Mining and analysis of miRNAs from Eucalyptus camaldulensis under low temperature stress based on high-throughput sequencing
-
摘要:目的
预测、挖掘和分析涉及赤桉Eucalyptus camaldulensis低温胁迫应答的miRNA,为研究其调控赤桉低温胁迫应答的分子网络奠定基础。
方法采用高通量测序对低温处理组和对照(CK)组的赤桉组培苗茎尖进行小RNA测序。以miRBase21.0、Rfam14.1和巨桉E. grandis基因组为参考数据库,利用Bowtie、miREAP和miRDeep2等软件进行miRNA预测,使用RNAfold对预测到的miRNA前体进行二级结构的折叠;采用psRNATarget预测靶基因,通过DEGSeq包分析差异表达的miRNA,并对它们进行GO注释和KEGG富集分析。
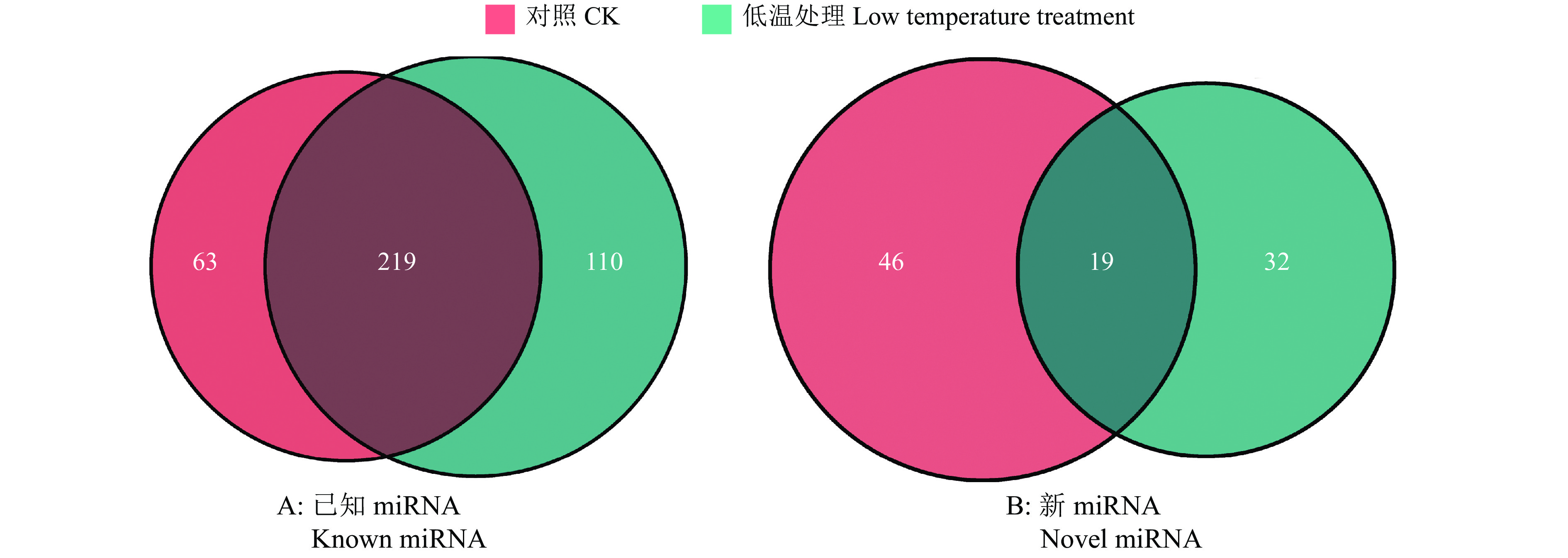
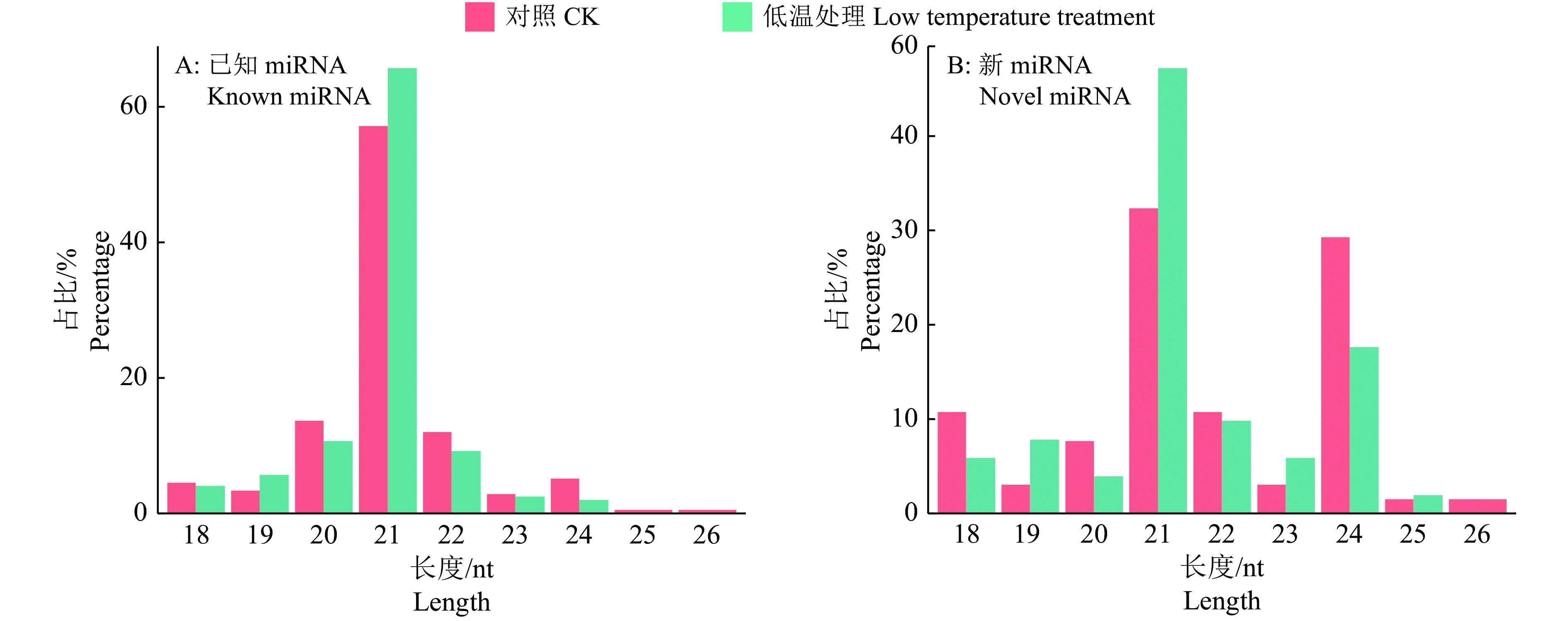
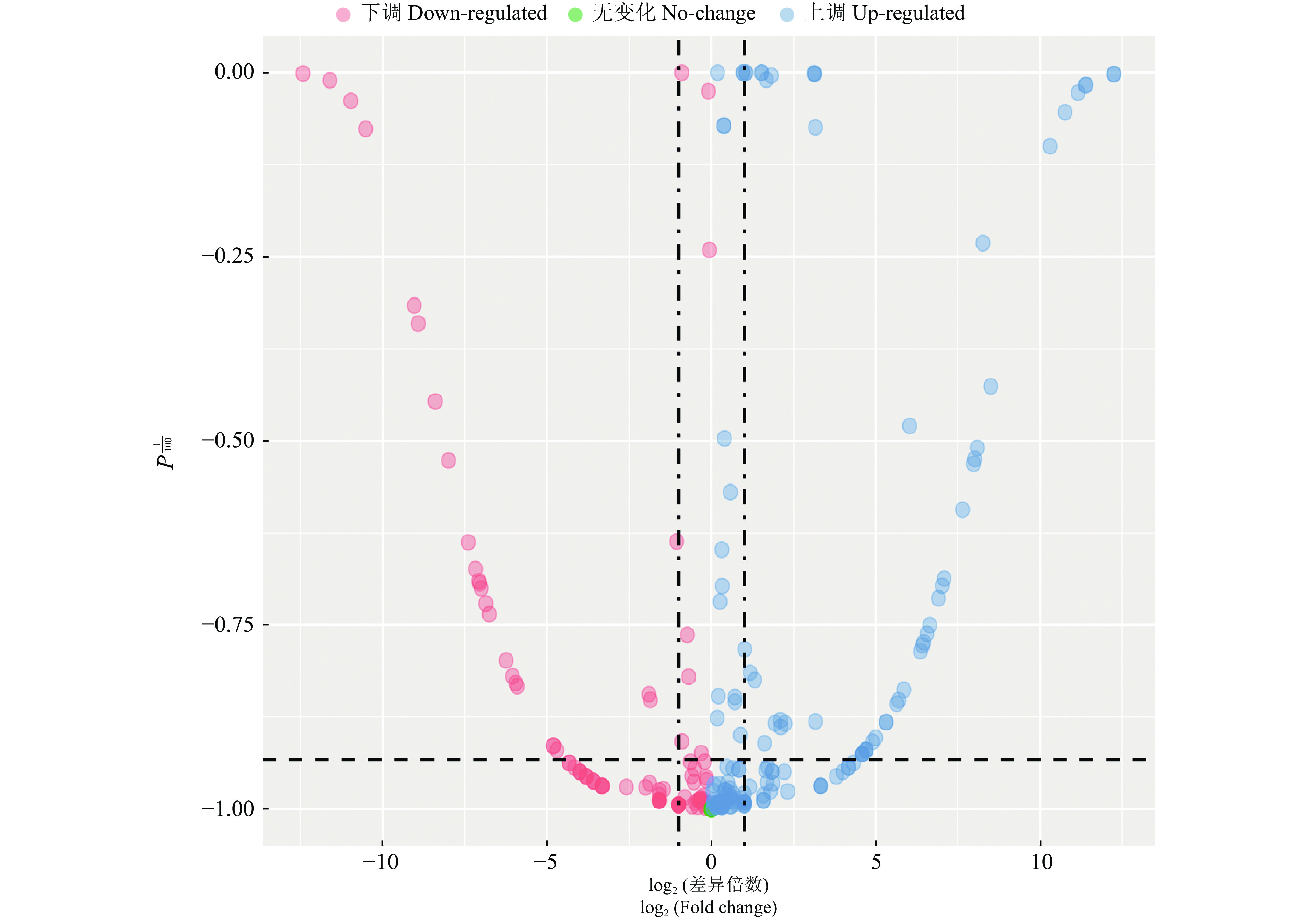
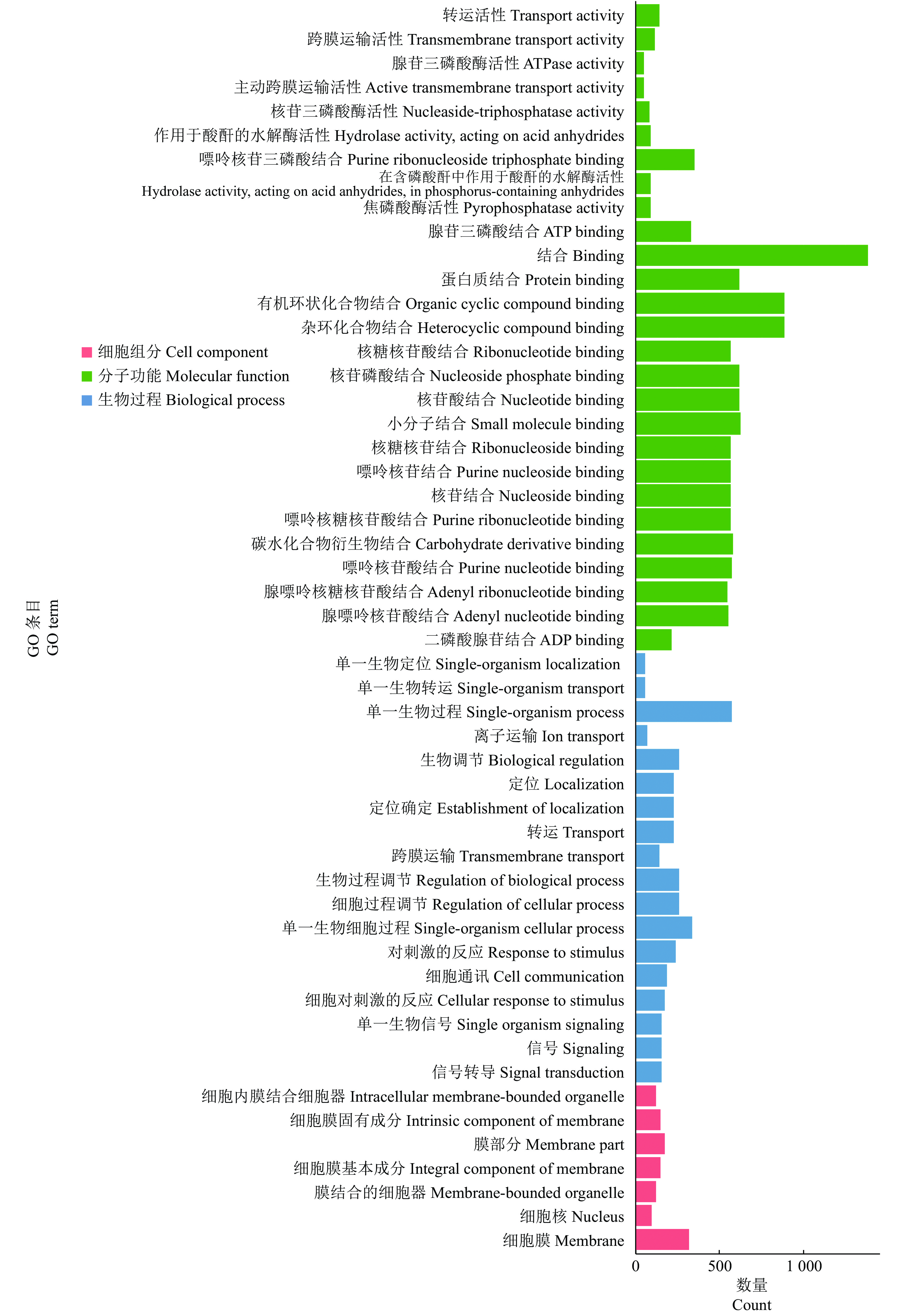
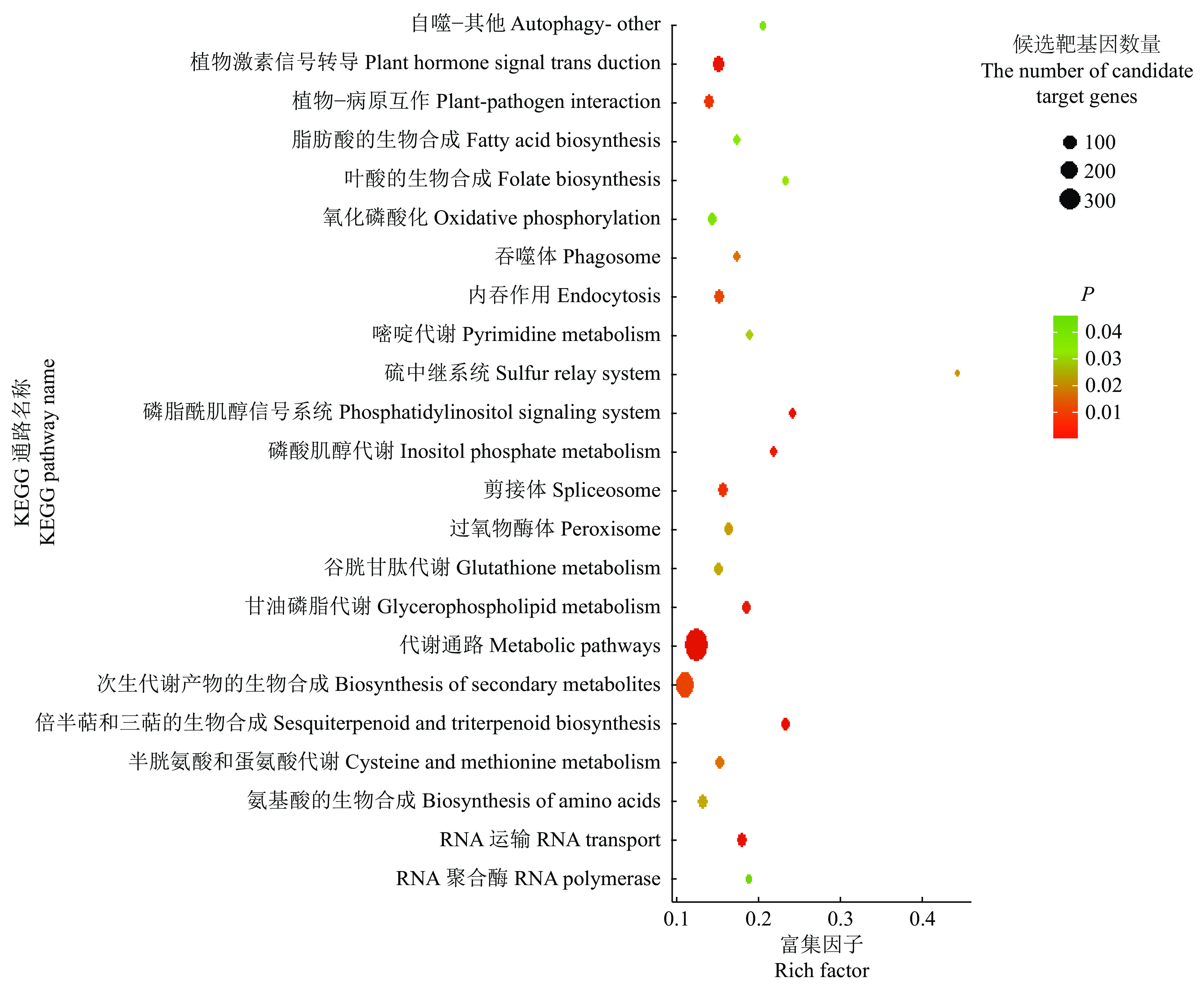
结果在赤桉中,共预测到隶属于54个家族的392个已知miRNA和97个新miRNA;其中,CK组共预测到282个已知miRNA,65个新miRNA;低温处理组共预测到329个已知miRNA,51个新miRNA。挖掘到80个在低温处理下显著差异表达的miRNA,包括55个上调和25个下调。GO基因功能注释和KEGG富集分析的结果表明,这些差异表达miRNA可能通过参与代谢通路、次生代谢物的生物合成、细胞膜的改变、信号转导和生物调节等响应低温胁迫。此外,还挖掘到25个可能与ICE1-CBFs-COR通路有关的miRNA。
结论借助高通量测序和生物信息学软件初步得到了低温胁迫下差异表达的赤桉miRNA,为进一步分析这些miRNA在赤桉低温胁迫中的分子功能提供一些参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo predict, mine and analyze the miRNAs involved in low temperature stress response of Eucalyptus camaldulensis, and lay a foundation for further study of the molecular network of regulating low temperature stress response.
MethodSmall RNAs were sequenced by high-throughput sequencing using the shoot tips of the tissue cultured seedlings of E. camaldulensis from the low temperature treatment group and the control group (CK). The miRBase21.0, Rfam14.1 and E. grandis genome were taken as reference databases. Bowtie, miREAP as well as miRDeep2 software were used for miRNA prediction. RNAfold was used to fold the secondary structure of the predicted miRNA precursors. psRNATarget was used to predict target genes. The miRNAs with differential expression were analyzed through DEGSeq package, and GO annotation and KEGG enrichment analysis were further performed.
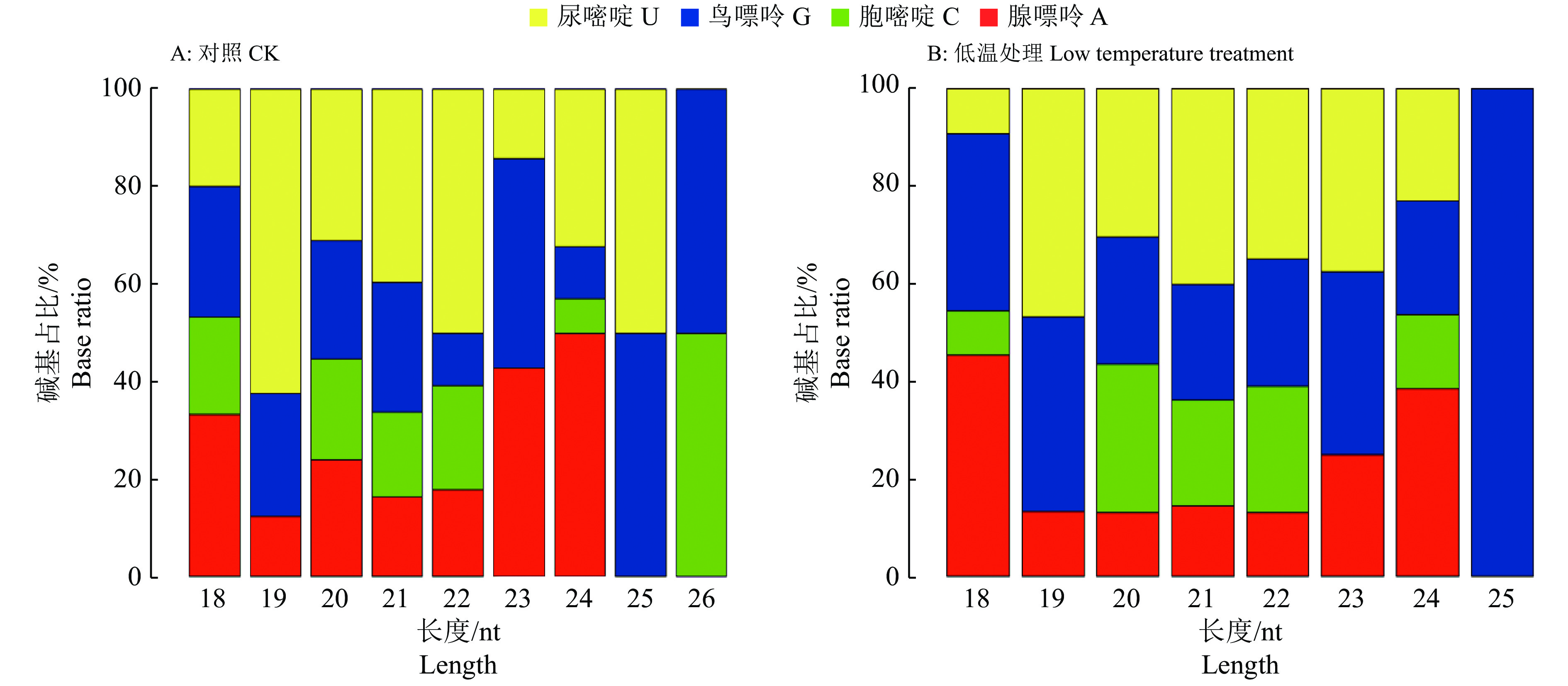
ResultA total of 392 known miRNAs and 97 novel miRNAs belonging to 54 families were predicted in E. camaldulensis. The 282 known miRNAs and 65 novel miRNAs were predicted in CK, while 329 known miRNAs and 51 novel miRNAs were predicted in the low temperature treatment group. At the same time, 80 significantly differentially expressed miRNAs in low temperature treatment group were mined, including 55 up-regulated and 25 down-regulated. The results of GO annotation and KEGG enrichment analysis indicated that these differentially expressed miRNAs might respond to low temperature stress by participating in metabolic pathways, biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, cell membrane changes, signal transduction, and biological regulation. In addition, we found 25 miRNAs that might be associated with the ICE1-CBFs-COR pathway.
ConclusionThe differentially expressed miRNAs are initially obtained by high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics software under low temperature stress, which can provide some references for further analysis of the molecular functions of these miRNAs in E. camaldulensis under low temperature stress.
-
据估计,全世界约50%的潜在耕地为酸性土壤[1],其中,约60%分布在热带亚热带地区[2]。我国南方省份(湖南、福建、浙江和江西)pH<4.5的土壤占各自省份土壤总面积的1.0%~8.8%,4.5≤pH<5.5和5.5≤pH<6.5的土壤相应分别占16.9%~72.2%和15.4%~56.4%[3]。土壤酸化是伴随着土壤形成和发育的自然过程[4],酸沉降[5]、化学肥料的不合理施用[6]、矿区酸性废水的排放[7]以及植物作用[4, 6]均会加速土壤的酸化,我国土壤酸化呈加速发展的趋势[3, 6]。土壤溶液中铝的浓度和形态受其pH影响,随着土壤的酸化,引起土壤盐基离子的淋失,促进活性铝的释放[8]。土壤铝毒性的发挥和土壤的pH密切相关[9],一般认为pH≤5.5时,就有活性铝释出,当土壤酸化至pH 4.3时,才会导致活性铝的大量释放[10]。铝在土壤中以多种形态存在,不同研究者出于研究目的不同将土壤中的铝进行了不同的形态划分[11]。土壤中铝的存在形态直接影响到土壤的结构和性质,影响人类和生物生存的生态环境[1]。然而,土壤成土母质、土地利用方式和土壤类型等的不同最终会导致土壤不同程度的酸化,具有不同pH的矿区土壤和非矿区土壤在酸性特征和铝形态分布上有何差异?且不同(强)酸性土壤的铝形态与其土壤性质之间有何内在联系?这些均有待进一步揭示。本研究选取广东和广西具有代表性的土壤,通过测定土壤pH、土壤交换性酸、交换性铝、阳离子交换量以及铝形态等指标,对不同(强)酸性土壤的酸化规律和铝形态分布规律进行研究,以期为华南地区土壤酸化研究及土壤改良提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试土壤
31个土壤样品(基本情况见表1)采自广东省广州、云浮、韶关、湛江、珠海、清远、惠州、深圳、河源以及广西壮族自治区钦州和防城港等地不同母质或者土地利用方式的代表性土壤,取样深度均为0~20 cm。1~14号为矿山土壤,其中1~6号为广东云浮硫铁矿矿区内便道旁的土壤、拦泥坝中的淤泥以及尾矿库矿渣,7~14号为广东粤北大宝山矿山废石场的弃土。根据种植于废土场的先锋植物五节芒Miscanthus floridulus的不同生长状况进行取样,由于人为的影响(添加石灰、有机肥等),土壤具有不同的pH等酸性特征(表2)。15~31号为不同土地利用类型以及不同母质的非矿山土壤,土壤类型有赤红壤和水稻土。母质包括沉积岩,花岗岩、玄武岩、砂页岩和第四纪红色黏土。所有样品经风干、混匀后,过20、60和100目筛备用。
表 1 土壤样品的基本状况Table 1. Basic conditions of soil samples土壤编号
Soil number地点
Site母岩
Parent rock土壤类型
Soil type土壤质地
Soil texture采样点现状
Site condition土地利用现状
Land use1 广东云浮 石灰岩 矿区弃土 粉质黏壤土 便道旁(相思) 采矿用地 2 广东云浮 石灰岩 矿区弃土 粉壤土 尾矿库淤泥 采矿用地 3 广东云浮 石灰岩 矿区弃土 壤质砂土 尾矿库坝坡 采矿用地 4 广东云浮 石灰岩 矿区弃土 壤土 尾矿库坝坡 采矿用地 5 广东云浮 石灰岩 矿区弃土 砂质黏壤 便道边坡 采矿用地 6 广东云浮 石灰岩 矿区弃土 壤质砂土 尾矿库中间 采矿用地 7 广东大宝山 花岗岩 矿区弃土 壤土 半死(五节芒) 采矿用地 8 广东大宝山 花岗岩 矿区弃土 壤土 死亡(五节芒) 采矿用地 9 广东大宝山 花岗岩 矿区弃土 壤土 正常生长(五节芒) 采矿用地 10 广东大宝山 花岗岩 矿区弃土 粉壤土 死亡状态(五节芒) 采矿用地 11 广东大宝山 花岗岩 矿区弃土 粉壤土 正常生长(五节芒) 采矿用地 12 广东大宝山 花岗岩 矿区弃土 粉壤土 正常生长(五节芒) 采矿用地 13 广东大宝山 花岗岩 矿区弃土 粉壤土 正常生长(五节芒) 采矿用地 14 广东大宝山 花岗岩 赤红壤 砂质壤土 裸露地表 采矿用地 15 广西钦州 第四纪红色黏土 赤红壤 壤质砂土 旱地 林地 16 广西防城港 第四纪红色黏土 赤红壤 黏壤土 旱地 林地 17 广东湛江 玄武岩 水稻土 黏土 作物(甘蔗) 水浇地 18 广东湛江 玄武岩 砖红壤 砂质黏壤土 作物(菜园) 园地 19 广东韶关 砂页岩 红壤 黏壤土 常绿阔叶林 林地 20 广东广州 花岗岩 赤红壤 砂质黏壤土 常绿阔叶林 林地 21 广东广州 花岗岩 赤红壤 砂质黏壤土 常绿阔叶林 林地 22 广东广州 花岗岩 赤红壤 砂质黏壤土 作物(荔枝) 果园 23 广东珠海 花岗岩 赤红壤 砂质壤土 常绿阔叶林 林地 24 广东惠州 花岗岩 水稻土 壤土 作物(玉米) 水浇地 25 广东惠州 花岗岩 赤红壤 壤土 旱地 林地 26 广东河源 花岗岩 赤红壤 黏土 常绿阔叶林 林地 27 广东江门 花岗岩 水稻土 粉质黏壤土 作物(水稻) 水田 28 广东韶关 花岗岩 红壤 黏土 常绿阔叶林 林地 29 广东深圳 花岗岩 赤红壤 砂质壤土 常绿阔叶林 林地 30 广东清远 花岗岩 赤红壤 粉壤土 作物(油茶) 旱地 31 广东揭阳 花岗岩 赤红壤 壤土 作物(油茶) 旱地 表 2 土壤样品的理化性质1)Table 2. Physicochemical properties of soil samples土壤编号
Soil numberpH
(H2O)pH
(KCl)w/% b/(cmol·kg–1) w(SOM)/
(g·kg–1)砂粒
Sand粉粒
Particle黏粒
ClayEx-Q Ex-H Ex-Al CEC 1 4.50 3.74 14.85 53.52 31.63 2.66 0.61 2.06 3.97 12.59 2 3.22 3.04 29.18 52.28 18.54 7.63 2.65 4.98 5.59 54.93 3 3.30 3.15 79.02 6.84 14.14 2.51 1.18 1.33 1.76 36.47 4 2.44 2.42 37.85 42.70 19.44 16.88 5.39 11.49 6.32 12.59 5 4.65 4.12 51.98 26.09 21.94 0.47 0.14 0.37 2.24 42.28 6 3.27 3.14 79.79 7.89 12.32 2.42 1.30 1.12 8.80 55.80 7 2.80 2.82 42.85 43.74 13.41 14.86 4.42 10.44 18.71 19.72 8 3.11 2.99 41.92 42.45 15.63 7.95 1.81 6.14 9.56 11.71 9 4.80 4.26 49.90 36.97 13.13 2.28 1.16 1.12 7.43 12.18 10 2.90 2.92 39.16 57.20 3.64 12.74 2.86 9.89 5.81 24.96 11 2.91 2.84 39.31 54.27 6.42 8.23 2.86 5.38 6.62 43.13 12 3.36 3.14 39.19 56.29 4.52 4.85 2.02 2.84 2.78 17.25 13 4.31 3.66 39.16 55.63 5.21 2.44 1.30 1.13 5.75 34.32 14 2.56 2.44 65.14 32.19 2.67 26.67 10.74 15.93 4.73 54.93 15 2.53 2.62 81.76 11.48 6.76 11.40 2.84 8.56 4.46 25.27 16 3.08 2.89 27.46 41.03 31.51 7.79 1.97 5.82 19.33 19.72 17 4.40 3.87 10.35 34.61 55.04 3.07 0.48 2.59 14.18 36.47 18 4.62 3.51 45.19 28.85 25.96 3.60 0.42 3.18 15.01 22.83 19 4.54 3.66 37.96 27.77 34.27 4.28 0.47 3.81 16.88 34.32 20 4.13 3.28 52.82 23.21 23.97 5.34 0.61 4.74 12.31 43.13 21 4.25 3.37 50.23 22.79 26.98 5.52 0.69 4.75 10.46 46.55 22 4.23 3.57 22.44 48.99 28.57 2.87 0.47 2.40 8.78 12.18 23 4.05 3.46 57.42 23.83 18.75 5.07 1.42 3.65 6.62 24.39 24 5.53 4.23 48.28 35.08 16.64 1.26 1.01 0.25 5.75 23.48 25 3.73 3.45 31.56 49.20 19.24 2.39 0.61 1.79 8.51 13.03 26 4.22 3.84 22.44 19.33 58.23 1.62 0.47 1.15 14.39 24.96 27 5.03 4.18 5.82 59.96 34.22 1.52 1.33 0.19 30.13 20.56 28 4.09 3.09 27.85 23.23 48.92 17.61 2.06 15.55 7.70 44.41 29 7.50 7.13 69.25 20.57 10.18 8.93 1.07 7.86 14.99 3.73 30 4.29 3.63 1.99 73.85 24.16 2.99 0.20 2.79 17.69 26.87 31 4.39 3.77 37.72 38.86 23.42 7.58 0.25 7.33 8.72 22.65 1) Ex-Q:总交换性酸;Ex-H:交换性氢;Ex-Al:交换性铝;CEC:阳离子交换量; SOM:土壤有机质
1) Ex-Q:Total exchangeable acid; Ex-H:Exchangeable hydrogen; Ex-Al: Exchangeable aluminum;CEC:Cation exchange capacity; SOM :Soil organic matter1.2 测定方法
称取1 g土壤分别加入无CO2水或1 mol·L–1氯化钾2.5 mL,混匀,pH计(雷磁PHS-3C)测定pH,土壤有机质(SOM)用重铬酸钾容量法–外加热法测定,黏粒(直径<0.002 mm)含量用吸管法测定(美国质地制),阳离子交换量(CEC)采用乙酸铵交换–原子吸收分光光度法测定,总交换性酸(Ex-Q)、交换性氢(Ex-H)和交换性铝(Ex-Al)的质量摩尔浓度采用1 mol·L–1氯化钾交换–中和滴定法测定,淋洗液消耗的标准NaOH量为Ex-Q总量,加入足量的氟化钠时消耗的碱量为Ex-H的质量摩尔浓度,两者之差即为Ex-Al的质量摩尔浓度[12]。
铝形态的连续浸提采用改进的连续分级方法,区分土壤样本之间铝形态分布差异。首先,准确称取过60目筛的土壤样品1 g,小心装入100 mL带盖的硬质塑料圆底离心管中,然后进行分步提取:
1)交换态铝(AlEx):在1 g土壤中加入0.1 mol·L–1的BaCl2溶液10 mL,室温下振荡30 min,离心5 min (3 500 r·min–1,下同),过滤上清液至塑料瓶中作为原液待用,提取2次,合并提取液,用去离子水洗涤残余物,离心,弃上清液;
2)弱有机结合态铝(AlOrw):向上一步残渣加入0.5 mol·L–1的CuCl2溶液10 mL,室温下振荡2 h,离心,过滤上清液至塑料瓶中作为原液待用,提取2次,合并提取液,用去离子水洗涤残余物,离心,弃上清液;
3)有机结合态铝(AlOr):向上一步残渣加入0.1 mol·L–1的Na4P2O7(pH 10)溶液40 mL,室温下振荡2 h,离心,过滤上清液至塑料瓶中作为原液待用,提取2次,合并上清液,用1 mol·L–1的Na2SO4洗涤残余物,离心,弃去上清液;
4)无定形态铝(AlAmo):向上一步残渣加入0.2 mol·L–1的草酸铵(pH 3.0)溶液40 mL,黑暗条件下振荡4 h,离心,过滤,用去离子水洗涤残余物,离心,去上清液;
5)氧化铁结合态铝(AlDCB):向上一步残渣加入0.3 mol·L–1Na3C6H5O7、1 mol·L–1NaHCO3和固体Na2S2O4,80 ℃水浴条件下搅拌15 min,离心,过滤,用1 mol·L–1的NaCl洗涤残余物,离心,弃上清液;
6)非晶态铝硅酸盐和三水铝石(AlAag):将上一步残渣转移至镍坩埚中,加入0.1 mol·L–1的NaOH,煮沸2.5 min,冷却后过滤[13-15];
7)矿物态铝(AlMin):将土壤全铝的量减去前6种形态之和作为矿物态铝。土壤全铝采用HF−HNO3−HClO4−H2O2消解[14]。最后用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES,Varian 710-ES)(工作参数:波长237.312 nm,雾化气压230 kPa,仪器的检测限度范围为:0~10 mol·L–1)测定各形态的铝。
1.3 数据统计
采用Microsoft Excel 2003进行数据整理,用SAS 9.0软件进行t检验和相关性分析。通过在R中导入ADE-4软件包对不同土壤样本的酸化和铝形态分布特征进行主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis, PCA)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 矿区和非矿区土壤基本理化性质的对比分析
矿区和非矿区31个土壤样本的基本理化指标测定结果列于表2,并对其理化性质进行t检验,结果(表3)显示,非矿区土壤的pH(H2O)、CEC和黏粒含量均显著高于矿区土壤(P<0.05),其中黏粒含量的差异达到了极显著水平(P<0.01)。而矿区土壤的Ex-H含量显著高于非矿区土壤(P<0.05)。
表 3 供试土壤的基本理化性质指标t检验1)Table 3. t-test of the basic physicochemical properties of soil samples土壤类型
Soli typepH
(H2O)pH
(KCl)w(黏粒Clay)/ % b/(cmol·kg–1) w(SOM)/
(g·kg–1)Ex-Q Ex-H Ex-Al CEC 矿区(n=14)
Mining area3.44 3.32 13.05 8.04 2.75 5.30 6.43 30.92 非矿区(n=17)
Non-mining area4.39 3.81 28.64 5.46 0.97 4.49 12.70 26.15 P 0.008 9 0.128 0 0.000 8 0.261 8 0.031 4 0.608 9 0.003 6 0.366 8 1) Ex-Q:总交换性酸;Ex-H:交换性氢;Ex-Al:交换性铝;CEC:阳离子交换量; SOM:土壤有机质
1) Ex-Q:Total exchangeable acid; Ex-H:Exchangeable hydrogen; Ex-Al:Exchangeable aluminum;CEC:Cation exchange capacity; SOM:Soil organic matter2.2 土壤铝形态分布特征
矿区和非矿区土壤铝形态分布如表4所示。从数量上看,矿区土壤b(AlEx)在0.00~76.79 mmol·kg–1,平均13.39 mmol·kg–1,最高为76.79 mmol·kg–1(土样14),pH高于4.50的3个样点(1、5和9号)AlEx含量极低,分别为1.94、0.15和0.00 mmol·kg–1。矿区土壤的b(AlOrw)为0.92~11.52 mmol·kg–1,其中13号土样含量最高;b(AlOr)为0.06~54.42 mmol·kg–1,平均为12.96 mmol·kg–1;b(AlAmo)介于12.17~181.09 mmol·kg–1之间;矿区土壤的b(AlDCB)介于24.29~90.74 mmol·kg–1之间,且大多在90.74 mmol·kg–1以下。对于非矿区土壤b(AlEx)在0.39~28.32 mmol·kg–1,平均为10.43 mmol·kg–1;b(AlOrw)为2.62~23.55 mmol·kg–1,平均为8.32 mmol·kg–1;b(AlOr)为1.59~155.90 mmol·kg–1,平均为41.46 mmol·kg–1;非矿区土壤b(AlAmo)介于10.30~98.38 mmol·kg–1之间,平均为36.43 mmol·kg–1;b(AlDCB)在7.34~152.21 mmol·kg–1范围内。非矿区土壤的b(AlAag)为0.60 mol·kg–1,高于矿区土壤(0.39 mol·kg–1)。所有土样的b(AlMin)含量均在0.64 mol·kg–1(15号)以上,最高为27号土样(2.78 mol·kg–1)。除15号土样(0.74 mol·kg–1)外,所有土样的b(AlTotal)在1.09 mol·kg–1以上,其中最高为17号土样(4.09 mol·kg–1)。t检验结果显示,非矿区土壤的AlOrw和AlOr含量显著高于矿区土壤(P<0.05,表4)。
表 4 供试土壤中的铝形态1)Table 4. Aluminum forms in soil samples土壤类型
Soli type土壤编号
Soil numberb/(mmol·kg–1) b/(mol·kg–1) AlEx AlOrw AlOr AlAmo AlDCB AlAag AlMin AlTotal 矿区
Mining area1 1.94 1.89 54.42 29.34 56.22 0.21 1.21 1.56 2 8.86 3.24 28.08 39.57 51.73 0.35 1.56 2.04 3 2.27 0.92 10.99 20.82 24.29 0.15 1.12 1.33 4 25.95 2.78 6.61 48.45 77.90 0.14 1.09 1.40 5 0.15 5.77 11.99 12.17 25.07 0.07 0.96 1.09 续表4 Continued table 4 土壤类型
Soil type土壤编号
Soil numberb/(mmol·kg–1) b/(mol·kg–1) AlEx AlOrw AlOr AlAmo AlDCB AlAag AlMin AlTotal 矿区
Mining area6 2.24 1.06 3.46 16.91 28.04 0.19 0.89 1.13 7 19.43 3.92 5.65 52.38 46.63 0.46 2.03 2.62 8 9.45 2.60 12.59 31.77 36.94 0.58 2.58 3.26 9 0.00 1.67 5.82 58.05 90.74 0.42 2.70 3.27 10 17.25 3.26 7.31 37.29 64.79 0.82 2.04 2.99 11 10.37 3.16 7.62 35.77 52.58 0.70 2.04 2.85 12 5.25 2.69 23.89 32.84 52.18 0.46 2.60 3.18 13 7.56 11.52 2.97 181.09 38.78 0.50 2.02 2.76 14 76.79 3.61 0.06 48.62 37.50 0.37 1.32 1.86 均值 Mean 13.39 3.44 12.96 46.08 48.81 0.39 1.73 2.24 中位数 Median 8.21 2.97 7.46 36.53 49.18 0.39 1.79 2.33 最大值 Max. 76.79 11.52 54.42 181.09 90.74 0.82 2.70 3.27 最小值 Min. 0.00 0.92 0.06 12.17 24.29 0.07 0.89 1.09 标准差 SD 19.82 2.64 14.23 41.09 19.45 0.22 0.64 0.84 非矿区
15 28.32 2.74 1.59 28.71 7.34 1.52 0.64 0.74 Non-mining 16 22.07 5.92 7.20 36.30 22.30 0.50 1.92 2.28 area 17 5.14 14.77 115.97 98.38 152.21 0.03 2.19 4.09 18 5.99 9.58 155.90 41.09 112.43 0.27 0.90 2.26 19 10.93 8.57 19.53 18.71 108.04 0.60 2.33 3.18 20 16.72 9.78 22.66 13.05 51.53 0.45 1.77 2.91 21 15.58 9.24 20.22 13.32 49.56 0.43 1.27 2.15 22 8.38 3.60 11.64 50.29 82.30 0.29 2.50 3.26 23 5.85 8.18 48.42 48.46 21.28 0.50 2.02 2.65 24 0.46 3.68 28.70 10.30 7.37 1.02 2.46 2.96 25 3.62 2.62 11.72 12.74 32.55 0.77 1.44 1.93 26 3.28 6.38 84.31 20.43 78.35 0.69 1.81 2.29 27 1.00 4.32 13.74 40.90 17.29 0.27 2.78 3.36 28 23.60 8.58 27.93 93.88 76.30 0.44 2.73 3.23 29 0.39 23.55 4.93 35.48 42.26 1.05 0.98 1.52 30 17.77 11.85 62.25 21.45 61.17 0.34 1.69 2.21 31 8.12 8.02 67.13 35.81 93.89 0.99 1.03 2.23 均值 Mean 10.43 8.32 41.46 36.43 59.77 0.60 1.79 2.54 中位数 Median 8.12 8.18 22.66 35.48 51.53 0.50 1.81 2.29 最大值 Max. 28.32 23.55 155.90 98.38 152.21 1.52 2.78 4.09 最小值 Min. 0.39 2.62 1.59 10.30 7.34 0.03 0.64 0.74 标准差 SD 8.71 5.15 43.26 25.86 41.34 0.37 0.67 0.80 P 0.609 4 0.002 3 0.018 9 0.432 0 0.341 6 0.075 5 0.783 2 0.304 1 1) AlEx:交换态铝;AlOrw:弱有机结合态铝;AlOr:有机结合态铝;AlAmo:无定形态铝;AlDCB:氧化铁结合态铝;AlAag:非晶态铝硅酸盐和三水铝石;AlMin:矿物态铝;AlTotal:全量铝
1) AlEx: Exchangeable aluminum; AlOrw: Weakly organically bound aluminum; AlOr: Organically bound aluminum; AlAmo: Amorphous aluminum; AlDCB: Iron oxide bound aluminum; AlAag: Amorphous aluminosilicate and gibbsite; AlMin: Mineral aluminum; AlTotal: Total aluminum2.3 土壤铝形态与土壤性质之间的相关性分析
矿区土壤铝形态与土壤性质的相关系数(r)如表5所示。结果表明,矿区土壤的AlEx含量与pH(H2O)、pH(KCl)分别呈显著的负相关关系(r=–0.577*和–0.638*);AlEx含量与Ex-Q、Ex-H和Ex-Al含量均呈正相关关系(r=0.927**,r=0.976**和r=0.870**)。此外,AlOr、AlAag含量分别与黏粒含量呈显著负相关关系(r=–0.666**和r=–0.635*);AlDCB含量与SOM含量呈显著负相关关系(r=–0.566*)。由表5还可以看出,与矿区土壤相似,非矿区土壤的AlEx含量与pH(H2O)和pH(KCl)分别呈显著负相关关系(r=–0.671*和r=–0.624**),与Ex-Q、Ex-H和Ex-Al含量分别呈正相关关系(r=0.662**,r=0.555**和r=0.632**)。与矿区土壤不同,非矿区土壤的AlOrw含量与pH(H2O)和pH(KCl)分别呈显著正相关关系(r=0.668*和r=0.717**),AlAmo和AlDCB含量与黏粒含量呈显著正相关关系(r=0.516*和r=0.603*)。AlDCB和AlAag含量与Ex-H含量呈显著负相关关系(r=–0.579*和r=–0.601*)。此外,AlMin和AlTotal含量分别与黏粒含量呈显著的正相关关系(r=0.523*和r=0.637**)。
表 5 土壤铝形态与土壤性质之间的相关系数(r)1)Table 5. Correlation coefficients (r) between aluminum forms and soil properties土壤类型
Soil type铝形态
Al formpH
(H2O)pH
(KCl)黏粒
ClayEx-Q Ex-H Ex-Al CEC SOM 矿区(n=14)
Mining
area交换态铝 AlEx −0.577* −0.638* −0.400 0.927** 0.976** 0.870** 0.076 0.270 弱有机结合态铝 AlOrw 0.272 0.209 −0.255 −0.058 −0.027 −0.074 −0.007 0.123 有机结合态铝 AlOr 0.344 0.270 0.666** −0.341 −0.371 −0.341 −0.295 −0.264 无定形态铝 AlAmo 0.218 0.142 −0.340 −0.015 0.035 −0.043 0.106 −0.059 氧化铁结合态铝 AlDCB 0.045 0.051 0.039 0.162 0.081 0.201 0.116 −0.566* 非晶态铝硅酸盐和三水铝 AlAag −0.273 -0.237 −0.635* 0.229 0.111 0.288 0.286 −0.159 矿物态铝 AlMin 0.071 0.116 −0.433 −0.047 −0.108 −0.011 0.287 −0.507 全量铝 AlTotal −0.013 0.024 −0.515 0.044 −0.033 0.086 0.300 −0.445 非矿区(n=17)
Non-mining
area交换态铝 AlEx −0.671** −0.624** −0.062 0.662** 0.555* 0.632** −0.212 0.477 弱有机结合态铝 AlOrw 0.668** 0.717** 0.014 0.179 −0.238 0.246 0.184 −0.028 有机结合态铝 AlOr 0.030 −0.065 0.412 −0.276 −0.474 −0.216 0.070 0.141 无定形态铝 AlAmo −0.025 −0.034 0.516* 0.421 0.212 0.429 −0.002 0.174 氧化铁结合态铝 AlDCB 0.070 −0.004 0.603* −0.075 −0.579* 0.030 0.080 0.278 非晶态铝硅酸盐和三水铝 AlAag 0.172 0.055 0.269 −0.303 −0.601* −0.220 0.088 0.311 矿物态铝 AlMin 0.051 −0.107 0.523* 0.153 −0.008 −0.170 0.269 0.205 全量铝 AlTotal 0.125 −0.071 0.637** −0.269 −0.335 −0.235 0.275 0.352 1) Ex-Q:总交换性酸;Ex-H:交换性氢;Ex-Al:交换性铝;CEC:阳离子交换量; SOM:土壤有机质; “*” 和 “**” 表示在0.05和0.01水平上显著相关
1) Ex-Q: Total exchangeable acid; Ex-H:Exchangeable hydrogen; Ex-Al: Exchangeable aluminum;CEC: Cation exchange capacity; SOM:Soil organic matter;“*” and “**” indicate significant correlation at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively2.4 土壤铝形态与土壤各指标的综合分析
矿区和非矿区土壤铝形态和各酸化指标及黏粒含量的主成分分析结果(图1)显示:第1主成分(PC1)累计方差贡献率为43.3%,第2主成分(PC2)累计方差贡献率为22.1%,第1、2主成分累计方差贡献率达到65.4%,可以反映不同土壤铝形态和各酸化指标的大部分信息,且受第1、2主成分的综合影响,不同处理样点空间分布差异极显著(P<0.01)。PC1和PC2的空间载荷图(图1a)表明:PC1主要与土壤pH(KCl)、pH(H2O)以及Ex-Al、Ex-H、Ex-Q和AlEx含量等酸性指标参数密切相关,受PC1酸化性质参数的影响,矿区和非矿区土壤样点空间分布差异极显著(P<0.01),非矿区土壤样点显著向土壤pH(H2O)和pH(KCl)升高的方向偏移,而矿区土壤则显著偏向Ex-Al、Ex-H、Ex-Q和AlEx含量升高的方向(图1b)。表明与非矿区土壤相比,矿区土壤酸性强,具有较强的酸性特征。PC2主要与土壤黏粒、AlOrw、AlOr、AlDCB和AlAag含量等参数密切相关(图1a),受PC2参数的影响,非矿区土壤显著向土壤黏粒、AlOrw、AlOr、AlDCB和AlAag含量升高的方向偏移(图1b),表明与矿区土壤相比,非矿区具有更高的土壤黏粒、AlOrw、AlOr、AlDCB和AlAag含量。
2.5 土壤pH与土壤铝形态、酸化指标和黏粒的主成分分析
对不同土壤的pH进行范围划分(pH<3.50、3.50≤pH<4.50、4.50≤pH<5.50和pH≥5.50),再综合土壤铝形态、酸化指标、黏粒指标的变化进行主成分分析,结果(图2a)显示:PC1累计方差贡献率为43.2%,PC2累计方差贡献率为23.2%,第1、2主成分累计方差贡献率达到66.4%,可以反映不同土壤参数的大部分信息,受第1、2主成分的综合影响,不同pH范围划分样点空间分布差异显著(P<0.01)。图2a表明:PC1主要与Ex-Al、Ex-H、Ex-Q和AlEx酸化性质参数密切相关,受PC1理化性质参数的影响,不同pH范围划分样点空间分布差异显著,pH≤3.50组样点显著地向Ex-Al、Ex-H、Ex-Q和AlEx含量增大的方向偏移,表明pH≤3.50组土壤具有较强的酸性特征。PC2主要与土壤AlOrw、AlDCB、AlOr和黏粒含量密切相关,受PC2理化性质参数的影响,3.50≤pH<4.50、4.50≤pH<5.50和pH≥5.50组样点显著地向AlOrw、AlDCB、AlOr和黏粒含量增多的方向偏移(图2b),表明3.50≤pH<4.50的供试土壤含有较多的AlOr、AlDCB和黏粒含量。
3. 讨论与结论
土壤酸化是伴随着土壤形成和发育的自然过程[16],由酸化而引起的铝毒问题日益受到广泛关注。铝是地壳中最丰富的元素之一,也是组成土壤无机矿物的主要元素,其丰度为82.3 g·kg–1[17]。我国土壤表层(A层)铝背景值的算术平均值为66.2±16.26 mg·kg–1,本研究土壤全铝质量分数为29.37~110.55 g·kg–1(1.09~4.09 mol·kg–1),由于土壤全铝含量与土壤的矿物类型有关[17],这说明本研究中的供试土壤类型差异较大。土壤pH主要取决于交换性酸的量,而交换性酸的大部分为交换性铝,因此交换性铝与土壤pH密切相关。土壤酸度主要决定着土壤交换性铝的含量,而土壤交换性铝在很大程度上制约着土壤的pH[18]。本研究结果显示,矿区和非矿区土壤的pH(H2O)与AlEx含量均呈显著负相关(r=–0.577**和–0.671**)关系,这与前人的研究结果一致[18]。土壤铝毒性的发挥和土壤的pH密切相关,一般认为pH≤5.5时,就有活性铝释出,当土壤酸化至pH 4.3时,才会导致活性铝的大量释放[10]。本研究分别有29和20个土样pH分别在5.5和4.3以下,说明大部分土壤样品已存在铝毒问题。一般情况下,土壤中的Ex-H含量远小于Ex-Al含量。当土壤pH<4.8时,一般认为土壤Ex-Al占Ex-Q的97%以上[18],即Ex-H占很小一部分,但实际上,Ex-H含量的占比更高一些,甚至达到40%[19]。本研究中的6、9、13、24和27号土样的Ex-H含量略高于Ex-Al含量,这与前人研究结果不一致。郭彦彪等[20]也发现个别大宝山矿区废石场土壤的Ex-H含量(0.55和0.64 mmol·kg–1)高于对应的Ex-Al含量(0.20和0.18 mmol·kg–1)。以上这种“反常”现象已有较多报道[21],这与有机物或者化学肥料的添加[22]和土壤的pH较高有关[23]。而本文的6、9、13(矿区土壤)和24、27(水稻土)号土样均为受人为干扰(施肥、有机物料和石灰等)较为强烈的土壤。
铝的迁移转化、生物有效性及生物毒性除与其含量有关外,还与其形态有密切的关系[24]。一般认为土壤交换态和有机络合态铝是土壤中最为活跃的部分,与土壤铝毒的发挥关系密切[17-18]。本研究供试土壤的AlEx含量在0.00~76.79 mmol·kg–1,仅占全铝量的0.00%~4.12%。虽然土壤AlEx占全铝量的含量比例较小,但其对土壤生物的毒性较强,因此其数量和活性应引起广泛的关注[18]。0.5 mol·L–1CuCl2提取的铝为弱有机结合态铝,常作为潜在活性铝[15]。本研究中矿区土壤AlOrw的平均含量(3.44 mmol·kg–1)低于非矿区土壤(8.32 mmol·kg–1,P<0.01),说明单独就本形态来说,矿区土壤的铝毒性较低,这可能与非矿区土壤受到了强烈的人为干扰(施肥、有机物料和石灰等)有关。0.5 mol·L–1Na4P2O7(pH 8.5)提取的有机结合态铝,是一种非晶态铝[25]。一方面,AlOr的形成既阻碍了铝的老化结晶和污染物的循环、周转,又使铝离子和羟基单体铝等对生物有毒性的形态转化为无毒或少毒的形态,从而降低其生物毒性[24]。另一方面,AlOr的增加能提高铝在土壤中的移动性,在某种程度上可降低铝的毒性[13]。本研究结果发现非矿区土壤的AlOr的平均含量(41.46 mmol·kg–1)显著高于矿区土壤(12.96 mmol·kg–1,P<0.05),表明对于此形态来说,非矿区土壤的铝毒性较低。草酸铵缓冲液提取的无定形态铝被认为是活性氧化铝,本研究中矿区土壤具有较多的AlAmo。在非矿区土壤中,无定形铝与黏粒含量显著正相关(r=0.516*)。AlDCB主要是指与氧化铁结合的游离铝[13]。本研究发现矿区土壤的AlDCB与有机质含量显著负相关(r=–0.566*),可能是因为游离氧化铁主要集中于黏粒部分。此外,本研究发现非矿区土壤的AlDCB与土壤的Ex-H含量呈显著负相关关系(r=−0.579*),但邵宗臣等[13]发现AlDCB含量与可滴定酸度呈显著正相关,具体机理尚不明确。而文中不同类型土壤AlDCB的量差异较大则与邵宗臣等[13]研究结果一致。本研究中矿区土壤的AlAgg含量与土壤黏粒含量、Ex-H含量均呈显著负相关关系(r=–0.635*,r=–0.605*),而邵宗臣等[13]研究结果表明AlAgg含量与土壤黏粒和可滴定酸度均呈显著正相关,其机理有待进一步揭示。土壤黏粒中含有较多的氧化铝和氧化铁,与铝产生复合作用,从而减少铝的溶出,使土壤中铝不断积累[26]。本研究中非矿区土壤的矿物态铝与土壤黏粒含量呈显著正相关(r=0.523*)。邵宗臣等[13]发现红壤中的铝主要以矿物态形式存在,平均约占全铝的62.04%,且花岗岩母质的红壤占58.93%~80.12%,平均占72.11%。本研究中矿区土壤的AlMin含量分别占全铝的71.07%~88.50%,比例范围变化不大;而非矿区土壤AlMin的含量比例在39.56%~86.68%,比例范围变化较大,其中17和18号为玄武岩发育而成的砖红壤,AlMin含量比例分别为53.35%和39.56%,平均为46.45%,这与邵宗臣等[13]研究结果一致(AlMin范围为33.98%~55.72%,平均47.39%)。黏粒是次生铝硅酸盐矿物,全铝含量高。本研究发现非矿区土壤的全铝含量和黏粒含量呈极显著的正相关关系(r=0.637**),这与王娅娅等[27]研究结果一致。
铝在土壤中的含量与土壤母质、成土过程以及人类活动等有关[28]。金属矿山由于矿产开采,金属硫化物暴露于空气后氧化而产生大量的酸性废水,导致矿区各类废弃物严重酸化[29],其pH更是低至3.0以下,同时伴随着Al的大量溶出[7]。本研究发现与非矿区土壤相比,矿区土壤酸性强,具有明显的酸性特征。一般情况下,由于矿山开采过程使原有土壤表层剥离,矿山土壤养分含量非常贫瘠,几乎不存在氮和有机质[30]。但本研究中的矿区土壤的平均有机质含量却高于非矿区土壤,这与矿区植被修复过程中有机物料的人为添加有关。土壤pH与有机质是影响茶园土壤中活性铝含量的主要因素[31]。本研究中,矿区土壤pH普遍偏低,而非矿区土壤则具有更高的土壤黏粒含量、弱有机结合态铝、有机结合态铝和CEC,所以2种土壤表现出了不同的特征。此外,通过对不同土壤的pH值进行范围划分后发现,pH<3.50、3.50≤pH<4.50、4.50≤pH<5.50和pH≥5.50组样点具有不同的分布特征,其中3.50≤pH<4.50组有较高的弱有机结合态铝、有机结合态铝和黏粒含量等,产生这种结果的原因可能是铝离子在不同pH下以Al3+、AlOH2+和
${\rm{Al(OH)}}^+_2 $ 等水合态的形式存在,这些水合态离子的溶解性与移动性不同,其含量又与土壤pH和有机质有关[32]。本研究得出以下结论:1)矿区和非矿区土壤的酸性特征具有显著差异,与矿区土壤相比,非矿区土壤具有更高的有机结合态铝、pH(H2O)、CEC和黏粒含量;2)矿区和非矿区土壤各指标间相关性有所不同;3)不同pH梯度的土壤的酸化特征也有显著性差异。因此,矿区土壤酸性改良和修复应重视土壤pH和有机质含量的提升。
-
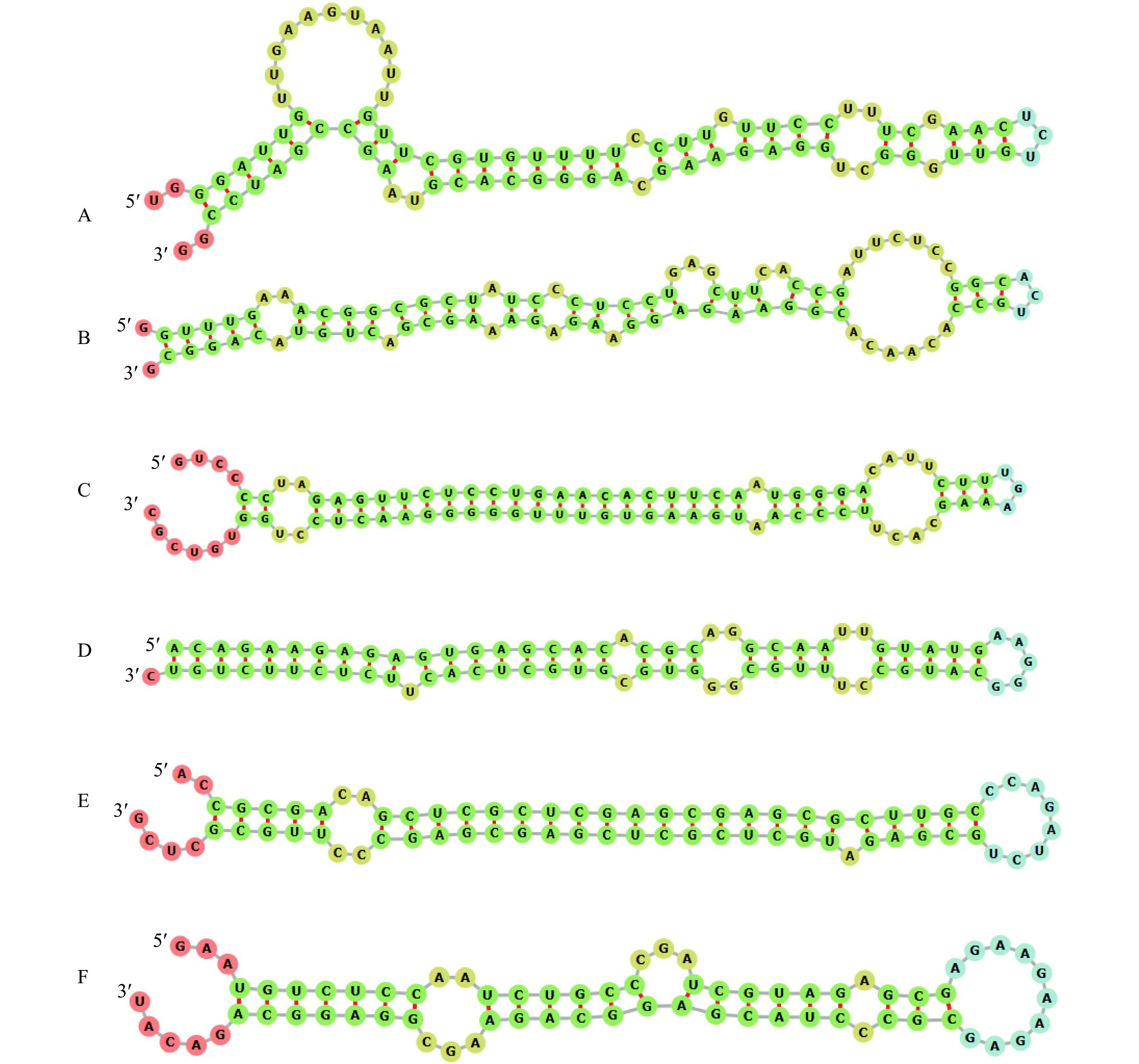
图 4 赤桉部分预测miRNA前体二级结构
A: eca-miR164b-3p, B: eca-miR390b-5p, C: eca-miR395f-3p, D: eca-miR-n40, E: eca-miR-n45, F: eca-miR-n51; A~C: 已知miRNA, D~F: 新miRNA
Figure 4. The secondary structure of some predicted miRNAs in Eucalyptus camaldulensis
A: eca-miR164b-3p, B: eca-miR390b-5p, C: eca-miR395f-3p, D: eca-miR-n40, E: eca-miR-n45, F: eca-miR-n51; A−C: Known miRNAs; D−F: Novel miRNAs
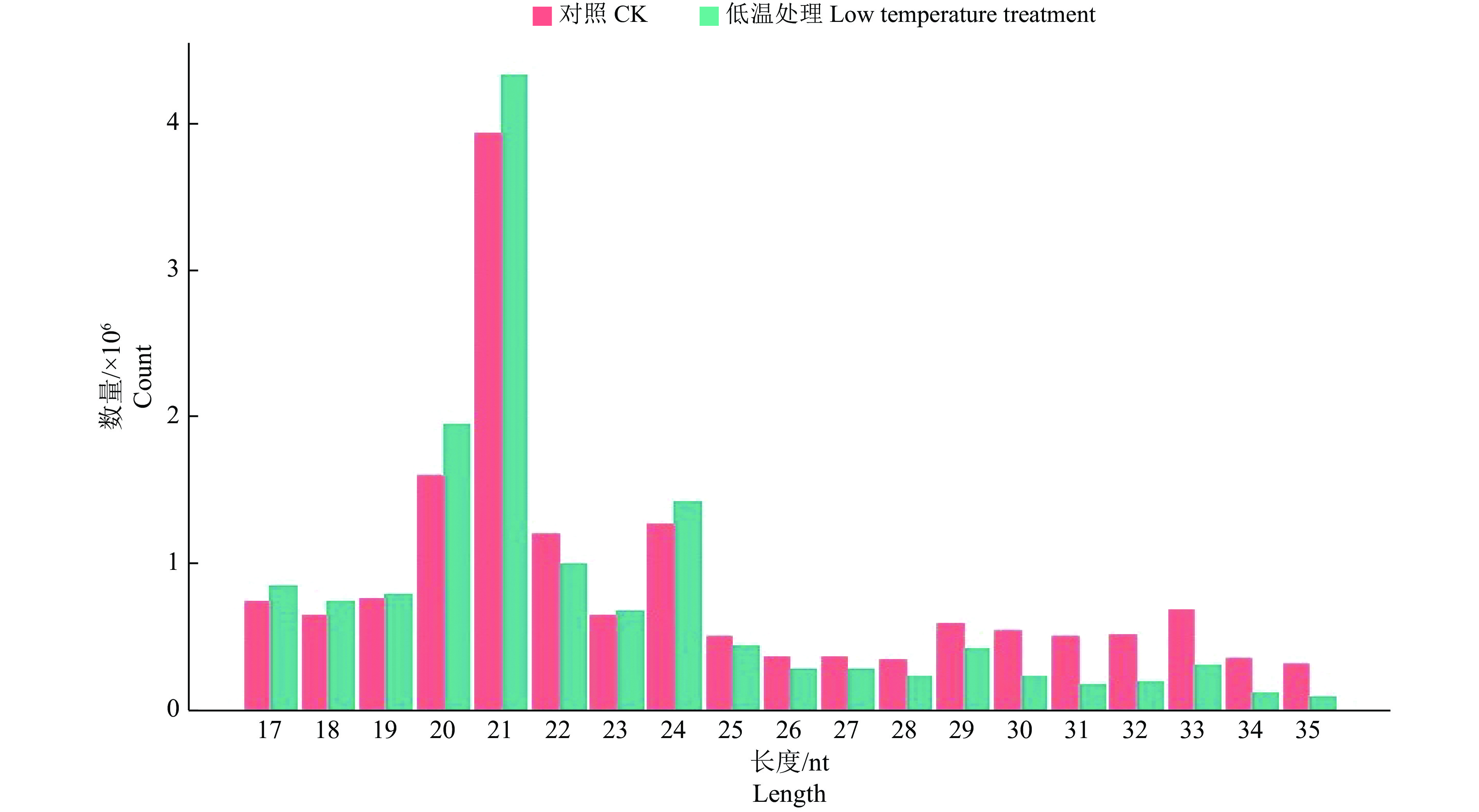
表 1 赤桉小RNA分类统计
Table 1 Classification statistics of small RNAs in Eucalyptus camaldulensis
种类
Type对照 CK 低温处理 Low temperature treatment 数量 Count 占比/% Percentage 数量 Count 占比/% Percentage 核糖体RNA rRNA 4 787 452 30.27 3 769 781 26.08 核内小RNA snRNA 55 640 0.35 32 977 0.23 核仁小RNA snoRNA 33 402 0.21 24 413 0.17 转运RNA tRNA 828 159 5.24 368 918 2.55 其他 Other 10 108 761 63.93 10 259 988 70.97 总计 Total 15 813 414 100.00 14 456 077 100.00 表 2 赤桉ICE1-CBFs-COR通路相关miRNA
Table 2 The miRNAs associated with ICE1-CBFs-COR pathway in Eucalyptus camaldulensis
miRNA1) 长度/nt
Length序列(5′→3′)
Sequence靶基因
Target gene基因ID
Gene ID蛋白质特征
Protein characteristiceca-miR-n33 21 ACGGAAUUGUUCGAGCCGACU ICE1 Eucgr.G01938 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR171g-3p 19 UGAGCCGGACCAAUAUCAC MPK6 Eucgr.L00026 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase eca-miR171j-3p 22 GAUGAGCCGGACCAAUAUCACG MPK6 Eucgr.L00026 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase eca-miR5780b-5p 23 UCCAGUCUCUGAUCAAUUUUGAC OST1 Eucgr.E00345 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase eca-miR390b-5p 21 GGCGCUAUCCCUCCUGAGCUU OST1 Eucgr.I00977 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase eca-miR-n51↓ 21 GAAUGUCUCCAAUCUGCCCGA OST1 Eucgr.H04745 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase eca-miR-n60 20 AGCUCAUCCAUCUGUAAGAG OST1 Eucgr.D02135 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase BZR1 Eucgr.H01239 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR156m-3p 20 UGCUCUCUCUCUUCUGUCAA BZR1 Eucgr.F01541 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR156o-3p 20 UGCUCUCUAUCUUCUGUCAA SOC1 Eucgr.A02846 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR156j-5p 21 UUGACAGAAGAGAGAGAGCAC SOC1 Eucgr.D02427 转录因子 Transcription factor 续表 2 Continued table 2 miRNA1) 长度/nt
Length序列(5′→3′)
Sequence靶基因
Target gene基因ID
Gene ID蛋白质特征
Protein characteristiceca-miR159k-3p 19 UUUGGAUUGAAUGGAGUCU SOC1 Eucgr.K00208 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR94a-3p 21 UCCCGGGAACAGAAUCAUUAC EIN3 Eucgr.J00631 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR845c-3p 20 CCUACAAUUGGUAUCAGAGC PIF3 Eucgr.B01825 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR-n38 21 AGGUGAAUUCUUAUAGAUCCA PIF3 Eucgr.B01825 转录因子 Transcription factor eca-miR482f-3p 21 UCUUUCCUAUUCCUCCAUUCC SIZ1 Eucgr.B02470 E3苏素化连接酶 E3 SUMO ligase eca-miR23a-5p 25 UGAGAGUGAGUGUAGAGUAGGGAAU HOS1 Eucgr.E00402 E3泛素化连接酶 E3 ubiquitin ligase eca-miR-n2 21 GCUCCCCAAACUGACUACCAA HOS1 Eucgr.E00402 E3泛素化连接酶 E3 ubiquitin ligase eca-miR-n41↓ 22 UCGGAAGUCUUUGAGGGAGAGA EBF1 Eucgr.C01723 E3泛素化连接酶 E3 ubiquitin ligase eca-miR862a-5p↓ 21 AGUUUCCUUGAAGACAUCCAA EBF1 Eucgr.C01524 E3泛素化连接酶 E3 ubiquitin ligase eca-miR845a-5p 20 AGCUCUGAUACCAAUUGUUG EBF1 Eucgr.C02778 E3泛素化连接酶 E3 ubiquitin ligase eca-miR396a-3p 21 AAGCUCAAGAAAGCUGUGGGA EBF1 Eucgr.C02778 E3泛素化连接酶 E3 ubiquitin ligase eca-miR7782a-5p 19 AGUGGUAUCAGAGCAGGUU BTF3 Eucgr.K02308 NAC蛋白β亚基 β-subunit of NAC protein) eca-miR7782b-5p 23 AGUGGUAUCAGAGCAGGUCGUCG BTF3 Eucgr.K02308 NAC蛋白β亚基 β-subunit of NAC protein) eca-miR827b-5p 22 UUUUGUUGAUGGCCAUCUAAUC CAMTA3 Eucgr.H04783 转录激活子 Transcription activator eca-miR164b-3p 20 UGGAGAAGCAGGGCACGUAA PhyB Eucgr.A00380 光感受器 Photoreceptor 1)“↓”表示在4 ℃低温处理24 h后显著下调
1)“↓” shows significant down-regulation after 4 ℃ low temperature treatment for 24 h -
[1] SHANG X H, ARNOLD R J, WU Z H, et al. Combining quantitative data on growth, wood density and other traits with SSR markers to evaluate genetic diversity and structure in a planted population of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn[J]. Forests, 2019, 10(12): 1090. doi: 10.3390/f10121090
[2] BARTEL D P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function[J]. Cell, 2004, 116(2): 281-297. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
[3] HAUSSER J, ZAVOLAN M. Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions-beyond repression of gene expression[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2014, 15(9): 599-612. doi: 10.1038/nrg3765
[4] SUN Y H, SHI R, ZHANG X H, et al. MicroRNAs in trees[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2012, 80(1): 37-53. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9864-z
[5] LI F, PIGNATTA D, BENDIX C, et al. MicroRNA regulation of plant innate immune receptors[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(5): 1790-1795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118282109
[6] KNIGHT M R, KNIGHT H. Low-temperature perception leading to gene expression and cold tolerance in higher plants[J]. New Phytologist, 2012, 195(4): 737-751. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04239.x
[7] SUNKAR R, ZHU J K. Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2004, 16(8): 2001-2019. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.022830
[8] 张紫阳, 刘艳, 魏瑞研, 等. 木本植物miRNAs参与环境胁迫应答的研究进展[J/OL]. 分子植物育种, 2020(2020-09-11) [2020-11-01]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20200910.1644.004.html. [9] LIN Y Z, ZHENG H Q, ZHANG Q, et al. Functional profiling of EcaICE1 transcription factor gene from Eucalyptus camaldulensis involved in cold response in tobacco plants[J]. Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2014, 23(2): 141-150. doi: 10.1007/s13562-013-0192-z
[10] ZHANG Z Y, CHENG L, ZHANG W H, et al. Characterization of transcription activation domain of EcaICE1 and its interaction with EcaSIZ1 in Eucalyptus camaldulensis[J]. Trees, 2020, 34(5): 1243-1253. doi: 10.1007/s00468-020-01994-9
[11] CHENG L, ZHANG W H, HU J L, et al. Characterization of the key region and putative phosphorylation sites of EcaICE1 in its molecular interaction with the EcaHOS1 protein in Eucalyptus camaldulensis[J]. Plant Biology, 2021, 23(2): 400-406. doi: 10.1111/plb.13205
[12] LIN Z, LI Q, YIN Q, et al. Identification of novel miRNAs and their target genes in Eucalyptus grandis[J/OL]. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 2018, 14(2018-07-19)[2020-11-01]. https//doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1273-x.
[13] FRIEDLÄNDER M R, MACKOWIAK S D, LI N, et al. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, 40(1): 37-52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr688
[14] 林元震. R与ASReml-R统计学[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2016: 381-415. [15] WANG L K, FENG Z X, WANG X, et al. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(1): 136-138. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp612
[16] DAI X B, ZHAO P X. psRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(2): 155-159.
[17] ASHBURNER M, BALL C A, BLAKE J A, et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology[J]. Nature Genetics, 2000, 25(1): 25-29. doi: 10.1038/75556
[18] KANEHISA M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, 32(22): 277-280.
[19] TIAN T, LIU Y, YAN H Y, et al. agriGO v2.0: A GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2017, 45(1): 122-129.
[20] XIE C, MAO X Z, HUANG J J, et al. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39(2): 316-322.
[21] SHI Y T, DING Y L, YANG S H. Molecular regulation of CBF signaling in cold acclimation[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2018, 23(7): 623-637. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2018.04.002
[22] ZHOU M Q, TANG W. MicroRNA156 amplifies transcription factor-associated cold stress tolerance in plant cells[J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2019, 294(2): 379-393. doi: 10.1007/s00438-018-1516-4
[23] LU S F, SUN Y H, CHIANG V L. Stress-responsive microRNAs in Populus[J]. Plant Journal, 2008, 55(1): 131-151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03497.x
[24] BAO H, CHEN M, CHEN H, et al. Transcriptome-wide identification of miRNA targets and a TAS3-homologous gene in Populus by degradome sequencing[J]. Genes & Genomics, 2019, 41(7): 849-861.
[25] YANG Y T, ZHANG X, SU Y C, et al. miRNA alteration is an important mechanism in sugarcane response to low-temperature environment[J]. BMC Genomics, 2017, 18(1): 818-833.
[26] 郭鹏, 张万筠, 马红玉, 等. 番茄Sly-miR167的抗冷性研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 2014, 34(7): 1371-1376. [27] 薄维平, 曾长英, 宋顺, 等. 木薯耐寒相关microRNA的差异表达分析[J]. 热带作物学报, 2010, 31(8): 1260-1265. [28] GAO N, QIANG X M, ZHAI B N, et al. Transgenic tomato overexpressing ath-miR399d improves growth under abiotic stress conditions[J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 2015, 62(3): 360-366. doi: 10.1134/S1021443715030061
[29] 张达巍, 王遂, 高源, 等. microRNA在植物响应低温胁迫中的作用[J]. 植物生理学报, 2019, 55(2): 117-124. [30] AGARWAL M, HAO Y, KAPOOR A, et al. A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2006, 281(49): 37636-37645. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605895200
[31] DONG, C H, AGARWAL M, ZHANG Y Y, et al. The negative regulator of plant cold responses, HOS1, is a RING E3 ligase that mediates the ubiquitination and degradation of ICE1[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(21): 8281-8286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602874103
[32] MIURA K, JIN J, LEE J, et al. SIZ1-mediated SUMOylation of ICE1 controls CBF3/DREB1A expression and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Cell, 2007, 19(4): 1403-1414. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048397
[33] DING Y L, LI H, ZHANG X Y, et al. OST1 kinase modulates freezing tolerance by enhancing ICE1 stability in Arabidopsis[J]. Developmental Cell, 2015, 32(3): 278-289. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.12.023
[34] LI H, DING Y L, SHI Y T, et al. MPK3- and MPK6-mediated ICE1 phosphorylation negatively regulates ICE1 stability and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis[J]. Developmental Cell, 2017, 43(5): 630-642. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.09.025
[35] LI H, YE K Y, SHI Y T, et al. BZR1 positively regulates freezing tolerance via CBF-dependent and CBF-independent pathways in Arabidopsis[J]. Molecular Plant, 2017, 10(4): 545-559. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.01.004
[36] JIANG B C, SHI Y T, ZHANG X Y, et al. PIF3 is a negative regulator of the CBF pathway and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2017, 114(32): E6695-E6702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706226114
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 吴家龙,李铤,梁春梅,张俊涛. 土壤酶活抑制剂和外源植物调节剂对薇甘菊的抑制效应. 热带作物学报. 2024(12): 2670-2677 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 庞晓艳,潘继花,陈迎港,刘飞,叶敦雨,马芳. 日照市茶园土壤活性铝形态特征及影响因素. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 185-193 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黎梅杰,段正山,姜华,周凯,罗富成,段新慧,韩博. 铝胁迫下楚雄南苜蓿的生理响应. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学). 2023(04): 615-620 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 覃圣峰,杨怡森,马俊卿,孙晨瑜,廖虹霖,黄京华. 酸性土壤条件下接种丛枝菌根真菌缓解铝对玉米生长抑制作用的研究. 江苏农业科学. 2022(02): 59-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 任富天,张秋英,杨广,柏杨巍,高红杰,李兆,刘山宝,王健祺. 离子型稀土尾矿深层土壤剖面铵态氮污染特征及影响因素. 土壤学报. 2022(02): 517-527 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 邓婷,吴家龙. 耕地土壤酸化现状及治理路径探析——以广东省为例. 中国农学通报. 2022(24): 70-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 梁宏卫,Prakash Lakshmanan,刘晓燕,黄柯钧,颜睿,罗霆. 具有固氮和耐酸特性甘蔗属野生割手密的筛选与鉴定. 西南农业学报. 2022(12): 2700-2707 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 肖家昶,郑开敏,马俊英,郑阳霞. NO对铝胁迫下西瓜根系生理及矿物质含量的影响. 华北农学报. 2021(06): 116-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈志为,邓慧华,洪滔,樊月,吴承祯,陈建忠,林晗. 闽北地区杉木、千年桐纯林与杉桐混交林的土壤活性铝形态特征. 应用与环境生物学报. 2020(01): 48-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张芸萍,易克,谢春凤,解燕,闫晨兵,何志明,刘加红,王瑞宝,李强. 云南富源红壤烟区酸碱度空间分布及其与主要养分关系研究. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版). 2020(05): 113-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(12)



 下载:
下载: