Recognition of mango fruit diseases based on image processing and deep transfer learning
-
摘要:目的
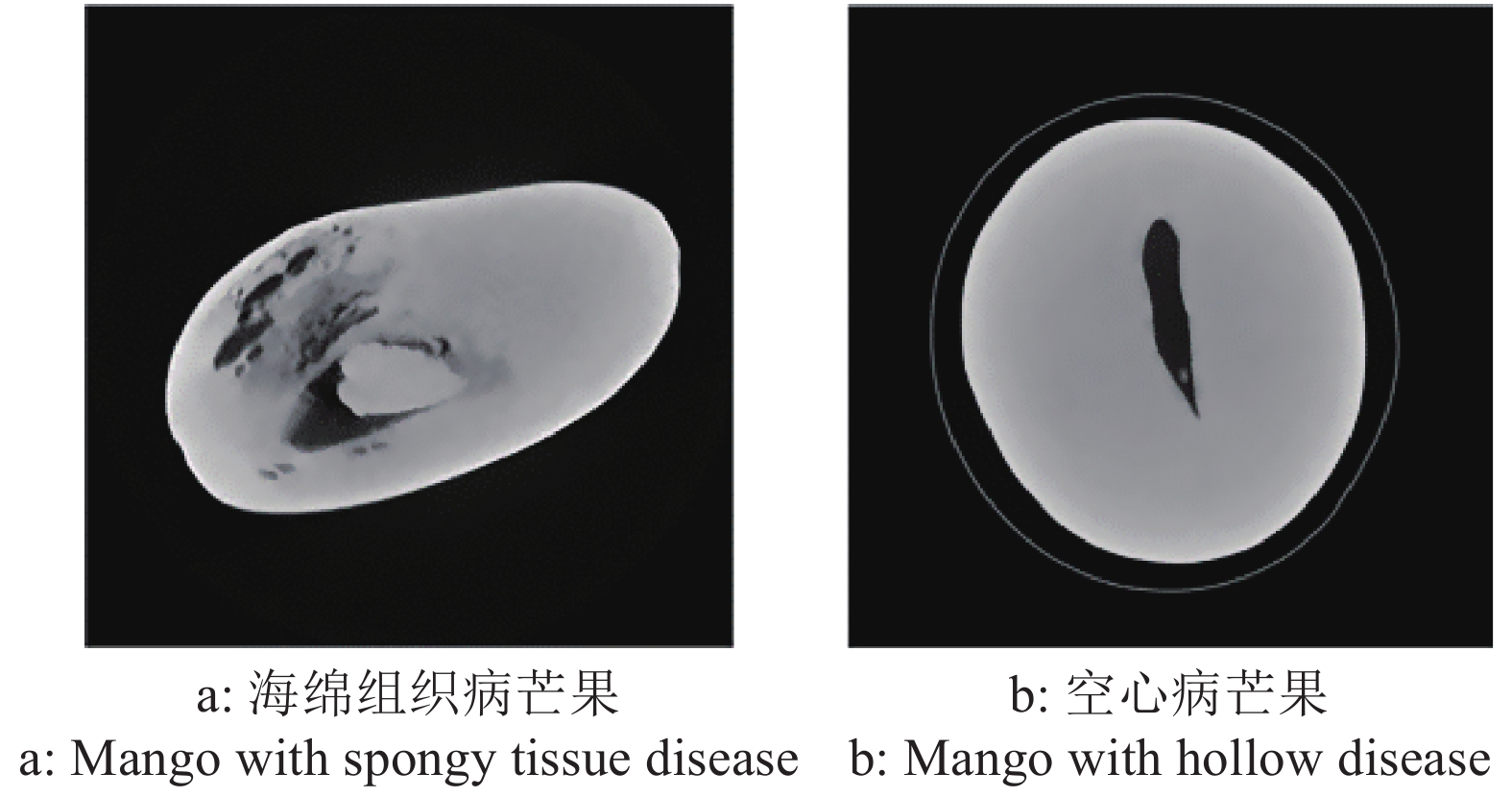
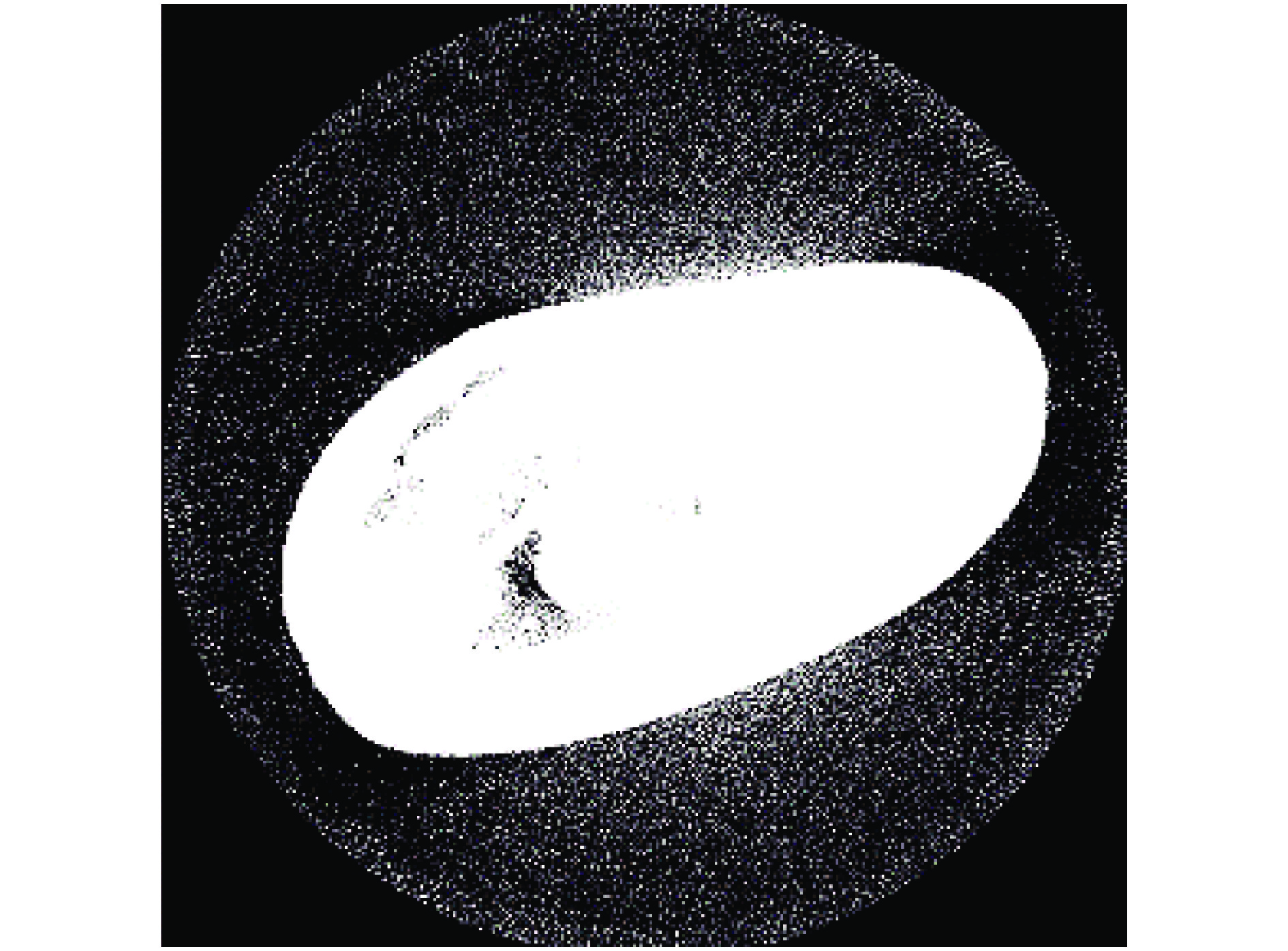
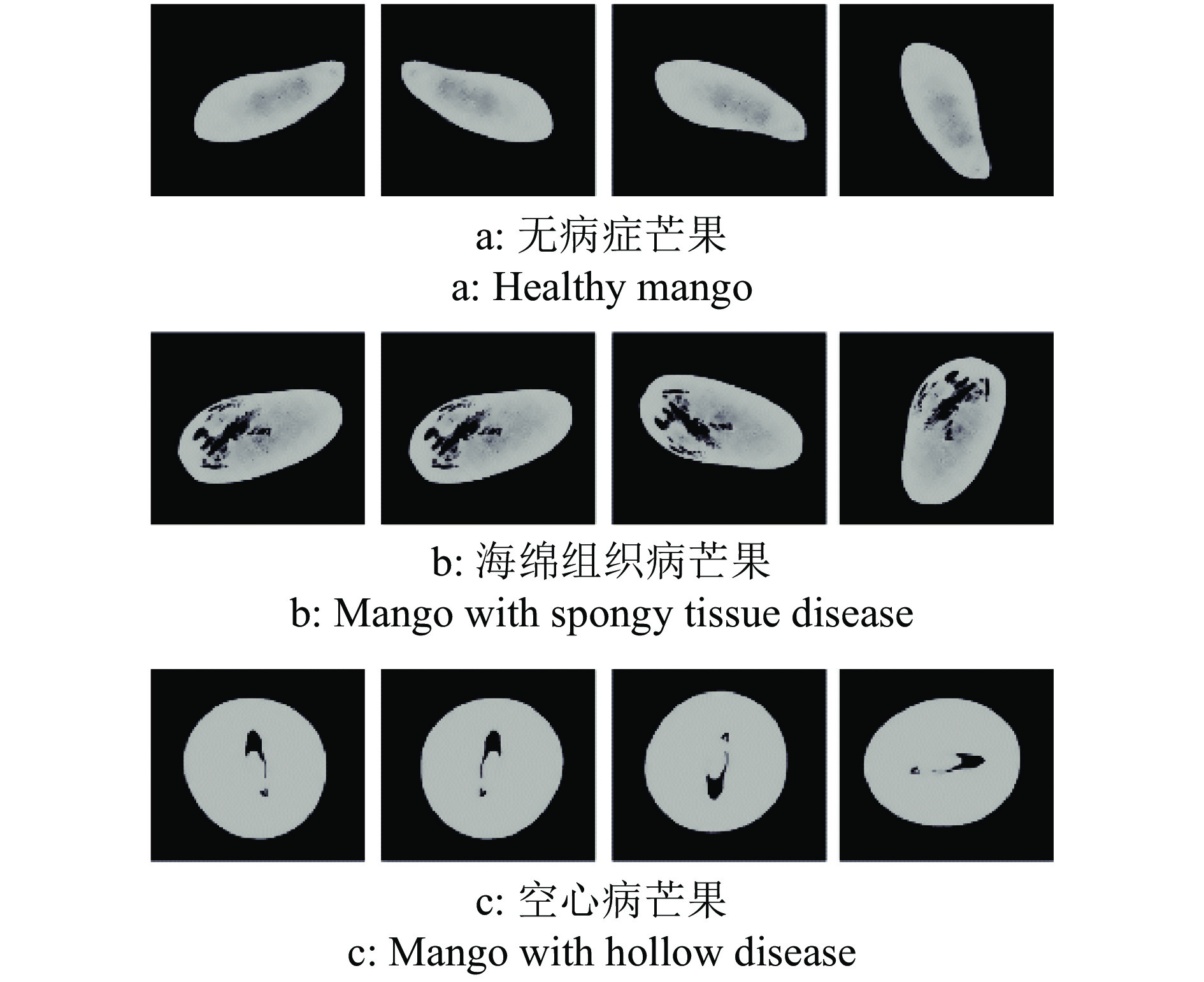
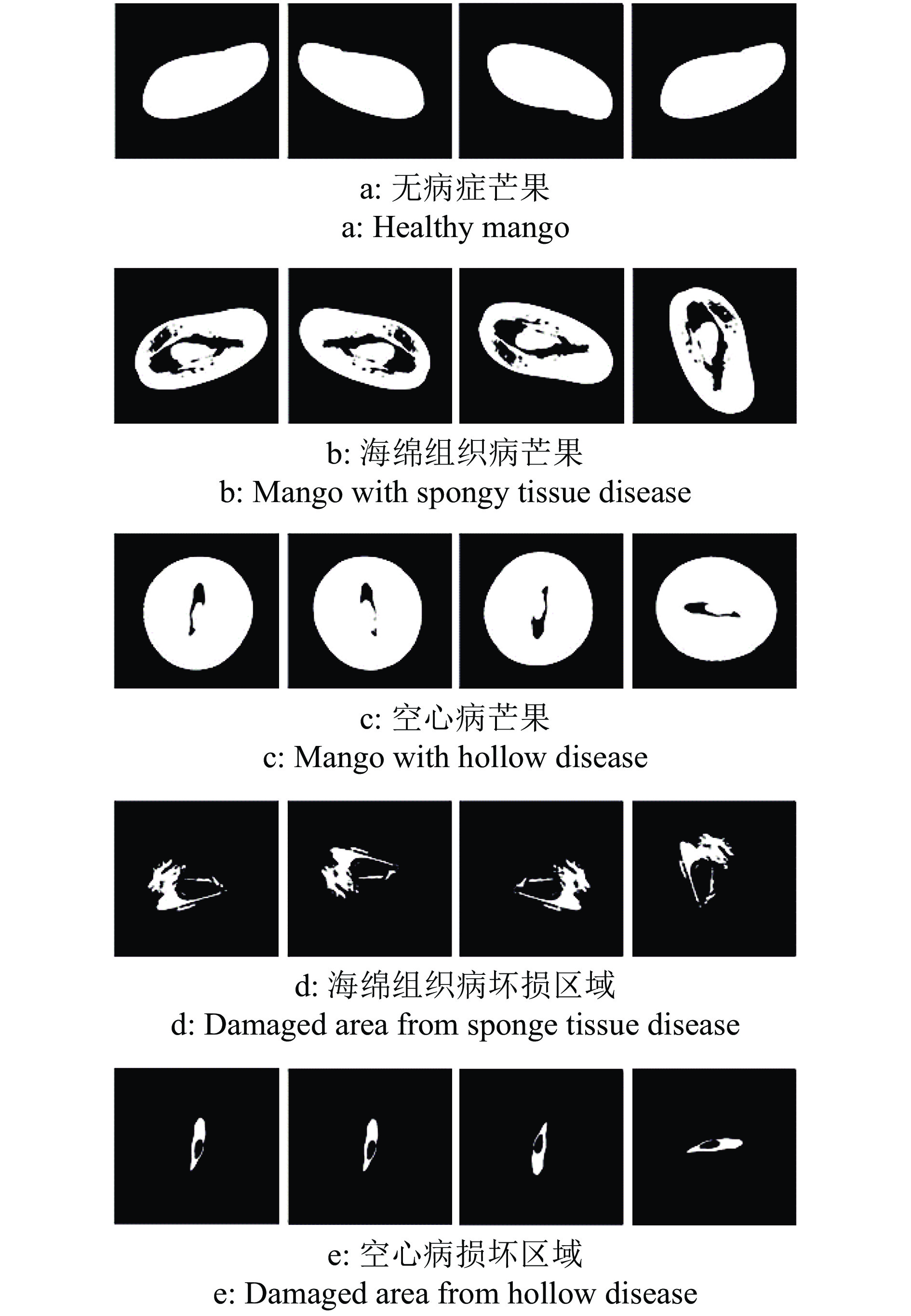
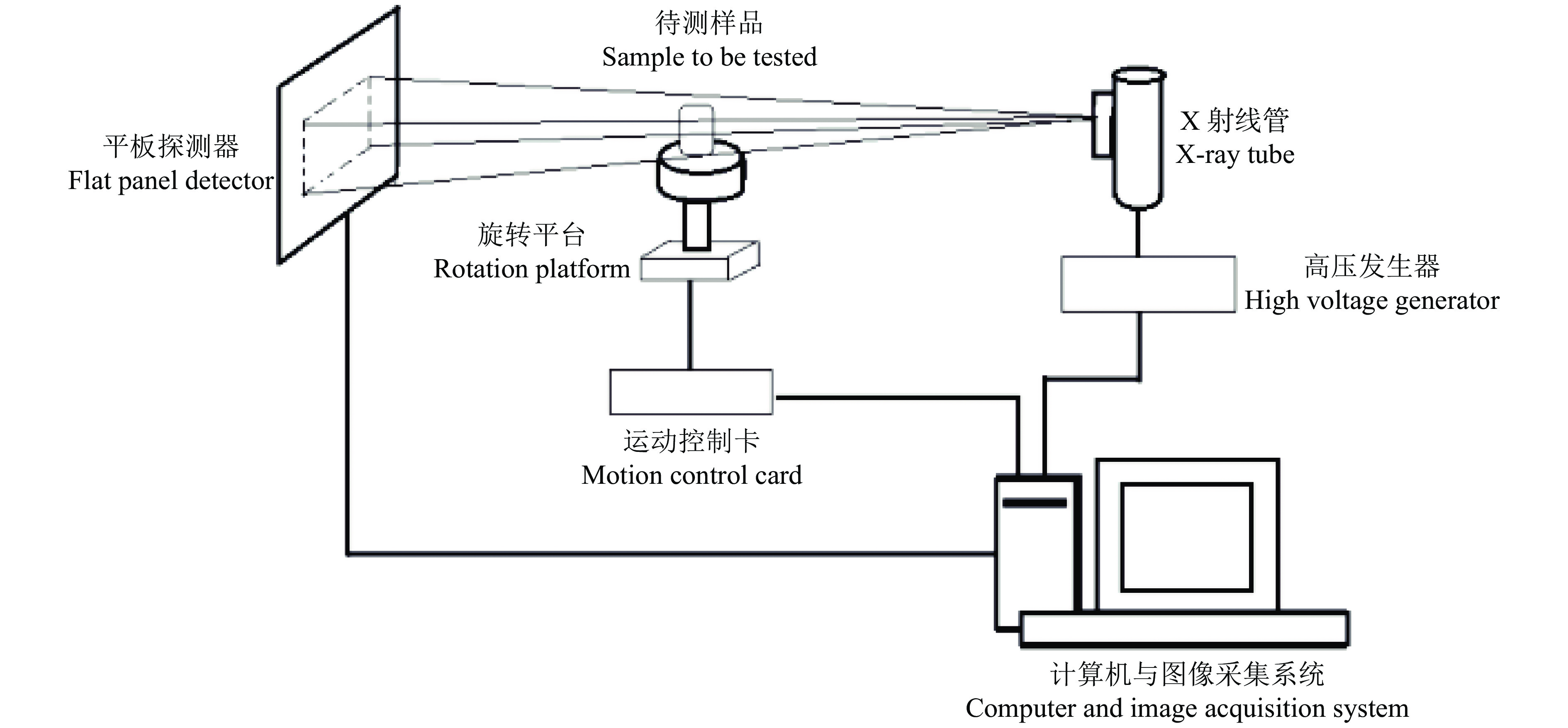
基于计算机层析成像(Computed tomography, CT)设备所得芒果CT序列图像,实现芒果内部品质的无损检测和病状识别分类。
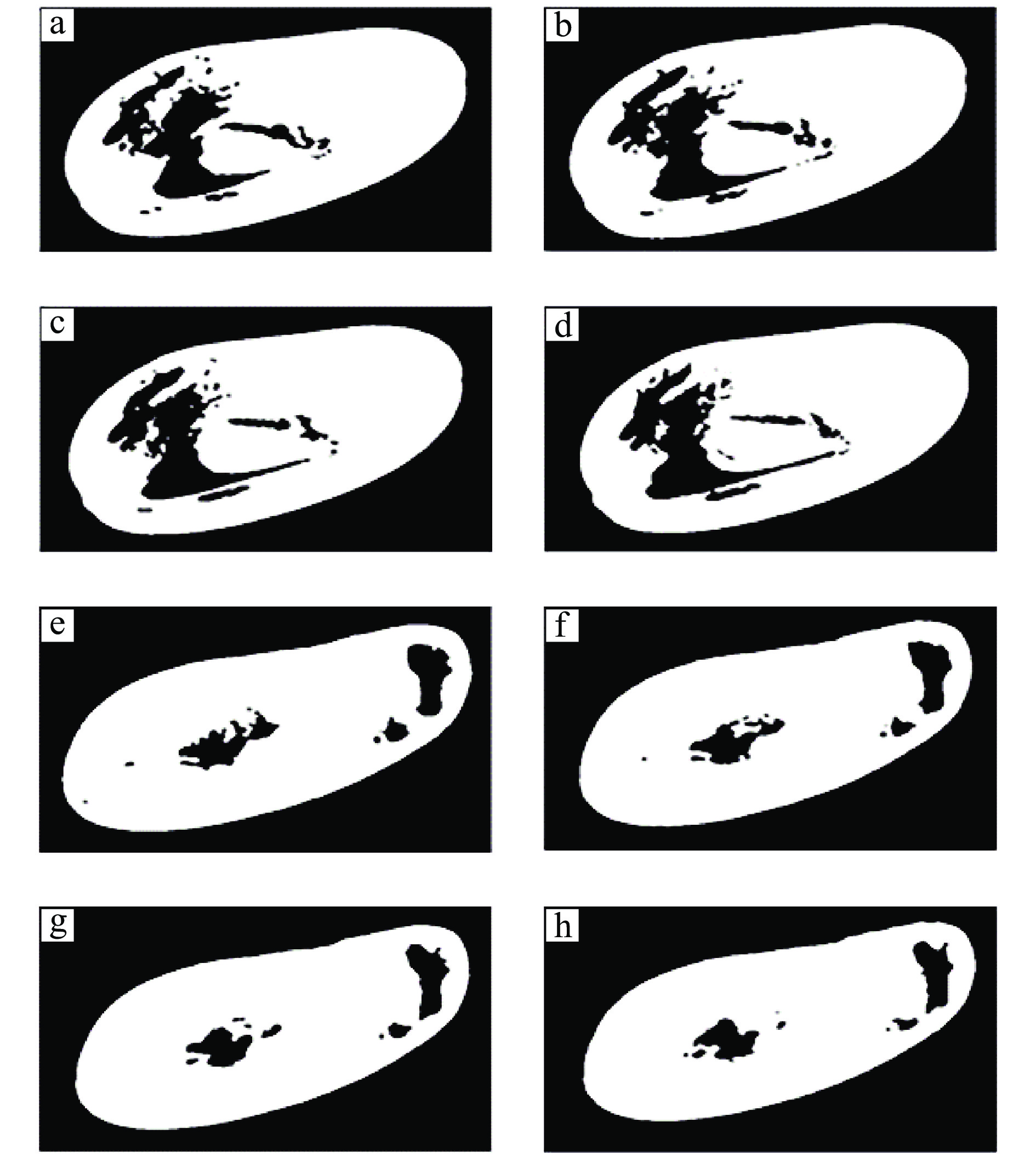
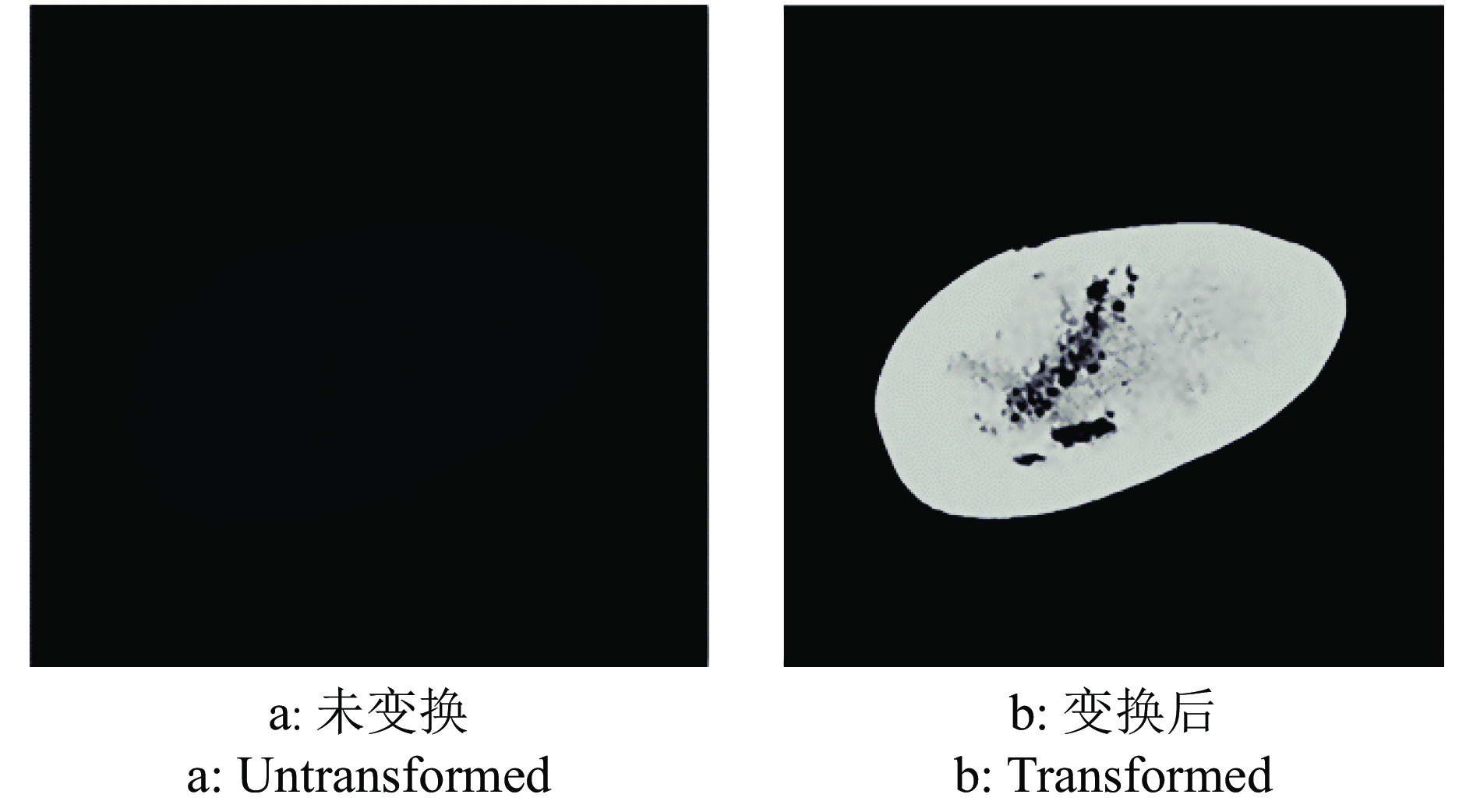
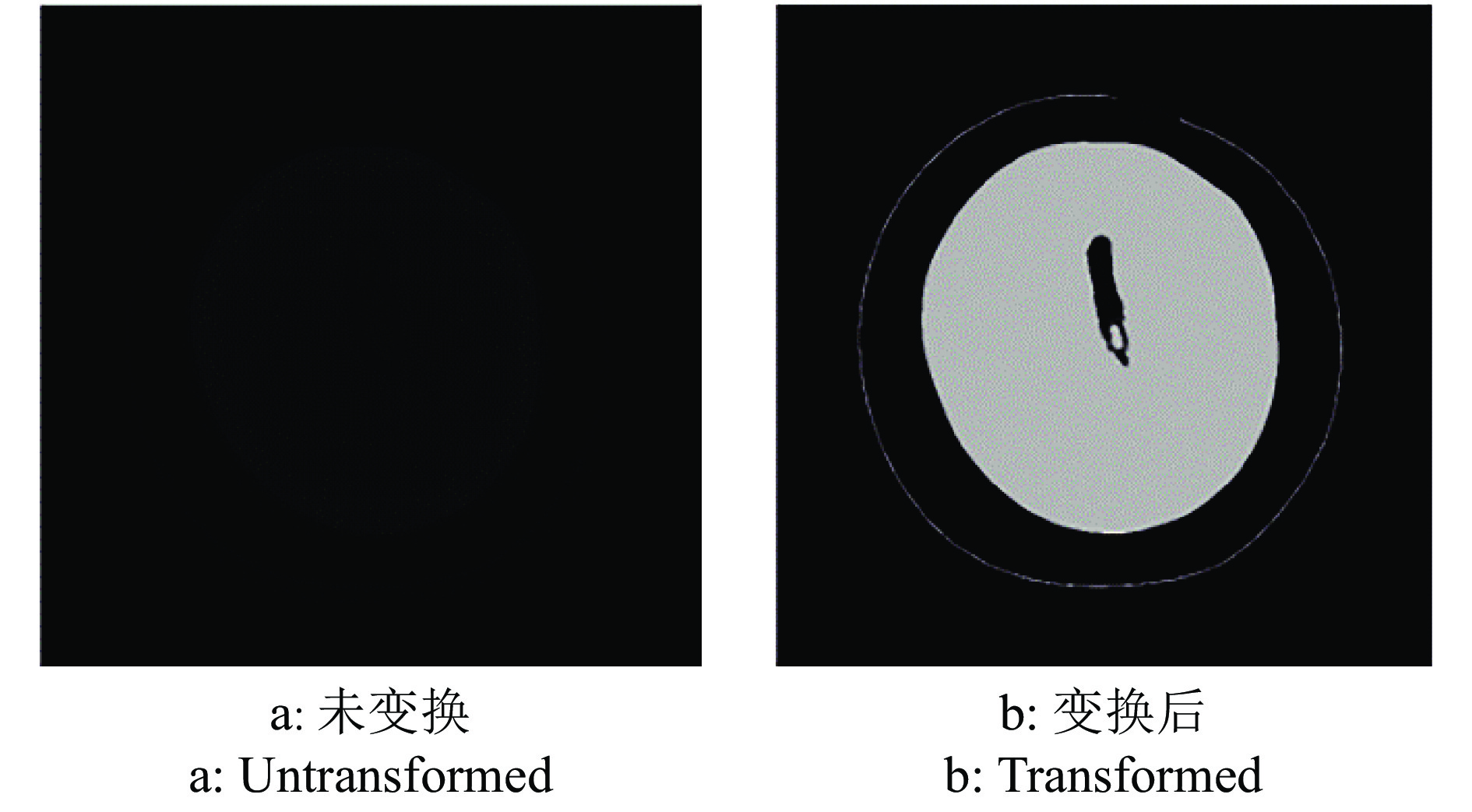
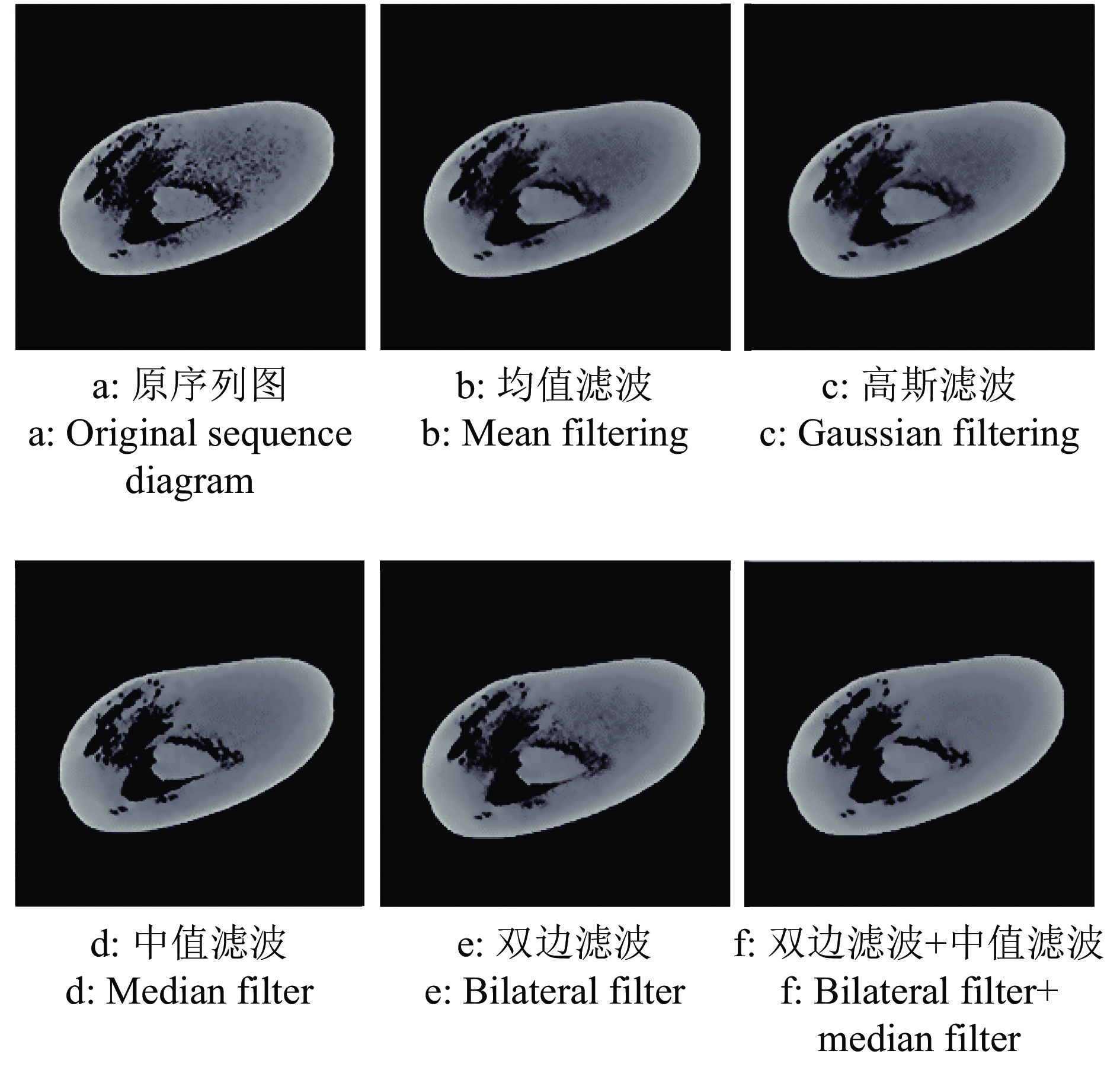
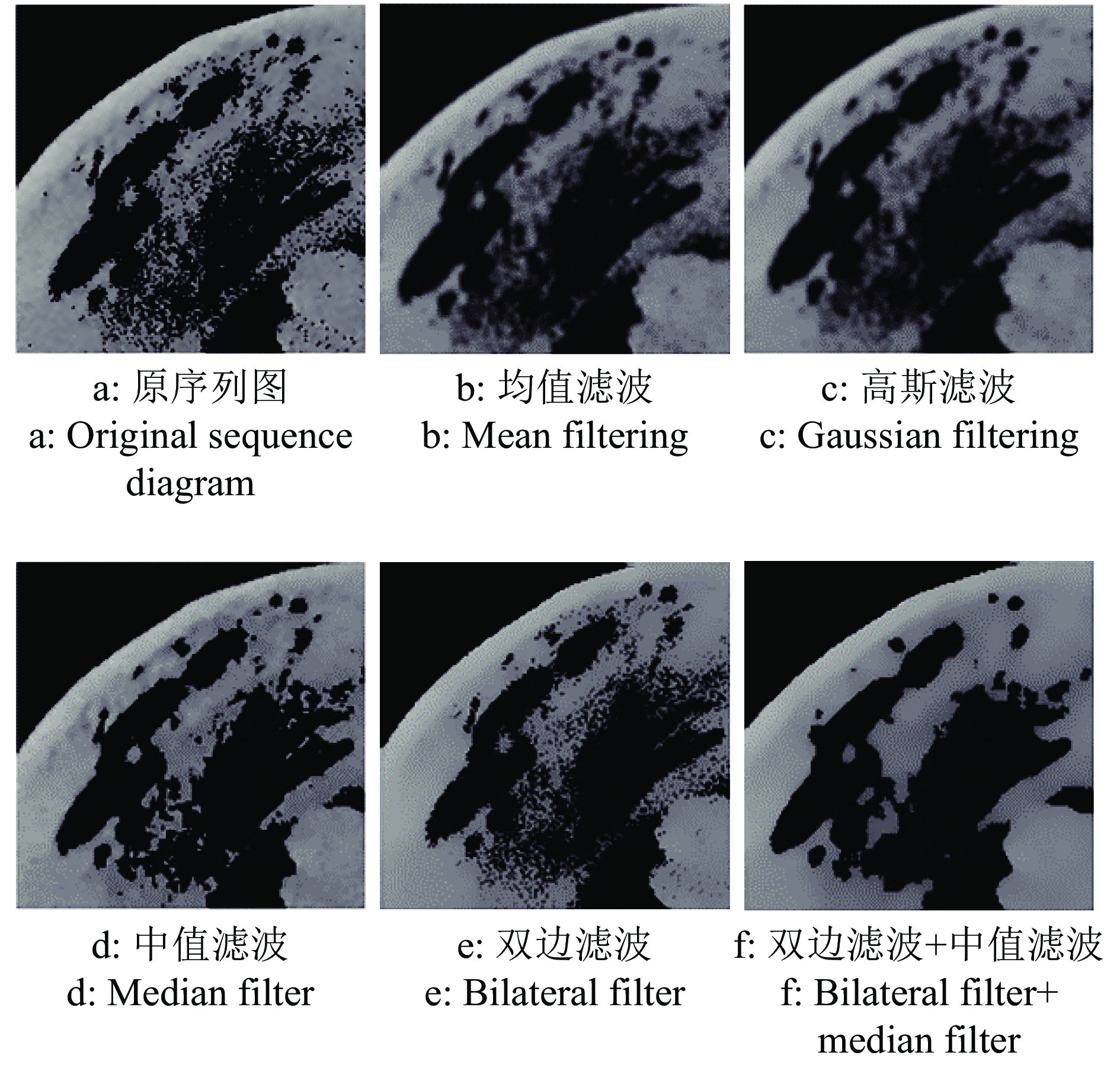
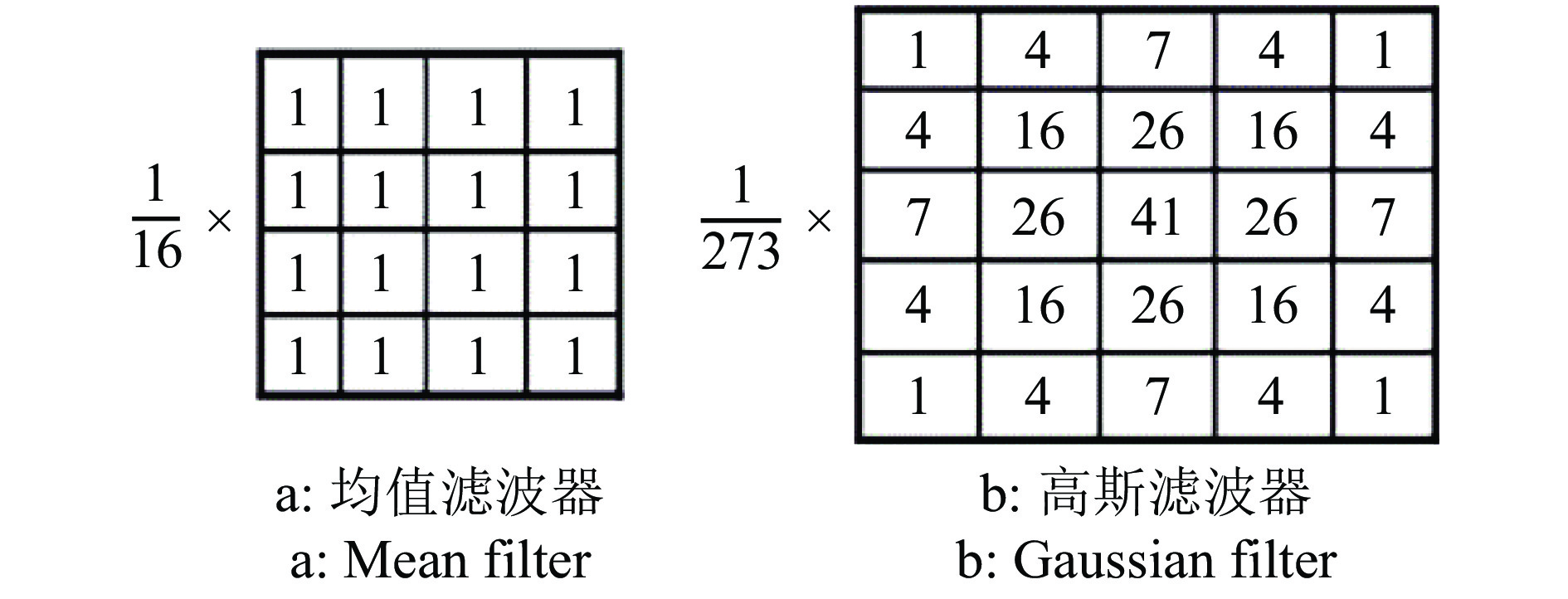
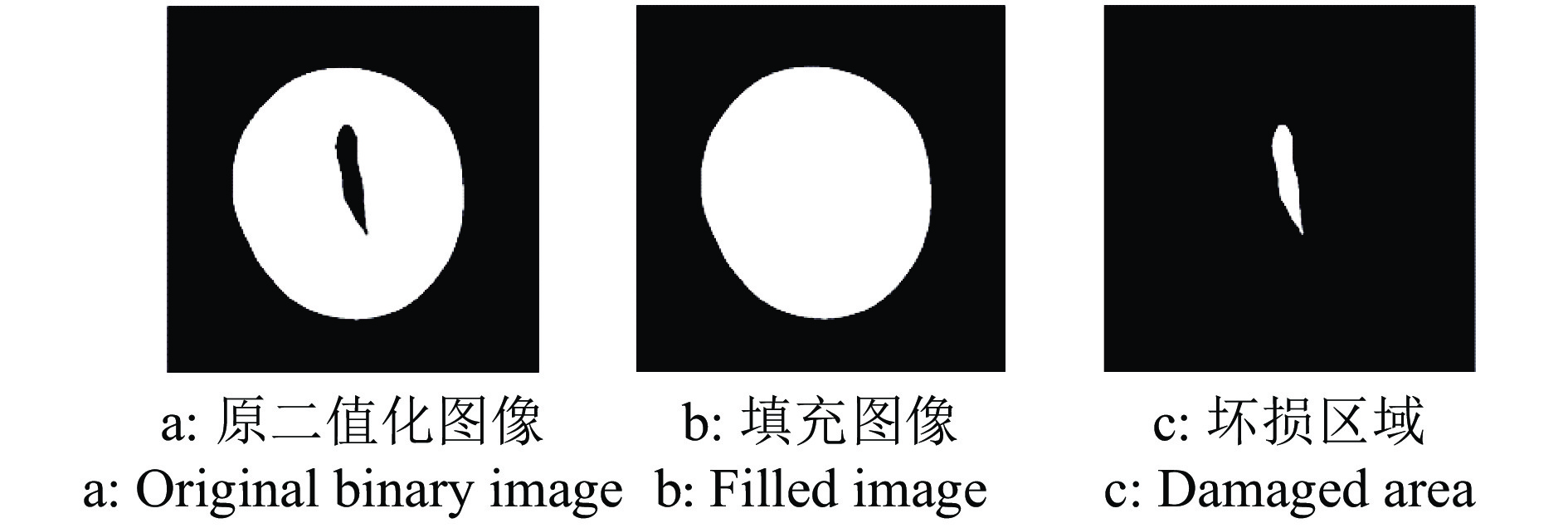
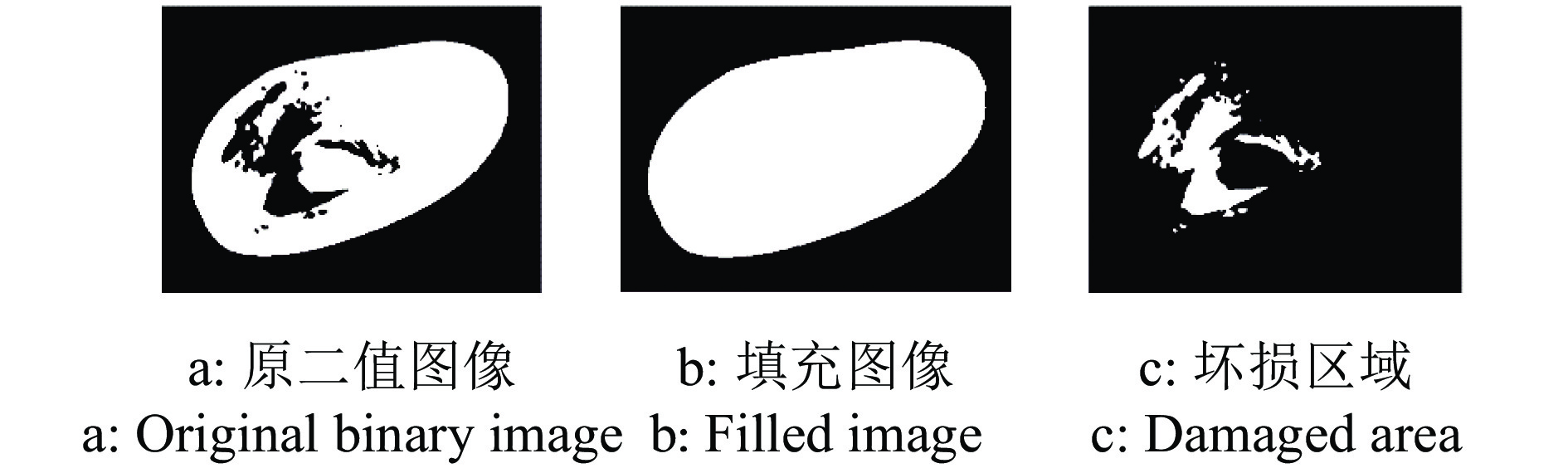
方法利用分段函数法、中值滤波结合双边滤波,实现芒果图像增强;采用局部自适应阈值法,实现二值化处理;采用种子填充法进行区域填充;最后通过差影法准确提取芒果果实内部组织的坏损区域。基于深度迁移学习模型,对未处理和已处理的芒果图像数据开展训练和测试,通过AlexNet和GoogLeNet深度学习网络开展迁移学习,调整超参数完成训练过程的网络微调,在不同模型中对比未处理和已处理的芒果测试集在模型上的分类结果。
结果基于未处理数据集,GoogLeNet模型在学习率为0.0002下训练,Accuracy和Macro-average指标分别为98.79%和98.41%。基于已处理数据集,GoogLeNet模型在学习率为0.0002下训练,Accuracy和Macro-average指标分别为100%和100%。深度迁移学习模型在已处理数据集下的模型分类指标较未处理的数据集下有较大的提升。基于同一数据集且超参数一致时,GoogLeNet网络的分类效果明显优于AlexNet网络。
结论设定学习率为0.0002、迭代轮数为3、最小批值为64,基于GoogLeNet网络开展深度迁移学习训练,将所得模型作为最终的分类模型。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo realize non-destructive detection of the internal quality of mangoes and disease identification and classification based on the CT sequence images of mangoes obtained by computed tomography (CT) equipment.
MethodWe used piecewise function method and median filter combined with bilateral filter to achieve image enhancement, used local adaptive threshold method to achieve binarization processing, used seed filling method to perform area filling, and used the image difference method to accurately extract the damaged area in inner tissue of mango fruit. Based on the deep transfer learning model, training and testing were carried out on unprocessed and processed mango image data. Transfer learning was carried out through the AlexNet and GoogLeNet deep learning networks, and hyperparameters were adjusted to complete the network fine-tuning of the training process. Under different models, the classification results of unprocessed and processed mango test sets on the model were compared.
ResultBased on the unprocessed data set, the GoogLeNet model was trained at a learning rate of 0.0002, and the Accuracy and Macro-average were 98.79% and 98.41% respectively. Based on the processed data set, the GoogLeNet model was trained at a learning rate of 0.0002, and the Accuracy and Macro-average were 100% and 100% respectively. The deep transfer learning model had a greater improvement in the model classification index of the processed data set than the unprocessed data set. Based on the same data set and consistent hyperparameters, the classification effect of the GoogLeNet network was significantly better than that of the AlexNet network.
ConclusionWhile learning rate is set to 0.0002, the Epoch value is 3, and the Mini Batch value is 64, deep transfer learning training is carried out based on the GoogLeNet network, and the resulting model is used as the final classification model.
-
Keywords:
- mango /
- disease recognition /
- CT imaging /
- damaged area extraction /
- deep transfer learning /
- image classification
-
-
表 1 深度迁移学习模型性能参数(未处理图像)
Table 1 Performance parameters of deep transfer learning model (Unprocessed image)
模型
Model学习速率
Learning rate图片类型
Image type精准率/%
Precision召回率/%
RecallF1分值/%
F1-score模型准确率/%
Accuracy of modelAlexNet 0.0008 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 87.58 92.63 90.03 84.88 海绵组织病芒果
Mango with spongy tissue disease94.90 77.40 85.26 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 64.84 82.08 72.45 0.0005 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 96.02 94.47 95.24 90.22 海绵组织病芒果
Mango with spongy tissue disease93.71 85.19 89.25 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 73.02 90.75 80.93 0.0002 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 97.22 96.77 97.00 94.15 海绵组织病芒果
Mango with spongy tissue disease96.70 91.43 93.99 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 82.63 93.64 87.80 GoogLeNet 0.0008 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 95.55 94.01 94.77 90.73 海绵组织病芒果
Mango with spongy tissue disease95.40 86.23 90.59 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 82.05 92.49 82.05 0.0005 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 98.12 93.61 97.21 95.36 海绵组织病芒果
Mango with spongy tissue disease97.32 94.29 95.78 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 85.49 95..38 90.16 0.0002 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 99.77 99.08 99.42 98.79 海绵组织病芒果
Mango with spongy tissue disease98.96 98.96 98.96 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 96.02 97.69 96.85 表 2 深度迁移学习模型性能参数(处理图像)
Table 2 Deep transfer learning model performance parameters (Processed image)
模型
Model学习速率
Learning rate图片类型
Image type精准率/%
Precision召回率/%
RecallF1分值/%
F1-score模型准确率/%
Accuracy of modelAlexNet 0.0008 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 100 96.48 98.21 95.39 海绵组织病坏损区域
Damaged area from spongy tissue disease96.16 97.92 97.03 空心病坏损区域
Damaged area from hollow disease86.46 95.95 90.96 海绵组织病芒果 Mango with spongy tissue disease 93.67 96.10 94.87 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 96.71 84.97 90.46 0.0005 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 97.42 97.42 98.57 97.40 海绵组织病坏损区域
Damaged area from spongy tissue disease98.44 98.44 98.44 空心病坏损区域
Damaged area from hollow disease100 100 95.58 海绵组织病芒果 Mango with spongy tissue disease 98.18 98.18 96.92 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 90.75 90.75 95.15 0.0002 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 100 100 100 100 海绵组织病坏损区域
Damaged area from spongy tissue disease100 100 100 空心病坏损区域
Damaged area from hollow disease100 100 100 海绵组织病芒果 Mango with spongy tissue disease 100 100 100 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 100 100 100 GoogLeNet 0.0008 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 97.93 99.77 98.84 98.05 海绵组织病坏损区域
Damaged area from spongy tissue disease99.21 98.70 98.96 空心病坏损区域
Damaged area from hollow disease93.51 100 96.63 海绵组织病芒果 Mango with spongy tissue disease 98.42 96.88 97.64 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 100 93.06 96.41 0.0005 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 100 100 100 100 海绵组织病坏损区域
Damaged area from spongy tissue disease100 100 100 空心病坏损区域
Damaged area from hollow disease100 100 100 海绵组织病芒果 Mango with spongy tissue disease 100 100 100 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 100 100 100 0.0002 无病症芒果 Healthy mango 100 100 100 100 海绵组织病坏损区域
Damaged area from spongy tissue disease100 100 100 空心病坏损区域
Damaged area from hollow disease100 100 100 海绵组织病芒果 Mango with spongy tissue disease 100 100 100 空心病芒果 Mango with hollow disease 100 100 100 -
[1] 曹霞, 周学成, 范品良. 基于近红外漫反射光谱技术的芒果糖度无损检测方法研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2013(1): 177-180. [2] 郭辉. 基于机器视觉的蜜柚品质检测方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2015. [3] 黄滔滔, 孙腾, 张京平. 基于CT图像的苹果内部品质无损检测[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2013, 39(1): 92-97. [4] 曹霞. 核桃果实内部品质的无损检测技术研究[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2013. [5] 孙腾. CT技术及图像变换对苹果内部品质的无损检测模型研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. [6] 郭文川, 孔繁荣, 王转卫, 等. 梨生长发育后期介电特性、生理特性和内部品质的关系[J]. 现代食品科技, 2015, 31(11): 56-61. [7] 吴迪, 杨万能, 牛智有, 等. 小麦分蘖形态学特征X射线−CT无损检测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(14): 196-201. [8] 王转卫, 赵春江, 商亮, 等. 基于介电频谱技术的甜瓜品种无损检测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(9): 290-295. [9] 张京平, 彭争, 汪剑. 苹果水分与CT值相关性的研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2003, 19(3): 180-182. [10] 余心杰. 农产品无损检测中的模式识别问题研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. [11] NASIRI A, TAHERI-GARAVAND A , ZHANG Y D. Image-based deep learning automated sorting of date fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 2019, 153: 133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.04.003
[12] WAN S H, GOUDOS S. Faster R-CNN for multi-class fruit detection using a robotic vision system[J]. Computer Networks, 2020(168): 107036. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2019.107036.
[13] OSAKO Y, YAMANE H, LIN S Y, et al. Cultivar discrimination of litchi fruit images using deep learning[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2020, 269: 109360. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109360.
[14] OQUAB M, BOTTOU L, LAPTEV I, et al. Learning and transferring mid-level image representations using convolutional neural networks[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus: IEEE, 2014: 1122-1129.
[15] GE W, YU Y. Borrowing treasures from the wealthy: Deep transfer learning through selective joint fine-tuning[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii: IEEE, 2017: 2102-2113.
[16] PAN S, YANG Q. A survey on transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345-1359. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191
[17] SUN C, SHRIVASTAVA A, SINGH S, et al. Revisiting unreasonable effectiveness of data in deep learning era[C]//IEEE. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice: IEEE, 2017: 843-852.
[18] ROJAS-CARULLA M, SCHOLKOPF B, TURNER R, et al. Invariant models for causal transfer learning[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2018, 19(36): 1-34.
[19] CORTES C, MOHRI M, MEDINA A M. Adaptation based on generalized discrepancy[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2019, 20(1): 1-30.
[20] MOHRI M, ROSTAMIZADEH A, TALWALKAR A. Foundations of Machine Learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2012.
[21] 刘慧力, 贾洪雷, 王刚, 等. 基于深度学习与图像处理的玉米茎秆识别方法与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(4): 207-215. [22] 马金林, 魏萌, 马自萍. 基于深度迁移学习的肺结节分割方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2020(7): 2117-2125. [23] 罗琪. 基于深度学习的水果图像识别系统[J]. 农业工程, 2018, 8(10): 31-34. [24] 岑冠军, 华俊达, 高燕. 基于深度学习芒果图像在线识别与计数方法研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2020, 41(3): 425-432. [25] 廉小亲, 成开元, 安飒, 等. 基于深度学习和迁移学习的水果图像分类[J]. 测控技术, 2019, 38(6): 15-18. [26] SMIRNOV E A, TIMOSHENKO D M, ANDRIANOV S N. Comparison of regularization methods for ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. AASRI Procedia, 2014, 6: 89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.aasri.2014.05.013
[27] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012, 1: 1097-1105.
[28] WAN L, ZEILER M, ZHANG S, et al. Regularization of neural networks using DropConnect[C]//ICML. Proceedings of The 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta: ICML, 2013.
[29] 李一海. 植物根系三维矢量模型的构建与分析方法[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学, 2016. [30] 陈郁淦, 周学成, 乐凯. 根系CT序列图像区域生长分割的新方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2011, 47(28): 158-161. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 孙海峰. 基于遥感技术的玉米生长监测与产量预测模型构建. 种子科技. 2025(10): 93-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 马晓涓,王维英,张晓娟,才让卓玛,马祥,李思达,刘凯强. 基于无人机多源影像数据预测的高寒地区燕麦和豌豆混播生产性能综合评价. 青海畜牧兽医杂志. 2024(05): 33-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: