Vehicle heading angle measure technology based on RTK-GNSS and MEMS gyroscope
-
摘要:目的
更好地满足车辆自动驾驶时航向角测量的精度要求。
方法提出卡尔曼滤波算法,把实时动态–全球导航卫星系统(RTK-GNSS)测量出来的经纬度和高程经过高斯投影转换为高斯平面坐标,和微电子机械系统(MEMS)陀螺仪测得的累积航向角进行融合处理,最终得到车辆更为精准的航向角。
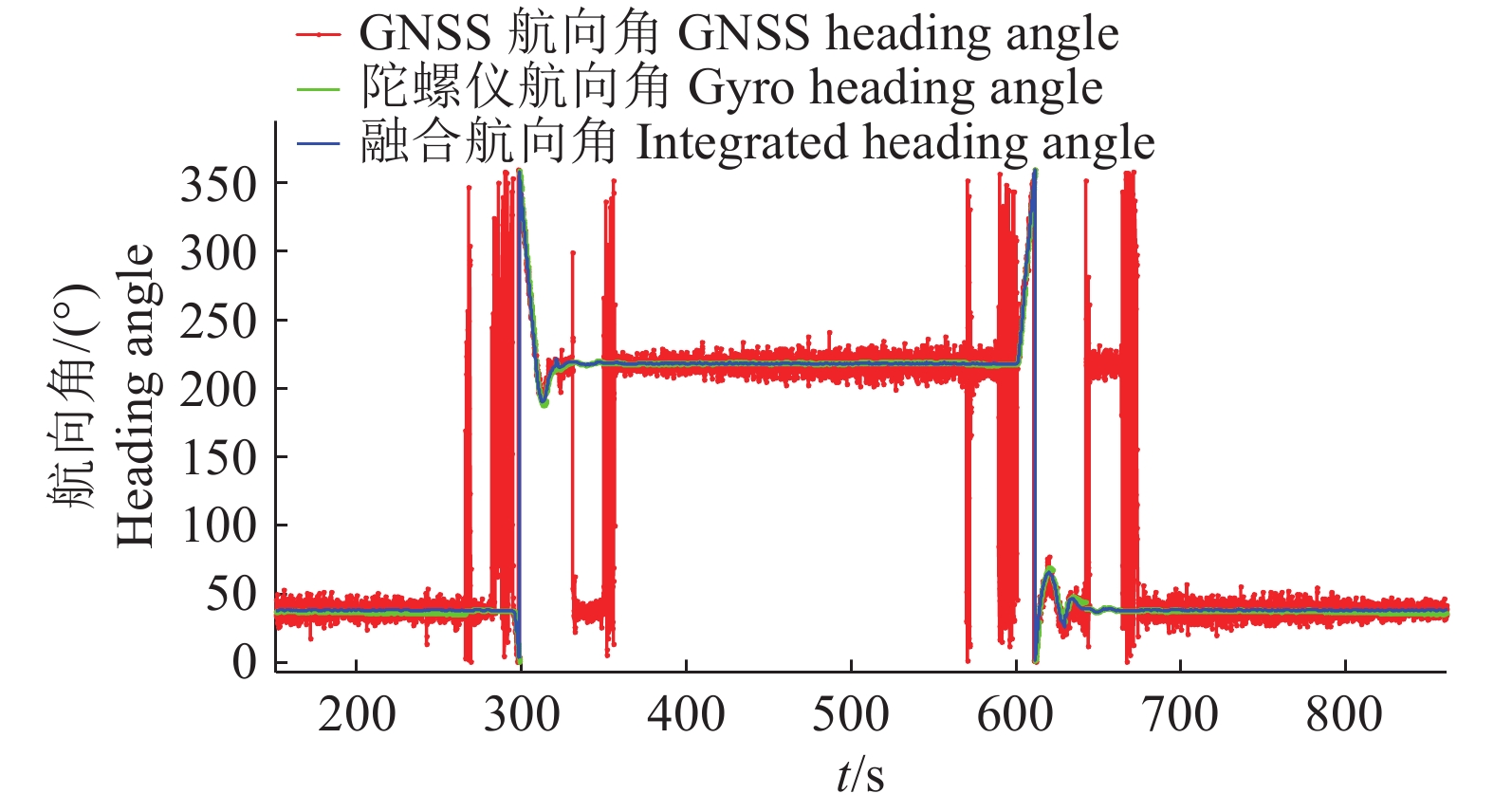
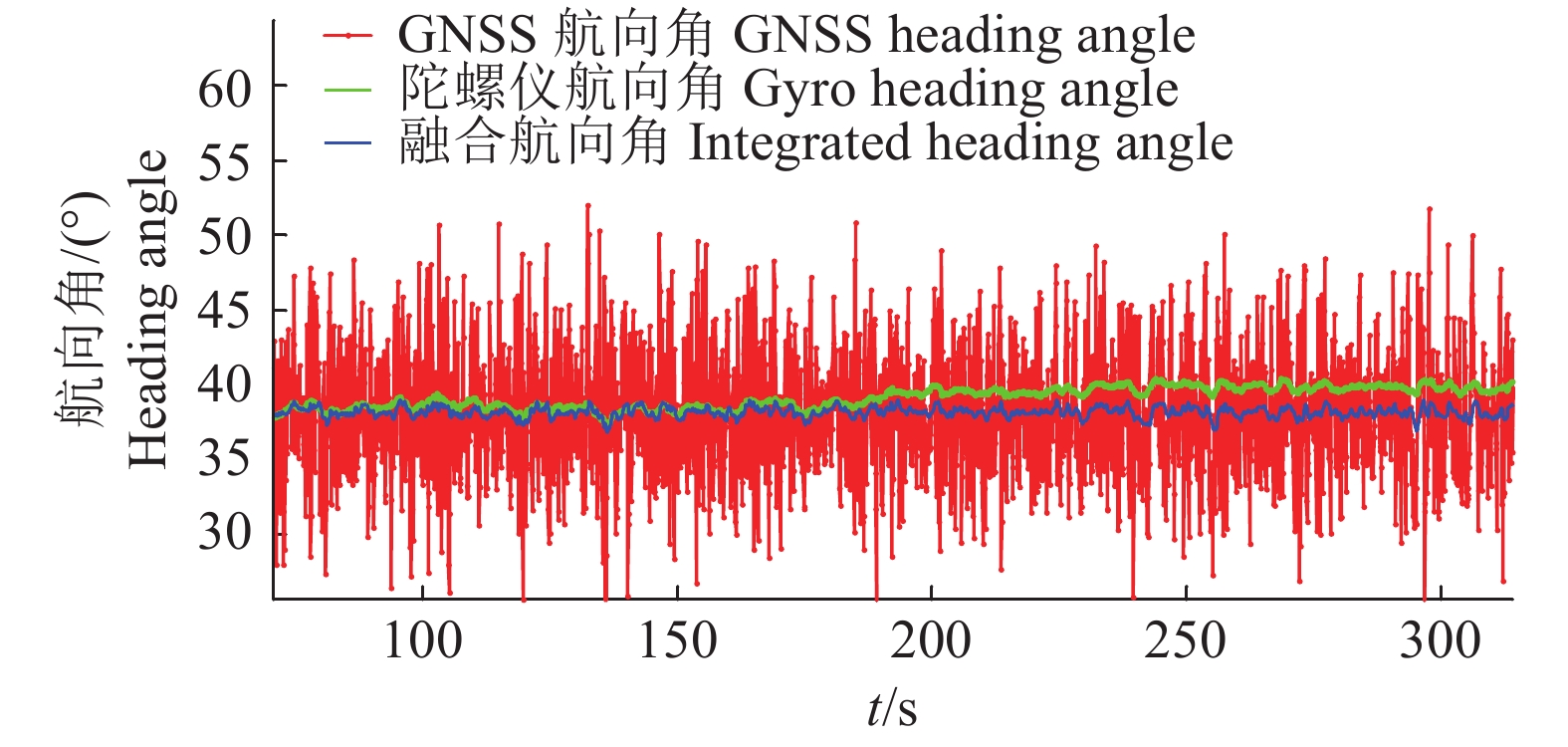
结果融合后的航向角度曲线既保持了GNSS航向的整体变化趋势,也保持了陀螺仪航向的细部变化趋势,且较GNSS和陀螺仪所得曲线更为平滑,可以跟踪车辆180°调头的转弯动作。
结论卡尔曼滤波算法可以实时在线且精准地测得车辆航向角数据,精度较GNSS测量结果提高80%以上。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo better meet the accuracy requirement of vehicle heading angle measure.
MethodKalman filter algorithm was proposed. The latitude, longitude and elevation measured by RTK-GNSS receiver were converted to plane coordinates using Gaussian projection. The Gaussian plane coordinates and the accumulated heading angle measured by gyroscope were integrated by Kalman filter, and finally more accurate heading angle was obtained.
ResultThe integrated curve kept the entire variation trend of the heading angle measured by GNSS receiver and the partial variation trend measured by MEMS gyroscope. The curve was smoother than that based on GNSS and gyroscope, and could follow action of vehicle 180° turning.
ConclusionThe Kalman filter algorithm can measure the vehicle heading angle data in real time and the precision was improved 80% more than the result measured by GNSS.
-
Keywords:
- RTK-GNSS /
- MEMS gyroscope /
- vehicle heading angle measure /
- Kalman filter /
- data fusion
-
-
-
[1] 别韦苇, 卢飞腾, 胡进, 等. 基于多器件的航向角优化算法[C]// 2018中国汽车工程学会年会论文集. 上海: 中国汽车工程学会, 汽车环境保护技术分会. 2018: 104-107. [2] 卢志才, 米东, 徐章遂, 等. 基于改进巨磁阻传感器的地磁定向系统[J]. 传感技术学报, 2011, 24(2): 304-307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2011.02.028 [3] 李秉玺. 基于系统芯片的捷联式定向系统研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2004. [4] HE P, CARDOU P, DESBIENS A, et al. Estimating the orientation of a rigid body moving in space using inertial sensors[J]. Multibody Syst Dyn, 2015, 35(1): 63-89. doi: 10.1007/s11044-014-9425-8
[5] LI Y, EFATMANESHNIK M, DEMPSTER A G. Attitude determination by integration of MEMS inertial sensors and GPS for autonomous agriculture applications[J]. GPS Solut, 2012, 16(1): 41-52. doi: 10.1007/s10291-011-0207-y
[6] 刘永彪. 基于GNSS双天线的定向研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2011. [7] 夏佩, 王峰, 黄祖德, 等. 基于双天线的RTK-GNSS定向方法[J]. 中国新通信, 2018, 20(22): 58-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2018.22.045 [8] 甘雨, 隋立芬, 戚国宾, 等. 陆地导航中GNSS/陀螺仪组合实时测姿方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2015, 40(3): 379-383. [9] HE J, XIE J, HE X, et al. Analytical study and compensation for temperature drifts of a bulk silicon MEMS capacitive accelerometer[J]. Sens Actuators A Phys, 2016, 239: 174-184. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2016.01.026
[10] 陈亮, 杨柳庆, 肖前贵. 基于梯度下降法和互补滤波的航向姿态参考系统[J]. 电子设计工程, 2016, 24(24): 38-41. [11] 姚卓. 基于双天线的车载GNSS/INS组合导航技术研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017. [12] 张智刚, 罗锡文, 胡炼, 等. 4种DGPS模块动态定位精度测试与分析[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2010, 31(1): 102-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-411X.2010.01.025 [13] MOUSAZADEH H. A technical review on navigation systems of agricultural autonomous off-road vehicles[J]. J Terramechanics, 2013, 50(3): 211-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jterra.2013.03.004
[14] NAGASAKA Y, SAITO H, TAMAKI K, et al. An autonomous rice transplanter guided by global positioning system and inertial measurement unit[J]. J Field Robot, 2010, 26(6/7): 537-548.
[15] CECHOWICZ R. Bias drift estimation for MEMS gyroscope used in inertial navigation[J]. Acta Mechanica Et Automatica, 2017, 11(2): 104-110. doi: 10.1515/ama-2017-0016



 下载:
下载: