Research progress on intelligent equipment and information technology for livestock and poultry breeding
-
摘要:
我国现代畜禽养殖正朝着规模化、设施化、标准化和信息化方向快速发展,智能养殖技术装备与信息化技术的研发与应用是促进畜禽养殖行业健康可持续发展的关键,对提升我国畜禽养殖产出效率、降低生产过程对劳动力的依赖、实现绿色高质量转型发展具有重要意义。本文从满足规模化畜禽生产对品质安全、健康管理、提质增效的需求出发,重点介绍了模块化装配式畜禽舍建筑与热环境耦合调控技术、养殖环境参数精准监测与智能调控技术以及畜禽智能化饲喂、饮水、投药设备、畜禽舍清粪工艺与自动清粪装备、畜禽生产信息实时采集与智能管理技术等方面的最新研究与应用进展;指出了畜牧装备产业的薄弱环节和卡脖子问题,并对中国畜牧业机械化与智能装备发展的方向进行了展望,为我国现代畜牧业绿色高质量转型升级与健康可持续发展提供参考。
Abstract:The modern livestock and poultry breeding industry in China has been rapidly developing towards scalization, facility, standardization and informatization. The research, development and application of intelligent farming equipment and information technology have become the key to promote healthy and sustainable development of livestock and poultry breeding industry. It is of great significance for improving the output efficiency, reducing the dependence on labor in the production process, and achieving green and high-quality transformational development of livestock and poultry breeding industry in China. To meet the needs of quality and safety of products, healthy management, and quality-efficiency improvement of large-scale livestock and poultry production, this paper mainly summarized the latest research and application progress of intelligent equipments and information technologies, including modularized assembled animal buildings and building-thermal environment coupling regulation technology, precise monitoring and intelligent controlling technology of farming environmental parameters, intelligent feeding, drinking and dosing equipment, automatic manure removal technology and equipment, real-time information collection and intelligent management technology etc. The weak links and bottlenecks for the development of intelligent equipment and information technology of livestock and poultry breeding industry were pointed out. The development direction of mechanization and intelligent equipment of livestock farm in China was prospected. This review provides a reference for the green and high-quality transformation and upgrading, healthy and sustainable development of livestock and poultry breeding industry in China.
-
Keywords:
- livestock and poultry /
- intelligent equipment /
- environmental control /
- feeding /
- manure removal /
- informatization
-
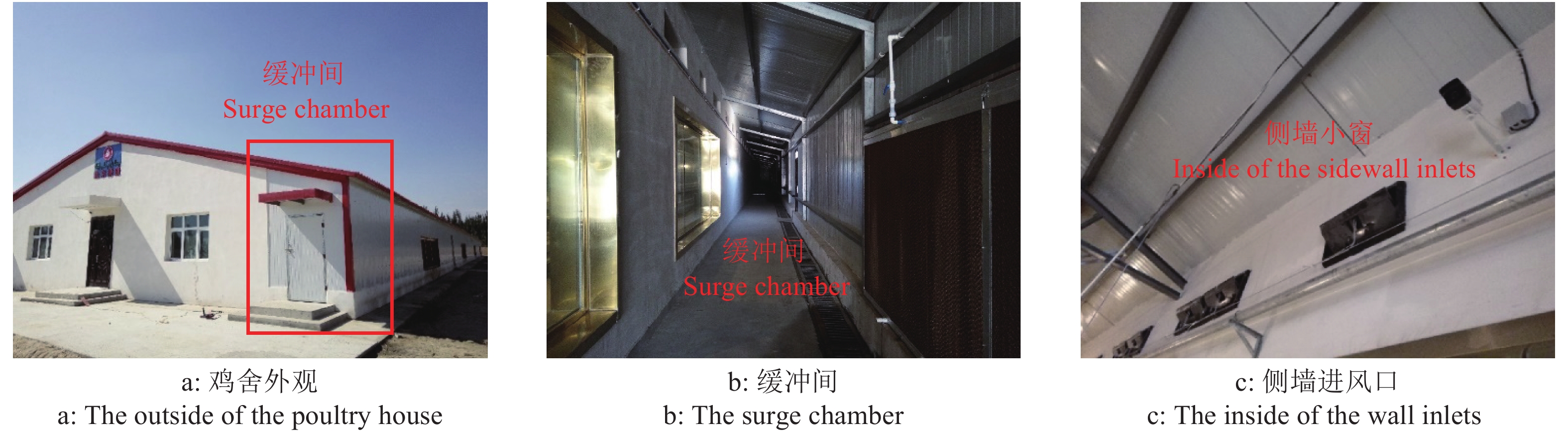
图 1 纵墙湿帘缓冲室山墙排风系统[19]
Figure 1. Sidewall inlets of the new ventilation system with surge chamber and bottom hinged flap
-
[1] 李保明, 王阳, 郑炜超, 等. 中国规模化养鸡环境控制关键技术与设施设备研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(16): 212-221. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.16.026 [2] 朱能武, 李保明, 邓昌彦, 等. 规模化畜禽养殖环境工程技术研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报, 2001, 17(7): 17-20. [3] 汪开英, 吴捷刚, 赵晓洋. 畜禽场空气污染物检测技术综述[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(8): 1458-1474. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.08.015 [4] 杨飞云, 曾雅琼, 冯泽猛, 等. 畜禽养殖环境调控与智能养殖装备技术研究进展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34(2): 163-173. [5] 姚向君, 郝先荣, 郭宪章. 畜禽养殖场能源环保工程的发展及其商业化运作模式的探讨[J]. 农业工程学报, 2002, 18(1): 181-184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2002.01.048 [6] 韩成吉, 王国刚, 朱立志. 畜禽粪污土地承载力系统动力学模型及情景仿真[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(22): 170-180. [7] 张庆东, 耿如林, 戴晔. 规模化猪场清粪工艺比选分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医, 2013, 40(2): 232-235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7236.2013.09.051 [8] 介邓飞, 泮进明, 应义斌. 规模化畜禽养殖污染气体现场检测方法与仪器研究进展[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(1): 236-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.01.032 [9] 罗娟, 赵立欣, 姚宗路, 等. 规模化养殖场畜禽粪污处理综合评价指标体系构建与应用[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(17): 182-189. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.17.022 [10] 付为森, 滕光辉, 杨艳. 种猪体重三维预估模型的研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2006, 22(S2): 84-87. [11] 李保明, 王阳, 郑炜超. 我国规模化养鸡环境控制技术的最新进展[J]. 中国家禽, 2019, 41(9): 1-7. [12] WANG Y, ZHENG W C, SHI H P, et al. Optimising the design of confined laying hen house insulation requirements in cold climates without using supplementary heat[J]. Biosystem Engineering, 2018, 174: 282-294. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2018.07.011
[13] 王阳, 李保明. 密闭式蛋鸡舍外围护结构冬季保温性能分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(7): 190-196. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.025 [14] 王阳, 王朝元, 李保明. 蛋鸡舍冬季CO2浓度控制标准与最小通风量确定[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(2): 240-244. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.02.033 [15] 王阳, 郑炜超, 石海鹏, 等. 夏季鸡舍屋顶隔热改善舍内热环境及蛋鸡生产性能[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(17): 207-213. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.17.027 [16] WANG Y, LI B M. An optimized solar-air degree-day method to evaluate energy demand for poultry buildings in different climate zones[J]. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(4): 478-489. doi: 10.15302/J-FASE-2020320
[17] WANG Y, LI B M, ZHENG W C. Optimum insulation thickness for the sandwich structure livestock building external envelopes in different climate regions of China[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2020, 13(1): 29-41. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20201301.5280
[18] WANG Y, LI B M, LIANG C, et al. Dynamic simulation of thermal load and energy efficiency in poultry buildings in the cold zone of China[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 168: 105127. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2019.105127
[19] WANG Y, ZHENG W C, TONG Q, et al. Reducing dust deposition and temperature fluctuations in the laying hen houses of Northwest China using a surge chamber[J]. Biosystem Engineering, 2018, 175: 206-218. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2018.09.016
[20] 王阳, 郑炜超, 李绚阳, 等. 西北地区纵墙湿帘山墙排风系统改善夏季蛋鸡舍内热环境[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(21): 202-207. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.21.024 [21] WANG Y, ZHENG W C, LI B M, et al. A new ventilation system to reduce temperature fluctuations in laying hen housing in continental climate[J]. Biosystem Engineering, 2019, 181: 52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.02.017
[22] 王阳. 健康高效养鸡稳温机理及热环境调控规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2020. [23] WANG X S, WU J G, YI Q Y, et al. Numerical evaluation on ventilation rates of a novel multi-floor pig building using computational fluid dynamics[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2021, 182: 106050. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2021.106050
[24] 沈盼, 高岩, 张杰, 等. 现代化猪舍降低废气排放措施的应用与研究[J]. 中国猪业, 2020, 15(1): 84-86. [25] QIN C, WANG X S, ZHANG G Q, et al. Effects of the slatted floor layout on flow pattern in a manure pit and ammonia emission from pit: A CFD study[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 177: 105677. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105677
[26] 李修松, 叶章颖, 李保明, 等. 不同通风模式对保育猪舍冬季环境的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(3): 317-325. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.03.036 [27] 李修松, 叶章颖, 李国铭, 等. 规模化猪场妊娠母猪舍改进湿帘降温系统的环境特性[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(20): 238-245. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.20.028 [28] ZHAO W Y, WANG M Z, LI H, et al. Field test and economic analysis of energy-saving renovation for an old nursery pig building in Beijing, China[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2020, 36(5): 619-628. doi: 10.13031/aea.13655
[29] 曹哲, 施正香, 安欣, 等. 基于热成像技术的牛舍围护结构传热阻测试方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(24): 235-241. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.24.031 [30] 鲁煜建, 王朝元, 赵浩翔, 等. 东北地区奶牛夏季热应激对其行为和产奶量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(16): 225-231. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.16.029 [31] 严格齐, 李浩, 施正香, 等. 奶牛热应激指数的研究现状及问题分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(23): 226-233. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.23.028 [32] 谭鹤群, 李鑫安, 艾正茂. 基于可调谐吸收光谱的畜禽舍氨气浓度检测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(13): 186-194. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.13.022 [33] 李帅, 李丽华, 邢雅周, 等. 基于LoRa的养鸡场有害气体监测系统设计[J]. 中国家禽, 2020, 42(9): 68-73. [34] 董丽媛, 李丽华, 白雪洁, 等. 基于AGA-ELM的鸡舍环境因子对蛋鸡生产影响预测研究[J]. 中国家禽, 2020, 42(10): 58-64. [35] 丁露雨, 鄂雷, 李奇峰, 等. 畜舍自然通风理论分析与通风量估算[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(15): 189-201. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.15.024 [36] DING L Y, LI Q F, WANG C Y, et al. Determination of the mass transfer coefficient of ammonia emissions from dairy open lots using a scale model[J]. Biosystem Engineering, 2020, 190: 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.12.008
[37] LI Q F, YAO C X, DING L Y, et al. Numerical investigation on effects of side curtain opening behavior on indoor climate of naturally ventilated dairy buildings[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2020, 13(5): 63-72. doi: 10.25165/j.ijabe.20201305.6033
[38] 关金森. 一种自走式撒料机: CN202652977U [P]. 2013. [39] 孙鹏. 围产期奶牛饲养管理关键技术[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2020. [40] 郑姗姗, 罗清尧, 杨亮, 等. 一种自调节奶水配比的猪仔补奶机: CN211268105U [P]. 2020. [41] ZHENG W, NI L, HUI X, et al. Optimization of slightly acidic electrolyzed water spray for airborne culturable bacteria reduction in animal housing[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2016, 9(4): 185-191.
[42] NI L, CAO W, ZHENG W, et al. Reduction of microbial contamination on the surfaces of layer houses using slightly acidic electrolyzed water[J]. Poultry Science, 2015, 94(11): 2838-2848. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev261
[43] ZHENG W, LI Z, SHAH S B, et al. Removal of ammonia and airborne culturable bacteria by proof-of-concept wind break wall with slightly acidic electrolyzed water spray for a layer breeding house[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2016, 32(3): 393-399.
[44] XIE Q J, NI J Q, BAO J, et al. A thermal environmental model for indoor air temperature prediction and energy consumption in pig building[J]. Build Environment, 2019, 161: 106238. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106238
[45] WANG H, ZENG Y Q, PU S H, et al. Impact of slatted floor configuration on manure drainage and growth performance of finishing pigs[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2020, 36(1): 89-94. doi: 10.13031/aea.13650
[46] 胡振楠, 孙红敏, 李晓明, 等. 猪舍自动清粪控制系统设计与实现[J]. 南方农机, 2021, 52(1): 8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3872.2021.01.005 [47] 刘安芳, 阮蓉丹, 李厅厅, 等. 猪舍内粪污废弃物和有害气体减量化工程技术研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(15): 200-210. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.15.025 [48] 阮蓉丹, 曾雅琼, 蒲施桦, 等. 不同机械干清粪频次对生长猪舍内环境和粪污排放的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2019, 55(8): 126-131. [49] 胡振楠, 孙红敏, 李晓明, 等. 基于加速度传感器的猪舍刮粪板运行状态监测装置设计与仿真[J]. 农业与技术, 2019, 39(17): 18-22. [50] 郭小龙, 王锐, 王先伟. 畜禽舍的养殖环境控制自动化系统研究与实现[J]. 畜禽业, 2019, 30(12): 30. [51] 王先伟, 李蕊蕊. 规模化养殖场畜禽粪污处理途径探究[J]. 农业科学, 2020(5): 179-180. [52] 陈洪伟, 孙国安, 薛龙, 等. 一种刮粪板整体涨紧装置: CN209299969U [P]. 2019. [53] CUAN K X, ZHANG T M, HUANG J D, et al. Detection of avian influenza-infected chickens based on a chicken sound convolutional neural network[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 178: 105688.
[54] FANG C, HUANG J D, CUAN K X, et al. Comparative study on poultry target tracking algorithms based on a deep regression network[J]. Biosystem Engineering, 2020, 190: 176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.12.002
[55] KANG X, ZHANG X D, LIU G. Accurate detection of lameness in dairy cattle with computer vision: A new and individualized detection strategy based on the analysis of the supporting phase[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2020, 103(11): 10628-10638. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-18288
[56] 康熙, 张旭东, 刘刚, 等. 基于机器视觉的跛行奶牛牛蹄定位方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(S1): 276-282. [57] 张旭东, 康熙, 马丽, 等. 基于热红外图像的奶牛乳房炎自动检测方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(S1): 248-255. [58] ZHANG X D, KANG X, FENG N N, et al. Automatic recognition of dairy cow mastitis from thermal images by a deep learning detector[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 178: 105754. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105754
[59] ZHANG Y Q, CAI J H, XIAO D Q, et al. Real-time sow behavior detection based on deep learning[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2019, 163: 104884. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2019.104884
[60] 初梦苑, 刘刚, 司永胜, 等. 基于三维重建的奶牛体重预估方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(S1): 378-384. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.S1.046 [61] 张馨月, 刘刚, 经玲, 等. 基于点云精简的奶牛背部体尺测点自动提取方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(S1): 267-275. [62] 冯宁宁, 刘刚, 张彦娥, 等. 基于EMD的奶牛动态称量算法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(S1): 305-312. [63] 任晓惠, 刘刚, 张淼, 等. 基于支持向量机分类模型的奶牛行为识别方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(S1): 290-296.



 下载:
下载:







