Comparative studies on alkaloids secreted by vemon gland of Solenopsis invicta based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis
-
摘要:目的
分析中国和美国2个入侵地红火蚁Solenopsis invicta毒腺生物碱的主要化学成分及其聚类特征.
方法以中国广州、惠州、深圳、珠海和东莞以及美国阿拉巴马州采样地共24巢红火蚁为样本, 提取各个蚁巢毒腺的生物碱流分, 分别以红火蚁顺式生物碱流分中的15种生物碱和反式生物碱流分中的7种生物碱相对含量作为变量, 建立2个数据矩阵, 进行主成分分析和聚类分析.
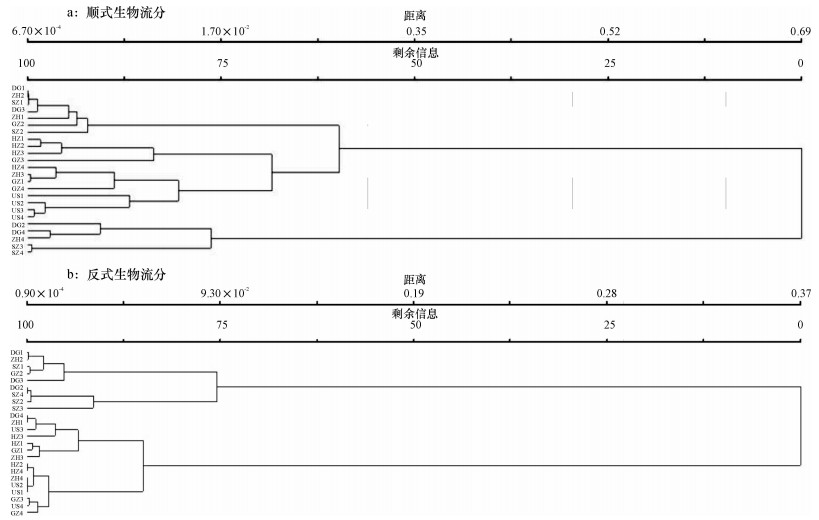
结果和结论主成分分析结果表明, 将红火蚁顺式生物碱流分中的15种生物碱综合成为2个主成分因子, 主要是顺式-2-甲基-6-(4′-十三烯)哌啶、2-甲基-6-(6′-十五烯)-Δ1, 6-哌啶、2-甲基-6-十五烷基-Δ1, 6-哌啶和顺式-2-甲基-6-十一烷基哌啶; 反式生物碱流分中的7种生物碱综合成1个主成分因子, 主要是反式-2-甲基-6-(4′-十三烯)哌啶和反式-2-甲基-6-(6′-十五烯)哌啶.顺式生物碱流分的聚类分析可以将美国种群与中国种群区分开来, 而反式生物碱流分不能.
Abstract:ObjectiveTo analyze the major components and cluster features of alkaloids, which are secreted by vemon gland of red imported fire ants, Solenopsis invicta, from China and USA.
MethodTwenty four colonies of S.invicta were collected from Guangzhou, Huizhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Dongguan of China and Alabama of USA.Alkaloids of vemon gland were extracted.Two data matrix were established with variable of relative contents of 15 kinds of cis-alkaloids and 7 kinds of trans-alkaloid respectively.The alkaloid fraction was analyzed by principal component analysis and cluster analysis.
Result and conclusionThe results showed that the 15 types of alkaloids from the cis-alkaloids fraction were consolidated into two principal components, including cis-2-methyl-6-(4′-tridecenyl) piperidine, 2-methyl-6-(6′-pentadecenyl) -Δ1, 6-piperidine, 2-methyl-6-pentadecyl-Δ1, 6-piperidine and cis-2-methyl-6-undecylpiperidine seven types of alkaloids from the trans-alkaloid fraction were consolidated into one principal component, including trans-2-methyl-6-(4′-tridecenyl) piperidine and trans-2-methyl-6-(6′-pentadecenyl) piperidine.The results of cluster analyses demonstrate that alkaloids from the cis-alkaloids fraction can distinguish the USA populations from the Chinese populations, but alkaloids from the trans-alkaloid fraction can not.
-
Keywords:
- Solenopsis invicta /
- vemon gland /
- alkaloid /
- principal component analysis /
- cluster analysis
-
-
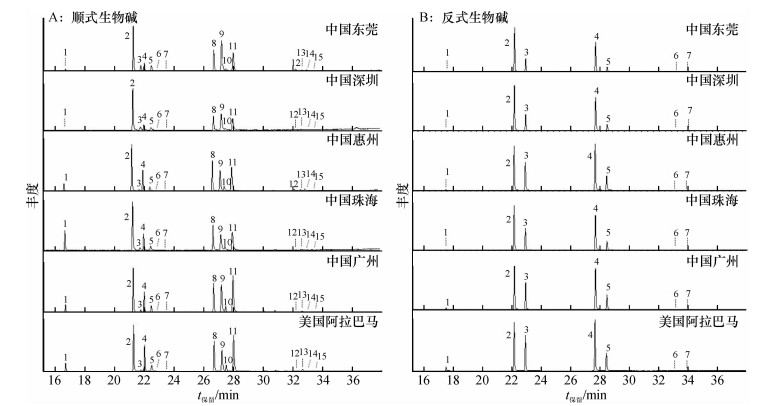
图 1 红火蚁工蚁顺式和反式生物碱流分总离子色谱图
A:1 ~ 15分别对应顺式-2-甲基-6-十一烷基哌啶、顺式-2-甲基-6-(4′-十三烯)哌啶、2-甲基-6-(4′-十三烯)-Δ1, 6-哌啶、顺式-2-甲基-6-十三烷基哌啶、2-甲基-6-十三烷基-Δ1, 6-哌啶、2-甲基-6-(4′-十三烯)-Δ1, 2-哌啶、2-甲基-6-十三烷基Δ1, 2-哌啶、顺式-2-甲基-6-(6′-十五烯)哌啶、2-甲基-6-(6′-十四烯)-Δ1, 6-哌啶、顺式-2-甲基-6-十五烷基哌啶、2-甲基-6十五烷基-Δ1, 6-哌啶、顺式-2-甲基-6-(8′-十七烯)哌啶、2-甲基-6-(8′-十七烯)-Δ1, 6-哌啶、顺式-2-甲基-6-十七烷基哌啶、2-甲基-6-十七烷基-Δ1, 6-哌啶; B:1 ~ 7分别对应反式-2-甲基-6-十一烷基哌啶、反式-2-甲基-6-(4′-十三烯)哌啶、反式-2-甲基-6-十三烷基哌啶、反式-2-甲基-6-(6′-十五烯)哌啶、反式-2-甲基-6-十五烷基哌啶、反式-2-甲基-6-(8′-十七烯)哌啶、反式-2-甲基-6-十七烷基哌啶.
Figure 1. Total ion chromatograms of the cis- and trans- alkaloid fractions extracted from red imported fire ant workers from different areas
表 1 顺式生物碱流分的主成分分析
Table 1 Principal component analysis of the cis-alkaloid fraction

表 2 顺式生物碱流分各化合物的载荷矩
Table 2 Component matrix of 15 compounds from the cis-alkaloid fraction

表 3 反式生物碱流分的主成分分析
Table 3 Principal component analysis of the trans-alkaloid fraction

表 4 反式生物碱流分各化合物的载荷矩
Table 4 Component matrix of 7 compounds from the trans-alkaloid fraction

-
[1] TSCHINKEL W R.The fire ants[M].Cambridge, Massachusetts:Harvard University Press, 2006:723.
[2] ZHANG R, LI Y, LIU N, et al.An overview of the red imported fire ant (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) in mainland China[J].Fla Entomol, 2007, 90(4):723-731. doi: 10.1653/0015-4040(2007)90[723:AOOTRI]2.0.CO;2
[3] 薛大勇, 李红梅, 韩红香, 等.红火蚁在中国的分布区预测[J].昆虫知识, 2005, 42(1):57-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0452-8255.2005.01.015 [4] 曾玲, 陆永跃, 何晓芳, 等.入侵中国大陆的红火蚁的鉴定及发生为害调查[J].昆虫知识, 2005, 42(2):144-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0452-8255.2005.02.007 [5] WANG L, LU Y Y, XU Y J, et al.The current status of research on Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera:Formicidae) in mainland China[J].Asian Myrmecol, 2013 (5):125-138. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287511686_Observation_of_nuptial_flights_of_the_red_imported_fire_ant_Solenopsis_invicta_Hymenoptera_Formicidae_in_Mainland_China
[6] 陆永跃, 梁广文, 曾玲.华南地区红火蚁局域和长距离扩散规律研究[J].中国农业科学, 2008, 41 (4):1053-1063. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.04.015 [7] VINSON S B.Impact of the invasion of the imported fire ant[J].Insect Sci, 2013, 20(4):439-455. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7917.2012.01572.x
[8] VINSON S B.Invasion of the red imported fire ant (Hymenoptera:Formicidae):Spread, biology, and impact[J].Am Entomol, 1997, 43(1):23-39. doi: 10.1093/ae/43.1.23
[9] 陆永跃.中国大陆红火蚁远距离传播速度探讨和趋势预测[J].广东农业科学, 2014, 41(10):70-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2014.10.017 [10] JONES T H, BLUM M S, FALES H M.Ant venom alkaloids from Solenopsis and Monorium species:Recent developments[J].Tetrahedron, 1982, 38(13):1949-1958. doi: 10.1016/0040-4020(82)80044-6
[11] MACCONNELL J G, BLUM M S, FALES H M.Alkaloid from fire ant venom:Identification and synthesis[J].Science, 1970, 168(3933):840-841. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.840
[12] MACCONNELL J G, BLUM M S, FALES H M.The chemistry of fire ant venom[J].Tetrahedron, 1971, 27 (6):1129-1139. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)90860-9
[13] BLUM M S, WALKER J R, CALLAHAN P S, et al.Chemical, insecticidal and antibiotic properties of fire ant venom[J].Science, 1958, 128(3319):306-307. doi: 10.1126-science.128.3319.307/
[14] MORRISON L W.Long-term impacts of an arthropod-community invasion by the imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta [J].Ecology, 2002, 83(8):2337-2345. doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[2337:LTIOAA]2.0.CO;2
[15] LECLERCQ S, THIRIONET I, BROEDERS F, et al.Absolute configuration of the solenopsins, venom alkaloids of the fire ants[J].Tetrahedron, 1994, 50 (28):8465-8478. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)85567-8
[16] YU Y, WEI H, FADAMIRO H, et al.Quantitative analysis of alkaloidal constituents in imported fire ants by gas chromatography[J].J Agr Food Chem, 2014, 62(25):5907-5915. doi: 10.1021/jf501423y
[17] 马伏宁, 曾鑫年, 潘达强.多后型红火蚁工蚁和蚁后毒液生物碱成分的比较[J].中国农学通报, 2009, 25 (17):57-61. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnxtb200917013 [18] 官迪, 廖晓兰, 陈立.中国和美国红火蚁毒腺生物碱组分的比较分析[J].昆虫学报, 2013, 56(4):365-371. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcxb201304005 [19] CHEN L, FADAMIRO H Y.Re-investigation of venom chemistry of Solenopsis fire ants:Ⅰ:Identification of novel alkaloids in S.richteri[J].Toxicon, 2009, 53(5):469-478. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.12.019
[20] CHEN L, FADAMIRO H Y.Re-investigation of venom chemistry of Solenopsis fire ants:Ⅱ:Identification of novel alkaloids in S.invicta[J].Toxicon, 2009, 53(5):479-486. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.01.016
[21] 王芳.主成分分析与因子分析的异同比较及应用[J].统计教育, 2003, 5(5):14-17. doi: 10.5713-ajas.2010.90642/ [22] ASCUNCE M S, YANG C, OAKEY J, et al.Global invasion history of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta[J].Science, 2011, 331(6020):1066-1068. doi: 10.1126/science.1198734



 下载:
下载: