Identification and description of Ditylenchus arachis from Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu Province
-
摘要:目的
明确甘肃省渭源县党参Codonopsis pilosula病样中的茎线虫种类。
方法采用形态学特征、ITS-rDNA与28S-rDNA序列系统发育分析、特异性引物PCR扩增、PCR-ITS-RFLP相结合的方法进行种类鉴定。
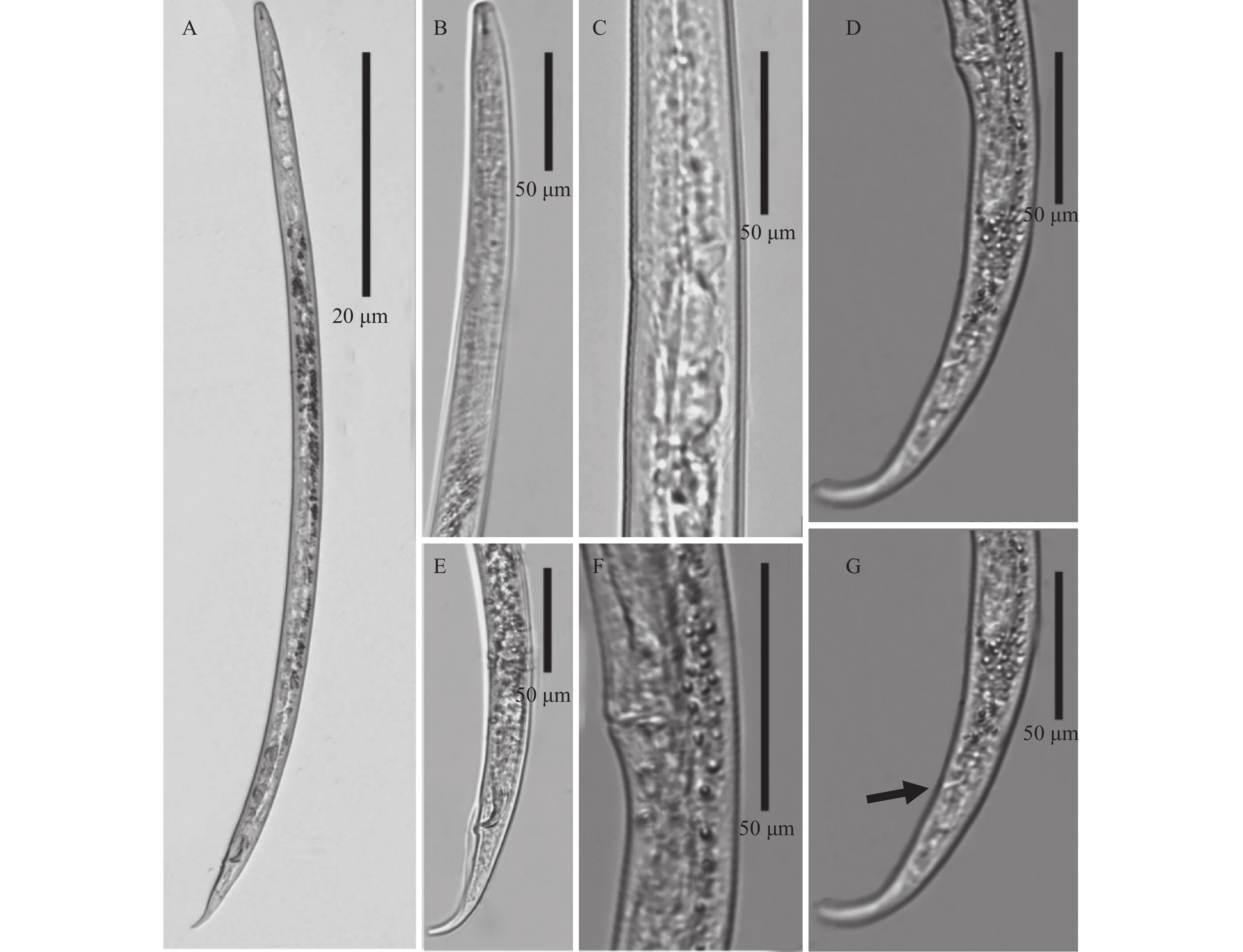
结果甘肃省党参茎线虫群体形态特征与花生茎线虫Ditylenchus arachis相似,形态测量均值虽存在差异,但是范围值基本一致;系统发育分析显示,该线虫与花生茎线虫聚为一支,特异性引物PCR扩增片段、PCR-ITS-RFLP图谱均与花生茎线虫相同。
结论结合形态特征与分子特征分析,将甘肃党参茎线虫群体鉴定为花生茎线虫,表明该线虫已在甘肃发生分布。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo clarify the species of stem nematode from diseased sample of Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu Province.
MethodSpecies identification of stem nematode was carried out by combing morphological analysis, phylogenetic analyses of ITS-rDNA and 28S-rDNA sequences, PCR with species-specific primers as well as PCR-ITS-RFLP.
ResultThe morphological characteristics of the stem nematode population from C. pilosula in Gansu was similar to those of Ditylenchus arachis. The ranges of measurement values were basically agreed with those of D. arachis although some average values were different. The phylogenetic analyses revealed that the tested population was clustered into the same branch withD. arachis. The fragment amplified with specific primers, and PCR-ITS-RFLP map of this population were consistent with those of D. arachi.
ConclusionThe stem nematode population from C. pilosula in Gansu was identified as D. arachis based on morphological and molecular characters. D. arachis has occurred and distributed in Gansu.
-
Keywords:
- Ditylenchus arachis /
- Morphological character /
- Phylogeny /
- Specific primer /
- ITS-RFLP
-
-
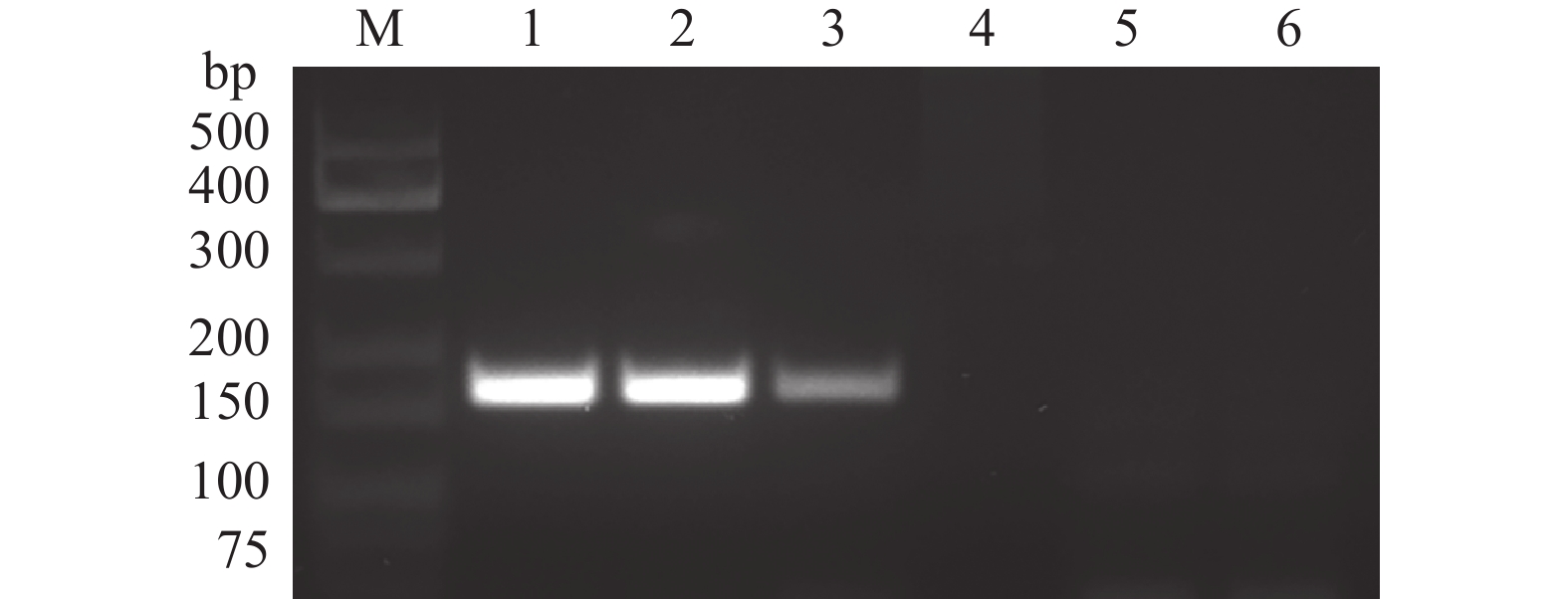
图 2 甘肃党参茎线虫群体与腐烂茎线虫ITS特异性引物扩增电泳图
M:DNA分子量标准(75~500 bp);1~3:甘肃党参茎线虫群体;4~6:腐烂茎线虫
Figure 2. Electrophoresis of PCR products amplified from Ditylenchus arachis from Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu and D. destructor using species-specific ITS primers
M:DNA marker (75−500 bp);1−3:D. arachis population from Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu;4−6:D. destructor
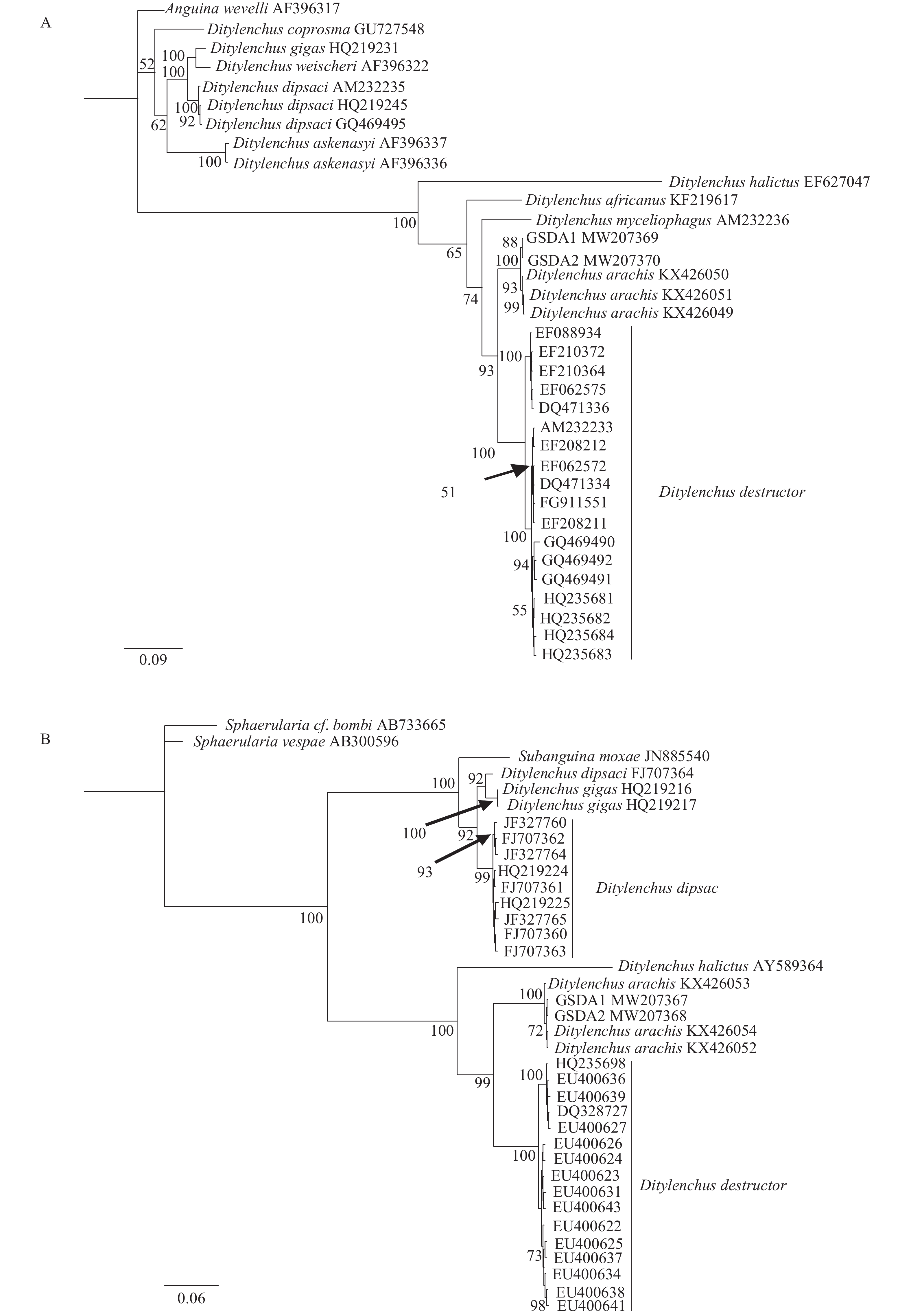
图 3 基于 ITS-rDNA (A) 和28s D2/D3 (B)的甘肃党参茎线虫(GSDA1、GSDA2)系统发育树
最佳模型均为GTR+I+G,分支上数字表示后验概率
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of stem nematode (GSDA1、GSDA2) from Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu Province based on ITS-rDNA (A) and 28s D2/D3 (B)
All best model were GTR+I+G; The posterior probability values exceeding 50% are given on appropriate clades
表 1 甘肃党参茎线虫群体与河北原始群体测量值比较1)
Table 1 Morphometrics comparison of Ditylenchus arachis population from Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu with original Hebei population of D. arachis
群体
Population来源
Originn L/μm a b c c′ V/% 口针/μm
Stylet体宽/μm
Body
width尾长/μm
Tail
length交合刺长/μm
Spiculum
length雌虫
Female甘肃 Gansu 15 909±44
(855~976)35±2.7
(30~39)6.9±0.6
(6.0~7.8)14±0.9
(13~16)3.8±0.5
(3.4~4.6)82±0.8
(80~83)9.1±0.5
(8.7~9.8)27±1.7
(23~29)66±4.6
(56~70)河北 Hebei 20 893±78
(680~1007)37±5.7
(28~48)7.1±0.9
(6.0~9.6)14±1.2
(11~16)4.5±0.6
(3.3~5.6)81±0.9
(80~83)8.9±0.4
(8.6~9.8)25±4.9
(16~33)63±5.7
(53~75)雄虫
Male甘肃 Gansu 15 844±30
(787~870)35±2.2
(32~38)6.5±0.4
(6.0~7.1)13±1.7
(12~16)3.7±0.5
(3.0~4.3)8.9±0.4
(8.2~9.5)24±1.8
(22~27)64±6.5
(50~69)19±1.8
(16~22)河北 Hebei 20 884±91
(730~1022)41±4.0
(39~48)6.8±0.6
(5.6~7.8)15±1.3
(12~17)4.4±0.5
(3.7~5.1)9.1±0.4
(8.5~9.6)22±3.0
(18~28)59±3.8
(49~63)21±2.2
(16~24)1)n 代表样本数;L 为体长;a 为体长与最大体宽的比值;b 为体长与头端至食道与肠连接处长度的比值;c 为体长与尾长的比值;c′为尾长与肛门处体宽的比值;V 为阴门至头端的长度与体长的比值×100;括号内数据表示范围
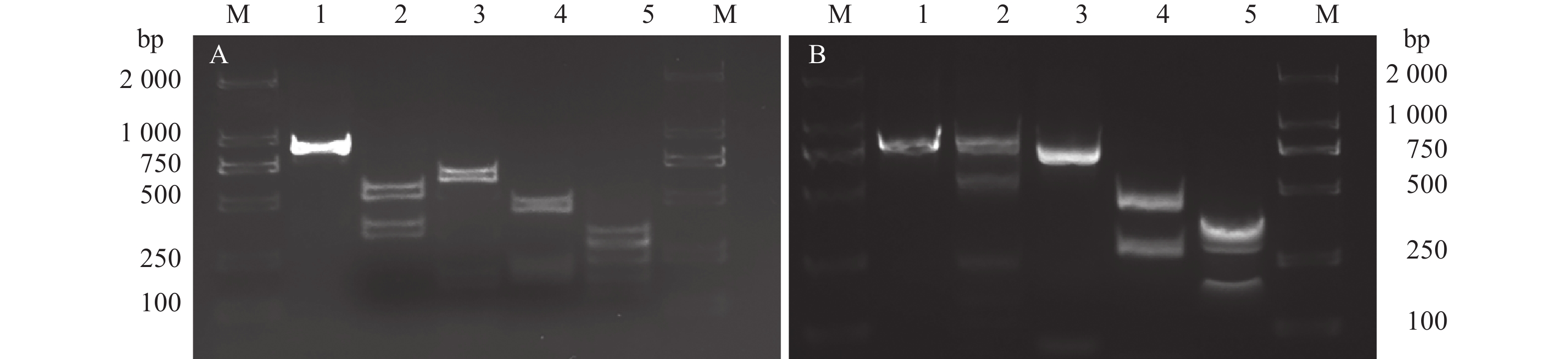
1)n: Number of specimens;L: Total body length;a: Body length/the maximum body width;b: Body length/distance from head end to junction of oesophagus and intestine;c: Body length/tail length;c': Tail length/body width at anus;V: Distance from vulva to head/body length ×100; The range is represented by the data in parentheses表 2 软件Wbcuter酶切甘肃党参茎线虫和腐烂茎线虫ITS序列结果
Table 2 Enzyme digestion results of Ditylenchus arachis population from Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu and D. destructor ITS sequences by Wbcuter
bp 处理
Treatment河北花生茎线虫群体
D. arachispopulation
in Hebei甘肃党参茎线虫群体
D. arachis population from
Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu腐烂茎线虫
D. destructorUnrestricted PCR 816 816 915 DdeI 485,151,103, 34, 33, 10 485, 151,103, 34, 33,10 551, 354, 10 HinfI 751,65 751, 65 649,174, 57, 35 Tru9 I (MseI ) 469, 307, 31, 9 469, 307, 31, 9 468, 215,192, 31, 9 Sdu I 347, 321,148 347, 321, 148 319, 256,191,149 -
[1] ANON. Tylenchida parasites of plants and insects[J]. Journal of Phytopathology, 2001, 149(7/8): 491. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0434.2001.0596k.x.
[2] 谢辉. 植物线虫分类学[M]. 第2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005. [3] VOVLAS N, TROCCOLI A, PALOMARES-RIUS-RIUS J E, et al. A new stem nematode, Ditylenchus oncogenus n. sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchida), parasitizing sowthistle from Adriatic coast dunes in southern Italy[J]. Journal of Helminthology, 2016, 90(2): 152-165. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X14000947
[4] STURHAN D, BRZESKI M W, NICKLE W R. Stem and bulb nematodes, Ditylenchus spp.[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2020.
[5] 段玉玺. 植物线虫学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011. [6] 龙海, 齐小峰, 谢泳桂, 等. 影响全球食品安全的植物线虫综述[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2017, 37(12): 78-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6820.2017.12.017 [7] 赵洪海, 梁晨, 张浴, 等. 腐烂茎线虫 (Ditylenchus destructor Thorne, 1945) 生物学研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报, 2021, 37(7): 45-55. [8] ZHANG S L, LIU G K, JANSSEN T, et al. A new stem nematode associated with peanut pod rot in China: Morphological and molecular characterization of Ditylenchus arachisn. sp. (Nematoda: Anguinidae)[J]. Plant Pathology, 2014, 63(5): 1193-1206. doi: 10.1111/ppa.12183
[9] 杜毛笑, 邱黛玉, 任凤英, 等. 间作植物和茬口对连作党参生长和品质产量的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(11): 1884-1892. [10] 徐雪芬, 倪春辉, 李惠霞, 等. 党参根腐病病原菌鉴定及其室内毒力测定[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2021, 33(1): 96-103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.01.12 [11] NI C H, ZHANG S L, LI H X, et al. First report of potato rot nematode, Ditylenchus destructor Thorne, 1945 infecting Codonopsis pilosula in Gansu province, China[J]. Journal of Nematology, 2020, 52: e2020-e2087. doi: 10.21307/jofnem-2020-087.
[12] HOOPER D J. Extraction and processing of plant and soil nematodes[M]//LUC M, SIKORA R A, BRIDGE J. Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Subtropical and Tropical Agriculture. Wallingford: CAB International, 1990: 45-68.
[13] 徐鹏刚. 甘肃定西马铃薯腐烂茎线虫的发生、病原学研究及品种抗性评价[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2016. [14] 谢辉, 冯志新. 丝尾垫刃属新种的描述 (线虫门: 垫刃科) Ⅱ: 异头丝尾垫刃线虫新种和香港丝尾垫刃线虫新种[J]. 植物病理学报, 1996, 26(3): 283-288. [15] 王江岭, 张建成, 顾建锋. 单条线虫DNA提取方法[J]. 植物检疫, 2011, 25(2): 32-35. [16] VRAIN T C, WAKARCHUK D A, LEVESQUE A C, et al. Intraspecific rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in the Xiphinema americanum group[J]. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 1992, 15(6): 563-573.
[17] SUBBOTIN S A, VIERSTRAETE A, DE LEY P, et al. Phylogenetic relationships within the cyst-forming nematodes (Nematoda, Heteroderidae) based on analysis of sequences from the ITS regions of ribosomal DNA[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2001, 21(1): 1-16. doi: 10.1006/mpev.2001.0998
[18] SUBBOTIN S A, STURHAN D, CHIZHOV V N, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Tylenchida Thorne, 1949 as inferred from D2 and D3 expansion fragments of the 28S rRNA gene sequences[J]. Nematology, 2006, 8(3): 455-474. doi: 10.1163/156854106778493420
[19] ZHANG S L, CHENG X, LIU G K, et al. Development of species-specific primer pairs for the molecular diagnosis of Ditylenchus arachis[J]. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2019, 21(1): 99-104.
[20] SUBBOTIN S A, DEIMI A M, ZHENG J W, et al. Length variation and repetitive sequences of Internal Transcribed Spacer of ribosomal RNA gene, diagnostics and relationships of populations of potato rot nematode, Ditylenchus destructor Thorne, 1945 (Tylenchida: Anguinidae)[J]. Nematology, 2011, 13(7): 773-785. doi: 10.1163/138855410X551923
[21] 章淑玲. 花生茎线虫 (Ditylenchus arachis n. sp. ) 新种鉴定、生物学及快速检测技术[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2016. [22] 王文玉. 花生茎线虫 (Ditylenchus arachis) 的生物学特性及种群多样性[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2017. [23] 邓明雪, 肖顺, 王文玉, 等. 花生茎线虫对花生根的趋向、定位及侵染特性[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 47(2): 148-152. [24] 陈思怡, 邓明雪, 陈晶伟, 等. 花生茎线虫的脱水存活方式及耐低温能力[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 49(5): 577-582. [25] 章淑玲, 林谷园, 肖顺. 花生茎线虫 Ditylenchus arachis 在真菌上的培养条件研究[J]. 植物保护, 2018, 44(2): 100-103. [26] 谢明惠, 陈浩梁, 张光玲, 等. 温度、土壤湿度和播种深度对花生种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 花生学报, 2017, 46(2): 52-59. [27] 中国农业百科全书总编辑委员会农业经济卷编辑委员会, 中国农业百科全书编辑部. 中国农业百科全书: 农业经济卷[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1991. [28] 王静. 中兽医中草药党参的临床应用与育苗栽培技术[J]. 中兽医学杂志, 2019(5): 105.



 下载:
下载: