Antibacterial mechanism of thymol to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
-
摘要:目的
探讨百里香酚对耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA)的抑菌作用机制,为开发高效低毒的抗MRSA药物提供可靠的理论依据。
方法采用微量肉汤稀释法和菌落计数法测定百里香酚对MRSA标准菌株USA300的最低抑菌浓度(MIC)和最低杀菌浓度(MBC);通过测定菌液电导率和DNA含量确定百里香酚对USA300细胞膜的影响;通过SDS-PAGE检测百里香酚对USA300可溶性蛋白质代谢的影响;利用透射电镜观察经百里香酚处理后USA300菌体细胞的超微结构;通过结晶紫染色法测定百里香酚对USA300生物被膜形成的影响。
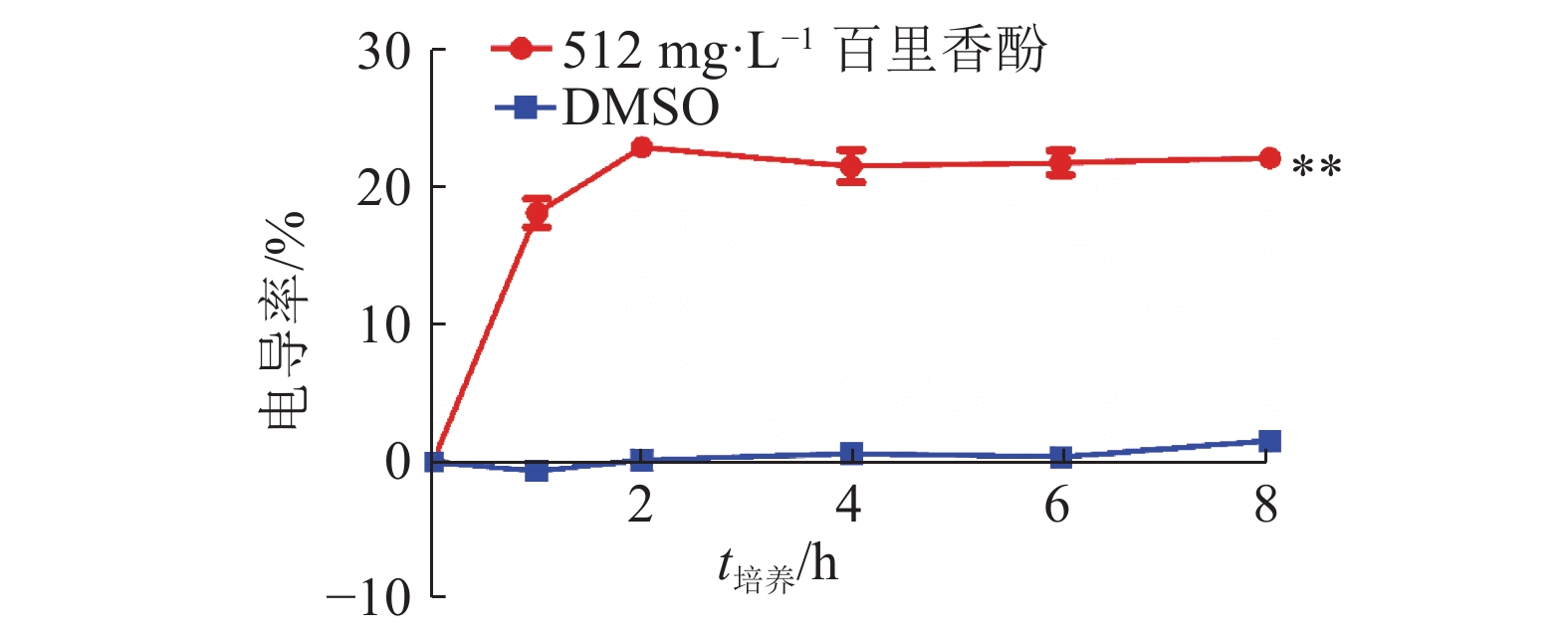
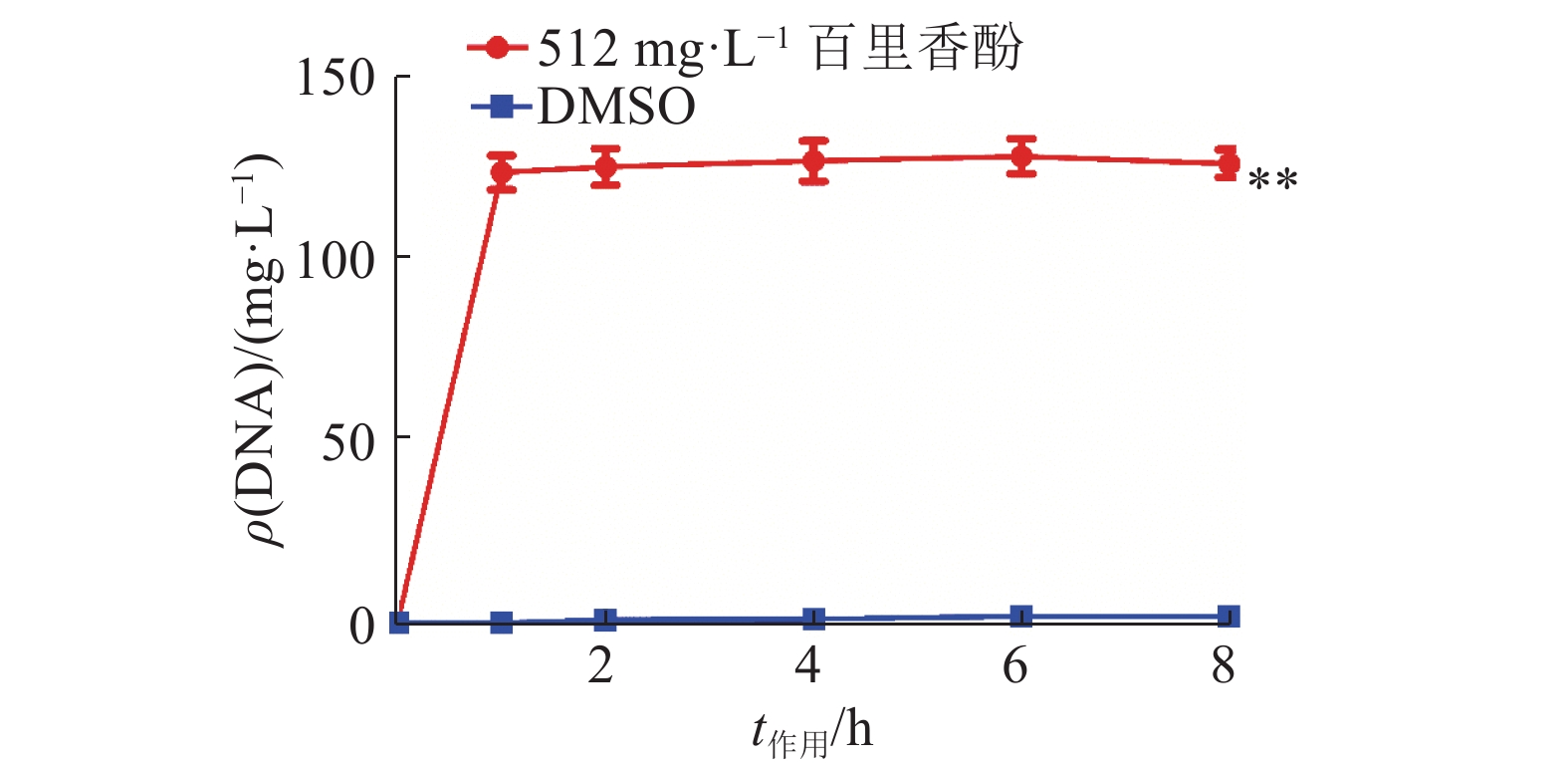
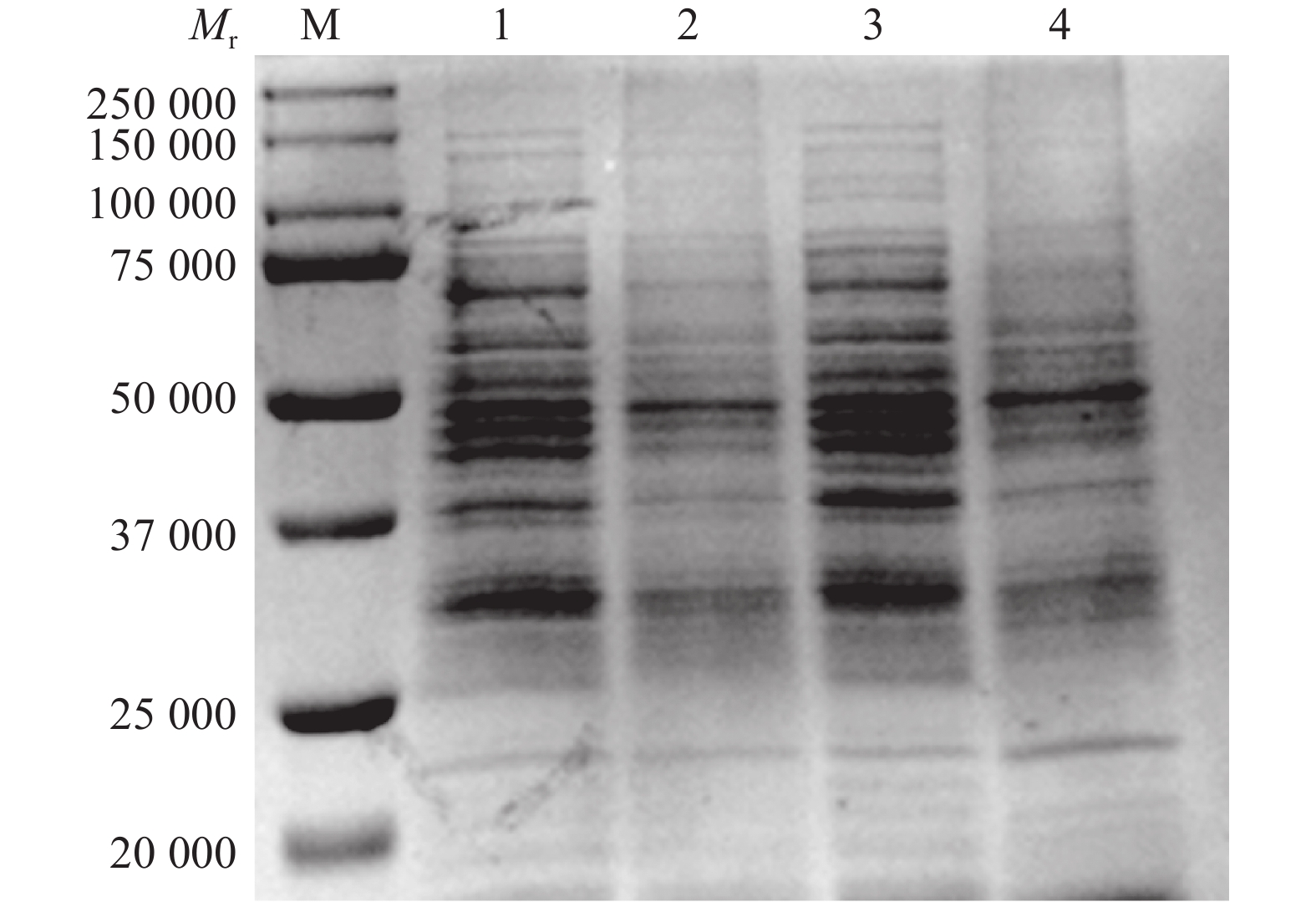
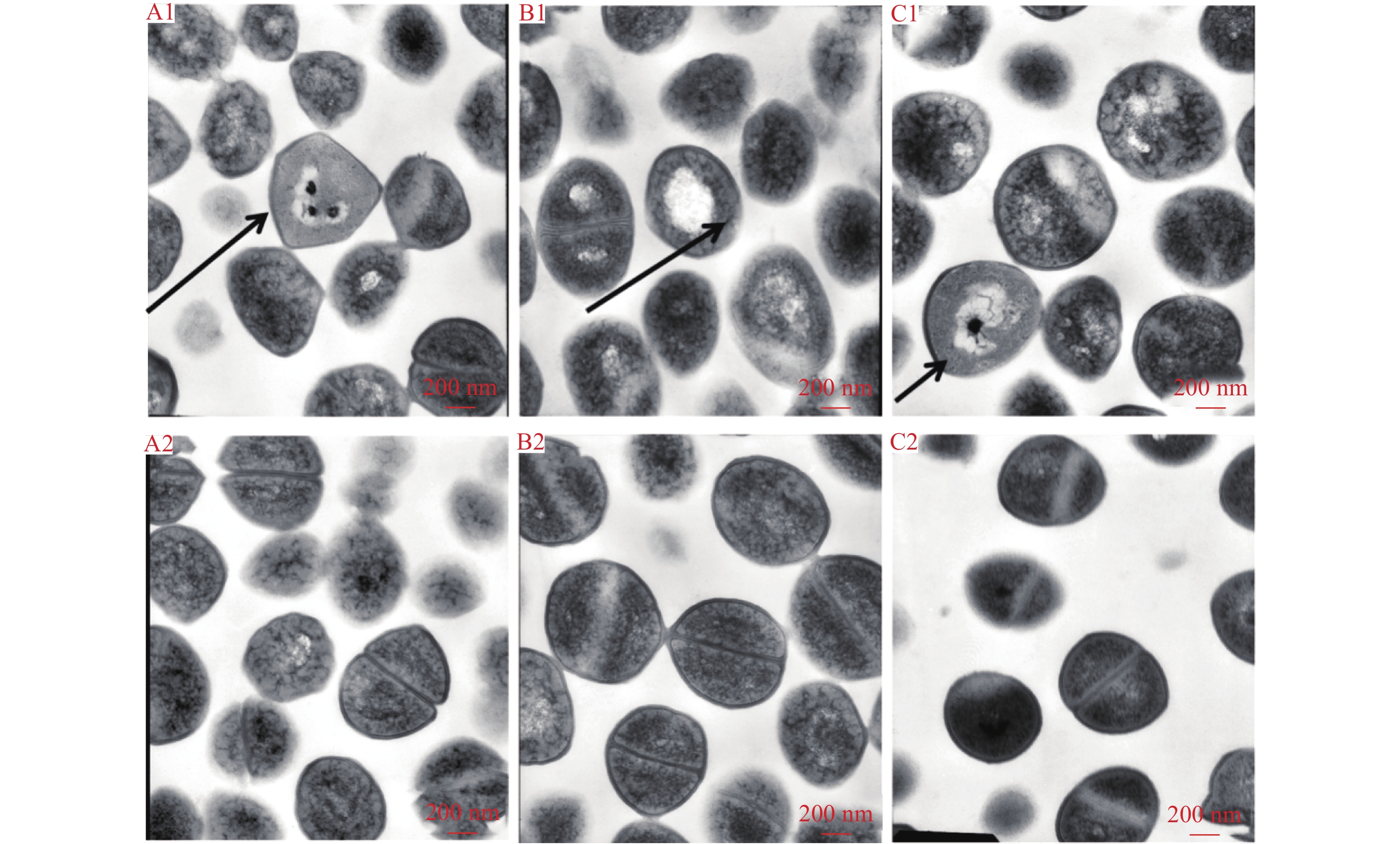
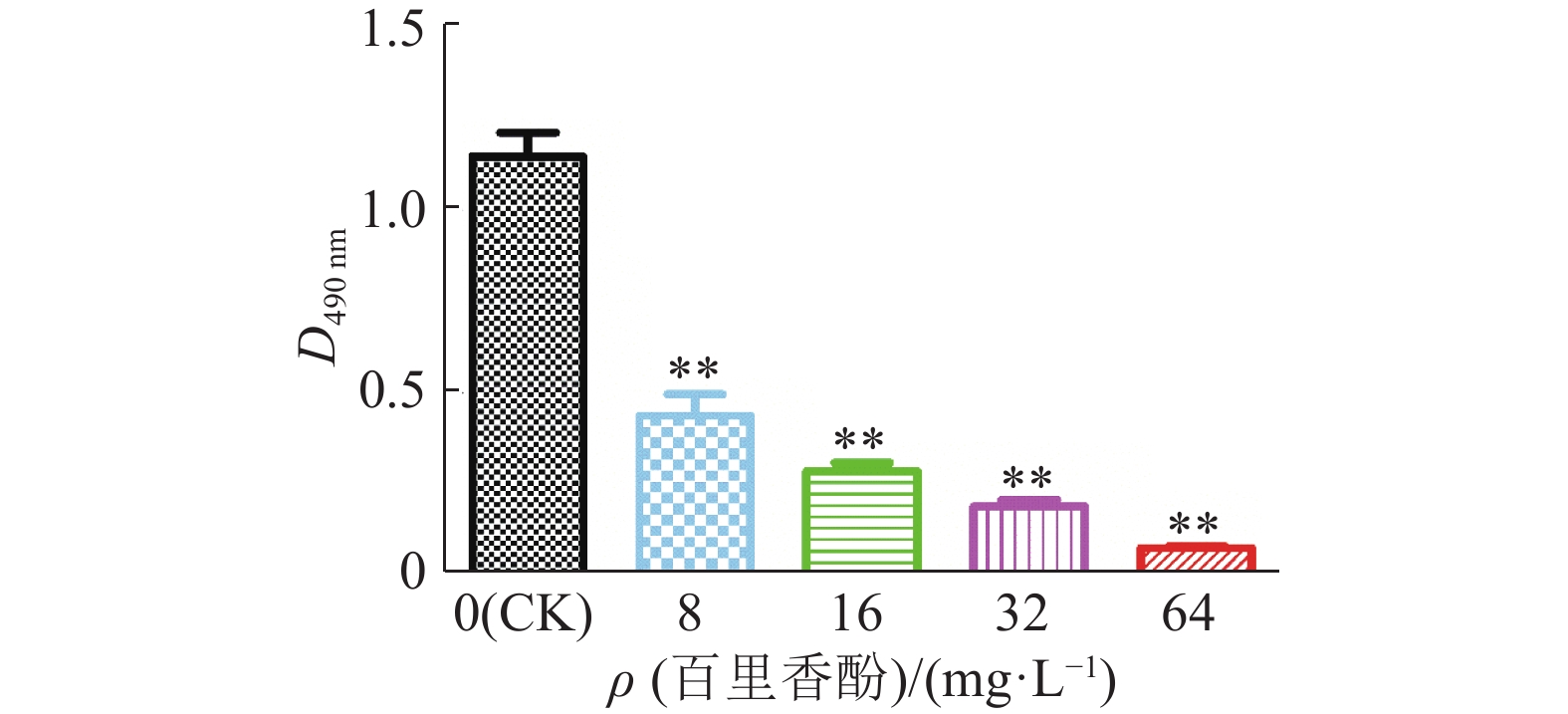
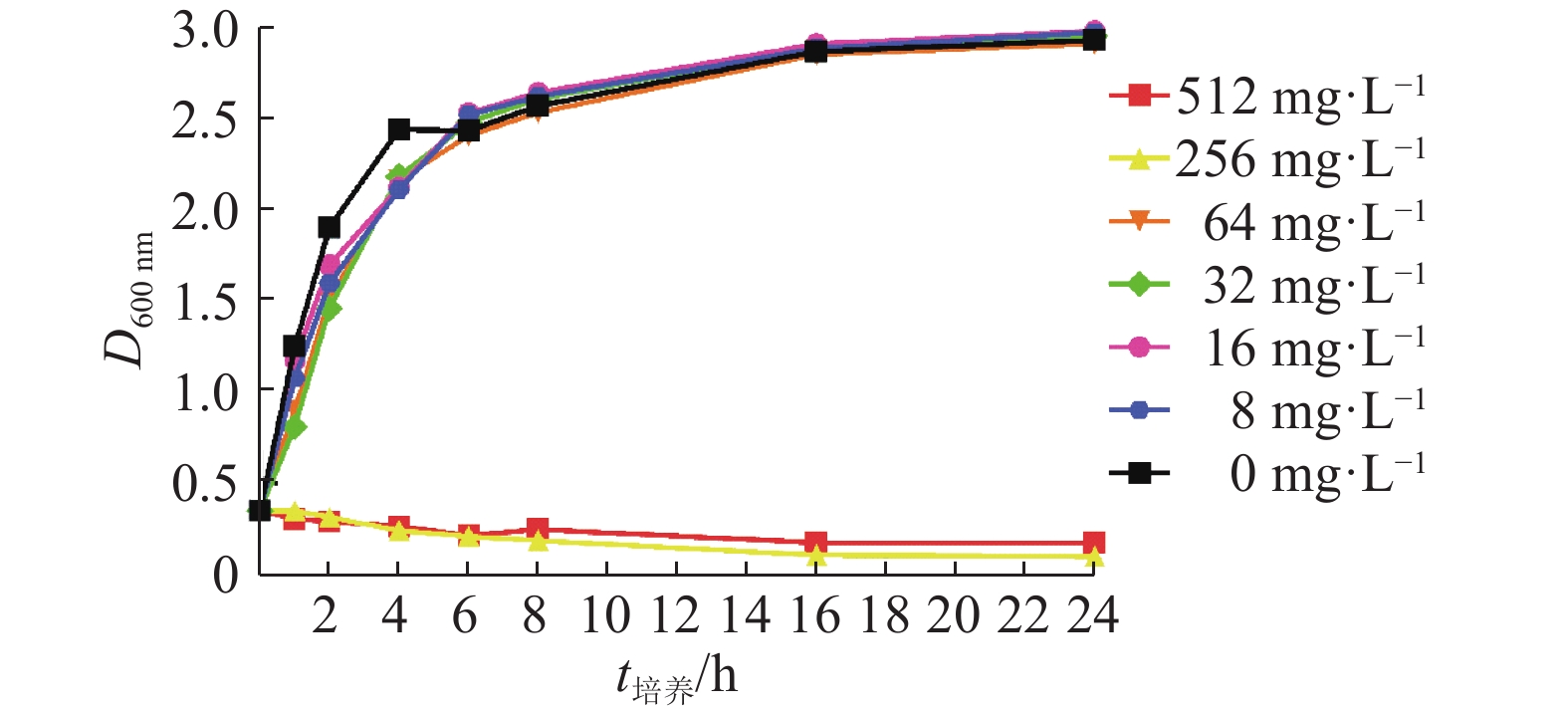
结果百里香酚对USA300具有一定的抑制作用,其MIC和MBC均为256 mg·L–1。与对照组相比,512 mg·L–1百里香酚作用菌体1 h后,菌液电导率增加18.08%±1.80%,DNA外渗量增加(123.40±8.06) mg·L–1,作用24 h后,菌体可溶性蛋白质含量比对照组降低68.20%±0.15%。百里香酚对USA300细胞壁和细胞膜具有破坏作用并干扰其正常的二分裂,亚抑菌浓度下对生物被膜的形成具有一定抑制作用。
结论百里香酚通过改变菌体细胞膜通透性,干扰蛋白质代谢和正常的二分裂来抑制细菌的生长,亚抑菌浓度下能够在不影响细菌生长的前提下抑制其生物被膜的形成。百里香酚具有开发为抗MRSA药物的潜力。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the antibacterial mechanism of thymol to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA), and provide a reliable theoretical basis for the exploitation of high efficient and low toxic anti-MRSA medicine.
MethodThe minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of thymol to MRSA standard strain USA300 were determined via microbroth dilution method and colony counting method. Bacterium solution conductivity and DNA amount were detected to investigate the effect of thymol on USA300 cell membrane. SDS-PAGE was used to detect the effect of thymol on USA300 soluble protein synthesis. The ultra structure of USA300 cell treated by thymol was observed through transmission electron microscope. The effect of thymol on USA300 biofilm formation was investigated via crystal violet staining method.
ResultThymol had definite inhibitory activity on USA300, both MIC and MBC of thymol to USA300 were 256 mg·L–1. Compared with the control group, after treating the strain with 512 mg·L–1 thymol for 1 h, the conductivity of bacterium solution was improved by 18.08%±1.80%, and DNA exosmosis amount increased by (123.40±8.06) mg·L–1; after treating for 24 h, the soluble protein content of USA300 was reduced 68.20%±0.15%. Thymol destroyed cytoderm and cytomembrane of USA300, disturbed its normal binary fission, and inhibited biofilm formation at subinhibitory concentration.
ConclusionThymol can inhibit bacterium growth by changing its cytomembrane permeability and disturbing protein synthesis and normal binary fission, and depress biofilm formation at subinhibitory concentration in the premise of not affecting bacterium growth. Thymol has the potential of developing as anti-MRSA medicine.
-
-
-
[1] TACCONELLI E, TUMBARELLO M, CAUDA R. Staphylococcus aureus infections[J]. N Engl J Med, 1998, 339(27): 2026-2027.
[2] 王小兵, 周雄英. 金黄色葡萄球菌感染现状分析[J]. 医学检验与临床, 2013, 24(5): 40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5013.2013.05.015 [3] CHAMBERS H F, DELEO F R. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2009, 7(9): 629-641. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2200
[4] HARRIS S R, FEIL E J, HOLDEN M T G, et al. Evolution of MRSA during hospital transmission and intercontinental spread[J]. Science, 2010, 327(5964): 469-474.
[5] 李德发, 祖莹, 陈虹宇, 等. 深圳地区儿童耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌感染的临床分布与耐药性特点分析[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2017, 27(15): 3563-3566. [6] 程禹, 罗敏玉, 陈代杰. 耐甲氧西林金葡菌到万古霉素高度耐药金葡菌的发展及其感染的药物治疗[J]. 世界临床药物, 2011, 32(8): 482-487. [7] 崔志斌, 蒋开年, 马晨, 等. 百里香酚的Mannich反应及其产物的抑菌活性[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2008, 20(12): 1626-1629. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2008.12.020 [8] 王新伟, 刘欢, 魏静, 等. 牛至油、香芹酚、柠檬醛和肉桂醛抑菌作用研究[J]. 食品工业, 2010(5): 13-16. [9] 张静, 冯岗, 袁旭超, 等. 百里香酚抑菌活性初探[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(21): 277-280. [10] 殷清华, 庄英帜, 严奉祥. 百里香酚的抗肿瘤作用[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2010, 10(11): 2073-2075. [11] LI Y, WEN J M, DU C J, et al. Thymol inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation via inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 491(2): 530-536. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.009
[12] 段雪娟, 吴克刚, 柴向华. 香辛料精油成分对生鲜食品中有害菌杀灭活性研究[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2012, 32(3): 87-91. [13] 王海涛. 大豆异黄酮的抑菌活性及其机制的研究[D]. 大连: 辽宁师范大学, 2009. [14] CHEN C Z S, COOPER S L. Interactions between dendrimer biocides and bacterial membranes[J]. Biomaterials, 2002, 23(16): 3359-3368. doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00036-4
[15] 周磊, 云宝仪, 汪业菊, 等. 大黄素对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌作用机制[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2011, 27(12): 1156-1160. [16] 薛东芳. 黄连生物碱及8–烷基小檗碱衍生物对嗜水气单胞菌抑菌机制的研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2015. [17] 方展强, 邱玫, 王春凤. 剑尾鱼鳃结构的光镜、扫描和透射电镜观察[J]. 电子显微学报, 2004, 23(5): 553-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2004.05.009 [18] 方克明, 邹兴, 苏继灵. 纳米材料的透射电镜表征[J]. 现代科学仪器, 2003(2): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8892.2003.02.004 [19] ZHANG B, TENG Z, LI X, et al. Chalcone attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence by targeting Sortase A and alpha-hemolysin[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.0715.
[20] POTTINGER P S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2013, 97(4): 601-619. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2013.02.005
[21] WUNDERINK R G. How important is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a cause of community-acquired pneumonia and what is best antimicrobial therapy[J]. Infect Dis Clin North Am, 2013, 27(1): 177-188. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2012.11.006
[22] CORNEO G, POGLIANI E, BIASSONI D, et al. Inhibition of DNA restriction enzyme digestion by anthracyclines[J]. Ric Clin Lab, 1988, 18(1): 19-22. doi: 10.1007/BF02918815
[23] 王晓君, 蒋琳琳, 程天印. 百里香酚和香芹酚对细菌形态结构的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医杂志, 2012, 31(3): 10-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2012.03.010 [24] 胡静, 赵小慧, 朱春玉, 等. 槐糖脂对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌机理[J]. 食品科学, 2012, 33(5): 33-36. [25] 盛清. 细菌生物膜[J]. 国外医学 (流行病学传染病学分册), 2003, 30(4): 241-243. [26] YOSHII Y, OKUDA K I, YAMADA S, et al. Norgestimate inhibits staphylococcal biofilm formation and resensitizes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to β-lactam antibiotics[J]. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes, 2017, 3(1): 30. doi: 10.1038/s41522-017-0038-x
[27] RASKO D A, SPERANDIO V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2010, 9(2): 117-128. doi: 10.1038/nrd3013



 下载:
下载: