Design and realization of a greenhouse temperature intelligent control system based on NB-IoT
-
摘要:目的
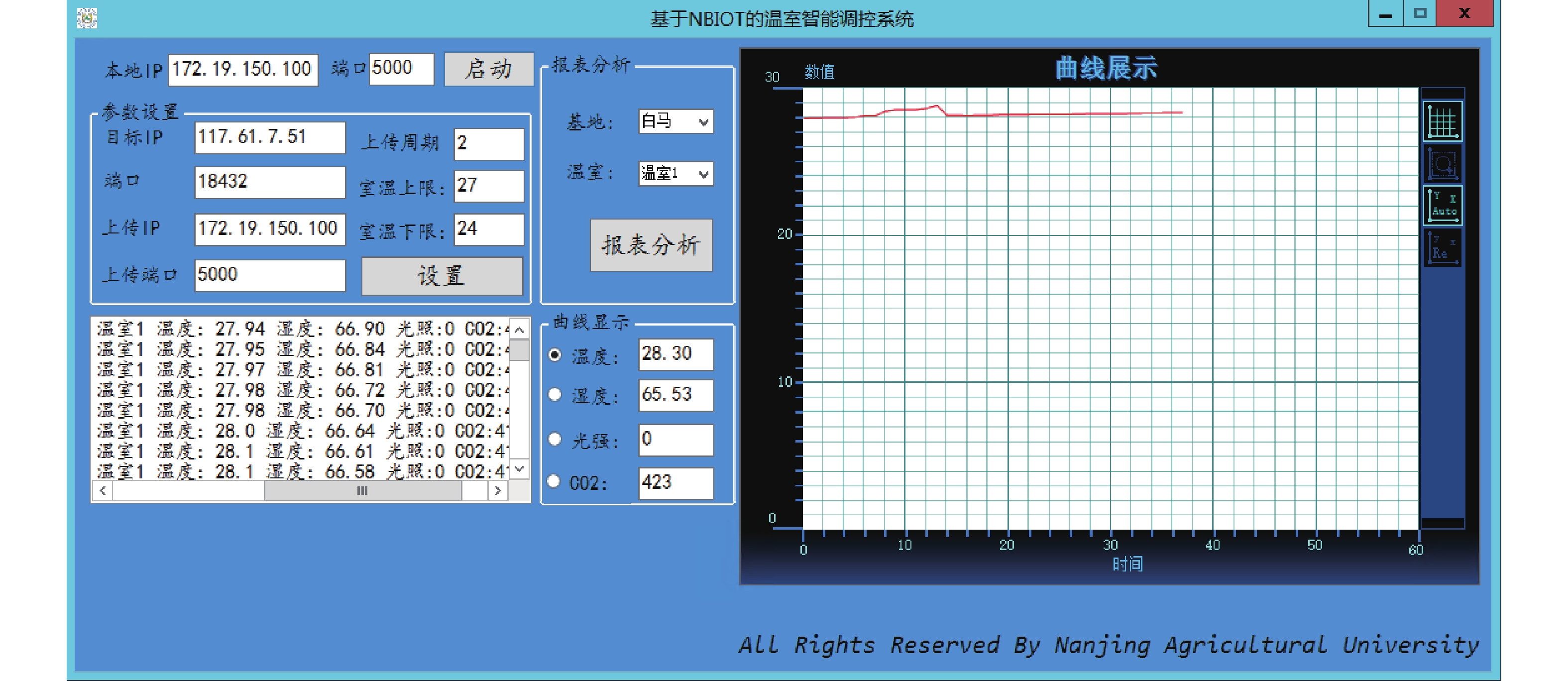
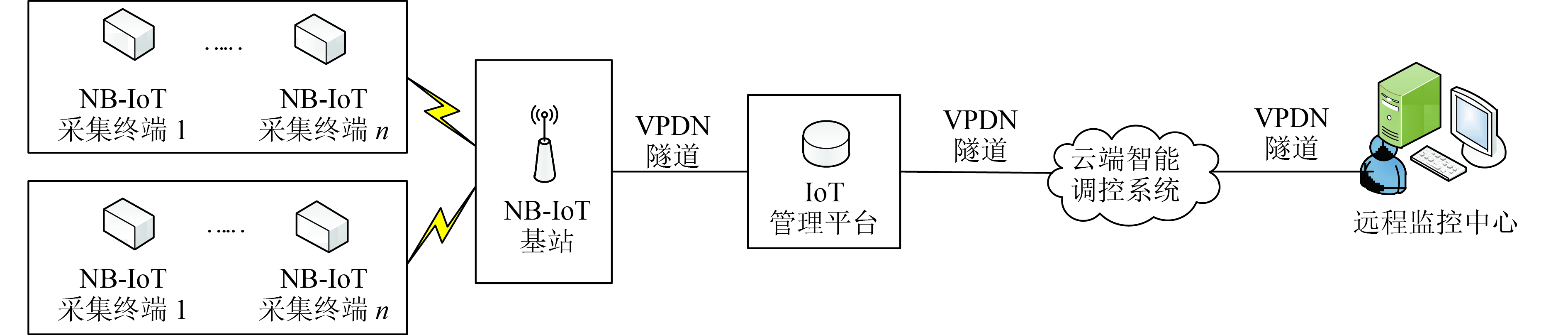
以NB-IoT低速率窄带宽物联网技术为核心,研制一套以5G低功耗海量连接场景前期技术为基础的智能温室环境自动调控系统。
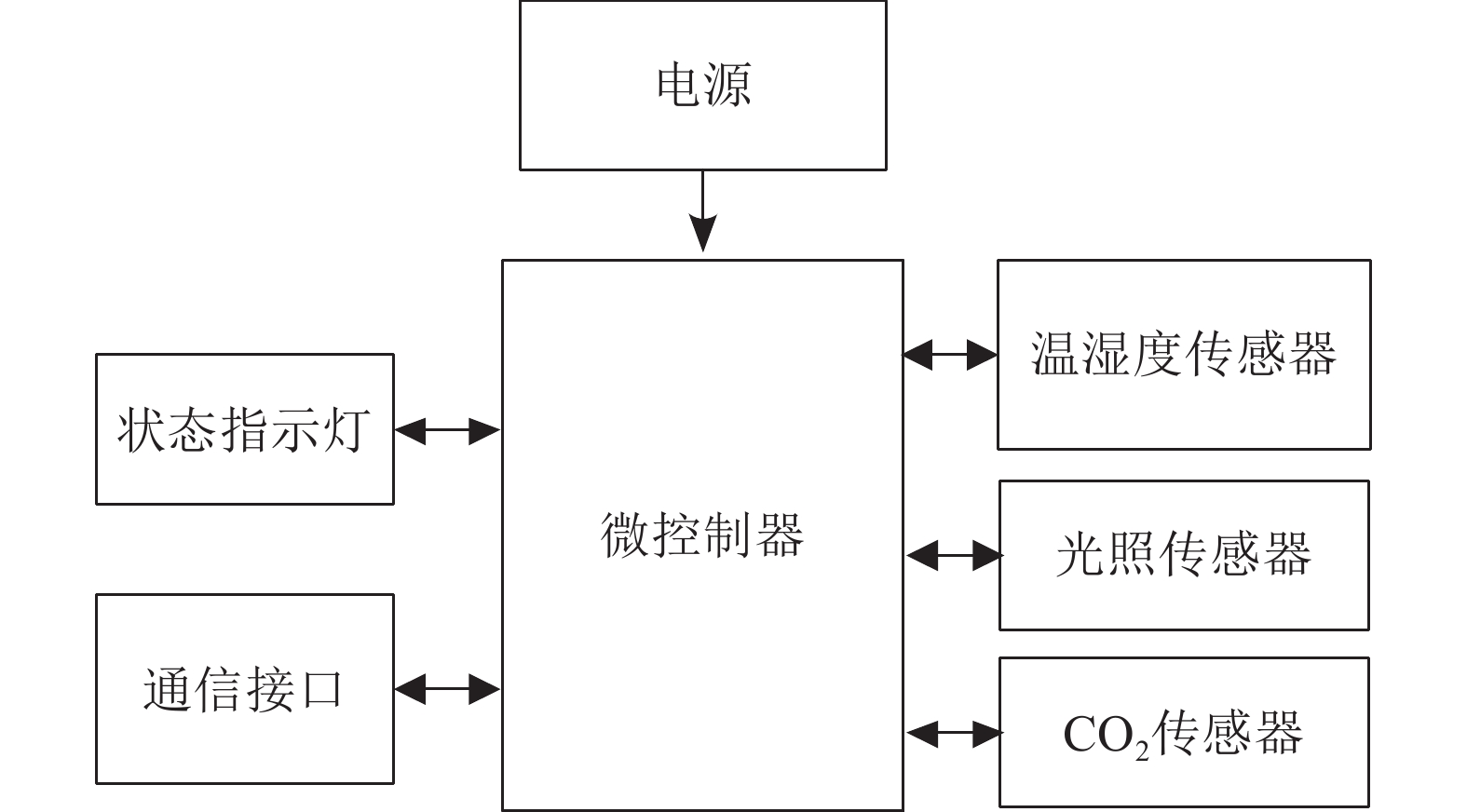
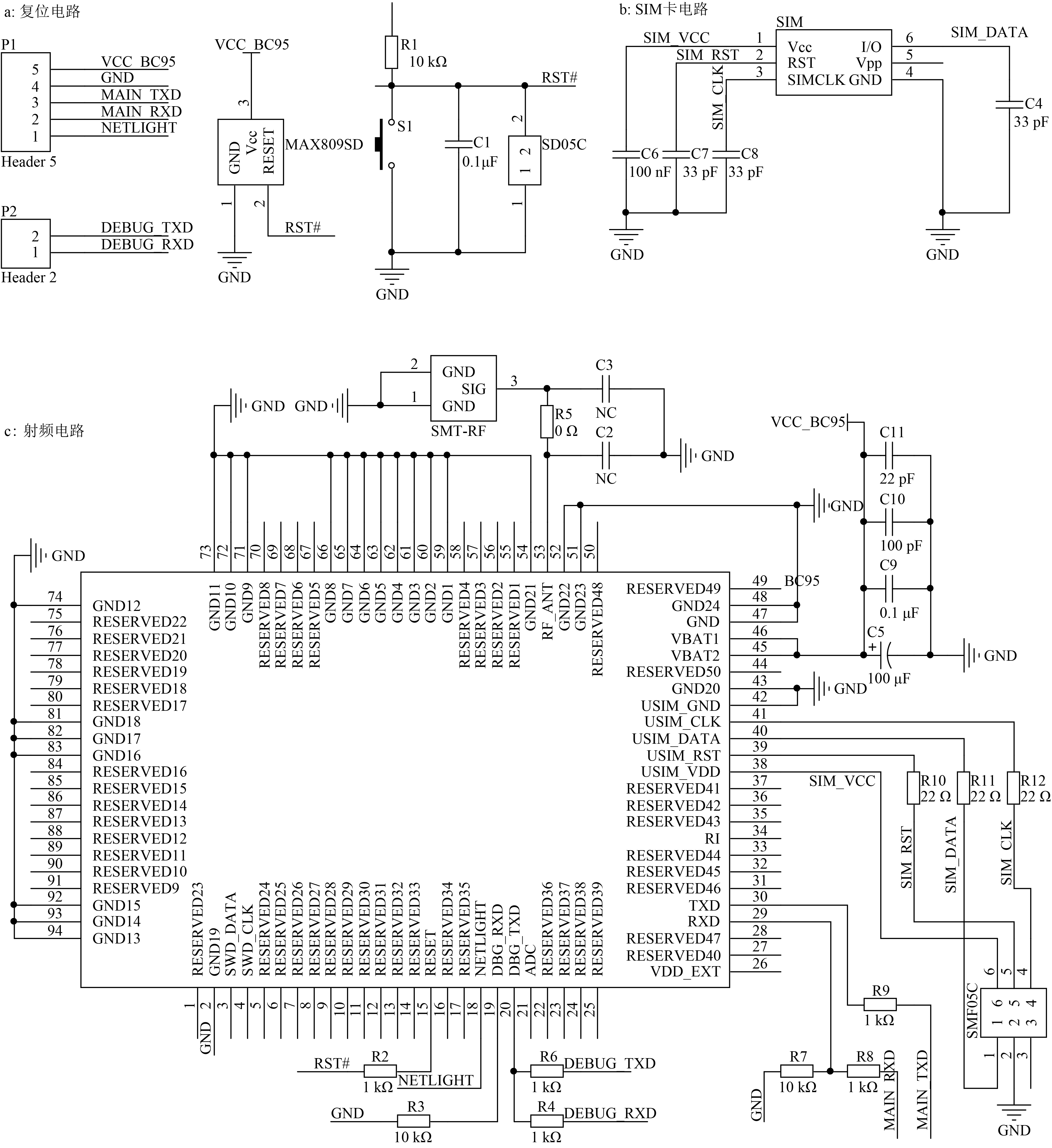
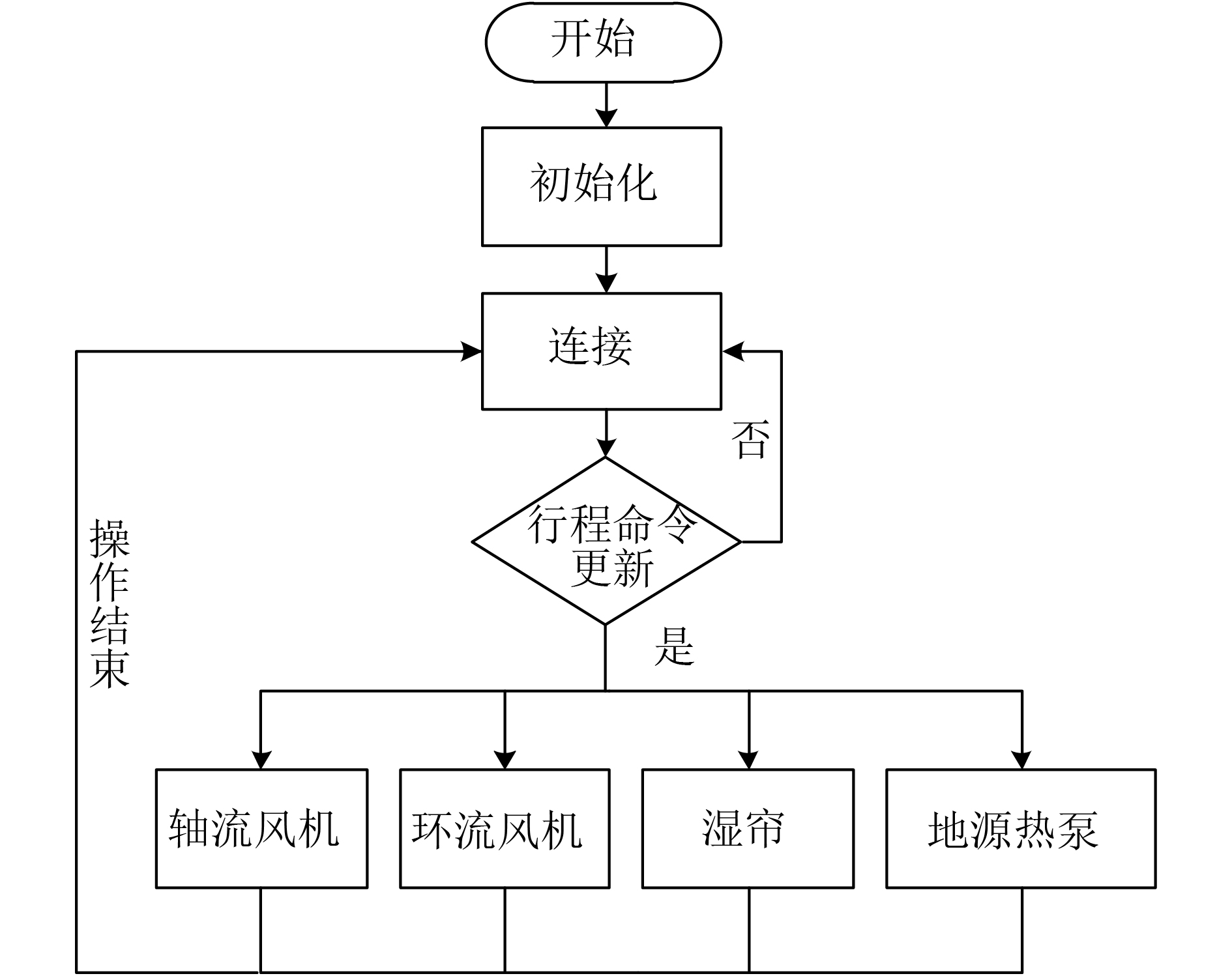
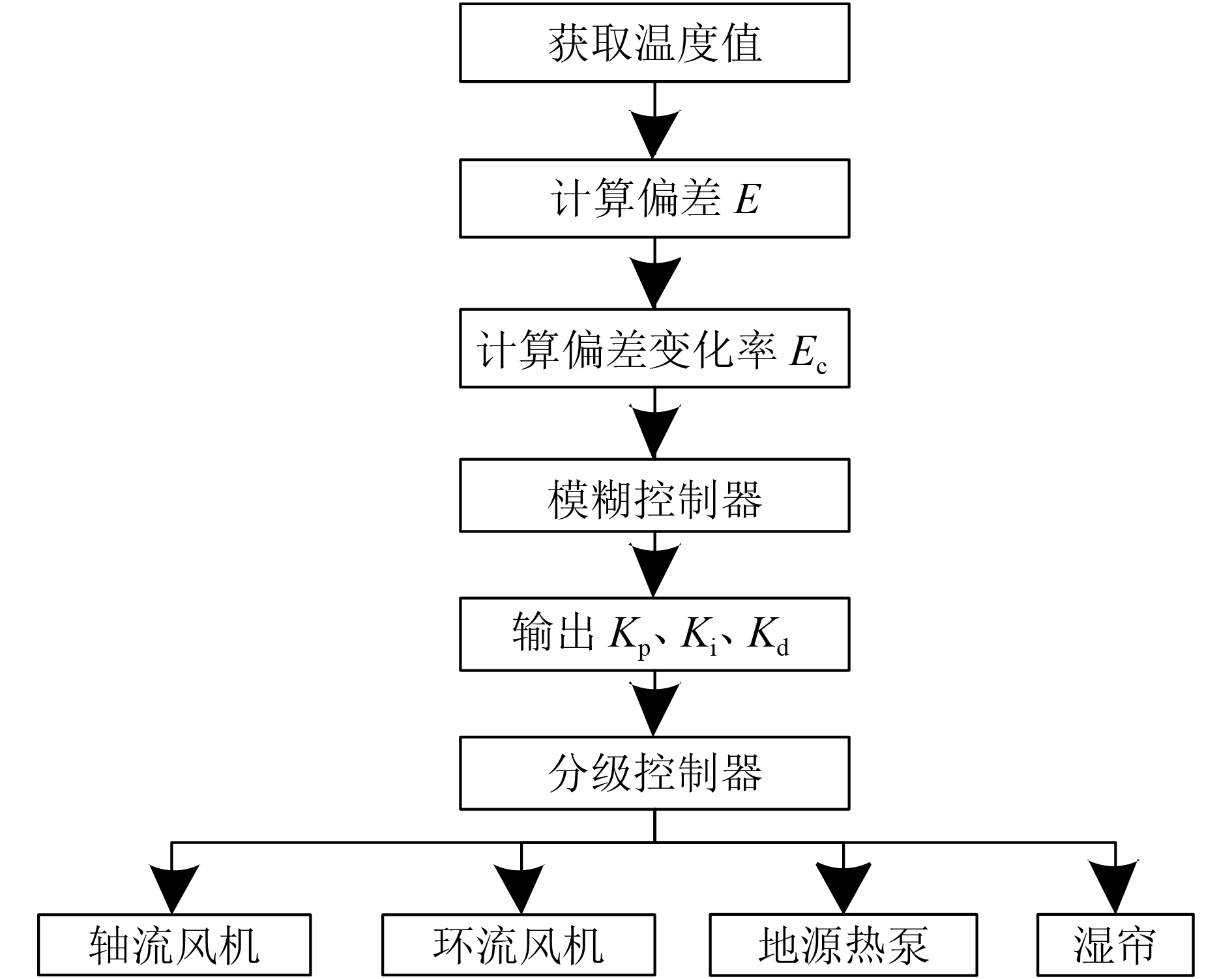
方法应用MSP430F149超低功耗芯片采集环境信息,依托NB-IoT蜂窝物联网平台,云端智能调控系统,结合多传感器融合与模糊PID–分级控制技术, 根据用户需求调节温室环境。
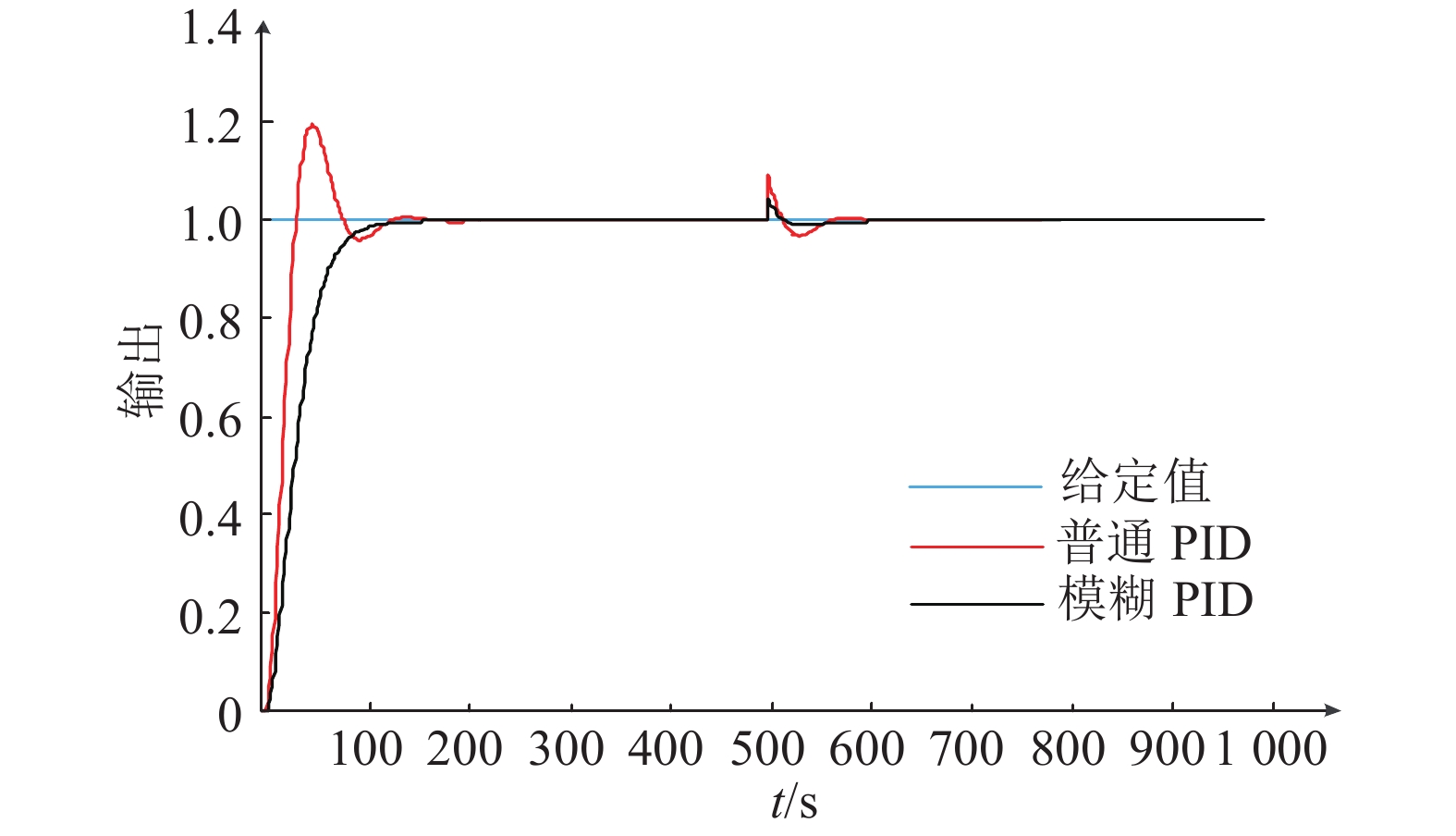
结果该系统在温室大棚内实地应用的结果表明:温室环境信息采集相对误差不超1%,平均控制精度在3.57%(±1.0 ℃),无传输距离限制,实现作物生长温度的自动调节。
结论该系统稳定可靠,为作物的生长提供良好环境,对作物的研究提供有力的技术支撑。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo develop an automated greenhouse environmental monitoring and control system based on an NB-IoT low-rate narrow bandwidth networking and 5G low-power massive connection technology.
MethodUltra-low power chip MSP430F149 was applied to collect environmental information. Using the NB-IoT's cellular networking platform and the cloud intelligent control system and combining multi-sensor fusion with fuzzy PID-grading control technology, greenhouse environment was controlled according to user needs.
ResultUsing the automated system in greenhouse, the relative error of greenhouse environmental information collection was below 1%, the average control accuracy was 3.57% (±1.0 ℃), the transmission distance was not limited and the automatic regulation of crop growth temperature was realized.
ConclusionThe system is stable and reliable, and provides a favorable environment for plant growth as well as a strong technical support for crop research.
-
Keywords:
- NB-IoT /
- 5G /
- multi-sensor fusion /
- fuzzy PID /
- greenhouse /
- temperature
-
-
表 1 数据帧传输格式
Table 1 Transmission format of data frame
基地
编号温室
编号终端
类型终端
编号数据
长度温度
高位温度
低位湿度
高位湿度
低位光强
高位光强
低位CO2
高位CO2
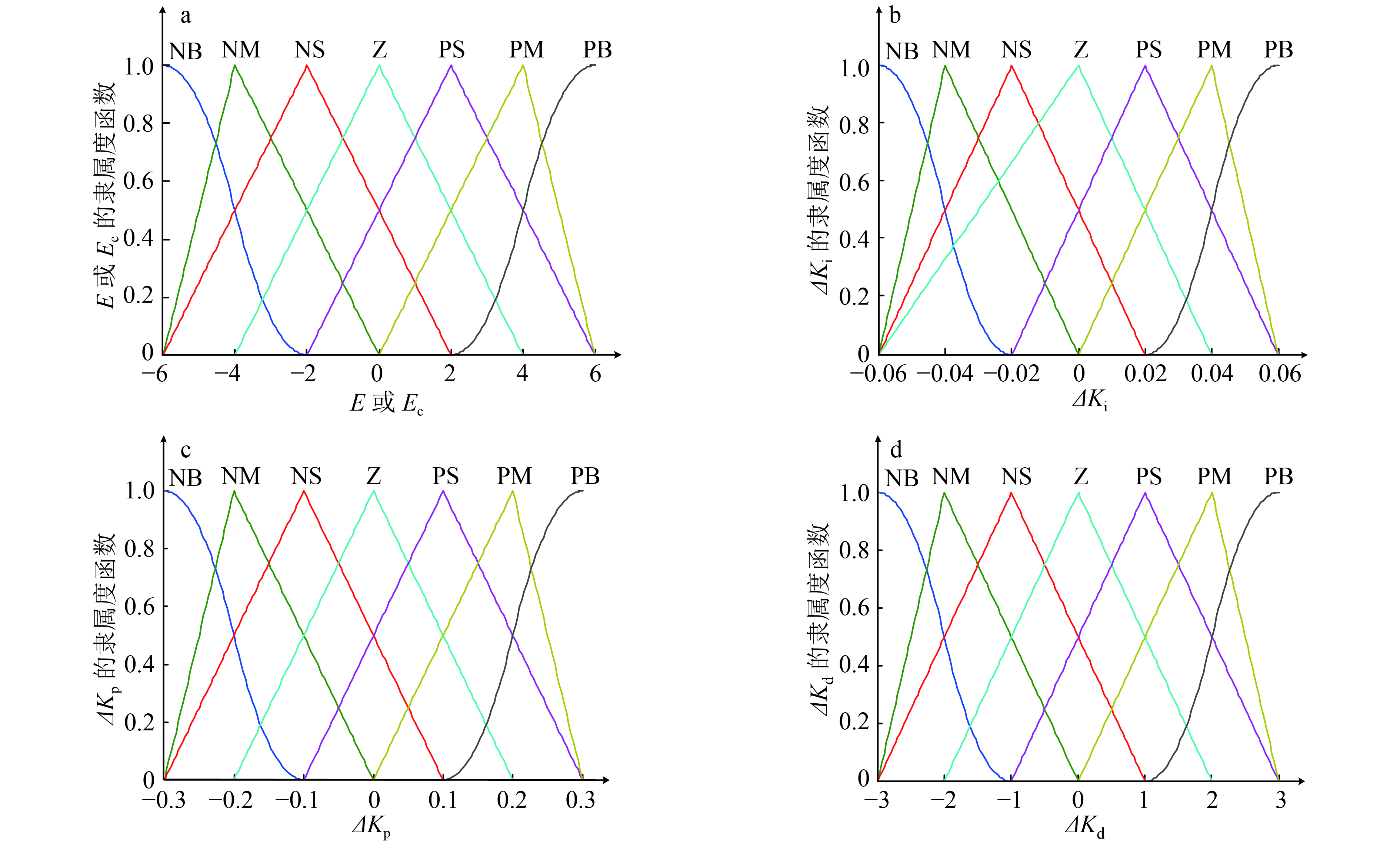
低位校验位 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N 表 2 ΔKp的模糊控制规则1)
Table 2 Fuzzy control rules for ΔKp
Ec E NB NM NS Z PS PM PB NB PB PB PM PM PS Z Z NM PB PB PM PM PS Z NS NS PM PM PM PS Z NS NS Z PM PM PS Z NS NM NM PS PS PS Z NS NS NM NM PM NS Z NS NM NM NM NB PB Z Z NM NM NM NB NB 1) NB、NM、NS、Z、PS、PM 和 PB 分别表示程度为负大、负中、负小、零、正小、正中和正大 表 3 多点温度测量值和融合值
Table 3 Multipoint temperature measurements and fusion values
℃ 指标 组1 组2 组3 组4 组5 组6 组7 组8 测量值[1] 34.40 33.70 33.20 31.10 33.50 32.70 36.31 30.22 测量值[2] 34.40 33.20 33.20 31.10 33.60 32.70 36.33 30.22 测量值[3] 34.60 33.90 33.20 33.40 33.50 32.70 36.35 30.20 测量值[4] 34.40 33.80 33.20 31.10 33.50 32.60 36.34 30.20 测量值[5] 34.50 33.80 33.10 31.10 33.60 32.70 36.33 30.22 融合值 33.46 33.80 33.20 31.10 33.54 32.70 36.33 30.21 JR912数显温度计读数 33.30 33.50 33.10 31.40 33.40 32.40 36.50 30.40 相对误差/% –0.47 0.90 0.30 –0.64 0.95 0.93 0.45 0.62 -
[1] 黄文超. NB-IoT低速率窄带物联网通信技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 电子测试, 2017(6): 29. [2] WANG Y P E, LIN X, ADHIKARY A, et al. A primer on 3GPP narrowband internet of things[J]. IEEE Commun Mag, 2017, 55(3): 117-123.
[3] ADHIKARY A, LIN X, WANG Y P E. Performance evaluation of NB-IoT coverage[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE 86th vehicular technology conference. Toronto: IEEE, 2017: 1-5.
[4] 曲井致. NB-IoT低速率窄带物联网通信技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2016(31): 115. [5] 李春玉. 密闭环境空气质量监测系统[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2016. [6] 张宏, 沈明霞, 陆明洲, 等. 穿戴式猪用心电监测系统设计[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2016, 39(5): 872-879. [7] 郑晓庆, 杨日杰, 杨立永, 等. 多路输出DC-DC电路设计[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2012, 31(9): 31-33. [8] HE J, XU L, WANG P, et al. A high precise E-nose for daily indoor air quality monitoring in living environment[J]. Integration, 2016, 58: 286-294.
[9] DENG H B, ZHANG L. Design on ZigBee wireless sensor network node[J]. Key Eng Mater, 2011, 474/475/476: 283-286.
[10] 熊本海, 蒋林树, 杨亮, 等. 奶牛饲喂自动机电控制系统的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(7): 157-163. [11] SU B, MA X. Water level sensor based on a new design structure for irrigation water measurement[J]. Ifac Proceedings Volumes, 2010, 43(26): 39-44.
[12] 刘叶玲, 朱艳伟. 加权数据融合算法及其应用举例[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2005, 25(2): 253-255. [13] 袁明月, 鸿雁, 杨志, 等. 基于Grubbs准则的小波阈值改进研究[J]. 人民长江, 2014(14): 69-71. [14] 涂川川, 朱凤武, 李铁. BP神经网络PID控制器在温室温度控制中的研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2012(2): 151-154. [15] 韦庆志. 基于ARM的模糊PID温度控制系统的研究[D].镇江: 江苏大学, 2010. [16] KUMAR A, KUMAR V. A novel interval type-2 fractional order fuzzy PID controller: Design, performance evaluation, and its optimal time domain tuning[J]. Isa T, 2017, 68: 251-275.
[17] 余欢乐, 方永锋. 基于模糊自整定PID的温室温度控制系统设计及仿真[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(12): 383-386.



 下载:
下载: