Effects of soil nutrients, planting years and methods on oligosaccharide content of Morinda officinalis
-
摘要:目的
分析土壤养分、种植年限、种植方式(林下和非林下)等3个重要因子对巴戟天Morinda officinalis品质核心指标寡糖含量的影响,为我国“四大南药”之一的巴戟天种植提供理论与数据支撑。
方法在广东省德庆县巴戟天道地产区选择18个非林下种植点,采用随机多点采样法采集土样和不同生长年限巴戟天样品,测定土壤养分和巴戟天肉质根寡糖含量,分析土壤养分含量和不同生长年限与巴戟天寡糖含量的关系;分别采集林下和非林下种植的巴戟天样品,通过主成分分析探究林下和非林下种植方式巴戟天的品质差异。
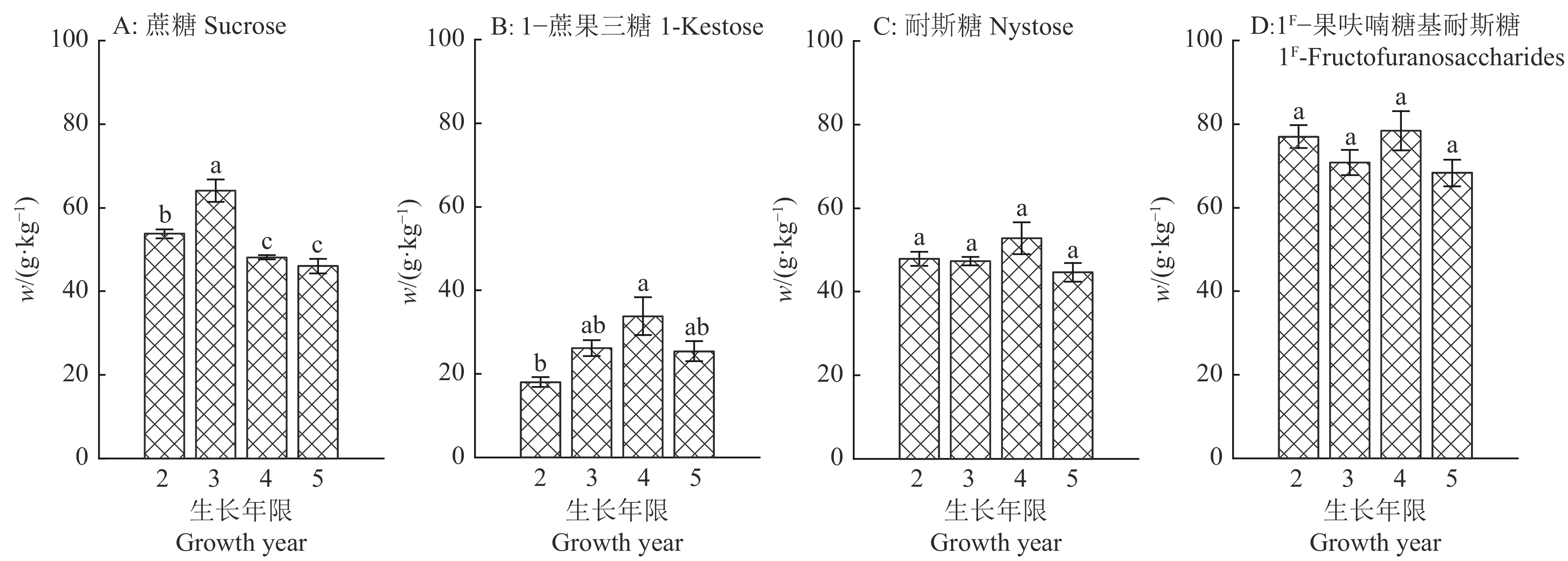
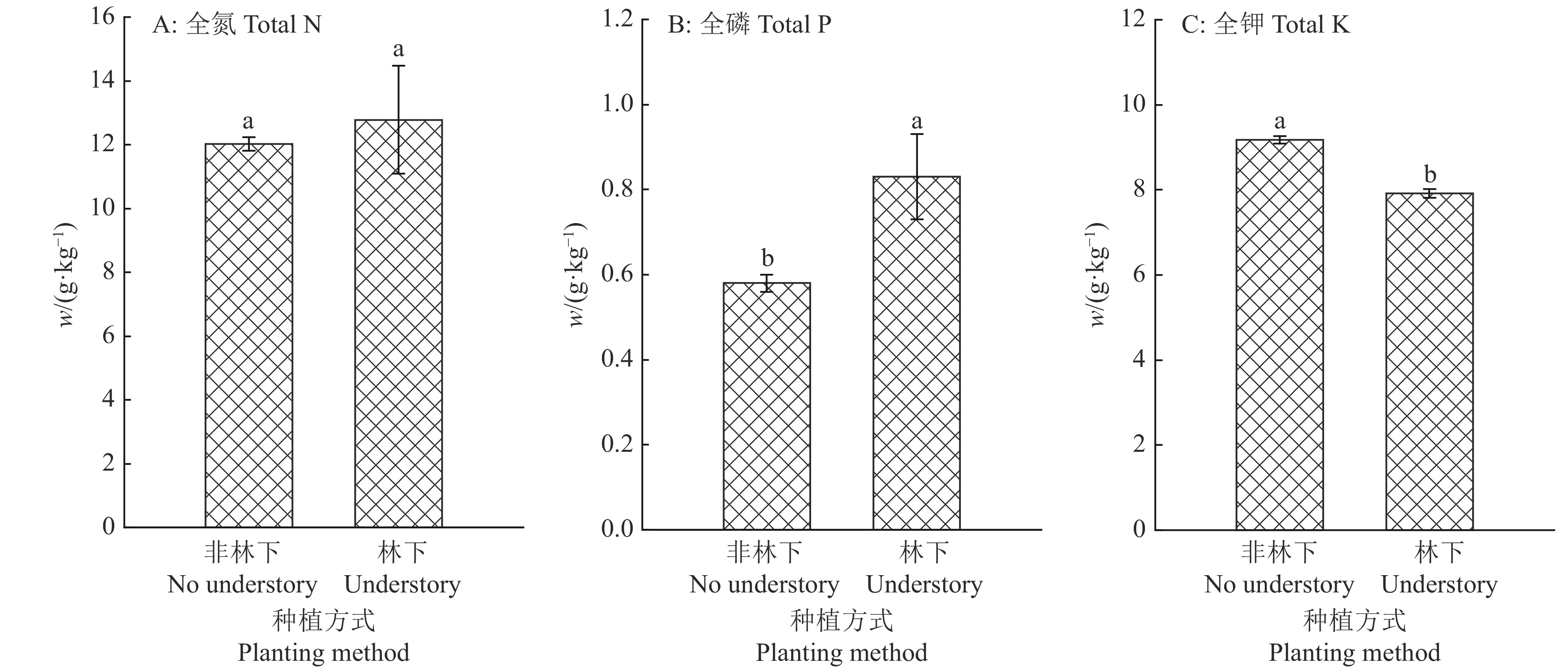
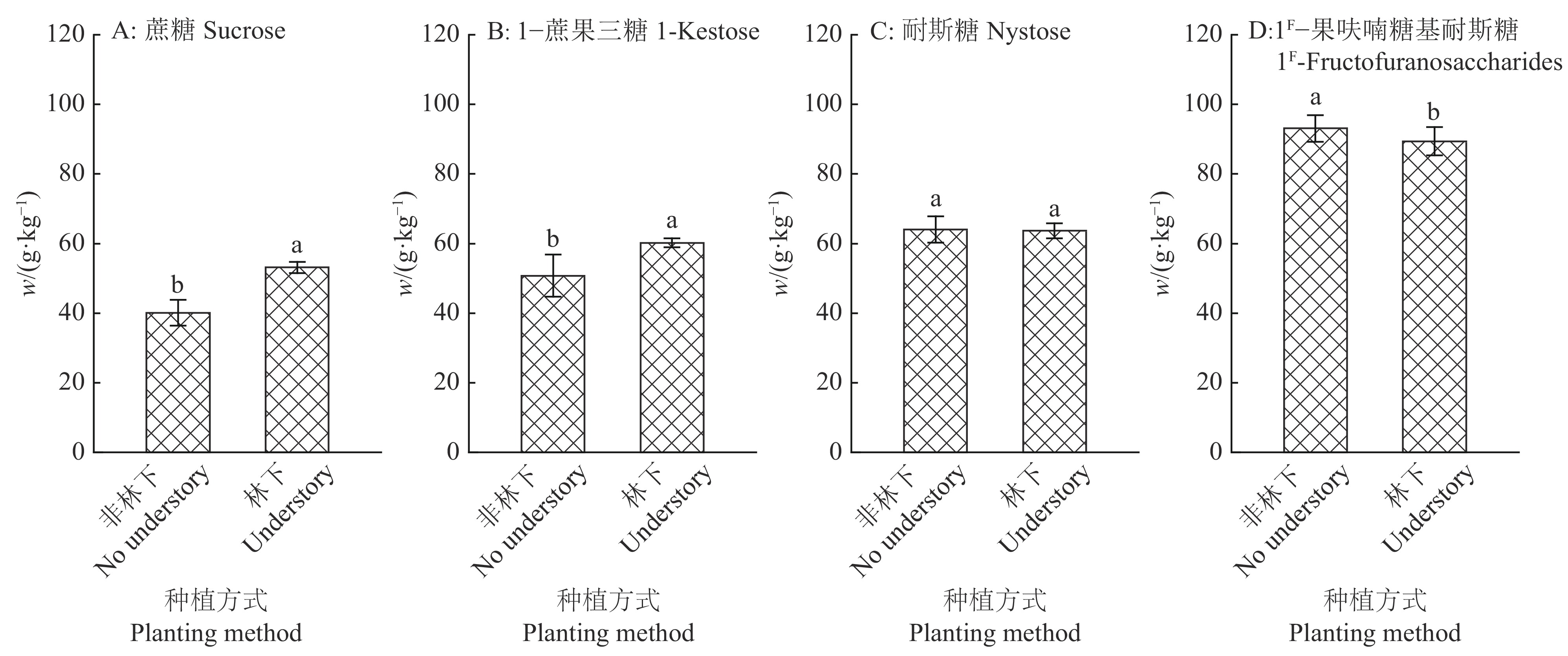
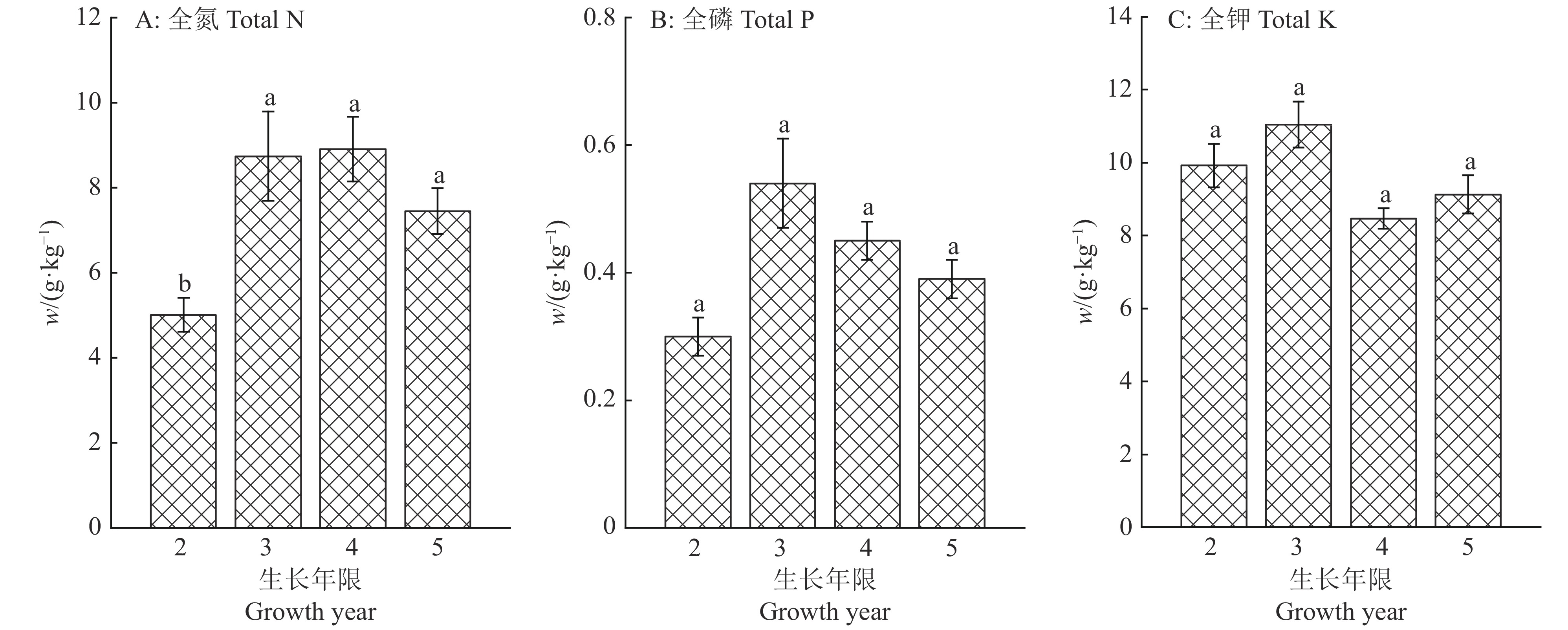
结果土壤pH与巴戟天蔗糖含量呈极显著的负相关关系(P<0.01),与寡糖含量呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05);土壤全磷、速效磷、速效钾与1−蔗果三糖、耐斯糖含量呈显著正相关关系(P<0.05)。3年生巴戟天的蔗糖含量显著高于其他生长年限的巴戟天,4年生巴戟天的1−蔗果三糖含量显著高于2年生巴戟天。林下种植巴戟天的品质优于非林下种植。
结论提高土壤中速效磷与速效钾含量可以提高巴戟天品质,4年生巴戟天的药材品质最佳,林下种植有利于提高巴戟天品质。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the effects of three important factors of soil nutrients, planting years and methods (understory and no understory) on oligosaccharide content which is one of the core index of Morinda officinalis quality, provide the theoretical and data supports for cultivation of M. officinalis which is one of the “Four Southern Herbs” in China.
MethodThis study selected eighteen no understory planting sites in the genuine producing area of M. officinalis in Deqing County, Guangdong Province. Soil samples and M. officinalis samples of different growth years were collected by random multi-point sampling method. The contents of soil nutrients and oligosaccharides in M. officinalis flesh root were determined to analyze the relationships of soil nutrient contents, growth years and oligosaccharides content of M. officinalis. In addition, samples in understory and no understory planting sites were collected to explore the quality differences of M. officinalis by principal component analysis.
ResultThe pH value was highly negatively correlated with sucrose content (P<0.01) and positively correlated with oligosaccharide content (P<0.05). Total phosphorus, available phosphorus and available potassium in soil were positively correlated with the contents of 1-kestose and nystose (P<0.05). The sucrose content of 3-year-oldM. officinalis was significantly higher than those of other growth years, and 1-kestose content of 4-year-old M. officinaliswas significantly higher than that of 2-year-old M. officinalis. The understoryM. officinalis showed better quality than that of no understory.
ConclusionImproving the contents of available P and available K in soil can improve the quality of M. officinalis. The quality of 4-year-old M. officinalis is the best in our study. Understory planting can improve the quality of M. officinalis.
-
Keywords:
- Morinda officinalis /
- active ingredient /
- oligosaccharide content /
- quality /
- understory planting /
- soil nutrient
-
-
图 3 不同种植方式对4年生巴戟天营养元素含量的影响
各图中,柱子上方的不同小写字母表示种植方式间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 3. Effects of different planting methods on nutrient element contents of 4-year-old Morinda officinalis
In each figure, different lowercase letters on the columns indicate significant differences between different planting methods (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
图 4 不同种植方式对4年生巴戟天寡糖含量的影响
各图中,柱子上方的不同小写字母表示种植方式间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)
Figure 4. Effects of different planting methods on oligosaccharide content of 4-year-old Morinda officinalis
In each figure, different lowercase letters on the columns indicate significant differences between different planting methods (P<0.05, Duncan’s method)
表 1 道地产区非林下种植巴戟天采样点基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of sample plot for no understory planting of Morinda officinalis in genuine producing areas
采样点编号
Sample plot number经纬度
Longitude and latitude村或镇
Village or town生长年限
Growth year1 111°58′3″ E,23°18′25″ N 回村 Hui Village 1 2 112°2′12″ E,23°20′49″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 5 3 112°7′23″ E,23°20′51″ N 南田村 Nantian Village 4 4 112°2′20″ E,23°20′46″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 4 5 112°2′24″ E,23°20′47″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 2 6 112°2′22″ E,23°20′39″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 2 7 112°2′36″ E,23°20′44″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 5 8 112°5′49″ E,23°20′50″ N 荔枝村 Litchi Village 3 9 112°2′36″ E,23°20′53″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 5 10 112°2′39″ E,23°20′59″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 6 11 112°2′40″ E,23°21′0″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 2 12 112°2′54″ E,23°21′2″ N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 3 13 112°3′5″ E,23°21′23″N 莫村镇 Mocun Town 3 14 111°55′21″ E,23°15′55″ N 高良镇 Gaoliang Town 5 15 111°55′45″E,23°14′18″ N 榃浪村 Tanlang Village 5 16 111°55′11″ E,23°13′36″ N 中雄村 Zhongxiong Village 4 17 111°55′31″ E,23°13′42″ N 中雄村 Zhongxiong Village 4 18 111°54′54″ E,23°15′0″ N 年宅村 Nianzhai Village 5 表 2 林下种植巴戟天采样点基本信息
Table 2 Basic information of sample plot for understory planting of Morinda officinalis
采样点编号
Sample plot
number经纬度
Longitude
and latitude村或镇
Village
or town伴生植物
Associated plant透光度/%
Transparency生长年限
Growth
year1 111°55′45″E,
23°17′37″N降底村
Jiangdi Village杉木 Cunninghamia lanceolata、
马尾松 Pinus massoniana57.59 2 2 111°54′8″E,
23°17′34″N大揽村
Dalan Village火炬松 Pinus taeda、
山菅兰 Dianella ensifolia37.91 2 3 111°53′52″E,
23°15′29″N高良镇
Gaoliang Town肉桂 Cinnamomum cassia、
青皮竹 Bambusa textilis25.34 3 4 111°55′45″E,
23°14′18″N榃浪村
Tanlang Village肉桂 C. cassia、
马尾松 P. massoniana、
山苍子 Litsea cubeba35.89 5 5 111°55′31″E,
23°14′11″N榃浪村
Tanlang Village肉桂 C. cassia、火炬松 P. taeda、
五指毛桃 Ficus simplicissima36.15 5 6 111°55′11″E,
23°13′36″N中雄村
Zhongxiong Village杉木 C. lanceolata、
乌毛蕨 Blechnum orientale33.39 4 7 111°55′10″E,
23°13′30″N中雄村
Zhongxiong Village橄榄 Canarium album、
山麻黄 Psilopeganum sinense、
五指毛桃 F. simplicissima79.07 4 8 111°54′54″E,
23°15′0″N年宅村
Nianzhai Village阴香 Cinnamomum burmanni、
肉桂 C. cassia、荔枝 Litchi chinensis、
乌毛蕨 B. orientale61.38 5 表 3 巴戟天道地产区土壤pH和养分含量
Table 3 Soil pH and nutrient content in genuine producing areas of Morinda officinalis
样品序号
Sample
number土壤类型
Soil typepH
w/(g·kg−1) w/(mg·kg−1) 全氮
Total N全磷
Total P全钾
Total K有机质
Organic
matter碱解氮
Available N速效磷
Available P速效钾
Available K1 红壤 Red soil 4.45 1.55 0.43 14.60 26.95 153.60 5.80 123.55 2 红壤 Red soil 4.25 1.91 0.62 11.18 27.72 157.52 46.26 154.32 3 红壤 Red soil 4.33 2.53 0.22 8.58 33.86 197.31 3.04 66.55 4 红壤 Red soil 4.50 2.35 0.25 9.13 43.09 188.70 4.67 68.00 5 红壤 Red soil 4.18 1.66 0.41 12.47 40.50 169.55 27.29 99.43 6 红壤 Red soill 4.10 2.00 0.20 12.89 30.25 199.93 3.62 71.67 7 红壤 Red soil 4.52 2.11 0.46 18.21 26.82 168.97 12.47 89.65 8 红壤 Red soil 4.51 2.06 0.26 10.05 37.04 202.02 11.27 131.75 9 红壤 Red soil 4.40 2.09 0.25 9.99 37.12 175.84 6.47 142.88 10 红壤 Red soil 4.25 1.40 0.21 17.32 36.23 342.07 3.45 74.70 11 红壤 Red soil 4.18 4.08 0.33 11.16 75.15 230.14 12.27 90.12 12 黄壤 Yellow soil 4.12 2.41 0.47 14.63 46.04 225.33 29.39 186.59 13 黄壤 Yellow soil 4.25 2.07 0.32 12.33 46.31 192.76 24.72 140.38 14 红壤 Red soil 4.08 1.06 0.27 6.78 37.05 162.21 14.09 90.78 15 红壤 Red soil 4.56 0.88 0.49 9.65 23.64 78.15 17.85 123.57 16 红壤 Red soil 4.66 2.70 0.66 7.17 33.68 118.69 38.14 146.22 17 红壤 Red soil 4.69 1.31 0.76 6.75 32.77 118.48 41.00 151.24 18 红壤 Red soil 4.68 1.47 0.47 4.99 28.03 136.20 32.77 136.34 平均值 Mean 4.37 1.98 0.39 10.99 36.79 178.75 18.59 115.99 最小值 Minimum 4.08 0.88 0.20 4.99 23.64 78.15 3.04 66.55 最大值 Maximum 4.69 4.08 0.76 18.21 75.15 342.07 46.26 186.59 标准误差 Standard error 0.01 0.04 0.01 0.20 0.65 3.13 0.79 1.97 变异系数/% Coefficient of variation 4.71 36.73 42.21 33.12 31.66 31.48 76.44 30.59 表 4 道地产区巴戟天肉质根全氮、全磷、全钾和寡糖含量
Table 4 Total N, total P, total K and oligosaccharide contents of succulent root of Morindus officinalis in genuine producing areas
w/(g·kg−1) 样品序号
Sample
number全氮
Total N全磷
Total P全钾
Total K蔗糖
Sucrose1−蔗果三糖
1-Kestose耐斯糖
Nystose1F−果呋喃糖基耐斯糖
1F- Fructo-
furanosaccharides1 3.97 0.26 6.47 54.35 24.62 52.62 80.44 2 9.22 0.60 11.61 57.72 29.51 43.25 57.77 3 7.32 0.33 9.16 50.73 12.58 27.93 46.60 4 4.30 0.31 6.36 50.04 16.65 48.37 74.99 5 3.97 0.23 11.82 52.18 14.44 51.72 85.78 6 4.75 0.26 9.69 57.43 21.47 49.55 75.85 7 5.93 0.38 13.20 46.25 10.64 29.77 47.46 8 4.09 0.22 8.28 59.65 21.73 51.75 81.96 9 5.96 0.56 10.80 57.72 19.69 42.22 67.56 10 7.90 0.34 10.64 65.43 28.93 37.91 55.72 11 6.30 0.42 8.26 51.73 18.17 42.33 69.34 12 12.30 0.68 13.19 76.16 34.97 43.91 58.06 13 9.84 0.71 11.65 56.42 21.83 46.15 72.50 14 2.81 0.22 6.47 46.33 9.99 31.85 53.77 15 8.77 0.47 6.13 34.06 40.60 62.00 95.48 16 11.70 0.61 9.31 46.49 46.79 65.46 97.12 17 12.33 0.54 9.05 45.33 59.30 69.41 95.10 18 11.99 0.12 6.58 34.09 42.18 58.77 87.70 平均值 Mean 7.41 0.40 9.37 52.34 26.34 47.50 72.40 最小值 Minimum 2.81 0.12 6.13 34.06 9.99 27.93 46.60 最大值 Maximum 12.33 0.71 13.20 76.16 59.30 69.41 97.12 标准误差 Standard error 0.18 0.01 0.13 0.56 0.76 0.65 0.92 变异系数/% Coefficient of variation 43.51 44.07 25.36 19.27 51.83 24.64 22.75 表 5 巴戟天品质与土壤养分含量的相关性分析1)
Table 5 Correlation analysis between Morinda officinalis quality and soil nutrient contents
指标
Index全氮
Total N全磷
Total P全钾
Total K蔗糖
Sucrose1−蔗果三糖
1-Kestose耐斯糖
Nystose1F−果呋喃糖基耐斯糖
1F- FructofuranosaccharidespH 0.373 −0.027 −0.349 −0.595** 0.578* 0.596** 0.570* 全氮 Total N 0.012 0.246 0.213 0.279 −0.246 −0.223 −0.193 碱解氮 Available N −0.192 −0.079 0.345 0.712** −0.384 −0.554* −0.570* 全磷 Total P 0.651** 0.424 0.105 −0.303 0.749** 0.609** 0.455 速效磷 Available P 0.700** 0.455 0.241 −0.156 0.650** 0.513* 0.366 全钾 Total K −0.228 0.111 0.593** 0.570* −0.363 −0.431 −0.458 速效钾 Available K 0.645** 0.610** 0.254 0.178 0.614** 0.471* 0.324 有机质 Organic matter −0.079 0.179 0.086 0.313 −0.258 −0.193 −0.131 1)“*”和“**”分别表示达0.05和0.01水平的显著相关(Pearson法)
1) “*” and “**” indicate significant correlations at 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively (Pearson method)表 6 巴戟天品质指标的主成分初始特征值及累计贡献率
Table 6 Initial characteristic values and cumulative contribution rates of principal components of Morinda officinalis quality index
变量1)
Variable初始特征值 Initial eigenvalue 提取载荷平方和 Squared sum of extracted load 特征值
Eigen
value贡献率/%
Contribution
rate累计贡献率/%
Cumulative
contribution rate特征值
Eigen
value贡献率/%
Contribution
rate累计贡献率/%
Cumulative
contribution rateX1 3.264 46.632 46.632 3.264 46.632 46.632 X2 2.740 39.144 85.776 2.740 39.144 85.776 X3 0.776 11.079 96.855 X4 0.166 2.370 99.225 X5 0.043 0.609 99.834 X6 0.011 0.159 99.993 X7 0.000 0.007 100.000 1)X1:全氮;X2:全磷;X3:全钾;X4:蔗糖;X5:1–蔗果三糖;X6:耐斯糖;X7:1F–果呋喃糖基耐斯糖
1)X1: Total N; X2: Total P; X3: Total K; X4: Sucrose; X5: 1-Kestose; X6: Nystose; X7: 1F- Fructofuranosaccharides表 7 巴戟天品质指标前2个主成分的载荷值
Table 7 Load values of the first two principal components of Morinda officinalis quality index
评价指标
Evaluation index载荷值 Loading value 第一主成分
The first principal component第二主成分
The second principal component全氮 Total N 0.41 −0.15 全磷 Total P 0.52 0.17 全钾 Total K −0.42 −0.11 蔗糖 Sucrose 0.36 0.45 1−蔗果三糖 1-Kestose 0.10 0.59 耐斯糖 Nystose −0.28 0.51 1F−果呋喃糖基耐斯糖 1F- Fructofuranosaccharides −0.42 0.36 表 8 4年生巴戟天品质指标前2个主成分得分与排名
Table 8 Scores and rankings of the first two principal components in the quality index of 4-year-old Morinda officinalis
采样点编号
Sample
plot number种植方式
Planting
method第一主成分
The first principal component第二主成分
The second principal component综合得分
Synthesis
score排名
Rank得分 Score 排名 Rank 得分 Score 排名 Rank 6 非林 No understory −1.58 4 1.09 2 −0.36 3 林下 Understory −0.33 2 1.43 1 0.48 2 7 非林下 No understory −0.87 3 −2.58 4 −1.65 4 林下 Understory 2.78 1 0.07 3 1.54 1 -
[1] 陈志霞, 林励. 巴戟天的研究进展[J]. 中药材, 2001, 24(3): 209-211. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2001.03.030 [2] 冯鸿耀, 曾令杰, 黄涵, 等. 巴戟天根、茎、叶中甲基异茜草素、水晶兰苷、多糖的分布与积累研究[J]. 华西药学杂志, 2017, 32(2): 208-210. [3] 冉志芳, 杨小彤, 许子欣, 等. 不同产地巴戟天中微量元素比较分析[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(7): 2954-2958. [4] 伍淳操, 吴文辉, 刘霞, 等. 巴戟天酒制炮制方法研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2018, 33(1): 97-99. [5] 赖满香, 阮志燕, 许意平. 补肾中药巴戟天药理作用研究进展[J]. 亚太传统医药, 2017, 1(13): 63-64. [6] SINGH B, SHARMA R A. Indian Morinda species: A review[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2019, 34(5): 924-1007.
[7] XU H L, LIU L L, CHEN Y X, et al. The chemical character of polysaccharides from processed Morinda officinalis and their effects on anti-liver damage[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 141: 410-421. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.213
[8] 林仁昌. 永定县野生巴戟天资源短缺原因与林下种植思路[J]. 现代农业科技, 2013(11): 218-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2013.11.144 [9] 陈立金, 江海涛, 李丽娟, 等. 马尾松肉桂人工复层林土壤理化性质的研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 2013, 40(11): 45-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2013.11.014 [10] WANG M Y, WANG Q L, YANG Q, et al. Comparison of anthraquinones, iridoid glycosides and triterpenoids in Morinda officinalis and Morinda citrifolia using UPLC/Q-TOF-MS and multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(1): 160.
[11] YIP K M, XU J, ZHOU S S, et al. Characterization of chemical component variations in different growth years and tissues of Morindae officinalis radix by integrating metabolomics and glycomics[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2019, 67(26): 7304-7314. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01910
[12] 高新开, 叶家宏, 曹子丰. 巴戟天环烯醚萜苷类及蒽醌类成分HPLC指纹图谱研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2014, 25(3): 315-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9783.2014.03.019 [13] 宫璐, 汪鹏, 谭瑞湘, 等. 南药巴戟天的全球产地区划[J]. 世界中医药, 2017, 12(5): 986-988. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2017.05.006 [14] 丁平, 潘超美, 徐鸿华. 不同生物有机肥料对巴戟天主要有效成分的影响[J]. 现代中药研究与实践, 2003, 17(4): 21-22. [15] 邵玲, 李美映, 黎学荣, 等. 肇庆巴戟天两种种植模式的植物学性状及药效成分研究[J]. 中药材, 2019, 42(11): 2480-2485. [16] 李美映, 邵玲, 林培华, 等. 种植模式对巴戟天生长的影响[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2020, 28(2): 163-170. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.4100 [17] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. [18] 李倩. 巴戟天炮制过程中化学成分变化规律的研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2015. [19] 黄钰辉, 张卫强, 甘先华, 等. 南亚热带杉木林分改造中不同树种组合模式评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(6): 956-964. [20] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015. [21] 苏为华. 多指标综合评价理论与方法问题研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2000. [22] 王树刚, 王振林, 王平, 等. 不同小麦品种对低温胁迫的反应及抗冻性评价[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(4): 1064-1072. [23] 刘瑾, 丁平, 邵艳华, 等. 巴戟天不同产地土壤理化性质对其质量的影响[J]. 现代中药研究与实践, 2011, 25(4): 3-5. [24] 刘瑾. 巴戟天道地药材形成的生态因子及分子机制研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2009. [25] 章润菁. 不同产地巴戟天资源调查及质量评价研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2016. [26] 罗新华, 陈瑞云. 巴戟天栽培技术[J]. 福建农业, 2010(8): 20-21. [27] 刘占锋, 傅伯杰, 刘国华, 等. 土壤质量与土壤质量指标及其评价[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(3): 901-913. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.03.036 [28] 吴凤云, 邱丽莎, 崔秀明, 等. 白及品质特征影响因素研究[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2016, 36(21): 1838-1844. [29] WU Z, CHEN D, LIN F, et al. Effect of bajijiasu isolated from Morinda officinalis F. C. how on sexual function in male mice and its antioxidant protection of human sperm[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2015, 164: 283-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.016
[30] XU L, XU D, HAN Y, et al. BDNF-GSK-3 beta-beta-catenin pathway in the mPFC is involved in antidepressant-like effects of Morinda officinalis oligosaccharides in rats[J]. International Journal of Neuropsycho-pharmacology, 2017, 20(1): 83-93.
[31] 陈地灵, 张鹏, 林励, 等. 巴戟天低聚糖对A β25-35致拟痴呆模型大鼠的保护作用[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2013, 38(9): 1306-1309. [32] 罗世琼, 林爱兰, 姚永红. 野生黄花蒿抗氧化成分与植株养分的相关性分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2013, 26(4): 1622-1626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4829.2013.04.066 [33] 王晖, 姜武, 陶正明, 等. 淳安县林下中药材复合种植模式[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2017, 58(7): 1190-1191.



 下载:
下载: