Prediction models of soil moisture content and electrical conductivity in citrus orchard based on internet of things and LSTM
-
摘要:目的
构建柑橘果园环境信息物联网实时采集系统,建立基于物联网和长短期记忆(LSTM)的柑橘园土壤含量和电导率预测模型,为果园灌溉施肥管理、效果预测评估提供参考依据。
方法利用土壤温度、含水量、电导率三合一传感器,在柑橘果园中设置5个节点和1个气象站,通过ZigBee短距离无线通信和GPRS远距离无线传输,将果园气象数据和土壤墒情数据传输至远程服务器。利用LSTM模型建立气象数据与土壤含水量和电导率的预测模型,计算均方根误差(RMSE)和决定系数(R2)以进行性能评估。
结果物联网系统能够实现远程传输柑橘果园环境数据,建立了基于LSTM和广义回归神经网络(GRNN)的土壤含水量和电导率预测模型,模型在5个节点的数据集的训练结果分别为:LSTM模型训练的土壤含水量和电导率的RMSE范围分别为6.74~8.65和6.68~8.50,GRNN模型训练的土壤含水量和电导率的RMSE范围分别为7.01~14.70和7.60~13.70。利用生成的LSTM模型和气象数据进行拟合,将土壤含水量和电导率的预测值与实测值进行回归分析,LSTM模型拟合的土壤含水量和电导率的R2范围分别为0.760~0.906和0.648~0.850,GRNN模型拟合的土壤含水量和电导率的R2范围分别为0.126~0.369和0.132~0.268,说明LSTM模型的性能表现较好。
结论建立了柑橘果园环境的物联网信息传输系统,构建的基于LSTM的果园土壤含水量和电导率预测模型具有较高的精度,可用于指导柑橘果园的灌溉施肥管理。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo build an internet of things (IoT) system for transmitting the environmental information of citrus orchards in real time, establish prediction models of soil moisture content and electrical conductivity in citrus orchard based on IoT system and long short-term memory (LSTM), and provide references for irrigation and fertilization management as well as effect prediction and evaluation.
MethodSoil temperature, moisture and electrical conductivity sensors were applied in five IoT nodes and a weather station was set in citrus orchard. The meteorological data and soil moisture data collected in the orchard were transmitted to a remote server via ZigBee, a short range wireless communication technique, and GPRS, a long distance wireless transmission technique. The prediction models of soil moisture content and electrical conductivity were established using weather data based on the LSTM model. The root mean square error (RMSE) and coefficient of determination (R2) were calculated to evaluate the performance of the model.
ResultThe IoT system was capable to transmit environmental data of the citrus orchard to a remote server. LSTM and general regression neural network (GRNN) model were built to predict soil moisture content and electrical conductivity. The performance of models in five nodes were as following: The RMSE of soil moisture content and electrical conductivity ranged from 6.74 to 8.65 and 6.68 to 8.50 respectively based on LSTM model, and ranged from 7.01 to 14.70 and 7.60 to 13.70 respectively based on GRNN model. With the generated LSTM model and meteorological data for predicting, regression analysis was conducted between predicted and measured values of soil moisture content and electrical conductivity. The R2 of soil moisture content and electrical conductivity ranged from 0.760 to 0.906 and 0.648 to 0.850 respectively based on LSTM model, and ranged from 0.126 to 0.369 and 0.132 to 0.268 respectively based on GRNN model. The results indicated that the LSTM model performed better than the GRNN model.
ConclusionThe IoT system for citrus orchard environmental information transmission is established. The LSTM model has high accuracy in predicting soil moisture content and electrical conductivity, and the model can be helpful for guiding irrigation and fertilization management.
-
柑橘Citrusspp.是一种重要的经济作物,主要分布在我国的广东、广西和四川等地[1-3]。我国的柑橘种植面积和年产量已经位居世界首位,并且连续多年不断增长[4-5]。目前我国的柑橘灌溉由传统的漫灌逐渐升级到滴灌,能够较好地实现节水灌溉[6]。但是滴灌作业主要还是由人为主观意识根据气象状况来进行判断,缺乏客观依据[7-8]。柑橘生长需要适宜的土壤含水量和电导率,过低或者过高的土壤含水量都会对根系生理活动产生负面影响[9],而土壤电导率则直接反映土壤的含盐量[10],过高的盐胁迫会导致柑橘产生盐毒害,过低的盐含量导致柑橘难以吸收所需的无机盐离子。因此,在柑橘种植作业中,及时获取柑橘果园的气象、土壤数据,以及建立果园的土壤含水量和电导率预测模型,对于制定和指导果园灌溉施肥管理具有重要意义。
近年来,物联网技术在农业中得到了广泛的应用,其结合相关传感器能够实现果园生长环境的远程实时监测。杨伟志等[11]建立了基于物联网和人工智能的柑橘灌溉系统,该研究利用传感器实时监测柑橘果园土壤水分等信息,整合物联网系统与专家系统知识库的灌溉规则来制定灌溉控制措施,该系统主要依靠已有的控制规则,部分参数的设置需要依靠经验来确定。李中良等[12]利用物联网和空气温湿度传感器、土壤温湿度传感器设计了实时监测柑橘环境的系统,综合了无线传感器网络、通用无线分组服务(General packet radio service,GPRS)网络与远程服务器网络来实现田间数据的远程传输,但该系统没有针对果园环境数据进行进一步的分析。罗党等[13]利用灰色神经网络,研究降雨量、温度、湿度、风速等因子对土壤含水量的影响,该模型说明了神经网络在土壤含水量预测方面是可行的,具有不错的精度。蔡亮红等[14]设计了基于极限学习机(Extremelearning machine,ELM)算法的土壤含水量预测模型,采用定点采集土壤样本并获取光谱数据的方法,经过小波变换和特征工程处理后,利用ELM算法建立非线性模型,实现土壤含水量的预测,但该系统没有利用物联网等实时传输方法,而且加入的训练因子较少,在复杂环境条件下,还需要进一步研究。张武等[15]利用反向传播(Back propagation,BP)神经网络和长短期记忆(Long short-term memory,LSTM)深度学习模型研究了不同采样间隔对茶园土壤墒情预测模型性能的影响,结果表明在30 min的采样间隔下,模型的性能表现最好,但是该研究的数据采集时间跨度较短,模型也未给出更多可解释性指标来描述其模型性能。
针对以上研究现状,本文设计一种基于物联网的柑橘园环境信息实时采集与传输系统,并建立基于LSTM的土壤含水量和电导率预测模型,为果园灌溉施肥管理提供指导。
1. 柑橘园环境信息物联网传输系统设计
1.1 系统总体架构
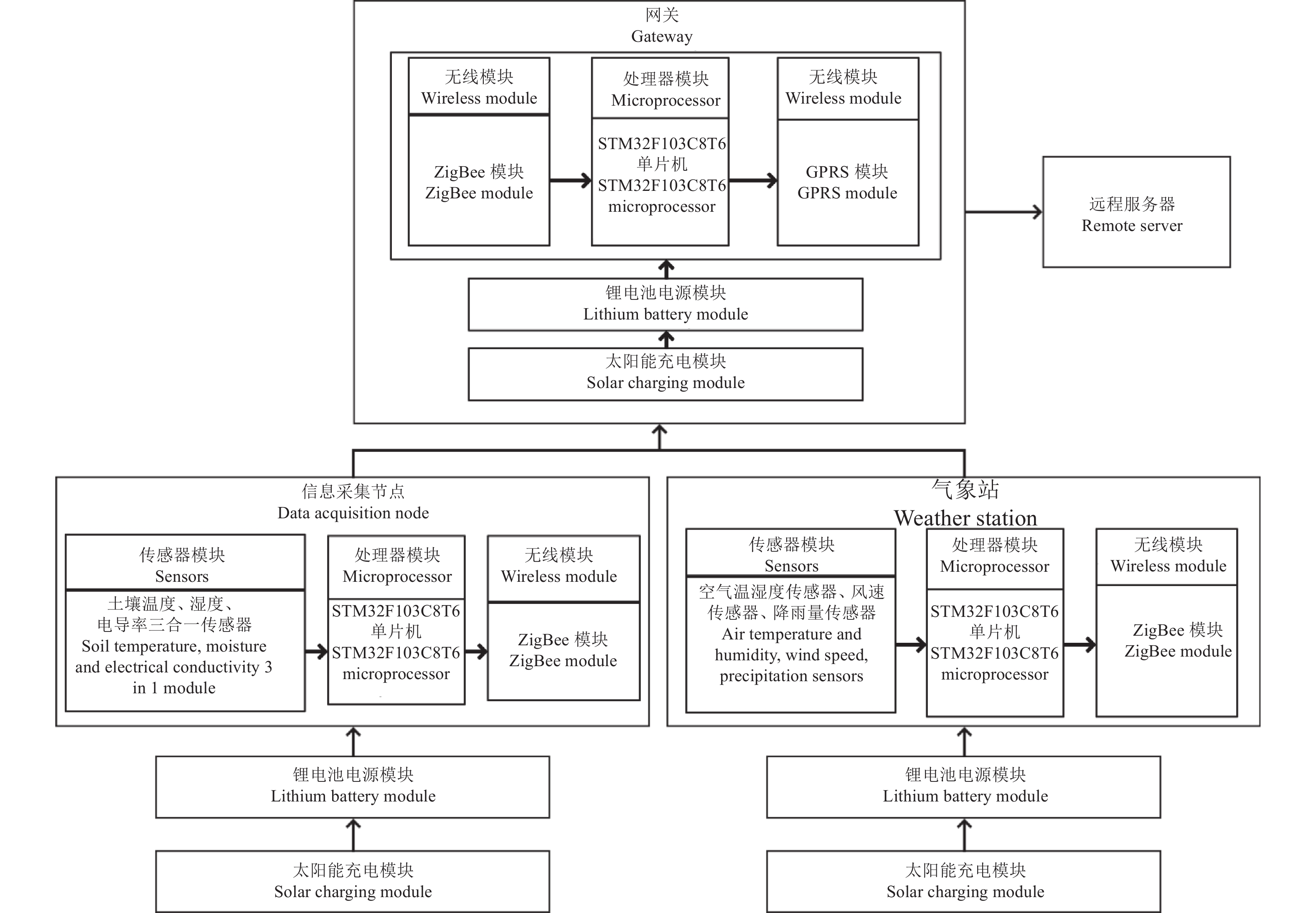
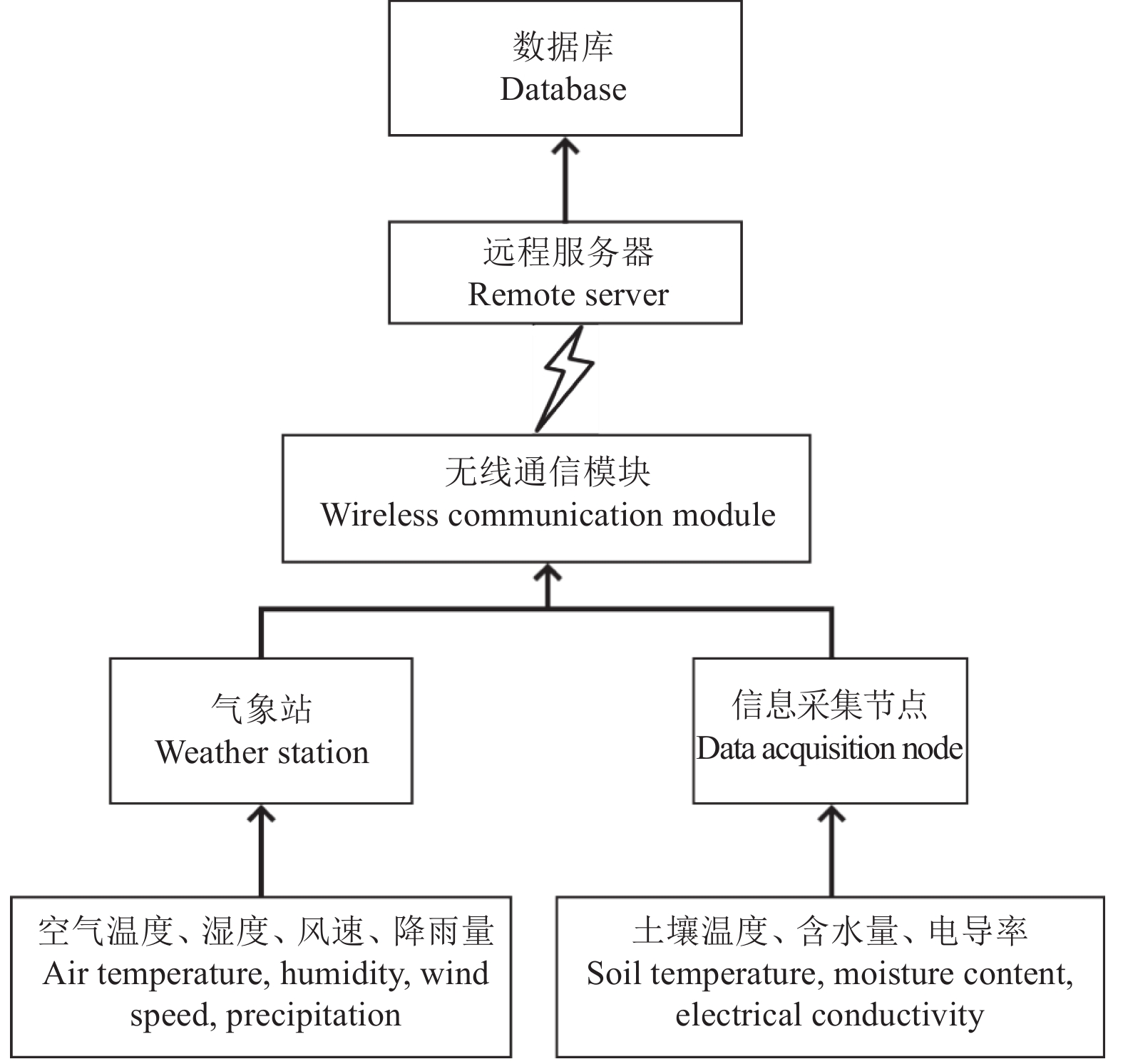
物联网传输系统包括远程服务器、数据库、无线通信模块、信息采集节点、气象站等[16]。物联网系统架构如图1所示。信息采集节点负责采集柑橘园中的土壤含水量和电导率信息,气象站负责采集果园中的气象信息,包括空气温度、湿度、风速、降雨量等,通过无线通信模块传输至物联网网关与远程服务器,传输的数据最终存储在数据库中。
1.2 物联网传输系统硬件
硬件系统包括STM32F103C8T6处理器模块、电源模块、GPRS模块、ZigBee模块、空气温湿度传感器、风速传感器、降雨量传感器和土壤温度、含水量、电导率三合一传感器。传感器模块用于直接采集相关果园环境信息,ZigBee模块负责各个节点与网关数据传输,GPRS模块将各个节点数据远程传输至远程服务器。硬件框图如图2所示。
1.3 物联网传输系统软件
1.3.1 ZigBee组网协议
常见的ZigBee组网协议主要包括树型组网、星型组网和网状型组网等[17-19]。本文信息采集节点和气象站布置于柑橘果园中,需要考虑节点数据传输性能和续航能力。由于星型组网方式下,各个节点需要与网关直连以传输数据,在果园中存在着数据无法传输的可能性。网状型组网方式需要经过多轮数据转发,容易引起额外的能量损耗和丢包。因此本文采用树型组网方式,能够利用少量的节点中继实现数据传输,也能够尽可能减少路由转发引起的丢包问题。
1.3.2 节点软件
系统节点主要负责数据采集与转换,包含2种工作模式,即正常模式和休眠模式[20-21]。在正常工作模式下,节点负责开启传感器并采集数据;而在休眠模式下,节点仅保留时钟唤醒机制,定时开启并采集数据,以实现节能的目的。节点软件工作流程如图3所示。
2. 材料与方法
2.1 区域概况与数据采集预处理
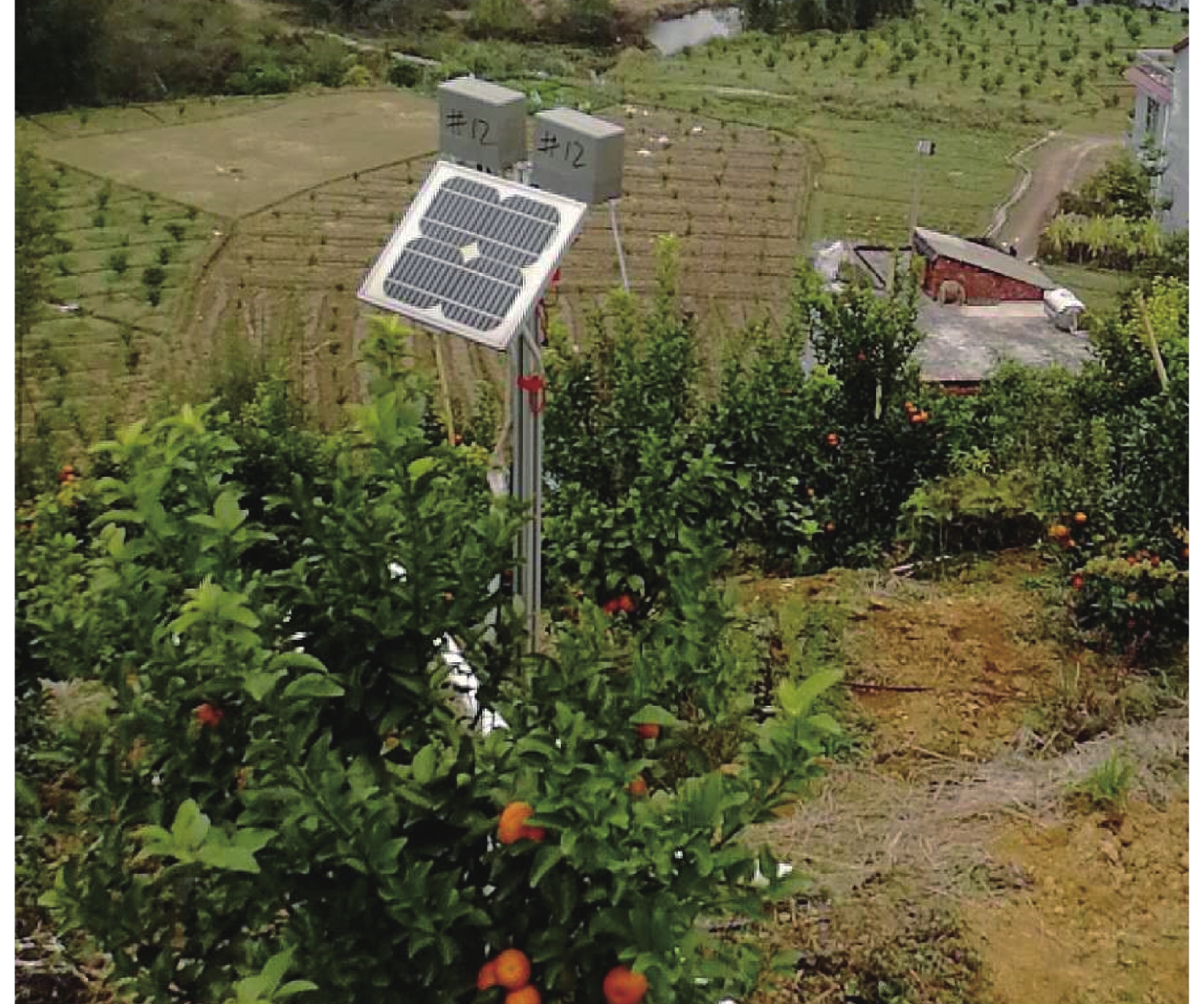
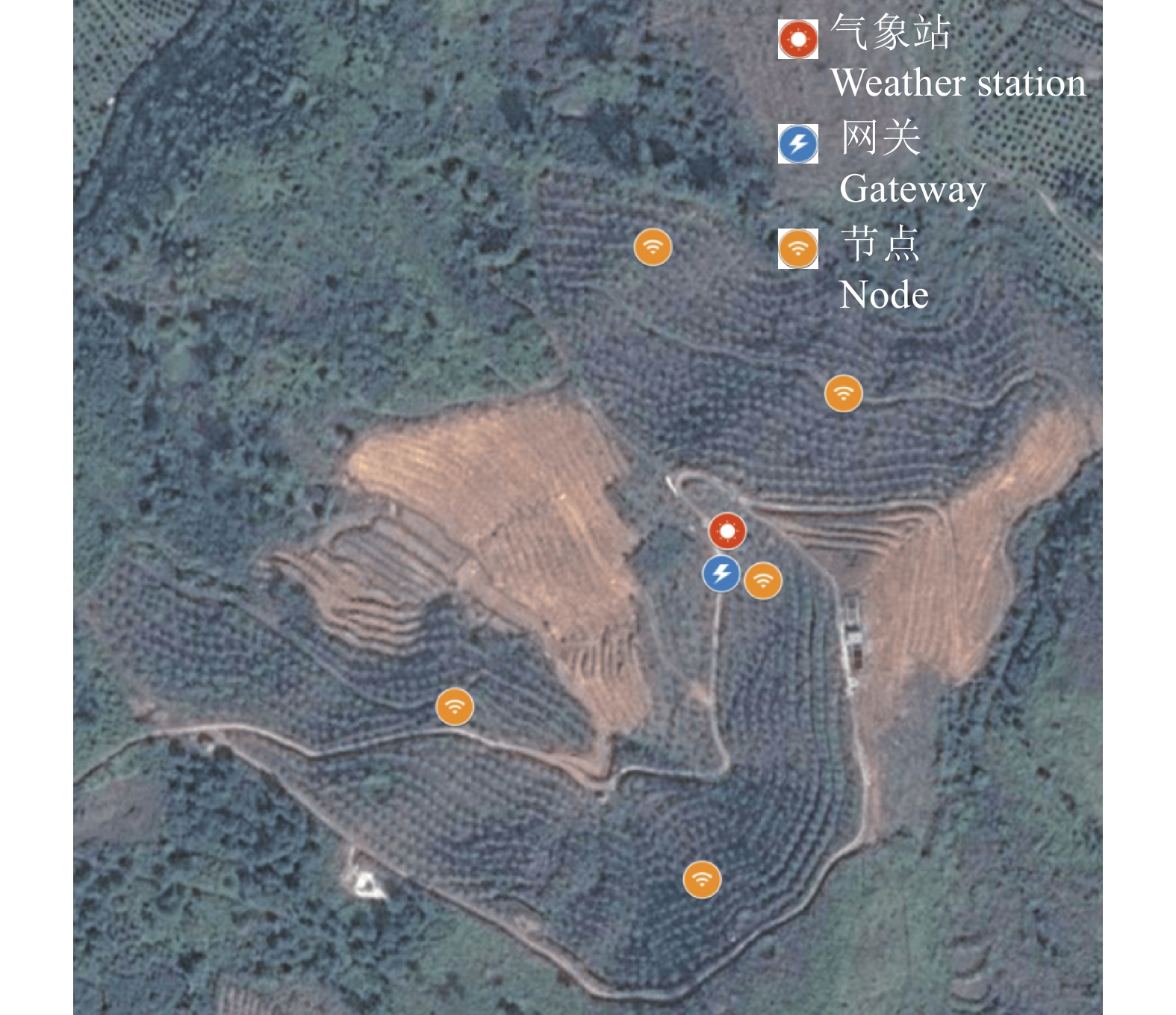
试验地点设在华南农业大学试验基地,该基地面积约13 hm2,海拔约为200 m,属于山地地形,土壤主要为含沙土质。该地区夏季高温多雨,年降雨量为1700 mm左右,但是冬季降雨较少,易干旱。昼夜温差较大,适合柑橘等作物的糖分积累。在果园设置了5个节点,气象站和网关位于果园中央位置;使用激光测距仪测量得到单节点之间最长距离为344 m,节点使用高度为2.5 m的支架进行固定以减少果树对无线信号传播的干扰。其布置示意图如图4所示。节点数据与气象站数据分别传输至网关,由网关负责将数据打包传输至远程服务器,完成数据的传输。
本文的系统搭建完成后正式数据采集时间为2019年10月1日至2020年6月16日,节点数据传输间隔设置为每10 min传输1个数据包,单个节点理论上每天的数据包量为144个。数据采集期间平均每个节点接收数据包总数为36326个,总平均丢包率为2.6%。利用汇总后的数据包统计当天的最高空气温度、最低空气温度、平均空气温度、空气湿度、降雨量、土壤含水量、土壤电导率和土壤温度。土壤含水量和电导率一般与蒸散量、降雨量、温度、湿度等相关,根据气象参数和彭曼公式计算蒸散量[22]:
$$ {\rm{E}}{{\rm{T}}}_{0}=\dfrac{0.408{\Delta }\left({R}_{n}-G\right)+{\gamma }\dfrac{900}{T+273}{u}_{2}\left({e}_{{\rm{s}}}-{e}_{{\rm{a}}}\right)}{{\Delta }+{\gamma }\left(1+0.34{u}_{2}\right)} ,$$ (1) 式中,ET0为日参考蒸散量,mm·d−1;Rn为净辐射量,MJ·m−2·d−1;G为土壤热通密度,MJ·m−2·d−1;T为离地2 m高的平均空气温度,℃;u2为离地2 m高的风速,m·s−1;es为饱和蒸汽压,kPa;ea为实际蒸汽压,kPa;Δ为蒸汽压力曲线斜率,kPa·℃−1;γ为温湿度常数,kPa·℃−1。采用估算公式(2)计算辐射数据[23]:
$$ {R}_{{\rm{s}}}=\left({a}_{{\rm{s}}}+{b}_{{\rm{s}}}\frac{t}{{t}_{{\rm{max}}}}\right){R}_{{\rm{a}}} ,$$ (2) 式中,Rs和Ra分别为太阳辐射和地外辐射,MJ·m−2·d−1;t为日照时长,h;tmax为最大日照时长,h;
${a}_{{\rm{s}}}$ 和${b}_{{\rm{s}}}$ 通常取常数0.25和0.50。由于各个环境参数具有不同的数量级,因此需要在数据预处理环节进行归一化处理。各个节点预处理后的数据取平均值后,分别建立各个环境参数与土壤含水量和电导率的相关性分析[24],结果如表1所示。
表 1 土壤含水量和电导率与环境参数的相关系数Table 1. Correlation coefficients of soil moisture, electrical conductivity and environmental parameters土壤因子
Soil factor空气温度 Air temperature 降雨量
Precipitation空气湿度
Air
humidity土壤温度
Soil
temperature蒸散量
Evapotranspiration最高值
Max.
最低值
Min.
平均值
Mean
含水量 Moisture content 0.490 0.598 0.644 0.123 0.430 0.652 0.158 电导率 Electrical conductivity 0.467 0.311 0.231 0.300 0.168 0.251 0.148 由表1可见,气象环境因子与土壤含水量和电导率存在一定的相关性,具备输入模型参与拟合的条件。
2.2 GRNN模型
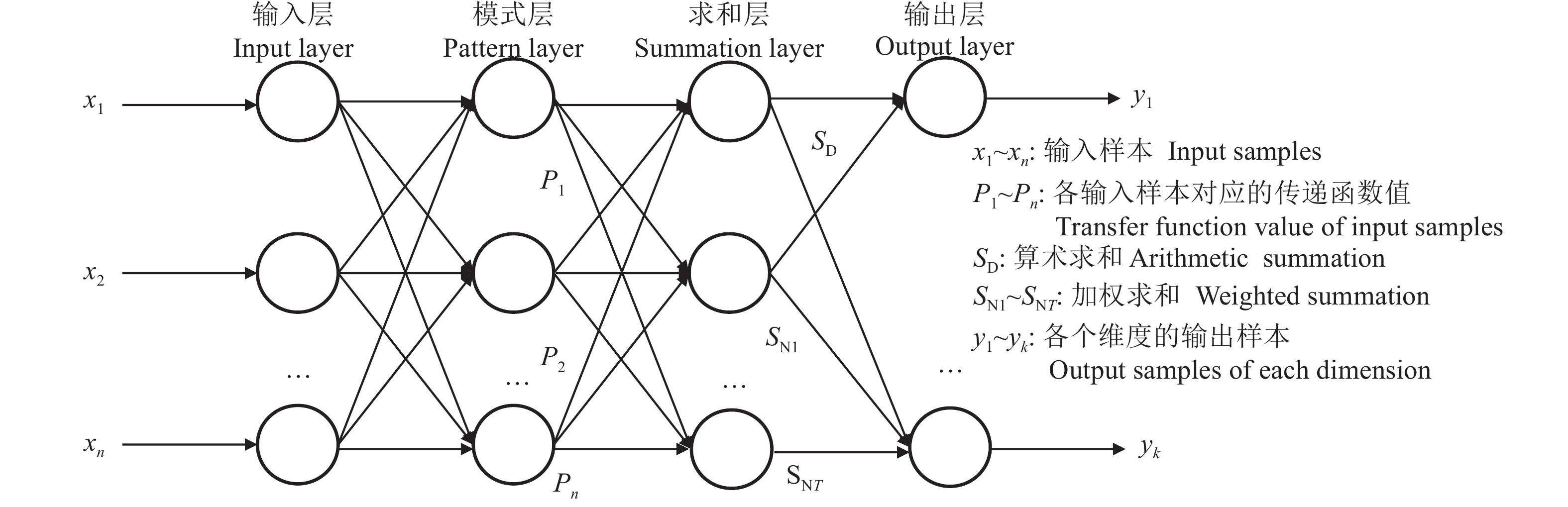
GRNN模型最早是由Specht[25]提出的。GRNN模型能够利用连续的非线性数据进行训练,并收敛于底层回归曲面,该算法能够应用在学习植物模型的动力学中。GRNN建立在非参数回归基础上,以样本数据为后验条件,执行Parzen非参数估计,依据最大概率原则计算网络的输出并传输给下一级。GRNN的基础是径向基网络,具有较好的非线性拟合功能,但在训练过程中需要选定合适的学习参数,否则会容易产生过拟合现象。GRNN的网络结构分为4层,分别是输入层、模式层、求和层和输出层。其基础结构图如图5所示。
GRNN的网络输入为矩阵X=
$[ $ x1,x2,…,xn$]^\top$ ,输出为矩阵Y=$[ $ y1,y2,…,yk$]^\top$ ,k为输出向量的维数。GRNN的模式层的神经元数目等于输入样本数目n,模式层的传输函数(pi)为公式(3):$$ {p}_{i}=\mathrm{exp}\left[-\frac{{\left({\boldsymbol{X}}-{{\boldsymbol{X}}}_{i}\right)}^\top \left({\boldsymbol{X}}-{{\boldsymbol{X}}}_{i}\right)}{2{\mathrm{\delta }}^{2}}\right],{\text{其中}},i=\mathrm{1,2},\cdots ,n ,$$ (3) 式中,i表示模式层中第i个神经元,Xi为第i个神经元对应的学习样本,
$ \delta $ 为平滑参数,改变$ \delta $ 即可改变网络学习率。GRNN网络求和层包含2种求和方式,即直接求和与加权求和,计算公式分别如公式(4)和(5)所示:
$${S_{\rm{D}}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{p_i}} ,$$ (4) $${S_{{\rm{N}}j}} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{y_{ij}}} {P_i},{\text{其中}},j = 1,2, \cdots ,k,$$ (5) 式中,
${S}_{{\rm{D}}}$ 为求和层神经元输出,${S}_{{\rm{N}}j}$ 为求和层加权神经元输出,j表示输出层中第j个神经元,$ {P}_{i} $ 为模式层第i个神经元的权值。GRNN网络的输出层中神经元数目等于输出向量的维数,如公式(6)所示:
$$ {y}_{j}=\frac{{S}_{{\rm{N}}j}}{{S}_{{\rm{D}}}},{\text{其中}},j={1,2},\cdots ,k{\text{。}} $$ (6) 2.3 LSTM模型
实践证明,神经网络能够有效地解决复杂的非线性问题,但传统的神经网络无法利用时间序列数据特征预测未来的情况,特别是对市场销售、股票价格、pm2.5等时间序列数据的时序建模。时间序列数据不仅与当前条件相关,而且与最后的数据具有很高的相关性,而传统的神经网络难以对时间序列进行建模。近年来,递归神经网络[26-28](Recursive neural network,RNN)在自然语言处理、机器翻译和文本预测等方面得到了成功的应用,其效果明显优于神经网络。不同于一般的前馈网络,RNN包含隐藏状态提取特征,然后转化为输出数据。另一方面,RNN在所有计算步骤中共享权值、偏差等,使其与所连接的节点相依赖。然而,标准RNN也有不足之处,如要求输入和输出数据大小相同。另外,RNN通过对前一层隐状态的变换,经过激活函数后得到新的隐状态,但当RNN进行反向传播时容易产生梯度消失或者梯度爆炸问题。因此,RNN有时不能很好地处理长期依赖问题。
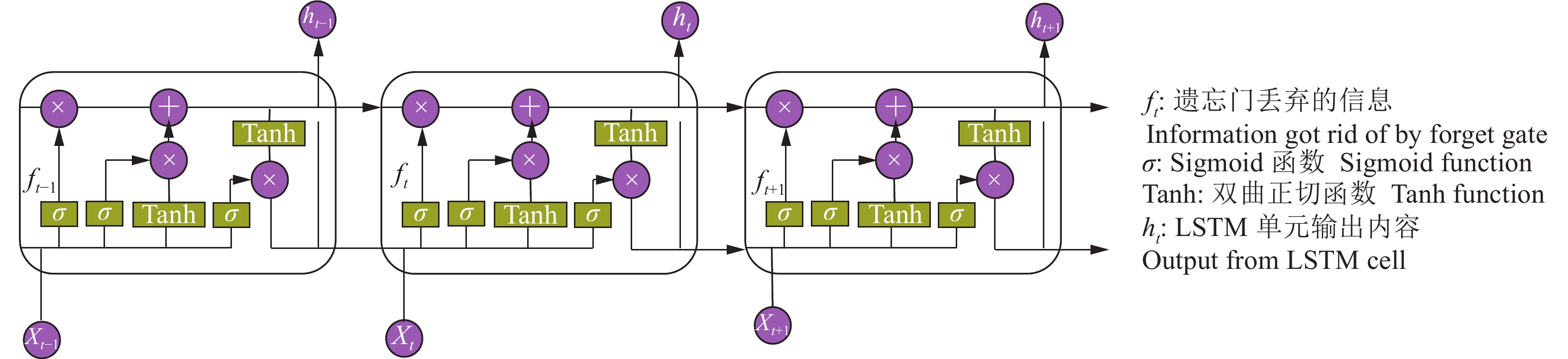
作为一种特殊的RNN网络,LSTM[29]包含了1个控制应该丢弃哪些信息的门,即遗忘门(Forget gate)。其次,为了避免梯度消失问题,在计算隐层状态时,用求和代替梯度导数。因此,理论上LSTM具有解决长期问题的能力。在本文中,LSTM网络是由3个部分组成的,即1个输入层用于处理数据,50个隐藏层用于训练和建模,1个输出层用于输出建模结果。模型的核心部分即LSTM节点[30],主要由3个部分组成,分别是输入门、输出门和遗忘门。其结构如图6所示。
其中,遗忘门控制丢弃的信息(ft),如公式(7)所示:
$${{{f}}_{{t}}} = \sigma \left( {{{{W}}_{\rm{f}}} \left[ {{{{h}}_{{{t}} - 1}},{{{x}}_{{t}}}} \right] + {{{b}}_{\rm{f}}}} \right),$$ (7) 式中,
$ {f}_{t} $ 的范围为[0,1],$ \mathrm{\sigma } $ 函数使得方程非线性化,更接近实际值从而提高预测精度。${{W}}_{\mathrm{f}}$ 和${{b}}_{\mathrm{f}}$ 分别为遗忘门的权重和偏差参数。${{h}}_{{t}-1}$ 和${{x}}_{{t}}$ 为上一状态值和当前输入值。输入门的功能是控制输入到当前单元中的信息,其状态更新如公式(8)和(9)所示:
$${{{i}}_{{t}}} = \sigma \left( {{{{W}}_{\rm{i}}} \left[ {{{{h}}_{{{t}} - 1}},{{{x}}_{{t}}}} \right] + {{{b}}_{\rm{i}}}} \right),$$ (8) $$\widetilde {{{{C}}_{{t}}}} = {\rm{tanh}}\left( {{{{W}}_{\rm{C}}} \left[ {{{{h}}_{{{t}} - 1}},{{{x}}_{{t}}}} \right] + {{{b}}_{\rm{C}}}} \right),$$ (9) 式中,
${{i}}_{{t}}{\text{由}}{\sigma }$ 激活函数控制输入数据,如果其值为0,表示输入数据被完全阻塞,如果值为1,则表示完全允许数据进入门中。细胞状态由$\widetilde {{{C}}_{{t}}}$ 负责,它的激活函数是tanh。Wi和bi表示激活函数的权重和偏差参数,WC和bC表示细胞状态方程的权重和偏差参数。输入门经过运算的数据,需要更新到细胞状态中,更新公式为:
$${{{C}}_{{t}}} = {{{f}}_{{t}}}{{{C}}_{{{t}} - 1}} + {{{i}}_{{t}}}\widetilde {{{{C}}_{{t}}}},$$ (10) 式中,
${f}_{t} {C}_{t-1}$ 代表遗忘的信息,${i}_{t} \widetilde {{C}_{t}}$ 代表需要更新到当前细胞状态的信息,两者之和共同决定向下一个状态传递的信息量。LSTM网络结构的最后一部分是输出门,其更新公式为:
$${{{o}}_{{t}}} = \sigma \left( {{{{W}}_{\rm{o}}}\left[ {{{{h}}_{{{t}} - 1}},{{{x}}_{{t}}}} \right] + {{{b}}_{\rm{o}}}} \right),$$ (11) $${{{h}}_{{t}}} = {{{o}}_{{t}}}{\rm{tanh}}\left( {{{{C}}_{{t}}}} \right),$$ (12) 式中,
$o_t $ 表示激活函数的输出,由σ函数决定,同时更新后的细胞状态值$C_t $ 在tanh函数作用下,与传递函数$o_t $ 的乘积作为向下一个单元输出的内容,Wo和bo表示激活函数的权重和偏差参数。经过上述LSTM单元的运算后,输出的信息能够被存储,也能够进入下一个节点进行运算,从而在训练过程中提取出信息。
2.4 模型性能测试标准
本文模型的性能表现使用均方根误差(RMSE)来表示,计算模型预测值与真实测量值的决定系数(R2)[31]来表征模型可解释性。相关公式为:
$${\rm{RMSE}} = \sqrt {\frac{{\displaystyle\sum _{m = 1}^{{N}}{{\left( {{{{y}}_{{\rm{pred}}}} - {{{y}}_{{\rm{cal}}}}} \right)}^2}}}{{{N}}}}, $$ (13) $${R^2} = \frac{{\displaystyle\sum _{m = 1}^N{{\left( {{{{y}}_{{\rm{pred}}}} - \overline {{{{y}}_{{\rm{cal}}}}} } \right)}^2}}}{{\displaystyle\sum _{m = 1}^N{{\left( {{{{y}}_{{\rm{cal}}}} - \overline {{{{y}}_{{\rm{cal}}}}} } \right)}^2}}},$$ (14) 式中,
$ {{y}}_{\rm{pred}} $ 表示预测值,$ {{y}}_{\rm{cal} }$ 表示实测值,$ \overline{{{y}}_{\rm{pred}}} $ 表示预测值均值,$ \overline{{{y}}_{\rm{cal}} }$ 表示实测值均值,N表示样本数。3. 结果与分析
3.1 LSTM和GRNN模型训练设置
试验中,使用了果园气象站气象数据和5个信息采集节点采集到的土壤墒情数据,现场布置的节点如图7所示。由于无线传感器网络传输过程中存在复杂因素的干扰,产生了个别异常(如空数据)与丢包数据,使得数据包不完整或整体丢失,本文将异常数据进行剔除,最终得到符合模型需求的数据。将70%数据划分为训练集,30%数据划分为测试集,5个节点数据划分结果如表2所示。训练参数设置方面,LSTM模型包含2层,每层128个LSTM单元,使用Relu激活函数,损失函数使用均方误差(MSE),优化算法使用Adam,共设置72个epoch和128个batch size。GRNN模型包含4层,模式层与输入样本相同,求和层使用128个神经元,激活函数、损失函数和优化算法、epoch和batch size等参数与LSTM模型保持一致。
表 2 节点数据信息Table 2. Datasets of nodes节点
Node数据总数
Total number训练集
Training dataset测试集
Testing dataset1 216 151 65 2 241 168 73 3 241 168 73 4 196 137 59 5 203 142 61 气象站
Weather station241 168 73 3.2 模型性能表现
基于本文所提出的模型和预处理的输入样本经过训练后的性能测试标准如表3所示。
表 3 模型性能表现Table 3. Performance of models节点
Node模型
Model土壤含水量
Soil moisture
content土壤电导率
Soil electrical
conductivityRMSE R2 RMSE R2 1 LSTM 8.65 0.811 6.88 0.850 GRNN 13.30 0.126 12.30 0.106 2 LSTM 7.30 0.906 6.68 0.727 GRNN 14.70 0.323 13.70 0.185 3 LSTM 6.74 0.814 8.22 0.648 GRNN 7.01 0.369 8.26 0.268 4 LSTM 7.93 0.760 8.50 0.767 GRNN 10.27 0.256 7.85 0.167 5 LSTM 8.40 0.768 7.78 0.769 GRNN 8.80 0.206 7.60 0.132 从表3中可以看出,在土壤含水量的预测模型表现中,LSTM模型的RMSE值范围为6.74~8.65,低于GRNN模型的7.01~14.70。LSTM模型中,节点2和3的RMSE在5个节点中较低,这可能是因为这2组训练样本数较多。节点4的RMSE比节点5更低,但其训练样本数比后者少,因此RMSE除了受训练样本数量影响外,还与数据集自身样本情况有关。GRNN模型的RMSE与训练样本数量没有呈现明显的关系或趋势。RMSE用来衡量离散程度,与原样本具有相同的量纲,而R2作为一种无量纲的性能指标,能够反映模型的可解释性。从表3可以看出,对于土壤含水量,虽然相较于GRNN模型,LSTM模型的RMSE没有表现出明显优势,但是其R2范围为0.760~0.906,远大于GRNN模型的0.126~0.369,这意味着LSTM模型预测的土壤含水量呈现出了较高的可解释性,意味着该模型给出的预测值能够较好地反映土壤含水量。表3中土壤电导率模型预测表现与土壤含水量呈现类似的趋势,同样表明LSTM模型在给定的试验样本下,适合用来对土壤电导率进行预测。
3.3 模型拟合分析
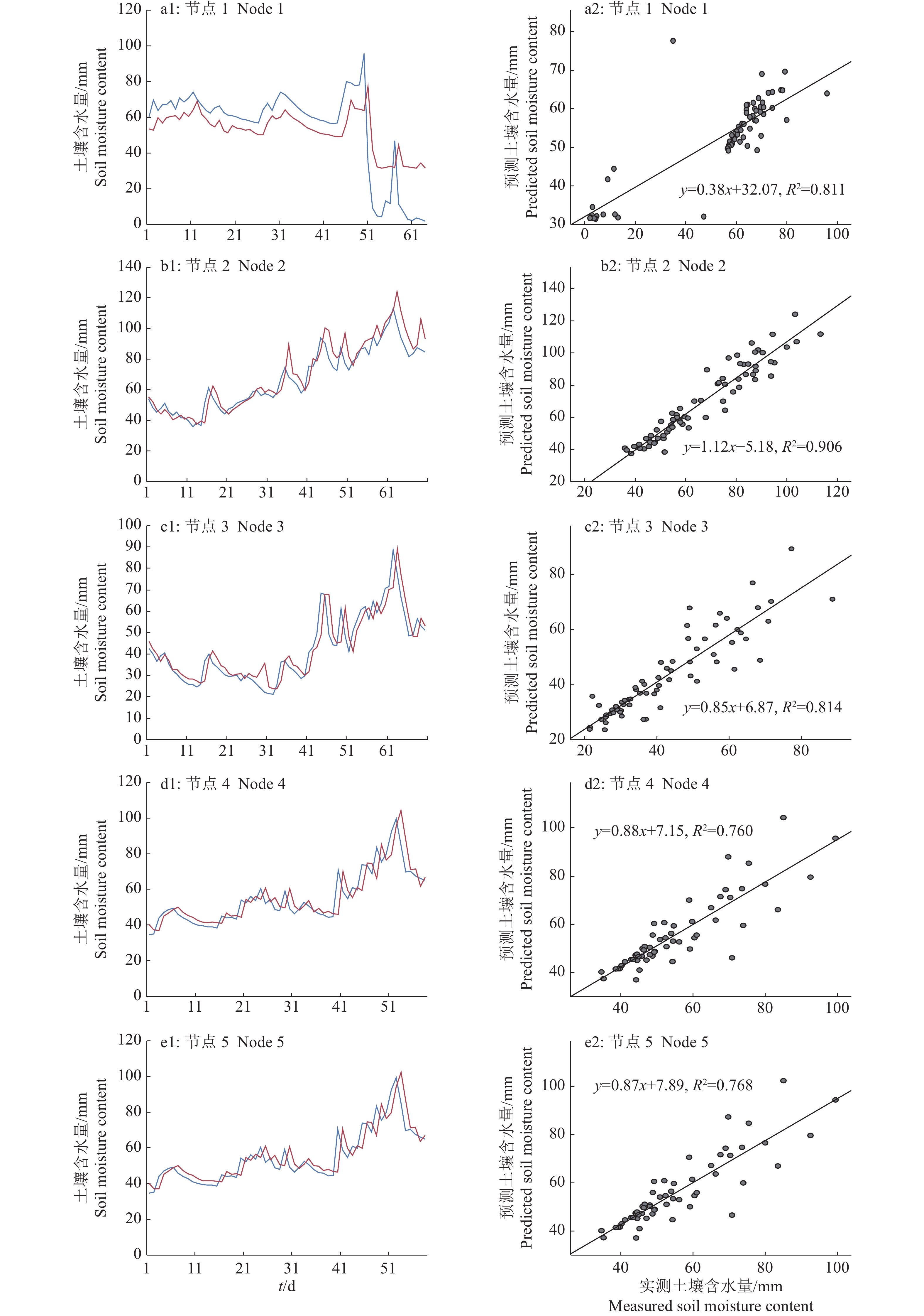
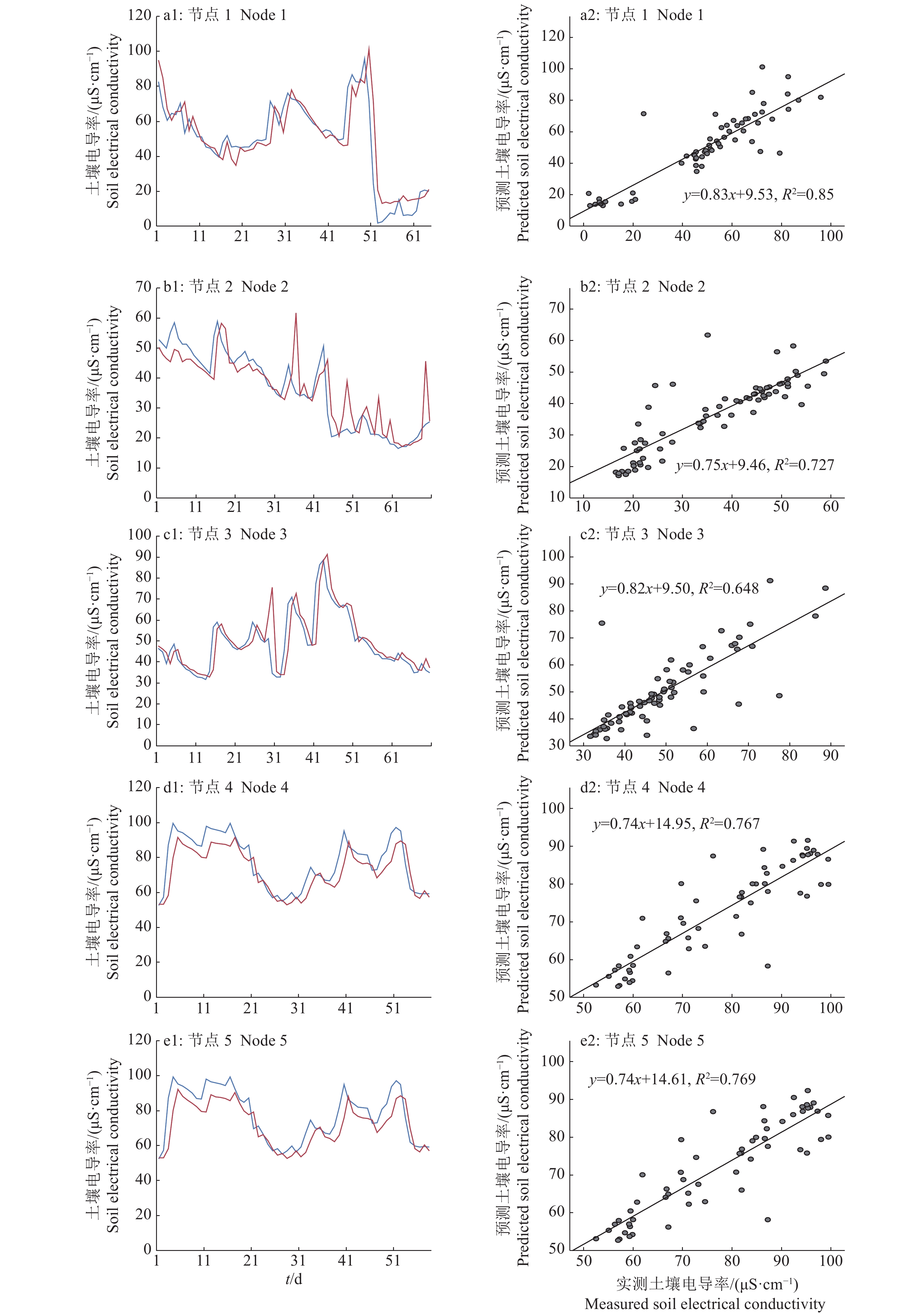
LSTM模型的预测精度较高、性能稳定,故而使用该模型观察预测效果。利用模型和气象数据得到预测值,与节点采集到的实测值进行对比,结果如图8和图9的a1~e1所示,之后利用最小二乘法进行回归拟合,其结果如图8和图9的a2~e2所示。其中,5个节点分别布置在果园5个分区中,由于果园面积较大,同时不同区域有高低落差,因此5个节点数据分别代表果园各个分区的土壤墒情。
节点1的土壤含水量(图8a1、a2)预测值相对于实测值偏小,而拟合得到的回归方程中,实测的土壤含水量数据点主要集中在56~76 mm区间,这个趋势在图8a1中的折线图中无法反映出来,这可能是由于节点1处在相对低洼的位置,加上外界环境变化如大量降雨积水或者人工灌溉导致的短时间内土壤含水量升高,在图9a1中可以观察到此时的土壤电导率在土壤含水量升高后迅速下降的现象。节点2土壤含水量(图8b1、8b2)的回归拟合决定系数高达0.906,折线图中,预测值很好地贴近了实测的土壤含水量。节点3(图8c1、8c2)的拟合效果与节点2接近,说明模型在节点2和3的数据集中能够获得较好的训练结果。节点4和5(图8d2、8e2)模型拟合的R2分别为0.760和0.768,低于0.8,根据回归方程图可以看到,主要是由于个别数据相对于其他样本偏差较大导致的。这2个节点对应模型的RMSE并不是最大的,这也再次说明了仅根据RMSE指标不能证明模型的性能高低。
从图9可以看出,节点3的土壤电导率(图9c1、9c2)数据点多集中在30~55 μS.cm−1区间,从折线图中可以看到预测值与实测值曲线比较接近,而其回归拟合R2仅为0.648,说明模型预测性能会受到数据分布的影响,较多的数据量可能会减少此种影响。虽然使用了同样的气象数据,但土壤电导率的预测模型性能总体上稍逊于土壤含水量预测模型,这可能是由于土壤电导率除了受气象因子、柑橘果树蒸散量影响外,还受到人工施肥、生物无机盐代谢等多种因素的影响,这可能是需要进一步研究的方向。
4. 结论
本文提出了利用物联网来实现远程实时获取柑橘果园土壤含水量和土壤电导率的方法,并搭建气象站获取柑橘果园气象信息,利用LSTM和GRNN模型对土壤墒情进行建模,实现对柑橘园土壤含水量与土壤电导率的预测。部分已有的对土壤墒情进行建模的研究,以BP神经网络或光谱反演方法为基础,存在着实时性不足、长时间预测精度较低的问题。本文利用物联网及相关传感器搭建远程获取果园环境数据的系统,在果园中设置5个土壤墒情采集节点和1个气象站,实现了实时采集和传输果园环境数据与气象数据的目的。
利用采集到的气象数据与节点土壤墒情数据在LSTM模型和GRNN模型上的训练结果表明:LSTM模型训练的土壤含水量和土壤电导率的RMSE范围分别为6.74~8.65和6.68~8.50,R2范围分别为0.76~0.906和0.648~0.850,相比于GRNN模型的RMSE和R2(7.01~14.70和7.60~13.70,0.126~0.369和0.132~0.268),表现出了较好的模型性能与预测效果。在LSTM模型的土壤含水量和土壤电导率拟合分析中可以发现,模型的RMSE与R2之间并没有明确的相关性,即较小的RMSE并不意味着较高的R2,因此只用RMSE来衡量模型性能可能是片面的。
LSTM模型的预测值与实测值的拟合回归方程和对应的折线图说明模型的预测效果较好,能够满足预测的需求。但是部分节点如节点3的土壤电导率拟合决定系数较低,说明数据样本分布可能会对模型效果产生影响。本文建立的LSTM预测模型在土壤电导率的预测性能方面稍逊于土壤含水量模型,这可能是由于土壤电导率受到环境中其他因素影响更多,需要更进一步地深入研究。另外,果园的土壤含水量和土壤电导率在不同的种植和生理条件下,存在一定的差异,根据生产过程中的灌溉与施肥情况,利用本文提出的方法能够为柑橘果园的灌溉和施肥提供一定的指导,也可以根据LSTM预测模型,结合未来一段时间的气象数据与当前田间土壤墒情数据,预测未来一段时间的土壤墒情数据,及时掌握土壤墒情变化趋势,方便果园管理者提前做好施肥灌溉准备工作,能够帮助实现科学精细的果园灌溉与施肥管理,带来较好的管理效益。
-
表 1 土壤含水量和电导率与环境参数的相关系数
Table 1 Correlation coefficients of soil moisture, electrical conductivity and environmental parameters
土壤因子
Soil factor空气温度 Air temperature 降雨量
Precipitation空气湿度
Air
humidity土壤温度
Soil
temperature蒸散量
Evapotranspiration最高值
Max.
最低值
Min.
平均值
Mean
含水量 Moisture content 0.490 0.598 0.644 0.123 0.430 0.652 0.158 电导率 Electrical conductivity 0.467 0.311 0.231 0.300 0.168 0.251 0.148 表 2 节点数据信息
Table 2 Datasets of nodes
节点
Node数据总数
Total number训练集
Training dataset测试集
Testing dataset1 216 151 65 2 241 168 73 3 241 168 73 4 196 137 59 5 203 142 61 气象站
Weather station241 168 73 表 3 模型性能表现
Table 3 Performance of models
节点
Node模型
Model土壤含水量
Soil moisture
content土壤电导率
Soil electrical
conductivityRMSE R2 RMSE R2 1 LSTM 8.65 0.811 6.88 0.850 GRNN 13.30 0.126 12.30 0.106 2 LSTM 7.30 0.906 6.68 0.727 GRNN 14.70 0.323 13.70 0.185 3 LSTM 6.74 0.814 8.22 0.648 GRNN 7.01 0.369 8.26 0.268 4 LSTM 7.93 0.760 8.50 0.767 GRNN 10.27 0.256 7.85 0.167 5 LSTM 8.40 0.768 7.78 0.769 GRNN 8.80 0.206 7.60 0.132 -
[1] 成家壮, 韦小燕, 范怀忠. 广东柑橘疫霉研究[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2004, 25(2): 31-33. [2] 张超博, 李有芳, 李思静, 等. 土壤管理方式对伏旱期柑橘生长及土壤温度和水分的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2019, 40(3): 45-52. [3] 肖畅, 彭婷, 刘继红. 基于WOS和CiteSpace分析我国近十年柑橘研究热点与前沿[J]. 果树学报, 2020.doi: 10.13925/j.cnki.gsxb.20200119. [4] 李莉萍. 柑橘产业化经营案例分析: 评《柑橘绿色生产与产业化经营》[J]. 中国果树, 2020(3): 151. [5] 罗省根, 双巧云, 陈团显, 等. 江西省柑橘出口现状及发展对策[J]. 中国果树, 2020(3): 138-140. [6] 赖俊桂, 孙道宗, 王卫星, 等. 基于无线传感器网络的山地柑橘园灌溉控制系统设计与试验[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2020, 48(7): 245-249. [7] 陈昱辛, 贾悦, 崔宁博, 等. 滴灌水肥一体化对柑橘叶片光合、产量及水分利用效率的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2018, 37(S2): 50-58. [8] 谢家兴, 高鹏, 莫昊凡, 等. 荔枝园智能灌溉决策系统模糊控制器设计与优化[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(8): 26-32. [9] 赖呈纯, 黄贤贵, 王琦, 等. 果实生长与果园土壤含水量的变化对‘茂谷柑’裂果的影响[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 48(4): 434-439. [10] 朱浩, 刘珂欣, 刘维维, 等. 极端耐盐碱菌株的筛选及其菌肥对盐碱条件下小麦生长和土壤环境的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(7): 2338-2344. [11] 杨伟志, 孙道宗, 刘建梅, 等. 基于物联网和人工智能的柑橘灌溉专家系统[J]. 节水灌溉, 2019(9): 116-120. [12] 李中良, 胡晨晓, 邹腾飞, 等. 基于物联网的柑橘土壤水分养分实时监测系统的设计与实现[J]. 农业网络信息, 2014(2): 21-24. [13] 罗党, 王浍婷. 灰色神经网络下的多变量土壤含水量预测模型[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 38(5): 70-75. [14] 蔡亮红, 丁建丽. 基于变量优选和ELM算法的土壤含水量预测研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(7): 2209-2214. [15] 张武, 洪汛, 李蒙, 等. 监测采样间隔对土壤墒情预测模型性能的影响[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 2020, 55(1): 221-228. [16] 何灿隆, 沈明霞, 刘龙申, 等. 基于NB-IoT的温室温度智能调控系统设计与实现[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2018, 39(2): 117-124. [17] 岳学军, 王叶夫, 刘永鑫, 等. 基于GPRS与ZigBee的果园环境监测系统[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2014, 35(4): 109-113. [18] 徐兴, 岳学军, 林涛. 基于ZigBee网络的水环境无线监测系统设计[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2013, 34(4): 593-597. [19] 余国雄, 王卫星, 谢家兴, 等. 基于物联网的荔枝园信息获取与智能灌溉专家决策系统[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(20): 144-152. [20] 姜晟, 王卫星, 孙道宗, 等. 能量自给的果园信息采集无线传感器网络节点设计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(9): 153-158. [21] 王卫星, 陈华强, 姜晟, 等. 基于低功耗的发射功率自适应水稻田WSN监测系统[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(3): 150-157. [22] ALLEN R G, PEREIRA L S, RAES D, et al. Crop evapotranspiration: Guidelines for computing crop water requirements: FAO irrigation and drainage paper 56[EB/OL]. [2020-06-30]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235704197.
[23] RALLO G, GONZÁLEZ-ALTOZANO P, MANZANO-JUÁREZ J, et al. Using field measurements and FAO-56 model to assess the eco-physiological response of citrus orchards under regulated deficit irrigation[J]. Agr Water Manag, 2017, 180: 136-147. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2016.11.011
[24] FENG Y, PENG Y, CUI N, et al. Modeling reference evapotranspiration using extreme learning machine and generalized regression neural network only with temperature data[J]. Comput Electron Agr, 2017, 136: 71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2017.01.027
[25] SPECHT D F. A general regression neural network[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Netw, 1991, 2(6): 568-576. doi: 10.1109/72.97934
[26] MAJHI B, NAIDU D, MISHRA A P, et al. Improved prediction of daily pan evaporation using Deep-LSTM model[J]. Neural Comput Appl, 2019, 4(6): 110-122.
[27] ZHANG J, ZHU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Developing a long short-term memory (LSTM) based model for predicting water table depth in agricultural areas[J]. J Hydrol, 2018, 561: 918-929. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.065
[28] CHENG H, XIE Z, WU L, et al. Data prediction model in wireless sensor networks based on bidirectional LSTM[J]. Eurasip J Wirel Comm, 2019, 2019(1): 203-212. doi: 10.1186/s13638-019-1511-4
[29] MAJHI B, NAIDU D, MISHRA A P, et al. Improved prediction of daily pan evaporation using Deep-LSTM model[J]. Neural Comput Appl, 2020, 32(12): 7823-7838.
[30] REDDY D S, PRASAD P R C. Prediction of vegetation dynamics using NDVI time series data and LSTM[J]. Model Earth Syst, 2018, 4(1): 409-419. doi: 10.1007/s40808-018-0431-3
[31] NASH J E, SUTCLIFFE J V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I: A discussion of principles[J]. J Hydrol, 1970, 10(3): 282-290. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 吴超,周紫静,黄锦铧,许啸寅,邱洪,彭业萍. 基于长短时记忆的农作物生长环境数据预测. 深圳大学学报(理工版). 2024(05): 563-573 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 谢妍,贾志军,王二英,贾永国,张旭东. 基于IPSO-BiLSTM和SVM的灌区农田土壤含水率预测研究. 节水灌溉. 2024(12): 63-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘嘉豪,刘浩. 基于LSTM神经网络模型的石油单井产量预测. 石油化工应用. 2023(03): 38-41+52 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王登亮,马创举,曹锦萍,吴雪珍,吴群,刘丽丽,陈骏,孙建城. 柑桔生产数字技术研究及应用进展. 中国南方果树. 2023(03): 228-235 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘丽贞,黄琪,迟殿委,方朝阳,楚明航. 基于随机森林回归模型和高频数据的鄱阳湖子湖电导率预测. 水电能源科学. 2023(10): 50-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 代秋芳,熊诗路,李震,宋淑然,陈梓蔚,王元. 基于LSTM的柑橘幼苗蒸发量预测. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 743-747 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 彭旭,饶元,乔焰. 基于宽度卷积神经网络的异常农情数据检测方法. 华南农业大学学报. 2022(02): 113-121 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 高鹏,杨明欣,周平,孙道宗,谢家兴,陆健强,王卫星. 基于物联网和Deep-LSTM的茶树净光合速率动态预测模型. 农业工程学报. 2022(04): 159-168 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王武,杨海建,洪林,杨蕾,王敏,李霜. 柑橘需水规律研究进展及趋势展望. 南方农业. 2022(19): 141-147+152 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: