Structure and succession of Artocarpus hypargyreus community in Neilingding Island, Guangdong
-
摘要:目的
揭示内伶仃岛植被的演替,为中国特有珍稀濒危植物白桂木Artocarpus hypargyreus种群的保护提供科学依据。
方法运用群落生态学方法对内伶仃岛白桂木群落进行样地调查,分析群落的组成和结构、地理成分性质以及物种多样性等,并且与其他3个热带或中亚热带植物群落进行比较。
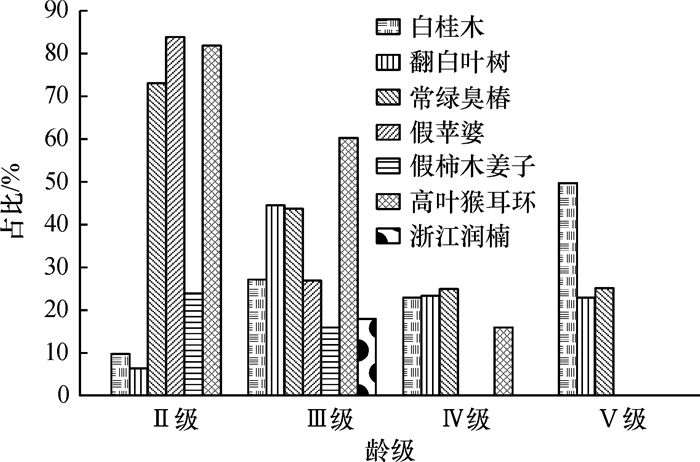
结果该群落共有维管植物73种,隶属于40科61属,其中蕨类植物有4科4属4种,种子植物有36科57属69种。种类组成以热带分布属占绝对优势,占总属数达98.18%,具有南亚热带成分向热带成分过渡的性质。群落垂直结构较明显,乔木层优势种主要有翻白叶树Pterospermum heterophyllum、白桂木、假柿木姜子Litsea monopetala和浙江润楠Machilus chekiangensis等,其重要值依次为43.86、31.64、12.75和10.39;灌木层则以破布叶Microcos paniculata和九节Psychotria rubra为主;层间藤本植物亦十分发达。群落中主要优势种群的分布格局皆为聚群分布,年龄结构以Ⅱ级(DBH<2.5 cm)和Ⅲ级(2.5 cm≤DBH<7.5 cm)立木占绝大多数,属增长型种群,但白桂木种群为衰退型种群。群落的Simpson多样性指数(E)=0.95,Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H)=3.27,Pielou均匀度指数(EH)=0.84。
结论内伶仃岛白桂木群落是一个处于群落演替中期的南亚热带常绿阔叶林类型。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo reveal the succession of vegetation in Neilingding Island, and provide a scientific basis for protection of Artocarpus hypargyreus, a rare and endangered species endemic to China.
MethodMethod in community ecology was used to survey the sample plots of A. hypargyreus community in Neilingding Island, Guangdong. The community composition and structure, characteristics of geographical components and species diversity were analyzed, and were compared to those of other three plant communities in tropic or mid-subtropical regions.
ResultA total of 73 species of vascular plants belonging to 61 genera of 40 families were discovered in the A. hypargyreus community.Among them, 4 species of pteridophyta belong to 4 genera of 6 families, and 69 species of seed plants belong to 57 genera of 36 families. Tropical genera (98.18%) occupied a foremost position in this community which shows a transitional property that range from south subtropical to tropical regions. The stratification of the community was obvious: the dominant populations in the arborous layer mainly were Pterospermum heterophyllum, A. hypargyreus, Litsea monopetala and Machilus chekiangensis, with the important values of 43.86, 31.64, 12.75 and 10.39 respectively, the dominant population in the shrub layer mainly were Microcos paniculata and Psychotria rubra, and the lianas were abundant among the layers. The dominant populations in this community had clustering distribution pattern, and were characterized by stumpage of level Ⅱ (DBH < 2.5 cm) and level Ⅲ (2.5 cm≤DBH < 7.5 cm), indicating that they belonged to the increasing population except the A. hypargyreus population was declining. In this community, Simpson diversity index (E) was 0.95, Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H) was 3.27, and Pielou evenness index (EH) was 0.84.
ConclusionThe A. hypargyreus community in Neilingding Island is a south subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest at the middle stage of succession.
-
致谢: 中山大学2012级本科生罗梦诗, 硕士研究生袁天天、迟盛南、刘宇等参加了野外调查, 特此鸣谢!
-
表 1 内伶仃岛白桂木群落种类组成
Table 1 Species composition of Artocarpus hypargyreus community in Neilingding Island
群落组成 科数 占比/% 属数 占比/% 种数 占比/% 蕨类植物 4 10.00 4 6.56 4 5.48 裸子植物 0 0 0 0 0 0 被子植物 36 90.00 57 93.44 69 94.52 合计 40 100.00 61 100.00 73 100.00 表 2 内伶仃岛白桂木群落种子植物属的分布区类型
Table 2 The generic areal-types of seed plants in Artocarpus hypargyreus community in Neilingding Island
分布类型 属数 区系比例/% 世界分布 2 扣除 泛热带分布 16 29.09 热带亚洲和热带美洲间断分布 1 1.82 旧世界热带分布 15 27.27 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 4 7.27 热带亚洲至热带非洲分布 2 3.64 热带亚洲分布 16 29.09 北温带分布 1 1.82 东亚及北美间断 0 0.00 旧世界温带分布 0 0.00 温带亚洲分布 0 0.00 地中海、西亚至中亚分布 0 0.00 中亚分布 0 0.00 东亚(东喜马拉雅-日本) 0 0.00 中国特有 0 0.00 合计(世界分布区类型除外) 55 100.00 表 3 内伶仃岛白桂木群落主要物种的重要值1)
Table 3 Important values (Ⅳ) of dominant populations in Artocarpus hypargyreus community in Neilingding Island
种名 类型/平均龄级 个体数 相对显著度 相对多度 相对频度 重要值 翻白叶树 乔木/Ⅴ 52 29.42 9.14 5.29 43.86 白桂木 乔木/Ⅴ 22 23.66 3.87 4.12 31.64 破布叶 乔木/Ⅲ 31 15.87 5.45 2.94 24.26 九节 灌木/Ⅲ 57 1.97 10.02 4.71 16.69 光叶紫玉盘 木质藤本/Ⅳ 40 0.50 7.03 6.47 14.01 刺果藤 木质藤本/Ⅳ 20 7.32 3.51 2.35 13.19 常绿臭椿 乔木/Ⅴ 16 8.83 2.81 1.18 12.82 假柿木姜子 乔木/Ⅲ 44 0.32 7.73 4.71 12.75 亮叶猴耳环 乔木/Ⅲ 38 1.24 6.68 4.12 12.03 浙江润楠 乔木/Ⅳ 28 0.18 4.92 5.29 10.39 假苹婆 乔木/Ⅲ 30 0.23 5.27 4.71 10.21 龙须藤 木质藤本/Ⅲ 25 0.41 4.39 2.94 7.75 刨花润楠 乔木/Ⅶ 16 0.08 2.81 4.12 7.01 香港大沙叶 乔木/Ⅲ 12 0.03 2.11 4.71 6.84 白藤 木质藤本/Ⅳ 6 3.39 1.05 2.35 6.80 山椒子 木质藤本/Ⅳ 14 0.10 2.46 2.94 5.50 轮叶木姜子 灌木/Ⅲ 12 0.06 2.11 2.94 5.11 柠檬清风藤 木质藤本/Ⅲ 7 0.11 1.23 3.53 4.87 广州山柑 灌木/Ⅲ 7 1.53 1.23 1.76 4.53 紫玉盘 木质藤本/Ⅳ 12 0.36 2.11 1.18 3.65 白楸 乔木/Ⅲ 4 0.58 0.70 2.35 3.63 苹婆 乔木/Ⅲ 10 0.05 1.76 1.76 3.57 1) 表中为重要值大于3.00的种群,共计22种。 表 4 白桂木群落7个主要种群的分布格局
Table 4 Distribution patterns of seven dominant populations in Artocarpus hypargyreus community
种名 种群多度均值
(X)扩散系数
(C)聚集度
(I)平均拥挤度
(M*)聚块性指数
(PAI)聚集指数
(Ca)负二项分布指数
(K)分布 白桂木 2.75 1.70 0.70 3.45 1.25 0.26 3.90 聚集 翻白叶树 5.78 3.22 2.22 8.00 1.38 0.38 2.60 聚集 常绿臭椿 8.00 4.50 3.50 11.50 1.44 0.44 2.29 聚集 亮叶猴耳环 4.75 2.09 1.09 5.84 1.23 0.23 4.35 聚集 浙江润楠 3.50 1.14 0.14 3.64 1.04 0.04 4.50 聚集 假苹婆 3.75 1.52 0.52 4.27 1.14 0.14 7.26 聚集 假柿木姜子 5.50 2.23 1.23 6.73 1.22 0.22 4.48 聚集 表 5 内伶仃岛及邻近地区几个南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落指数比较
Table 5 Comparison of indexes of south subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest communities in Neilingding Island and neighboring regions
群落 地理位置 海拔/m 土壤
类型气候类型 Simpson
多样性指数Shannon-Wiener
多样性指数Pielou
均匀度指数香港岛黄桐森林群落[27] 22°10′~22°20′N,
114°0′~114°10′E439 赤红壤 热带亚热带
海洋气候区4.74 0.79 内伶仃岛黄牛木群落[29] 22°23′~22°25′N,
113°46′~113°49′E175 赤红壤 南亚热带
季风气候区2.33 0.78 珠海淇澳岛肉实树群落[28] 22°25′N,113°39′E 100 山地黄壤 南亚热带
季风气候区13.70 4.12 0.82 内伶仃岛白桂木群落 22°23′~22°25′N,
113°46′~113°49′E175 赤红壤 南亚热带
季风气候区0.95 3.27 0.84 -
[1] 黎国运, 徐佩玲, 陈光群.濒危植物白桂木组培育苗技术研究[J].热带林业, 2011, 39(3): 24-29. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDLY201103010.htm [2] 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 中国科学院. 中国生物多样性红色名录: 高等植物卷[EB/OL]. [2016-02-08]. http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgg/201309/W020130917614244055331.pdf. [3] 范繁荣. 濒危植物白桂木的濒危机制与迁地保育研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2008. [4] 陈黎明, 谢平, 肖庆青, 等.白桂木化学成分研究[J].中草药, 2007, 38(6): 815-818. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10246-1011198065.htm [5] 欧阳胜, 申作洁, 潘琳娜.白桂木抗炎镇痛作用有效部位筛选[J].中草药, 2010, 41(11): 1850-1853. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO201011032.htm [6] 申作洁, 乔玉丹, 欧阳胜, 等.白桂木抗类风湿性关节炎的有效部位筛选及其作用机制研究[J].中草药, 2011, 42(9): 1792-1795. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO201109038.htm [7] 黎国运, 徐佩玲, 陈光群.濒危植物白桂木种子育苗技术研究[J].热带林业, 2010, 38(3): 23-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDLY201003008.htm [8] 范繁荣.濒危植物白桂木的遗传多样性研究[J].浙江农林大学学报, 2010, 27(2): 266-271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJLX201002020.htm [9] 周德义, 杨尔滨, 邓勇, 等.白桂木凝集素的纯化与性质的研究[J].生物化学与生物物理学报, 1995, 27(1): 61-66. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHWL501.008.htm [10] 周素芳, 周德义.两种亲和层析法纯化白桂木凝集素的比较[J].广西医科大学学报, 1997, 14(3):17-19. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYD703.005.htm [11] 邓家珍, 何志义, 梁国容, 等.白桂木凝集素-HPR夹心法在过敏性哮喘患者唾液SIgA含量检测中的应用[J].广西医科大学学报, 2001, 18(2): 226-227. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYD200102032.htm [12] WU Y S, ZHANG H, ZHOU S F, et al. Characterization of Artocarpus hypargyreus lectin interacting with glycoproteins [J]. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol, 2000, 16(2): 210-214.
[13] 蓝崇钰, 王勇军.广东内伶仃岛自然资源与生态研究[M].北京:中国林业出版社, 2001: 37. [14] 蓝崇钰, 廖文波, 王勇军.广东内伶仃岛的生物资源及自然保护规划[J].植物资源与环境学报, 2002, 11(1): 47-52. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGZO200011001059.htm [15] 崔大方, 廖文波, 昝启杰, 等.广东内伶仃岛国家级自然保护区的植物资源[J].华南农业大学学报, 2000, 21(3): 48-52. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.2000.03.013 [16] 昝启杰, 廖文波, 陈继敏, 等.广东内伶仃岛植物区系的研究[J].西北植物学报, 2001, 21(3): 507-519. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNYX200103022.htm [17] 王伯荪, 余世孝, 彭少麟, 等.植物群落学实验手册[M].广州:广东高等教育出版社, 1996: 1-56. [18] 洪伟.闽江流域森林生态研究[M].厦门:厦门大学出版社, 2000: 176-183. [19] 孙儒泳, 李博, 诸葛阳, 等.普通生态学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 1996: 136-137. [20] 吴征镒.中国种子植物属的分布区类型[J].云南植物研究, 1991, 13(增刊): 1-179. http://youxian.cnki.com.cn/yxdetail.aspx?filename=GXZW20170726000&dbname=CAPJ2015 [21] 吴征镒.中国种子植物属的分布区类型的增订和勘误[J].云南植物研究, 1993 (增刊Ⅳ): 141-178. [22] 彭少麟, 方炜.广州白云山次生常绿阔叶林的群落结构动态[J].应用与环境生物学报, 1996, 2(1):22-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYHS601.003.htm [23] 谢宗强, 陈伟烈, 路鹏, 等.濒危植物银杉的种群统计与年龄结构[J].生态学报, 1999, 19(4): 523-528. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB199904016.htm [24] 王伯荪, 余世孝, 彭少麟, 等.植物种群学[M].广州:广东高等教育出版社, 1995: 8-15. [25] 许晴, 张放, 许中旗, 等. Simpson指数和Shannon-Wiener指数若干特征的分析及"稀释效应"[J].草业科学, 2011, 28(4): 527-531. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYKX201104002.htm [26] 吴昊.不同类型群落物种多样性指数的比较研究[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 2015, 35(5): 84-89. http://youxian.cnki.com.cn/yxdetail.aspx?filename=GXZW20170927003&dbname=CAPJ2015 [27] 王伯荪, 陆阳, 张宏达, 等.香港岛黄桐森林群落分析[J].植物生态学与地植物学学报, 1987, 11(4): 241-251. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWSB198704000.htm [28] 田广红, 丁明艳, 杨雄邦, 等.珠海市淇澳岛肉实树群落及其物种多样性特征[J].植物科学学报, 2013, 31(5): 461-466. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WZXY201305005.htm [29] 袁天天, 赵万义, 徐华林, 等.广东内伶仃岛马尾松群落和布渣叶群落的演替动态[J].广东林业科技, 2015, 31(1): 49-55. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLY201501011.htm



 下载:
下载:
