Effect of pendimethalin on soil enzyme activities in cotton field
-
摘要:目的
研究新疆棉田土壤施用二甲戊灵对土壤酶活性的影响。
方法棉田土壤施用二甲戊灵0、2 700、4 050、5 400 g·hm-2,分析不同处理时间、不同深度土壤酶活性的变化规律。
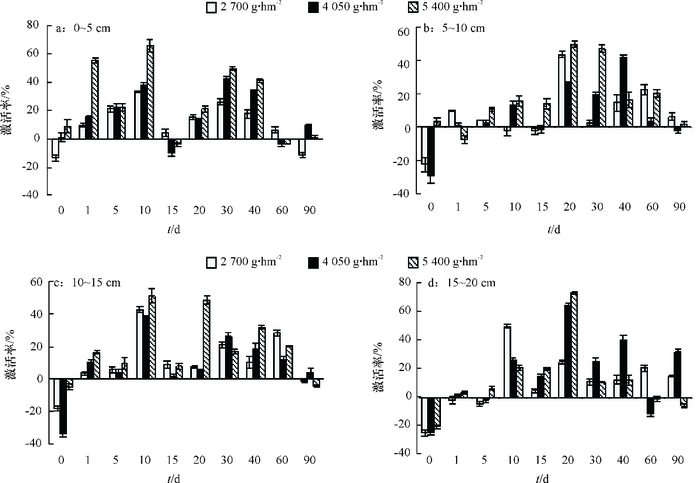
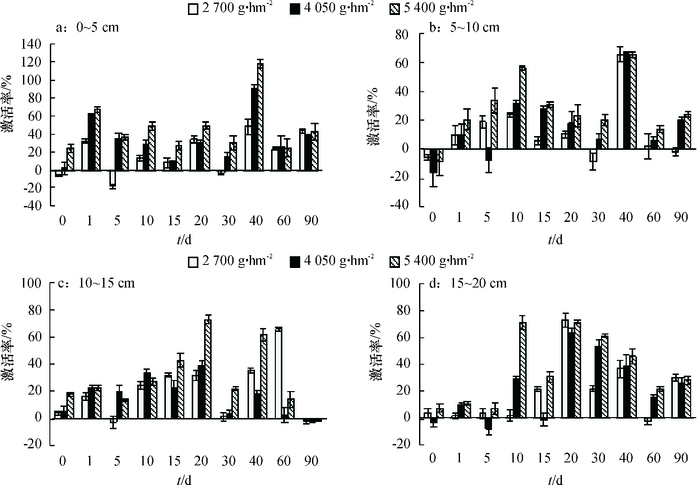
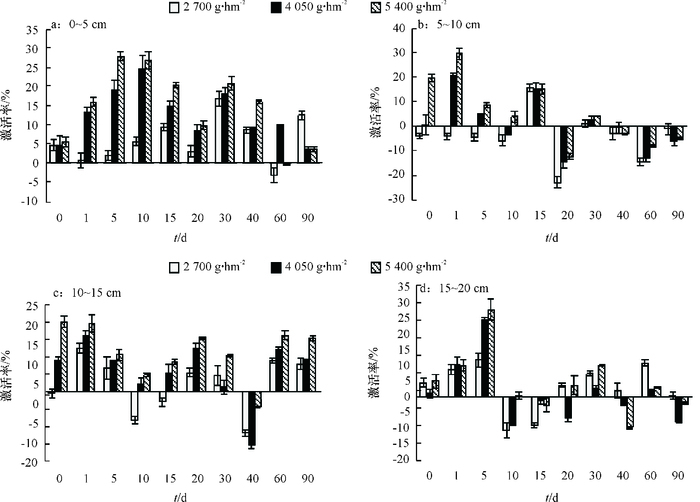
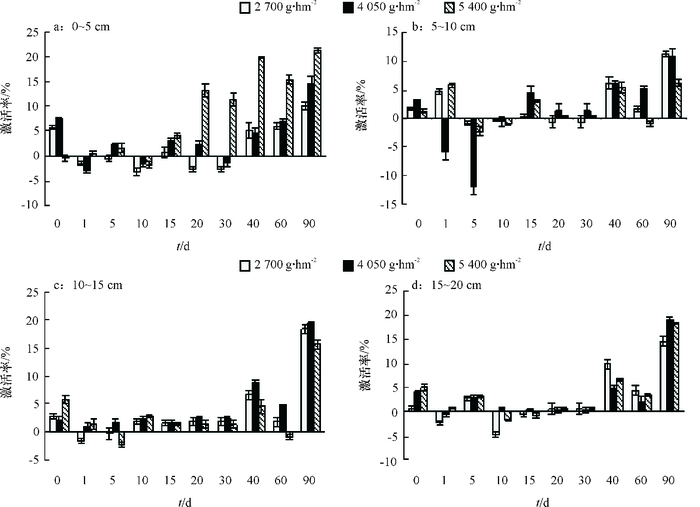
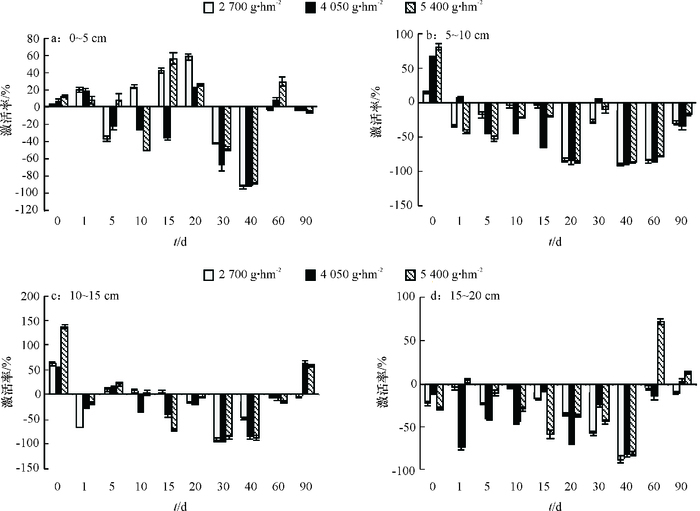
结果施用二甲戊灵后,土壤碱性磷酸酶活性明显被抑制,处理40 d后,5~10 cm土壤层碱性磷酸酶活性被抑制作用最强,二甲戊灵2 700、4 050、5 400 g·hm-2处理的碱性磷酸酶活性抑制率分别为93.79%、90.77%、87.43%;脲酶活性总体表现激活趋势;蔗糖酶和脱氢酶活性随二甲戊灵浓度增高而增强,表层土壤酶活性较10~20 cm深层土壤激活作用显著;随着处理时间的增加,0~10 cm土壤层过氧化氢酶活性呈现先抑制后激活的趋势。
结论棉田土壤经二甲戊灵处理后,表现为脲酶、过氧化氢酶的激活效应;但二甲戊灵会抑制碱性磷酸酶活性,降低土壤有效磷素,长期施用会导致土壤营养失衡。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo study the effects of pendimethalin on soil enzyme activities in cotton field.
MethodPendimethalin at different concentrations (0, 2 700, 4 050, 5 400 g·hm-2) were applied to cotton field. Changes in soil enzyme activities at different soil depth and treatment time were investigated.
ResultAfter treating with pendimethalin, alkaline phosphatase activity was substantially inhibited, and was inhibited the most at the soil depth of 5-10 cm 40 days after treatment.The inhibition rates of 2 700, 4 050 and 5 400 g·hm-2 treatments were 93.79%, 90.77% and 87.43% respectively. Urease activity had been continuously activated. Sucrase and dehydrogenase activities increased with the concentration of pendimethalin increasing, and the enhancements of the soil surface were significantly stronger than those at the soil depth of 10-20 cm. Catalase at the soil depth of 0-10 cm was firstly inhibited and then activated with the treatment time increasing.
ConclusionPendimethalin can activate urease and catalase, inhibit alkaline phosphatase, and reduce the soil available phosphorus content in cotton field. Long-term application of pendimethalin can cause soil nutrient imbalance.
-
Keywords:
- cotton field /
- pendimethalin /
- alkaline phosphatase /
- urease /
- sucrase /
- dehydrogenase /
- catalase
-
-
[1] GIANFREDA L, RAO M A. Interactions between xenobiotics and microbial and enzymatic soil activity[J]. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec, 2008, 38(4): 269-310. doi: 10.1080/10643380701413526
[2] KOTROCZÓ Z, VERES Z, FEKETE I, et al. Soil enzyme activity in response to long-term organic matter manipulation[J]. Soil Biol Biochem, 2014, 70: 237-243.doi:10.1016/j.sojlbio.2013.12.028" target="_blank">http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.sojlbio.2013.12.028.
[3] EMILIO B, RAQUEL M, ROGELIO N. Estimating soilresilience to a toxic organic waste by measuring enzyme activities[J].Soil Biol Biochem, 2004, 36(10): 1615-1623. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.014
[4] JUNG J, PHILIPPOT L, PARK W. Metagenomic and functional analyses of the consequences of reduction of bacterial diversity on soil functions and bioremediation in diesel-contaminated microcosms[J]. Sci Rep, 2016(6): 23012. doi: 10.1038/srep23012.
[5] KALAM A, TAH J, MUKHERJEE A K. Pesticide effects on microbial population and soil enzyme activities during vermicomposting of agricultural waste[J].J Environ Biol, 2004, 25(2): 201-208.
[6] 姜虎生, 王宏燕.除草剂对土壤脱氢酶活性及呼吸强度的影响[J].吉林农业科学, 2011, 36(5): 53-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLNK201105017.htm [7] 傅丽君, 杨文金. 4种农药对枇杷园土壤磷酸酶活性及微生物呼吸的影响[J].中国生态农业学报, 2007, 15(6): 113-116. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN200706026.htm [8] SWARCEWICZ M K, GREGORCZYK A. The effects of pesticide mixtures on degradation of pendimethalin in soils[J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2012, 184(5): 3077-3084. doi: 10.1007/s10661-011-2172-x
[9] 梁友, 贾会娟, 董雪, 等. 4种土壤处理除草剂对龙葵的防除效果及安全性评价[J].江西农业大学学报, 2014, 36(1): 102-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXND201401016.htm [10] 王宇, 黄春艳, 黄元炬, 等.除草剂在向日葵田除草效果及安全性试验[J].农学学报, 2014, 4(6): 20-23. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2013-1132 [11] ZAIT Y, SEGEV D, SCHWEITZER A, et al. Development and employment of slow-release pendimethalin formulations for the reduction of root penetration into subsurface drippers[J]. J Agr Food Chem, 2015, 63(6): 1682-1688. doi: 10.1021/jf504839q
[12] 贾会娟, 金前, 梁友, 等.高效液相色谱测定棉田不同土壤深度二甲戊灵残留量[J].石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 33(6): 689-693. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHZN201506006.htm [13] 金前, 贾会娟, 李雪玲, 等.二甲戊灵胁迫下的土壤酶活性变化[J].新疆农业科学, 2015, 52(5): 889-894. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJNX201505018.htm [14] 关松荫.土壤酶及其研究法[M].北京:农业出版社, 1986:1-327. [15] 杨兰芳, 曾巧, 李海波, 等.紫外分光光度法测定土壤过氧化氢酶活性[J].土壤通报, 2011, 42(1): 207-210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201101044.htm [16] 呼蕾, 和文祥, 王旭东, 等.草甘膦的土壤酶效应研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(4): 680-685. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200904011.htm [17] 傅丽君, 赵士熙, 王海, 等. 4种农药对土壤微生物呼吸及过氧化氢酶活性的影响[J].福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 34(4): 441-445. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJND200504008.htm [18] 郭明, 尹亚梅, 何良荣, 等.农用化学物质对土壤脲酶活性的影响[J].农业环境保护, 2000, 19(2): 68-71. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200002001.htm [19] 崔荟萍, 赵桂琴, 刘欢.除草剂对燕麦田土壤脲酶和碱性磷酸酶活性的影响[J].中国草地学报, 2014, 36(1): 37-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCD201401008.htm [20] CYCON M, PIOTROWSKA S Z, KOZDRO J.Dehydrogenase activity as an indicator of different microbial responses to pesticide-treated soils[J]. Chem Ecol, 2010, 26(4): 243-250. doi: 10.1080/02757540.2010.495062
[21] ÁLVAREZ M A, HILTON S L, BENDING G D, et al. Changes in activity and structure of the soil microbial community after application of azoxystrobin or pirimicarb and an organic amendment to an agricultural soil[J]. Appl Soil Ecol, 2016, 106: 47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.05.005
[22] 马彦霞, 郁继华, 张晶, 等.设施蔬菜栽培茬口对生态型无土栽培基质性状变化的影响[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(14): 4071-4079. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201414031.htm [23] 张学鹏, 宁堂原, 杨燕, 等.不同浓度石灰氮对黄瓜连作土壤微生物生物量及酶活性的影响[J].应用生态学报, 2015, 26(10): 3073-3082. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYSB201510021.htm [24] 荆瑞勇, 王丽艳, 王彦杰, 等.乙草胺对土壤微生物数量和酶活性的影响[J].中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(6): 1302-1305. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN201006029.htm [25] 林晓燕, 王玮, 赵宇华, 等.苄嘧磺隆对淹水稻田土壤呼吸和酶活性的影响[J].浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2008, 34(1): 109-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJNY200801019.htm



 下载:
下载: