Comparing different height-diameter models of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in sandy land
-
摘要:目的
比较不同树高(H)–胸径(D)模型精度,确定适合章古台地区樟子松Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica的H-D模型。
方法以Sibbesen模型为基础模型,将优势木平均高(HT)、胸高断面积(AB)和平方平均胸径(DQM) 3个林分变量以不同组合加入基础模型中,分别建立了H-D的基础模型(1个)和广义模型(3个)及对应的基础混合模型(1个)和广义混合模型(3个)。对固定效应模型平均水平预测(FPA)、混合模型的总体平均响应预测(MPA)和主体响应预测(MPS)的精度进行比较。对混合模型在使用随机抽取样本木和抽取平均木(胸径接近平均值的样本)2种抽样方案计算随机参数时分析MPS精度与样本数量的关系。
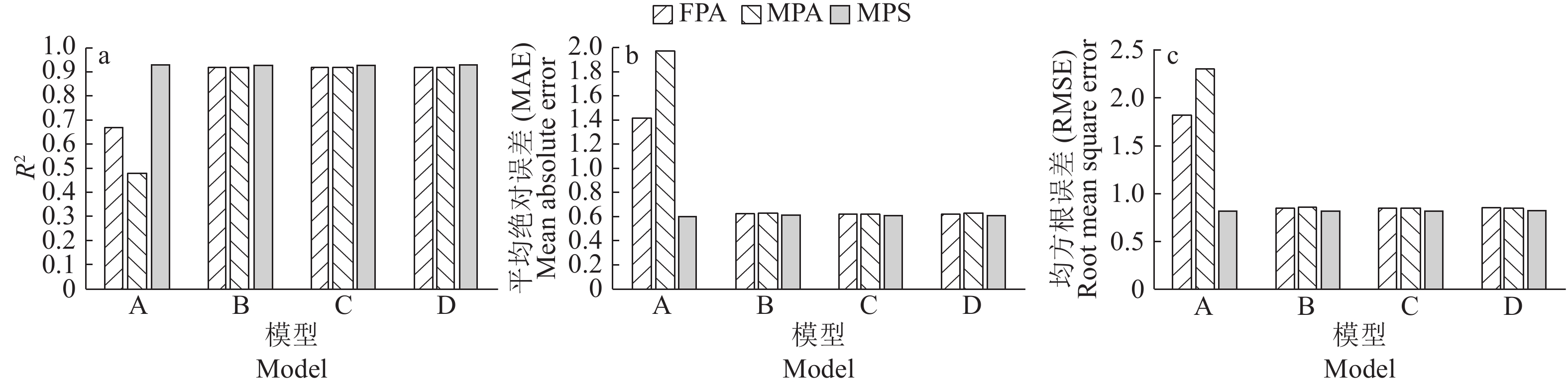
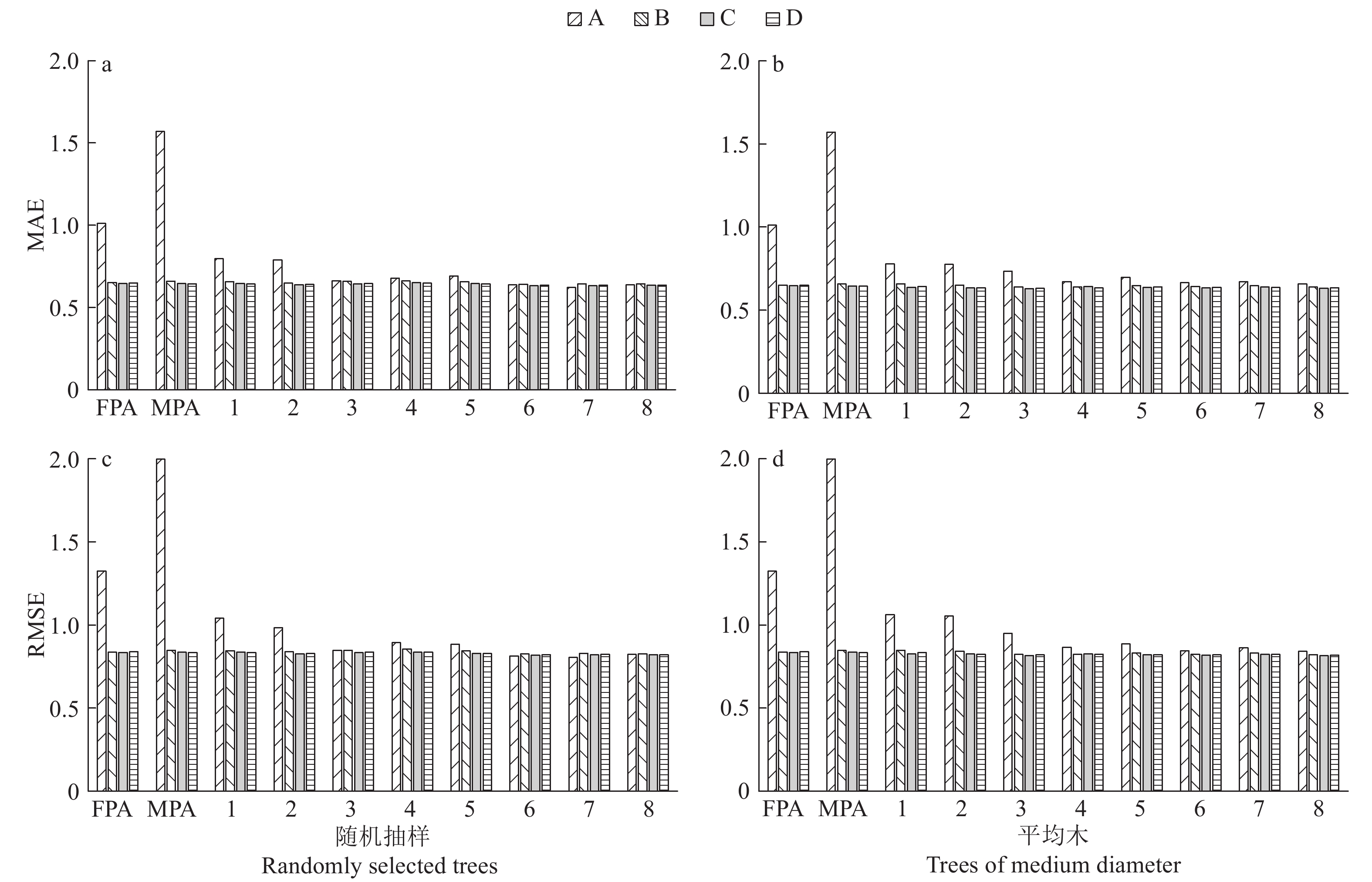
结果表征樟子松H-D关系的4种固定效应模型中,含HT和AB的广义模型拟合精度最高,Akaike信息量准则(AIC)=2 167.7,Bayesian信息量准则(BIC)=2 196.3。相同预测变量的各模型预测精度均表现为:MPS>FPA>MPA,仅含预测变量D的模型的3种预测精度差异最大。广义模型、广义混合模型、基础混合模型预测精度差异不大。使用验证数据检验模型精度时,每块标准地中随机抽取3株样本木计算基础混合模型随机参数时,该模型精度提升最为明显,MAE和RMSE分别降低了57.97%和57.63%;而广义混合模型精度随抽取样本木数量的增多未出现大的变化。
结论含有林分变量优势木平均高、胸高断面积的广义模型和基础混合模型均能较好地预测沙地樟子松人工林的单木树高。此外,利用混合模型预测树高时,推荐在标准地中随机抽取3株林木测量其树高,并依此来计算随机参数。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the accuracy of different height(H)-diameter (D) models to determine the optimal models for Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in Zhanggutai area.
MethodSibbesen model was used as the basic model. Dominant height (HT), stand basal area (AB), and quadratic mean diameter (DQM) with different combinations were added into Sibbesen model. We established one basic, three generalized, one basic mixed and three generalized mixed H-D models. The accuracies of population-averaged prediction (FPA) of fixed effects models, and mean response prediction (MPA) and specific-plot prediction (MPS) of mixed effects models were compared. For mixed models, two sampling designs, random sampling and medium-diameter tree sampling were used for random parameters estimation, and the relationship between MPS accuracy and sample size was analyzed.
ResultIn four fixed H-D models, the generalized model with HT and AB has the highest prediction precision. Akaike’s information criterion (AIC) is 2 167.7. Bayesian information criterion (BIC) is 2 196.3. Models with the same predictor variables have precision in order of MPS> FPA>MPA, and models withD as the only variable have the largest variation among three types of prediction. There are little difference in prediction accuracy among generalized models, generalized mixed models and basic mixed model. Using three randomly selected sample trees per plot to estimate random parameters of basic mixed model results in the highest model precision based on the validation data, and MAE and RMSE decrease by 57.97% and 57.63% respectively. The accuracies of generalized mixed models do not change significantly with the increase of sample size.
ConclusionBoth generalized model including HT and AB and basic mixed model can well predict tree height for P. sylvestris var. mongolica. We recommend to randomly select three sample trees per plot measuring tree heights for parameters estimation of mixed models, and calculating random parameters.
-
中国是一个农业大国,作为国家发展的根本,农业在国家经济总量中占有很大的比重。如今全球粮食供给偏紧,农业是国家战略性、基础性核心产业,在农作物的生长发育过程中,气候环境、病虫迫害、病菌侵染等严重影响其产量和品质。目前常见的农作物病害有上千种,传统的依靠人工识别农作物病害,不但耗费时间精力,而且效率低。精确迅速地辨识出农作物病害有助于及时救助,对降低农作物病害带来的产量和品质影响具有重大意义。
随着深度学习技术在物体分类方面的深入研究与计算机图像处理能力的增强,计算机视觉技术也应用在农作物病害识别上,并且取得许多成果。刘翱宇等[1]提出一种基于深度残差网络的植物病害检测网络,引入Focal Loss损失函数,对植物病害图像的检测平均准确率高达97. 96%。Srdjan等[2]将深度卷积神经网络用于植物病害识别,能够区分植物叶片与周围环境,并能够区分健康叶片与13种不同的植物病害,在开发模型测试中,单类病害的识别平均准确率高达96.3%。Albattah等[3]提出了一种改进的CenterNet网络,以DenseNet-77为基础网络对病害样本图片特征进行提取,在PlantVillage数据集上训练,然后分别对番茄、葡萄等在内的14种植物26类病害及健康叶片进行识别,检测精度比当时精确率最高的EfficientNet网络更高。刘洋等[4]针对PlantVillage数据集14种植物中的26种病害对比研究了2个轻量级网络系统MobileNet和Inceptionv3,结果表明MobileNet模型的程序数量更小,执行速率也更快,可部署于安卓操作系统中,在手机端也实现了图像识别。Saleem等[5]对Xception网络精修后,选择性能提升最明显的Adam优化器,对PlantVillage数据集中的26种植物病害进行检测,准确率达到了97.81%。孙俊等[6]使用AlexNet作为基础网络,然后通过批归一化方法、引入全局池化层和减少特征图量等方式,共获得了8种改进模式,对PlantVillage数据集14种植物的26种病害特征进行了鉴别,效果最好的检测模式平均准确度超过了98.1%。李书琴等[7]提出了一种基于轻量级残差网络,通过缩减网络卷积核数目和轻量级残差模块减少网络参数,网络参数大幅减少的同时,在PlantVillage数据集上的检测精度达到98.45%。
上述深度学习方法不仅在检测准确度方面有了较高的提升,也有向低内存、少参数量改进的趋势,从而达到高精度识别、迅速检测、易部署移动端的目的。然而,检测精度提升的同时,网络参数量也在不断增多,网络深度和宽度也不断加深,浮点运算量加大从而带来较高的延迟,实时检测的效果较差。人工智能公司旷视科技提出的YOLOX-Nano[8],有着参数量小、浮点运算快、延迟低、易部署移动端的优势且检测精度保持着中高水平。本文在原始YOLOX-Nano网络结构的基础上进行改进,在不显著增加网络内存和运算参数量的基础上,提出一种混合卷积注意力模块CBAM[9]、Mixup数据增强策略[10]、Focal Loss分类损失函数[11]和本文设计的基于CenterIOU回归损失函数的改进YOLOX-Nano模型。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 数据集的获取
试验所需要的所有病害图片数据来自于公开数据集PlantVillage网站(http://plantvillage.psu.edu),数据集记录包含54309张图像,这些图像涵盖了14种作物:苹果、蓝莓、樱桃、玉米、葡萄、柑橘、桃、甜椒、马铃薯、覆盆子、大豆、南瓜、草莓和番茄。考虑到应尽可能研究某一类农作物的多种病害(3种及以上),因此剔除数据集内仅含健康叶片的农作物数据和仅有2类病害的农作物数据,最终在公开数据集上精心挑选苹果叶片图像4645张,其中,苹果黑星病1000张、苹果黑腐病1000张、苹果松锈病1000张、健康叶片1645张;玉米叶片4354张,其中,玉米灰斑病1000张、玉米锈病1192张、玉米大斑病1000张、健康叶片1162张;葡萄叶片4369张,其中,葡萄黑腐病1180张、葡萄轮斑病1076张、葡萄褐斑病1383张、健康叶片1000张;马铃薯叶片3000张,其中,马铃薯早疫病、马铃薯晚疫病、健康叶片各1000张;草莓叶片4218张,其中,草莓叶焦病2218张,健康叶片为2000张;番茄叶片18835张,其中,番茄疮痂病1404张、番茄早疫病1000张、番茄晚疫病1909张、番茄叶霉病1000张、番茄斑枯病1771张、番茄红蜘蛛损伤1676张、番茄斑点病2127张、番茄黄叶曲叶病5357张、番茄花叶病毒病1000张和健康叶片1591张,共计6类农作物27种病害,保证各类样本间数量均衡。此外,考虑到真实场景背景复杂的情况,数据集添加了无叶片背景图像1143张。试验样本图像如图1所示。
![]() 图 1 PlantVillage部分数据集1~4 依次为苹果黑星病、黑腐病、松锈病和健康叶;5~8依次为玉米灰斑病、锈病、健康叶和大斑病;9~12依次为葡萄黑腐病、轮斑病、褐斑病和健康叶;13~15依次为马铃薯早疫病、晚疫病和健康叶;16~17 依次为草莓叶焦病和健康叶;18~27 依次为番茄疮痂病、早疫病、晚疫病、叶霉病、斑枯病、红蜘蛛损伤、斑点病、黄叶曲叶病、花叶病毒病和健康叶;28为无叶片背景图Figure 1. Partial dataset of PlantVillage1−4 are apple scab, apple black rot, cedar apple rust and apple healthy leaves in turn; 5−8 are corn Cercospora zeaemaydis Tehon and Daniels, corn Puccinia polysora, corn healthy leaves and corn Curvularia leaf spot fungus; 9−12 are grape black rot, grape black measles, grape leaf blight fungus and grape healthy leaves in turn; 13−15 are potato early blight, potato late blight and potato healthy leaves in turn; 16−17 are strawberry leaf scorch and healthy leaves in turn; 18−27 are tomato bacterial spot bacteria, tomato early blight, tomato late blight water mold, tomato leaf mold, tomato septorial leaf spot, tomato spider mite damage, tomato target spot bacteria, tomato YLCV virus, tomato ToMV disease and tomato healthy leaves in turn; 28 is bladeless background image
图 1 PlantVillage部分数据集1~4 依次为苹果黑星病、黑腐病、松锈病和健康叶;5~8依次为玉米灰斑病、锈病、健康叶和大斑病;9~12依次为葡萄黑腐病、轮斑病、褐斑病和健康叶;13~15依次为马铃薯早疫病、晚疫病和健康叶;16~17 依次为草莓叶焦病和健康叶;18~27 依次为番茄疮痂病、早疫病、晚疫病、叶霉病、斑枯病、红蜘蛛损伤、斑点病、黄叶曲叶病、花叶病毒病和健康叶;28为无叶片背景图Figure 1. Partial dataset of PlantVillage1−4 are apple scab, apple black rot, cedar apple rust and apple healthy leaves in turn; 5−8 are corn Cercospora zeaemaydis Tehon and Daniels, corn Puccinia polysora, corn healthy leaves and corn Curvularia leaf spot fungus; 9−12 are grape black rot, grape black measles, grape leaf blight fungus and grape healthy leaves in turn; 13−15 are potato early blight, potato late blight and potato healthy leaves in turn; 16−17 are strawberry leaf scorch and healthy leaves in turn; 18−27 are tomato bacterial spot bacteria, tomato early blight, tomato late blight water mold, tomato leaf mold, tomato septorial leaf spot, tomato spider mite damage, tomato target spot bacteria, tomato YLCV virus, tomato ToMV disease and tomato healthy leaves in turn; 28 is bladeless background image1.2 数据预处理网络训练参数设置
首先将所有样本图像的分辨率转变成416×416,使用标注工具LabelImg将所有样本按Pascal VOC数据集的标注,生成.xml类型的标注文件。此外,从试验数据集图像中随机选择60%样本(约23235张)用于训练模型,20%的样本(约7675张)用来验证,20%样本(约7675张)用于测试。
试验运用迁移学习,让YOLOX-Nano在大规模公开数据集Image Net上进行训练,获得一个收敛的预训练权重,然后利用这个预训练权重迁移到改进的YOLOX-Nano网络模型中进行参数调优。训练过程中超参数设置为每批量样本数为32,1次遍历完全部训练集数据称为1次迭代,批量设置为100。采用随机梯度下降(Stochastic gradient descent,SGD)优化算法调优网络参数,初始学习率设置为0.01,动量因子为0.9,每经过10次迭代训练,将学习率降低1/10,模型迭代1次保存1次权重。
1.3 基于改进YOLOX-Nano的农作物叶片病害检测与识别
1.3.1 YOLOX-Nano网络
YOLOX-Nano作为YOLOX系列的最轻量化版本,对比YOLOX-X、YOLOX-L、YOLOX-M、YOLOX-S、YOLOX-Darknet和YOLOX-Tiny高性能版本,其通过降低网络的宽度和深度、减少模型运算的参数量、取消训练时Mixup数据增强方式等改进,使网络结构更简单,速度更快。
YOLOX-Nano的结构如图2a所示,整个YOLOX-Nano可以分为3个部分,分别是CSPDarkNet主干提取网络[12]、特征金字塔网络(Feature pyramid network,FPN)[13]和路径聚合网络(Path aggregation network,PAN)[14]中间层以及YoloHead输出层。
输入的图片首先在CSPDarkNet进行特征提取,提取到3个特征层进行下一步网络的构建,FPN是YOLOX-Nano的加强特征提取网络,在主干部分获得的3个特征层会在这一部分进行特征融合,获取不同尺度的特征信息。在FPN部分,已经获得的有效特征层被用于继续提取特征,在PAN层中,网络会对特征进行阶段上采样和下采样操作实现特征融合。YoloHead是YOLOX-Nano的分类器与回归器,输入图片通过CSPDarkNet、FPN和PAN层已经获得了3个加强特征层,每一个特征图看作每一个特征点的集合,而YoloHead会对特征点进行判断,判断特征点是否有物体与其对应。YOLOX-Tiny的YoloHead被分为了2部分,分别实现检测和分类操作,最后在预测阶段将两者整合输出结果。
由于YOLOX-Nano宽度和深度较浅,没有充分学习输入特征向量通道与空间之间的重要程度关系,对近似的难分辨目标预测效果较差,其次数据集内多种农作物病害图像样本复杂多样,二分类交叉熵损失(Binary cross entropy loss,BCELoss)作为分类损失函数将困难样本和容易样本赋予相同的权重进行训练,这样造成一些困难样本分类效果不理想,GIOU损失函数对2个候选框没有相交时,IOU=0,不能反映两者的距离大小,也无法精确反映两者的重合度大小,不利于梯度回传和学习训练,致使密集病害定位缺失。
综合以上问题,本文在YOLOX-Nano模型混合了卷积注意力CBAM模块,引入了Mixup数据增强方式来充实样本集,让网络训练地更充分,最后分类损失函数将BCELoss替换为Focal Loss,回归损失函数将GIOU Loss替换为CenterIOU Loss,改进后的YOLOX-Nano网络结构图如图2b所示。
1.3.2 混合卷积注意力机制CBAM模块
在农作物病害检测与识别任务中,农作物叶片病害特征大体相似,只有细节部分略有差异。YOLOX-Nano作为浅层模型,检测精度不够高,这是需要注意的地方。
注意力机制是运用在深度学习模型中常见的小技巧,是实现网络自适应注意的一个方式,核心重点是让网络关注到它需要关注的特征,忽略不重要的特征,主要分为通道注意力机制和空间注意力机制,卷积注意力机制结构如图3所示。卷积注意力机制的前半部分为通道注意力机制,通道注意力机制先针对输入进来的单个特征层,依次执行全局平均池化方法和全局最大池化方法,之后再针对平均池化和最大池化的结果,利用共享的全连接层进行处理,然后再对处理后的2个结果进行相加,之后再通过Sigmoid激活函数,得到输入特征层中每一条通道的加权值(0~1)。将这个权值乘上原输入特征层即可得到经过通道注意力机制处理后的特征图。卷积注意力机制的后半部分为空间注意力机制,首先对通过通道注意力机制处理的特征层每一个特征点的通道取最大值和平均值,之后将这2个结果进行堆叠,利用通道数为1的卷积核卷积调整通道数,再经过Sigmoid激活函数,获得输入特征层每一个特征点的权值(0~1),然后将这个权值乘上原输入特征层即可得到最终处理的特征层。
本文引入CBAM注意力机制模块,结合通道注意力机制和空间注意力机制,对输入的特征层分别进行通道注意力机制和空间注意力机制的处理,卷积注意力机制对不同通道的特征图进行权重的重新分配,加强网络结构深层信息提取,让网络关注到它需要关注的特征,忽略不重要的特征。
输入图像经过主干特征提取网络后获得3个有效特征层,在构建FPN层上采样前首先将经由加强特征提取网络的3个有效特征层送入CBAM模块,自动学习特征通道之间的相关性,输出3个尺度的检测结果,再经过卷积层提取特征。随后进行PAN的构建,在PAN融合的下采样前,把主干特征网络获得的3个有效特征层,再经过CBAM注意力机制模块进行融合,然后经过另一个卷积模块再一次提取特征,将最后一个有效特征层卷积,最终获得3个特征。
1.3.3 引入Mixup数据增强策略
Mixup是一种混类增强的数据增强策略,它可以将不同类的图像进行混合,从而扩充训练数据集。 Mixup数据增强策略原理是假设
${\text{batch}}_{x1}$ 是一个批次的图像样本,${\text{batch}}_{y1}$ 是该批次图像样本对应的标签;${\text{batch}}_{x2}$ 是另一个批次图像样本,${\text{batch}}_{y2}$ 是另一个批次图像样本对应的标签,λ是由参数为α、β的Beta分布计算出来的混合系数。由此可以得到Mixup原理公式为
$$ { \lambda =}{\rm{Beta}}(\alpha ,\beta ) \text{,} $$ (1) $$ {\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{d}\_\mathrm{b}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{h}}_{{x}}=\mathrm{\lambda }\times {{\rm{batch}}}_{x1}+(1-\mathrm{\lambda })\times {{\rm{batch}}}_{x2} \text{,} $$ (2) $$ {\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{d}\_\mathrm{b}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{h}}_{{y}}=\mathrm{\lambda }\times {{\rm{batch}}}_{y1}+(1-\mathrm{\lambda })\times {{\rm{batch}}}_{y2} 。 $$ (3) 以玉米病害图像为例,在训练时先读取1张样本图像,图像两侧填充,放大图片到416×416(图4a),再随机选取1张样本图像,也放大到416×416(图4b)。然后设置1个融合系数,如0.5,将2张图像加权融合,最终得到完整的图像(图4c)。
在YOLOX中以Mosaic为基础,Mixup策略作为一种额外的数据增强策略,在浅层模型用Mixup数据增强策略会降低平均精确率(Average precision,AP),所以YOLOX-Nano没有使用Mixup数据增强策略。本文使用Mixup数据增强策略,加大样本数据量防止模型欠拟合。根据图5中的Beta分布概率密度曲线,当α=β= 1时,等于(0,1)均匀分布;当α=β < 1时,表现为两头的概率大,中间的概率小,当α=β→0时,相当于{0,1}二项分布,要么取0,要么取1,等于原始数据没有增强,本试验随机设置Mixup参数α=β∈[0.1,0.9],就可以得到多样化的λ∈(0,1)区间内的概率分布,使数据增强更具有随机性,模型更具有鲁棒性。
1.3.4 分类损失函数的改进
一个好的损失函数对于网络参数调优达到事半功倍的效果。由于多种农作物叶片病害纹理特征大致形似,模型对一些病害样本计算的分类置信度产生偏差,进而影响样本分类效果,造成错误分类病害的情况。
基于以上计算样本分类置信度偏差的问题,YOLOX-Nano将分类损失函数由BCE Loss损失函数替换为Focal Loss损失函数,其能控制容易分类和难分类样本的权重,通过减少易分类样本的权重,使得模型在训练时更专注于难分类的样本,让容易样本对损失产生贡献小,难样本对损失产生贡献大。
Focal Loss分类损失函数公式定义如式(4)所示,
$ \hat {p} $ [$ \hat {p} $ ∈(0,1) ]表示预测值,$ y $ 表示真实值,$ \gamma $ ($ \gamma $ ≥0)表示调节因子。设$p_{\rm{t}}$ 表示预测某真实标签的概率,定义如式(5)所示,范围为[0,1]。由式(4)、(5)归纳后Focal Loss (FL)损失函数公式如式(6)所示:$$ {\rm{f}}\left(x\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{l}-{(1-\hat {p})}^{\gamma }\mathrm{ln}\left(\hat {p}\right), {\rm{if}}\;y=1\\ -{\hat {p}}^{\gamma }\mathrm{ln}\hat {p},{\rm{if}}\;y=0\end{array}\right. \text{,} $$ (4) $$ {\rm{f}}\left(x\right)=\left\{\begin{array}{l}\hat {p},{\rm{if}}\;y=1\\ 1-\hat {p},其他\end{array}\right. \text{,} $$ (5) $$ {\rm{FL}}\left({p}_{{\rm{t}}}\right)=-{(1-{p}_{{\rm{t}}})}^{\gamma }\mathrm{ln}{p}_{{\rm{t}}} 。 $$ (6) 与交叉熵函数损失函数相比,公式(6)多了一个
${(1-{p}_{{\rm{t}}})}^{\gamma }$ 系数,实质是对交叉熵损失函数的优化。如图6所示,可以通过改变$ \gamma $ 调节因子的值,从而控制容易分类和难分类样本对损失的贡献。由公式(6)可知,若某样本类别概率${ p_{\rm{t}} }$ 趋于1,说明预测值$\hat {p}$ 接近于真实值$ y $ ,这类样本就属于容易区分的样本,此时系数${(1-{p}_{{\rm{t}}})}^{\gamma }$ 趋于0,对损失贡献极少。1.3.5 回归损失函数的改进
YOLOX-Nano在回归候选框时仍使用GIOU损失函数,本文根据数据集图片样本特点,设计出利于回归候选框的CenterIOU损失函数。
如图7所示,已知候选框中心点(
$ {x}_{\mathrm{p}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}} $ ,$ {y}_{\mathrm{p}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}} $ )、真实框中心点($ {x}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{g}} $ ,$ {y}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{g}} $ )与最小外接矩形中心点(${{x}}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{t}}$ ,$ {y}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{t}} $ )。根据公式(7)计算候选框和真实框的IOU,式中,${{\mathrm{B}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{X}}_{\mathrm{交}\mathrm{集}}}$ 、${{\mathrm{B}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{X}}_{\mathrm{并}\mathrm{集}}} $ 分别表示候选框和真实框的交集和并集;构造候选框中心点和真实框中心点两点的一般直线方程$ Y = Ax + By + C $ ;根据公式(8)计算最小外接矩形中心点($ {x}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{t}} $ ,$ {y}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{t}} $ )到两框中心点的直线距离(Distance);最后代入公式(9),得到候选框回归损失。$$ \mathrm{I}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{U}=\dfrac{{\mathrm{B}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{X}}_{\mathrm{交}\mathrm{集}}}{{\mathrm{B}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{X}}_{\mathrm{并}\mathrm{集}}} \text{,} $$ (7) $$ \mathrm{D}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{e}=\dfrac{|A{x_0}+B{y_0}+C|}{\sqrt{({A}^{2}+{B}^{2})}} \text{,} $$ (8) $$ \mathrm{C}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{I}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{U}\_\mathrm{L}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{s}= 1-(\mathrm{I}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{U}-\mathrm{D}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{s}\mathrm{t}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{e}) \text{。} $$ (9) 由于定位损失函数更换为CenterIOU损失函数,较原GIOU函数让网络学习到预测框和目标框的相对位置,网络在反向传播时能更好地调优回归参数。
1.4 病害检测系统的设计
为获取实际状态下病害检测所需时间,对比网络改进前后的效果,以训练好的模型为基础,开发手机端病害识别系统。利用IOS官方的Core ML Tools模型转换库将训练好的pth格式模型转换为IOS平台使用的格式。前端界面提供图库、识别、保存3个按钮,对应调用相册上传识别图片、快速识别作物病害、保存识别记录3种功能。编译后生成安装文件部署在iPhone 8手机,显示如图8所示。
1.5 评价指标
对于农作物叶片病害检测,需要网络具有高精确率和实时性。本文采用 COCO mAP@[0.50:0.05:0.95][15-16] 作为农作物病害检测评价指标来综合评估模型对苹果、玉米、苹果、玉米、葡萄、马铃薯、草莓、番茄6类农作物的27种病害和无叶片背景图像的检测性能,即分别在IOU阈值设置以0.05的步距从0.50开始遍历至0.95,取这些阈值条件下评估所得到的平均准确率(Average precision,AP)及其均值(Mean average precision,mAP)。mAP与准确率(Precision,P)、召回率(Recall, R)有关,其计算公式如下所示:
$$ {P}=\dfrac{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}+\mathrm{A}\mathrm{P}}\times 100{\text{%}} \text{,} $$ (10) $$ {R}=\dfrac{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{T}\mathrm{P}+\mathrm{F}\mathrm{N}}\times 100{\text{%}} \text{,} $$ (11) $$ \mathrm{A}\mathrm{P}={\displaystyle\int }_{0}^{1}\mathrm{P}\left(R\right)\mathrm{d}R \text{,} $$ (12) $$ \mathrm{m}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{P}=\dfrac{1}{{M}}{\displaystyle\sum} _{k=1}^{\mathrm{M}}\mathrm{A}\mathrm{P}\left(k\right)\times 100\mathrm{{\text{%}}} \text{,} $$ (13) 式中,TP表示被模型预测正确的正样本数,FP为被模型预测错误的正样本数,FN为被模型预测错误的负样本数,M为类别总数,AP(k)为第k类平均准确率。
将训练好的模型部署移动端系统后,检测单张样本图像所消耗的平均时间(包含程序加载图片所耗时间和检测时间)作为实时性指标,单位为 s。参数量指标指深度网络模型中可训练参数的个数,以百万为单位,表示为1×106。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 改进方法性能分析
使用YOLOX-Nano模型为基础网络,分别引入CBAM卷积注意力机制、Mixup数据增强策略、使用Focal Loss替换原分类损失函数BCELoss,本文设计CenterIOU损失函数替换原回归损失函数GIOU作为改进网络。
2.1.1 融合CBAM卷积注意力机制
YOLOX-Nano对农作物病害叶片检测与识别的精度较低,单张样本图片检测精准率仅为97.97%,其原因是6种农作物27类病害的叶片病态特征表现比较相似。通道注意力可对特征图的不同通道赋予不同特征,选择性增大不同病害斑点特征通道的权重值;空间注意力对同一特征图不同位置特征点给予不同权重,区别对待特征图内部像素点。
引入CBAM卷积注意力机制模块后,虽然模型参数量由0.92×106增加到0.96×106、单张样本推断时间增加18 ms,但平均精确率由97.97%提升到98.89%,提升了0.92个百分点,在很大程度上提升了对两者叶片病害识别的准确率。两者结合可总体提升识别准确率,表明了CBAM模块区别相似物体的有效性。
利用Grad-CAM[17]工具可视化进入FPN层前第一个CBAM卷积注意力机制[18],明确对特征提取的效果。由于玉米病害的样本特征更为接近,可视化效果更佳,本文以玉米灰斑病样本、玉米锈病样本、玉米大斑病样本和健康玉米样本为例进行展示,如图9所示,引入卷积注意力机制前,网络对样本特征提取较随机,对叶片病害区域特征点关注不够。引入CBAM卷积注意力机制后,网络在前向传播过程中,重要特征通道逐渐占有更大的比重,能让网络学习到需重点关注的部分,使改进的YOLOX-Nano模型可以更高效地提取图像难区分的特征信息。
![]() 图 9 Grad-CAM可视化添加CBAM前后玉米叶片特征提取的热力图图片的颜色由黑到蓝再到黄直到红,依次表示网络对某区域特征关注逐渐增多Figure 9. Grad-CAM visual characteristic extraction thermal diagram of corn leaf before and after adding CBAMThe color of the image changes from black to blue, then yellow to red, indicating that the network gradually pays more attention to the characteristics of a certain area
图 9 Grad-CAM可视化添加CBAM前后玉米叶片特征提取的热力图图片的颜色由黑到蓝再到黄直到红,依次表示网络对某区域特征关注逐渐增多Figure 9. Grad-CAM visual characteristic extraction thermal diagram of corn leaf before and after adding CBAMThe color of the image changes from black to blue, then yellow to red, indicating that the network gradually pays more attention to the characteristics of a certain area2.1.2 训练引入Mixup数据增强策略
使用Mixup数据增强策略训练的网络模型单张样本图片检测时间较改进前平均减少了4 ms,其检测准确率却增加了1.02个百分点,一方面减少了检测推断所用时间,另一方面可以提高对农作物病害检测精度,可见引入Mixup数据增强策略扩充数据集可以提升农作物病害检测的效率,模型可以训练更充分,减少推断时间。
2.1.3 引入Focal Loss损失函数试验
由式(6)可知,调节因子γ可以控制样本对损失的贡献,从而影响到病害分类的性能。试验中通过调节γ值来检测病害分类的效果,试验结果表明,γ取0时mAP为97.97%,γ取1时mAP为98.69%,γ取2时mAP为99.02%,γ取3时mAP为98.42%,γ取4时mAP为97.32%,mAP随γ值的增大呈现先升高后降低的趋势,当γ设置为2时,mAP最大,检测效果最好。
图10a、10b是选取γ为2时Focal Loss损失函数和原BCELoss损失函数在训练和测试阶段的分类损失的变化曲线,可以发现,改进后的YOLOX-Nano分类损失总体趋势都是低于YOLOX-Nano的。
改进后的YOLOX-Nano网络训练到100个迭代结束,训练和测试阶段均呈现出持续下降的趋势,且还存在下降空间,说明网络仍在学习,分类精度仍有上升的可能性,而曲线逐渐趋于稳定,说明网络过拟合已经没有学习必要。
2.1.4 引入CenterIOU损失函数
不同的回归框损失函数对检测精度带来不同程度的影响。试验通过比较GIOU和本文设计的CenterIOU损失函数的性能,来确定最适合的回归损失函数,最终试验表明使用GIOU的YOLOX-Nano在mAP50、mAP50:95的检测精度分别为98.23%和97.97%,而使用CenterIOU损失函数的YOLOX-Nano在mAP50、mAP50:95的检测精度分别为98.53%和98.20%,较改进前分别提高了0.30和1.23个百分点,本文设计的CenterIOU损失函数与YOLOX-Nano网络组合后,在数据集上对不同阈值表现得更好,能够明显地提高农作物病害的检测精度。
2.2 YOLOX-Nano改进前后总体性能分析
改进后的YOLOX-Nano模型参数量虽然增加了0.06×106,单张图片检测时间增加了11 ms,但是改进后的YOLOX-Nano网络对所有农作物病害的平均检测精度达到了99.56%,较改进前精度(97.97%)提升了1.59个百分点。改进后的模型对苹果松锈病、葡萄黑腐病、马铃薯早疫病、马铃薯晚疫病、番茄叶霉病、番茄斑枯病和番茄黄叶曲叶病的识别精度都达到了100%,对玉米灰斑病识别精度(98.66%)稍低,主要原因是玉米大斑病与灰斑病病害症状相似,不易判断,导致出现错分类现象。
同时,无叶片背景图这一类别存在背景中包含叶片的情况,模型能检测出叶片的存在,进而导致2个模型对无叶片背景图识别精度都表现较低,这也证明了本模型没有出现过拟合的现象,改进的网络有很好的农作物病害检测与识别能力。
图11是改进前后网络训练平均精度和训练迭代的效果图,可见在训练10个迭代时,改进的YOLOX-Nano就能比改进前产生整体较高的mAP,预训练权重很快适应改进网络,趋于平稳,直到100个迭代训练结束,最终改进后的YOLOX-Nano精度更高。
2.3 不同算法的对比试验
本文还与现阶段较成熟的轻量型模型ResNet-18、MobileNet-v2、YOLOv4-Tiny、YOLOX-Tiny[19-24]进行对比,试验结果如表1所示,改进后的YOLOX-Nano检测准确率较其他轻量型网络高出1.0~2.2个百分点。在真机测试的检测时间对比中,本文提出方法的优势更加明显,单张样本图片检测时间仅需0.187 s,较其他各类模型节省大约20~240 ms的计算时间。不仅如此,在参数量方面,本文方法较ResNet-18减少了91.3%、较YOLOv4-Tiny减少了83.9%、较YOLOX-Tiny减少了80.7%、较MobileNet-v2减少了72.0%,更小的参数量意味着更少的部署成本,因此改进后模型的综合性能非常优秀,对于农业应用具有明显的优势。
表 1 与主流轻量型网络性能对比Table 1. Performance of the model versus mainstream lightweight network模型
Model参数量(×106)
No. of parameters平均精确率/%
Mean average precision单张图片检测时间/s
Detection time of single imageYOLOX-Nano 0.92 97.97 0.176 ResNet-18 11.24 98.60 0.429 MobileNet-v2 3.40 97.33 0.189 YOLOv4-Tiny 6.06 97.42 0.382 YOLOX-Tiny 5.06 98.58 0.286 改进YOLOX-Nano
Improved YOLOX-Nano0.98 99.56 0.187 2.4 病害检测系统识别效果
为验证本网络移动端部署可行性和所提出网络的实际分类效果,从试验数据集中,随机取出50张图片,录入手机端系统进行识别,手机端检测部分结果如图12a、12b所示。经检测,所有图片病害全部识别准确,置信度保持在99.4%以上,最高置信度表现在苹果、葡萄和马铃薯3种作物的病害检测,均保持在99.8%以上,实际运行最多耗时0.324 s,最少耗时0.169 s,平均耗时为0.187 s。此外,从苹果、玉米、葡萄、马铃薯、草莓、番茄6类农作物病害样本中各筛选5张田间拍摄照片进行检测,部分检测结果如图12c、12d所示,所有病害依然识别准确,仍保持着99%以上的置信度,识别速度并未减弱,也无漏检错检的情况。可见本改进模型的检测效果和运行速度都保持着较高的水平,同时达到了精度和速度的平衡。
3. 结论
相对于人工诊断农作物病害,利用计算机视觉方法检测农作物病害具有成本低、准确率高、时延短的优点。本文通过在YOLOX-Nano分类模型中引入空间和通道注意力机制和Mixup数据增强策略,将分类损失函数更换为Focal Loss,提出一种改进的YOLOX-Nano优化网络,利用此网络对农作物病害数据集进行训练与测试,得出以下结论。
1) 改进的YOLOX-Nano网络对PlantVillige数据集中6种农作物27种病害的检测总体mAP达到了99.56%,较YOLO-Nano基础网络提升了1.59个百分点,单张图片平均检测时间为0.187 s,仅仅较基础网络增加11 ms的推断延迟,达到了精度与速度的平衡,而且网络参数量为0.98×106,利于植保无人机设备和移动端设备的部署。
2) 卷积注意力机制可以对不同通道的特征图进行权重的重新分配,加强网络结构深层信息的提取,对于很多细粒度特征的提取具有很好的效果,此外Mixup数据增强策略对一些小型网络也能起到促进作用;Focal Loss能控制容易分类和困难分类样本的权重,通过减少易分类样本的权重,在训练时更专注于难分类的样本,让容易样本对损失贡献小,难样本对损失贡献大。
3) 本文提出的CenterIOU损失函数对本数据集训练具有促进作用,也可以推广应用到其他数据集。
-
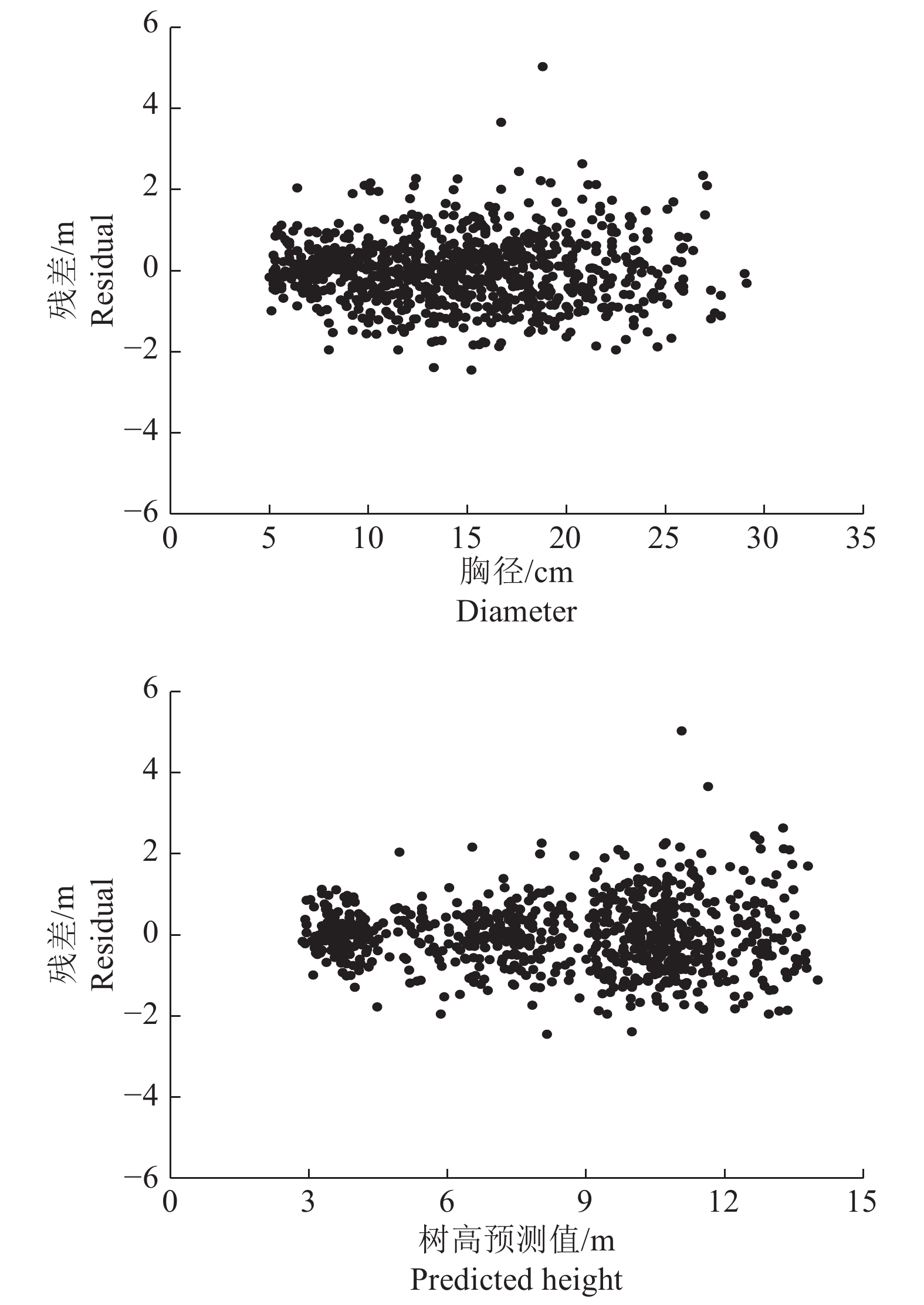
图 3 不同抽样方案下各模型平均绝对误差(MAE)和均方根误差(RMSE)随样本木数量变化情况
FPA中,A~D依次为式(6)~(9);MPA及1~8抽样中,A~D依次为式(10)~(13)
Figure 3. Relationship between mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE) and number of sample trees based on different sampling designs
FPA: A-D are eq.(6)-(9); MPA and different sampling design: A-D are eq. (10)-(13)
表 1 沙地樟子松标准地的林分与树木指标统计
Table 1 Summary statistics of stand and tree indices of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica sample plot
变量1)
Variable总数据 Total data 建模数据 Modeling data 检验数据 Validation data $\overline x \pm {\rm{SE}} $ 最小值
Min.最大值
Max.$\overline x \pm {\rm{SE}} $ 最小值
Min.最大值
Max.$\overline x \pm {\rm{SE}} $ 最小值
Min.最大值
Max.H/m 8.5±0.1 2.1 16.1 8.3±0.1 2.1 16.1 9.2±0.2 2.2 14.3 D/cm 14.6±0.2 5.0 29.1 14.3±0.2 15.0 29.1 15.8±0.3 5.1 28.6 Drange/cm 10.9±0.4 5.7 16.5 10.9±0.4 5.7 16.5 11.0±0.9 7.3 14.2 Dmax/cm 22.0±0.9 10.0 29.1 22.0±1.0 10.0 29.1 21.9±2.1 11.9 28.6 Dmin/cm 11.0±0.8 1.9 18.0 11.1±0.9 1.9 18.0 10.9±1.9 3.3 18.0 A/a 36±2 13 62 36±3 13 62 36±6 13 56 N/(trees·hm–2) 842±80 300 2 500 862±96 300 2 500 764±112 450 1 175 HT/m 9.7±0.5 3.2 13.6 9.7±0.6 3.2 13.6 10.0±1.1 4.1 12.7 AB/(m2·hm–2) 15.26±1.04 2.92 33.34 15.16±1.19 4.28 33.34 15.65±2.31 2.92 21.97 DQM/cm 16.7±0.9 7.0 24.0 16.6±1.0 7.0 23.9 16.8±1.9 7.7 21.9 1) Drange、Dmax 和Dmin 分别为样地内胸径的分布范围值、最大值和最小值;A:树龄;N:林分密度;HT:优势木平均高;AB:胸高断面积;DQM:平方平均胸径
1) Drange, Dmax and Dminare the distribution range value, maximum and minimum of DBH in the plot; A: Age of stand; N: Stand density; HT: Dominant height; AB: Stand basal area; DQM: Quadratic mean diameter表 2 基础和广义模型各参数估计结果及统计量
Table 2 Parameter estimates and evaluation statistics of basic and generalized models
公式 Formula β1 β2 β3 β4 β5 β6 σ2 AIC BIC LL (6) 14.242 3 –27.039 5 1.784 9 3.305 1 3 498.3 3 517.4 –1 745.2 (7) –0.105 1 –5.428 3 1.442 1 1.073 6 0.724 7 2 184.8 2 208.6 –1 087.4 (8) 0.190 2 –4.472 6 1.217 7 1.112 6 0.055 7 0.709 8 2 167.7 2 196.3 –1 077.9 (9) 0.404 3 –4.646 1.222 3 1.177 7 0.045 9 –0.034 5 0.709 3 2 168.2 2 201.5 –1 077.1 表 3 混合模型参数估计及统计量
Table 3 Parameter estimates and evaluation statistics of mixed model
公式 Formula β1 β2 β3 β4 β5 β6 σi2 σ2 AIC BIC LL (10) 10.258 1 –7.630 1 1.565 7 9.617 6 0.682 2 284.3 2 308.2 –1 137.2 (11) 0.211 3 –6.414 4 1.491 4 1.046 9 7.98×10−3 0.681 2 163.3 2 191.9 –1 075.7 (12) 0.248 3 –5.571 8 1.378 5 1.030 0 0.043 0 5.81×10−3 0.680 2 158.2 2 191.6 –1 072.1 (13) 0.375 3 –5.693 8 1.380 3 1.085 9 0.034 9 –0.029 1 5.65×10−3 0.680 2 159.3 2 197.4 –1 071.6 -
[1] SHARMA M. Comparing height-diameter relationships of boreal tree species grown in plantations and natural stands[J]. For Sci, 2016, 62(1): 70-77.
[2] HUANG S M, TITUS S J. An age-independent individual tree height prediction model for boreal spruce-aspen stands in Alberta[J]. Can J For Res, 1994, 24(7): 1295-1301. doi: 10.1139/x94-169
[3] 陈义刚, 谢正生, 张祥生, 等. 粤北低山丘陵地区小红栲生长过程分析[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 1994, 15(2): 124-128. [4] CORRAL-RIVAS S, ÁLVAREZ-GONZÁLEZ J G, CRECENTE-CAMPO F, et al. Local and generalized height-diameter models with random parameters for mixed, uneven-aged forests in Northwestern Durango, Mexico[J]. For Ecosyst, 2014, 1(1): 6. doi: 10.1186/2197-5620-1-6
[5] 臧颢, 雷相东, 张会儒, 等. 红松树高–胸径的非线性混合效应模型研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2016, 38(6): 8-16. [6] 樊伟, 许崇华, 崔珺, 等. 基于混合效应的大别山地区杉木树高–胸径模型比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 2017, 28(9): 2831-2839. [7] HUANG S M, WIENS D P, YANG Y Q, et al. Assessing the impacts of species composition, top height and density on individual tree height prediction of quaking aspen in boreal mixed woods[J]. For Ecol Manage, 2009, 258(7): 1235-1247. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2009.06.017
[8] LEI X D, PENG C H, WANG H Y, et al. Individual height-diameter models for young black spruce (Picea mariana) and jack pine (Pinus banksiana) plantations in New Brunswick, Canada[J]. For Chron, 2009, 85(1): 43-56. doi: 10.5558/tfc85043-1
[9] ZEIDE B, VANDERSCHAAF C. The effect of density on the height-diameter relationship[C]// OUTCALT K W. Proceedings of the 11th biennial southern silvicultural research conference. Knoxville: General Technical Report SRS-48, 2002: 463-466.
[10] VAN LAAR A, ACKA A. Forest Mensuration[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2007: 383.
[11] SHARMA M, ZHANG S Y. Height-diameter models using stand characteristics for Pinus banksiana and Picea mariana[J]. Scand J For Res, 2004, 19(5): 442-451. doi: 10.1080/02827580410030163
[12] 符利勇, 张会儒, 唐守正. 基于非线性混合模型的杉木优势木平均高[J]. 林业科学, 2012, 48(7): 68-71. [13] 王冬至, 张冬燕, 张志东, 等. 基于非线性混合模型的针阔混交林树高与胸径关系[J]. 林业科学, 2016, 52(1): 30-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1126.2016.01.006 [14] CALAMA R, MONTERO G. Interregional nonlinear height-diameter model with random coefficients for stone pine in Spain[J]. Can J For Res, 2004, 34(1): 150-163. doi: 10.1139/x03-199
[15] 符利勇, 孙华, 张会儒, 等. 不同郁闭度下胸高直径对杉木冠幅特征因子的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(8): 2434-2443. [16] SHARMA R P, BREIDENBACH J. Modeling height-diameter relationships for Norway spruce, Scots pine, and downy birch using Norwegian national forest inventory data[J]. For Sci Technol, 2015, 11(1): 44-53.
[17] ZANG H, LEI X, ZENG W. Height-diameter equations for larch plantations in northern and northeastern China: A comparison of the mixed-effects, quantile regression and generalized additive models[J]. Forestry, 2016, 89(4): 434-445. doi: 10.1093/forestry/cpw022
[18] 雷泽勇, 周晏平, 赵国军, 等. 竞争对辽宁西北部樟子松人工固沙林树高生长的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2018(1): 144-149. [19] 韩辉, 张学利, 党宏忠, 等. 基于树干液流通量的沙地樟子松合理林分密度的确定[J]. 林业科学研究, 2015, 28(6): 797-803. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1498.2015.06.006 [20] HUANG S, TITUS S J, WIENS D P. Comparison of nonlinear height-diameter functions for major Alberta tree species[J]. Can J For Res, 1992, 22(9): 1297-1304. doi: 10.1139/x92-172
[21] SIBBESEN E. Some new equations to describe phosphate sorption by soils[J]. J Soil Sci, 1981, 32(1): 67-74. doi: 10.1111/ejs.1981.32.issue-1
[22] YANG Y, HUANG S. Allometric modelling of crown width for white spruce by fixed- and mixed-effects models[J]. For Chron, 2017, 93(2): 138-147. doi: 10.5558/tfc2017-020
[23] MENG S X, HUANG S M, YANG Y Q, et al. Evaluation of population-averaged and subject-specific approaches for modeling the dominant or codominant height of lodgepole pine trees[J]. Can J For Res, 2009, 39(6): 1148-1158. doi: 10.1139/X09-039
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 王丽亚,陈哲. 基于多特征融合的番茄叶片病害智能诊断系统开发. 电子制作. 2025(05): 41-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李文雪,孟洪兵,孙丽丽,韩璐宇. 融合多尺度注意力机制的棉花枯萎病识别算法研究. 现代农业装备. 2025(02): 86-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 樊江川,王源桥,苟文博,蔡双泽,郭新宇,赵春江. 基于实例分割技术的草莓叶龄及冠幅表型快速提取方法. 智慧农业(中英文). 2024(02): 95-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李坤,刘婧,齐赫. 基于分层特征交叉注意力的小样本马铃薯病害叶片识别. 江苏农业科学. 2024(10): 210-216 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 冯玉涵,孙剑,张志芳. 基于层间特征蒸馏网络的作物叶片病害检测. 中国农机化学报. 2024(09): 271-277 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李凤妹,龚青松,李奔奔,张敏,丁一,吕军. 基于改进YOLO v5s模型的水稻病虫害监测系统. 农业工程技术. 2024(20): 17-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 杨欢,王钧,李广,吴江琪,谈燕. 大田环境下青贮玉米枯叶病检测模型. 软件导刊. 2024(09): 193-199 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 方晓捷,严李强,张福豪,高心雨. 基于深度学习的农作物图像识别的发展. 江苏农业科学. 2024(20): 18-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 麻剑钧,刘晓慈,金龙新,熊伟,易森林,封春芳,刘阳,夏先亮. 基于机器视觉的农作物病害识别研究进展. 湖南农业科学. 2023(09): 97-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 郭文娟,冯全. 基于类激活映射的可解释性方法在农作物检测识别中的发展现状与趋势. 智能化农业装备学报(中英文). 2023(04): 41-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(13)




 下载:
下载: