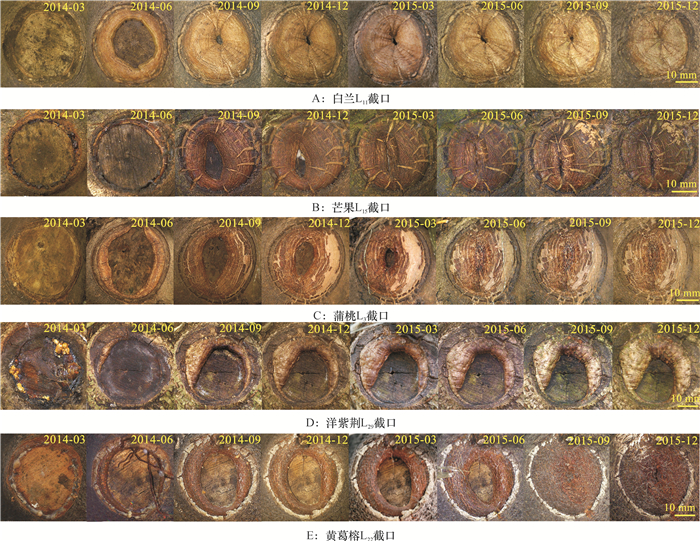
Closure characteristics in pruning wounds of five species of landscape trees in South China
-
摘要:目的
研究华南地区园林树木修剪截口在修剪2年内的愈合进程,探究修剪截口愈合特性,为园林树木修剪提供理论依据。
方法于2013年12月对5种园林树木3种规格的450个枝条进行修剪试验,修剪后每3个月跟踪测量修剪截口的愈合进程,分析树种特性、截口规格以及季节变化等因素在截口愈合反应中的表现差异。
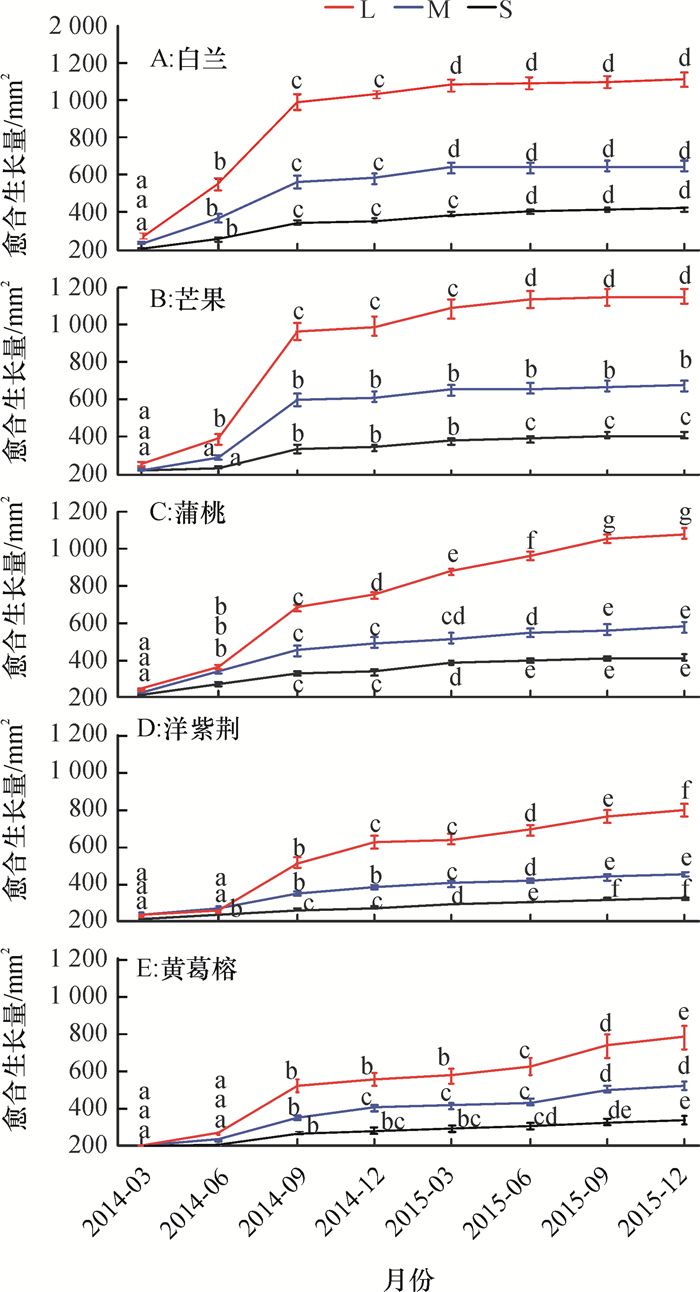
结果白兰Michelia alba和芒果Mangifera indica截口愈合速度较快,修剪2年后愈合率分别达94.80%和92.38%,且在截口直径20~ < 30 mm和30~ < 40 mm的规格水平下愈合速度较快;蒲桃Syzygium jambos、洋紫荆Bauhinia variegata、黄葛榕Ficus viren截口愈合速度较慢,修剪2年后愈合率分别为82.23%、64.95%和70.99%,且在10~ < 20 mm规格下愈合速度较快;截口愈合进程总体表现为第1年由修剪初始到3月增长缓慢,3—6月增长加速,6—9月增长最快,9—12月增长减缓,与树木年生长物候相一致;第2年愈合速度减慢。
结论修剪规格对截口愈合的影响因树种而异,截口愈合速度与树木生长速度有紧密联系。
Abstract:ObjectiveClosing process of landscape trees in South China was studied in two years after pruning, in order to explore the closure mechanism of pruning wounds, and provide a theoretical basis for landscape tree pruning practice.
MethodBranches in three sizes from five species of landscape trees were trimmed in December 2013. Measurements of the wound closing process were taken every three months from December 2014 to December 2015. Differences in wound closure abilities caused by species characteristics, wound sizes and seasonal changes were analyzed.
ResultThe wound closure rates of Michelia alba and Mangifera indica were relatively higher (94.80% and 92.38%) compared to other species, and the wounds of 20- < 30 mm and 30- < 40 mm diameters closed faster compared to 10- < 20 mm wounds. The wound closure rates of Syzygium jambos, Bauhinia variegata and Ficus virens were relatively lower (82.23%, 64.95% and 70.99%), and the wounds of 10- < 20 mm diameter closed faster. The wound closure process was generally slow from the time of pruning to March, accelerated from March to June, was the fastest from June to September, and slowed down from September to December in the first year, which was consistent with the changes in tree growth rates during annual growth periods. The wound closure process was slow in the second year.
ConclusionWound size influences wound closure rate differentially among species. Wound closure rate is closely associated with the tree growth rate
-
Keywords:
- landscape tree /
- pruning diameter /
- wound closure /
- closure rate /
- closure area
-
烟草青枯病是一种由青枯雷尔菌Ralstonia solanacearum引起的系统性侵染病害,现已成为世界各产烟区最主要的病害之一[1]。该病在我国河南、山东、江苏、云南、广西、广东、福建等地普遍发生,烟株一旦染病,往往整株死亡,其危害是毁灭性的,给生产造成重大经济损失[2]。因此,研究青枯菌致病机理和寻找有效的防治青枯病的方法是当前植物病理学研究的重要课题之一, 其中抗病育种防治青枯病的生化机制最为重要。国内外学者对大量的相关病害进行研究,发现植物在受病害侵袭过程中表现出一系列复杂的生理生化变化,包括体内代谢的变化、细胞内活性氧的积累与清除、抗病信号的产生与转导、防卫反应的表达与调控等[3-4]。在这一复杂过程中,一些与植物抗病性相关的酶类起着很重要的调控作用[5-6],如苯丙氨酸解氨酶(Phenylalanine ammonium lyase, PAL)、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化物酶(Peroxidase,POD)和多酚氧化酶(Polyphenol oxidase,PPO)等。同工酶谱分析作为一种认识基因存在和表达的工具已被大量运用于种质分类与种间遗传差异分析[7-9],其规律性变化可以作为一种早期的鉴别手段,用来研究植物的抗病性问题。因此,笔者选择了2个不同抗性的烟草品种,进行青枯病菌的接种试验,在接菌后不同时段及时采样,测定与病程相关的防御性酶活性以及代谢组分,从而了解烟草抗、感青枯病的变化过程,旨为烟草抗青枯病育种提供生化方面的依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
试验所用烟草品种:高度感病品种长脖黄及高度抗病品种粤烟97,均由广东南雄烟草科学研究所提供;烟草青枯雷尔菌由广东省农科院何自福研究员惠赠;病菌的保存与增殖参照匡传富等[10]的方法。
仪器:LRH型生化培养箱(广东省韶关市鑫腾科普有限公司);FC—18R台式高速冷冻离心机(厦门仪达仪器有限公司);DYCZ-24DN型垂直电泳槽(北京六一仪器厂);DYY 11B三恒电泳仪(北京六一仪器厂);10 μL微量进量器(德国Eppendorf AG);UV-8500PC型紫外-可见分光光度计(上海天美科学仪器公司);1702-MP8型电子天平(德国Startorius公司);岛津GC-MS Q2010 Ultra(日本Shimadzu公司)。
1.2 试验方法
选取长势一致、3~4叶龄的健康烟草植株供试,将其移栽至装有灭菌土的18 cm×23 cm的塑料盆中,每个处理为5株,设置3个重复,放置于室外环境下。待烟苗生长7 d后,接菌组参照黎定军等[11]茎部注射法,用注射器将1 mL青枯雷尔菌液(5×108 cfu·mL-1)从叶腋处注入烟茎基部的维管束里,并在接菌处注意保湿,对照组为清水处理的烟苗。分别在处理1、3、5、7、9、11 d后,取同一叶位处的烟叶进行相关生化指标的测定,其中代谢组分差异分析选择接菌后的第3天进行。
1.2.1 防御性酶活性测定
PAL的提取及活性测定参照薛应龙等[12]方法;SOD的提取与测定参照邹琦[13]163-165的方法;POD的提取与测定参照张志良[14]的方法;PPO的提取与活性测定参照李靖等[15]的方法。PAL以每分钟D290 nm变化0.01所需要的酶量定义为1个酶活性单位(U);POD和PPO分别以每分钟D470 nm、D410 nm变化1.00所需要的酶量定义为1个酶活性单位(U);SOD以每分钟D560 nm抑制50 %所需要的酶量定义为1个酶活性单位(U)。
1.2.2 POD和PPO同工酶电泳
酶液制备:取0.1 g样品,加入0.1 mol·L-1预冷的Tris-HCl (pH 6.8)缓冲液1.5 mL,冰浴研磨,12 000 r·min-1、4 ℃条件下离心15 min,取上清液,于-70 ℃冰箱保存备用。
电泳:采用不连续的聚丙烯酰胺凝胶垂直板电泳技术[13]131-135,上样缓冲液不加SDS和β-巯基乙醇,电极缓冲液为pH 8.3的Tris-Gly缓冲液,样品不经加热处理。同工酶电泳采用聚丙烯酰胺为7.5%的分离胶、4%的浓缩胶。样品上样量为10 μL[V(样品缓冲液): V(粗酶液)=1: 1],于4 ℃条件下电泳,浓缩胶80 V、电泳30 min,分离胶120 V、电泳1.5 h。以溴酚蓝作指示剂,电泳结束后,取下胶进行染色。
POD同工酶染色:称取0.1 g联苯胺,加少量无水乙醇溶解,依次加入5 mol·L-1的醋酸溶液10 mL,1.5 mol·L-1的醋酸钠溶液10 mL,水70 mL,最后加入3~5滴质量分数为30%的过氧化氢溶液。将凝胶电泳胶带放入装有染色液的塑料小盆中,并轻轻晃动,待条带清晰后,立即用相机拍照记录。
PPO同工酶染色:3份质量分数为1%邻苯二酚溶液,1份0.05 mol·L-1磷酸缓冲液(pH6.8),1份质量分数为0.06%对苯二胺溶液,混合均匀后,将胶带放入染色液中3~5 min,即可见到棕红色的多酚氧化酶酶带。
1.2.3 代谢组分差异分析
烟草样品前处理方法:参考Tikunov等[16]和Roessner等[17]建立的方法。
气相色谱条件:进样口温度250 ℃。升温程序:初始温度50 ℃,保持1 min,以5 ℃·min-1升温速度升到150 ℃保持2 min,最后以10 ℃·min-1升温速度升到250 ℃,保持10 min。以高纯氦气(体积分数大于99.999%)为载气采用不分流进样方式,进样量1 μL,载气流速1 mL·min-1。
质谱条件:电子轰击源(EI),离子源温度200 ℃,四极杆温度150 ℃,接口温度250 ℃,电子能量70 eV,溶剂延迟时间4 min;调谐方式为标准调谐,质谱扫描方式为全扫描,扫描范围为50~500 aum。使用NIST 2011谱库进行图谱检索。
1.3 数据分析
试验数据采用Microsoft Excel 2003和SPSS11.5数据处理软件进行数据统计分析,酶活性数值均为平均值±标准差。应用Duncan's新复极差法进行差异显著性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 几种防御性酶活性变化
2.1.1 PAL活性变化
从图 1可知,抗病品种粤烟97的PAL活性在整个测定时期,接菌组与对照组均高于感病品种长脖黄。抗病品种粤烟97在接菌后第7天酶活性显著高于对照组(P<0.05),其余时间酶活性均低于对照组;感病品种长脖黄在接菌后第5天,PAL活性显著高于对照组(P<0.05),其余时间酶活性均低于对照组。
2.1.2 SOD活性变化
从图 2可知,抗病品种粤烟97的SOD活性在整个测定时期,接菌组与对照组均高于感病品种长脖黄。抗病品种粤烟97在接菌后第3、5、7、9天,SOD活性均高于对照组,其中第7天差异显著(P<0.05);感病品种长脖黄在接菌后第1、3、5天,SOD活性均高于对照组,其中第5天差异显著(P<0.05)。由此得知,抗、感品种在受到青枯菌侵害后,均能使SOD迅速被激活,从而起到清除或阻止病原菌所造成伤害的作用。
2.1.3 POD活性变化
从图 3可知,抗病品种粤烟97的POD活性在整个测定时期,接菌组与对照组均高于感病品种长脖黄。抗病品种粤烟97在接菌后第3天,酶活性显著高于对照组(P<0.05),其余时间酶活性均显著低于对照组(P<0.05);感病品种长脖黄在接菌后第3、5天,酶活性高于对照组,其中第5天差异显著(P<0.05),其余时间POD活性均低于对照组。
2.1.4 PPO活性变化
从图 4可知,抗病品种粤烟97对照组、接菌组的PPO活性均高于感病品种长脖黄的。接菌后第3天,粤烟97和长脖黄的PPO活性略高于各自的对照组,其余时间均低于各自的对照组。
2.2 接菌处理对不同品种烟草叶片中POD和PPO同工酶表达的影响
2.2.1 对POD同工酶的影响
从图 5A可看出,抗病品种粤烟97接菌后,整个测定期间POD同工酶谱带未增加,但凝胶电泳谱带宽度与色度均发生变化。接菌后第3天,接菌组的同工酶谱带较对照组谱带宽,且颜色较深;接菌后第1、11天,接菌组POD同工酶谱带色度比对照组弱;接菌后第5天,接菌组POD同工酶谱带条数比对照组少,且部分条带颜色较浅;接菌后第7、9天,接菌组与对照组POD同工酶谱带无明显差异。从图 5B可看出,感病品种长脖黄在接菌后第1、5、7、9天,接菌组POD同工酶谱带颜色均比对照组颜色浅;接菌后第3、11天,同工酶谱带宽度和颜色与对照基本无差别。对比图 5 A、图 5 B可知,抗病品种粤烟97的POD同工酶谱带为6条,感病品种长脖黄的POD同工酶谱带为2条,说明抗病品种粤烟97的POD同工酶类型多于感病品种长脖黄的POD同工酶类型。
2.2.2 对PPO同工酶的影响
从图 6A可以看出,抗病品种粤烟97接菌后第1、7天,接菌组与对照组的PPO同工酶谱带无明显差异;接菌后第3天,PPO同工酶谱带宽度与色度均高于对照组;接菌后第5天,PPO同工酶谱条带数与色度均低于对照组;接菌后第9、11天,部分PPO同工酶谱带色度略低于对照组。从图 6B可以看出,感病品种长脖黄接菌后第1、9、11天,PPO同工酶谱带条数、色度与对照组无明显差异;接菌后第3天,PPO同工酶谱带色度均低于对照组;接菌后第5和7天,PPO同工酶谱带色度略高于对照组。对比图 6 A、图 6 B可知,抗病品种粤烟97的PPO同工酶谱带最多为6条,最少为4条,感病品种长脖黄的POD同工酶谱带为2条,说明抗病品种粤烟97的PPO同工酶类型多于感病品种长脖黄的PPO同工酶类型。
2.3 代谢组分差异分析
对不同抗病品种接菌处理后叶片提取物进行GC-MS测定, 得到总离子流图(图 7)。从图 7可以直观地看出不同抗病品种间存在明显差异,接菌组与对照组间,峰的数量和强度也都存在差异。
通过岛津质谱工作站对总离子流图的处理解析, 峰面积归一化法测量了各组分的百分含量。通过检索和解析初步分离最多确定了70个化合物。鉴定的各组分及相对质量分数见表 1。
表 1 不同抗病烟草品种接种青枯雷尔菌后品种间代谢物差异比较1)Table 1. Comparison of metabolites from resistant and susceptible tobacco cultivars after inoculation of Ralstonia solanacearum
从表 1可以看出烟株被青枯雷尔菌侵染后代谢物差异较为明显,粤烟97接菌后烟叶样本中代谢物相对质量分数高于其对照组,且长脖黄接菌后相对质量分数低于其对照组的是乳酸、甘油酸、肌肉肌醇、L-苏糖酸、苹果酸、L-吡咯烷酮-5-羧酸、烟碱、丝氨酸、L-苏氨酸、D-来苏糖、核糖醇、β-D-果糖、D-(+)-塔罗糖、棕榈酸、硬脂酸,说明烟草抗青枯病能力的强弱可能与这些物质有关,或者与参与形成上述代谢物的酶活性有关;2个不同抗病品种接菌后共同产生或者相对质量分数比对照增高的物质分别为:L-缬氨酸、草酸、L-异亮氨酸、丙二酸、磷酸、L-天冬氨酸、赤藓糖醇、L-苯丙氨酸、十四烷醇、L-阿拉伯糖、D-木糖,不同抗病品种烟草在受到青枯雷尔菌侵袭时均会刺激体内代谢物含量的改变,其含量的增高说明上述代谢物可能参与抗病相关物质的形成。
3. 讨论与结论
与植物抗病相关的PAL、SOD、PPO和POD均属于植物防卫系统相关酶,因此可作为植物抗病的生化指标。在植物体内,PAL是苯丙烷类代谢途径的关键酶和限速酶,催化L-苯丙氨酸解氨生成反式肉桂酸(合成各种酚类及木质素的前体物质),因而调控与植物抗病有关的酚类物质和木质素在植物体中的合成和积累[18]。研究表明,PAL活性与植物抗病性呈正相关[15, 19]。本研究中,在整个测定期间,抗病品种粤烟97的PAL活性均高于感病品种长脖黄,说明烟草品种抗病强弱,与体内PAL活性呈正相关。SOD作为植物体内活性氧清除系统重要保护酶之一,能清除超氧化物阴离子自由基,提高植物抗逆性[20]。本研究表明,抗病品种粤烟97在接菌后第3、5、7、9天,SOD活性均大于对照,感病品种长脖黄在接菌后第1、3、5天,SOD活性均高于对照,抗病品种SOD活性在接菌组与对照组中均高于感病品种,说明在青枯雷尔菌侵染后抗病品种可高效地清除活性氧的伤害,感病品种由于本身SOD活性低,接菌后酶活性增长幅度较小而使其受到伤害。POD是一种应激酶,其活性与植物抗病性有着密切的关系,在活性氧的清除和维持植物体内活性氧的正常水平中起作用;POD还能催化木质素合成,木质化的细胞壁机械性能加强,不透水气,阻止营养物质、水分、色素等的扩散,使病原菌无法获得营养而死亡[21-22]。研究表明,POD活性与植物的抗病性具有正相关关系[23-26]。PPO是一类广泛分布于植物体内的质体金属酶,能直接以O2为氧化底物将酚氧化成醌,从而抑制病虫害的侵袭。PPO不仅参与酚类物质的氧化,同时也参与木质素的形成[27]。本研究发现抗病品种粤烟97的POD活性高于感病品种长脖黄,且POD同工酶谱分析表明,抗病品种粤烟97的谱带条数均要多于感病品种长脖黄。接菌后抗病品种的POD活性迅速升高,而感病品种则较弱,2品种的POD活性随着时间延长均降低,说明青枯雷尔菌侵染烟草后均能刺激体内POD活性的提高,且抗病品种总体强于感病品种。抗病品种粤烟97和感病品种长脖黄接菌后第3天,PPO活性略高于对照组,随着时间延长酶活性均降低。抗病品种粤烟97中PPO活性高于感病品种长脖黄,可能与其抗病性强有关。
烟草植株受到病菌侵染时,引起相关酶活性的改变,继而引起植株体内代谢物质的改变,形成的代谢物本身具有抗病作用或者进一步通过转化形成与抗病有关的次级代谢物。例如PAL酶活性高低会影响L-苯丙氨酸含量[28],POD酶活性影响某些糖类、氨基酸类等与木质素合成有关物质的含量[29]。本研究发现,粤烟97与长脖黄在接菌处理3 d时,SOD、POD、PPO活性均比对照高,而PAL活性均低于对照组,因此植株体内相关酶催化形成的物质应该有所提高,或者酶促反应的底物应该有所降低。代谢物检测表明,2个抗病性不同的品种接菌后共同产生或者相对质量分数相比对照增高的物质分别为:L-缬氨酸、草酸、L-异亮氨酸、丙二酸、磷酸、L-天冬氨酸、赤藓糖醇、L-苯丙氨酸、十四烷醇、L-阿拉伯糖、D-木糖,说明此类代谢物含量的变化可能与防御性酶活性有关;粤烟97接菌后烟叶样本中代谢物相对质量分数高于其对照组,但长脖黄接菌后相对质量分数低于其对照组的物质分别为:乳酸、甘油酸、肌肉肌醇、L-苏糖酸、苹果酸、L-吡咯烷酮-5-羧酸、烟碱、丝氨酸、L-苏氨酸、D-来苏糖、核糖醇、β-D-果糖、D-(+)-塔罗糖、棕榈酸、硬脂酸,说明此类代谢物含量的变化与防御性酶活性变化无关,可能与其他酶活性变化有关。研究表明,肌醇在植物体内通过自身氧化途径可以代谢为与植物细胞壁合成息息相关的多糖,从而提高植物抗病性[30]。烟碱作为一种防御性物质,在烟草受到病虫害侵袭时会刺激体内产生大量烟碱[31],此外,相关研究表明,在细胞质中苹果酸酶催化苹果酸脱羧形成的丙酮酸参与莽草酸途径,进一步形成丙酮酸族氨基酸和一些与防御反应有关的次生代谢物质[32]。L-苏糖酸作为L-抗坏血酸的一种降解产物,广泛存在于植物体内,其含量的增加,说明抗坏血酸积极参与抗氧化作用,保护机体免于自由基的威胁[33]。不同烟草品种抗青枯病的机理,不仅与其体内防御性酶活性有关,可能还与某些代谢物或与其相关的酶活性变化有关。
-
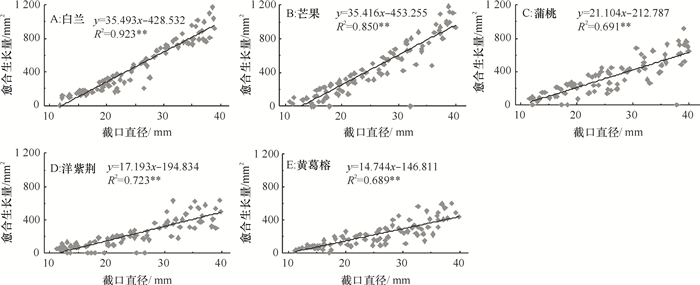
表 1 不同园林树种修剪2年后截口愈合情况1)
Table 1 Wound closure of five tree species after two years of pruning
树种 胸径/cm 愈合率/% 愈合生长量/mm2 CCN ICN NRN 白兰 10.18~15.21 94.80±0.84Aa 528.18±39.85Aa 72 17 1 芒果 11.47~16.88 92.38±0.76Aa 543.80±43.76Aa 71 15 4 蒲桃 9.90~16.68 82.23±1.88ABb 488.27±39.05Aa 33 53 4 洋紫荆 9.48~16.81 64.95±2.64Bc 321.06±32.16Bb 23 61 6 黄葛榕 12.19~19.68 70.99±2.59Bbc 347.49±32.21Bb 23 66 1 1) 同列数据后凡具有一个相同小、大写字母者,分别表示不同树种间差异未达0.05、0.01的显著水平(Duncan’s法);CCN为完全闭合的截口数,ICN为有愈合反应但未完全闭合的截口数,NRN为无愈合反应的截口数。 表 2 修剪1年和2年后5个树种3种规格的截口愈合率分析
Table 2 Closure ratio of wounds with three different sizes in five tree species one year and two years after pruning
树种 2014-12的愈合率/% 2015-12的愈合率/% S M L S M L 白兰 74.54±3.80Bb 90.47±2.10Aa 87.66±2.51Aa 92.67±1.86Ab 96.52±1.01Aa 95.21±1.39Aa 芒果 64.65±7.01Bb 86.89±3.09Aa 83.29±3.54Aa 86.96±0.84Bb 96.65±1.33Aa 93.52±1.80Aa 蒲桃 66.98±4.13Aa 59.63±5.61ABab 53.29±2.36Bb 86.95±2.10Aa 80.31±4.08Bb 79.42±2.15Bb 洋紫荆 47.38±3.53Aa 42.89±3.82Bb 41.68±3.58Bb 69.38±4.34Aa 63.03±5.23Bb 62.44±3.44Bb 黄葛榕 48.65±2.53Aa 38.75±2.66Bb 36.61±2.56Bb 80.70±2.77Aa 71.93±4.17Aa 60.34±4.69Bb 1) 同一树种相同时间同行数据后凡具有一个相同小、大写字母者,分别表示不同截口规格间差异未达0.05、0.01的显著水平(Duncan’s法);S、M、L分别表示直径为10~ < 20、20~ < 30、30~ < 40 mm的截口。 -
[1] SHIGO A L. Compartmentalization of decay in trees[J]. Sci Am, 1985, 252(4):96-103. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0485-96
[2] DUJESIEFKEN D, STOBBE H. The hamburg tree pruning system: A framework for pruning of individual trees[J]. Urban For Urban Gree, 2002, 1(2):75-82. doi: 10.1078/1618-8667-00008
[3] 胡兵, 邵卓平.树洞周边愈伤木与正常木的化学组成及物理力学特性的比较[J].东北林业大学学报, 2013, 41(10):86-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2013.10.018 [4] 艾沙江·买买提, 梅闯, 张校立, 等.短截对富士苹果萌芽前后枝条不同部位碳氮营养的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(8):140-146. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBNY201508021.htm [5] 吴媛琳, 王世军, 张社奇, 等.修剪对苹果枝(梢)皮层总黄酮含量的影响[J].西北林学院学报, 2013, 28(6):103-107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBLX201306022.htm [6] 张乃文, 董彩霞, 徐阳春.梨树修剪枝和果实从树体移走的养分研究[J].南京农业大学学报, 2013, 36(4):37-42. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJNY201304008.htm [7] 刘球, 李志辉, 陈少雄, 等.托里桉修枝伤口愈合研究[J].西北林学院学报, 2010, 25(4):92-96. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBLX201004021.htm [8] 张群. 人工修枝对提高杉木木材质量影响的研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2011. [9] 马永春. 杨树人工林修枝机理及修枝技术体系的研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2012. [10] 北京市园林绿化局. 北京市地方标准: 行道树修剪规范: DB11/T 839—2011[S]. 北京: 北京市质量技术监督局, 2013-12-23. [11] 广东省林业厅. 广东省地方标准: 木本园林植物修剪技术规范: DB44/T 1784—2015[S]. 广州: 广东省质量技术监督局, 2015-12-23. [12] DEFLORIO G, BARRY K M, JOHNSON C, et al. The influence of wound location on decay extent in plantation-grown Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus nitens[J]. Forest Ecol Manag, 2007, 242(2):353-362.
[13] OW L F, GHOSH S, SIM E K. Mechanical injury and occlusion: An urban tropical perspective[J]. Urban For Urban Gree, 2013, 12(2):255-261. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2013.02.004
[14] BAI S, CHANEY W R, QI Y. Wound closure in trees affected by paclobutrazol[J]. J Arboric, 2005, 31(6):273-279. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238750756_Wound_closure_in_trees_affected_by_paclobutrazol
[15] DUJESIEFKEN D, LIESE W, SHORTLE W, et al. Response of beech and oaks to wounds made at different times of the year[J]. Eur J Forest Res, 2005, 124(2):113-117. doi: 10.1007/s10342-005-0062-x
[16] O′HARA K L. Pruning wounds and occlusion: A long-standing conundrum in forestry[J]. J Forest, 2007, 105(3):131-138. http://escholarship.org/uc/item/2nh227fr
[17] FINI A, FRANGI P, FAORO M, et al. Effects of different pruning methods on an urban tree species: A four-year-experiment scaling down from the whole tree to the chloroplasts[J]. Urban For Urban Gree, 2015, 14(3):664-674. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2015.06.011
[18] MAURIN V, DESROCHERS A. Physiological and growth responses to pruning season and intensity of hybrid poplar[J]. Forest Ecol Manag, 2013, 304(4):399-406. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378112713003381?via%3Dihub
[19] OLESEN T, MENSEL C M, MCCONCHIE C A, et al. Pruning to control tree size, flowering and production of litchi[J]. Sci Hortic, 2013, 156(3):93-98. http://era.daf.qld.gov.au/id/eprint/3954/1/ScientiaHort_156_2013_Olesen.pdf
[20] CLARK J R, MATHENY N. The research foundation to tree pruning: A review of the literature[J]. Arboric Urban For, 2010, 36(3):110-120. http://www.isa-arbor.com/education/resources/educ_Portal_Pruning_AUF.pdf
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 梁丽丽, 钟璐瑶, 张辽, 侯俊, 束良佐. 生物炭及其替代泥炭比例对樱桃萝卜生长的影响. 中国瓜菜. 2025(06)  百度学术
百度学术
2. 侯赛赛,仝姗姗,王鹏企,谢冰雪,张瑞芳,王鑫鑫. 生物炭和秸秆对不同作物生长性状和养分吸收的影响. 中国农业科技导报(中英文). 2025(04): 179-191 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吉光鹏,张栋海,牛蛉磊,吴玉蓉,常学艳. 密植苹果根系空间分布特征研究. 农业科技通讯. 2024(03): 111-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 杨凌,陈泽涛,陈嘉显,陈祝锋,曾曙才,何茜,苏艳,邱权. 减氮配施生物炭对闽楠生长和光合特性的影响. 林草资源研究. 2024(02): 116-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 兰宇,孟军,韩晓日,陈温福. 生物炭基产品及其对土壤培肥改良效应的研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报. 2024(07): 1396-1412 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘丹妮,陈伟盛,黄连喜,刘忠珍,王艳红,魏岚. 生物炭-椰糠栽培基质特性及其对香蕉组培苗生长的影响. 中国农学通报. 2024(28): 112-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: