Genetic analysis and mapping of bacterial leaf streak resistance genes in Oryzae rufipogon Griff
-
摘要:目的
挖掘水稻Oryza sativa L. 抗细菌性条斑病(Bacterial leaf streak, BLS)主效基因,为丰富水稻抗病基因资源和培育水稻抗病品种奠定基础。
方法建立作图群体,对普通野生稻Oryza rufipogon Griff抗源‘DY19’抗BLS的基因采用集团分离分析法进行遗传分析,用SSR分子标记对其抗病基因bls2进行初步定位。
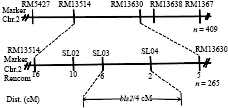
结果F2群体中抗病与感病单株符合1∶3的理论分离比例,说明普通野生稻抗源‘DY19’的抗BLS符合单基因遗传模式,受1对主效隐性基因bls2控制。初步将该基因定位在第2号染色体分子标记SL03(23 474 851 bp)与SL04(24 484 154 bp)之间约4 cM区域内,这是一个新的抗BLS基因位点。
结论普通野生稻抗源‘DY19’对细菌性条斑病的抗性受1对新的主效隐性基因bls2控制,为进一步的精细定位提供参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo exploit major resistance genes of rice (Oryza sativa L.) to bacterial leaf streak (BLS), and provide a basis for enriching rice disease resistant gene resources and breeding resistant cultivars.
MethodConstructing a mapping population, we conducted genetic analyses of BLS resistance genes in Oryzae rufipogon Griff ‘DY19’ using the bulk segregant analysis method, and preliminarily mapped the BLS resistance gene bls2 through SSR molecular markers.
ResultThe ratio of resistant and susceptible individual plants in F2 population was in accordance with the theoretical segregation ratio of 1∶3, which showed that the resistance gene to BLS in O. rufipogon ‘DY19’ was consistent with single gene genetic pattern and controlled by one pair of main recessive gene bls2. This gene was mapped in a 4 cM region between molecular markers SL03 (23 474 851 bp) and SL04 (24 484 154 bp) on the second chromosome. This locus was a new disease resistance locus.
ConclusionThe BLS resistance in O. rufipogon ‘DY19’ is controlled by one pair of new major recessive gene bls2. It can provide a reference for further fine mapping.
-
Keywords:
- rice /
- bacterial leaf streak /
- resistant gene /
- genetic analysis /
- gene mapping
-
-
表 1 亲本及杂交和回交后代对细菌性条斑病菌株JZ28的抗性反应
Table 1 Resistance reaction of parents and their cross and backcross progenies to bacterial leaf streak strain JZ28
材料
Material总株数
Total plant number各病情指数的材料份数 Plant number with different disease indexes 0(Ⅰ) 1(HR) 3(R) 5(MR) 7(S) 9(HS) 9311 15 0 0 0 0 0 15 DY19 15 0 15 0 0 0 0 F1 15 0 0 0 0 1 14 BC1 15 0 0 0 0 1 14 表 2 用于bls2标记的SSR引物序列
Table 2 SSR primer sequences used for bls2 mapping
引物名称
Primer name上游引物
Forward primer (5′→3′)下游引物
Reverse primer (5′→3′)RM5427 TGCTGTTGACACTTGACAGGTAGC CACAATTATTGCGGCTCATCG RM13514 ATCTGATGATGGCCACGACAGTAACG TGATCTGATCCCGTATTCCCATGC SL02 CTTGTGGACGACGAGGTAT AACAGAGTAGGGAGGAGGAG SL03 GCAAATTCCTCTGTTCTGTG ACTTGCAAAGCAAATTCTGT SL04 TAAAAGTGGAGTCATCCGTC GAGAATGGGTTGTGGATTAG RM13630 GCCGCTGATCTCTTACCTGTTACGG GTGCTTCGGCACAGGTCAATGC RM13638 CGTCAACTGACTGGTCCCACTACTGC CTTGGGCCCACCTGTCATACCC RM1367 CGCTGCTACTCCTAGCTGCTACC CATGCATGTGTGTACGTAGGATCG -
[1] 方中达, 任欣正, 陈泰英, 等. 水稻白叶枯病及条斑病和李氏禾条斑病病原细菌的比较研究[J]. 植物病理学报, 1957, 3(2): 99-124. [2] NIÑO-LIU D O, RONALD P, BOGDANOVE A. Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: Model pathogens of a model crop[J]. Mol Plant Pathol, 2006, 7(5): 303-324. doi: 10.1111/mpp.2006.7.issue-5
[3] OU S, NUQUE F, BANGDONG J. Relation between qualitative and quantitative resistance to rice blast (Pyricularia oryzae, fungus diseases)[J]. Phytopathology, 1975, 65(11): 155-158.
[4] 张荣胜, 陈志谊, 刘永锋. 水稻细菌性条斑病研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2014, 30(4): 901-908. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2014.04.034 [5] 孙乃昌. 南宁地区一九七八年晚稻细菌性条斑病发生情况调查[J]. 广西农业科学, 1979(2): 32-33. [6] TANG D, WU W, LI W, et al. Mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2000, 101(1/2): 286-291.
[7] XIE X, CHEN Z, CAO J, et al. Toward the positional cloning of qBlsr5a, a QTL underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak, using overlapping sub-CSSLs in rice[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e95751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095751
[8] CHEN C H, ZHENG W, HUANG X M, et al. Major QTL conferring resistance to rice bacterial leaf streak[J]. Agric Sci China, 2006, 5(3): 216-220. doi: 10.1016/S1671-2927(06)60041-2
[9] 郑景生, 李义珍, 方宣钧. 水稻第2染色体上细菌性条斑病抗性QTL的检测[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(9): 1923-1925. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2005.09.031 [10] TRIPLETT L R, COHEN S P, HEFFELFINGER C, et al. A resistance locus in the American heirloom rice variety Carolina Gold Select is triggered by TAL effectors with diverse predicted targets and is effective against African strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola[J]. Plant J, 2016, 87(5): 472-483. doi: 10.1111/tpj.2016.87.issue-5
[11] HE W A, HUANG D H, LI R B, et al. Identification of a resistance gene bls1 to bacterial leaf streak in wild rice Oryza rufipogon Griff[J]. J Integr Agric, 2012, 11(6): 962-969. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(12)60087-2
[12] 岑贞陆, 黄思良, 李容柏, 等. 稻种材料抗细菌性条斑病性鉴定[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2007, 35(22): 6850-6851. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2007.22.078 [13] 农秀美, 廖恒登, 刘志明, 等. 广西水稻细菌性条斑病菌致病力分化研究初报[J]. 西南农业学报, 1994(4): 94-97. [14] KHUSH G S. The genetic basis of epidemics in agriculture[M]. New York: New York Academy of Sciences, 1977: 296.
[15] 何月秋, 文艳华, 黄瑞荣, 等. 杂交水稻对细菌性条斑病抗性遗传研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 1994, 16(1): 62-65. [16] 张红生, 陆志强, 朱立宏. 四个籼稻品种对细菌性条斑病的抗性遗传研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 1996, 10(4): 193-196. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7216.1996.04.001 [17] 周明华, 许志刚, 粟寒, 等. 两个籼稻品种对水稻细菌性条斑病抗性遗传的研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 1999, 22(4): 27-29. [18] 徐建龙, 王汉荣, 林贻滋, 等. 水稻细菌性条斑病和白叶枯病抗性遗传研究[J]. 遗传学报, 1997, 24(4): 330-335. [19] 黄大辉, 岑贞陆, 刘驰, 等. 野生稻细菌性条斑病抗性资源筛选及遗传分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2008, 9(1): 11-14. [20] 贺文爱, 黄大辉, 刘驰, 等. 普通野生稻抗源对细菌性条斑病的抗性遗传分析[J]. 植物病理学报, 2010, 40(2): 180-185. [21] 邹丽芳, 陈功友, 武晓敏, 等. 中国水稻条斑病细菌avrBs3/PthA家族基因的克隆和序列分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005, 38(5): 929-935. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2005.05.011



 下载:
下载:
