Design and experiment of the beating-leveler controlled by laser for paddy field
-
摘要:目的
满足水稻种植对田面平整度的要求,减少拖拉机进田次数,提高打浆平地质量和效果,实现一次进田完成水田打浆和平地作业。
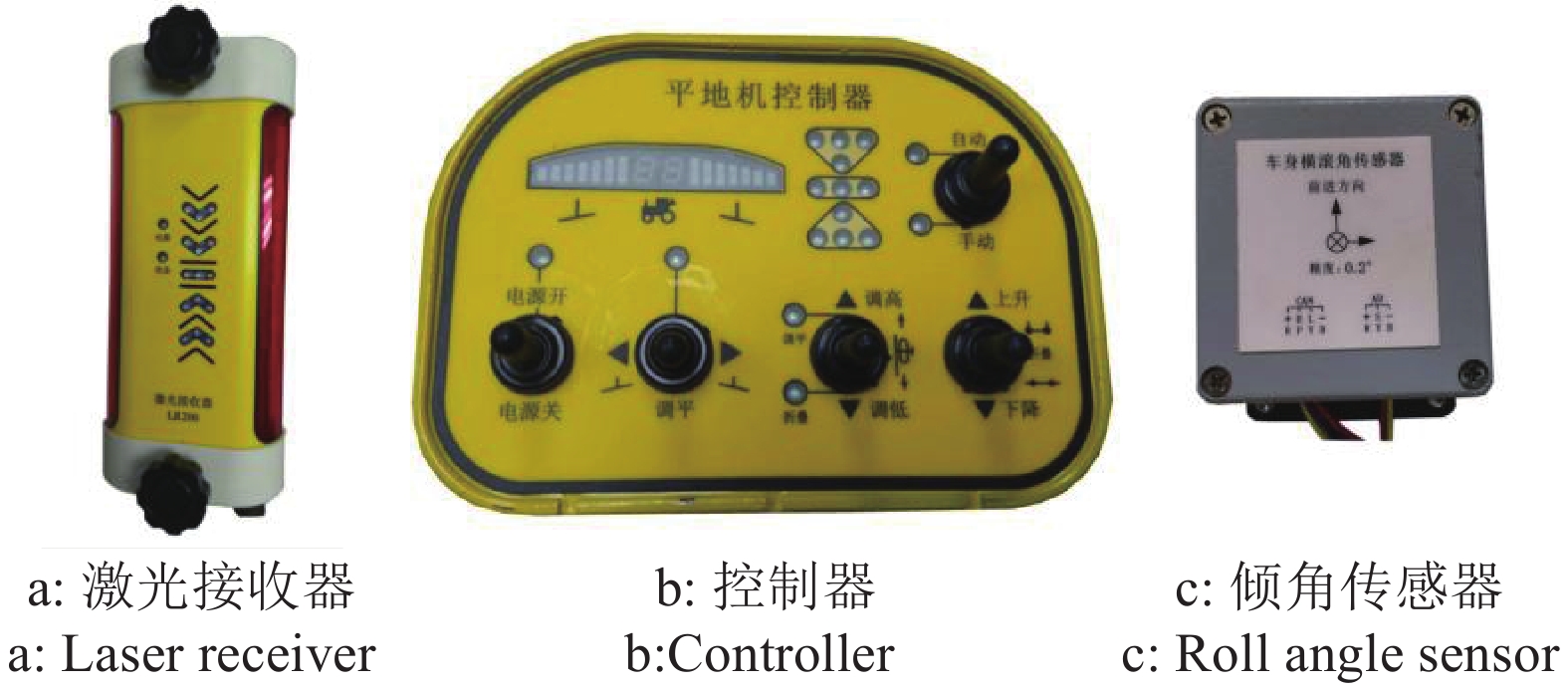
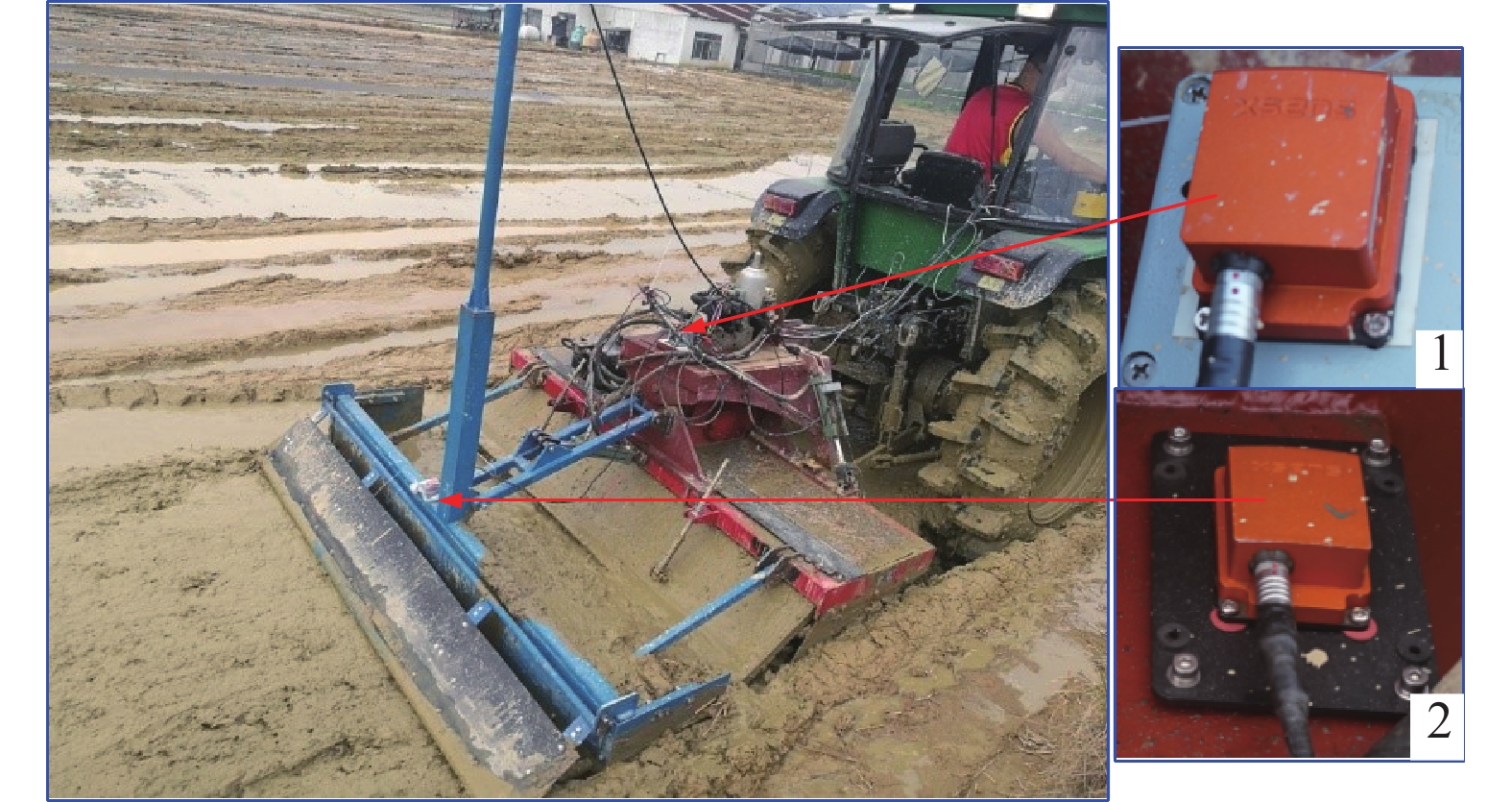
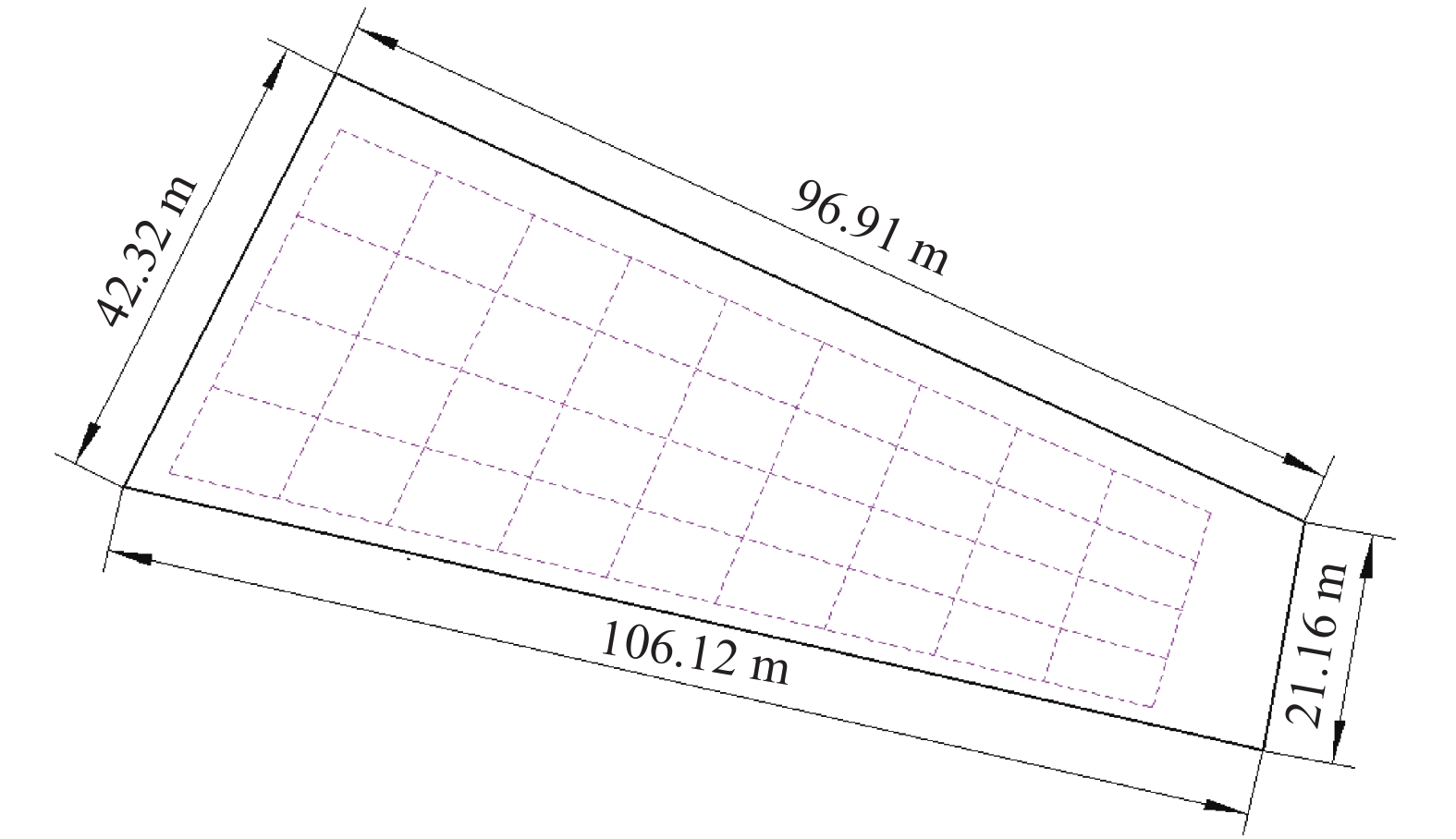
方法采用先打浆后平地原理,设计了激光控制水田打浆平地机、打浆机与平地铲自动调平机构、平地铲高程自动调节机构和通过集成带自动调平的激光平地控制系统,并进行田间试验;利用2台姿态航向参考系统分别测量拖拉机车身和打浆平地机的横滚角,采用水准测量试验田块作业前后的田面平整度。
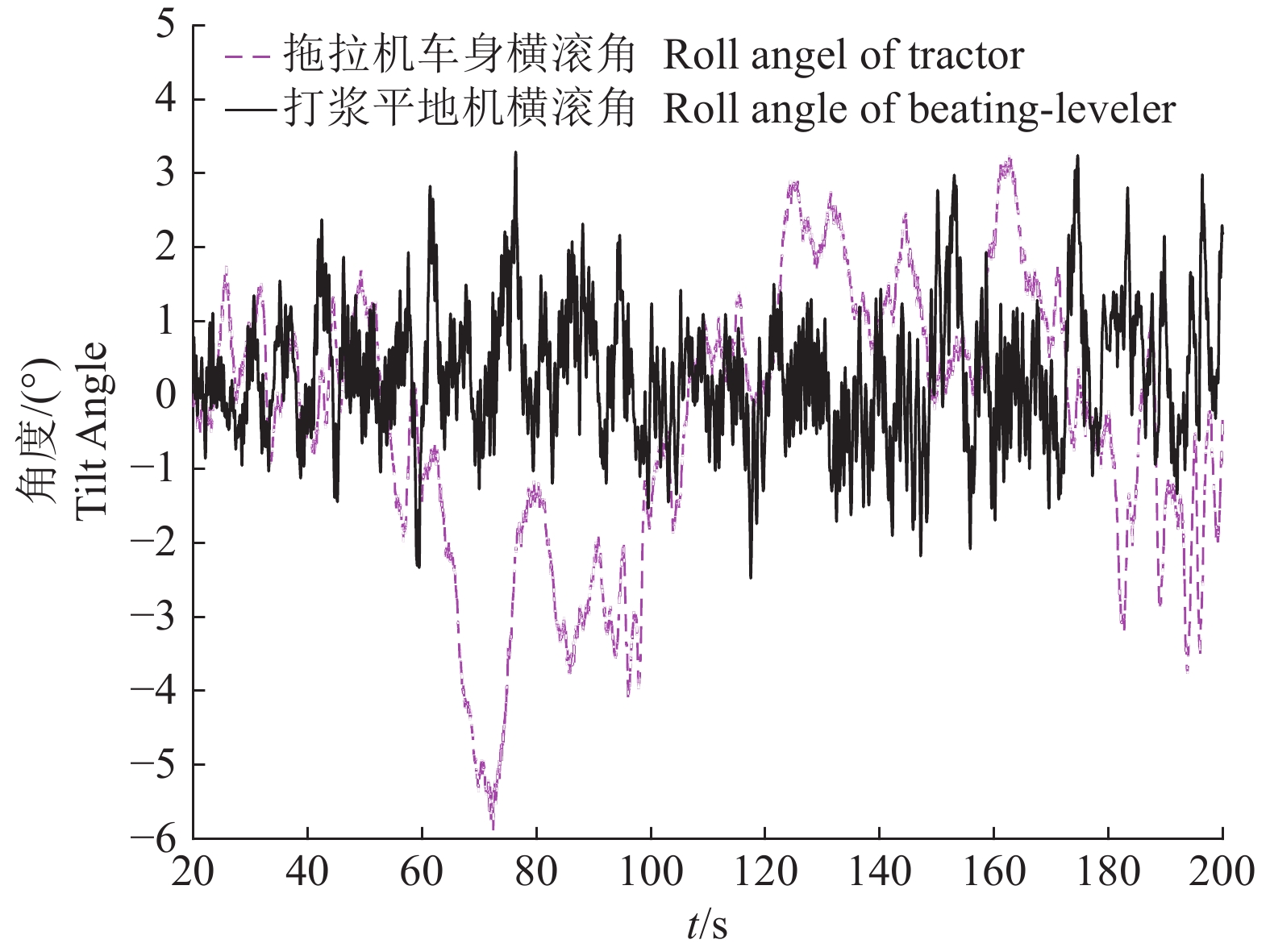
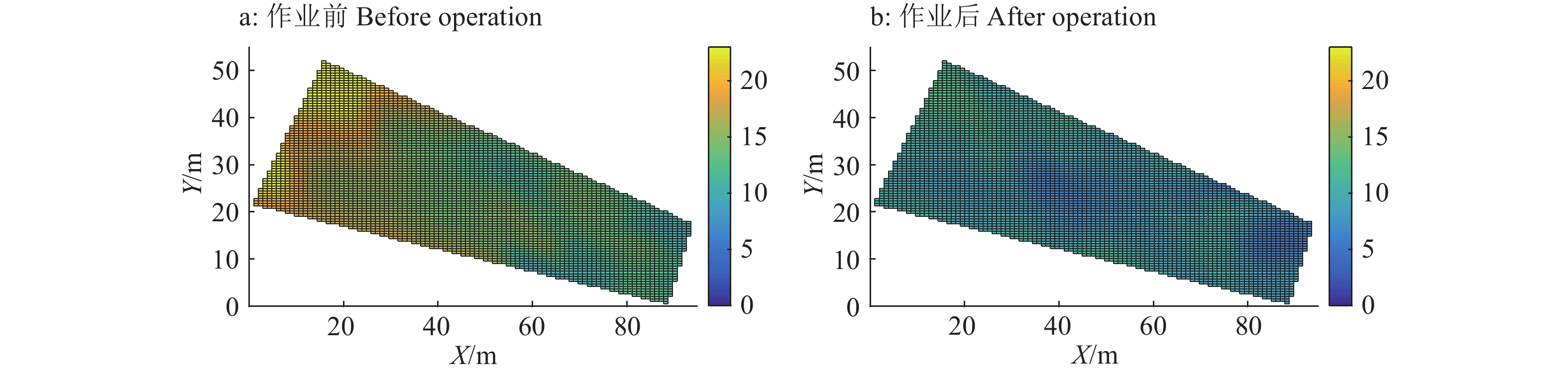
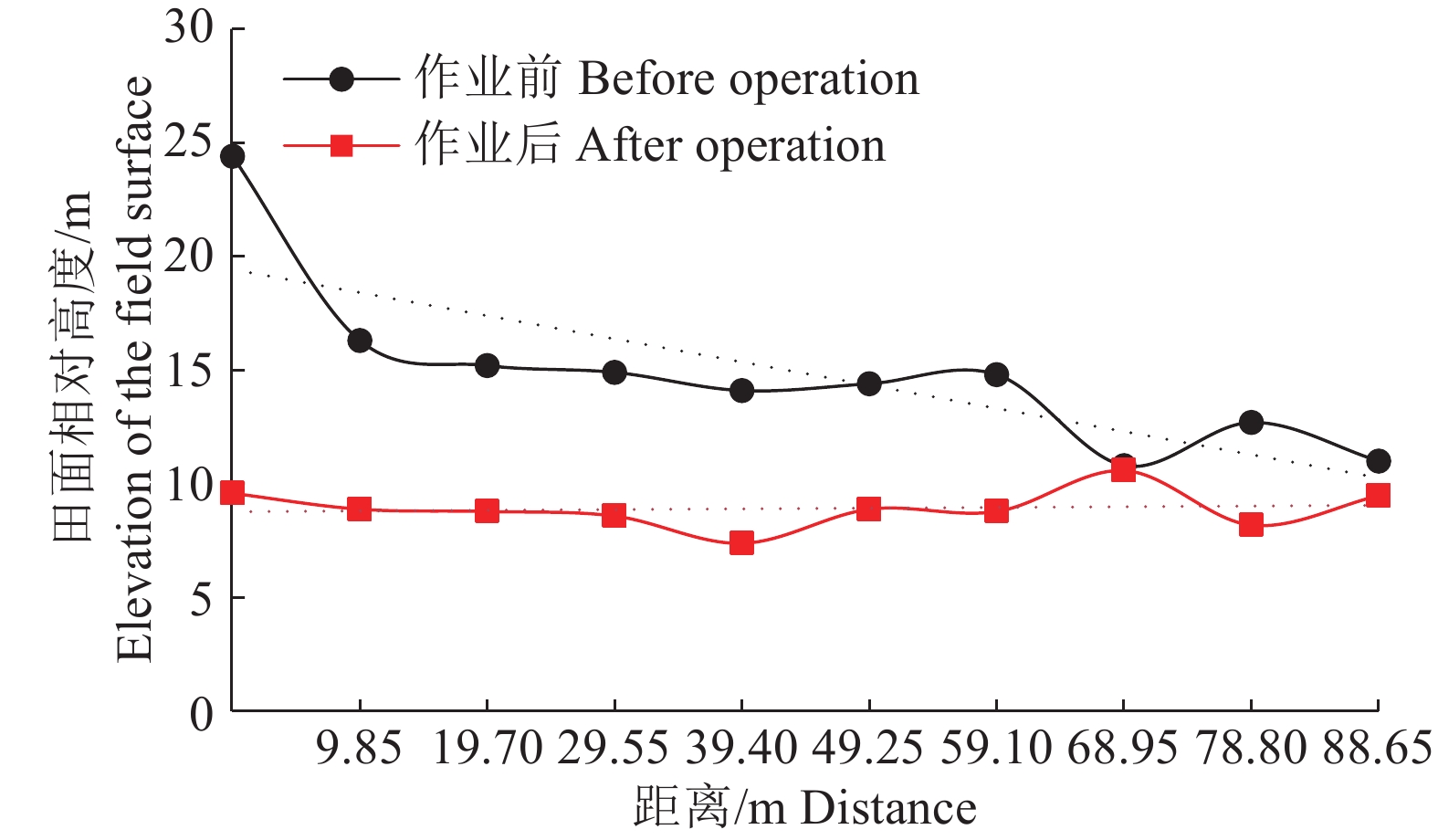
结果拖拉机横滚角在±4.5°内变化,打浆平地机的横滚角始终保持在±1°内,表明调平自动控制系统明显提高了水田打浆平地机构水平稳定性;打浆平地作业后田面最大高差从作业前的17.7 cm降低到6.7 cm,标准偏差值从作业前的4.08 cm下降到1.75 cm,绝对差值不大于3 cm的平整度采样点占比由作业前的62%提高到82%以上。
结论激光控制水田打浆平地机打浆平地作业后可显著改善田面平整情况。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo meet the requirement of field flatness in rice planting, reduce the number of times that tractors enter the field, improve the effect and quality of beating and leveling, and realize beating and leveling through one field entry.
MethodA beating-leveler was developed using the principle of beating followed with leveling. The beating machine, automatic leveling mechanism and automatic elevation adjusting mechanism were developed. Field experiments were performed using the laser-controlled leveling system integrated with automatic leveling function. The roll angles of the tractor and the beating-leveler were respectively measured using two attitude and heading reference systems (AHRS). Field flatness before and after leveling operation was measured using a balance level.
ResultThe roll angle of the beating-leveler maintained within ±1°, while the roll angle of the tractor varied within ±4.5°, indicating that the automatic leveling system obviously improved the leveling stability of the beating-leveler in paddy field. The maximum height difference of the field surface reduced from 17.7 cm (before operation) to 6.7 cm (after operation). Its standard deviation reduced from 4.08 cm (before operation) to 1.75 cm (after operation). The percentage of sampling points with absolute difference of ≤ 3 cm increased from 62% (before operation) to 82% (after operation).
ConclusionThe laser-controlled beating-leveler can significantly enhance the flatness of the field surface.
-
Keywords:
- laser-control /
- beating-leveler /
- paddy field /
- surface flatness
-
-
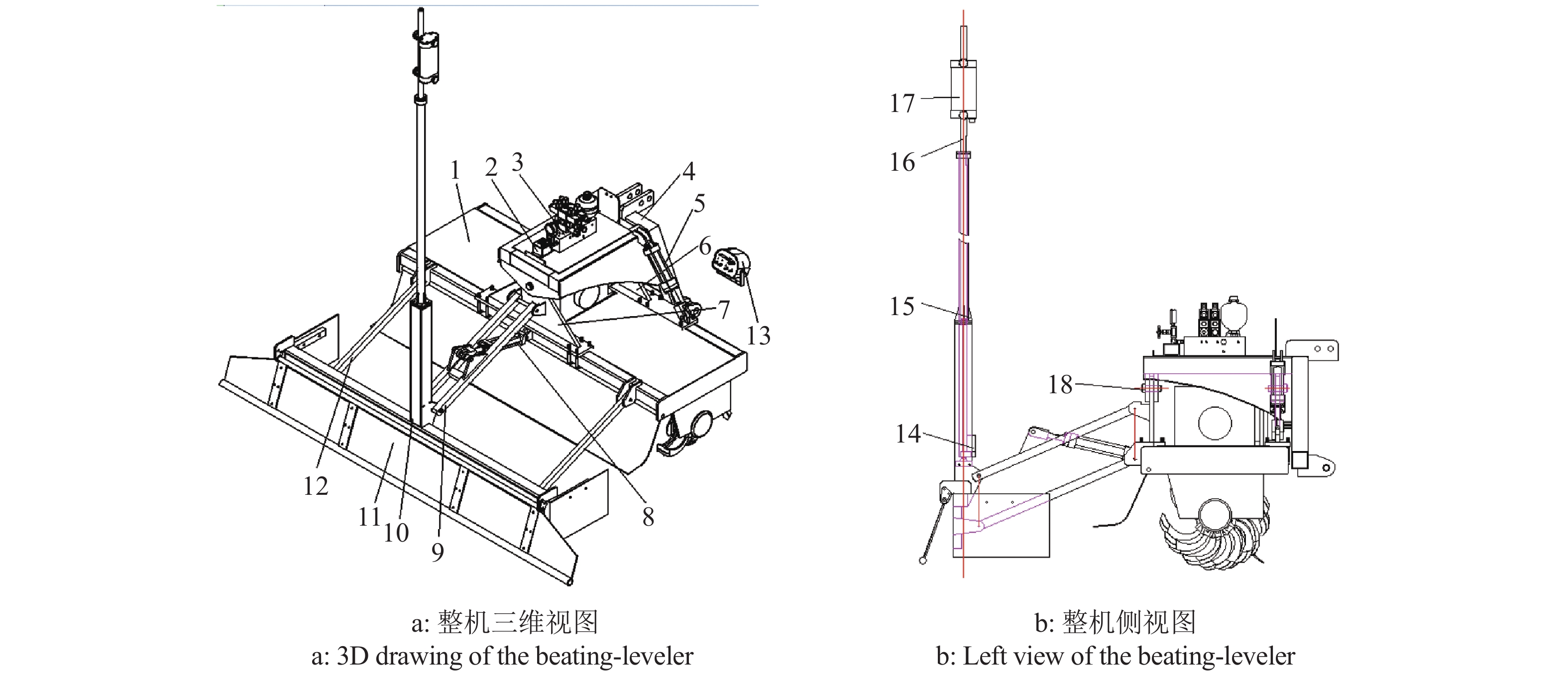
图 1 整机结构简图
1:打浆机构;2:倾角传感器;3:液压阀块及阀组;4:调平支撑架;5:调平油缸;6:前调平连接板;7:后调平连接板;8:高程油缸;9:上平地连接架;10:平地机构;11:平地拖板;12:下连接杆;13:控制器;14:直线电机;15:接收器升降杆安装座;16:接收器升降杆;17:激光接收器;18:调平销轴
Figure 1. Sketch map of the beating-leveler
1: Beating mechanism; 2: Roll angle sensor; 3: Hydraulic valve module; 4: Tilt adjustment bracket; 5: Tilt adjustment cylinder; 6: Front leveling connection plate; 7: Back leveling connection plate; 8: Elevation cylinder; 9: Upper grade connection bracket; 10: Leveling mechanism; 11: Tail plate; 12: Lower connection rod; 13: Controller; 14: Linear motor; 15: Mounting plate of lifting rod for laser receiver; 16: Lifting rod for laser receiver; 17: Laser receiver; 18: Leveling pin
-
[1] AGARWAL M C, GOEL A C. Effect of field leveling quality on irrigation efficiency and crop yield[J]. Agric Water Manage, 1981, 4(1/2/3): 89-97.
[2] ARYAL J P, MEHROTRA M B, JAT M L, et al. Impacts of laser land leveling in rice-wheat systems of the north-western indo-gangetic plains of India[J]. Food Secur, 2015, 7(3): 725-738. doi: 10.1007/s12571-015-0460-y
[3] FINNEY C. The benefits of land leveling on irrigation schemes in Turkey and Sindh Province, Pakistan[J]. ICID J, 1996, 45(1): 1523-1539.
[4] 李福祥, 许迪, 李益农. 农田土地平整设计与激光控制土地平整技术适应性研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2002, 2: 27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2002.10.010 [5] LUO X W, ZHAO Z X, LI Q. Study on leveling control for a paddy laser leveler[C]. ASAE Annual Meeting Presentation. USA: ASAE, 2007: 071078.
[6] 李庆, 罗锡文, 汪懋华, 等. 采用倾角传感器的水田激光平地机设计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2007, 23(4): 88-93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2007.04.017 [7] 赵祚喜, 罗锡文, 李庆, 等. 基于MEMS惯性传感器融合的水田激光平地机水平控制系统[J]. 农业工程学报, 2008, 24(6): 119-124. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2008.06.023 [8] 陈君梅, 赵祚喜, 陈嘉琪, 等. 水田激光平地机非线性水平控制系统[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(7): 79-84. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.07.013 [9] 陈嘉琪, 赵祚喜, 施垒, 等. 水田激光平地机调平系统动力学建模[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(7): 18-23. [10] 胡炼, 林潮兴, 罗锡文, 等. 农机具自动调平控制系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(8): 15-20. [11] 严乙桉, 罗锡文, 资双飞, 等. 基于50马力轮式拖拉机的水田激光平地机设计与试验[C]. 中国农业工程学会2011年学术年会, 重庆: 中国农业工程学会, 2011. [12] 胡炼, 罗锡文, 林潮兴, 等. 1PJ-4.0型水田激光平地机设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(4): 146-151. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.04.023 [13] ONODERA T, TSURUTA M, OSARI H. Leveling rice paddies using a laser land leveler when tilling[J]. Trans JSIDRE, 2002, 6: 1-8.
[14] 丁为民, 孙元昊, 赵思琪, 等. 犁旋一体机自动调平系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(17): 25-31. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.17.004 [15] 刘林. 基于拖拉机三点悬挂机构耕作机具调平系统研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2014. [16] 王益新. 旋耕机组液压水平自动控制系统的研发[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2015. [17] 于志成, 王熙. 水田复式整地机自动调平装置的设计与研究[J]. 农机化研究, 2017, 8: 175-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2017.08.035 [18] 李明金. 水田搅浆机平地装置的设计与试验研究[D]. 黑龙江: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2014. [19] XU C L, ZHANG C L, LI L, et al. Optimization of working parameters for puddling and flatting machine in paddy field[J]. Int J Agr Biol Eng, 2016, 9(3): 88-96.
[20] 万松, 陈子林, 展鹏程, 等. 基于传感技术的水田旋耕机平地系统的设计与试验[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2016, 35(4): 129-135. [21] 杨青丰. 水田激光搅浆平地系统设计[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2018. [22] 周浩, 胡炼, 罗锡文, 等. 旋耕机自动调平系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016(S1): 117-123. [23] 李益农, 许迪, 李福祥, 等. 农田土地激光平整技术应用及初步评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 1999, 15(2): 85-90. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.1999.02.018



 下载:
下载: