Dynamic changes of cadmium and non-protein thiol in different organs of different soybean genotypes under cadmium stress
-
摘要:目的
探讨不同大豆品种各器官镉和非蛋白巯基物质的动态变化,揭示巯基物质在大豆镉抗性和积累中的作用。
方法在镉(Cd)污染的土壤中种植镉抗性和籽粒积累不同的大豆品种中黄24和华夏3号,采集不同生育时期的根、茎和叶,分析各品种的Cd抗性指标(根系和地上部鲜质量)、Cd积累指标(各器官Cd浓度)和非蛋白巯基物质[总非蛋白巯基肽(NPT)、谷胱甘肽(GSH)和植物螯合肽(PC)]的浓度变化。
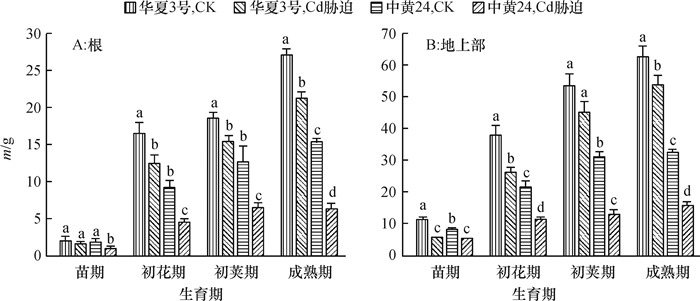
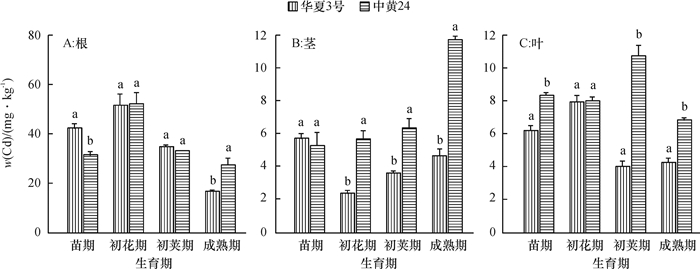
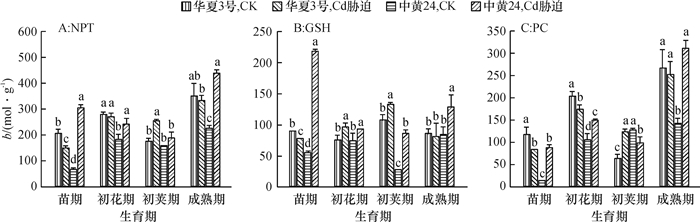
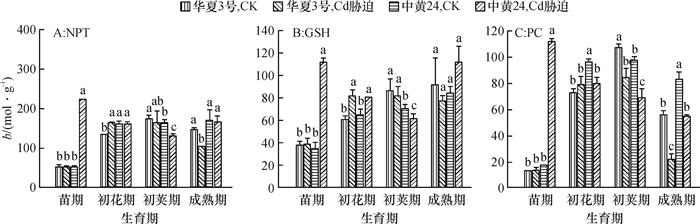
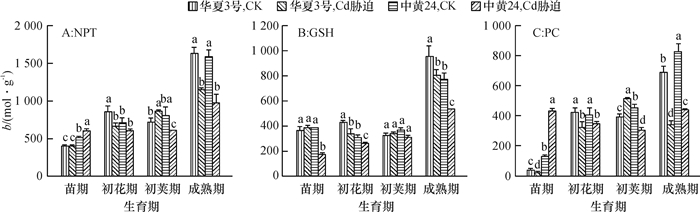
结果在10 mg·kg-1的Cd胁迫下,中黄24不同时期Cd抗性指标明显低于华夏3号,而中黄24初花期后各器官Cd浓度均显著地高于华夏3号。Cd胁迫下2个品种随发育进程根系中NPT、GSH和PC浓度上升,而叶片中则下降;敏感品种中黄24各器官中巯基物质对Cd胁迫响应比抗性品种华夏3号更显著。关联分析发现,大豆根部巯基物质浓度与各器官Cd浓度呈正相关,且以成熟期最为显著,而初花期后地上部的PC与各器官Cd浓度呈负相关。
结论在大豆不同生育期不同器官中Cd和非蛋白巯基物质浓度变化复杂,非蛋白巯基物质在大豆抵抗Cd胁迫中扮演多种角色。
Abstract:ObjectiveDynamic changes of cadmium and non-protein thiols in different soybean genotypes were researched to investigate effects of non-protein thiols on Cd tolerance and accumulation of soybean.
MethodThe soybean varieties of Zhonghuang24 and Huaxia3 were planted in the pots with contaminated soil. Roots, shoots and leaves were collected in different periods. Cd tolerance indexes (including root and shoot fresh mass), Cd accumulation and the concentrations of non-protein thiols [including the total of non-protein thiol peptides (NPT), glutathione (GSH) and phytochelatins(PC)] of soybeans in different periods were determined.
ResultThe resistance indexes of Zhonghuang24 were significantly lower than those of Huaxia3 in different periods at the Cd concentration of 10 mg·kg-1, and Cd accumulations in all organs were higher than those of Huaxia3 after flowering stage (especially at pod and mature stages). The NPT, GSH and PC concentrations increased in root and reduced in leaf along with the development progress, and the effects of non-protein thiols in Zhonghuang24 under Cd stress were stronger those of Huaxia3. The correlation analysis indicated that there was a positive correlation between thiol concentration in root and the Cd concentration in all organs, especially at mature stage. There was a negative correlation between PC concentrations in stem and leaf after flowering stage, especially more significant at pod and mature stages.
ConclusionThe concentrations of thiols and Cd in soybean organs show complex changes at different growth stages under Cd stress. Non-protein thiols play multiple roles in Cd detoxification and transportation at different growth stages.
-
Keywords:
- Cd stress /
- soybean /
- non-protein thiol /
- glutathione /
- phytochelatin
-
贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区位于贵州大方县与黔西市交界处(E 105°45′30″~106° 04′ 45″,N 27° 08′ 30″~27° 20′ 00″),保存有地球同纬度范围内中低海拔区面积最大的天然杜鹃林[1]。马缨杜鹃Rhododendron delavayi Franch是该保护区的建群种和优势种,面积约25.16 km2,占百里杜鹃林区总面积的20%。马缨杜鹃又名马缨花,是杜鹃花科Ericaceae杜鹃属Rhododendron的一种常绿灌木或小乔木[2]。因花大、颜色鲜艳,且形似马头饰上的璎珞而得名。其分布广泛,花色艳红,观赏价值高,是杜鹃属重要的育种亲本,具有较高研究利用价值[3]。但随着旅游业发展,频繁的人为活动使杜鹃花病害发生日益严重,不仅对观赏性产生影响,对物种的生存也产生了威胁。因此,开展马缨杜鹃病原菌生物学特性研究以及室内药剂的筛选,对该病害防治具有重要意义。
杨秀梅等[4-5]调查发现云南省昆明市晋宁区高山杜鹃盆花种植基地炭疽病Colletotrichum boninense、枯梢病Neofusicoccum parvum发生严重,田间发病率达20%以上。Wang等[6]对台湾地区杜鹃花调查发现春秋季节杜鹃叶肿病Exobasidium japonicum发生严重,该病原菌导致杜鹃幼嫩组织发育受损,对杜鹃花产业具有极大破坏性。童俊等[7]对武汉周边以龟峰山景区为代表的杜鹃自然群落的主要病虫害进行了系统调查,发现杜鹃叶肿病、黑斑病Cercospora rhododendri发生严重。刘浩凯等[8]调查发现浙江省景宁县上山头云锦杜鹃叶斑病Phomopsis asparagi频繁发生,严重影响了杜鹃林的健康生长和景观效果。胡芳菲[9]对吉安市苗圃几种常见树木病害进行调查发现,西洋杜鹃褐斑病Ce. rhododendri发生相对较严重,苗期发病会造成植株整株死亡。陈明珠等[10]调查发现,贵州省贵阳市凤凰山锦绣杜鹃叶肿病发生严重,发病率高达80%,严重影响其观赏性。研究大多聚焦于不同种类杜鹃花病害调查和病原菌鉴定,关于杜鹃病害的生物学特性及防治药剂筛选研究较少。任纬恒[11]对百里杜鹃花腐病Alternaria alternata进行了室内药剂防治筛选,认为咪鲜胺、异菌脲、苯醚甲环唑、戊唑醇4种药剂是可进行花腐病防治的候选药剂。
笔者于2021年7月在贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区进行病害调查,发现了1种杜鹃真菌病害,经多基因构建系统发育树并结合形态特征,确定该病害是由松针炭疽菌Colletotrichum fioriniae引起[12]。为明确该真菌的生物学特性及适宜防治药剂,采用菌丝生长速率法对松针炭疽菌生物学特性进行研究,同时测定10种杀菌剂对该病原菌室内毒力及2种药剂混配对病原菌的联合毒力,了解松针炭疽菌生物学特性,筛选出有效抑制该病原菌菌丝生长的药剂,以期为贵州百里杜鹃自然保护区马缨杜鹃炭疽病的科学防治提供指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
于2021年7月从贵州省百里杜鹃自然保护区采集马缨杜鹃具有典型炭疽病症状的叶片,带回实验室进行分离培养,经贵州大学烟草品质研究重点实验室分离、鉴定并保存。
供试培养基为马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂(PDA)培养基、马铃薯蔗糖(PSA)培养基、燕麦片琼脂(OMA)培养基、查氏(Czapek)培养基和高氏1号(GSA)培养基[13]。PDA培养基用于培养病原真菌、生物学测定及室内药剂筛选等试验。PSA、OMA、Czapek、GSA培养基用于病原菌生物学特性测定。
供试药剂:22.7% (w) 二氰蒽醌SC(江西禾益化工股份有限公司)、25.0% (w) 吡唑醚菌酯SC(江苏托球农化股份有限公司)、25.0% (w) 溴菌腈EC(江苏托球农化股份有限公司)、50.0% (w) 丙环唑ME(青岛格力斯药业有限公司)、10.0% (w) 苯醚甲环唑WDG(先正达南通作物保护有限公司)、75.0% (w) 肟菌·戊唑醇 WDG(拜耳作物科学有限公司)、0.3% (w) 四霉素AS(辽宁微科生物工程股份有限公司)、80.0% (w) 乙蒜素EC(南阳新卧龙生物化工有限公司)、1.0% (w) 蛇床子素ME(云南南宝生物科技有限责任公司)及8.0% (w) 宁南霉素AS(德强生物股份有限公司)。
1.2 病原菌生物学特性
采用菌丝生长速率法[13]测定不同培养基对病原菌菌丝生长的影响,将直径为6 mm的菌饼分别转接于PDA、Czapek、OMA、PSA和GSA培养基,置于25 ℃恒温培养箱黑暗培养7 d后,测量各培养基上的菌落直径。每处理4皿,重复3次。
取直径为6 mm菌饼置于PDA培养基中央,分别放入5、10、15、20、25、30、35、40 ℃恒温培养箱黑暗培养7 d后,十字交叉法测量菌落直径[13],得到菌丝生长适宜温度,每处理4皿,重复3次。
将直径为6 mm菌饼分别接种到pH为5、6、7、8、9、10、11的PDA培养基(用1 mol/L HCl和1 mol/L NaOH进行调节),置于25 ℃恒温培养箱暗培养7 d后,测量菌落直径,得出菌丝生长适宜pH,每处理4皿,重复3次。
以Czapek培养基为基础培养基[13],分别以等质量的果糖、葡萄糖、可溶性淀粉、乳糖、麦芽糖替代Czapek培养基中的蔗糖作为碳源,以等质量的硫酸铵、硝酸钠、蛋白胨、硝酸钾、磷酸二氢铵替换Czapek中的硝酸钠作为氮源,以不添加碳源和氮源的Czapek为对照,25 ℃恒温箱黑暗培养7 d后测量菌落直径,筛选最适碳、氮源。每处理4皿,重复3次。
1.3 室内药剂毒力
1.3.1 单剂毒力测定
采用菌丝生长速率法测定10种杀菌剂(6种常用化学药剂和4种生物农药)对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌的抑菌活性。供试药剂母液用无菌水溶解稀释,分别设置 5个质量浓度梯度。二氰蒽醌为1271.00、635.60、317.80、158.90、79.45 mg/mL;吡唑醚菌酯为0.3000、0.1500、0.0750、0.0375、0.0188 mg/mL;溴菌腈为500.00、250.00、125.00、62.50、31.25 mg/mL;丙环唑为10.000、5.000、2.500、1.250、0.625 mg/mL;苯醚甲环唑为4.8、2.4、1.2、0.6、0.3 mg/mL;肟菌·戊唑醇为1.200、0.600、0.300、0.150、0.075 mg/mL;四霉素为3.0000、1.5000、0.7500、0.3750、0.1875 mg/mL;乙蒜素为400、200、100、50、25 mg/mL;蛇床子素为20.00、10.00、5.00、2.50、1.25 mg/mL;宁南霉素为80、40、20、10、5 mg/mL。
在无菌操作条件下,将不同质量浓度的杀菌剂溶液分别加入到灭菌的PDA 培养基中,充分摇匀后等量倒入培养皿(直径为85 mm)中,制成含有相应质量浓度药剂的平板,以加入等量无菌水的PDA 培养基为对照。将供试病原菌接种于PDA培养基上培养5 d后,取直径为6 mm菌饼分别置于含不同质量浓度药剂平板和对照PDA平板中央,待对照菌丝长满平板时,采用十字交叉法测量菌落直径,计算抑菌率。
1.3.2 混剂毒力测定
根据单剂毒力测定结果,采用菌丝生长速率法,选择作用机制不同、防治效果较好且EC50差异较小的2种药剂进行混配,测定混剂对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌的联合毒力。分别设置体积比9 ∶ 1、8 ∶ 2、7 ∶ 3、6 ∶ 4、5 ∶ 5、4 ∶ 6、3 ∶ 7、2 ∶ 8和1 ∶ 9共9种配比为母液。按照上述方法测定混剂对松针炭疽菌的抑制率, 求出毒力回归方程和EC50 ,参考Sun等[14]的毒力评判法计算复配农药的共毒系数 (Co-toxicity coefficient,CTC),评价药剂混用的增效作用。CTC小于80为拮抗作用,大于120为增效作用,80 ~ 120为相加作用。相关计算公式如下:
$$ 单剂毒力指数= \dfrac{{\rm{EC}}_{50}(标准药剂)}{ {\rm{EC}}_{50}(供试单剂)}\times 100\text{,} $$ (1) $$ 混剂实测毒力指数({\rm{ATI}})=\dfrac{{\rm{EC}}_{50}(标准药剂)}{ {\rm{EC}}_{50}(供试混剂)}\times 100\text{,} $$ (2) $$ \begin{split} &混剂理论毒力指数({\rm{TTI}})= 药剂{\rm{A}}的毒力指数 \times \\ &\quad \quad 混剂中药剂{\rm{A}}的百分含量 +药剂{\rm{B}}的毒力指数 \times\\ &\quad \quad 混剂中药剂{\rm{B}}的百分含量 \text{,}\\[-10pt] \end{split} $$ (3) $$ 共毒系数({\rm{CTC}})= \dfrac{混剂实测毒力指数({\rm{ATI}})} {混剂理论毒力指数({\rm{TTI}})}\times 100。 $$ (4) 1.4 数据分析
采用
$ {\rm{Excel}}$ 2010进行数据统计处理;使用SPSS 17.0和DPS 7.05对数据进行单因素方差分析。2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同培养基、温度、pH、氮源、碳源对菌丝生长的影响
试验结果表明,菌丝在5种培养基上均能生长(图1A),且5种培养基对菌丝的生长影响差异显著。在PSA培养基上生长最快,平均菌落直径为7.60 cm,显著高于其他处理;其次是PDA培养基,平均菌落直径为7.05 cm。病原菌在OMA、Czapek、GSA培养基上均能生长,但生长较为缓慢且菌丝极其稀疏,不适宜该菌的培养。
![图 1 不同培养基(A)、温度(B)和pH(C)对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌菌丝生长的影响]() 图 1 不同培养基(A)、温度(B)和pH(C)对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌菌丝生长的影响各图中,柱子上方不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)Figure 1. Effects of different culture medium, temperature and pH on mycelial growth of Colletotrichum fioriniae on Rhododendron delavayiIn each diagram, different lowercase letters on the columns indicate significant differences (P<0.05,Duncan’s method)
图 1 不同培养基(A)、温度(B)和pH(C)对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌菌丝生长的影响各图中,柱子上方不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05,Duncan’s法)Figure 1. Effects of different culture medium, temperature and pH on mycelial growth of Colletotrichum fioriniae on Rhododendron delavayiIn each diagram, different lowercase letters on the columns indicate significant differences (P<0.05,Duncan’s method)由图1B可知,病原菌在10~35 ℃均可生长,在15~25 ℃生长较好,且最适生长温度为25 ℃,与其他温度处理有明显差异(P< 0.05),平均菌落直径为7.05 cm。温度为10 或35 ℃时生长较缓慢,3 d后才开始生长,平均菌落直径分别为4.21 和2.69 cm。在5、40 ℃温度条件下,病原菌菌丝未生长。
由图1C可知,该菌在pH为5~11的范围内均可正常生长,且随着pH的增大,菌丝生长愈发致密。pH 7~9长势较好,其中最适pH为8,平均菌落直径达到8.04 cm,显著高于其他处理。
如表1所示,病原菌在不同的碳、氮源培养基上均可生长。在葡萄糖和可溶性淀粉为碳源的培养基上长势最好,平均菌落直径分别为(5.72±0.15)和(5.59±0.02) cm,显著高于对照的(3.49±0.16) cm以及其他3种不同碳源的。在乳糖为碳源的培养基上长势最差,平均菌落直径为(3.05±0.24) cm,显著低于其他处理的。氮源以蛋白胨最好,平均菌落直径为(7.63±0.12) cm,显著高于其他氮源培养基的,其次是硝酸钾,平均菌落直径为(6.08±0.26) cm。在以硫酸铵为氮源的培养基上长势最差,平均菌落直径为(1.75±0.39) cm,显著低于其他处理及对照的。由此表明,供试的5 种碳源和氮源中,最适宜病原菌菌丝生长的碳源为葡萄糖和可溶性淀粉,最适宜的氮源为蛋白胨。
表 1 碳、氮源对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌菌丝生长的影响1)Table 1. Effects of carbon and nitrogen sources on mycelial growth of Colletotrichum fioriniae on Rhododendron delavayi碳源
Carbon source菌落直径/cm
Diameter of colony氮源
Nitrogen source菌落直径/cm
Diameter of colony对照 CK 3.49±0.16c 对照 CK 3.02±0.11d 葡萄糖 Glucose 5.72±0.15a 蛋白胨 Peptone 7.63±0.12a 可溶性淀粉 Soluble starch 5.59±0.02a 硝酸钾 Potassium nitrate 6.08±0.26b 果糖 Fructose 3.99±0.18b 硝酸钠 Sodium nitrate 5.05±0.08c 麦芽糖 Maltose 3.65±0.31bc 硫酸铵 Ammonium sulfate 1.75±0.39e 乳糖 Lactose 3.05±0.24d 磷酸二氢铵 Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate 2.81±0.18d 1)同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著 (P< 0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences(P< 0.05, Duncan’s method)2.2 杀菌剂室内毒力测定
供试的10种杀菌剂对病原菌菌丝生长均有不同程度的抑制作用,EC50如表2所示。化学药剂中,肟菌·戊唑醇、吡唑醚菌酯、苯醚甲环唑和丙环唑抑制效果最好,EC50分别为0.102、0.118、1.202和2.101mg/L。二氰蒽醌和溴菌腈的抑菌活性最低,EC50分别为196.501和95.402 mg/L。生物农药中,四霉素抑菌效果最好,EC50为1.107 mg/L,其次是蛇床子素,EC50为6.803 mg/L。乙蒜素和宁南霉素抑菌效果相对较差,EC50分别为82.711和64.712 mg/L。
表 2 10 种杀菌剂对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌的抑菌活性Table 2. Antibiotic activities of 10 fungicides to Colletotrichum fioriniae on Rhododendron delavayi供试药剂
Trial fungicidew(有效成分)/%
Mass concentration of
the active ingredients毒力回归方程1)
Toxicity regression
equationEC502)/(mg·L−1) 相关系数
Correlation
coefficient肟菌·戊唑醇
Trifloxystrobin·tebuconazole75.0 y=0.6232x+7.5465 0.102±0.021a 0.9802 吡唑醚菌酯
Pyraclostrobin25.0 y=0.6906x+7.9656 0.118±0.012a 0.9642 苯醚甲环唑
Difenoconazole10.0 y=0.5163x+6.5124 1.202±0.037ab 0.9998 丙环唑
Propiconazole50.0 y=0.9880x+7.6430 2.101±0.099a 0.9898 溴菌腈
Bromothalonil25.0 y=1.4748x+6.5053 95.402±1.718e 0.9890 二氰蒽醌
Dithianon22.7 y=0.8520x+5.6021 196.501±5.117f 0.9931 四霉素
Tetramycin0.3 y=0.8794x+7.6164 1.107±0.015a 0.9970 乙蒜素
Ethylicin80.0 y=1.4409x+6.5599 82.711±2.597d 0.9850 蛇床子素
Cnidiadin1.0 y=1.2111x+7.6279 6.803±0.147b 0.9913 宁南霉素
Ningnanmycin8.0 y=0.5785x+5.6878 64.712±1.124c 0.9350 1)x:杀菌剂浓度的对数;y:杀菌剂对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌的抑制率;2)同列数据后不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著 (P< 0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) x: Logarithm of fungicide concentration; y: Inhibition rate of fungicide against Colletotrichum fiorinia on Rhododendron delavayi; 2) Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences (P< 0.05, Duncan’s method)根据单剂毒力测定结果,选择抑菌效果较好、作用机制不同且EC50相近的10.0%(w) 苯醚甲环唑和0.3% (w)四霉素按照体积比9 ∶ 1、8 ∶ 2、7 ∶ 3、6 ∶ 4、5 ∶ 5、4 ∶ 6、3 ∶ 7、2 ∶ 8和1 ∶ 9进行混配后测定其EC50、CTC及联合毒力,结果(表3)表明,9种配比组合的EC50均较小,且小于2种单剂的EC50,说明以这9种配比组合进行混配均对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌菌丝生长具有较强的抑制作用;9种配比组合的CTC分别为302.51、511.49、584.56、549.23、423.58、339.93、314.25、326.69和279.91,均大于120。其中,配比为8 ∶ 2、7 ∶ 3、6 ∶ 4时CTC均大于500,表现为显著增效作用,且9种比例中7∶3 配比EC50最小,为0.1930 mg/L,CTC最大(584.56),为室内毒力测定最佳混剂配比。
表 3 四霉素与苯醚甲环唑不同配比混剂对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌的毒力Table 3. Bioactivities of mixtures containing different ratios of tetramycin and difenoconazole against Colletotrichum fioriniae on Rhododendron delavayiV(四霉素)∶V(苯醚甲环唑)
V (Tetramycin)∶V(Difenoconazole)毒力回归方程1)
Toxicity regression equation相关系数
Correlation coefficientEC502)/(mg·L−1) 共毒系数
Co-toxicity coefficient9∶1 y=1.0766x+5.4695 0.9992 0.3664±0.011e 302.51 8∶2 y=1.0903x+5.7206 0.9982 0.2183±0.020b 511.49 7∶3 y=0.8994x+5.6426 0.9889 0.1930±0.015a 584.56 6∶4 y=0.9324x+5.6378 0.9978 0.2070±0.028ab 549.23 5∶5 y=1.1314x+5.6421 0.9888 0.2707±0.027c 423.58 4∶6 y=0.9365x+5.4386 0.9984 0.3401±0.019d 339.93 3∶7 y=0.8895x+5.3829 0.9894 0.3711±0.021e 314.25 2∶8 y=0.9220x+5.4090 0.9956 0.3601±0.014de 326.69 1∶9 y=1.1020x+5.4110 0.9984 0.4237±0.022f 279.91 1) x:杀菌剂浓度的对数;y:杀菌剂对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌的抑制率;2)同列数据后不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著 (P< 0.05,Duncan’s法)
1) x: Logarithm of fungicide concentration; y: Inhibition rate of fungicide against Colletotrichum fiorinia on Rhododendron delavayi; 2) Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant differences (P< 0.05, Duncan’s method)3. 结论与讨论
明确病原菌生物学特性是了解病害发生规律的前提,本研究通过测定马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌生物学特性发现,该菌在pH 5~11均可生长,最适pH为8;菌丝对温度适应范围较广,10~35 ℃均可生长,最适温度为25 ℃。这与Baroncelli 等[15]报道的红花炭疽病菌C. chrysanthemi和张琳等[16]报道的南瓜炭疽病菌C. brevisporum生物学特性研究结果相似。供试的5种碳源中,以葡萄糖为碳源的培养基最适宜该菌的生长,而以乳糖为碳源的培养基明显不利于该菌生长,这与黄蔚等[17]报道的西瓜新炭疽病菌C. gloesporioides研究结果相同。供试的5种氮源中,菌株在以蛋白胨作氮源的培养基上的生长显著优于其他氮源,而以硫酸铵作为氮源时菌株菌丝生长速率显著低于其他氮源,说明蛋白胨为该菌生长最佳氮源,硫酸铵则不适合作为培养该菌的氮源。此研究结果与曹尚等[18]对高粱炭疽病菌C. sublineola生物学特性测定结果一致。
目前,化学防治仍是田间病害防治的主要手段,对化学药剂进行筛选是植物病害防治的重要内容。宋慧云等[19]对宫粉羊蹄甲炭疽病菌C. glo-eosporioides进行室内毒力测定,结果表明98% (w) 溴菌腈和97% (w) 吡唑醚菌酯对宫粉羊蹄甲炭疽病菌菌丝生长具有较强的抑制作用。冉飞等[20]对百香果炭疽病菌C. karstii进行室内杀菌试验发现75% (w) 肟菌·戊唑醇和25% (w) 吡唑醚菌酯抑菌效果最好,EC50分别为0.067和0.463 mg/L。孟珂等[21]对9种薄壳山核桃炭疽病病原菌的毒力测定结果表明,戊唑醇对C. fioriniae、C. liaoningense和C. tamarilloi等炭疽菌生长具有较强抑制作用,平均EC50为0.49 mg/L。本研究也表明,75% (w) 肟菌 · 戊唑醇和25.0% (w) 吡唑醚菌酯对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌抑制效果较好,EC50分别为0.102和0.118 mg/L。试验还发现10.0% (w) 苯醚甲环唑和50.0% (w) 丙环唑ME对该病原菌也具有较好抑制效果,EC50分别为1.202和2.101mg/L。另外,生物农药0.3% (w) 四霉素和1.0% (w) 蛇床子素对该菌也有较好抑制作用,EC50分别为1.107和6.803 mg/L,以上药剂均可作为田间防治马缨杜鹃炭疽病的候选药剂。
苯醚甲环唑是三唑类广谱杀菌剂,通过抑制麦角甾醇的生物合成、破坏细胞膜结构功能,从而达到杀菌效果[22]。四霉素为不吸水链霉菌梧州亚种的发酵代谢产物,其有效成分可通过抑制菌丝体生长、诱导植物抗性并促进作物生长而达到防治病害的目的[23]。王晓琳等[24]测定了0.3% (w) 四霉素与30%丙硫菌唑对草莓炭疽病菌C. gloeosporioides的室内毒力,结果表明四霉素与丙硫菌唑质量比为1∶15时抑菌效果最佳,EC50仅为0.0224 mg/L,增效系数为1.73。韦薇等[25]测定95% (w) 苯醚甲环唑和90% (w) 代森锰锌不同比例复配对柑桔炭疽病菌C. gloeosporioides的影响,结果表明前者与后者1 ∶ 7体积配比时CTC达到最大(150.25),是防治该病原菌的最佳配比。贤小勇等[26]测定98% (w) 吡唑醚菌酯和96% (w) 苯醚甲环唑不同配比混剂对核桃炭疽病菌C. gloeosporioides菌丝生长的影响,发现2种药剂按质量比3∶2和1∶1进行复配时,毒力均表现增效作用。本研究前期单剂毒力测定结果表明10.0% (w) 苯醚甲环唑和0.3% (w) 四霉素对马缨杜鹃炭疽病菌均有较好抑制作用,为延缓病原菌抗药性、减少化学农药的使用量,故选择这2种不同作用机理的药剂进行复配以增强防治效果。结果表明,较单剂而言,试验所设置的9种复配比例均有增效作用,以7 ∶ 3为最佳混剂体积比,EC50最小,CTC最大。
综合分析认为,75.0% (w) 肟菌·戊唑醇、25.0% (w) 吡唑醚菌酯、50.0% (w) 丙环唑、0.3% (w) 四霉素和10.0% (w) 苯醚甲环唑可作为马缨杜鹃炭疽病的候选防治单剂;将0.3% (w) 四霉素与10.0% (w)苯醚甲环唑进行复配能显著增效。本研究可为百里杜鹃自然保护区马缨杜鹃炭疽病田间药剂筛选及合适的施用浓度提供理论依据,为延缓该地区马缨杜鹃炭疽病病菌抗药性,选择适宜复配药剂提供一定参考。
-
表 1 大豆各器官中巯基物质与镉浓度和抗性指数的相关分析1)
Table 1 Correlation analysis of non-protein thiol and Cd contents in organs, and tolerance indexes of two soybean genotypes

-
[1] 曾希柏, 徐建明, 黄巧云, 等.中国农田重金属问题的若干思考[J].土壤学报, 2013, 50(1): 186-193. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trxb201301023 [2] SANITA D, TOPPI L, GABBRIELLI R. Response to cadmium in higher plants [J]. Environ Exp Bot, 1999, 41(2): 105-130. doi: 10.1016/S0098-8472(98)00058-6
[3] BENAVIDES M P, GALLEGO S M, TOMARO M L. Cadmium toxicity in plants [J]. Brazil J Plant Physiol, 2005, 17(1): 21-34. doi: 10.1590/S1677-04202005000100003
[4] LUX A, MARTHINK M, VACULIK M, et al. Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: A review [J]. J Exp Bot, 2011, 62(1): 21-37. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq281
[5] ZHAO Y, FANG X, MU Y, et al. Metal pollution (Cd, Pb, Zn, and As) in agricultural soils and soybean, Glycine max, in southern China [J]. B Environ Contam Tox, 2014, 92(4): 427-432. doi: 10.1007/s00128-014-1218-5
[6] ZHUANG P, LI Z A, ZOU B, et al. Heavy metal contamination in soil and soybean near the Dabaoshan Mine, South China [J]. Pedosphere, 2013, 23(3): 298-304. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(13)60019-3
[7] 赵云云, 钟彩霞, 方小龙, 等.华南地区夏播大豆品种镉耐性及籽粒镉积累的差异[J].大豆科学, 2013, 32(3): 336-340. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddkx201303012 [8] 赵云云, 钟彩霞, 方小龙, 等.华南地区11个春播大豆品种抗镉性的差异[J].华南农业大学学报, 2014, 35(3): 111-113. http://xuebao.scau.edu.cn/zr/hnny_zr/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=201403020&journal_id=hnny_zr [9] GRANT C A, CLARKE J M, DUGUID S, et al. Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2008, 390(2/3): 301-310. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ026480049/
[10] 赵云云, 郭秀兰, 钟彩霞, 等. 大豆抗镉污染低积累育种的研究进展[J/OL]. 分子植物育种(网络版), 2011, 9: 1692-1699(2011-08-12)[2015-03-08]. http://www.biopublisher.cn/index.php/mpb/article/html/576/.DOI:10.5376/mpb.cn.2011.09.0096. [11] SHARMA S S, DIETZ K. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance [J]. Trends Plant Sci, 2009, 14(1): 43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.10.007
[12] CUYPERS A, KAREN S, JOS R, et al. The cellular redox state as a modulator in cadmium and copper responses in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings [J]. J Plant Physiol, 2011, 168(4): 309-316. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.07.010
[13] LIN Y F, AARTS M G. The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants [J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2012, 69(19): 3187-3206. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1089-z
[14] SETH C S, REMANS T, KEUNEN E, et al. Phytoextraction of toxic metals: A central role for glutathione [J]. Plant Cell Environ, 2012, 35(2): 334-346. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02338.x
[15] HARTLEY-WHITAKER J, AINSWORTH G, VOOIJS R, et al. Phytochelatins are involved in differential arsenate tolerance in Holcus lanatus [J]. Plant Physiol, 2001, 126(1): 299-306. doi: 10.1104/pp.126.1.299
[16] GALLEGO S M, PENA L B, BARCIA R A, et al. Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: Insight into regulatory mechanisms [J]. Environ Exp Bot, 2012, 83: 33-46. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.04.006
[17] GUO J, DAI X, XU W, et al. Overexpressing GSH1 and AsPCS1 simultaneously increases the tolerance and accumulation of cadmium and arsenic in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 72(7): 1020-1026. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.018
[18] SARWAR N, ISHAQ W, FARID G, et al. Zinc-cadmium interactions: Impact on wheat physiology and mineral acquisition[J]. Ecotox Environ Safe, 2015, 122: 528-536. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.09.011
[19] 高可辉. 镉胁迫及缺硫对水稻非蛋白巯基物质含量和谷胱甘肽硫转移酶活性的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2011. [20] EBBS S, LAU I, AHNER B, et al. Phytochelatin synthesis is not responsible for Cd tolerance in the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (J. & C. Presl) [J]. Planta, 2002, 214(4): 635-640. doi: 10.1007/s004250100650
[21] LI Y, DHANKHER O P, CARREIR L, et al. Overexpression of phytochelatin synthase in Arabidopsis leads to enhanced arsenic tolerance and cadmium hypersensitivity[J]. Plant Cell Physiol, 2004, 45(12): 1787-1797. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch202
[22] WOJAS S, CLEMENS S, HENNIG J, et al. Over expression of phytochelatin synthase in tobacco: Distinctive effects of AtPCS1 and CePCS genes on plant response to cadmium[J]. J Exp Bot, 2008, 59(8): 2205-2219. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern092
[23] ANETOLI M, VOOIJS R, TEN BOOKUM W, et al. Arsenate tolerance in Silene paradoxa does not rely on phytochelatin-dependent sequestration[J]. Environ Pollut, 2008, 152(3): 585-591. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.07.002
[24] MAIER E A, MATTHEWS R D, MCDOWELL J A, et al. Environmental cadmium levels increase phytochelatin and glutathione in lettuce grown in a chelator-buffered nutrient solution[J]. J Environ Qual, 2003, 32(4): 1356-1364. doi: 10.2134/jeq2003.1356
[25] JOZEFCZAK M, REMANS T, VANGRONSVELD J, et al. Glutathione is a key player in metal-induced oxidative stress defenses[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2012, 13(3): 3145-3175. doi: 10.3390/ijms13033145
[26] JOZEFCZAK M, KEUNEN E, SCHAT H, et al. Differential response of Arabidopsis leaves and roots to cadmium: Glutathione-related chelating capacity vs antioxidant capacity[J]. Plant Physiol Bioch, 2014, 83: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.07.001
[27] ZAGORCHEV L, SEAL C E, KRANNER I, et al. A central role for thiols in plant tolerance to abiotic stress [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2013, 14(4): 7405-7432. doi: 10.3390/ijms14047405
[28] VAZQUEZ S, GOLDSBROUGH P, CARPENA R O. Comparative analysis of the contribution of phytochelatins to cadmium and arsenic tolerance in soybean and white lupin[J]. Plant Physiol Bioch, 2009, 47(1): 63-67. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.09.010
[29] WEI S, LI Y, ZHAN J, et al. Tolerant mechanisms of Rorippa globosa (Turcz.) Thell. hyper accumulating Cd explored from root morphology[J]. Bioresource Technol, 2012, 118: 455-459. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.05.049
[30] RAMA DEVI S, PRASAD M. Copper toxicity in Ceratophyllum demersum L. (Coontail), a free floating macrophyte: Response of antioxidant enzymes and antioxidants[J]. Plant Sci, 1998, 138(2): 157-165. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00161-7
[31] GUPTA M, RAI U N, TRIPATHI R D, et al. Lead induced changes in glutathione and phytochelatin in Hydrilla verticillata (lf) Royle[J]. Chemosphere, 1995, 30(10): 2011-2020. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(95)00075-J
[32] BHARGAVA P, KUMAR SRIVASTAVA A, URMI S, et al. Phytochelatin plays a role in UV-B tolerance in N2-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena doliolum[J]. J Plant Physiol, 2005, 162(11): 1220-1225. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2004.12.006
[33] GILL S S, TUTEJA N. Cadmium stress tolerance in crop plants[J]. Plant Signal Behav, 2011, 6(2): 215-222. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.2.14880
[34] LI H, DONG Y, YIN H, et al. Characterization of the stress associated micro RNAs in Glycine max by deep sequencing[J]. BMC Plant Biol, 2011, 11: 170. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-170
[35] VERBRUGGEN N, HERMANS C, SCHAT H. Molecular mechanisms of metal hyper accumulation in plants[J]. New Phytol, 2009, 181(4): 759-776. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02748.x
[36] LI T, DI Z, ISLAM E, et al. Rhizosphere characteristics of zinc hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii involved in zinc accumulation[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 185(2/3): 818-823. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0223879793
[37] AHSAN N, NAKAMURA T, KOMATSU S. Differential responses of microsomal proteins and metabolites in two contrasting cadmium (Cd)-accumulating soybean cultivars under Cd stress[J]. Amino Acids, 2012, 42(1): 317-327. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0809-7
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 兰桃芳, 武佳玥, 魏奇, 刘恩科, 郑少文. 不同药剂对菜豆炭疽病的防效研究. 安徽农业科学. 2025(11)  百度学术
百度学术
2. 贺圆,徐云红,管朝旭,保华,陈剑英,吴子欢,张永祥,陈鹏. 不同光周期处理、覆土厚度和基质对马缨杜鹃种子萌发的影响. 林业科技通讯. 2025(02): 62-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 裴张新,王志华,于静亚,毛润萍,刘超,董立坤. 园林植物炭疽病研究进展. 中国森林病虫. 2023(06): 33-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)









 下载:
下载: