Remote diagnosis system of banana diseases based on deep learning
-
摘要:目的
实现香蕉病害的远程诊断。
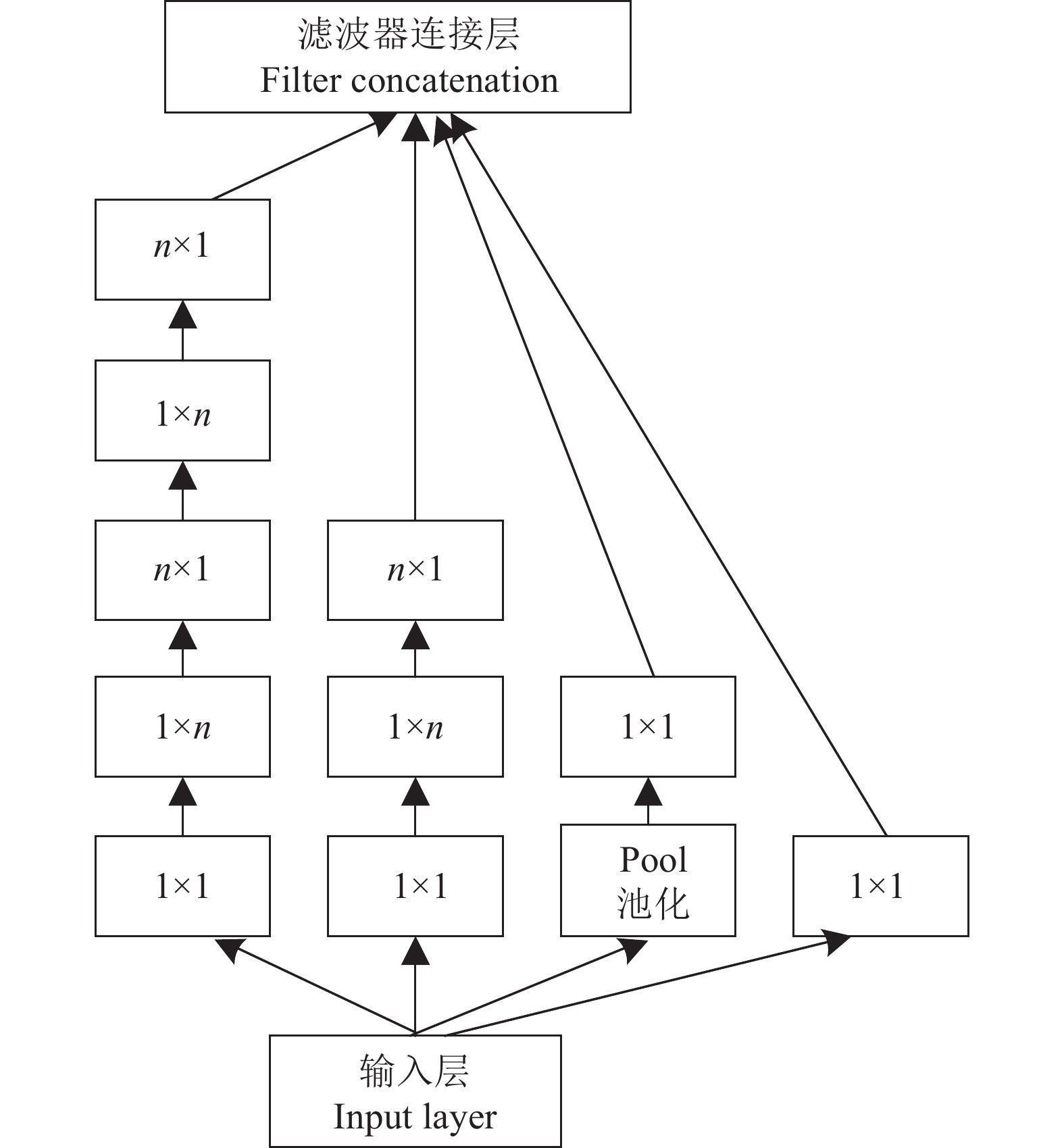
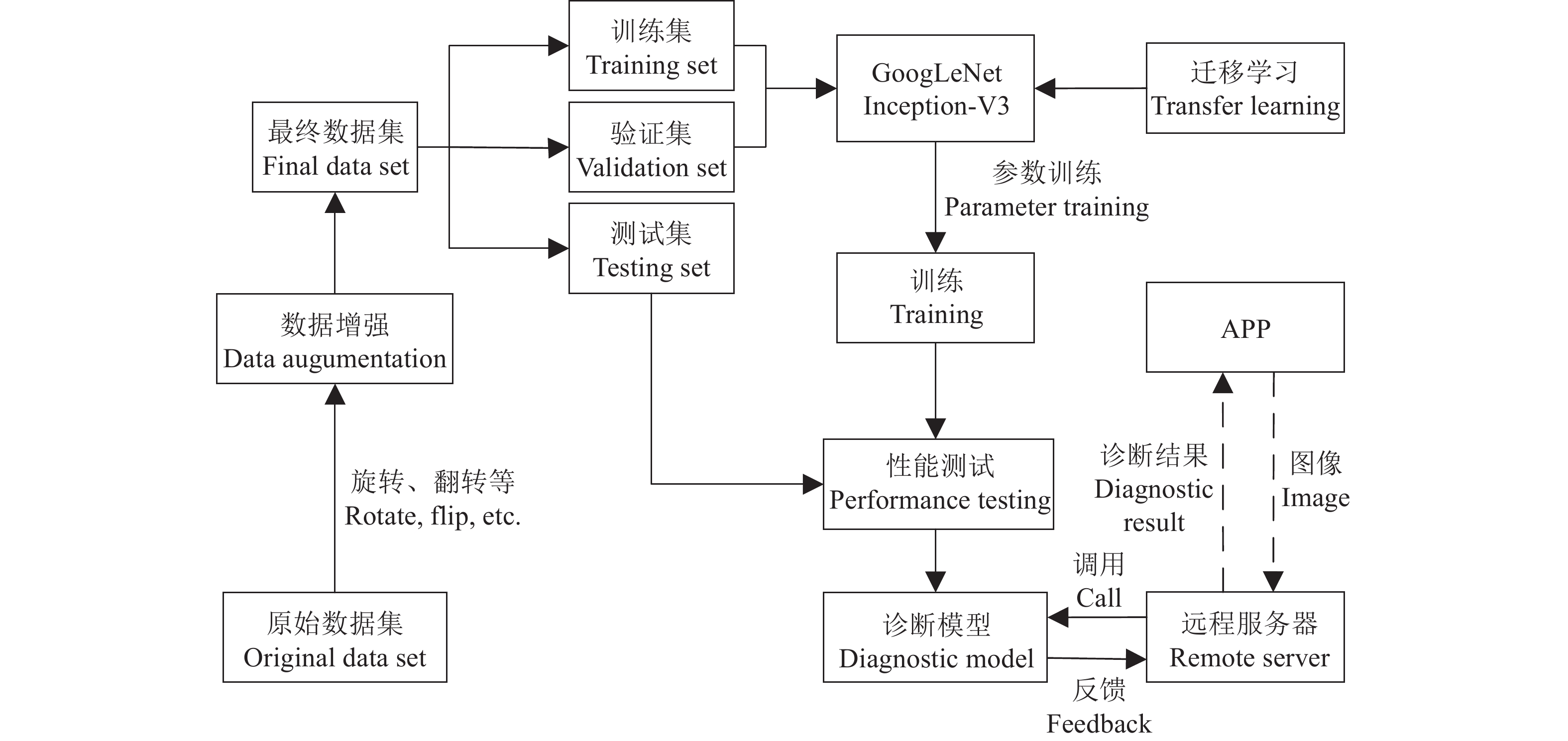
方法基于深度学习方法对香蕉作物的7种常见病害进行诊断。收集了5944幅健康及染病香蕉植株图像,按7∶1∶2分为训练集、验证集和测试集。利用迁移学习对GoogLeNet深度卷积神经网络训练获取诊断模型。进一步开发了包含手机移动应用程序(APP)和远程服务器的软件系统。
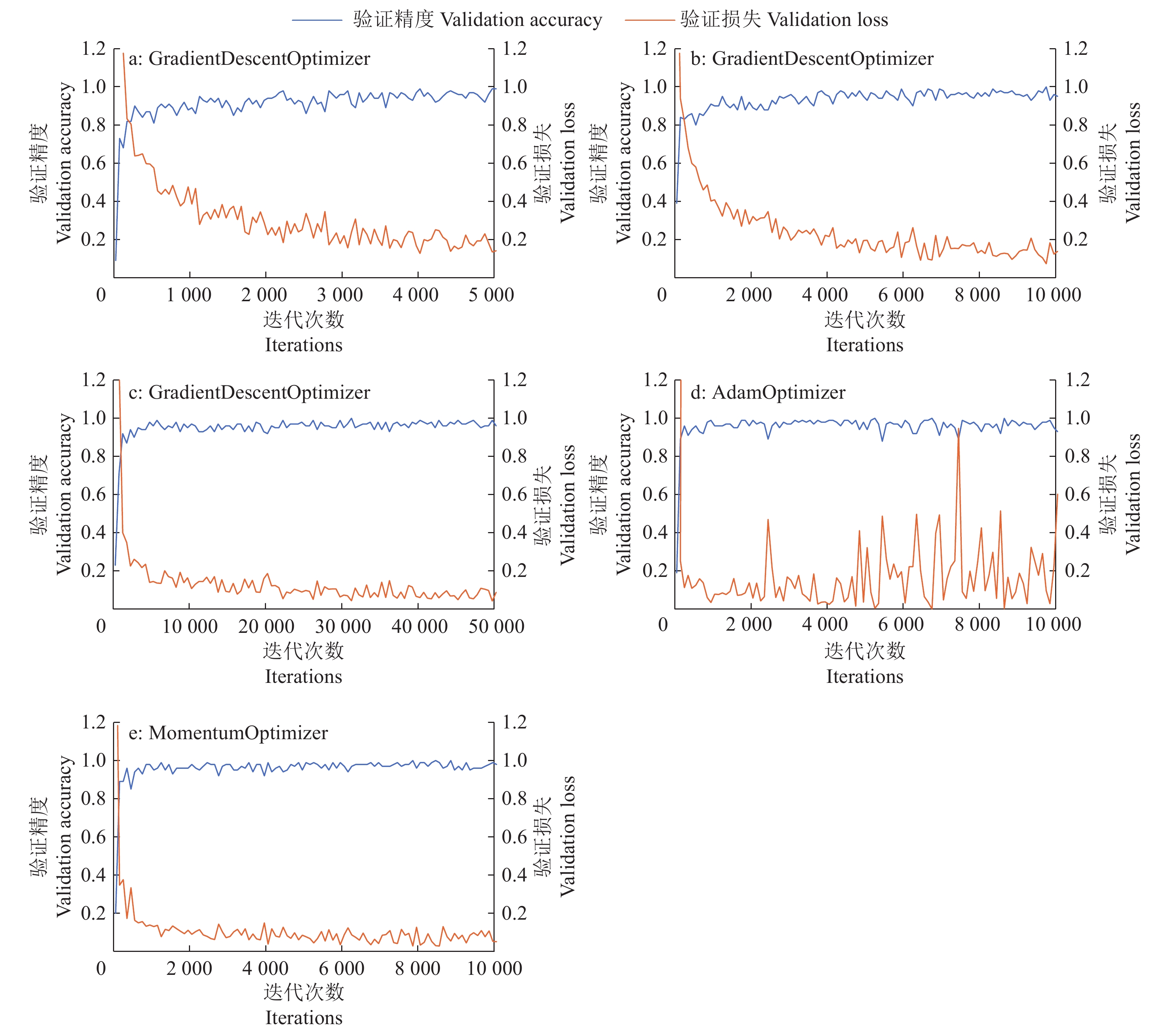
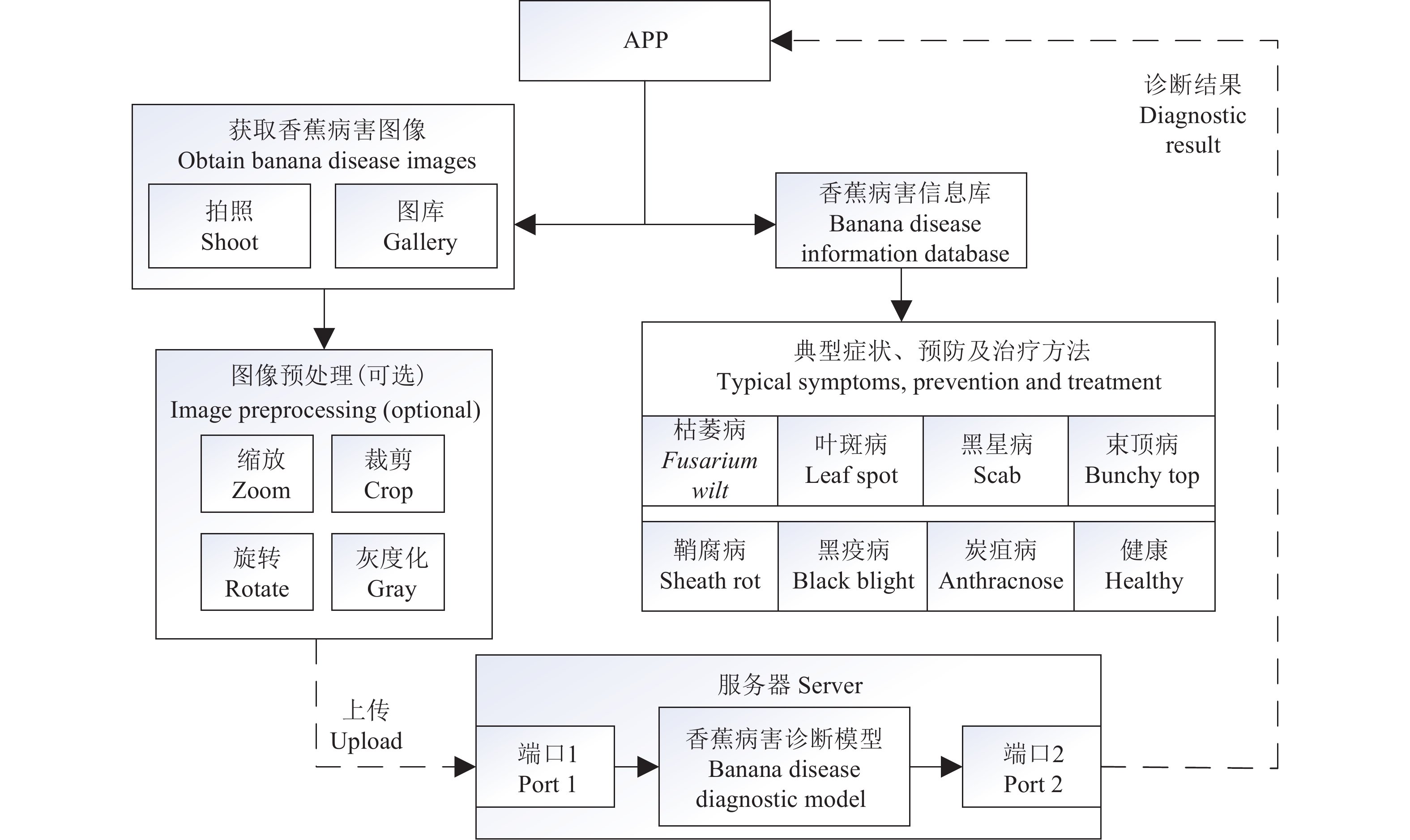
结果通过对比不同迭代次数及不同优化器,最终采用了MomentumOptimizer迭代10000次的模型,平均测试精度达到了98%。设计的APP能够就地获取香蕉图像,并通过网络与集成了诊断模型的远程服务器通信,实时获取诊断结果。
结论该病害诊断模型识别主要病害的精度高,在线诊断系统简单易操作,可快速有效地在线诊断香蕉常见病害,具有良好的应用前景。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo realize remote diagnosis of banana diseases.
MethodDeep learning method was used to diagnose seven common diseases of banana plant. A total of 5 944 images of diseased and healthy banana plants were collected and divided into training set, validation set and testing set according to the ratio of 7∶1∶2. Transfer learning was used to train GoogLeNet which is a deep convolutional neural network for obtaining the diagnosis model. A software system including a mobile application (APP) and a remote server was further developed.
ResultBy comparing different iteration times and optimizers, the model of MomentumOptimizer with 10000 iteration times was finally selected, and the average test accuracy was 98%. The designed mobile APP could acquire banana images in situ, and communicate with the remote server which was integrated with a diagnosis model via the network to obtain diagnosis results in real time.
ConclusionThe disease diagnosis model can identify the main diseases with high accuracy. The online diagnosis system is simple and easy to operate, it can diagnose common banana diseases online quickly and effectively, and therefore it has a wide application prospect.
-
Keywords:
- banana disease /
- deep learning /
- GoogLeNet /
- image recognition /
- mobile application /
- transfer learning
-
-
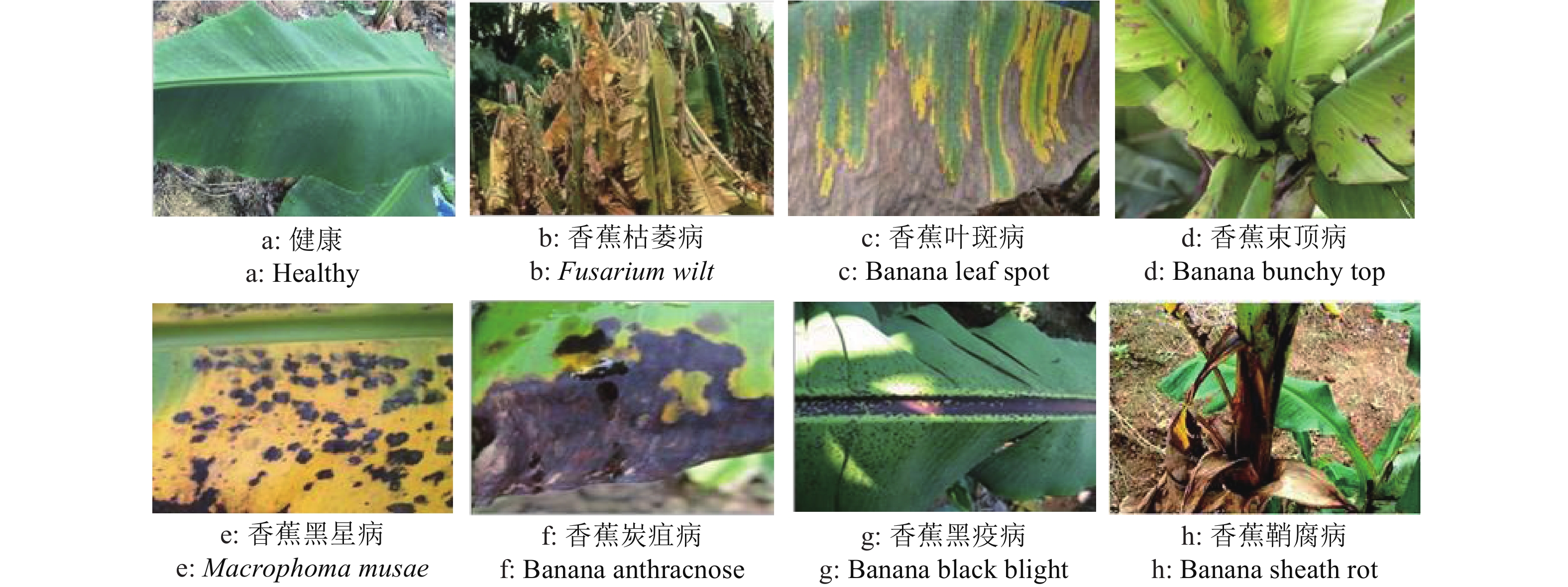
表 1 各类别样本图像数量
Table 1 Number of sample images in each category
幅 植株类别
Category原始图像
Original
image数据增强
Data
augmentation健康 Healthy 130 1048 香蕉枯萎病 Fusarium wilt 217 1736 香蕉叶斑病 Banana leaf spot 170 1360 香蕉束顶病 Banana bunchy top 44 352 香蕉黑星病 Macrophoma musae 86 696 香蕉炭疽病 Banana anthracnose 38 304 香蕉黑疫病 Banana black blight 32 256 香蕉鞘腐病 Banana sheath rot 24 192 总计 Total 741 5944 表 2 模型的训练时间和平均测试精度
Table 2 Model training time and average test accuracy
迭代次数
Iteration优化器
Optimizer训练时间/min
Training time平均测试精度/%
Average test accuracy5000 GradientDescentOptimizer 11 94.5 10000 GradientDescentOptimizer 22 96.0 50000 GradientDescentOptimizer 110 98.0 10000 MomentumOptimizer 23 98.0 10000 AdamOptimizer 21 97.8 表 3 模型测试的混淆矩阵
Table 3 Confusion matrix of model testing result
类别
Category健康
Healthy香蕉枯萎病
Fusarium
wilt香蕉叶斑病
Banana
leaf spot香蕉束顶病
Banana
bunchy top香蕉黑星病
Macrophoma
musae香蕉炭疽病
Banana
anthracnose香蕉黑疫病
Banana
black blight香蕉鞘腐病
Banana
sheath rot总计
Total健康
Healthy210 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 211 香蕉枯萎病
Fusarium wilt0 345 0 1 0 0 0 2 348 香蕉叶斑病
Banana leaf spot0 0 263 0 3 1 0 0 267 香蕉束顶病
Banana bunchy top0 1 0 73 0 0 0 0 74 香蕉黑星病
Macrophoma musae0 0 7 0 134 1 0 0 142 香蕉炭疽病
Banana anthracnose0 0 2 0 0 59 2 0 63 香蕉黑疫病
Banana black blight0 0 0 0 2 0 49 0 51 香蕉鞘腐病
Banana sheath rot0 1 0 0 0 0 0 37 38 总计Total 210 347 272 75 139 61 51 39 1194 表 4 模型测试精度
Table 4 Model testing accuracy
类别
Category生产者精度/%
Producer’s accuracy用户精度/%
User’s accuracy健康
Healthy100 99.5 香蕉枯萎病
Fusarium wilt99.4 99.1 香蕉叶斑病
Banana leaf spot96.7 98.5 香蕉束顶病
Banana bunchy top97.3 98.6 香蕉黑星病
Macrophoma musae96.4 94.5 香蕉炭疽病
Banana anthracnose96.7 93.7 香蕉黑疫病
Banana black blight96.1 96.1 香蕉鞘腐病
Banana sheath rot94.9 97.4 总体分类精度/%
Overall accuracy98.0 -
[1] MARTINELLI F, SCALENGHE R, DAVINO S, et al. Advanced methods of plant disease detection: A review[J]. Agron Sustain Dev, 2015, 35(1): 1-25. doi: 10.1007/s13593-014-0246-1
[2] 黄文江, 师越, 董莹莹, 等. 作物病虫害遥感监测研究进展与展望[J]. 智慧农业, 2019, 1(4): 1-11. [3] ALVAREZ A M. Integrated approaches for detection of plant pathogenic bacteria and diagnosis of bacterial diseases[J]. Annu Rev Phytopathol, 2004, 42(8): 339-366.
[4] 李翠玲, 姜凯, 马伟, 等. 基于高光谱的番茄叶片斑潜蝇虫害检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(1): 253-257. [5] POLDER G, BLOK P M, VILLIERS H A C, et al. Potato virus Y detection in seed potatoes using deep learning on hyperspectral images[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2019, 10(1): 1-13.
[6] 杨晨, 董丽芳, 赵海士, 等. 基于模糊判别成分分析法的高光谱作物信息提取与分类[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(21): 158-165. [7] AKHTAR A, KHANUM A, KHAN S A, et al. Automated plant disease analysis (APDA): Performance comparison of machine learning techniques[C]//IEEE. International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology. New York: IEEE, 2013: 60-65.
[8] SANNAKKI S S, RAJPUROHIT V S, NARGUND V B, et al. Diagnosis and classification of grape leaf diseases using neural networks[C]//IEEE. Fourth International Conference on Computing, Communications and Networking Technologies. New York: IEEE, 2014: 13-18.
[9] MOKHTAR U, EL-BENDARY N, HASSANEIN A E, et al. SVM-based detection of tomato leaves diseases[C]// Springer, Cham. Intelligent Systems 2014. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2015: 641-652.
[10] MIZUNO K, TERACHI Y. Architectural study of HOG feature extraction processor for real-time object detection[C]//IEEE. IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing, New York: IEEE, 2012: 197-202.
[11] KOBAYASHI T. BoF meets HOG: Feature extraction based on histograms of oriented p. d. f. gradients for image classification[C]//IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2013: 747-754.
[12] PUN C M, LEE M C. Extraction of shift invariant wavelet features for classification of images with different sizes[J]. IEEE T Pattern Anal, 2004, 26(9): 1228-1233. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.67
[13] ANDREAS K, PRENAFETA-BOLDÚ F X. Deep learning in agriculture: A survey[J]. Comput Electron Agr, 2018, 147(1): 70-90.
[14] ALVARO F, SOOK Y, KIM S C, et al. A robust deep-learning-based detector for real-time tomato plant diseases and pests recognition[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(9): 2022-2043. doi: 10.3390/s17092022
[15] ZHANG X H, QIAO Y, MENG F F, et al. Identification of maize leaf diseases using improved deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 370-377.
[16] 陈桂芬, 赵姗, 曹丽英, 等. 基于迁移学习与卷积神经网络的玉米植株病害识别[J]. 智慧农业, 2019, 1(2): 34-44. [17] RONNEL R, PARK D. A multiclass deep convolutional neural network classifier for detection of common rice plant anomalies[J]. J Netw Comput Appl, 2018, 9: 67-70.
[18] RAMCHARAN A, BARANOWSKI K, MCCLOSKEY P, et al. Deep learning for image-based cassava disease detection[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2017, 8: 1852-1859. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01852
[19] MWEBAZE E, OWOMUGISHA G. Machine learning for plant disease incidence and severity measurements from leaf images[C]//IEEE. International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. New York: IEEE, 2017: 158-163.
[20] FERENTINOS K P. Deep learning models for plant disease detection and diagnosis[J]. Comput Electron Agr, 2018, 145: 311-318. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2018.01.009
[21] 吴华瑞. 基于深度残差网络的番茄叶片病害识别方法[J]. 智慧农业, 2019, 1(4): 42-49. [22] SRDJAN S, MARKO A, ANDERLA A, et al. Deep neural networks based recognition of plant diseases by leaf image classification[J]. Comput Intel Neurosc, 2016, 2016: 1-11.
[23] SI M M, DENG M H, HAN Y. Using deep learning for soybean pest and disease classification in farmland[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University (English Edition), 2019, 26(1): 64-72.
[24] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y Q, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//IEEE. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-9.
-
期刊类型引用(18)
1. 崔紫宁,陈建平,梁丽梅. “交叉融合”:“微生物天然产物化学”的跨界教育模式. 工业微生物. 2024(01): 194-196 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邓杰,尚楠. 芽孢杆菌群体感应系统研究进展. 生物加工过程. 2024(05): 492-499 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 乔真,李佳霖,秦松. C6-HSL信号及群体淬灭对海洋聚球藻(Synechococcus)菌藻共栖体系的调控作用. 海洋科学. 2024(09): 52-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李凤兰,吴天祥,邓代霞,袁丹丹,江守发. 太子参乙醇提取物对灰树花菌体生长及胞外多糖的影响机理初步研究. 食品与发酵科技. 2023(02): 28-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 欧凯玉,逄建龙,张一敏,董鹏程,罗欣,毛衍伟. 天然酚类化合物的抑菌作用及在肉与肉制品中的应用研究进展. 食品科学. 2023(09): 358-366 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 高鑫,李博. 水产腐败群体感应系统与天然抑菌剂的研究进展. 保鲜与加工. 2023(06): 73-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 郑爱娟,陈星,张广民,王泽栋,陈志敏,常文环,蔡辉益,刘国华. N-酰基高丝氨酸内酯酶对肉仔鸡生长性能、屠宰性能和养分表观代谢率的影响. 动物营养学报. 2023(06): 3607-3616 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 熊儒恒,阎俊,谢晶. 生物被膜初始黏附调控机制及其在食品品质控制中的应用研究进展. 食品科学. 2023(13): 203-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 杨约萍,高倩倩,宁静,宫佳,胡媛媛,施祖荣. 细菌群体通讯信号及其淬灭研究进展. 仲恺农业工程学院学报. 2022(01): 65-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 廖才江,李会,王士源,熊静,梅翠,刘丹,何玉张,彭练慈,宋振辉,陈红伟. 生物被膜:益生菌肠道定植的新策略. 生物工程学报. 2022(08): 2821-2839 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 乔真 ,李佳霖 ,秦松 . 海洋藻际环境中细菌群体感应研究进展. 生物学杂志. 2022(05): 93-97+107 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 王亚军,司运美,李彦娟. 群体感应在生物强化功能菌定殖及降解能力增强中的作用研究进展. 应用生态学报. 2022(10): 2871-2880 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李艳群,陈柔雯,林宗豪,田新朋,尹浩. 一株群体感应抑制活性海洋放线菌的筛选与鉴定. 热带海洋学报. 2021(01): 75-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 杨艳北,许晶,沈城辉,许继国,饶友生. N-酰基高丝氨酸内酯酶的生物信息学分析. 甘肃农业科技. 2021(02): 31-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 杨艳北,许晶,李袁飞,贡继尚,饶友生. 沼泽红假单胞菌LuxR家族调控蛋白的生物信息学分析. 江苏农业科学. 2021(06): 40-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 郑钰婷,胡宇如,胡方平,蔡学清. 利用aiiA基因筛选抗烟草青枯病生防菌株及其鉴定. 核农学报. 2021(06): 1322-1328 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 宋凯,周莲,何亚文. DSF-家族群体感应信号生物合成途径与调控机制研究进展. 微生物学通报. 2021(04): 1239-1248 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 赵祯,肖翎,戚建华,刘韵怡,王年,郁小娟,宋增福. 群体感应淬灭酶YtnP对草鱼肠道菌群结构的影响. 南方农业学报. 2020(11): 2817-2826 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(13)



 下载:
下载: