Bentonite modification and adsorption capacity for Cr(VI) in water
-
摘要:目的
提高膨润土对水中Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能。
方法采用氢氧化钠和壳聚糖对膨润土进行改性,分别得到碱改性膨润土(B−NaOH)、壳化膨润土(B−CS)和壳化碱改性膨润土(B−NaOH−CS)。以钠基膨润土(B)为对照,利用红外光谱仪、扫描电镜和比表面积分析仪表征3种改性膨润土的理化性质,研究其对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附性能。
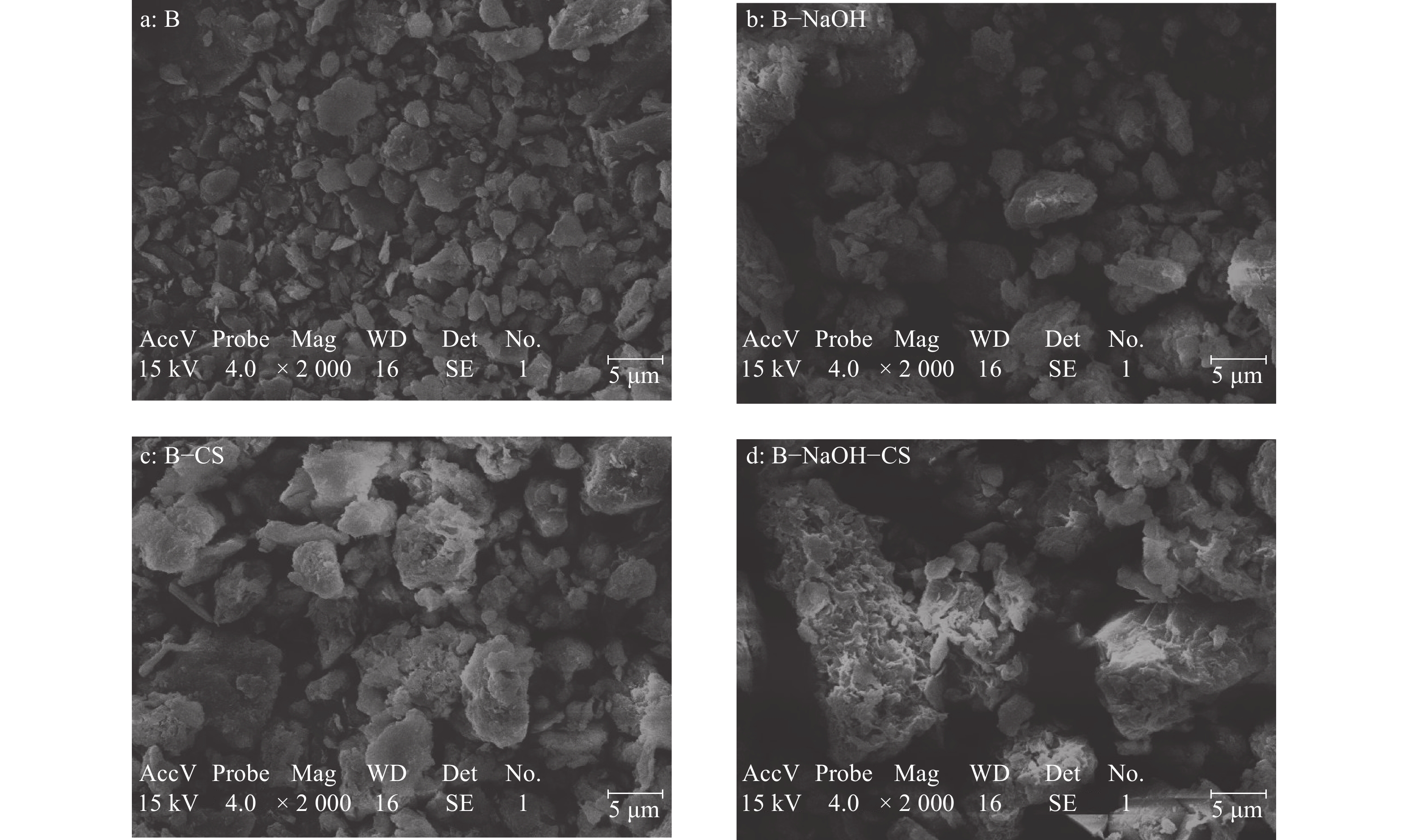
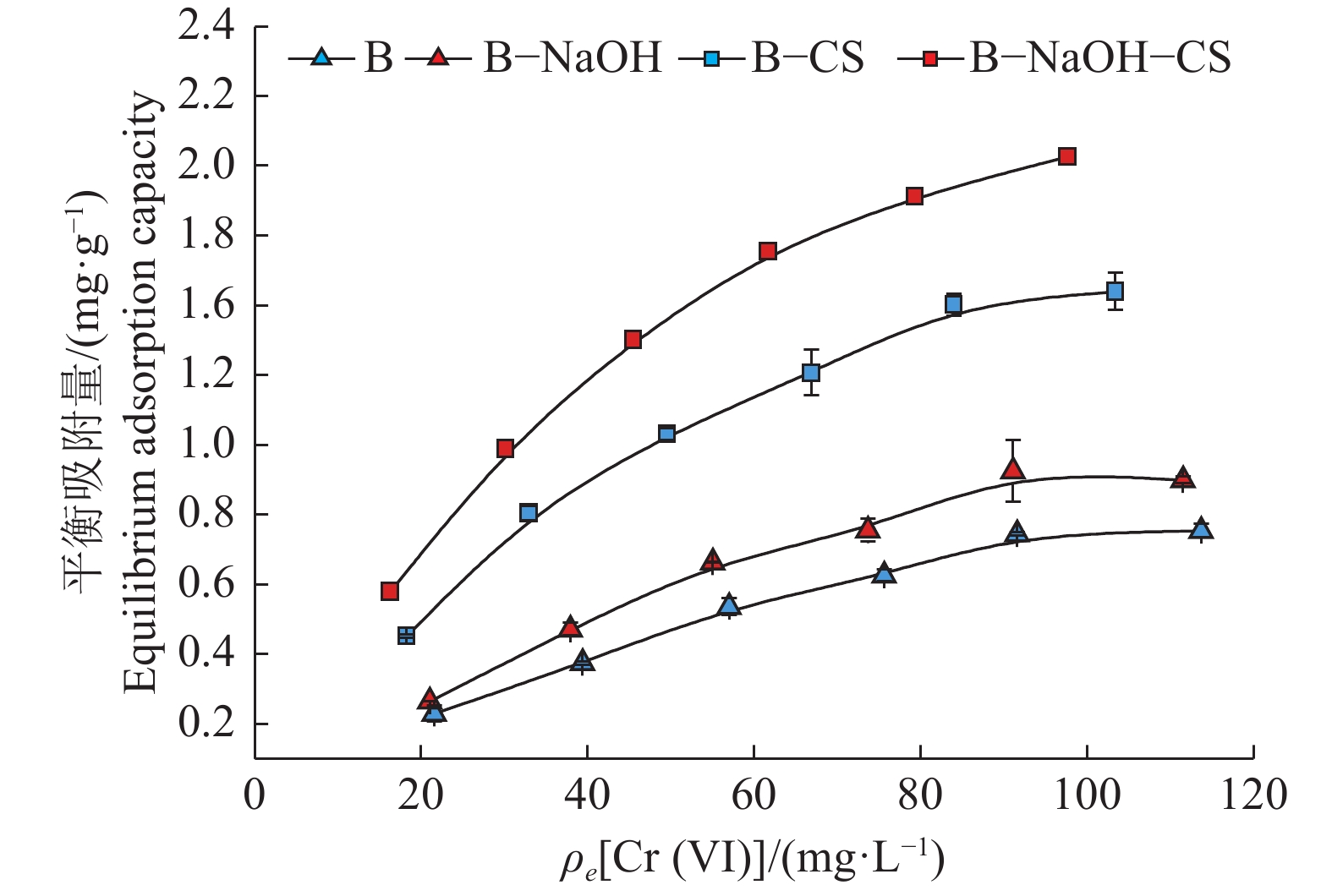
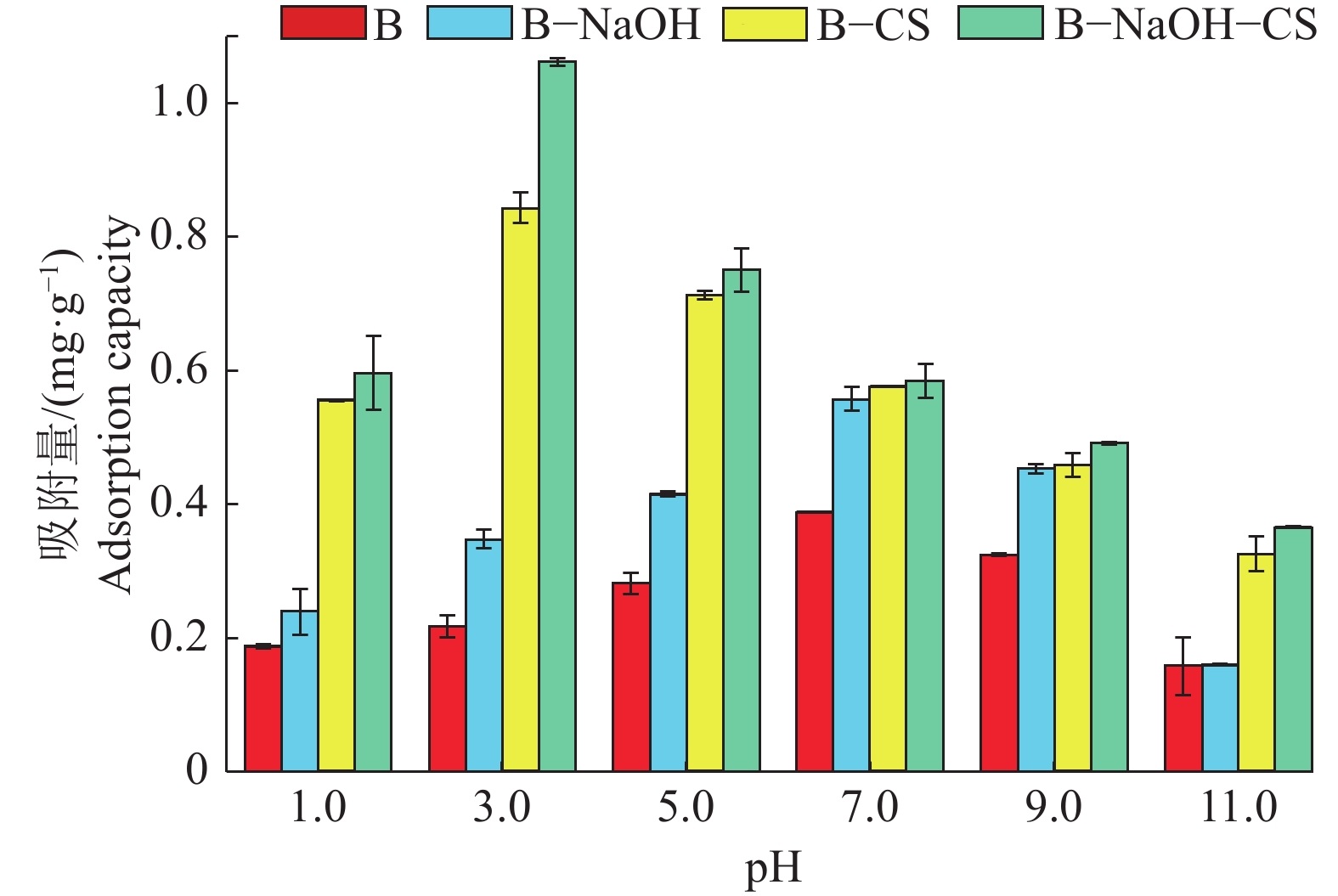
结果B−NaOH−CS中出现了强N—H吸收峰以及增强的C—H对称弯曲峰,同时B−NaOH−CS表面片状结构卷曲分散,层间孔隙增多,比表面积是其他膨润土的1.2倍以上。当Cr(Ⅵ)质量浓度为50 mg·L−1时,B−NaOH−CS对Cr(Ⅵ)的平衡吸附量为1.03 mg·g−1,分别是B−CS、B−NaOH的1.26、1.84倍。描述膨润土吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的动力学过程,准二级动力学模型优于准一级动力学模型;描述膨润土吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的热力学过程,Langmuir等温模型优于Freundlich等温模型。热力学参数△H>0、△G<0、△S>0,表明膨润土吸附Cr(Ⅵ)为吸热、自发、无序反应。B−NaOH在pH=7.0时对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附量最大,B−CS、B−NaOH−CS在pH = 3.0时对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附量最大。
结论B−NaOH−CS对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附效果最好,改性膨润土对去除Cr(Ⅵ)污染有重要作用。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo improve the adsorption capacity of bentonite for Cr (VI) in water.
MethodNaOH and chitosan were used for modifying bentonite. Alkali modified bentonite (B-NaOH), chitosan modified bentonite (B-CS) and chitosan-alkali modified bentonite (B-NaOH-CS) were obtained. Using sodium bentonite (B) as the control, we characterized physicochemical properties of three kinds of modified bentonite through infrared spectrometer, scanning electron microscope and specific surface area analyzer, and analyzed their adsorption capacities for Cr (VI).
ResultA strong N—H absorption peak and an enhanced C—H symmetric bending peak appeared in B-NaOH-CS. The surface sheet structure of B-NaOH-CS was curly dispersed, the interlayer pores increased, and the specific surface area was 1.2 times more than other bentonite. When the concentration of Cr (VI) was 50 mg·L−1, the equilibrium adsorption capacity of B-NaOH-CS for Cr (VI) was 1.03 mg·g−1, which was 1.84 and 1.26 times of B-NaOH and B-CS respectively. The quasi-second-order kinetic equation and Langmuir equation could more accurately describe adsorption process of bentonite for Cr (VI). Thermodynamic parameters of △H>0, △G<0 and △S>0 indicated the adsorption process of bentonite for Cr (VI) was endothermic, spontaneous and disordered. B-NaOH had the maximum adsorption capacity for Cr (VI) at pH = 7.0, while B-CS and B-NaOH-CS at pH = 3.0.
ConclusionB-NaOH-CS has the best adsorption effect on Cr (VI). Modified bentonite plays an important role in Cr (VI) pollution remove.
-
Keywords:
- bentonite /
- chitosan /
- modification /
- Cr (VI) /
- adsorption
-
-
表 1 吸附剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附动力学参数1)
Table 1 Adsorption kinetic parameters of adsorbents for Cr(Ⅵ)
样品
Sample准一级动力学方程
Quasi-first-order kinetic equation准二级动力学方程
Quasi-second-order kinetic equationQe,1/(mg·g−1) k1 r Qe,2/(mg·g−1) k2 r B 0.35 0.025 0.872** 0.37 0.101 0.911** B−NaOH 0.51 0.049 0.798** 0.55 0.136 0.938** B−CS 0.76 0.076 0.823** 0.82 0.131 0.958** B−NaOH−CS 0.98 0.104 0.890** 1.04 0.140 0.966** 1) Qe, 1与Qe, 2表示平衡吸附量;k1与k2表示吸附速率常数;r表示相关系数;“**”表示显著相关(P<0.001,Pearson法)
1) Qe, 1 and Qe, 2 indicated equilibrium adsorption capacity; k1 and k2 indicated adsorption rate constant; r indicated correlation coefficient; “**” indicated significant correlation (P<0.001, Pearson method)表 2 不同吸附剂吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的Langmuir和Freundlich等温线参数1)
Table 2 Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm parameters of adsorbents adsorbing Cr(Ⅵ)
样品
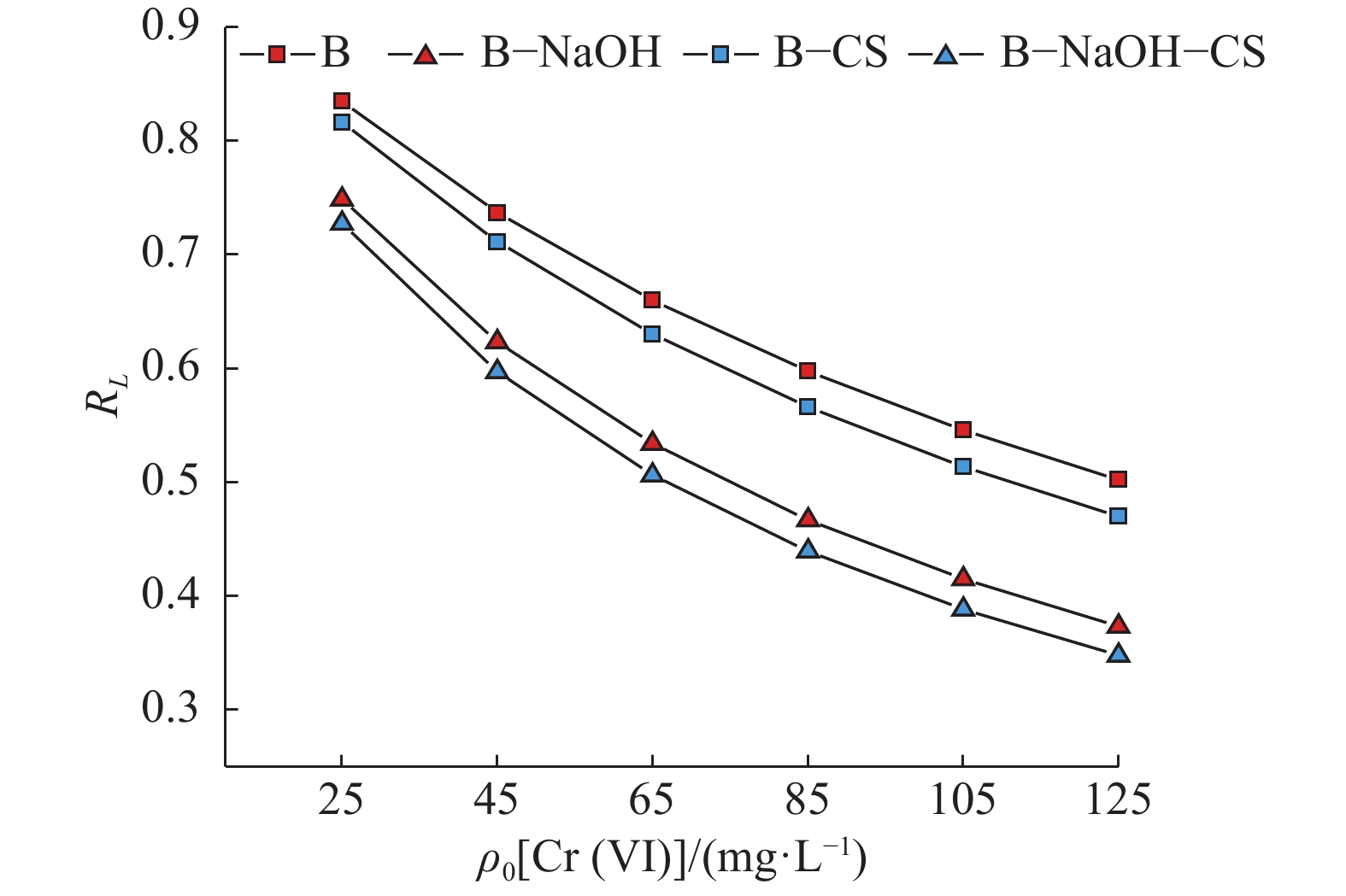
SampleLangmuir Freundlich qm/(mg·g−1) KL r n KF r B 1.67 447.665 0.977** 1.130 43.658 0.977** B−NaOH 1.91 470.368 0.961** 1.517 49.749 0.929** B−CS 2.55 698.740 0.987** 1.694 56.259 0.959** B−NaOH−CS 2.72 979.747 0.988** 1.889 60.036 0.951** 1) qm表示饱和吸附量;KL、KF表示吸附常数;r表示相关系数;n表示吸附系数;RL表示无量纲化分离因子;“**”表示显著相关(P<0.001,Pearson 法)
1) qm indicated saturated adsorption capacity; k1 and k2 indicated adsorption constant; r indicated correlation coefficient; n indicated adsorption coefficient; RL indicated dimensionless separation factor;“**” indicated significant correlation (P<0.001, Pearson method)表 3 不同吸附剂吸附Cr(Ⅵ)的热力学参数
Table 3 Thermodynamic parameters of different adsorbents adsorbing Cr(Ⅵ)
样品 Sample T/K △G/
(kJ·mol−1)△H/
(kJ·mol−1)△S/
(kJ·mol−1·K−1)B 288 −13.743 9.43 0.08 298 −15.123 308 −15.365 B−NaOH 288 −14.509 22.75 0.13 298 −15.246 308 −17.084 B−CS 288 −15.389 34.39 0.17 298 −16.226 308 −18.825 B−NaOH−CS 288 −15.243 47.79 0.22 298 −17.064 308 −19.612 -
[1] SUNDAR V J, MURALIDHARAN C, MANDAL A B. A novel chrome tanning process for minimization of total dissolved solids and chromium in effluents[J]. J Clean Prod, 2013, 59: 239-244. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.07.002
[2] 王瑾瑜, 孙亚兵, 缪虹. 电晕放电等离子体同时去除水中Cr(Ⅵ)和苯酚的实验研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(10): 2415-2421. [3] XU H M, WEI J F, WANG X L. Nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes with high charge density prepared by simultaneous electron beam radiation-induced graft polymerization for removal of Cr(VI)[J]. Desalination, 2014, 346: 122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2014.05.017
[4] ALVARADO L, TORRES I R, CHEN A. Integration of ion exchange and electrodeionization as a new approach for the continuous treatment of hexavalent chromium wastewater[J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2013, 105: 55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2012.12.007
[5] 刘军海, 聂峰, 李利华, 等. 改性膨润土对制革废水中六价铬的吸附过程研究[J]. 中国皮革, 2013, 42(7): 39-41. [6] 高宇超, 潘军标, 王趁义, 等. 膨润土基壳聚糖吸附剂处理污水中Pb(Ⅱ)、Cd(Ⅱ)[J]. 非金属矿, 2018, 41(1): 98-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2018.01.029 [7] 罗平, 田英, 张辉, 等. 酸改性膨润土对废水中铬的吸附性能研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2012, 35(6): 77-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2012.06.025 [8] 高凯芳, 简敏菲, 余厚平, 等. 裂解温度对稻秆与稻壳制备生物炭表面官能团的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(8): 1663-1669. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.08.2016010607 [9] 梁龄予, 王耀晶, 闫颖, 等. 玉米芯吸附水中Cr(Ⅵ)的特性及SEM-EDS表征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(2): 305-309. [10] 国家环境保护局. 水质六价铬的测定: 二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法: GB 7467—87[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1987. [11] CHEN H, ZHAO J, DAI G, et al. Adsorption characteristics of Pb(II) from aqueous solution onto a natural biosorbent, fallen Cinnamomum camphora leaves[J]. Desalination, 2010, 262(1): 174-182.
[12] 范世锁, 李雪, 胡凯, 等. 污泥基生物炭吸附重金属Cd的动力学和热力学[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(10): 5971-5977. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201505069 [13] 林涛, 李雪, 徐永建, 等. 用于除硅的铝盐改性膨润土的制备与表征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(3): 567-573. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.03.014 [14] 江旭, 刘全军, 纪慧超, 等. 不同改性膨润土对含磷废水的吸附试验研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2018, 41(2): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2018.02.007 [15] 刘桃香, 许中坚, 邱喜阳, 等. 壳聚糖改性膨润土及其对水中Pb2+的吸附性能[J]. 矿业工程研究, 2012, 27(1): 68-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5876.2012.01.015 [16] 闫继红, 孙海梅, 尚宏伟, 等. 可注射性壳聚糖基温敏性凝胶的制备及其生物相容性[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2011, 33(5): 522-526. [17] ALSHAMERIA, YAN C, Al-ANI Y, et al. An investigation into the adsorption removal of ammonium by salt activated Chinese (Hulaodu) natural zeolite: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics[J]. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng, 2014, 45(2): 554-564. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2013.05.008
[18] 林丽敏, 梁新强, 周柯锦, 等. 氯化钙活化稻草秸秆生物质炭的制备工艺及其吸磷性能研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2016, 36(4): 1176-1182. [19] 王迎亚, 施华珍, 张寒冰, 等. 磁性柠檬酸膨润土对六价铬吸附性能的研究[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2017, 31(3): 726-732. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2017.03.030 [20] ZHU J, BAIG S A, SHENG T, et al. Fe3O4 and MnO2 assembled on honeycomb briquette cinders (HBC) for arsenic removal from aqueous solutions[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2015, 286: 220-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.004
[21] VIEIRA M G A, NETO A F A, GIMENES M L, et al. Sorption kinetics and equilibrium for the removal of nickel ions from aqueous phase on calcined Bofe bentonite clay[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2010, 177(1/2/3): 362-371.
[22] 王倩, 王亚萍, 由晓芳, 等. 膨润土对溶液中阴离子态Cr(VI)的吸附特性及机理研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 28(8): 131-138. [23] 李小芳, 冯小强, 杨声. 膨润土负载壳聚糖季铵盐处理含铬废水[J]. 天水师范学院学报, 2016, 36(2): 29-32.




 下载:
下载: