Isolation and genetic characteristics of epidemic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 6 (EHDV-6) strains from Yunnan and Guangdong Provinces
-
摘要:目的
分离流行于我国南方地区的流行性出血病病毒血清6型毒株(EHDV-6),掌握分离毒株的遗传特征。
方法对设立于我国云南和广东省的哨兵动物定期采血,进行EHDV感染情况监测与病毒分离培养。通过血清中和试验确定分离EHDV的血清型,采用一步法RT-PCR对分离的EHDV-6毒株基因节段2、3、6(Seg-2、-3、-6)进行扩增与序列分析。
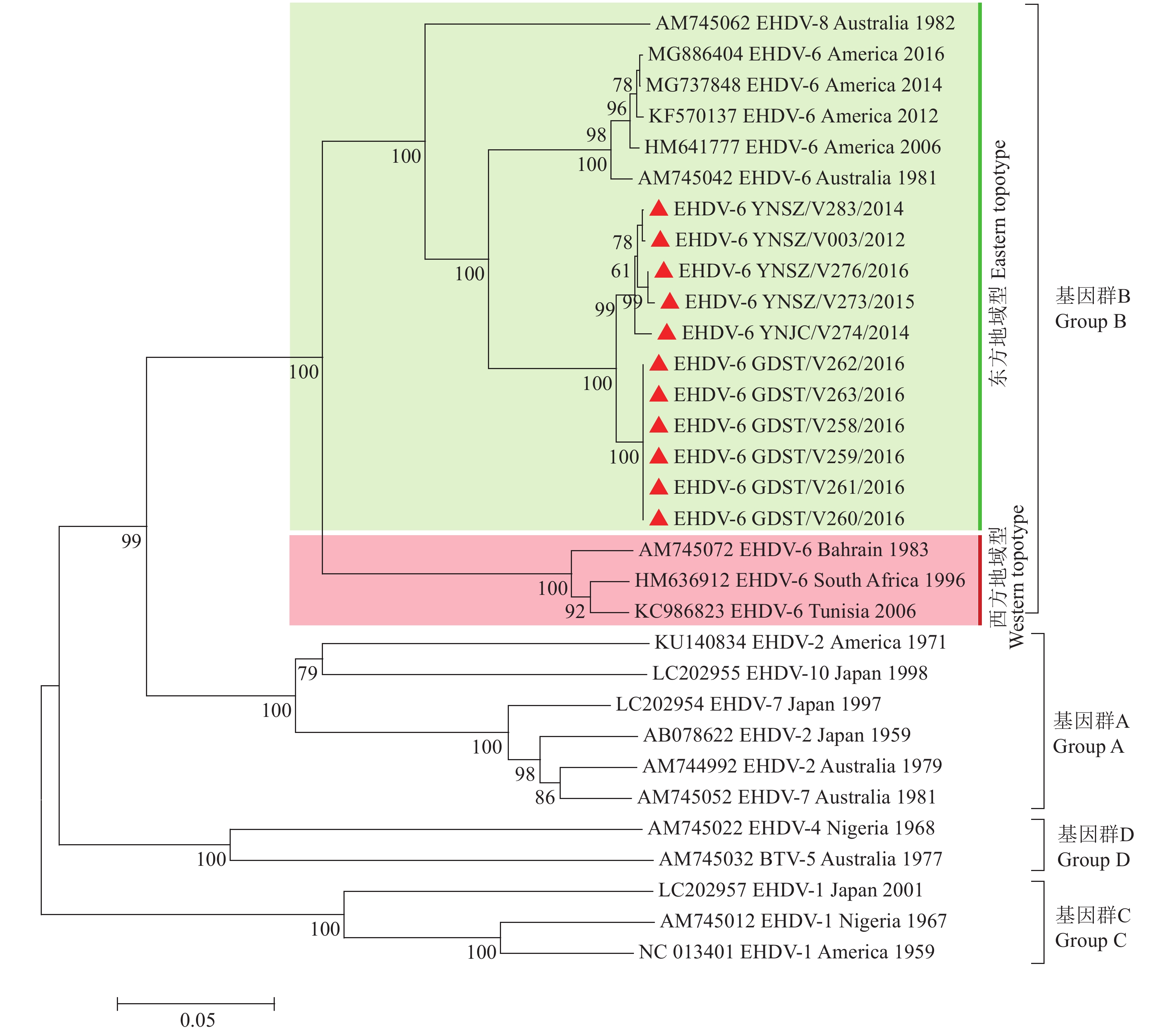
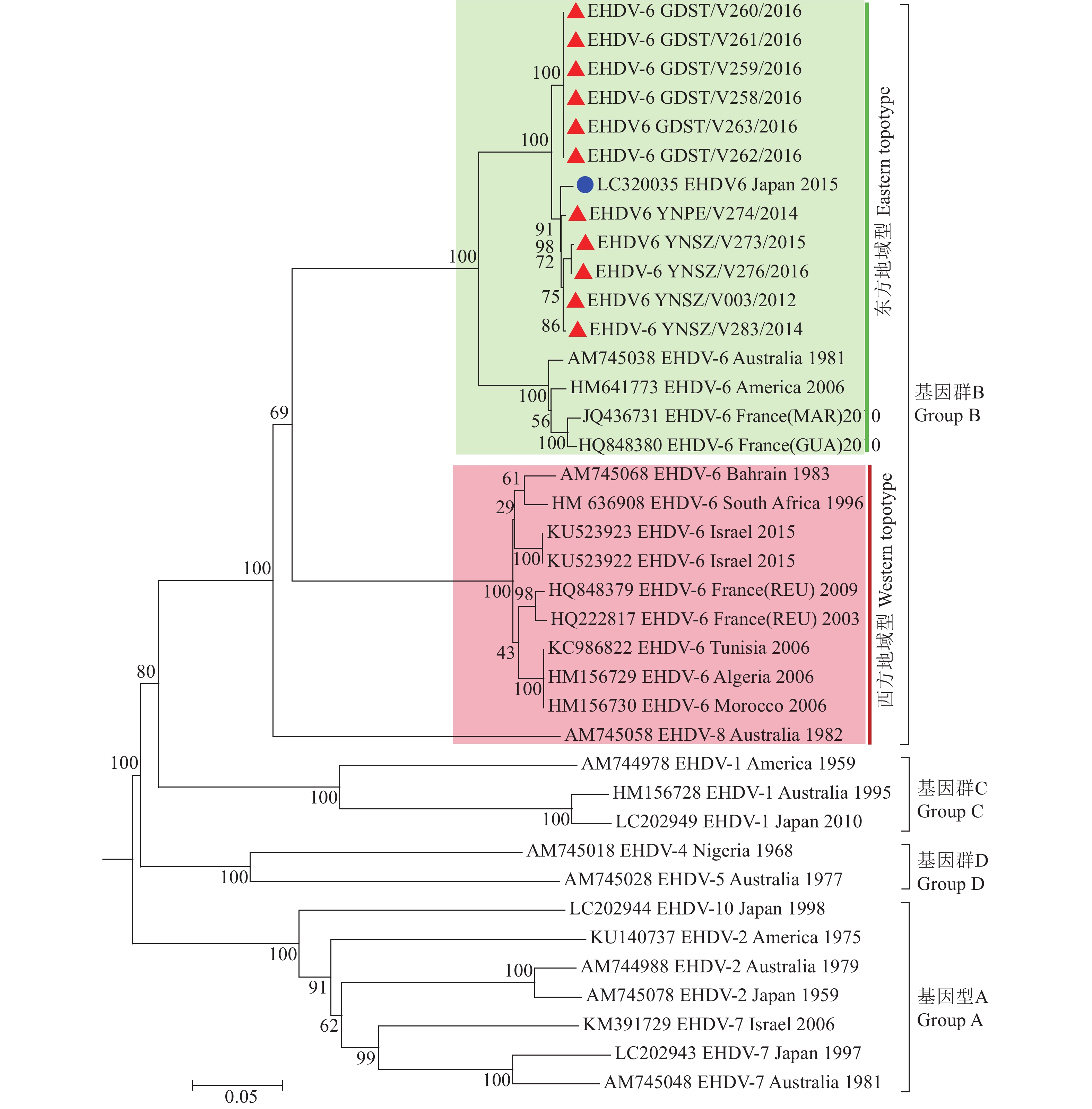
结果2012—2016年,从云南省和广东省的哨兵动物中分离出25株EHDV毒株,其中,11株为EHDV-6型。中国EHDV-6型毒株的Seg-2、-3与-6均属Eastern型,核酸序列相似性分别为99.1%、98.9%和98.8%,在系统发生树上分别聚为1个独立的中国支系。在日本引起疫病暴发的EHDV-6型毒株与中国EHDV-6型毒株具有最近的亲缘关系。日本EHDV-6型毒株在系统发生树上处于中国支系内部,Seg-2、Seg-3与中国毒株的核酸序列相似性分别为98.5%和93.9%。
结论云南和广东省流行的EHDV-6型毒株核酸与氨基酸序列高度相似;日本和中国的EHDV-6型毒株具有最近的亲缘关系,提示中日之间可能存在EHDV的流动。研究结果为进一步开展我国EHDV-6型毒株流行病学分析、致病性、病原学诊断与疫苗制备等研究提供了基础。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo isolate epidemic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 6 (EHDV-6) strains prevalent in southern China, and investigate the genetic characteristics of the isolated strains.
MethodBlood samples were collected from sentinel animals in Yunnan and Guangdong Provinces in China. EHDV infection was monitored and the virus was isolated. The serum types of isolated strains were determined by serum neutralization test, and segments 2, 3 and 6 (Seg-2, -3 and -6) of EHDV-6 isolated strains were amplified by one-step RT-PCR and subsequently sequenced.
ResultFrom 2012 to 2016, 25 EHDV strains were isolated from sentinel animals in Yunnan and Guangdong Provinces and 11 strains of them were EHDV-6. Seg-2, -3 and -6 of Chinese EHDV-6 strains were of Eastern topotype, and the nucleic acid sequence similarities were 99.1%, 98.9% and 98.8% respectively, which were clustered into an independent Chinese branch on the phylogenetic tree. Chinese EHDV-6 strains had the closest relationship with the EHDV-6 strains which caused epidemic outbreaks in Japan. The Japanese EHDV-6 strain was within the Chinese branch on the phylogenetic tree. The similarities of nucleic acid sequences of Seg-2 and Seg-3 between the Japanese and Chinese strains were 98.5% and 93.9% respectively.
ConclusionThe sequences of EHDV-6 strains prevalent from Yunnan and Guangdong Provinces are highly similar. The closest genetic relationship between Japanese and Chinese EHDV-6 strains suggests that there may be flow of EHDV between China and Japan. The results provide a basis for further research on epidemiological analysis, pathogenicity, etiological diagnosis and vaccine preparation of EHDV-6 strains in China.
-
-
图 1 邻近法构建的EHDV-6型毒株Seg-2系统发生树
“▲”表示本研究获取的中国EHDV-6型毒株序列,“●”表示与中国EHDV-6型毒株具有最近亲缘关系的日本毒株序列
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of Seg-2 of EHDV-6 strain contructed by Neighbor-joining method
“▲” indicated sequence of Chinese EHDV-6 strain isolated in this study, “●” indicated sequence of Japanese strain that had the closest relationship with Chinese EHDV-6 strain
图 3 邻近法构建的EHDV-6型毒株Seg-3系统发生树
“▲”表示本研究获取的中国EHDV-6型毒株序列,“●”表示与中国EHDV-6型毒株具有最近亲缘关系的日本毒株序列
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree of Seg-3 of EHDV-6 strain constructed by Neighbor-joining method
“▲” indicated sequence of Chinese EHDV-6 strain isolated in this study, “●” indicated sequence of Japanese strain that had the closest relationship with Chinese EHDV-6 strain
表 1 中国EHDV-6型分离毒株Seg-2、Seg-3与Seg-6节段扩增引物
Table 1 Primers for amplifying Seg-2, Seg-3 and Seg-6 of EHDV-6 isolates in China
引物名称
Prime name引物序列(5′→3′)
Primer sequence引物位置
Primer location产物大小/bp
Product sizeEHDV-6-S2-F AGTTGCCCAAGAGTATGTGA Seg-2 (1 247~1 266 bp) 913 EHDV-6-S2-R CATCATTCTGTAAAGATAGGTCG Seg-2 (2 139~2 161 bp) EHDV-6-S3-F CAAAARATAATYGATGGRGTGAAAG Seg-3 (204~228 bp) 1 095 EHDV-6-S3-R GGYGCTGGTTCTCTATTTTCAA Seg-3 (1 276~1 299 bp) EHDV-6-S6-F CRGGTGAATCYTACGGTGAA Seg-6 (210~230 bp) 1 149 EHDV-6-S6-R CGCCYTCTTGTTGAAYCGCTAT Seg-6 (1 315~1 337 bp) 表 2 中国EHDV-6型毒株分离信息表
Table 2 Information of EHDV-6 strains isolated in China
毒株
Strain来源动物
Animal source分离年份
Isolation year分离地点
Isolation place经度
Longitude纬度
Latitude海拔/m
AltitudeYNSZ/V003/2012 黄牛 Cattle 2012 云南师宗 Shizong, Yunnan E104°17′ N24°36′ 940 YNSZ/V003/2012 黄牛 Cattle 2012 云南师宗 Shizong, Yunnan E104°17′ N24°36′ 940 YNSZ/V283/2013 黄牛 Cattle 2013 云南师宗 Shizong, Yunnan E104°17′ N24°36′ 940 YNJC/V274/2014 黄牛 Cattle 2014 云南江城 Jiangcheng, Yunnan E101°51′ N22°35′ 1 129 YNSZ/V273/2015 黄牛 Cattle 2015 云南师宗 Shizong, Yunnan E104°17′ N24°36′ 940 GDST/V263/2016 奶牛 Dairy cattle 2016 广东汕头 Shantou, Guangdong E116°40′ N23°21′ 5 GDST/V258/2016 奶牛 Dairy cattle 2016 广东汕头 Shantou, Guangdong E116°40′ N23°21′ 5 GDST/V259/2016 奶牛 Dairy cattle 2016 广东汕头 Shantou, Guangdong E116°40′ N23°21′ 5 GDST/V260/2016 奶牛 Dairy cattle 2016 广东汕头 Shantou, Guangdong E116°40′ N23°21′ 5 GDST/V261/2016 奶牛 Dairy cattle 2016 广东汕头 Shantou, Guangdong E116°40′ N23°21′ 5 YNSZ/V276/2016 黄牛 Cattle 2016 云南师宗 Shizong, Yunnan E104°17′ N24°36′ 940 表 3 世界范围内EHDV-6型毒株Seg-2/VP2、Seg-3/VP3和Seg-6/VP5核酸与氨基酸序列相似性1)
Table 3 Nucleic acid and amino acid sequence similarities among Seg-2/VP2, Seg-3/VP3 and Seg-6/VP5 of EHDV-6 strains around the world
% 国家/地域 Country/Region Seg-2 VP2 Seg-6 VP5 Seg-3 VP3 中国 China 99.1±0.7 99.1±0.7 98.8±0.9 99.9±0.2 98.9±0.7 99.9±0.1 日本 Japan 98.5±0.4 98.9±0.4 — — 93.9±2.9 99.6±0.3 澳大利亚 Australia 90.5±0.3 93.9±0.2 90.5±0.2 98.1±0.2 92.5±1.4 99.8±0.3 美国 America 90.0±0.4 93.3±0.3 90.1±0.1 98.5±0.1 80.2±0.3 96.9±0.3 非洲 Africa 71.0±0.2 73.6±0.5 79.8±0.1 96.3±0.2 80.0±0.3 97.2±0.2 中东 Middle East 71.0±0.1 73.1±0.1 79.7±0.1 96.3±0.2 79.4±0.4 97.0±0.2 1)“—”表示缺乏相应的毒株序列信息
1) “—” indicated no corresponding sequence information of strain -
[1] SAVINI G, AFONSO A, MELLOR P, et al. Epizootic heamorragic disease[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2011, 91(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2011.05.004
[2] YADIN H, BRENNER J, BUMBROV V, et al. Epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus type 7 infection in cattle in Israel[J]. Vet Rec, 2008, 162(2): 53-56. doi: 10.1136/vr.162.2.53
[3] TEMIZEL E M, YESILBAG K, BATTEN C, et al. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease in cattle, western Turkey[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2009, 15(2): 317-319. doi: 10.3201/eid1502.080572
[4] CORBEL M J, MACMILLAN A P. Office International des Epizooties OIE Manual of standards for diagnostic tests and vaccines[M]. Paris: Office International des Epizooties O.I.E, 2008: 1092-1106.
[5] MERTENS P P C, MAAN S, SAMUEL A, et al. Orbiviruses, Reoviridae[M]. FAUQUET C M, MAYO M A, MANILOFF J, et al. Virus taxonomy: Eighth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. London: Elsevier academic press, 2005: 466-483.
[6] ANTHONY S J, MAAN S, MAAN N, et al. Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of the outer-coat proteins VP2 and VP5 of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV): Comparison of genetic and serological data to characterise the ehdv serogroup[J]. Virus Res, 2009, 145(2): 200-210. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.07.012
[7] HUISMANS H, BREMER C W, BARBER T L. The nucleic acid and proteins of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus[J]. Onderstepoort J Vet Res, 1979, 46(2): 95-104.
[8] ANTHONY S J, MAAN N, MAAN S, et al. Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of the core proteins VP1, VP3, VP4, VP6 and VP7 of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV)[J]. Virus Res, 2009, 145(2): 187-199. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.07.011
[9] SHIRAFUJI H, KATO T, YAMAKAWA M, et al. Characterization of genome segments 2, 3 and 6 of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus strains isolated in Japan in 1985-2013: Identification of their serotypes and geographical genetic types[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2017, 53: 38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.05.010
[10] 李占鸿, 肖雷, 杨振兴, 等. 牛源流行性出血病病毒(EHDV)血清10型毒株在我国的分离鉴定[J]. 病毒学报, 2019, 35(1): 112-120. [11] YUKA K, MASAHIRO K, YASUYUKI O, et al. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 6 infection in cattle, Japan, 2015[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2018, 24(5): 902-905. doi: 10.3201/eid2405.171859
[12] 曹颖颖, 吴健敏, 林俊, 等. 广西首例牛源鹿流行性出血热病毒的分离鉴定[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2015, 37(10): 746-750. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0589.2015.10.04 [13] 张怡轩, 林俊, 曹颖颖, 等. 广西鹿流行性出血热病毒血清型调查及分布影响分析[J]. 上海畜牧兽医通讯, 2016(4): 19-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7725.2016.04.006 [14] 张胜男, 李华春, 朱建波, 等. 2015年内蒙古地区蓝舌病及流行性出血热流行病学调查及血清型鉴定[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2016, 38(12): 939-943. [15] 杨振兴, 孟锦昕, 肖雷, 等. 流行性出血病病毒(EHDV)血清7型毒株在中国的首次分离与鉴定[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2019, 50(3): 150-158. [16] 朱建波, 杨振兴, 肖雷, 等. 流行性出血病多克隆抗体C-ELISA检测方法的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018, 49(7): 1440-1450. doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.07.013 [17] 杨振兴, 朱建波, 李占鸿, 等. 蓝舌病病毒和流行性出血病病毒双重荧光定量RT-PCR检测方法的建立及应用[J]. 中国兽医科学, 2019, 49(9): 1104-1111. [18] BATTEN C A, HENSTOCK M R, BIN-TARIF A, et al. Bluetongue virus serotype 26: Infection kinetics and pathogenesis in Dorset Poll sheep[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2012, 157(1/2): 119-124.
[19] TAMURA K, STECHER G, PETERSON D, et al. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 2013, 30(12): 2725-2729. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197
[20] MAAN N S, MAAN S, NOMIKOU K, et al. RT-PCR assays for seven serotypes of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus & their use to type strains from the Mediterranean region and North America[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(9): e12782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012782
[21] ALLISON A B, GOEKJIAN V H, POTGIETER A C, et al. Detection of a novel reassortant epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV) in the USA containing RNA segments derived from both exotic (EHDV-6) and endemic (EHDV-2) serotypes[J]. J Gen Virol, 2010, 91(2): 430-439. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.015651-0
[22] LEE F, TING L J, LEE M S, et al. Genetic analysis of two taiwanese bluetongue viruses[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2011, 148(2/3/4): 140-149.
[23] YANG H, ZHU J, LI H, et al. Full genome sequence of bluetongue virus serotype 4 from China[J]. J Virol, 2012, 86(23): 13122-13123. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02393-12
[24] BREARD E, BELBIS G, VIAROUGE C, et al. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 6 experimentation on adult cattle[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2013, 95(2): 794-798. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2013.06.026
[25] 冯云, 章域震, 杨卫红, 等. 阿卡斑病毒云南分离株全基因组序列特征研究[J]. 病毒学报, 2016, 32(2): 161-169. [26] LIAO Y K, INABA Y, LI N J, et al. Epidemiology of bovine ephemeral fever virus infection in Taiwan[J]. Microbiol Res, 1998, 153(3): 289-295. doi: 10.1016/S0944-5013(98)80014-1



 下载:
下载: