Spatial patterns and environmental factors of rapidly degraded mangroves at Dongzhaigang Harbor in Hainan
-
摘要:目的
对我国一些红树林湿地生态系统近期出现的急速退化现象作相关分析.
方法以海南东寨港整个港湾红树林区为研究典型区域,应用3S技术,分析近30年间东寨港红树林湿地景观格局的演变过程;同时采用高分辨率影像数据,聚焦分析了演丰东河沿岸、塔市及三江3个片区红树林群落退化特征及空间分布规律;结合大量野外样方调查数据,系统分析了近海岸红树林生态系统退化的主要影响因素.
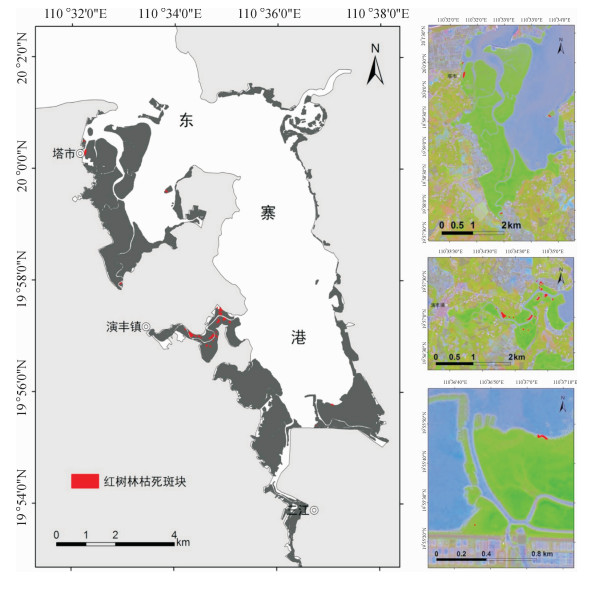
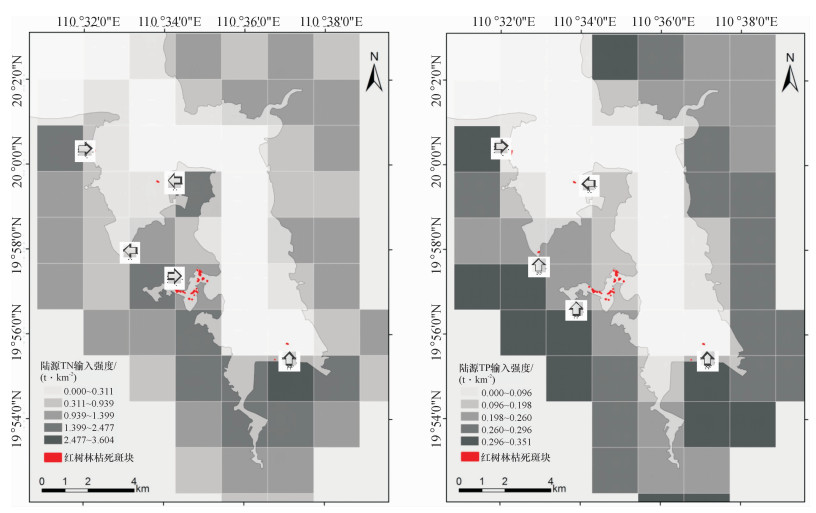
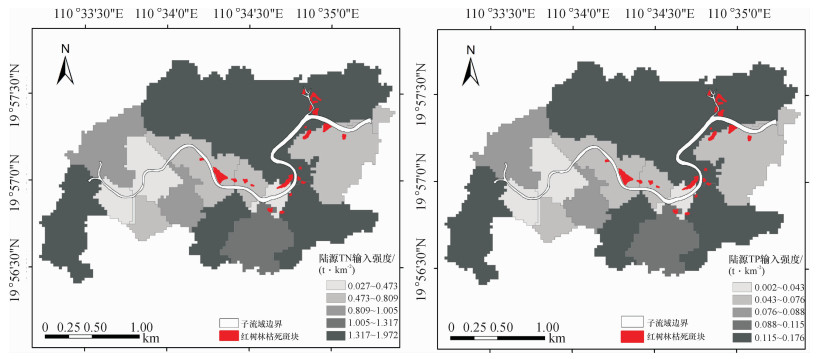
结果和结论从1999-2013年,东寨港红树林面积由1 709.4 hm2减少至1 679.5 hm2,年均减少2.1 hm2.而沿海岸线2 km缓冲区范围内,周边养殖塘面积则由1987年的59.1 hm2增至2013年的1 986.9 hm2.截止2013年,东寨港红树林枯死面积约为4 hm2.从空间分布上来看,红树林枯死群落主要分布于地形低洼积水处或污染物传输通道两侧.东寨港河流型红树林群落退化最为严重,集中分布于演丰东河中下游河段;同时,近海湾的前沿地段也有退化群落零星分布.处于地带性演替后期的红树林群落,退化程度较高.陆源污染物输入强度是影响红树林退化群落分布的重要因素.
Abstract:ObjectiveThe purpose of this study was to analyze mangrove degradation in some coastlandsof southern China.
MethodMangrove of Dongzhaigang Harbor in Hainan Province was investigated as acase study. Landscape pattern dynamics of mangrove wetland from 1987 to 2013 were analyzed at Dongzhaigang Harbor by interpreting five phase remote sensing images. The degradation characteristics of mangrove forest and its spatial patterns were also further studied using SPOT5 and aerial imagery. Furthermore, the influencing factors of mangrove degradation such as topographical factors and terrestrial contaminant loading were analyzed by surveying numerous sampling plots.
Result and conclusionIt was foundthat mangrove area decreased from 1 709.4 hm2 in 1999 to 1 679.5 hm2 in 2013, while the area of pondsin the 2 km coastal buffers increased from 59.1 hm2 in 1987 to 1 986.9 hm2 in 2013. The dead area ofmangrove patches had reached 4 hm2 by the end of 2013. Spatially, mangrove degradation mainly locatedin low-lying land and both sides of contaminant transport channels. The degradation degree of River-typemangrove communities was the most serious, whose major distribution was in the middle and lower reaches of Yanfengdong River. Meanwhile, the degraded mangrove communities also distributed sporadicallyin frontier areas of Dongzhaigang Harbor. The degradation degree was higher for mangrove communities inthe climax stage of succession. The distribution of degraded mangrove communities was mainly determined by terrestrial pollutant loading.
-
-
表 1 研究区N、P输出系数1)
Table 1 Nitrogen and phosphorus export coefficients in the study area

表 2 1987-2013年东寨港红树林面积变化情况
Table 2 Changes of mangrove area in Dongzhaigang Harbor from 1987 to 2013

表 3 各样地的群落退化特征1)
Table 3 Community degradation characteristics of sample plots

表 4 各样地的群落特征与退化特征相关性分析1)
Table 4 The correlation analyses of community characteristics and degradation characteristics of sample plots

表 5 各样地的地形因子与退化特征相关性分析1)
Table 5 The correlation analyses of topographical factors and community degradation characteristics of sample plots

-
[1] ALONGI D. Present state and future of the World' s mangrove forests[J]. Envir Conserv, 2002, 29 (3):331-349. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ029814689
[2] RAKOTOMAVO A, FROMARD F. Dynamics of mangrove forests in the Mangoky River delta, Madagascar, under the influence of natural and human factors[ J]. Forest Ecol Management, 2010, 259 (6):1161-1169. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2010.01.002
[3] 伍淑婕, 梁士楚.人类活动对红树林生态系统服务功能的影响[J].海洋环境科学, 2008, 27 (5):537-542. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2008.05.033 [4] 赵晓涛, 杨威, 周丹, 等.影响我国河口地区可持续发展的五大问题[J].海洋开发与管理, 2008, 25 (3):91- 93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2008.03.020 [5] REDDI E U B, RAMAN A V, SATYANARAYANA B, et al. Degradation of mangrove ecosystem due to hinterland farm practices: A case for Coringa, East Coast of India [J].南京林业大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 27 (2):1- 6. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-NJLY200302001.htm [6] 廖宝文, 李玫, 陈玉军, 等.海南东寨港红树林生态系统研究[M].青岛:中国海洋大学出版社, 2007:2-31. [7] 徐蒂, 廖宝文, 朱宁华, 等.海南东寨港红树林退化原因初探[J].生态科学, 2014, 33 (2):294-300. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=STKX201402017&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [8] BROOK R A. Discovery of Sphaeroma terebrans, a woodboring isopod, in the red mangrove, Rhizophora mangle, habitat of Northern Florida Bay[J]. AMBIO:J Human Envir, 2004, 33 (3):171-173. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447-33.3.171
[9] 邱勇, 李俊, 黄勃, 等.影响东寨港红树林中光背团水虱分布的生态因子研究[ J].海洋科学, 2013, 37 (4): 21-25. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx201304004 [10] 王胤, 左平, 黄仲琪, 等.海南东寨港红树林湿地面积变化及其驱动力分析[ J].四川环境, 2006, 25 (3):44-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2006.03.011 [11] LIU K, LI X, SHI X, et al. Monitoring mangrove forest changes using remote sensing and GIS data with decisiontree learning[J]. Wetlands, 2008, 28 (2):336-346. doi: 10.1672/06-91.1
[12] 吴哲, 陈歆, 刘贝贝, 等.基于InVEST模型的海南岛氮磷营养物质负荷的风险评估[ J].热带作物学报, 2013, 34 (9):1791-1797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2013.09.029 [13] 李廷友, 林振山.海水围塘混合养殖生态系统氮磷平衡的研究[ J].井冈山大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 31 (2):32-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jgsxyxb201002008 [14] 王兵, 郑秋红, 郭浩.基于Shannon - Wiener指数的中国森林物种多样性保育价值评估方法[ J].林业科学研究, 2008, 21(2):268-274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2008.02.025 [15] 薛春汀.人类活动对密克罗尼西亚联邦库赛埃岛红树林海岸的影响[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2002, (2):17-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2002.02.003 [16] 范航清, 刘文爱, 钟才荣, 等.中国红树林蛀木团水虱危害分析研究[J].广西科学, 2014, 21 (2):140-152. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxkx201402012 [17] 廖宝文, 李玫, 陈玉军, 等.中国红树林恢复与重建技术[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010:120-122.



 下载:
下载: