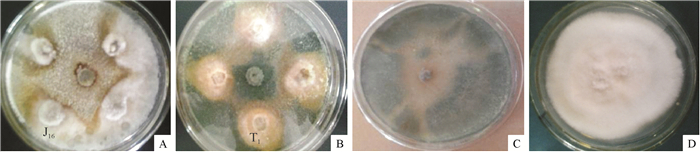
Screening fungal endophytes from apple trees and their antagonistic characteristics
-
摘要:目的
筛选苹果树腐烂病菌Valsa malimiyabe与苹果树炭疽病菌Glomeralla cingalata的内生拮抗真菌,并研究其抑菌效果。
方法分离发病地区健康苹果树的根、茎及其根际土壤中的拮抗内生真菌,室内抑菌试验测定其对苹果树腐烂病菌和苹果树炭疽病菌的抑制作用; 发酵培养试验检测其内生真菌中抑菌物质的耐热性。
结果分离到的18株内生真菌分属3个属,其中茎分离到的内生真菌的种类和数量较多;对峙试验表明,对苹果树腐烂病菌和炭疽病菌的抑菌率高于60%的有8株,其中菌株J2、J16、J17对苹果树腐烂病的抑制率分别为82.75%、84.31%和82.35%,菌株T1对苹果树菌株炭疽病的抑制率为80.67%。拮抗真菌J2、J16、J17、J24、T1发酵液对2种病原菌分生孢子萌发的抑制率均不小于39.55%,最高达69.75%;在121 ℃时,J11和T1无菌滤液的热稳定性较好,而J2无菌滤液在100 ℃时就失去了生物活性。
结论拮抗真菌J2、J11、J16、J17、T1均对苹果树腐烂病菌及苹果树炭疽病菌有较强拮抗作用,可为开展这2种病害的生物防治研究提供潜在资源。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo screen fungal endophytes against Valsa malimiyabe and Glomeralla cingulata from apple trees and explore their inhibitory effects.
MethodFungal endophytes were isolated from roots, stems and rhizosphere soil of healthy apple plants. Their antifungal activities against V. malimiyabe and G. cingulata were examined using in vitro dual culture assay. Heat-resistant properties of antifungal substances were tested using the fermentation culture of the isolated fungal endophytes.
ResultEighteen endophytic fungus strains belonging to three genera were isolated and half of the 18 strains were from stem. The dual culture assay showed eight strains had above 60% inhibition rate against V. malimiyabe and G. cingulata. J2, J16 and J17 strains strongly inhibited V. malimiyabe with the inhibition rates of 82.75%, 84.31% and 82.35% respectively. The inhibition rate of T1 to G. cingulata reached 80.67%. The culture filtrates of fungal endophytes J2, J16, J17, J24, T1 inhibited the conidia germination of both pathogens, and all of the inhibition rates were not less than 39.55% and the highest value was 69.75%. The sterile filtrate of J11 and T1 showed high heat stability at 121 ℃, while J2 lost bioactivity at 100 ℃.
ConclusionFungal endophytes J2, J11, J16, J17 and T1 have strong inhibitory effects against V. malimiyabe and G. cingulata, and therefore are potential candidates for biological control of these two pathogens.
-
Keywords:
- apple tree /
- Valsa malimiyabe /
- Glomeralla cingulata /
- fungal endophyte /
- antifungal activity /
- heat resistance
-
沉香是瑞香科Thymelaeaceae沉香属Aquilaria植物受到自然或人为因素刺激后产生的次生代谢物与木质部结合的油脂性木材[1]。沉香作为我国传统的名贵药材,因其独特的香味,在亚洲、中东和欧洲等地被广泛用于制作香水、熏香和工艺品等[2-6]。由于掠夺式的过度采伐,导致野生沉香属植物濒于枯竭,现已被列为濒危物种[7]。为保护野生沉香资源和提高沉香产量,营建土沉香A. sinensis人工林势在必行。然而,健康的沉香树体并不产香,如何提高结香产量和质量是目前沉香产业发展的重大难题之一。
目前,国内外相关学者关于CO2诱导林木心材的研究显示, CO2可调控心材的形成,其作用在于促使树体内部代谢反应偏向合成萜类物质,但对酚类物质的合成起到抑制作用[8-10]。Nilsson 等[11]研究了樟子松Pinus sylvestris树干填充C2H4、CO2和N2对心材形成的影响,发现填充C2H4或CO2可促使近似天然心材的形成。刘小金[8]对檀香Santalum album 树干填充C2H4、CO2和N2发现,仅填充CO2处理的檀香心材中提炼的精油含量可达国际标准,说明填充气态类物质可作为一种新型外源物质诱导土沉香结香的方式。目前,关于液态物质诱导结香技术研究颇多,但采用气态类物质诱导土沉香结香的研究相对较少。Chowdhury等 [12]认为化学物质可刺激沉香的形成,其中以亚硫酸氢钠、酵母提取物和铁粉按质量比1︰1︰3混合诱导处理的效果最优。潘质洪[13]研究发现,茉莉酸甲酯、乙烯利及其混合溶液亦能诱导土沉香木质部次生代谢产物的积累,二者均以2%体积分数配置的混合溶液所产倍半萜类种类及相对含量的效果最好,茉莉酸甲酯次之,乙烯利最差。Subasinghe等[14]利用黑曲霉菌 Aspergillus niger和腐皮镰刀菌 Fusarium solani分别侵染土沉香发现,二者均可有效促进结香,其中腐皮镰刀菌诱导的沉香质量相对较好。Faizal等[15]采用腐皮镰刀菌通体结香研究也发现,诱导6个月时可取得较好的结香效果。因此,本研究在热带林业研究所珍贵树种培育课题组前期试验及研究报道的较优诱导方式基础上[12-17],选用树干填充CO2进行优良配方耦合的方式,开展土沉香结香试验,旨在探究气−液耦合对沉香形成和成分的影响,为人工诱导土沉香结香提供新技术和新理论。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
试验地位于广东省惠州市博罗县横河镇老圩村人工种植基地(114°6′E,23°20′N) ,选用生长健康、长势均匀的 13 年生土沉香为试验材料,平均胸径(12.58±0. 29) cm,平均树高(7.82±0. 31) m。
1.2 试验设计
采用随机区组试验设计,在研究报道的较优诱导方式[12-17]基础上,共设置4个气–液联合处理,分别是T1处理:CO2与体积比为1︰1的腐皮镰孢菌、黑绿木霉混合液;T2处理:CO2与浓度为30 mol·L−1的NaCl+20 mol·L−1的 FeCl2混合液;T3处理:CO2与浓度为0.5 mol·L−1的茉莉酸甲酯+3 mol·L−1的乙烯利混合液;T4处理:CO2与浓度为20 mol·L−1的NaCl+0.1 mol·L−1的茉莉酸甲酯+腐皮镰孢菌混合液;并且以只充CO2为对照处理(CK-1),只打孔不充气作为空白对照(CK-2),具体见表1。每个处理5株,3次重复,试验共计处理90 株。2020年11月,选择晴天开展试验。在诱导处理结束1年后,在处理中随机选取样株,进行各项指标测定。
表 1 CO2与液体物质组合处理Table 1. Combined treatment of CO2 and liquid substances处理
Treatment打孔
Perforate气态物质
Gaseous matter液体物质组合
Liquid substance combinationT1 打孔 CO2 腐皮镰孢菌+黑绿木霉(体积比为 1︰1) T2 打孔 CO2 NaCl (30 mol·L−1)+ FeCl2(20 mol·L−1 ) T3 打孔 CO2 茉莉酸甲酯(0.5 mol·L−1)+ 乙烯利(3 mol·L−1) T4 打孔 CO2 NaCl (20 mol·L−1)+ 茉莉酸甲酯(0.1 mol·L−1)+腐皮镰孢菌 CK-1 打孔 CO2 CK-2 打孔 1.3 处理方法
充气处理:在距离树干基部40 cm处钻取1个充气孔(直径10 mm),充气具体操作步骤参照专利方法[18],待充气完成后,使用铁夹将橡胶管夹紧以保证管内气体充盈。每隔15 d填充1次气体,持续处理3个月。
输液处理:距充气孔垂直上方及树干对面35 cm处各钻取1个输液孔,控制流速保证输液完全滴注(250 mL/袋),待输液完成后利用土沉香枝条填堵注射孔并用AB胶密封,之后进行充气处理。每隔1个月滴注1次液体, 持续处理3个月,垂直纵向输液孔两两间隔为40 cm。
1.4 指标测定
1.4.1 木质部组织结构内含物观察
每个处理随机选取1棵样株,在充气孔上方3 cm处,用生长锥钻取木芯,样品置于 FAA 固定液带回实验室后,制成2 mm厚的薄片,使用扫描电镜(JSM-6510LV,Japan) 观察木质部组织结构的变化并拍照记录。
1.4.2 木质部油脂类物质观察
取样方法同“1.4.1”,将样品置于FAA 固定液带回实验室后,采用石蜡切片法[19]固定样品,运用德国莱卡滑动切片机(Leica RM2255, Germany) 切取样品三切面(横切面、径切面和弦切面),并使用高清数码相机(Pixera Pro 600ES,USA) 和光学显微镜( Olympus BX51,Japan) 拍照、观察。
1.4.3 木质部变色范围测定
每个处理随机选取3株,分别在处理孔(充气孔和输液孔)上下方使用内径0.5 cm的生长锥每隔3~5 cm钻取木芯,直至钻取木芯全为白木为止,室内绘制变色距离直观图。
1.4.4 醇溶性挥发油含量及成分测定
每个处理均选用5棵样株,在充气孔上方5 cm处,截取5 cm厚半圆片,将其置于40 ℃恒温干燥箱烘至恒质量。分别用小刀除去白木部分,将剩余的深色树脂部分(沉香区)粉碎后过40目筛网。称取2.00 g木粉粉末,置离心管中,加入φ为95%乙醇溶液20 mL,在水浴中超声处理30 min,取上清液,并重复上述操作1次。用0.45 μm滤膜将2次上清液定容到50 mL,通过旋转蒸发浓缩后计算精油含量[20],最后求平均值。
精油成分采用气相色谱质谱(GC-MS)系统(安捷伦7890B-5977A,美国)进行测定。搜索NIST14库,依据保留指数鉴定化合物,计算峰面积,得到各组分的相对含量。色谱条件:色谱柱HP-5MSZ (30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 µm);升温程序:起始温度70 ℃,保持1 min后,以10 ℃/min升至150 ℃,保持5 min;再以 5 ℃/min升至200 ℃,保持5 min;然后以8 ℃/min升至280 ℃,保持1 min。进样口温度250 ℃;载气为高纯He(φ为99.999%),载气流量10 mL/min,进样量0.2 µL(不分流),溶剂延迟4 min。质谱条件:色谱–质谱接口温度280 ℃;离子源温度230 ℃;电离方式 EI;电子能量70 eV,质量扫描范围35~350 AMU。
1.5 数据分析
采用Excel进行数据录入及预处理,运用SPSS 22.0和Origin 2021软件进行数据统计分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 木质部组织结构内含物变化
以CK-1和T2处理为例,土沉香木质部组织结构内含物见图1。处理前土沉香木质部导管、木射线细胞内存在大量淀粉粒(图1A~C),导管纹孔、管壁结构清晰,但导管内未观察到累积形成的侵填物或油脂类物质(图1D),诱导处理1年后,CK-1处理的导管、木射线出现絮状内含物的富集,淀粉粒在木射线细胞内逐渐消失,木薄壁细胞内开始积累絮状内含物,并通过导管–薄壁细胞的半具缘纹孔进入到相邻导管内,进一步在导管内或薄壁细胞内累积,但未完全堵塞导管和木射线细胞(图1E~G)。T2处理的导管、射线细胞内内含物大量富集,淀粉粒在木射线细胞内完全消失,导管和木射线细胞内油脂类物质或内含物累积增多乃至完全堵塞(图1I~L)。由此可知,诱导结香过程可能与组织细胞内淀粉粒转化程度有关,与CK-1处理相比,T2处理明显促进了淀粉粒的分解转化,加快了导管和射线细胞内含物的形成和转运。
![图 1 扫描电镜下不同处理的土沉香木质部内含物变化情况]() 图 1 扫描电镜下不同处理的土沉香木质部内含物变化情况A~D:处理前;E~H:CK-1处理;I~L:T2处理;A、D、E、I横切面上箭头所指为导管、木射线和木纤维;B、C中箭头所指为木射线内淀粉粒;F、J、K中箭头所指为导管内油脂粒和侵填物;G、H、L中箭头所指为木射线细胞侵填物Figure 1. Changes of xylem inclusions of Aquilaria sinensis in different treatments under scanning electron microscopyA−D: Before treatment; E−H: CK-1 treatment; I−L: T2 treatment; Arrows in cross-sections of A, D, E and I are vessel, wood rays and wood fibres; Arrows in B and C are starch grains in wood rays; Arrows in F, J and K are oil grains and infestations in ducts; Arrows in G, H and L are infestations in wood ray cells
图 1 扫描电镜下不同处理的土沉香木质部内含物变化情况A~D:处理前;E~H:CK-1处理;I~L:T2处理;A、D、E、I横切面上箭头所指为导管、木射线和木纤维;B、C中箭头所指为木射线内淀粉粒;F、J、K中箭头所指为导管内油脂粒和侵填物;G、H、L中箭头所指为木射线细胞侵填物Figure 1. Changes of xylem inclusions of Aquilaria sinensis in different treatments under scanning electron microscopyA−D: Before treatment; E−H: CK-1 treatment; I−L: T2 treatment; Arrows in cross-sections of A, D, E and I are vessel, wood rays and wood fibres; Arrows in B and C are starch grains in wood rays; Arrows in F, J and K are oil grains and infestations in ducts; Arrows in G, H and L are infestations in wood ray cells2.2 木质部油脂类物质分布
从图2可见,不同诱导处理的土沉香木质部结构相似,横切面导管呈椭圆形或卵圆形,多个单管孔排列为径向复管孔或管孔团,弦切面导管以单列型射线为主,呈现为两头细中间宽的梭形或椭圆形,均匀分布,径切面木射线内涵韧皮部呈不间断的横向分布。其主要区别在于,不同诱导处理下木质部累积褐色或深褐色油脂类的范围不同。经诱导处理1年后,显微观察树干木质部三切面(横切面、径切面和弦切面)褐色或深褐色油脂类累积形成的区域(图2A~O),发现油脂类物质大多累积在导管、木射线细胞和内涵韧皮部中,而未处理样品三切面(图2P~R)并未在细胞内观察到油脂类物质存在。经显微对比分析发现,T2处理(图2D~F)深褐色油脂类在导管、木射线细胞和内含韧皮部积累最多,其诱导效果最好;其次为T1(图2A~C)和T3处理(图2G~I),也可明显观察到导管、木射线细胞和内涵韧皮部中存在油脂类物质;仅单独充CO2的CK-1处理的效果较差,仅在薄壁组织和导管内发现少量油脂类物质(图2M~O)。空白对照组CK-2处理,在导管、木射线和薄壁细胞内并未观察到油脂类物质存在(图2P~R)。
![图 2 光学显微镜下不同诱导处理的土沉香木质部三切面解剖差异]() 图 2 光学显微镜下不同诱导处理的土沉香木质部三切面解剖差异图中箭头尾部大写字母V:导管,O:油脂,IP:薄壁细胞,F:木纤维,XR:木射线Figure 2. Anatomical differences of three-section planes of Aquilaria sinensis xylem in different induction treatments under light microscopyFor the capital letter at the end of the arrow in the diagram, V: Vessel, O: Wood grease, IP: Parenchyma cell, F: Wood fiber, XR: Wood ray
图 2 光学显微镜下不同诱导处理的土沉香木质部三切面解剖差异图中箭头尾部大写字母V:导管,O:油脂,IP:薄壁细胞,F:木纤维,XR:木射线Figure 2. Anatomical differences of three-section planes of Aquilaria sinensis xylem in different induction treatments under light microscopyFor the capital letter at the end of the arrow in the diagram, V: Vessel, O: Wood grease, IP: Parenchyma cell, F: Wood fiber, XR: Wood ray2.3 树干木质部木芯变色距离
由图3可见,不同诱导处理对土沉香树干木质部木芯变色距离影响不同,其相似点在于木芯纵向和横向变色距离随着距处理孔位置越远变色距离越短。经诱导处理1年后, T2处理诱导土沉香变色距离效果最好,其纵向变色距离最长,达100 cm,是CK-1处理的2.86倍,其次为T1处理纵向变色距离达89 cm,效果最差为CK-1和CK-2处理。在木芯横向变色距离上,各处理之间尽管差异不显著,但均高于CK-2。T2处理下木芯变色区和沉香区的横向变色距离均最长,分别为6.21和3.02 cm, T1处理木芯变色区和沉香区变色距离最长,分别达6.12和2.17 cm。根据表观估计,不同诱导处理诱导变色范围(纵向变色距离和横向木芯变色距离)大小排序为:T2处理>T1处理>T3处理>T4处理>CK-1处理>CK-2处理。
![图 3 不同诱导处理土沉香树干木质部木芯变色距离]() 图 3 不同诱导处理土沉香树干木质部木芯变色距离横坐标0和35 cm分别代表充气孔和输液孔位置,负值代表纵向充气孔以下诱导变色距离Figure 3. Distance of discoloration of wood cores in woody parts of treated Aquilaria sinensis trunks in different induction treatmentsThe horizontal coordinates 0 and 35 cm represent the location of the inflation and infusion holes, respectively, and the negative values represent the distance of induced discoloration below the longitudinal inflation hole
图 3 不同诱导处理土沉香树干木质部木芯变色距离横坐标0和35 cm分别代表充气孔和输液孔位置,负值代表纵向充气孔以下诱导变色距离Figure 3. Distance of discoloration of wood cores in woody parts of treated Aquilaria sinensis trunks in different induction treatmentsThe horizontal coordinates 0 and 35 cm represent the location of the inflation and infusion holes, respectively, and the negative values represent the distance of induced discoloration below the longitudinal inflation hole2.4 醇溶性挥发油含量及化学成分分析
由图4可见,经诱导处理1年后,不同诱导处理的土沉香醇溶性挥发油含量较对照组(CK-1、CK-2)均有不同程度的提高。其中,T2处理的土沉香醇溶性挥发油质量分数最高,达17.11%,分别是CK-1、CK-2处理的1.17和3.96倍;其次为T3处理,其醇溶性挥发油质量分数达16.00%;空白对照组(CK-2)的效果最差,其醇溶性挥发油质量分数仅达到4.00%。方差分析结果显示,T1~T4处理间的土沉香醇溶性挥发油含量差异不显著,但T2处理的醇溶性挥发油含量较T1、T3和T4处理均有所提升,与CK-1处理相比,仅T2处理诱导的土沉香醇溶性挥发油含量差异显著,其余3个处理与CK-1处理挥发油含量差异虽不显著,但均有不同程度的提高。
不同诱导处理的土沉香挥发油成分种类及含量列于表2。CK-2处理并未检测出倍半萜和色酮类物质,主要成分以脂肪酸类为主。T1~T4和CK-1处理土沉香样品醇溶性挥发油中分别检测到38、44、34、39、23个色谱峰,共鉴定出74种化学成分,主要包含33种萜烯类化合物、9种色酮类化合物、16种芳香族化合物和15种脂肪酸/烷烃类化合物,用峰面积归一化法测定的这些色谱峰在T1~T4和CK-1处理样品中的总相对含量之和分别为85.57%、92.97%、85.24%、83.86%、73.58%,其中,倍半萜类化合物和2−(2−苯乙基)色酮类成分相对含量之和分别为59.25%、78.26%、60.95%、54.82%和46.42%。5种诱导方式下的挥发性成分中,共有的成分主要为11种,包括倍半萜类:白木香醛、α−愈创木烯、香橙烯、长叶烯、沉香螺醇、苯甲醛、苄基丙酮;色酮类:2−(2−苯乙基)色酮、2−[2−(4−甲氧基)苯乙基]色酮、6,7−二甲氧基−2−(2−苯基乙基)色酮和6−甲氧基−2−(4−甲氧基苯乙基)色酮。其中,7种特征性物质成分白木香醛、α−愈创木烯、香橙烯、长叶烯、沉香螺醇、苯甲醛、苄基丙酮相对含量之和分别占5种诱导处理倍半萜类总相对含量的52.74%、56.08%、35.47%、46.96%和40.71%。
表 2 不同处理下土沉香挥发油成分及相对含量Table 2. Chemical constituents and relative contents of agarwood extracted oils under different treatments序号
No.化合物1)
Compound分子式
Molecular formula相对含量/% Relative content T1 T2 T3 T4 CK-1 1 苯甲醛1 Benzaldehyde C7H6O 3.33 3.23 4.20 2.70 2.48 2 苄基丙酮1 2-Butanone, 4-phenyl- C10H12O 2.86 4.74 4.71 1.40 3.72 3 石竹烯−(I1)1 Caryophyllene-(I1) C15H24 — — 0.13 1.21 — 4 5−甲氧基−1,3−二甲基吡唑
5-Methoxy-1,3-dimethyl-pyrazoleC6H10N2O 0.47 0.74 — 0.32 — 5 2,5−二甲基庚−1,3,5−三烯2 2,5-Dimethylhepta-1,3,5-triene C9H14 — 0.38 — 0.21 — 6 (−)−蓝桉烯3 (-)-Globulol C14H22O — — — 0.97 — 7 2−异丙氧基丙酸乙酯 2-Isopropoxyethyl propionate C8H16O3 — — 1.78 — — 8 白菖烯1 Alloaromadenderen C15H24 3.56 4.69 2.52 1.86 — 9 苯丙醛1 Benzenepropanal C9H10O 0.36 — 5.65 — 0.52 10 氢化肉桂酸1 Hydrocinnamic acid C9H10O2 — — 3.07 1.06 1.32 11 2,4−二叔丁基苯酚3 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol C14H22O — 0.49 — — — 12 2′−羟基−5′−甲氧基苯乙酮3
Ethanone,1-(2-hydroxy-5-methoxyphenyl)-C9H10O3 — — 0.69 1.95 — 13 β−水芹烯3 Beta-phellandrene C10H16 0.42 — — 0.75 — 14 1−甲基−4−(2−甲基环氧)−7−氧双环[4.1.0]庚烷2
7-Oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptane, 1-methyl-4-(2-methyloxiranyl)-C10H16O2 0.45 — 0.70 — — 15 二十烷2 Eicosane C20H42 1.31 1.58 — 1.84 4.21 16 十二烷−9−酮2
Oxatetracyclo[5.3.2.0(2,7).0(2,8)]dodecan-9-oneC11H14O2 0.53 — 0.72 0.93 — 17 异香橙烯环氧化物1 Isoaromadendrene epoxide C15H24O 2.75 — 1.56 1.20 0.85 18 赤藓糖醇1 Erythritol C4H10O4 — 1.73 5.02 — 1.17 19 戊烯醇1 Valerenol C15H24O — — 0.34 — 0.62 20 木香醇1 Costol C15H24O — 0.47 — 1.52 — 21 沉香螺醇1 Agarospirol C15H26O 0.56 2.47 1.11 0.97 0.43 22 缬草−4,7(11)−二烯1 Valerena-4,7(11)-diene C15H24 1.77 1.21 — 2.47 1.47 23 白木香醛1 Baimuxinal C15H22O2 4.39 7.84 3.75 3.56 1.65 24 缬草素1 Valerenic acid C15H22O2 — 1.81 0.38 1.53 2.42 25 α−愈创木烯1 α-Guaiene C15H24 1.34 1.47 0.56 1.44 0.84 26 2−羟基−3−丙基−1,4−萘醌
1,4-Naphthalenedione, 2-hydroxy-3-propyl-C13H12O3 1.33 — — — — 27 1,3−二氢−5−甲乙基−1−苯甲基甲酮
1,3-dihydro-5-(1-methylethyl)-1-(phenylmethyl)-
2H-imidazole-2-thioneC13H16N2S 5.35 — — — 3.85 28 β−朱栾3 β-Vatirenene C15H22 — 2.58 1.39 1.71 — 29 2,2,8,8−四甲基−3,6−壬二烯−5−酮
3,6-Nonadien-5-one,2,2,8,8-tetramethyl-C13H18O 0.41 1.42 — — — 30 (+)−香橙烯1 Aromandendrene C15H24 2.28 2.38 1.04 1.95 0.73 31 长叶烯1 Longifolene C15H24 1.46 1.30 1.28 2.45 0.43 32 1H−茚−4−羧酸,2,3,6,7−四氢−7−甲基鸟苷−,乙酯
1H-indene-4-carboxylic acid, 2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-7-methyl-, ethyl esterC13H18O2 0.97 — — — 0.62 33 β−紫罗兰酮3 Trans-β-ionone C13H20O 1.46 2.40 — — 0.70 34 芹子烯1 α-Selinene C15H24 1.24 3.27 2.10 0.86 0.32 35 β−芸烯3 β-Vatirenene C15H22 0.94 — — 1.79 — 36 长叶香芹酮1 Longipinocarvone C15H22O — 2.53 — — 0.84 37 氧化二烯(I)1 Cycloheptane C15H10ClN3O 0.60 — — — 0.53 38 2−乙基吖啶3 2-Ethylacridine C15H10ClN3 1.19 — — — 0.74 39 1−苄氧基−8−萘酚2 8-Naphthol, 1-(benzyloxy)- C17H14O2 — — 1.15 — 0.58 40 间苯乙基苯甲腈3 Benzonitrile, m-phenethyl- C15H13N 1.87 — 1.58 — — 41 2−异丙基噻唑烷−3,4−二羧酸,3−苄酯2
2-Isopropyl-thiazolidine-3,4-dicarboxylic acid, 3-benzyl esterC15H19NO4S 1.46 0.13 — 0.37 4.27 42 2−二甲基−1,2,3,4, 4a,5,6,8a−八氢萘−2−丙烯醛2
2-Dimethyl-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,8a-octahydronaphthalen-2-acrylaldehydeC15H22O — 1.41 — — — 43 3,4,4−三甲基−3−(3−甲基−1,3−丁二烯基)−双环[4.1.0]庚烷−2−酮2
Bicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-2-one, 3,4,4-trimethyl-3-(3-methyl-1,3-butadienyl)-C15H22O 1.18 — — 0.38 — 44 1,5−二甲基−8−(1−甲基亚乙基)−1,5−环癸二烯
1,5-Cyclodecadiene, 1,5-dimethyl-8-(1-methylethylidene-, E,E)-C15H24 0.90 0.58 — 1.41 — 45 3−羟基−2−对甲苯基−2−丁烯腈3
3-Hydroxy-2-p-tolyl-2-butenenitrileC11H11NO 2.25 — — — 1.45 46 蛇麻烯3 Humulene C15H24O 0.89 1.37 0.58 1.57 — 47 甲基丁香酚3 Methyleugenol C11H14O2 — 1.47 — 0.51 — 48 Α−乙基苯甲醇乙酸酯3
Acetic acid, 1-phenylpropyl esterC11H14O2 1.78 1.54 — 1.42 2.53 49 4−(4−甲氧苯基)−2−丁酮3
2-Butanone, 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-C11H14O2 — 0.29 1.43 1.74 1.53 50 香树烯1 Alloaromadendrene C15H24 0.85 1.72 0.37 — — 51 Bicyclo[7.2.0]undecane, 10,10-dimethyl-2,6-bis(methylene)-,
[1S-(1R*,9S*)]-C15H24 0.59 0.32 — 1.04 — 52 别香氧化物1 Alloaromadendrene oxide-(2) C15H24O 0.87 — 0.56 — 1.69 53 檀香醇α1 Santalol, cis, alpha- C15H24O — 1.38 — 1.06 1.42 54 新氯芬−(I),二氢 Neoclovene−(I), dihydro- C15H26 — 0.58 — — 1.54 55 N−丁基乙酰胺2 Acetamide, N-butyl- C6H13NO 0.70 — — — — 56 2−乙酰基噻吩2 Ethanone,1-(2-thienyl)- C6H6OS — 0.32 — 0.82 — 57 1−十六烯1 Hexadecane C16H32 — — 3.46 — — 58 2−苯乙基−4H−色烯−4−酮4
2-Phenethyl-4H-chromen-4-oneC17H14O2 4.41 7.04 8.23 5.02 4.46 59 6−甲氧基−2−苯乙基−4H−苯并吡喃−4−酮4
6-Methoxy-2-phenethyl-4H-chromen-4-oneC18H16O3 0.75 2.08 — — — 60 2−[2−(4−甲氧基)苯乙基]色酮4
2-(2-(4-Methoxyphenethyl)) chromenC18H16O3 5.80 3.32 4.87 3.17 2.73 61 2−甲基腺苷 Adenosine, 2-methyl- C11H15N5O4 — 0.24 — 0.42 — 62 十八烯酸2 Oleic Acid C18H34O2 1.34 0.67 — 0.85 0.68 63 2−(2−羟基丙酰基)苯基乙醛酸甲酯3
2-(2-Hydroxypropionyl)phenylglyoxylic acid, methyl esterC12H12O5 1.01 — — — — 64 3−(4−氨基苯基)甲基−4−戊二酮3
4-pentanedione, 3-[(4-aminophenyl)methyl]-C12H15NO2 — — 0.31 — — 65 1,2,4−三乙苯3 Benzene, 1,2,4-triethyl- C12H18 — 0.45 — 0.18 — 66 正十八烷2 Octadecane C18H38 — — 1.48 0.42 — 67 3−甲基−2−(4−甲氧基苯乙基)色酮4
3-Methoxyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-chromoneC19H18O3 — 3.58 — — 5.79 68 6−甲氧基−2−(4−甲氧基苯乙基)色酮4
6-Methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)chromoneC19H18O4 3.40 12.25 3.22 2.49 1.48 69 6,7−甲氧基−2−(2−苯乙基)−4−色酮4
6,7-Methoxy-2-phenethyl-4H-chromenC19H18O4 15.19 10.64 3.12 15.06 — 70 6,7−二甲氧基−2− (4−甲氧基苯基)−4H−乙基色酮4
6,7-Dimethoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenethyl)-4H-
chromen-4-oneC20H20O5 2.80 3.03 — — 1.28 71 2−甲基十九烷2 Nonadecane, 2-methyl- C20H42 0.57 — — — 0.74 72 姜烯酮 A1 Gingerenone A C21H24O5 0.86 — 0.64 0.31 — 73 正二十六烷2 Hexacosane C26H54 — — 0.57 — 1.72 74 6,7−二甲氧基−2−(2−苯乙基)色酮4
6,7-Dimethoxy-2-(2-phenethyl)chromoneC31H45NO5 4.45 7.41 4.63 5.84 10.9 主要有效成分
Main active ingredients倍半萜类
Sesquiterpenoids28.21 34.27 41.92 32.23 24.35 色酮类
Chromones36.81 49.35 24.59 35.61 29.76 芳香族
Aromatic11.81 9.35 5.98 7.14 8.24 脂肪酸/烷烃类
Fatty acids/alkanes6.08 5.36 14.17 9.88 10.43 合计 Total 82.91 98.33 86.66 84.86 72.78 1)上角标数字表示物质类别,其中,1:倍半萜类物质,2:脂肪酸/烷烃类物质,3:芳香族物质,4:色酮类物质;“—”表示未检测出该物质 1)Upper corner numbers indicate substance groups, where 1: Sesquiterpenes, 2: Chromones, 3: Aromatic substances, 4: Fatty acids/alkanes; “—” indicates that the substance was not detected 3. 讨论与结论
沉香是树体受到外界刺激或损伤后激活树体防御反应,经长期缓慢累积而成的[16]。为提高沉香的产量和质量,探索高效的人工诱导方法迫在眉睫。本研究发现,诱导处理后内涵韧皮部、木射线和导管中均出现褐色或黑褐色油脂类物质积累现象,油脂类物质或内含物通过导管–薄壁细胞间纹孔进入相邻导管内积累甚至完全堵塞,并伴随着类似心材变色现象,该现象与前人研究结果一致[17,21]。变色区域在一定程度上反映了土沉香次生代谢物积累的程度,且与沉香质量及挥发油含量存在直接的关系,表现为木质部含有的黑褐色物质越多,挥发油含量越高。
沉香富含多种有机物质,不同诱导方式所产沉香成分存在差异,但其主要成分为倍半萜类和色酮类物质[14]。对本研究所产沉香样品检测发现,CO2与真菌、无机盐联合诱导所产沉香样品中的色酮类成分相对百分含量更高,这与廖格等[22]、Ma等[23]研究结果一致,但色酮类成分相对百分含量略低,这可能是诱导处理材料及处理时间的差异引起的。另外,由于检测方式中Nist和Wiley质谱库包含的2−(2−苯乙基)色酮类化合物的质谱数据极其有限,而目前已报道的2−(2−苯乙基)色酮类化合物多达几十种,因此,对于评价沉香品质的2−(2−苯乙基)色酮类色谱库的建立极有必要。相比而言,CO2与激素联合诱导所产沉香样品中倍半萜类相对百分含量更高,这与宋晓琛等[17]、王之胤[24]研究的结论一致,其主要原因可能是激素刺激启动了土沉香信号转导途径,促进沉香成分中脂类和倍半萜类物质的积累[13,25]。相较于前期仅采用生物和化学方式诱导结香试验[17-18],本试验采用了耦合的方式,所产沉香成分中色酮类和倍半萜类相对百分含量均有提升,尤其是倍半萜类相对百分含量提升更多,这可能与充入CO2对土沉香树体造成高度物理损伤以及CO2自身可促进萜类物质的生物代谢与合成有关。此外,本试验诱导处理所结沉香中均检测到富含与天然沉香相似的挥发性成分苄基丙酮和沉香螺醇,以及与沉香品质相关的倍半萜类特征性成分白木香醛、香橙烯、长叶烯等。杨锦玲等[26]、Hashim等[27]研究报道,通过对沉香成分中另一类特征性成分2−(2−苯乙基)色酮类化合物含量进行沉香品质定量评价,结果显示,沉香色酮含量与品质呈正相关。本研究通过GS-MS技术分析色酮类特征性成分2−(2−苯乙基)色酮和2−[2−(4−甲氧基)苯乙基]色酮相对含量,结果显示,5种诱导处理的色酮类特征成分含量之和达到7.19%~13.1%,显著高于黄熟香和吊口沉香色酮类特征成分含量[26]。在诸多研究中,均以这些具有药理活性的特征成分相对百分含量作为评价沉香等级和沉香质量的重要参考指标[28]。本研究通过比较不同诱导方式所产沉香特征性成分(白木香醛、α−愈创木烯、香橙烯、长叶烯、沉香螺醇、苯甲醛、苄基丙酮)及含量,发现CO2与无机盐联合诱导所产沉香倍半萜类特征性成分的总含量最高, 为23.43%,其次为CO2与真菌联合诱导所产沉香(16.22%),而单独CO2处理所产沉香含量最低(10.28%),因此在诱导所产沉香品质评价中,以CO2与无机盐联合诱导更具有优势。
综上所述,本试验以不同诱导方式所产沉香为研究对象。通过对所产沉香微观特征、醇溶性挥发油含量、沉香特征成分和含量分析发现,均符合《LY/T 2904—2017 沉香》[29]的相关要求,且诱导所产沉香样品醇溶性挥发油含量明显高于《中国药典》标准。其中CO2与无机盐耦合诱导土沉香特征性成分和含量均高于其他处理,醇溶性挥发油质量分数达17.11%,诱导所产沉香品质最好;其次为CO2与真菌联合诱导所产沉香,醇溶性挥发油质量分数达16.00%;仅填充CO2所产沉香较差,醇溶性挥发油质量分数为11.12%。
-
表 1 不同部位的真菌分离结果
Table 1 Isolated fungi from different parts of apple tree

表 2 苹果拮抗真菌对苹果树腐烂病菌菌丝生长的抑制作用1)
Table 2 Inhibiory effects of antagonistic fungi on mycelial growth of Valsa ceratosperma and Glomeralla cingulata in apple tree

表 3 发酵液和菌丝体提取物对病原菌菌丝生长的抑制作用1)
Table 3 Inhibition rates of sterile fermentation filtrates and extracts from endophytic fungal mycelium on mycelial growth of pathogen

表 4 内生真菌发酵液对苹果树腐烂病菌和炭疽病菌分生孢子萌发的抑制作用1)
Table 4 Inhibitory effect of zymotic fluid of antagonistic fungi on conidial germination of Valsa ceratosperma and Glomeralla cingulata in apple tree

表 5 苹果树腐烂病菌拮抗真菌J2, J16和J17发酵滤液的热稳定性
Table 5 Heat stability of zymotic fluid of antagonistic fungi J2, J16 and J17 against Valsa ceratosperma

表 6 苹果树炭疽病菌拮抗真菌J2, J11和T1发酵滤液的热稳定性1)
Table 6 Heat stability of zymotic fluid of antagonistic fungi J2, J11 and T1 against Glomeralla cingulata

-
[1] 刘如香. 苹果树腐烂病菌分生孢子的萌发、存活和侵染条件的研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2011. [2] 李培夫.苹果腐烂病防治新技术[J].农村科技, 2005(4): 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6193.2005.04.013 [3] 杨万宝.苹果炭疽病发生原因及防治措施[J].现代农村科技, 2011(19): 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5329.2011.19.021 [4] 王敬尊.苹果炭疽病的识别与防治[J].安徽农业科学, 2009, 37(18): 8560-8561. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2009.18.105 [5] 邓振山, 白重炎, 李军, 等.陕北苹果常见真菌病害病原菌的分离鉴定研究[J].延安大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 25 (4):65-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-602X.2006.04.019 [6] 李培, 王永斌.植物内生真菌的研究与展望[J].饮料工业, 2008, 11(7): 11-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7871.2008.07.004 [7] AZEVEDP J L, MACCHERONI J R W, PEREIRA J O, et al. Endophytic microorganisms: A review on tropical plants[J]. Electron J Biotechn, 2000, 3(1): 40-65.
[8] 王现坤, 张晓华, 赫双红.侧柏内生真菌的分离鉴定及抗菌活性筛选[J].农药, 2010, 49(7): 519-521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0413.2010.07.018 [9] 蔡光华, 战峰, 王晓玲.苹果树腐烂病拮抗内生细菌PG-10-8-11v菌株抗菌物质的初步研究[J].西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 37(6): 945-949. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnmzxyxb201106019 [10] 邓振山, 赵龙飞, 张薇薇, 等.银杏内生真菌的分离及其对苹果腐烂病病原菌的拮抗作用[J].西北植物学报, 2009, 29(3): 608-613. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4025.2009.03.028 [11] 郭建新, 孙广宇, 张荣, 等.银杏内生真菌抗真菌活性菌株的分离和筛选[J].西北农业学报, 2005, 14(4): 14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1389.2005.04.004 [12] 徐涛, 胡同乐, 王亚南, 等.苹果树皮内生真菌的分离及其对腐烂病的生物防治潜力[J].植物保护学报, 2012, 39 (4): 327-333. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201204007 [13] 周宗山, 徐成楠, 吴玉星, 等.苹果树腐烂病病菌分生孢子获取方法研究[J].中国果树, 2011(2): 41-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhongggs201102015 [14] 杨润亚, 李艳华, 柳娜娜.连翘内生真菌的分离及其抑菌活性初步研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2007, 35 (15): 4561-4563. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2007.15.085 [15] 夏伟, 张红, 颜艳伟, 等.棘孢木霉L4对立枯丝核菌的拮抗机制[J].植物保护学报, 2010, 37 (5): 477-478. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwbhxb201005019 [16] 孙杰, 杨润亚, 任晓明.三种海藻内生真菌的分离及其抑菌活性研究[J].食品科学, 2007(11): 357-359. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.11.082 [17] 王艳红, 吴晓民, 朱艳萍, 等.温郁金内生真菌Chaetomium globosum L18对植物病原菌的抑菌谱及拮抗机理[J].生态学报, 2012, 32(7): 2040-2046. [18] 蒋继宏, 李晓储, 陈凤美, 等.植物抽提物对苹果炭疽病菌分生孢子的抑制作用[J].江苏林业科技, 2004, 31 (4): 23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2004.04.006 [19] 邓振山, 候改成, 孙志宏, 等.番茄灰霉病菌拮抗菌D6和D10发酵条件的优化及其抑菌效果[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41 (9): 73-77. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbnydxxb201309013 [20] 展丽然. 苹果腐烂病菌拮抗放线菌的筛选、鉴定及发酵条件的优化[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2008. [21] 王东昌, 辛玉成, 郝秀青, 等.苹果树枝干病害的生物防治[J].吉林农业科学, 2001, 26 (2): 49-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8701.2001.02.013 [22] XIN Y F, SHANG J J. Bio-control trials of Chaetominum spirale ND35 against apple canker[J]. J Forest Res-Jpn, 2005, 16 (2): 121-124. doi: 10.1007/BF02857904
[23] 郭晓, 高克祥, 印敬明, 等.螺旋毛壳ND35 β-1, 3-葡聚糖酶的诱导、性质及其抑菌作用[J].植物病理学报, 2005, 35(6): 493-503. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-0914.2005.06.003 -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: