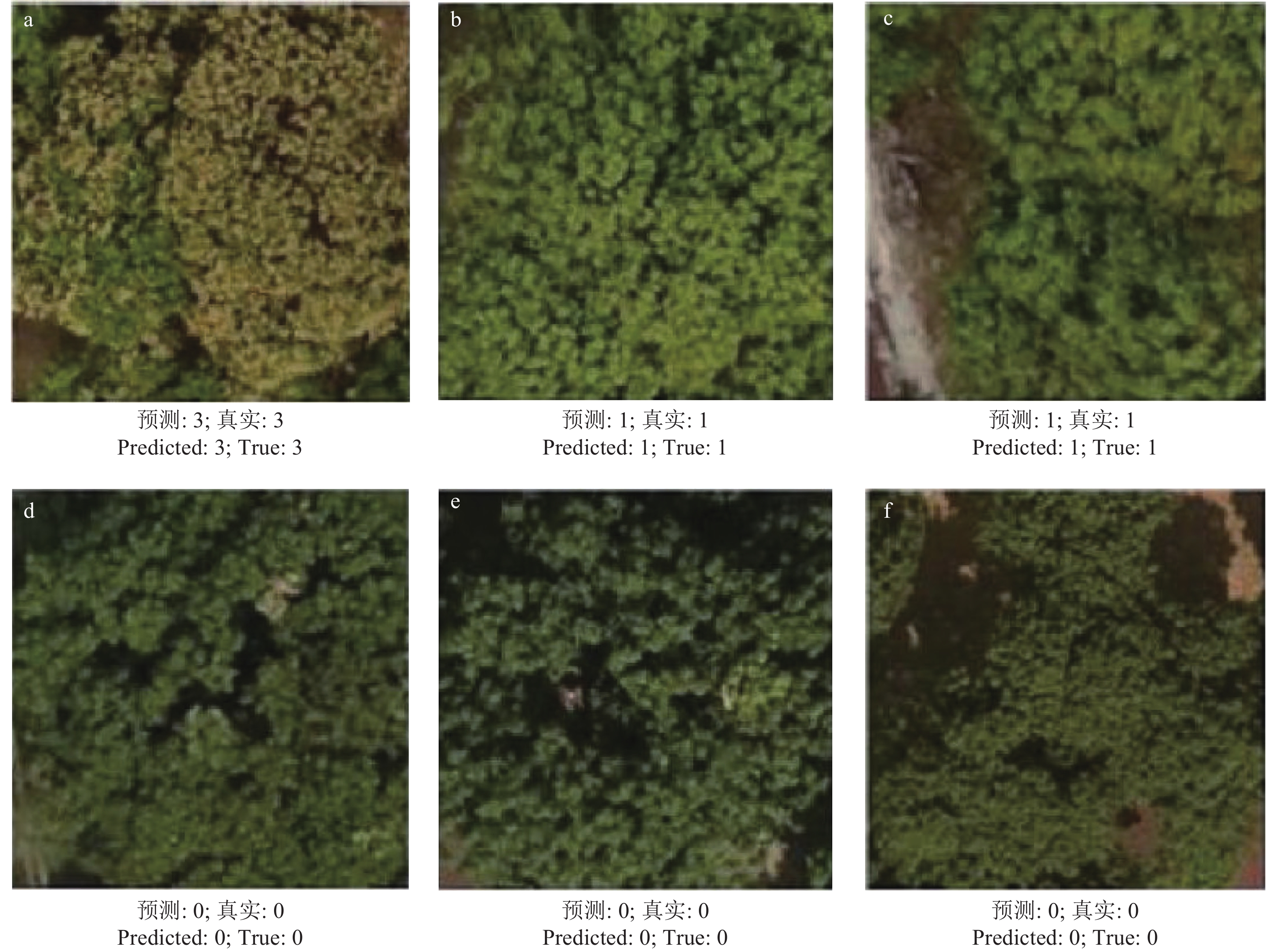
方法以遥感图像为研究对象,利用实例分割的方法分割每棵荔枝冠层后,结合园艺专家的综合判断,按开花率为0、10%~20%、50%~60%、80%及以上将开花率分为4类,使用ResNet、ResNeXt、ShuffleNetv2进行开花率分类比较,试验过程中发现ShuffleNetv2在识别准确率、参数量、训练和验证时间都有很大优势;在ShuffleNetv2上引入了空间注意力模块(Spatial attention module,SAM)后,增加了模型对位置信息的学习,在不显著增加参数量的情况下,提升荔枝冠层花期分类的精度。
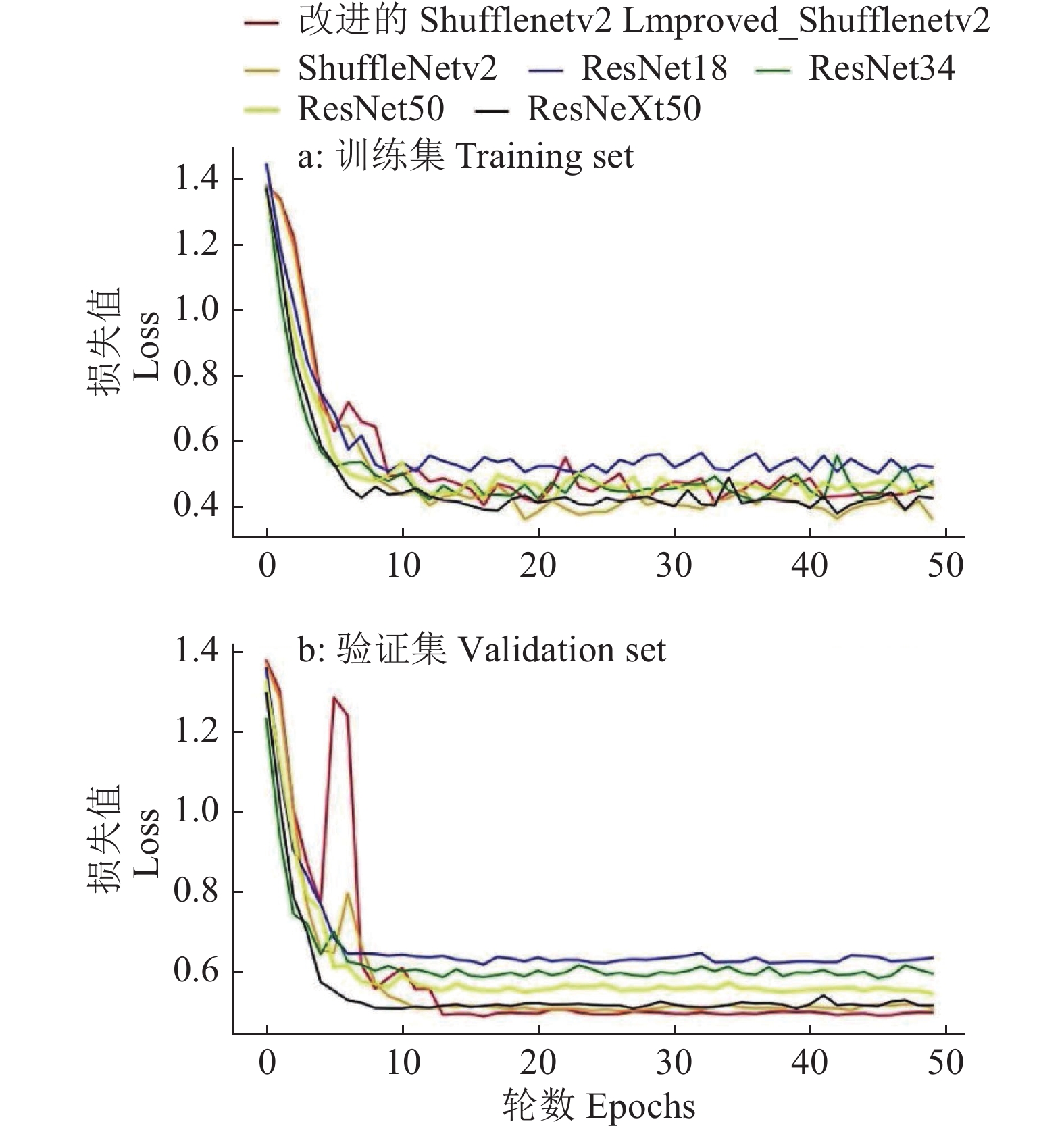
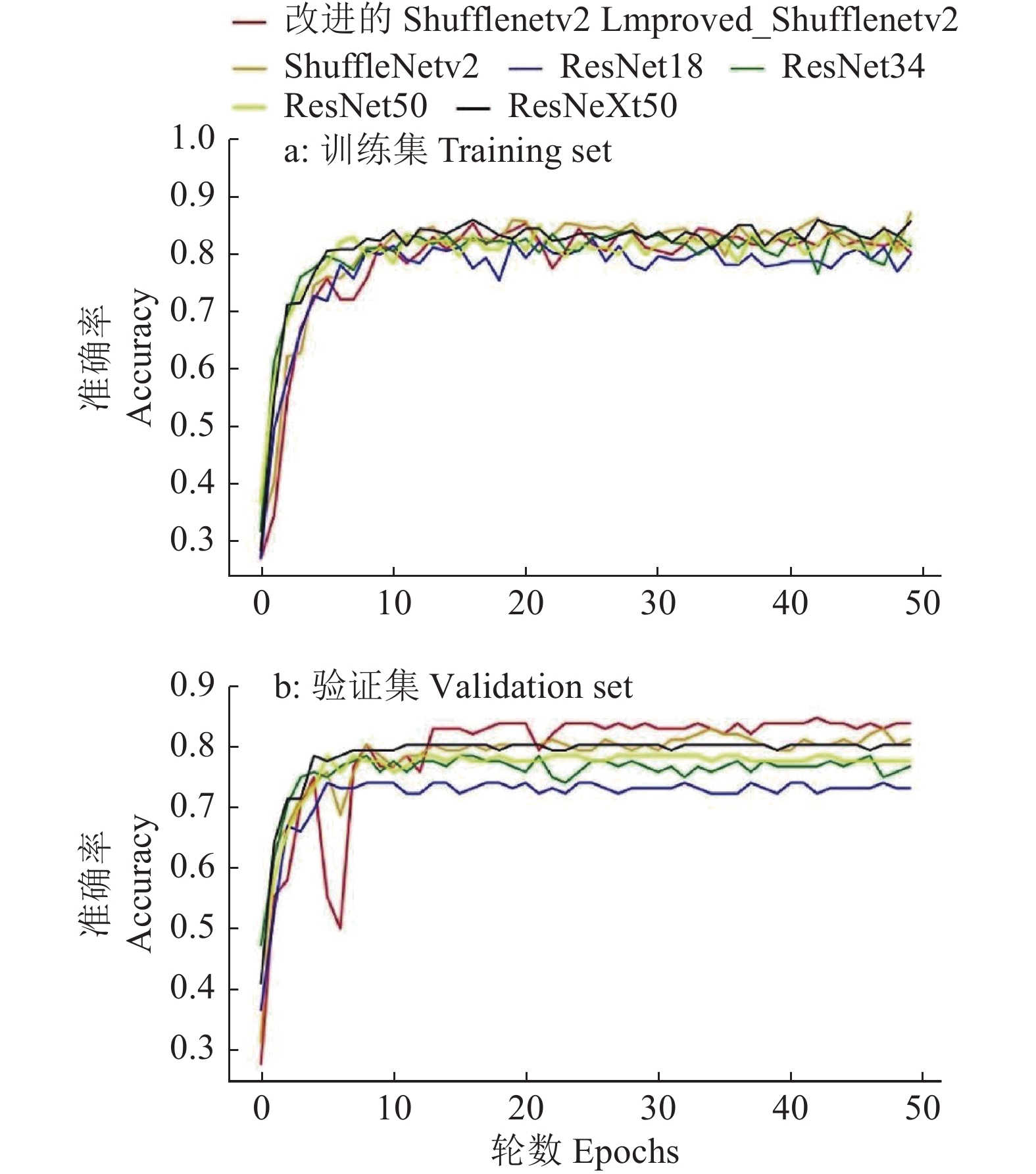
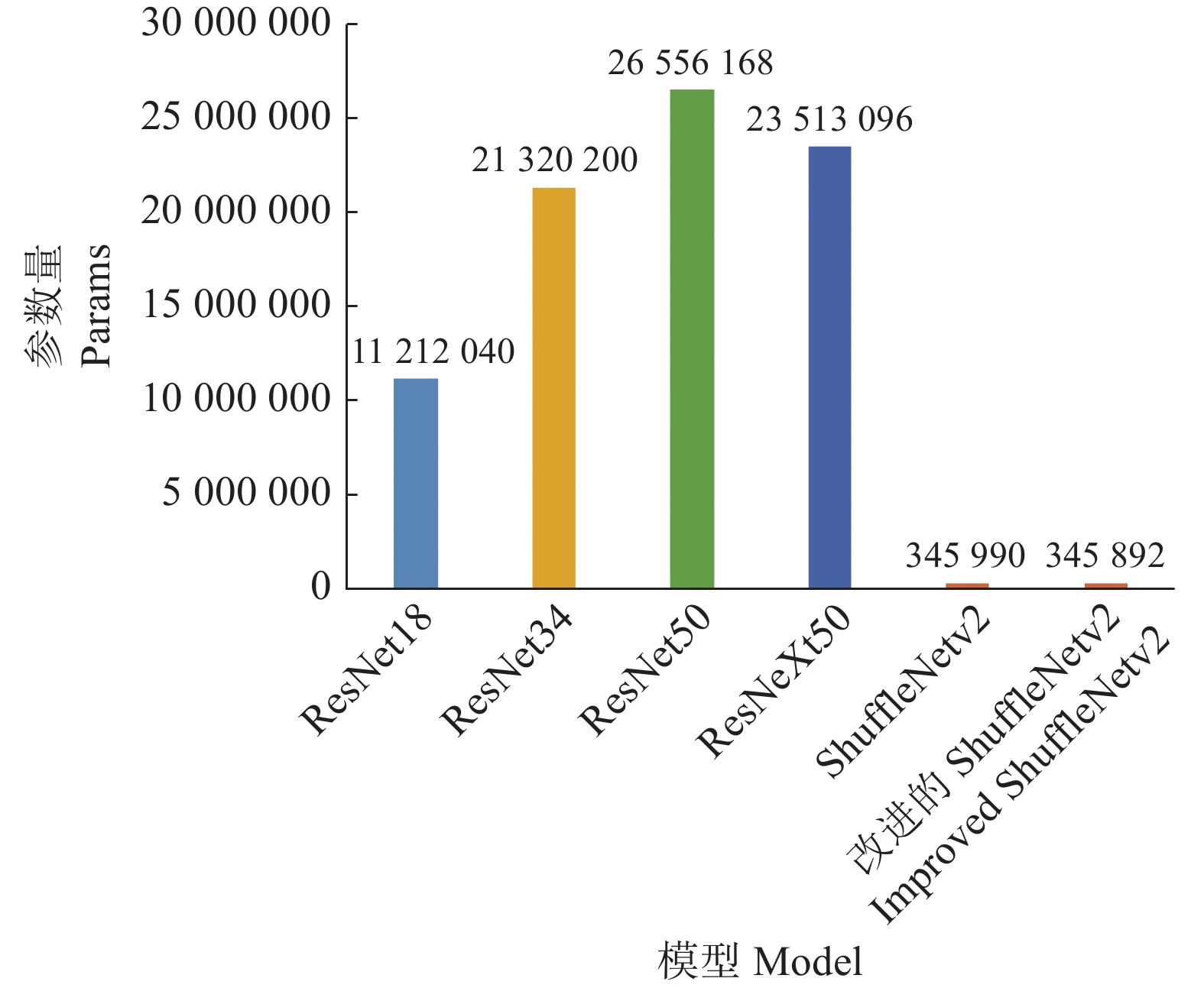
结果通过对多个主流深度神经网络的比较分析,ResNet50、ResNeXt50、ShuffleNetv2的分类精度分别达到85.96%、87.01%和86.84%,而改进后的ShuffleNetv2分类精度更高,达到88.60%;ResNet50、ResNeXt50、ShuffleNetv2和改进后的ShuffleNetv2对测试集单张冠层图像验证的时间分别为8.802、9.116、7.529和7.507 ms,改进后的ShuffleNetv2单张冠层图像验证时间最短。
结论改进后的ShuffleNetv2能够挖掘学习更为细节的荔枝冠层花期信息,具有较高的识别准确率,对荔枝花期的评估有很大的优势,可为荔枝保花疏花、生产精准管控提供智能决策支持。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn order to provide decision-making basis for subsequent litchi flower thinning, fruit retention and precise fertilization application, this work evaluated the flowering rate of each litchi by analyzing UAV remote sensing images of litchi canopy.
MethodThe remote sensing image of each litchi canopy was segmented through instance segmentation algorithm. The flowering rates were classified into four categories combining with comprehensive judgment of horticultural experts, which were 0, 10%−20%, 50%−60%, 80% and above. ResNet50, ResNeXt50 and ShuffleNetv2 were adopted to compare flowering rate classification. Due to the great advantages in recognition accuracy, number of parameters, training and verification time, ShuffleNetv2 was adopted as the instance segmentation algorithm, and optimized by introducing the spatial attention module (SAM) to increase the model’s learning of location information, and improve the accuracy of litchi canopy flowering classification without significantly increasing the number of parameters.
ResultThrough comparison of the mainstream deep learning algorithms, the classification accuracy of ResNet50, ResNeXt50 and ShuffleNetv2 reached 85.96%, 87.01% and 86.84% respectively, and the improved ShuffleNetv2 reached 88.60%, higher than the above three algorithms. The verification time of single canopy image on test set using ResNet50, ResNeXt50, ShuffleNetv2 and the improved ShuffleNetv2 were 8.802, 9.116, 7.529 and 7.507 ms respectively, showing that the improved ShuffleNetv2 single canopy image got the shortest verification time.
ConclusionThe improved ShuffleNetv2 can excavate and learn more detailed flowering information of litchi canopy, with high recognition accuracy and great advantages in the evaluation of litchi flowering, providing an intelligent decision support for flower protection and sparseness, and precise control of production.
-
表 1 不同模型的性能对比
Table 1 Performance comparison of different models
模型 Model t训练/s Training time t验证/ms Validation time 分类准 确率/% Classification accuracy 2类准 确率/% Category 2 accuracy ResNet18 120.4 7.352 83.33 60.0 ResNet34 135.8 7.812 83.33 52.0 ResNet50 175.6 8.802 85.96 60.0 ResNeXt50 199.2 9.116 87.01 60.0 ShuffleNetv2 114.4 7.529 86.84 64.0 改进的 ShuffleNetv2 109.0 7.507 88.60 68.0 Improved ShuffleNetv2 -
[1] 李建国. 荔枝学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008. [2] 侯延杰, 秦献泉, 邱宏业, 等. 疏花对无核荔枝果实和树体营养的影响[J]. 中国南方果树, 2019, 48(5): 52-55. doi: 10.13938/j.issn.1007-1431.20180715 [3] 陈艳艳, 陈国帅, 罗红卫, 等. 不同时期修剪花穗对桂味荔枝花果发育的影响[J]. 中国南方果树, 2017, 46(4): 47-48. doi: 10.13938/j.issn.1007-1431.20160645 [4] 罗剑斌, 何凤, 王祥和, 等. 一疏二控三割控穗疏花技术提高“妃子笑”荔枝产量的生理原因分析[J]. 中国南方果树, 2019, 48(1): 20-24. doi: 10.13938/j.issn.1007-1431.20180126 [5] 胡福初, 何舒, 范鸿雁, 等. 不同留花量对A4无核荔枝开花坐果的影响[J]. 中国热带农业, 2014(6): 54-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0658.2014.06.015 [6] 胡慧敏, 杨雲, 肖秋生, 等. 疏花处理对晚熟荔枝开花坐果的影响[J]. 中国热带农业, 2020(4): 54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0658.2020.04.012 [7] WANG Z L, VERMA B, WALSH K B, et al. Automated mango flowering assessment via refinement segmentation[C]//International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand. Palmerston North, New Zealand: IEEE, 2016: 66-71.
[8] YOUSEFI D B M, MOHD RAFIE A S, ABD AZIZ S, et al. Classification of oil palm female inflorescences anthesis stages using machine learning approaches[J]. Information Processing in Agriculture, 2021, 8(4): 537-549. doi: 10.1016/j.inpa.2020.11.007
[9] LU J, LIN W, CHEN P, et al. Research on lightweight Citrus flowering rate statistical model combined with anchor frame clustering optimization[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(23): 7929. doi: 10.3390/s21237929.
[10] 朱永宁, 周望, 杨洋, 等. 基于Faster R-CNN的枸杞开花期与果实成熟期识别技术[J]. 中国农业气象, 2020, 41(10): 668-677. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2020.10.006 [11] 杨其晟, 李文宽, 杨晓峰, 等. 改进YOLOv5的苹果花生长状态检测方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(4): 237-246. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2107-0523 [12] 熊俊涛, 刘柏林, 钟灼, 等. 基于深度语义分割网络的荔枝花叶分割与识别[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(6): 252-258. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.06.026 [13] 邓颖, 吴华瑞, 朱华吉. 基于实例分割的柑橘花朵识别及花量统计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(7): 200-207. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.07.023 [14] 邓继忠, 任高生, 兰玉彬, 等. 基于可见光波段的无人机超低空遥感图像处理[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2016, 37(6): 16-22. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.2016.06.003 [15] PATHAK R, BARZIN R, BORA G C. Data-driven precision agricultural applications using field sensors and unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. International Journal of Precision Agricultural Aviation, 2018, 1(1): 19-23.
[16] YANG H B, ZHAO J, LAN Y B, et al. Fraction vegetation cover extraction of winter wheat based on spectral information and texture features obtained by UAV[J]. International Journal of Precision Agricultural Aviation, 2019, 2(2): 54-61.
[17] TAHIR M N, LAN Y B, ZHANG Y L, et al. Real time estimation of leaf area index and groundnut yield using multispectral UAV[J]. International Journal of Precision Agricultural Aviation, 2020, 3(1): 1-6.
[18] 杜蒙蒙, ROSHANIANFARD A, 刘颖超. 可见光波段无人机遥感图像的小麦茎蘖密度定量反演[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(12): 3828-3836. [19] 朱圣, 邓继忠, 张亚莉, 等. 基于无人机低空遥感的水稻田间杂草分布图研究[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2020, 41(6): 67-74. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.202006058 [20] 杨蜀秦, 刘江川, 徐可可, 等. 基于改进CenterNet的玉米雄蕊无人机遥感图像识别[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(9): 206-212. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2021.09.024 [21] MO J W, LAN Y B, YANG D Z, et al. Deep learning-based instance segmentation method of Litchi canopy from UAV-acquired images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 3919. doi: 10.3390/rs13193919.
[22] 李继宇, 胡潇丹, 兰玉彬, 等. 基于文献计量学的 2001−2020 全球农用无人机研究进展与展望[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(9): 328-339. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.09.037 [23] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016: 770-778.
[24] XIE S N, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017: 5987-5995.
[25] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016: 2818-2826.
[26] ZHANG X Y, ZHOU X Y, LIN M X, et al. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: IEEE, 2018: 6848-6856.
[27] MA N N, ZHANG X Y, ZHENG H T, et al. ShuffleNet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Cham: Springer, 2018: 122-138.
[28] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Cham: Springer, 2018: 3-19.




 下载:
下载: