Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cucurbitacae vegetables
-
摘要:目的
探讨多环芳烃(PAHs)在瓜类蔬菜体内的分布特征和积累规律,并对南宁市不同年龄不同性别人群摄食每种瓜类蔬菜果实的健康风险进行评估。
方法采集黄瓜Cucumis sativus、苦瓜Momordica charantia、丝瓜Luffa cylindrical和节瓜Benincasa hispida var. chieh-qua根系各30株和果实各20个,并分别称取茎1 kg、叶片1 kg和叶柄1 kg,用超声波提取、固相萃取对蔬菜进行前处理,用高效液相色谱法检测各部位中16种PAHs含量。
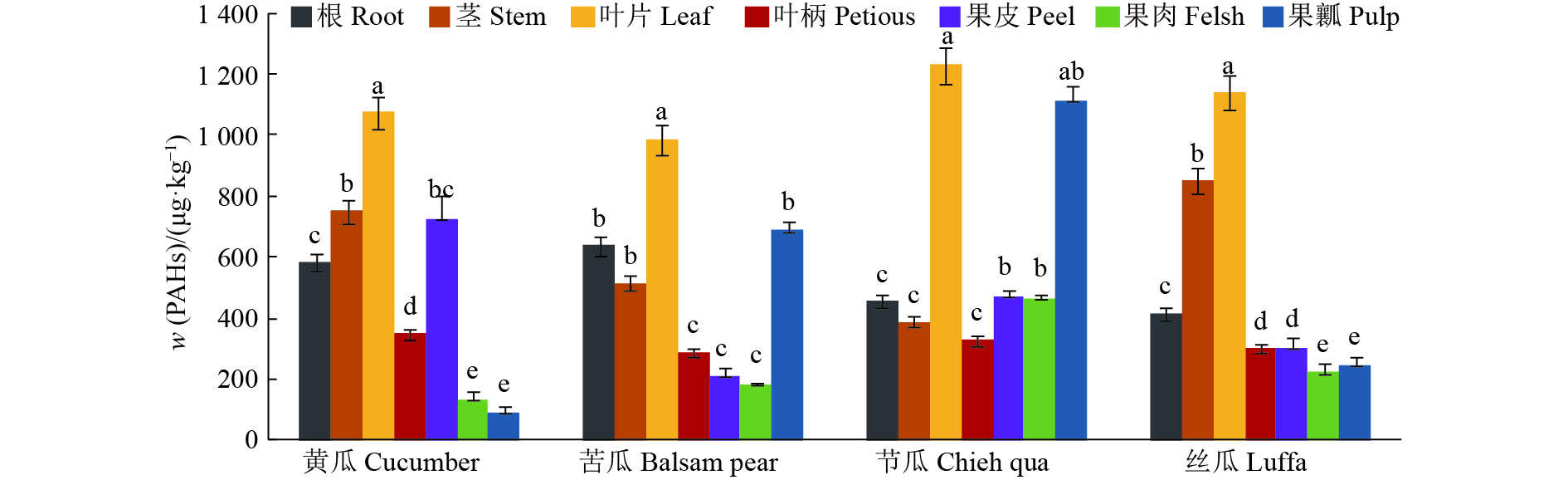
结果16种PAHs在4种瓜类蔬菜中均有检出,PAHs的总质量分数为88.44~1 229.85 μg·kg–1,其中各环数PAHs含量顺序为5环>6环>2环>4环>3环。南宁市不同人群食用瓜类果实引起的致癌风险值在1.48×10–6~7.84×10–5范围内,仅摄入可食用部分引起的致癌风险值在2.23×10–7~3.35×10–6范围内。
结论比较同种瓜类不同部位,4种瓜皆是叶片PAHs含量最高,黄瓜果瓤含量最低,苦瓜和丝瓜果肉含量最低,节瓜叶柄含量最低;比较4种瓜类叶片,节瓜叶片PAHs含量最高,苦瓜叶片含量最低。在目前蔬菜消费量下,南宁市民摄食瓜类蔬菜果实存在潜在致癌风险。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the distribution characteristics and accumulation rules of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in cucurbitacae vegetables, and evaluate the health risks of each cucurbitacae vegetable to people in different age groups and genders in Nanning.
MethodThe samples of Cucumis sativus, Momordica charantia, Luffa cylindrical and Benincasa hispida var. chieh-qua were collected. For each type of vegetable, we collected roots of 30 plants, 1 kg stems, 1 kg leaves, 1 kg petioles and 20 fruits. The vegetables were pretreated by ultrasonic extraction and solid phase extraction. The contents of 16 different PAHs in different parts of vegetables were detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
ResultSixteen types of PAHs were all detected in four kinds of cucurbitacae vegetables, the contents of total PAHs ranged from 88.44 to 1 229.85 μg.kg–1. The order of detected PAHs amounts in cucurbitacae vegetables was 5-ring PAHs > 6-ring PAHs > 2-ring PAHs > 4-ring PAHs > 3-ring PAHs. The cancer risk levels of diverse population groups in Nanning by ingesting fruit from cucurbitacae vegetables were in the range of 1.48×10 –6 and 7.87×10–5. The cancer risk levels caused by ingesting only edible portions were in the range of 2.23×10–7 and 3.35×10–6.
ConclusionComparing different organs of the same cucurbitacae vegetables, leaves had the highest PAH contents for all four vegetables, C. sativus pulp had the lowest PAHs content, M. charantia and L. cylindrical flesh had the lowest PAHs contents, B. hispida var. chieh-qua petious had the lowest PAHs content. Comparing leaves of different cucurbitacae vegetables, PAHs content was the highest in B. hispida var. chieh-qua while the lowest in M. charantia. Under the current consumption amount of vegetables, potential carcinogenic risks exist for Nanning residents by ingesting fruits of cucurbitacae vegetables.
-
Keywords:
- cucurbitacae vegetable /
- PAHs /
- distribution characteristic /
- risk assessment /
- HPLC
-
立地质量是影响林分生长的关键因素,准确评价立地质量是科学经营森林的前提和基础[1-2]。在“碳达峰碳中和”的战略背景下,科学的立地质量评价对提高林分生长收获预估准确性、优化抚育经营设计、提升森林碳汇经营水平以及森林生态系统应对气候变化能力具有极其重要的意义[3]。林分生产力的立地质量评价方法分为生物因子法和地理因子法2大类,其中,生物因子法的地位级和立地指数是立地质量评价最常用的指标。采用不同方法评价立地质量各有优缺点[4-5]。地理因子法易于分类,却缺乏立地条件影响林分生长的生物学解释。地位级法简便易行,但其精度和准确性低于立地指数的。立地指数的无偏估计要求准确的年龄测量值。相较基于年龄和树高的地位级和立地指数而言,已有研究者[6-8]提出了立地形(Site form)的方法,即用基准胸径时林分优势高表示立地质量,回避林分年龄,对混交异龄林具有较好的评价效果,但胸径和树高的关系也受林分的竞争程度影响[9-11]。
林业生产实践中树龄数据往往不准确或缺失,而林分胸径准确数据通过测量即可获取,理论上能修正由于树龄误差而导致的立地质量评价偏差。全国林分的情况复杂多样,天然林与人工林、混交林与纯林、异龄林与同龄林等差异会进一步影响立地质量评价方法的选择和评价结果的准确性[12],缺乏统一的评价模型也导致同一树种各区域间立地质量评价结果不具可比性。采用胸径与树高关系评价森林立地质量在一定程度上减少了其他评价方法的限制条件,同时在森林资源连续清查和森林资源规划设计调查中均有相应的因子调查要求,因此在实际生产管理中应用更便捷[13-15]。建立覆盖全国范围的主要针叶林分类型的胸径与树高模型,并编制指数模型表,不仅是森林经营管理的基础性工作[16],也能为建立大区域尺度的森林立地质量评价体系提供科学参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据来源及描述性统计
数据来源于全国森林资源连续清查第6次(1999—2003年)、第7次(2004—2008年)、第8次(2009—2013年)和第9次(2014—2018年)结果。根据全国主要针叶林分样地数量,划分为16个针叶树种组。每种树种中样本数量足够的单列,不够的合并为其他,优势树种组中的3种混交类型未纳入主要针叶林分立地形指数模型。主要针叶林分立地形指数模型研建数据描述性统计分析见表1。其中,数量最多的是马尾松林分样地,共
15430 块,数量最少的是铁杉林分样地,共182块。林分胸径均值为10.6~32.8 cm,林分树高均值为6.1~19.8 m,样地数量及规格均能满足建模和检验要求。表 1 立地形指数模型研建数据描述性统计Table 1. Descriptive statistics of model establishment data for site form index林分类型 Stand types 样地数量
Number of plots林分胸径/cm Stand DBH 林分树高/m Stand height 区间 Range 均值 Mean 标准差 SD 区间 Range 均值 Mean 标准差 SD 冷杉 Abies fabri 4363 6.5~77.1 32.8 11.05 2.8~43.7 19.8 5.95 云杉 Picea asperata 11869 5.0~60.0 27.2 10.61 1.7~41.5 17.0 6.11 铁杉 Tsuga chinensis 182 6.9~58.0 29.9 9.61 4.0~29.0 16.6 4.42 油杉 Keteleeria fortunei 217 6.9~27.1 13.0 4.18 2.8~18.3 7.2 2.97 落叶松 Larix gmelinii 9105 5.0~69.7 16.4 9.19 2.0~36.2 13.5 5.00 红松 Pinus koraiensis 290 5.0~58.9 17.5 10.52 1.5~29.2 12.1 5.83 樟子松 Pinus sylvestris 563 5.4~43.2 16.9 7.13 2.8~26.7 11.6 4.78 赤松 Pinus densiflora 296 5.3~23.1 10.6 3.55 1.8~16.7 6.1 3.06 黑松 Pinus thunbergii 346 5.3~20.0 10.8 3.13 2.2~16.0 6.3 2.46 油松 Pinus tabuliformis 4525 5.0~35.0 13.2 5.16 1.5~23.0 7.7 3.27 华山松 Pinus armandii 1029 5.0~34.3 13.9 5.60 1.5~25.0 9.3 3.83 马尾松 Pinus massoniana 15430 5.0~39.9 12.9 4.90 1.5~28.5 9.2 3.58 云南松 Pinus yunnanensis 3510 5.0~43.0 14.6 6.58 2.2~30.0 9.6 4.48 思茅松 Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis 478 5.7~33.4 16.5 5.14 2.9~27.2 12.4 4.13 高山松 Pinus densata 5125 5.3~40.0 27.9 6.53 2.0~28.0 17.8 4.41 其他松类1) Other pines 1350 5~27.4 12.8 4.44 2.5~18.7 8.1 3.06 1) 其他松类指样地数量较少的针叶林分类型。
1) Other pines indicate stand types with less sample plots.1.2 地位级指数模型构建及编表
1.2.1 导向曲线拟合
导向曲线的选择直接影响模型对立地质量评价的准确性,因此,导向曲线的形式既需要符合树高生长的生物学规律,又要能对数据进行最优化的拟合。良好的导向曲线应该呈平滑的“S”型,且具有上限渐近线。本文采用Richards、Logistic和Korf 3个胸径−树高生长模型拟合径阶中值和林分树高均值,如公式(1)~(3)所示。根据决定系数(Coefficient of determination,R2)、标准估计误差(Standard estimation error,SEE)和曲线形式等选择导向曲线模型。
$$ {H_{\mathrm{S}}} = 1.3 + a {\left( {1 - {{\text{e}}^{ - b {{\mathrm{DBH}}_{\mathrm{S}}}}}} \right)^c} \text{,} $$ (1) $$ {H_{\mathrm{S}}} = {{1.3 + a} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{1.3 + a} {\left( {1 + b {{\text{e}}^{c {{\mathrm{DBH}}_{\mathrm{S}}}}}} \right)}}} \right. } {\left( {1 + b {{\text{e}}^{c {{\mathrm{DBH}}_{\mathrm{S}}}}}} \right)}} \text{,} $$ (2) $$ {H_{\mathrm{S}}} = 1.3 + a {{\text{e}}^{\frac{b}{{{\mathrm{DB}}{{\mathrm{H}}_{\mathrm{S}}}^c}}}} \text{,} $$ (3) $$ {R^2} = 1 - \sum {\frac{{{{\left( {{y_i} - {{\hat y}_i}} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {{y_i} - {{\bar y}_i}} \right)}^2}}}} \text{,} $$ (4) $$ {{\mathrm{SEE}}} = \sqrt {\frac{{\displaystyle\sum {{{\left( {{y_i} - {{\hat y}_i}} \right)}^2}} }}{{ {n - p} }}} \text{,} $$ (5) 式中,HS为林分树高,DBHS为林分平均胸径,a、b、c为待求解参数,
$ {y_i} $ 为实际观测值,$ {\hat y_i} $ 为模型预估值,$ \bar y_i $ 为样本平均值,n为样本单元数,p为参数个数。1.2.2 基准胸径确定
基准胸径对立地形指数模型编表具有十分显著的影响,基准胸径选择不恰当会造成立地质量评价结果的偏差。在确定基准胸径时,本研究利用大量样地历史调查监测数据分析树高的生长过程,同时计算各径阶的树高变异系数及变化幅度,并绘制曲线图,根据曲线图中树高生长趋于平缓且能灵敏反映立地质量的原则确定基准胸径。
1.2.3 指数表编制
适宜的编表方法取决于树种、编表数据量等,编表方法不当会造成较大误差。本文利用林分树高生长及树高标准差曲线,依据 ± 2倍标准差原则确定立地形级的上、下限曲线,根据上、下限曲线所夹的面积及预定的5个指数级,采用相对系数法确定各指数级上、下限,编制全国主要针叶林分立地形表。该方法按照一定比例将胸径−树高生长曲线平移,在确定导向曲线模型后,将林分胸径代入模型,得到理论树高,将基准胸径代入模型得到树高理论值,调整系数和各指数级树高计算公式如下:
$$ {K_j} = \frac{{{H_{0j}}}}{{{H_{0k}}}} \times 100{\text{%}} \text{,} $$ (6) $$ {H_{ij}} = {K_j} \times {H_{ik}} \text{,} $$ (7) 式中,Kj为立地形曲线簇调整系数,H0j为基准胸径各指数级树高,H0k为基准胸径导向曲线树高,Hij为各指数级树高,Hik为导向曲线树高。
1.3 模型统计检验
为了检验立地形指数模型对全国针叶林分立地质量评价的准确性和适用性,对编制的立地形表进行落点检验和适用性检验。
1.3.1 落点检验
将林分平均胸径−树高数据作成散点图,并绘制到立地形曲线簇中,算出散点落在曲线簇内的概率,即立地形表能够解释林分平均树高生长的概率。一般认为,落点检验值大于90%时,新编的立地形表满足使用要求。否则,应进行必要的调整。
1.3.2 适用性检验
采用连续的调查监测数据对新编的立地形表进行适用性检验。根据林分平均胸径及树高由立地形指数表确定其立地形等级,然后,比较多期调查数据下林分立地形等级有无跳级的现象,并统计出跳级个数占总个数的百分比。一般认为,跳级个数小于5%时,新编的立地形表满足使用要求。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 立地形指数模型拟合结果
由表2可知,Richards模型拟合所有针叶树种决定系数均值为0.96,标准估计误差均值为0.98;Logistic模型拟合所有针叶树种决定系数均值为0.96,标准估计误差均值为1.10;Korf模型拟合所有针叶树种决定系数均值为0.96,标准估计误差均值为1.00。Richards模型的普遍适用性更强,但油杉和高山松2个优势树种林分的上限渐近线参数均超过45,与Richards模型参数所反映的林分生物学规律存在差异,即林分平均树高的上限水平应不超过45 m。油杉和高山松2个优势树种林分的Korf模型拟合参数也出现了偏离合理值的情况,因此这2个优势树种林分应选择Logistic模型作为导向曲线。
表 2 主要针叶林分胸径和树高模型参数Table 2. Model parameters of DBH and height for major coniferous stands林分
Stand typesRichards Logistic Korf a b c R2 SEE a b c R2 SEE a b c R2 SEE 冷杉 34.9304 0.0278 1.2032 0.94 2.08 29.7918 6.2168 − 0.0711 0.92 2.25 71.0181 − 8.2024 0.5228 0.94 2.07 云杉 35.0515 0.0292 1.2862 0.99 0.83 27.6166 7.9591 − 0.0872 0.98 1.12 104.1793 − 7.7122 0.4304 0.99 0.82 铁杉 42.7731 0.0100 0.7756 0.84 2.36 25.0287 4.3132 − 0.0612 0.81 2.52 228.4099 − 6.1365 0.2395 0.84 2.35 油杉 49.4001 0.0217 1.5328 0.96 0.94 17.6832 15.4880 − 0.1514 0.95 0.96 356.5069 − 9.6653 0.3327 0.96 0.94 落叶松 21.7763 0.0825 1.6565 0.92 1.54 21.4231 5.7592 − 0.1286 0.91 1.63 24.4672 − 16.0920 1.1943 0.91 1.63 红松 23.7699 0.0706 1.9944 0.95 1.54 22.4409 9.9858 − 0.1324 0.95 1.64 31.3234 − 15.3821 0.9800 0.95 1.60 樟子松 23.1622 0.0573 1.6375 0.97 1.07 19.8216 9.2197 − 0.1350 0.96 1.27 69.4325 − 7.1841 0.4718 0.97 1.06 赤松 11.2997 0.1945 5.7997 0.89 1.32 10.6562 48.3629 − 0.3444 0.92 1.14 15.2157 − 32.2581 1.4462 0.88 1.43 黑松 32.0888 0.0315 1.4875 0.97 0.60 13.1164 14.9074 − 0.2020 0.98 0.49 646.3492 − 8.9301 0.2569 0.97 0.62 油松 34.1642 0.0217 1.2051 0.99 0.28 17.6943 9.4751 − 0.1219 0.99 0.49 474.2441 − 8.0463 0.2431 0.99 0.26 华山松 23.2458 0.0527 1.5916 0.99 0.59 17.9922 10.4218 − 0.1496 0.98 0.68 69.1080 − 7.7007 0.4897 0.99 0.59 马尾松 20.7730 0.0585 1.4939 0.99 0.28 17.5935 8.1581 − 0.1427 0.99 0.55 41.5400 − 7.4772 0.5971 0.99 0.24 云南松 32.6336 0.0345 1.4617 0.99 0.38 22.9034 10.6239 − 0.1183 0.99 0.67 182.4129 − 7.9799 0.3567 0.99 0.38 思茅松 23.3830 0.0688 1.8721 0.97 0.87 19.5171 10.3107 − 0.1589 0.96 1.01 42.3634 − 10.2905 0.7343 0.98 0.84 高山松 47.8737 0.0196 1.2483 0.99 0.71 25.0354 10.2222 − 0.1076 0.98 0.89 378.0811 − 8.2583 0.2902 0.99 0.71 其他松类1) 15.6588 0.0804 1.7907 0.99 0.35 13.0084 10.8083 − 0.1960 0.99 0.28 36.7931 − 7.3685 0.5885 0.99 0.40 1) 其他松类指样地数量较少的针叶林分类型。
1) Other pines indicate stand types with less sample plots.导向曲线的选择不仅需要考虑模型的拟合决定系数和参数范围,同时也需要考虑导向曲线的良好形式,尤其是幼龄林阶段。拟合的导向曲线应能反映逻辑合理性,即林分胸径为0 cm,林分树高应为1.3 m,模型形式需要反映出此特征。大区域尺度的调查数据中,不同径阶段的样地数量呈现正态分布,导致小径阶林分的调查数据较少,也无法全面反映小径阶林分的生长情况,各针叶树种在小径阶的标准差范围也较小,如图1所示。其中,油杉、赤松、黑松、油松、华山松、马尾松、云南松、思茅松、高山松和其他松类胸径建模数据未超过60 cm,这也导致林分胸径−树高拟合曲线未出现明显的生长平缓阶段,这就意味着生产实践中应尽可能对中龄林、近熟林和成熟林进行评价,减少采用小径阶林分评价森林立地质量,从而避免出现跳级现象和评价结果的不确定。
2.2 立地形指数模型检验结果
根据主要针叶林分立地形指数模型曲线簇落点检验结果(图2)可知,冷杉林分落点检验值为95.67%、云杉林分落点检验值为97.42%、铁杉林分落点检验值为96.70%、油杉林分落点检验值为95.39%、落叶松林分落点检验值为97.90%、红松林分落点检验值为94.48%、樟子松林分落点检验值为96.80%、赤松林分落点检验值为92.23%、黑松林分落点检验值为97.69%、油松林分落点检验值为96.40%、华山松林分落点检验值为96.11%、马尾松林分落点检验值为99.16%、云南松林分落点检验值为97.55%、思茅松林分落点检验值为94.98%、高山松林分落点检验值为98.97%、其他松林分落点检验值为97.93%。落点检验值均大于90%,均值达96.59%,表明可以在实际生产中使用。此外,基于落点检验曲线簇分析可知,由于森林资源连续清查数据能获取准确的林分胸径数据,因而大区域尺度立地形指数模型相较于地位级指数模型具有更好的检验效果。
2.3 林分立地质量动态变化分析
根据主要针叶林分立地形等级占比动态分析结果(图3)可知,2003年16个针叶树种组立地形等级占比均值为Ⅰ级8.09%、Ⅱ级23.87%、Ⅲ级38.28%、Ⅳ级24.51%、Ⅴ级5.25%,2008年16个针叶树种组立地形等级占比均值为Ⅰ级8.51%、Ⅱ级24.56%、Ⅲ级36.70%、Ⅳ级25.19%、Ⅴ级5.04%,2013年16个针叶树种组立地形等级占比均值为Ⅰ级8.76%、Ⅱ级25.41%、Ⅲ级37.21%、Ⅳ级23.96%、Ⅴ级4.67%,2018年16个针叶树种组立地形等级占比均值为Ⅰ级9.64%、Ⅱ级29.91%、Ⅲ级34.79%、Ⅳ级21.55%、Ⅴ级4.12%。4次森林资源连续清查期间,针叶林分Ⅰ级和Ⅱ级占比均值合计增长了7.60个百分点,Ⅲ级均值合计减少了3.50个百分点,Ⅳ级和Ⅴ级均值合计减少了4.10个百分点。基于立地形等级的评价方法,20年间中国针叶林分立地质量表现为较好的改善趋势,比较典型的针叶林分包括冷杉林、云杉林、油杉林、落叶松林、油松林、华山松林、马尾松林、云南松林、高山松林和思茅松林,其中,马尾松林分有
15430 个样地,样本量大使得立地形等级变化趋势规律更加明显。铁杉林、油杉林、红松林、樟子松林、赤松林、黑松林和其他松类林则出现波动情况,以红松立地形Ⅲ级为例,2003、2008、2013和2018年的占比分别为60.00%、20.00%、40.00%和30.00%,出现了明显的跳跃,是因为小样本量分析导致的,20年间仅有10个样地未发生优势树种的变化,整体可用于立地形等级占比变化分析。3. 讨论与结论
3.1 讨论
不同区域间的气候差异导致林木生长速率差异,进而对林龄−树高关系产生影响,因此,采用林龄−树高关系评价立地质量主要受树种、气候、土壤肥力等主导因素的交互作用,无法建立统一的大尺度立地质量评价模型。相较于传统的立地指数和地位级法,胸径−树高关系在不同气候区域和林龄结构中具备一定的稳定性[17],常用于不同遗传种源林木的基因表观评估[18],受树种、土壤肥力和林分密度等主导因素的交互作用影响,这就为相同树种不同区域建立统一的立地质量评价模型提供了前提条件[19-20]。本文16个林分类型胸径−树高关系的拟合决定系数(均值0.96)大于林龄−树高关系的(均值0.94),以冷杉林为例,林龄−树高和胸径−树高关系的拟合决定系数分别为0.86和0.93。统一的胸径−树高立地质量评价模型使不同地区的相同林分评价结果具有可比性,但在实际应用过程中仍存在挑战,难以排除经营措施对林分密度等竞争指标的影响[21],导致胸径−树高关系评价立地质量偏差的不确定性增加,从而出现跳级现象,这也是后续研究中需要重点关注的环节。
在实际林业生产实践中,作为森林立地质量的关键因素,土壤类型、厚度、质地、养分的状况在无人为干扰的情况下,将在较长时间内维持在比较稳定的水平[1,22],因此,立地质量在一定周期内具有稳定性。与此同时,长期积累和分解的森林凋落物可以增加土壤中的速效磷、速效氮等养分含量,促进森林立地质量的改善;不合理的经营措施导致土壤有机物持续减少、土壤养分流失,也可能导致森林立地质量的恶化,因此,在一定周期内立地质量也具有波动性。胸径−树高关系评价森林立地质量的优势是简便和动态,劣势则是灵敏的动态变化可能是人为干扰(如采伐、补植)或气候变化(如降雨、有效积温增加)等综合因素导致,而非真实的立地质量改善[23-24],同时其也受建模评价样本量的影响,本文中样地数量小于500的铁杉林、油杉林、红松林、赤松林、黑松林和思茅松林均出现了不同程度的跳跃现象,即小样本分析导致的不确定性结果。因此,在林业生产实践中,应综合利用多种方法进行比较分析[7],全面、准确、客观和科学地反映森林立地质量及动态变化,这也是本文后续需要持续完善的地方。
3.2 结论
本研究中Richards、Logistic和Korf模型拟合导向曲线决定系数均值均大于0.95,结合模型形式和参数分析结果可用于建立全国主要针叶林分立地形指数模型,建立的立地形指数模型落点检验值均大于90%,均值达96.59%,可以在实际生产中使用。基于胸径−树高关系建立全国统一的立地质量评价模型具有可行性和合理性,通过减少气候差异导致基于树龄的生长速率对立地质量评价的影响偏差,使不同地区相同林分的评价结果具有可比性,在大尺度水平具有较好的适用性,但仍然需要警惕经营措施和小样本数据导致的评价结果不确定。
-
表 1 不同人群对瓜类蔬菜的摄取量
Table 1 Ingestion amounts of cucurbitacae vegetables for different groups of people
g·d–1 蔬菜种类
Vegetable type蔬菜部位
Vegebable part儿童 Child 青少年 Adolescent 成年人 Adult 老年人 Senior 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 苦瓜
Balsam pear果实 Fruit 2.19 2.07 3.68 3.22 5.52 5.06 5.29 4.60 可食用部位 Edible portion 1.79 1.70 3.02 2.64 4.53 4.15 4.34 3.77 节瓜
Chieh qua果实 Fruit 1.43 1.35 2.40 2.10 3.60 3.30 3.45 3.00 可食用部位 Edible portion 0.97 0.92 1.63 1.43 2.45 2.24 2.35 2.04 丝瓜
Luffa果实 Fruit 0.95 0.90 1.60 1.40 2.40 2.20 2.30 2.00 可食用部位 Edible portion 0.74 1.25 1.25 1.79 1.87 1.72 1.79 1.56 表 2 不同人群对黄瓜的摄取量
Table 2 Ingestion amounts of Cucumis sativus for different groups of people
g·d–1 黄瓜部位
Cucumber part儿童 Child 青少年 Adolescent 成年人 Adult 老年人 Senior 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 果实 Fruit 3.99 3.78 6.72 5.88 10.08 9.24 9.66 8.40 果肉和果瓤 Flesh and pulp 3.47 3.29 5.12 2.64 8.77 8.04 8.44 7.31 果肉 Flesh 2.63 2.49 4.44 3.88 6.65 6.10 6.38 5.54 表 3 黄瓜各部位中多环芳烃含量1)
Table 3 PAHs contents in various parts of Cucumis sativus
苯环数
Benzene ringsPAHs w/(μg·kg–1) 根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf叶柄
Petious果皮
Peel果肉
Flesh果瓤
Pulp2 Nap 42.61±2.02b 30.63±2.04c 128.74±4.68a 21.19±2.32d 18.14±10.47e — — Acy 39.13±0.38b 28.24±5.06c 109.42±11.01a 18.86±0.21d 17.83±1.01d 1.89±0.30e — Ace 96.83b±7.23b 72.42±10.28c 218.33±27.48a 47.31±1.76d 40.54±3.15d 14.18±0.24e 12.07±1.76e Flu 32.23±13.48b 18.02±17.11c 63.65±1.05a 12.94±2.67c 10.56±0.94c 7.56±0.07c 12.30±0.50c 合计 Total 210.80±24.08b 149.31±22.69bc 520.14±31.55a 100.30±4.07cd 87.07±5.10cd 23.64±3.01d 24.37±2.12d 3 Phe 20.26±1.56a 13.94±0.45b 13.32±1.77b 8.74±1.17c 7.55±1.86c 19.37±3.87 6.05±2.76 Ant — — — — — — — Fla 32.05±0.76a 23.08±0.98ab 43.39±8.58a 13.93±1.33b 8.66±7.51b 13.55±3.65b 8.01±1.70b 合计 Total 52.31±2.15a 37.02±1.16b 56.71±10.36a 22.67±2.39cd 16.21±9.35d 32.92±7.51bc 14.06±4.39d 4 Pyr 47.36±4.66a 31.36±4.56ab 27.35±15.9ab 13.92±10.24b 3.60±1.67b 40.17±12.24a 27.56±11.89ab BaA 22.63±4.61ab 23.14±18.56a 12.55±23.8abc 3.54±6.13abc — 6.34±3.07abc 2.88±3.65bc Chr 2.02±3.49b — 8.79±1.50a — — 3.66±0.27ab 3.61±1.14ab 合计 Total 72.01±5.41a 54.50±21.17ab 53.48±12.94ab 17.46±12.24cd 3.60±1.67d 50.17±14.84ab 34.05±14.11bc 5 BbF 8.07±0.19b — 15.23±0.25a 4.77±2.09bc 1.51±2.02bc 3.80±0.02bc 2.90±0.14bc BkF 15.36±5.07b 21.32±10.38b 4.94±1.12b 23.96±17.56b 65.43±31.82a 7.17±2.35b 7.04±5.01b BaP — — 166.63±42.37a — — — 0.05±0.04b DBA 182.67±8.12a 164.41±20.54a 17.90±7.06b 34.66±17.68b 22.84±9.08b 0.40±3.72b 1.13±9.27b 合计 Total 206.10±24.19a 185.73±50.93a 204.70±35.59a 63.39±35.80b 89.78±22.67bc 11.37±2.49c 11.12±4.89c 6 BPE 24.77±5.16a 2.21±1.99b 4.53±7.84b 11.70±3.67b 10.94±11.92b 4.80±0.04b 3.39±0.17b IPY 17.15±1.80e 321.83±15.03b 231.52±29.20c 134.50±14.40d 517.76±71.25a 11.51±0.40e 1.45±1.09e 合计 Total 41.92±6.81e 324.04±19.11b 236.04±33.37c 146.23±18.06d 528.69±83.16a 16.31±0.36e 4.84±1.12e 1) 同行数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著 (P<0.05, Duncan’s 法)
1) Different lowercase letters in the same row indicate significant difference(P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 4 苦瓜各部位中多环芳烃含量1)
Table 4 PAHs contents in various parts of Momordica charantia
苯环数
Benzene ringsPAHs w/(μg·kg–1) 根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf叶柄
Petious果皮
Peel果肉
Flesh果瓤
Pulp2 Nap 65.90±1.01b 36.56±19.76cd 92.44±1.14a 31.01±0.81d 13.37±0.44e 13.57±0.20e 45.82±3.25c Acy 45.09±4.72b 54.59±2.44a — 29.11±1.81c 11.16±0.70d 12.38±1.04d — Ace 131.82±23.98a 79.58±5.23bc — 44.58±5.28c 73.48±0.52b 68.61±1.02b 67.39±1.47bc Flu 22.27±19.43a 24.73±11.81a — 13.81±1.56ab 11.01±2.19ab 19.61±4.52a 17.31±0.81ab 合计 Total 2 645.08±10.80a 167.43±14.53b 92.44±1.14e 118.52±16.70cd 109.02±2.27de 114.17±3.41cd 130.52±5.03c 3 Phe 15.84±1.39a 16.50±0.85a 1.01±0.47e 7.58±0.74c 3.80±0.68d 4.46±0.12d 10.93±0.58b Ant — — — — — — — Fla 26.22±23.13a 36.31±5.59a 15.82±0.47a 16.29±0.94a 21.19±23.77a 39.00±0.31a 20.90±0.24a 合计 Total 42.06±24.53ab 52.81±14.53a 16.83±0.80b 23.87±16.69b 24.99±24.22b 43.46±0.19ab 31.83±0.81ab 4 Pyr 16.43±4.87b 18.62±0.99b — 12.90±2.18bc 5.98±0.56bc 12.87±0.52bc 23.19±0.88a BaA 14.84±9.67b 11.21±9.31b — 7.25±7.55b 10.30±0.08b 0.96±1.34b 57.04±19.06a Chr — — 328.73±77.31a — 1.64±0.08d 4.44±0.22c 8.29±7.20b 合计 Total 31.27±9.31cd 29.82±5.64cd 328.73±77.31a 20.15±1.59d 17.92±25.75b 18.26±2.08d 88.51±27.11bc 5 BbF — — — — — 3.47±1.87a — BkF 109.84±12.35a 80.34±7.58a — 11.03±9.47b 2.86±0.01b 1.38±0.87b — BaP — 53.98±6.60a — — — — — DBA 78.38±6.67cd 108.43±13.48c 227.15±37.24a 63.4±22.69d 0.26±8.75e 0.75±0.24e 180.23±21.23b 合计 Total 188.22±11.47a 242.74±8.69a 227.15±37.24a 74.43±9.59b 3.12±0.01b 5.60±2.60b 180.23±21.23a 6 BPE 0.65±1.10c 21.15±12.03c 199.35±1.93b 3.17±5.49c 28.44±1.11c 0.59±0.47c 241.77±43.53a IPY 110.80±13.10a — 123.32±42.53a 49.56±35.44b 27.96±2.34bc 2.43±1.46c 12.78±18.08bc 合计 Total 111.46±13.78c 21.15±12.03d 322.67±43.86a 52.73±31.96d 56.35±2.66d 3.02±1.00d 254.55±40.48b 1) 同行数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著 (P<0.05,Duncan’s 法)
1) Different lowercase letters in the same row indicate significant difference(P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 5 节瓜各部位中多环芳烃的含量1)
Table 5 PAHs contents in various parts of Benincasa hispida var. chieh-qua
苯环数
Benzene ringsPAHs w/(μg·kg–1) 根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf叶柄
Petious果皮
Peel果肉
Flesh果瓤
Pulp2 Nap 11.22±9.71ab 9.55±9.28ab 15.65±4.38a 3.94±6.85b 7.71±2.57ab 3.91±1.57b 4.12±0.53b Acy — — — 14.25±24.69a — 8.07±13.97a 8.79±15.23a Ace 38.55±33.39bc 3.77±6.53c 64.87±4.43b 9.25±8.92c 10.90±15.59c 321.16±9.95a 44.40±23.00c Flu — 16.66±15.38bc 38.39±8.69a 38.31±5.91ab — 5.39±4.76c 19.06±25.19abc 合计 Total 49.77±43.11cd 29.99±15.49cd 118.91±15.77b 62.43±18.07c 18.62±13.11d 338.83±2.71a 76.37±34.81c 3 Phe 10.61±9.20bc 14.04±7.33bc 31.23±3.28a 8.44±7.31cd 19.11±4.98b — — Ant 22.52±3.90a 2.83±2.60a 3.13±5.42a 5.84±4.76a 8.15±7.26a 3.41±5.90a — Fla 63.47±6.91a 30.56±15.68ab 34.07±2.87ab 24.02±14.81ab 30.87±5.89ab 48.29±4.54ab 12.33±0.30b 合计 Total 96.60±39.19a 47.43±6.54b 68.43±11.32ab 38.30±12.13bc 58.13±15.02b 51.69±7.22b 12.33±0.30c 4 Pyr 51.29±0.49ab 9.85±17.07b 65.20±35.60a 36.19±12.68ab 23.77±10.86b 7.63±1.50b 8.71±0.34b BaA 35.23±1.70a 31.26±0.82a 49.24±9.40ab 23.13±1.11ab 30.45±13.23a 3.22±0.47b 4.26±1.45b Chr 32.34±1.36a 14.72±7.90a 17.76±1.69ab 12.41±8.48ab 22.77±4.35a 3.61±0.07b 4.45±3.92b 合计 Total 118.86±0.31a 55.84±13.75b 132.19±46.19a 71.73±20.00b 77.99±16.87b 14.46±1.82c 17.42±3.49c 5 BbF 30.14±2.55c 27.65±10.83c 147.29±28.36b 37.84±1.79dc 43.28±11.92c 45.58±47.8c 931.05±36.01a BkF 28.84±0.05ab 18.72±4.84abc 38.98±7.80a 15.98±10.61abc 34.26±18.77ab 6.60±2.89c 12.58±8.34bc BaP 17.18±14.88a 12.35±8.18a 17.33±1.28a 7.37±12.76a 27.04±10.95a 7.13±4.27a 19.43±14.39a DBA 41.14±2.32c 40.61±9.81c 78.39±16.98b 18.50±4.09c 103.08±16.55a 15.75±40.67c 19.86±13.68c 合计 Total 117.29±14.76cd 99.35±7.10cd 281.98±39.32b 70.41±29.11cd 207.66±39.46c 60.75±34.09d 982.88±33.33a 6 BPE 15.30±1.08b 19.92±3.09b 154.93±40.35a 27.21±17.89b 30.90±14.67b — 21.57±19.68b IPY 58.13±4.42c 135.63±34.15b 473.40±24.00a 58.36±24.38c 79.17±26.11c 1.53±0.46d 1.58±0.50d 合计 Total 73.43±5.49d 155.55±33.34b 628.32±18.61a 85.57±9.17cd 110.08±12.10c 1.53±0.46e 23.14±19.97e 1) 同行数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著 (P<0.05,Duncan’s 法)
1) Different lowercase letters in the same row indicate significant difference(P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 6 丝瓜各部位中多环芳烃的含量1)
Table 6 PAHs contents in various parts of Luffa cylindrica
苯环数
Benzene
ringsPAHs w/(μg·kg–1) 根
Root茎
Stem叶
Leaf叶柄
Petious果皮
Peel果肉
Flesh果瓤
Pulp2 Nap 0.77±1.18b 14.40±14.60a 7.18±4.15ab 10.09±11.61ab 10.42±2.88ab 1.86±0.85ab 2.76±1.28ab Acy — — — — — — — Ace 124.23±30.42b 172.12±64.00a — 26.68±5.30c — 29.56±12.17c 32.18±1.61c Flu 12.31±10.67b 40.01±0.10a 15.56±26.95b 6.72±5.82b 20.16±2.35ab 13.09±2.01b 20.61±0.69b 合计 Total 137.31±35.01b 226.59±51.45a 22.01±31.53c 43.49±4.07c 30.58±2.70c 44.51±14.49c 53.56±1.85c 3 Phe 20.16±2.55d 23.92±2.60c 33.64±1.69a 15.13±1.13e 13.99±2.05e 35.58±1.78b 49.48±0.54a Ant 3.58±3.10b 3.89±3.40b 12.09±0.20a 3.44±3.24b 2.95±2.56b 3.05±0.45b 3.15±0.46b Fla 31.73±4.34c 30.46±4.20c 41.94±1.59b 18.97±1.78d 17.01±3.24d 36.12±2.31b 62.88±1.94a 合计 Total 55.47±3.54d 58.28±5.84d 87.67±3.45b 37.54±5.10e 33.95±2.93e 74.75±0.060c 115.51±3.01a 4 Pyr 39.88±5.64b 40.37±1.40b 54.34±1.50a 35.11±7.40bcd 15.24±13.31de 23.10±9.49cd 24.05±6.6bc BaA 36.36±21.18bc 41.20±1.30bc 55.06±1.30a 30.64±10.92bcd 17.11±6.86de 20.43±5.22cde 6.50±0.54e Chr 14.97±4.27b 14.98±2.40b 23.06±0.58a 8.90±1.40b 13.89±9.36b 7.25±0.75b 6.87±0.11b 合计
Total
91.21±16.83b 96.56±5.15b 132.47±3.26a 74.65±13.95c 46.25±16.35c 50.78±10.74c 57.06±7.11c 5 BbF 14.51±3.14b 15.80±2.50b 147.11±74.77a 10.27±1.49b 21.60±16.27b 6.02±0.80b 5.44±0.20b BkF 23.93±2.90bc 42.85±4.30bc 256.64±79.21a 23.92±9.97bc 79.24±3.39b 11.71±4.96c 12.06±18.51c BaP 12.43±1.07b 13.50±2.40b 23.16±1.94a 6.18±0.32c 5.44±4.75c 0.93±0.32d 0.84±0.14d DBA 17.33±7.21b 32.99±25.30b 134.52±83.90a 37.20±0.86b 30.66±13.15b 1.45±6.64b 1.92±2.38b 合计 Total 68.20±2.68d 105.14±28.94bc 561.43±33.79a 77.57±9.60cd 136.94±13.02b 20.11±0.15e 20.26±0.78e 6 BPE 29.98±6.64b 33.22±12.30b 84.97±42.57a 19.03±5.19b 15.49±7.62b 9.28±2.03b 8.56±0.35b IPY 34.71±5.64c 330.01±42.60a 248.36±94.32b 48.70±27.62c 37.95±7.52c 21.61±3.35c 6.84±0.09c 合计 Total 64.68±12.27b 363.24±35.02a 333.34±76.10a 67.73±12.85b 53.44±5.85b 30.89±5.03b 15.40±0.31b 1) 同行数据后的不同小写字母表示差异显著 (P<0.05,Duncan’s 法)
1) Different lowercase letters in the same row indicate significant difference(P<0.05, Duncan’s test)表 7 人群摄食瓜类果实产生的PAHs终生致癌风险
Table 7 Lifetime cancer risks from PAHs for people ingesting fruits of cucurbitacae vegetables
蔬菜种类
Vegetable type儿童 Child 青少年 Adolescent 成年人 Adult 老年人 Senior 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 苦瓜 Balsam pear 2.18×10–6 2.16×10–6 1.88×10–6 1.74×10–6 1.31×10–5 1.40×10–5 2.99×10–6 3.03×10–6 节瓜 Chieh qua 1.22×10–5 1.21×10–5 1.05×10–5 9.77×10–6 7.31×10–5 7.84×10–5 1.67×10–5 1.69×10–5 丝瓜 Luffa 1.85×10–6 1.84×10–6 1.60×10–6 1.48×10–6 1.11×10–5 1.19×10–5 2.54×10–6 2.58×10–6 表 8 人群摄食瓜类可食用部位产生的PAHs终生致癌风险
Table 8 Lifetime cancer risks from PAHs for people ingesting edible portions of cucurbitacae vegetables
蔬菜种类
Vegetable type儿童 Child 青少年 Adolescent 成年人 Adult 老年人 Senior 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 苦瓜 Balsam pear 3.41×10–7 3.40×10–7 2.95×10–7 2.73×10–7 2.05×10–6 2.20×10–6 4.77×10–7 4.75×10–7 节瓜 Chieh qua 2.83×10–7 2.81×10–7 2.44×10–7 2.27×10–7 1.70×10–6 1.82×10–6 3.90×10–7 3.94×10–7 丝瓜 Luffa 1.78×10–7 2.76×10–7 2.41×10–7 2.23×10–7 1.67×10–6 1.80×10–6 3.67×10–7 3.88×10–7 表 9 人群摄食黄瓜产生的PAHs终生致癌风险
Table 9 Lifetime cancer risk from PAHs for people ingesting Cucumis sativus
黄瓜部位
Cucumber part儿童 Child 青少年 Adolescent 成年人 Adult 老年人 Senior 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 男性 Male 女性 Female 果实 Fruit 1.01×10–5 9.99×10–6 8.68×10–6 8.05×10–6 6.02×10–5 6.47×10–5 1.38×10–5 1.40×10–5 果肉和果瓤 Flesh and pulp 5.21×10–7 5.18×10–7 4.50×10–7 4.18×10–7 3.21×10–6 3.35×10–6 4.70×10–7 4.75×10–7 果肉 Flesh 2.83×10–7 2.81×10–7 2.44×10–7 2.27×10–7 1.70×10–6 1.82×10–6 3.90×10–7 3.94×10–7 -
[1] 李新荣, 赵同科, 于艳新, 等. 北京地区人群对多环芳烃的暴露及健康风险评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(8): 1758-1765. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2009.08.036 [2] 赵文昌, 程金平. 环境中多环芳烃(PAHs)的来源与监测分析方法[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2006, 29(3): 105-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2006.03.042 [3] 宋冠群, 林金明. 环境样品中多环芳烃的前处理技术[J]. 环境科学学报, 2005, 25(10): 1287-1296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2005.10.001 [4] BUEHLER S, HITES R A. The Great Lakes’ integrated atmospheric deposition network[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2002, 36(17): 354A-359A. doi: 10.1021/es0224030
[5] 秦宁, 何伟, 王雁, 等. 巢湖水体和水产品中多环芳烃的含量与健康风险[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(1): 230-239. [6] GUILLEN M D, SOPELANA P, PARTEARROYO M A. Food as a source of polycyclic aromatic carcinogens.[J]. Rev Environ Health, 1997, 12(3): 133-146.
[7] ZUO Q, LIN H, ZHANG X L, et al. A two-compartment exposure device for foliar uptake study.[J]. Environ Pollut, 2006, 143(1): 126-128. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2005.11.004
[8] LISA M. CAMICHAEL T, RUSSELL F, et al. Desorption and mineralization kinetics of phenanthrene and chrysene in contaminated Soils[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1997, 31(1): 126-132. doi: 10.1021/es9602105
[9] 刘永波, 薛瑞芳, 崔磊. 超声波提取−气相色谱−质谱联用法测定城市污水处理厂脱水污泥中16种多环芳烃[J]. 化学分析计量, 2015, 24(6): 77-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2015.06.020 [10] 刘庆学, 王磊, 安彩秀, 等. 硫酸净化法测定土壤中的六六六、滴滴涕及多环芳烃[J]. 分析试验室, 2009, 28(S2): 116-121. [11] 龙明华, 龙彪, 唐璇, 等. 南宁市不同区域五种蔬菜的多环芳烃含量分析[J]. 北方园艺, 2018(5): 7-14. [12] 龙彪. 南宁市菜地土壤及蔬菜中多环芳烃的含量及来源分析[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2017. [13] NISBET I C, LAGOY P K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)[J]. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol, 1992, 16(3): 290-300. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(92)90009-X
[14] MASCLET P, MOUVIER G, Nikolaou K. Relative decay index and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Atmos Environ, 1986, 20(3): 439-446. doi: 10.1016/0004-6981(86)90083-1
[15] 翟凤英, 杨晓光. 中国居民营养与健康状况调查报告: 膳食与营养素摄入状况[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006. [16] 张珏坪. 广西南宁市蔬菜种子产业发展现状与对策研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2014. [17] ZHAO Z, ZHANG L, CAI Y, et al. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) residues in several tissues of edible fishes from the largest freshwater lake in China, Poyang Lake, and associated human health risk assessment[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2014, 104(2): 323-331.
[18] XIA Z, DUAN X, QIU W, et al. Health risk assessment on dietary exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Taiyuan, China[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2010, 408(22): 5331-5337. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.08.008
[19] BRUNE H, DEUTSCH-WENZEL R P, HABS M, et al. Investigation of the tumorigenic response to benzo(a)pyrene in aqueous caffeine solution applied orally to Sprague-Dawley rats[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 1981, 102(2): 153-157. doi: 10.1007/BF00410666
[20] 杨晓光, 翟凤英, 朴建华, 等. 中国居民营养状况调查[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2010, 11(1): 5-7. [21] 赵秀阁, 段小丽. 中国人群暴露参数手册(成人卷)概要[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2014. [22] LIAO C M, CHANG K C. Probabilistic risk assessment for personal exposure to carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Taiwanese temples[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 63(9): 1610-1619. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.08.051
[23] 秦宁, 朱樱, 吴文婧, 等. 多环芳烃在小白洋淀挺水植物中的分布、组成及其影响因素[J]. 湖泊科学, 2010, 22(1): 49-56. [24] 程琪琪, 葛蔚, 李敬锁, 等. 辣椒中多环芳烃的累积特征及健康风险评估[J]. 环境化学, 2018(2): 229-238. [25] 郭雪. 上海市郊区土壤−蔬菜系统中多环芳烃污染效应研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2015. [26] SINONICH S L, HITES R A. Organic pollutant accumulation in vegetation[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1995, 29(12): 2905-2914. doi: 10.1021/es00012a004
[27] MOECKEL C, THOMAS G O, BARBER J L, et al. Uptake and storage of PCBs by plant cuticles[J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2008, 42(1): 100-105. doi: 10.1021/es070764f
[28] WINGFORS H, LINDSTROM G, BAVEL B V, et al. Multivariate data evaluation of PCB and dioxin profiles in the general population in Sweden and Spain[J]. Chemosphere, 2000, 40(9/10/11): 1083-1088.
[29] WILD S R, JONES K C. Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon uptake by carrots grown in sludge amended soil[J]. J Environ Qual, 1992, 21(2): 217-225.
[30] SOCEANU A, DOBRINAS S, POPESCU V. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Romanian body foods and fruits[J]. Polycycl Aromat Comp, 2016, 36(4): 364-375.
[31] 杨慧仙. 种子大小和海拔对青藏高原东北缘常见植物种子主要营养成分含量的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016. [32] 焦杏春, 介崇禹, 丁力军, 等. 多环芳烃在水稻植株中的分布[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2005, 11(6): 657-659. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2005.06.001 [33] TERZAGHI E, ZACCHELLO G, SCACCHI M, et al. Towards more ecologically realistic scenarios of plant uptake modelling for chemicals: PAHs in a small forest[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2015, 505: 329-337. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.108
[34] HOWSAM M, JONES K C, INESON P. PAHs associated with the leaves of three deciduous tree species. I : Concentrations and profiles[J]. Environ Pollut, 2000, 108(3): 413-424. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00195-5
[35] 杨博. 城市典型植物叶片中PAHs的时空分布特征及迁移转化机理[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2017. [36] 李艳, 顾华, 黄冠华, 等. 北京东南郊灌区多环芳烃污染风险与人体健康风险评估[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(9): 237-249. [37] TAO S, CUI Y H, XU F L, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soil and vegetables from Tianjin[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2004, 320(1): 11-24. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00453-4
[38] 郜红建, 魏俊岭, 马静静, 等. 安徽省典型城市周边土壤−蔬菜中PAHs的污染特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(10): 1913-1919. [39] URBAT M, LEHNDORFF E, SCHWARK L. Biomonitoring of air quality in the Cologne conurbation using pine needles as a passive sampler: Part Ⅰ: Magnetic properties[J]. Atmos Environ, 2004, 38(23): 3781-3792. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.03.061
[40] 解莹然, 张娟, 李乐, 等. 北京市常用常绿树种冬季叶片多环芳烃含量及其富集特征[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2017, 39(10): 95-100. [41] GUNTHER F A, BUZZETTI F, WESTLAKE W E. Residue behavior of polynuclear hydrocarbons on and in oranges[J]. Residue Rev, 1967, 17: 81-104.
[42] 龙明华, 龙彪, 梁勇生, 等. 南宁市蔬菜基地土壤多环芳烃含量及来源分析[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2017(3): 52-57. [43] SCHROLL R, BIERLING B, CAO G, et al. Uptake pathways of organic chemicals from soil by agricultural plant[J]. Chemosphere, 1994, 28(2): 297-303. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(94)90126-0
[44] 董继元, 刘兴荣, 张本忠, 等. 上海市居民暴露于多环芳烃的健康风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(1): 126-132. [45] 葛蔚, 程琪琪, 柴超, 等. 青岛市城郊蔬菜中多环芳烃污染特征和健康风险评估[J]. 环境科学学报, 2017, 37(12): 4772-4778. [46] 吴敏敏, 夏忠欢, 张倩倩, 等. 南京市蔬菜中多环芳烃污染特征及健康风险分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(4): 447-454. [47] 殷婧, 夏忠欢, 周彦池, 等. 临汾市售蔬菜中多环芳烃污染特征及致癌风险分析[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2016, 11(3): 265-271. [48] 王丽萍, 夏忠欢, 吴敏敏, 等. 徐州市售蔬菜中多环芳烃污染与健康危害[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(3): 526-534.



 下载:
下载: