Effects of inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and phosphorus uptake of soybean under low phosphorus conditions
-
摘要:目的
阐明不同磷(P)高效基因型大豆在不同生育期对接种丛枝菌根真菌的反应及其与P效率的关系,为接种丛枝菌根真菌提高作物P效率的研究提供理论依据。
方法以3个基因型大豆‘威廉姆斯82’‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’为试验材料,设置接种和不接种丛枝菌根真菌2个处理,在开花期和结荚期采样,分析接种丛枝菌根真菌对大豆植株干质量、菌根侵染率、P营养状况、根系性状以及菌根诱导的P转运蛋白基因表达的影响。
结果不同基因型大豆在不同生育期对接种丛枝菌根真菌的菌根反应存在显著差异。与不接菌相比,接菌在开花期显著提高了3个菌根诱导表达的P转运蛋白基因GmPT8、GmPT9和GmPT10在3个基因型大豆根系中的表达,从而显著提高了3个基因型大豆根部的P浓度;接菌在结荚期显著提高了3个基因型大豆的根部干质量,以及‘巴西10号’的地上部干质量、P浓度和总P吸收量;此外,在开花期,不接菌的‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’的地上部干质量、总P吸收量、总根长和根表面积均显著高于‘巴西10号’,而接菌的‘巴西10号’的菌根生长反应和菌根P反应显著高于‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’。
结论‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’具有更高的P效率,而‘巴西10号’具有更高的菌根依赖性;大豆生育期的延长有利于菌根植物吸收的P转化为生物量,促进大豆与菌根真菌的有益共生。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo illuminate the response of different P-efficient soybean genotypes to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation at different growth stages and the relationship with P efficiency, and provide a theoretical basis for research of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation improving crop P efficiency.
MethodThe experiments were conducted using three soybean genotypes of ‘Weilianmusi 82’ ‘Yuechun 04-5’ and ‘Baxi 10’ under mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal inoculation treatments at flowering and podding stages. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on soybean plant dry weight, arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization rate, P nutrition status, root traits, and expression of arbuscular mycorrhizal inducible phosphate transporter genes were analyzed.
ResultThe mycorrhizal responses of different soybean genotypes to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation were significantly different at different growth stages. Compared with non-mycorrhizal inoculation treatment, the inoculation treatment significantly improved the expression levels of three arbuscular mycorrhizal inducible P transporter genes of GmPT8, GmPT9 and GmPT10 in the roots of three soybean genotypes at flowering stage, which resulted in the significant increase of P concentrations in roots of these three soybean genotypes, and the inoculation treatment significantly improved the root dry weight of these three soybean genotypes, as well as shoot dry weight, P concentration and total P uptake amount of ‘Baxi 10’ at podding stage. At flowering stage, non-mycorrhizal ‘Weilianmusi 82’ and ‘Yuechun 04-5’ plants had significantly higher shoot dry weight, total P uptake, total root length and root surface area than ‘Baxi 10’, while mycorrhizal growth response and mycorrhizal P response of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculated ‘Baxi 10’ were significantly higher than those of ‘Weilianmusi 82’ and ‘Yuechun 04-5’.
Conclusion‘Weilianmusi 82’ and ‘Yuechun 04-5’ have higher P efficiency, while ‘Baxi 10’ has higher mycorrhizal dependence. The prolonged growth period from flowering stage to podding stage promotes the transformation of acquired P by mycorrhizal plants into biomass, which further stimulates the beneficial symbiosis between soybean and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi.
-
丛枝菌根真菌(Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi)是一类重要的内生菌根真菌,能与80%以上的陆生植物形成共生关系,帮助宿主植物从土壤中获取矿质营养,特别是磷(P)[1-3]。在丛枝菌根真菌与植物共生过程中,孢子萌发并在宿主植物根周围形成根外菌丝,从而扩大植物对养分的吸收范围,根外菌丝进一步侵染,进入植物根中形成根内菌丝、泡囊和丛枝等侵染结构[4]。菌根植物有2条P吸收途径:直接吸收和菌根吸收[5]。在直接吸收途径中,植物通过根表皮的P转运蛋白从根际吸收P [6-7];而菌根吸收途径中,位于丛枝预共生膜上的菌根诱导的P转运蛋白帮助植物将根外菌丝从外界吸收的P转运给植物[8]。研究发现,在许多作物中,菌根吸收途径比直接吸收途径发挥更重要的作用,菌根吸收途径吸收的P占植物总P吸收量的70%~100%[9-12]。
菌根生长反应(Mycorrhizal growth response)和菌根P反应(Mycorrhizal phosphorus response)是衡量一个共生系统中菌根对植物生长和P吸收贡献的重要指标[13]。菌根生长反应和菌根P反应在不同的植物种类,甚至同一植物的不同品种之间都存在较大差异[14]。前期研究发现,P高效的大麦和小麦品种接种丛枝菌根真菌后菌根P反应降低,表现出低菌根依赖性[15-16]。辣椒不同基因型间菌根依赖性差异较大,对8个不同基因型的辣椒进行丛枝菌根真菌接种后发现,5个品种对丛枝菌根真菌的接种表现为正的菌根生长反应,3个品种表现为负的菌根生长反应[17]。并且,菌根生长反应和菌根P反应也与植物的生育时期有密切关系,有些植物种类或品种接种4~6周即表现出正的菌根生长反应或菌根P反应,而有些植物种类或品种接种丛枝菌根真菌后需要更长的时间才能促进生长和P吸收[15, 18-20]。
在大豆中,P高效大豆品种的菌根生长反应或菌根P反应显著低于P低效大豆品种[21-22]。但目前对于不同的P高效大豆品种以及大豆基因组测序品种‘威廉姆斯82’对接种丛枝菌根真菌的生长响应还少有研究。本研究在低P条件下,以3个P高效大豆为试验材料,设置接种和不接种丛枝菌根真菌2个处理,分别在大豆的开花期和结荚期采样,探究接种丛枝菌根真菌对不同基因型大豆在不同生育时期生长、P吸收、菌根诱导的P转运蛋白基因表达的影响,及其与P效率的关系,以期为接种丛枝菌根真菌提高作物P效率的研究提供理论依据,指导微生物菌肥在农业生产中的合理应用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
供试植物材料为3种基因型大豆:‘威廉姆斯82’‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’。丛枝菌根真菌菌种为根内球囊霉属Rhizophagus的根内球囊霉R. irregularis。盆栽试验所用的石英砂属于商业购买,分为粗砂、中砂和细砂。营养液为改良版1/2 Hoagland低P营养液,营养液含有以下营养元素:50 μmol/L KH2PO4、250 μmol/L K2SO4、80 μmol/L Fe-EDTA (Na)、4.50 μmol/L MnCl2·4H2O、0.30 μmol/L ZnSO4·7H2O、0.16 μmol/L CuSO4·5H2O、0.16 μmol/L (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O、20 μmol/L H3BO3、1 000 μmol/L MgSO4·7H2O,营养液pH为5.8~6.0。
1.2 试验方法
试验包括不同采样时间、不同接菌处理以及不同大豆基因型3个因素。其中,采样时间包括植物开花期(播种后40 d)和结荚期(播种后75 d);接菌处理包括接菌和不接菌;大豆基因型有‘威廉姆斯82’‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’3种。试验共12个处理,每个处理设4次重复。石英砂按粗砂、中砂、细砂的质量比为1∶2∶1均匀混合,经过2次121 ℃灭菌40 min处理,每次间隔24 h,灭菌后的石英砂装入2 kg花盆中备用。
大豆种子使用氯气熏蒸灭菌法灭菌3 h。每盆播种3颗,待种子出苗1周后保留长势均匀的1株作为试验材料。在播种的时候接种孢子,接菌处理每盆接种约2 000个孢子,不接菌处理不接种孢子。试验期间,每周浇1次200 mL低P(50 µmol/L KH2PO4)的1/2 Hoagland营养液,其余时间视干湿情况浇100~200 mL二级水保持石英砂湿润。
1.3 收获与分析测定
大豆植株分别在开花期和结荚期收获。根系清洗干净后,首先称取一定质量的根系样品用于基因表达分析,然后称取剩余根系质量,利用根系扫描仪(Epson1460XL,日本)进行扫描,再通过根系分析软件WinRHIZO(Regent Instruments Inc.,加拿大)分析根系性状,包括总根长、根表面积和根系体积[15, 19]。
扫描之后,将根剪成1 cm根段混匀,随机取一部分根样,加入100 g/L氢氧化钾溶液,在室温下放置1周左右,待根系透明后,用5%(φ)醋酸墨水染色液进行染色,采取网格交叉划线法,通过显微镜观察并记录根系的菌根侵染率。
地上部和根部样品于烘箱105 ℃条件下杀青30 min,75 ℃条件下烘干至恒质量后称质量。使用磨样机将样品磨碎,P含量采用干灰化−钼锑抗比色法[23]测定,使用酶标仪(Thermo Fisher,美国)于700 nm波长处测定光密度,根据测定的标准曲线计算P浓度,最终计算P含量。
1.4 RNA提取与基因表达的定量分析
使用Trizol法提取根部RNA,将RNA样品反转录后的cDNA样品稀释20倍作为实时荧光定量PCR的反应模板,使用实时荧光定量PCR仪(Applied Biosystems7500,美国)对菌根诱导表达的P转运蛋白基因GmPT8、GmPT9和GmPT10进行基因表达的定量分析,引物见参考文献[21, 24],以大豆看家基因EF1-α(NCBI编号:X56856)为参照基因[20, 25],采用2−∆∆CT方法对表达数据进行归一化[25]。
1.5 菌根反应的计算公式
菌根侵染率=侵染的根段在纵横2个方向的总交叉点数/根段的总交叉点数×100%[26]。
菌根生长反应和菌根P反应分别根据下面公式[27]计算:
菌根生长反应=(菌根植物干质量–非菌根植物干质量)/非菌根植物干质量×100%;
菌根P反应=(菌根植物P含量–非菌根植物P含量)/非菌根植物P含量×100%。
1.6 数据处理
试验数据均采用Microsoft Excel 2016(Microsoft Company,美国)软件进行平均值和标准误计算;采用SPSS Statistics 23(SPSS Institute,美国)统计分析软件进行双因素和三因素方差分析,多重比较采用Duncan’s法进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 接种丛枝菌根真菌对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的地上部、根部干质量的影响
由方差分析结果(表1)可知,不同生育期极显著影响大豆地上部和根部干质量(P<0.001);不同接菌处理极显著影响根部干质量(P<0.001);地上部和根部干质量存在极显著基因型差异(P<0.001);不同生育期和不同接菌处理以及不同生育期和基因型之间对地上部干质量和根部干质量存在显著交互作用(P<0.05、P<0.01)。如表2所示,从不同接菌处理来看,在开花期时,3个基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间的地上部和根部干质量均无显著差异;在结荚期时,与不接菌处理相比,接菌处理的‘巴西10号’地上部干质量显著增加了14.1%,3个基因型大豆根部干质量分别显著增加28.6%、27.8%和38.7%。从不同基因型来看,随着处理时间的延长,无论是否接菌,3个基因型大豆的地上部和根部干质量都呈现增加的趋势。在结荚期时,在不接菌条件下,‘威廉姆斯82’的地上部干质量显著高于‘巴西10号’,根部干质量显著高于‘粤春04-5’;而在接菌条件下,‘威廉姆斯82’的地上部干质量显著高于‘巴西10号’和‘粤春04-5’,而根部干质量显著高于‘粤春04-5’。
表 1 不同生育期、接菌处理和基因型对大豆生理和分子指标影响的三因素方差分析Table 1. Three-way ANOVA of the effects of different growth stages, inoculation treatments and genotypes on physiological and molecular indicators of soybean指标 Indicator F1) S I G S×I S×G I×G S×I×G 地上部干质量 Shoot dry weight 538.68*** 1.24 14.91*** 5.10* 3.53* 0.12 0.64 根部干质量 Root dry weight 239.65*** 34.72*** 12.19*** 10.91** 8.81** 0.47 0.95 地上部P浓度 Shoot P concentration 43.56*** 10.56** 3.30* 0.04 0.38 0.30 0.21 根部P浓度 Root P concentration 0.24 15.56*** 2.57 9.78 0.43 0.38 0.67 总P吸收量 Total P uptake amount 70.84*** 25.10*** 3.36* 2.74 4.31* 2.31 0.32 总根长 Total root length 219.27*** 7.17* 11.40*** 2.59 2.92 0.33 2.65 根表面积 Root surface area 118.70*** 11.40** 0.45 1.35 11.55*** 0.34 1.23 根系体积 Root volume 52.18*** 11.38** 2.82 0.48 26.59*** 0.45 0.57 GmPT8表达量 Expression of GmPT8 0.49 36.72*** 2.67 1.12 0.02 1.08 0.10 GmPT9表达量 Expression of GmPT9 0.24 36.88*** 0.22 1.79 0.91 0.65 0.06 GmPT10表达量 Expression of GmPT10 0.17 4.82* 0.64 1.66 0.27 1.35 1.35 1) S:生育期,I:接菌处理,G:基因型,×:不同因素之间的交互作用;“*”:P<0.05,“**”:P<0.01,“***”:P<0.001
1) S: Stage, I: Inoculation, G: Genotype, ×: Interactions between different factors; “*”: P<0.05,“**”:P<0.01,“***”:P<0.001表 2 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的地上部和根部干质量的影响1)Table 2. Effects of inoculation treatments on plant shoot and root dry weight of different soybean genotypes at different growth stagesm/g 植株部位
Plant part生育期
Growth stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10地上部
ShootⅠ 1.87±0.19a 1.85±0.21a 1.20±0.06b 1.63±0.13ab 1.65±0.15ab 1.38±0.07b Ⅱ 3.53±0.03ab 3.22±0.01bc 2.96±0.19c 3.87±0.13a 3.23±0.05bc 3.37±0.11b 根部
RootⅠ 0.71±0.08a 0.60±0.04ab 0.47±0.03b 0.72±0.08a 0.75±0.60a 0.59±0.05ab Ⅱ 1.18±0.06b 0.88±0.06c 1.00±0.07bc 1.52±0.09a 1.13±0.02b 1.39±0.04a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)2.2 接种丛枝菌根真菌对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的P营养状况的影响
由方差分析结果(表1)可知,不同生育期极显著影响地上部P浓度和总P吸收量(P<0.001);接菌处理对地上部P浓度、根部P浓度和总P吸收量有显著影响(P<0.01、P<0.001和P<0.001);地上部P浓度和总P吸收量存在显著基因型差异(P<0.05)。
如表3所示,从不同接菌处理来看,在开花期时,与不接菌处理相比,接菌显著提高‘威廉姆斯82’‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’3个基因型大豆的根部P浓度,分别提高了64.3%、80.4%和65.6%;接菌后‘巴西10号’的总P吸收量显著增加了68.8%。在结荚期时,与不接菌处理相比,‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’的地上部P浓度分别显著增加了19.7%和25.1%;3个基因型大豆的总P吸收量也都有增加的趋势,‘巴西10号’显著增加了63.5%。从不同基因型来看,开花期时,在不接菌条件下,‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’的总P吸收量显著高于‘巴西10号’;结荚期时,在接菌条件下,‘巴西10号’的总P吸收量显著高于‘粤春04-5’。
表 3 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的P营养状况的影响1)Table 3. Effects of inoculation on P nutrition status of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages指标
Index生育期
Growth stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10地上部P质量分数/(mg·g−1)
Shoot P concentrationⅠ 0.63±0.09a 0.70±0.08a 0.53±0.01a 0.73±0.09a 0.75±0.05a 0.68±0.03a Ⅱ 0.44±0.03bc 0.45±0.03bc 0.39±0.00c 0.52±0.02ab 0.54±0.02a 0.49±0.02ab 根部P质量分数/(mg·g−1)
Root P concentrationⅠ 0.59±0.05b 0.56±0.06b 0.65±0.04b 0.97±0.05a 1.01±0.14a 1.08±0.13a Ⅱ 0.83±0.11a 0.71±0.05a 0.83±0.10a 0.78±0.08a 0.71±0.12a 1.16±0.31a 总P吸收量/mg
Total P uptake amountⅠ 1.62±0.34a 1.64±0.26a 0.93±0.03b 1.88±0.22a 1.94±0.10a 1.57±0.18a Ⅱ 2.53±0.12bc 2.09±0.16c 2.00±0.22c 3.20±0.11ab 2.55±0.05bc 3.26±0.36a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)2.3 接种丛枝菌根真菌对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的根系性状的影响
由方差分析结果(表1)可知,不同生育期极显著影响大豆总根长、根表面积和根系体积(P<0.001);接菌处理显著影响总根长(P<0.05)、根表面积和根系体积(P<0.01);总根长存在极显著基因型差异(P<0.001)。
如表4所示,从不同接菌处理来看,在开花期时,3个基因型大豆的根系性状在不同接菌处理间无显著差异;而在结荚期时,与不接菌处理相比,‘威廉姆斯82’的总根长显著增长了22.1%。从不同基因型来看,开花期时,在不接菌的条件下,‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’的总根长和根表面积显著高于‘巴西10号’;在接菌条件下,‘粤春04-5’的总根长、根表面积和根系体积均显著高于‘巴西10号’。而结荚期时,在不接菌的条件下,‘巴西10号’的根系体积显著高于‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’;在接菌条件下,’巴西10号’的根表面积显著高于‘粤春04-5’,而‘威廉姆斯82’的总根长显著高于‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’。
表 4 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的根系性状的影响1)Table 4. Effects of inoculation on root characteristics of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages指标
Index生育期
Growth stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10总根长/m
Total root lengthⅠ 2.84±0.02ab 2.74±0.19ab 2.11±0.09c 2.58±0.21abc 3.10±0.19a 2.45±0.15bc Ⅱ 4.70±0.24b 4.63±0.34b 3.82±0.23b 5.74±0.36a 4.72±0.49b 4.47±0.12b 根表面积/dm2
Root surface areaⅠ 4.38±0.35ab 4.46±0.39ab 3.27±0.14c 4.30±0.59ab 5.08±0.19a 4.12±0.45bc Ⅱ 6.42±0.45bc 5.79±0.43c 6.86±0.43abc 7.90±0.68ab 6.85±0.66bc 8.26±0.21a 根系体积/cm3
Root volumeⅠ 5.44±0.87abc 5.86±0.61ab 3.49±0.46c 5.73±0.67ab 7.40±0.65a 4.90±0.75bc Ⅱ 6.98±0.63cd 5.91±0.83d 9.81±0.72b 8.68±0.97bc 6.80±0.62cd 12.15±0.41a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)2.4 接种丛枝菌根真菌对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的P转运基因表达的影响
由方差分析结果(表1)可知,接菌处理显著影响GmPT8、GmPT9和GmPT10的表达(P<0.001、P<0.001和P<0.05)。由表5可知,从不同接菌处理来看,在开花期时,与不接菌处理相比,接菌后显著提高了3个基因型大豆根系中GmPT8、GmPT9和GmPT10的表达;在结荚期时,与不接菌处理相比,‘粤春04-5’根系GmPT8和GmPT9的表达量分别提高了6.7和19.0倍,‘巴西10号’根系的GmPT10表达量提高了52.9倍。从不同基因型来看,在不接菌条件下,在开花期时,‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’根系GmPT8的表达量显著高于‘巴西10号’;而在接菌条件下,无论在哪个生育期,3个P转运蛋白基因的表达在3个基因型大豆间都无显著差异。
表 5 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的根系菌根诱导P转运蛋白基因表达的影响1)Table 5. Effects of inoculation on the expression of arbuscular mycorrhizal-inducible P transporter genes in roots of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages基因
Gene生育期
Growth
stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10GmPT8 Ⅰ 1.07±0.17b 1.07±0.17b 0.27±0.07c 8.52±2.10a 10.02±2.19a 5.46±2.50a Ⅱ 2.37±1.73bc 1.08±0.13bc 0.31±0.10c 6.38±1.46ab 8.27±4.23b 3.97±0.87abc GmPT9 Ⅰ 2.33±1.41b 2.58±0.26b 2.49±1.17b 1 149.44±278.42a 1 896.10±588.61a 1 617.45±630.78a Ⅱ 475.87±471.67ab 64.82±38.09b 2.17±0.71b 1 265.27±160.46a 1 296.43±647.04a 955.27±235.69ab GmPT10 Ⅰ 10.42±10.42b 2.40±0.98b 2.75±0.66b 68.20±19.46a 384.27±154.98a 261.38±193.35a Ⅱ 141.34±128.79ab 208.36±203.52ab 5.69±3.46b 117.56±24.20a 112.45±103.24ab 306.82±175.38a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)2.5 接种丛枝菌根真菌对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的菌根侵染率和菌根反应的影响
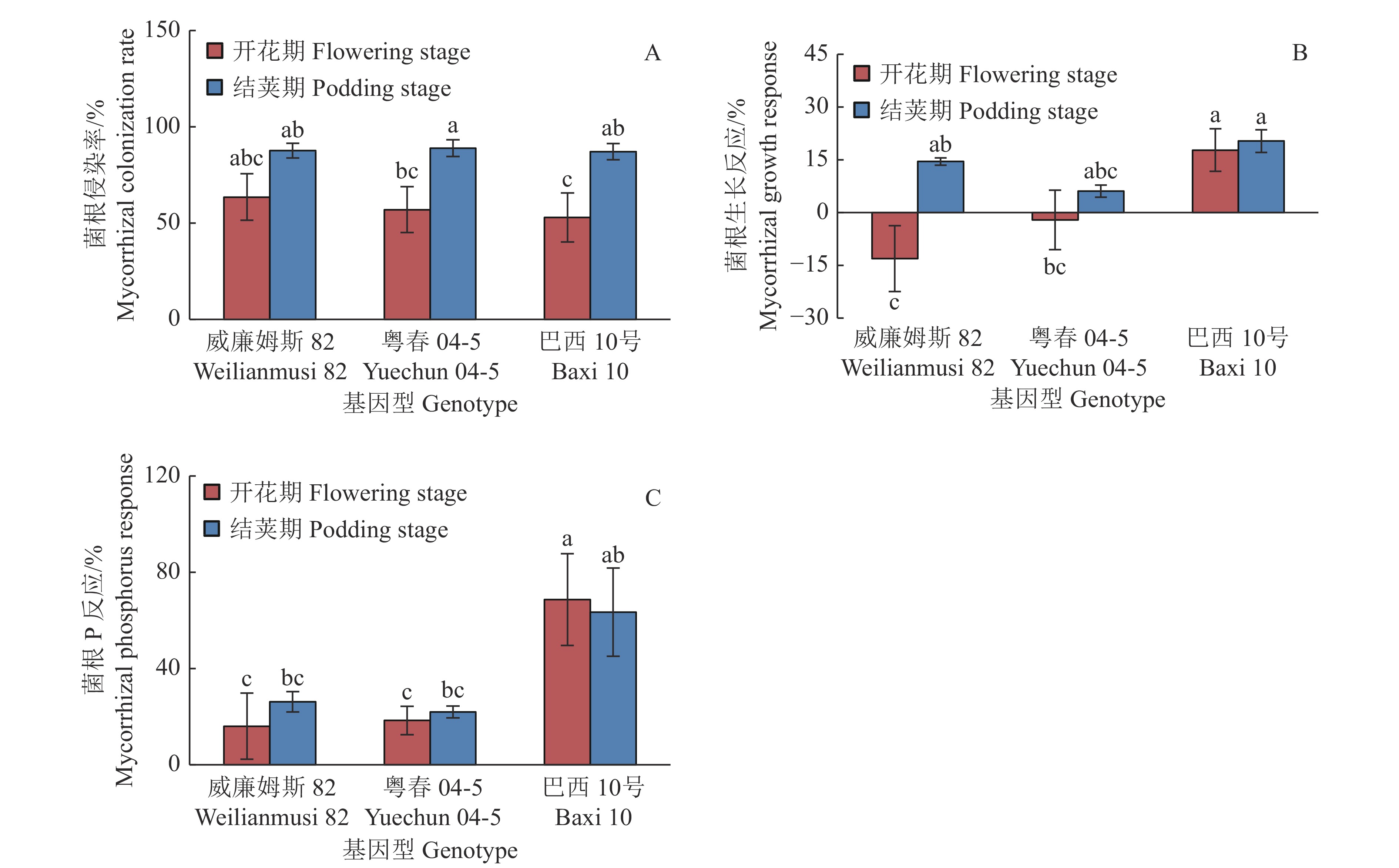
由方差分析结果(表6)可知,不同生育期显著影响菌根侵染率(P<0.01)和菌根生长反应(P<0.05);菌根生长反应和菌根P反应存在显著的基因型差异(P<0.05、P<0.01)。从不同生育期来看,‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’结荚期的菌根侵染率显著高于开花期的;从不同基因型来看,在开花期和结荚期,3个基因型大豆间的菌根侵染率均无显著差异(图1A)。3个基因型大豆在结荚期时均表现出正的菌根生长反应,且与开花期相比,‘威廉姆斯82’结荚期的菌根生长反应显著增加(图1B)。在开花期,‘巴西10号’的菌根生长反应和菌根P反应显著高于‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’;而在结荚期,3个基因型的菌根生长反应和菌根P反应无显著差异(图1B、1C)。
![图 1 接种丛植菌根真菌时不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的菌根侵染率、菌根生长反应和菌根P反应]() 图 1 接种丛植菌根真菌时不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的菌根侵染率、菌根生长反应和菌根P反应各小图柱子上方不同小写字母表示不同基因型大豆在不同生育期间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)Figure 1. Mycorrhizal colonization rate, mycorrhizal growth response and mycorrhizal phosphorus response of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages while inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungiDifferent lowercase letters on the columns in each figure indicate significant differences among different soybean genotypes at different growth stages (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)表 6 生育期和基因型对大豆菌根生长指标影响的双因素方差分析Table 6. Two-way ANOVA of the effects of growth stages and genotypes on soybean mycorrhizal growth indicators
图 1 接种丛植菌根真菌时不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的菌根侵染率、菌根生长反应和菌根P反应各小图柱子上方不同小写字母表示不同基因型大豆在不同生育期间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)Figure 1. Mycorrhizal colonization rate, mycorrhizal growth response and mycorrhizal phosphorus response of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages while inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungiDifferent lowercase letters on the columns in each figure indicate significant differences among different soybean genotypes at different growth stages (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)表 6 生育期和基因型对大豆菌根生长指标影响的双因素方差分析Table 6. Two-way ANOVA of the effects of growth stages and genotypes on soybean mycorrhizal growth indicators指标
IndexF1) 生育期
Growth stage基因型
Genotype生育期×基因型
Growth stage × genotype菌根侵染率 Mycorrhizal colonization rate 14.93** 0.18 0.16 菌根生长反应 Mycorrhizal growth response 5.86* 5.66* 1.84 菌根P反应 Mycorrhizal phosphorus response 0.07 8.05** 0.18 1)“*”:P<0.05,“**”:P<0.01 3. 讨论与结论
丛枝菌根真菌能够帮助植物吸收生长发育所需的P,促进植物生长[4, 21]。本研究发现,接种丛枝菌根真菌后,在开花期,不同基因型大豆的干质量与不接菌处理无显著差异,但‘巴西10号’的总P吸收量提高了68.8%,这与前期研究结果[22]一致;在结荚期,‘巴西10号’的地上部干质量以及3个基因型大豆的根部干质量均比不接菌处理显著提高,但只有‘巴西10号’的总P吸收量显著增加。结果说明,接种丛枝菌根真菌能够促进大豆的生长和P吸收,但不同基因型对接种丛枝菌根真菌的反应不同;不同基因型大豆菌根生长反应和菌根P反应的差异验证了该结论。
在低P水平下,菌根反应用于表示植物接种丛枝菌根真菌后生物量和P吸收量的变化,反映植物对菌根的依赖性[28]。‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’的菌根生长反应在开花期为负值,而菌根P反应为正值,说明接种丛枝菌根真菌虽然可以帮助‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’吸收P,但并未对其生长产生促进作用;而在结荚期时,3种基因型大豆的菌根生长反应和P反应都为正值,说明接种时间的延长有利于菌根植物吸收的P转化为生物量,更好地促进大豆与菌根真菌的有益共生;此外‘巴西10号’的菌根生长反应和P反应在不同生育期均为正值,且在开花期显著高于‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’,表明不同基因型大豆的菌根反应有所不同,‘巴西10号’的反应更加敏感。有研究认为,菌根生长反应出现负值是由于共生系统中丛枝菌根真菌碳(C)消耗较高,而提供给宿主植物的P较少,二者不平衡所致[29-30],丛枝菌根真菌需要依靠宿主植物提供C源完成其生活史,而不同基因型大豆在低P条件下的净光合速率有所不同,植株体内的C分配也存在差异[31];因此,丛枝菌根真菌从不同基因型大豆植株中获取C的多少及时间早晚不同都可能造成菌根生长反应和菌根P反应的差异[14]。
‘威廉姆斯82’是用于大豆基因组测序的品种,‘粤春04-5’和‘巴西10号’为P高效大豆品种[32-33]。本研究发现,不接菌条件下,‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’开花期的地上部干质量、总P吸收量、总根长和根表面积均显著高于‘巴西10号’,说明‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’比‘巴西10号’具有更高的P效率;但接菌后‘威廉姆斯82’的根系性状与‘巴西10号’相比无明显差异,表明接菌促进了‘巴西10号’的根系生长,有利于‘巴西10号’通过根系和菌根2条途径吸收土壤中的P。有研究表明,P低效品种比P高效品种具有更高的菌根依赖性[22, 34],‘巴西10号’在2个生育期的接菌条件下都有较高的总P吸收量,表明‘巴西10号’比‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’具有更高的菌根依赖性。
在菌根吸收途径中,由菌根诱导表达的P转运蛋白将丛枝菌根真菌从土壤中吸收的P转运到植物体内,目前已鉴定到的菌根诱导表达的P转运蛋白基因包括水稻Oryza sativa的OsPT11[35]、苜蓿Medicago truncatula的MtPT4[36]以及大豆Glycine max L.的GmPT8、GmPT9和GmPT10[21, 37]。在开花期,GmPT8、GmPT9和GmPT10在根部的表达受接菌诱导显著上调,且菌根侵染率达到50%以上,这与不同基因型大豆根部P浓度显著增加的结果一致,表明GmPT8、GmPT9和GmPT10在大豆从菌根界面摄取P中起重要作用,这也部分解释了尽管‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’的菌根生长反应为负值,但接菌后根部P浓度仍然显著增加的原因;而在结荚期,接菌显著诱导GmPT8和GmPT9在‘粤春04-5’根系中的表达、GmPT10在‘巴西10号’根系中的表达。结果说明3个菌根诱导的P转运蛋白在菌根界面的P运输中可能起不同的作用[21]。
相比于‘威廉姆斯82’和‘粤春04-5’,‘巴西10号’对菌根的依赖性更强,接菌对‘巴西10号’的生长促进作用更加明显;随着接种时间的延长,菌根对大豆生长的促进作用更加明显。研究结果将为提高作物P效率提供理论依据,并指导微生物菌肥在农业生产中的合理应用。
-
图 1 接种丛植菌根真菌时不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的菌根侵染率、菌根生长反应和菌根P反应
各小图柱子上方不同小写字母表示不同基因型大豆在不同生育期间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 1. Mycorrhizal colonization rate, mycorrhizal growth response and mycorrhizal phosphorus response of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages while inoculating arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
Different lowercase letters on the columns in each figure indicate significant differences among different soybean genotypes at different growth stages (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
表 1 不同生育期、接菌处理和基因型对大豆生理和分子指标影响的三因素方差分析
Table 1 Three-way ANOVA of the effects of different growth stages, inoculation treatments and genotypes on physiological and molecular indicators of soybean
指标 Indicator F1) S I G S×I S×G I×G S×I×G 地上部干质量 Shoot dry weight 538.68*** 1.24 14.91*** 5.10* 3.53* 0.12 0.64 根部干质量 Root dry weight 239.65*** 34.72*** 12.19*** 10.91** 8.81** 0.47 0.95 地上部P浓度 Shoot P concentration 43.56*** 10.56** 3.30* 0.04 0.38 0.30 0.21 根部P浓度 Root P concentration 0.24 15.56*** 2.57 9.78 0.43 0.38 0.67 总P吸收量 Total P uptake amount 70.84*** 25.10*** 3.36* 2.74 4.31* 2.31 0.32 总根长 Total root length 219.27*** 7.17* 11.40*** 2.59 2.92 0.33 2.65 根表面积 Root surface area 118.70*** 11.40** 0.45 1.35 11.55*** 0.34 1.23 根系体积 Root volume 52.18*** 11.38** 2.82 0.48 26.59*** 0.45 0.57 GmPT8表达量 Expression of GmPT8 0.49 36.72*** 2.67 1.12 0.02 1.08 0.10 GmPT9表达量 Expression of GmPT9 0.24 36.88*** 0.22 1.79 0.91 0.65 0.06 GmPT10表达量 Expression of GmPT10 0.17 4.82* 0.64 1.66 0.27 1.35 1.35 1) S:生育期,I:接菌处理,G:基因型,×:不同因素之间的交互作用;“*”:P<0.05,“**”:P<0.01,“***”:P<0.001
1) S: Stage, I: Inoculation, G: Genotype, ×: Interactions between different factors; “*”: P<0.05,“**”:P<0.01,“***”:P<0.001表 2 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的地上部和根部干质量的影响1)
Table 2 Effects of inoculation treatments on plant shoot and root dry weight of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages
m/g 植株部位
Plant part生育期
Growth stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10地上部
ShootⅠ 1.87±0.19a 1.85±0.21a 1.20±0.06b 1.63±0.13ab 1.65±0.15ab 1.38±0.07b Ⅱ 3.53±0.03ab 3.22±0.01bc 2.96±0.19c 3.87±0.13a 3.23±0.05bc 3.37±0.11b 根部
RootⅠ 0.71±0.08a 0.60±0.04ab 0.47±0.03b 0.72±0.08a 0.75±0.60a 0.59±0.05ab Ⅱ 1.18±0.06b 0.88±0.06c 1.00±0.07bc 1.52±0.09a 1.13±0.02b 1.39±0.04a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 3 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的P营养状况的影响1)
Table 3 Effects of inoculation on P nutrition status of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages
指标
Index生育期
Growth stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10地上部P质量分数/(mg·g−1)
Shoot P concentrationⅠ 0.63±0.09a 0.70±0.08a 0.53±0.01a 0.73±0.09a 0.75±0.05a 0.68±0.03a Ⅱ 0.44±0.03bc 0.45±0.03bc 0.39±0.00c 0.52±0.02ab 0.54±0.02a 0.49±0.02ab 根部P质量分数/(mg·g−1)
Root P concentrationⅠ 0.59±0.05b 0.56±0.06b 0.65±0.04b 0.97±0.05a 1.01±0.14a 1.08±0.13a Ⅱ 0.83±0.11a 0.71±0.05a 0.83±0.10a 0.78±0.08a 0.71±0.12a 1.16±0.31a 总P吸收量/mg
Total P uptake amountⅠ 1.62±0.34a 1.64±0.26a 0.93±0.03b 1.88±0.22a 1.94±0.10a 1.57±0.18a Ⅱ 2.53±0.12bc 2.09±0.16c 2.00±0.22c 3.20±0.11ab 2.55±0.05bc 3.26±0.36a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 4 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的根系性状的影响1)
Table 4 Effects of inoculation on root characteristics of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages
指标
Index生育期
Growth stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10总根长/m
Total root lengthⅠ 2.84±0.02ab 2.74±0.19ab 2.11±0.09c 2.58±0.21abc 3.10±0.19a 2.45±0.15bc Ⅱ 4.70±0.24b 4.63±0.34b 3.82±0.23b 5.74±0.36a 4.72±0.49b 4.47±0.12b 根表面积/dm2
Root surface areaⅠ 4.38±0.35ab 4.46±0.39ab 3.27±0.14c 4.30±0.59ab 5.08±0.19a 4.12±0.45bc Ⅱ 6.42±0.45bc 5.79±0.43c 6.86±0.43abc 7.90±0.68ab 6.85±0.66bc 8.26±0.21a 根系体积/cm3
Root volumeⅠ 5.44±0.87abc 5.86±0.61ab 3.49±0.46c 5.73±0.67ab 7.40±0.65a 4.90±0.75bc Ⅱ 6.98±0.63cd 5.91±0.83d 9.81±0.72b 8.68±0.97bc 6.80±0.62cd 12.15±0.41a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 5 接菌处理对不同基因型大豆在不同生育期的根系菌根诱导P转运蛋白基因表达的影响1)
Table 5 Effects of inoculation on the expression of arbuscular mycorrhizal-inducible P transporter genes in roots of different soybean genotypes at different growth stages
基因
Gene生育期
Growth
stage不接菌 No inoculation 接菌 Inoculation 威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10威廉姆斯82
Weilianmusi 82粤春04-5
Yuechun 04-5巴西10号
Baxi 10GmPT8 Ⅰ 1.07±0.17b 1.07±0.17b 0.27±0.07c 8.52±2.10a 10.02±2.19a 5.46±2.50a Ⅱ 2.37±1.73bc 1.08±0.13bc 0.31±0.10c 6.38±1.46ab 8.27±4.23b 3.97±0.87abc GmPT9 Ⅰ 2.33±1.41b 2.58±0.26b 2.49±1.17b 1 149.44±278.42a 1 896.10±588.61a 1 617.45±630.78a Ⅱ 475.87±471.67ab 64.82±38.09b 2.17±0.71b 1 265.27±160.46a 1 296.43±647.04a 955.27±235.69ab GmPT10 Ⅰ 10.42±10.42b 2.40±0.98b 2.75±0.66b 68.20±19.46a 384.27±154.98a 261.38±193.35a Ⅱ 141.34±128.79ab 208.36±203.52ab 5.69±3.46b 117.56±24.20a 112.45±103.24ab 306.82±175.38a 1)Ⅰ:开花期,Ⅱ:结荚期;同行数据后不同小写字母表示相同生育期不同基因型大豆在不同接菌处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Ⅰ: Flowering stage, Ⅱ: Podding stage; Different lowercase letters in the same line indicate significant differences between different inoculation treatments and among different soybean genotypes (P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 6 生育期和基因型对大豆菌根生长指标影响的双因素方差分析
Table 6 Two-way ANOVA of the effects of growth stages and genotypes on soybean mycorrhizal growth indicators
指标
IndexF1) 生育期
Growth stage基因型
Genotype生育期×基因型
Growth stage × genotype菌根侵染率 Mycorrhizal colonization rate 14.93** 0.18 0.16 菌根生长反应 Mycorrhizal growth response 5.86* 5.66* 1.84 菌根P反应 Mycorrhizal phosphorus response 0.07 8.05** 0.18 1)“*”:P<0.05,“**”:P<0.01 -
[1] SMITH S E, SMITH F A. Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant nutrition and growth: New paradigms from cellular to ecosystem scales[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2011, 62(1): 227-250. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103846
[2] 张淑彬, 王幼珊, 殷晓芳, 等. 不同施P水平下AM真菌发育及其对玉米氮P吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2017, 23(3): 649-657. doi: 10.11674/zwyf.16406 [3] 冯艳梅, 冯固, 王敬国, 等. 植物P营养状况对丛枝菌根真菌生长及代谢活性的调控[J]. 菌物系统, 2003, 22(4): 589-598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6472.2003.04.016 [4] PARNISKE M. Arbuscular mycorrhiza: The mother of plant root endosymbioses[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2008, 6(10): 763-775. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1987
[5] CHIU C H, PASZKOWSKI U. Mechanisms and impact of symbiotic phosphate acquisition[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2019, 11(6): a034603. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034603
[6] MISSION J, THIBAUD M C, BECHTOLD N, et al. Transcriptional regulation and functional properties of Arabidopsis Pht1; 4, a high affinity transporter contributing greatly to phosphate uptake in phosphate deprived plants[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2004, 55(5): 727-741. doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-1965-5
[7] SHIN H, SHIN H S, DEWBRE G R, et al. Phosphate transport in Arabidopsis: Pht1; 1 and Pht1; 4 play a major role in phosphate acquisition from both low- and high-phosphate environments[J]. Plant Journal, 2004, 39(4): 629-642. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02161.x
[8] SMITH S E, READ D J. Mycorrhizal symbiosis[J]. Quarterly Review of Biology, 2008, 3(3): 273-281.
[9] SMITH S E, SMITH F A, JAKOBSEN I. Mycorrhizal fungi can dominate phosphate supply to plants irrespective of growth responses[J]. Plant Physiology, 2003, 133(1): 16-20. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.024380
[10] SMITH S E, SMITH F A, JAKOBSEN I. Functional diversity in arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbioses: The contribution of the mycorrhizal P uptake pathway is not correlated with mycorrhizal responses in growth or total P uptake[J]. New Phytologist, 2004, 162(2): 511-524. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01039.x
[11] LI H Y, SMITH S E, HOLLOWAY R E, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi contribute to phosphorus uptake by wheat grown in a phosphorus-fixing soil even in the absence of positive growth responses[J]. New Phytologist, 2006, 172(3): 536-543. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01846.x
[12] YANG S Y, GRONLUND M, JAKOBSEN I, et al. Nonredundant regulation of rice arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis by two members of the PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 gene family[J]. Plant Cell, 2012, 24(10): 4236-4251. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.104901
[13] MAHERALI H. Is there an association between root architecture and mycorrhizal growth response?[J]. New Phytologist, 2014, 204(1): 192-200.
[14] SMITH F A, GRACE E J, SMITH S E. More than a carbon economy: Nutrient trade and ecological sustainability in facultative arbuscular mycorrhizal symbioses[J]. New Phytologist, 2009, 182(2): 347-358. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02753.x
[15] ZHU Y G, SMITH S E, BARRITT A R, et al. Phosphorus (P) efficiencies and mycorrhizal responsiveness of old and modern wheat cultivars[J]. Plant and Soil, 2001, 237(2): 249-255.
[16] ZHU Y G, SMITH F A, SMITH S E. Phosphorus efficiencies and responses of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi grown in highly calcareous soil[J]. Mycorrhiza, 2003, 13(2): 93-100.
[17] SENSOY S, DEMIR S , TURKMEN O, et al. Responses of some different pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) genotypes to inoculation with two different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2007, 113(1): 92-95.
[18] WRIGHT D P, READ D J, SCHOLES J D. Mycorrhizal sink strength influences whole plant carbon balance of Trifolium repens L[J]. Plant Cell and Environment, 1998, 21(9): 881-891.
[19] ZHU Y G, SMITH S E. Seed phosphorus (P) content affects growth, and P uptake of wheat plants and their association with arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi[J]. Plant and Soil, 2001, 231(1): 105-112. doi: 10.1023/A:1010320903592
[20] QIN J, WANG H, CAO H, et al. Combined effects of phosphorus and magnesium on mycorrhizal symbiosis through altering metabolism and transport of photosynthates in soybean[J]. Mycorrhiza, 2020, 30(2/3): 285-298.
[21] WANG X, ZHAO S, BÜCKING H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal growth responses are fungal specific but do not differ between soybean genotypes with different phosphate efficiency[J]. Annals of Botany, 2016, 118(1): 11-21. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw074
[22] 辜晓婷, 覃金转, 王秀荣. 接种菌根真菌对不同P效率基因型大豆生长和P吸收的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 2020, 28(3): 357-364. [23] 崔广娟, 曹华元, 陈康, 等. 镉胁迫对4种基因型大豆生长和体内元素分布的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2020, 41(5): 49-57. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.201911023 [24] CUI G, AI S, CHEN K, et al. Arbuscular mycorrhiza augments cadmium tolerance in soybean by altering accumulation and partitioning of nutrient elements, and related gene expression[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.093
[25] ZHAO S P, CHEN A, CHEN C, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals the possible roles of sugar metabolism and export for positive mycorrhizal growth responses in soybean[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2019, 166(3): 712-728. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12847
[26] 刘润进, 陈应龙. 菌根学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. [27] TAWARAYA K. Arbuscular mycorrhizal dependency of different plant species and cultivars[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2003, 49(5): 655-668.
[28] JANOS D P. Plant responsiveness to mycorrhizas differs from dependence upon mycorrhizas[J]. Mycorrhiza, 2007, 17(2): 75-91. doi: 10.1007/s00572-006-0094-1
[29] PENG S, EISSENSTAT D M, GRAHAM J H, et al. Growth depression in mycorrhizal citrus at high-phosphorus supply[J]. Plant Physiology, 1993, 101(3): 1063-1071. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.3.1063
[30] KAHILUOTO H, KETOJA E, VESTBERG M. Plant-available P supply is not the main factor determining the benefit from arbuscular mycorrhiza to crop P nutrition and growth in contrasting cropping systems[J]. Plant and Soil, 2012, 350: 85-98. doi: 10.1007/s11104-011-0884-x
[31] 赵静, 刘嘉儿, 严小龙, 等. P有效性对大豆碳代谢的生理调控及基因型差异[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2010, 31(3): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-411X.2010.03.001 [32] ZHAO J, FU J B, LIAO H, et al. Characterization of root architecture in an applied core collection for phosphorus efficiency of soybean germplasm[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(15): 1611-1620. doi: 10.1007/BF03184131
[33] 程凤娴, 涂攀峰, 严小龙, 等. 酸性红壤中P高效大豆新种质的P营养特性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 16(1): 71-81. [34] YAO Q, LI X L, CHRISTIE P. Factors affecting arbuscular mycorrhizal dependency of wheat genotypes with different phosphorus efficiencies[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2001, 24(9): 1409-1419. doi: 10.1081/PLN-100106991
[35] PASZKOWSKI U, KROKEN S, ROUX C, et al. Rice phosphate transporters include an evolutionarily divergent gene specifically activated in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2002, 99(20): 13324-13329.
[36] JAVOT H, PENMETSA R V, TERZAGHI N, et al. A Medicago truncatula phosphate transporter indispensable for the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(5): 1720-1725.
[37] ZHANG S, ZHOU J, WANG G H, et al. The role of mycorrhizal symbiosis in aluminum and phosphorus interactions in relation to aluminum tolerance in soybean[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2015, 99(23): 10225-10235. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6913-6
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 黎武元,黄诗宸,林会. 根瘤菌和丛枝菌根真菌单双接种对不同品系大豆生长的影响. 华中农业大学学报. 2024(04): 140-149 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄亦雄. VA菌根接种及外源钙对大叶相思抗旱性影响. 陕西林业科技. 2024(06): 13-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄活志,刘洋,陈阿,陈康,王秀荣. 接种丛枝菌根真菌促进磷高效基因型大豆生长和磷吸收. 植物营养与肥料学报. 2024(12): 2354-2365 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李秋桦,尹敏,裴妍,陈秀,任禛,夏体渊,徐胜光. 健康与患黑胫病烟株根内AMF多样性和群落结构差异分析. 云南大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 186-198 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 胡湘云,王奕文,方幽文,邵烨瑶,姚慧,唐星宇,连旖晴,谭莹,朱怡杰,江帆,李春俣,吴玉环,蔡妙珍,徐根娣,刘鹏. 酸性土壤下缓解大豆铝胁迫的研究进展. 科学通报. 2023(33): 4517-4531 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 温云英,张金莲,许诗萍,曾诗媛,陈廷速. 不同丛枝菌根真菌对长春花生长和养分吸收的影响. 南方农业. 2023(18): 1-4 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赖明丽,董晓全,谢姗宴,冯嘉仪,邢鹤严,曾曙才,吴道铭. 污泥施用下园林植物生长适应性和重金属吸收. 华南农业大学学报. 2022(04): 47-57 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 李干蓉,张友,方小宁. 茶园土壤磷生物活化研究. 绿色科技. 2022(18): 23-27+32 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: