Photosynthetic characteristics of Camellia gauchowensis
-
摘要:目的
阐明高州油茶光合生理特征, 为优良种质资源选择及高效栽培管理提供理论基础和技术指导.
方法利用LI-6400便携式光合仪, 测定高州油茶主要光合生理指标.
结果和结论高州油茶净光合速率的日变化均呈“双峰型”曲线, 其光饱和点为1 417 μmol·m-2·s-1, 光补偿点为18.92 μmol·m-2 ·s-1, 最大净光合速率为12.58 μmol·m-2·s-1.蒸腾速率各季度变化均呈“单峰型”曲线, 最高值为3.65 mmol·m-2·s-1.胞间CO2浓度日变化趋势为“ U”型曲线.水分利用效率日变化均呈“降-升-降”的趋势.气孔导度日变化曲线有“单峰型”和“双峰型”2种, 其中7、9、11月和次年1月为“双峰型”, 次年3月为“单峰型”.光合有效辐射、空气温度、大气CO2浓度, 蒸腾速率和气孔导度与光合速率的相关性最大.
Abstract:ObjectiveThe purpose of this study was to explain photosynthetic characteristics of the leaves of Camellia gauchowensis, providing a theoretical basis and technical guidance for the selection of fine resources, as well as effective management and cultivation of C.gauchowensis.
MethodPhotosynthetic characteristics of the leaves of C.gauchowensis were determined by a LI-6400 portable photosynthesis analysis system.
Result and conclusionDiurnal variations in net photosynthetic rate (Pn) of the mature trees of C.gauchowensis presented a double-peak curve.The light saturation point was 1 417 μmol·m-2·s-1, with the light compensation point being 18.92 μmol·m-2·s-1, Pnmax being 12.58 μmol·m-2·s-1.The diurnal variation in transpiration rate (Tr) of the mature trees of C.gauchowensis was characterized by a single-peak curve.The maximum of Tr of the mature trees was 3.65 mmol·m-2·s-1. The diurnal variations in intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) of C.gauchowensis presented a "U" curve in each month.The diurnal variations in water use efficiency (WUE) of mature trees presented a "down-up-down" curve all the year round.The diurnal variations in stomatal conductance (Gs) of mature trees presented a double-peak curve or a single-peak curve.In July, September, November and January, the diurnal variations in Gs of mature trees were both double-peak curves, and in March it was single-peak curves.Photosynthetically-active radiation, air temperature, atmospheric CO2 concentration, Tr and Gs were the main factors which influence the Pn of C.gauchowensis.
-
光合生理是植物生长发育最重要的评价指标, 它与其生境选择和产量形成密切相关.不同物种在特定生境中能够形成比较稳定的生理特征和调节机制.因此揭示和阐明植物光合生理指标是种质资源评价利用和创制的重要依据之一[1].
油茶Camellia oleifera为山茶科Theaceae山茶属常绿灌木或小乔木, 是我国主要经济林树种, 亦是世界四大木本油料树种之一[2].高州油茶C.gauchowensis又名越南油茶、大果油茶、华南油茶, 主要分布于广东和广西, 以其树形高大、经济寿命长、果实大、产量高和品质好而著称, 同时具有耐高光、高温、高湿等优良性状[3], 是华南区域优良油茶资源之一.然而目前其研究主要集中在良种选育、丰产栽培和病虫害防治等方面, 而光合生理方面的研究较少且缺乏系统性[4].本文通过对其主要光合生理指标及其影响因子的研究, 旨在阐明其光合生理特征, 为该种质资源的发掘、评价和有效利用提供理论基础, 同时为华南热带亚热带地区油茶优良种质资源选择利用及高效栽培管理提供技术指导.
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究区域概况
研究区位于广东省广州市天河区树木公园, 该区属南亚热带季风气候, 全年水热同期, 雨量充沛, 光热充足.年均温度22 ℃, 最热月(7月)平均气温28.5 ℃, 最冷月(1月)平均气温13.3 ℃, 极端最低温度0 ℃, 最高温度39.1 ℃.年均降雨量1982.7 mm, 平均相对湿度68 %.土壤为红壤, 养分丰富, 适合油茶生长[5].
1.2 试验材料
参试对象为园内高州油茶试验林.于20世纪80年代造林, 株行距3 m × 4 m, “品”字形种植, 管理规范.目前该林分处于盛产期, 树体生长旺盛.在林分调查的基础上, 选择3株生长健壮、无病虫害、基本特征相似的植株为供试样树.经测定, 样树平均树高(6.0 ± 0.5) m, 平均冠幅(4.5 ± 0.3) m × (5.0 ±0.2) m.
1.3 研究内容与方法
1.3.1 测定时间
2013年7、9、11月和2014年1、3月的中旬.
1.3.2 测定叶样选择
在每株样树上, 选取树冠中上部向阳的当年生枝条顶端的第3 ~ 5片成熟功能叶片进行活体测定[6].
1.3.3 光合、蒸腾特征因子测定
在各测定时间内选择晴朗天气, 从每日的08:00-18:00, 测定步长为2 h.采用美国LI-6400型光合仪, 分别测定记录其净光合速率(Pn)、气孔导度(Gs)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、胞间CO2浓度(Ci)、叶温(θl)、相对空气湿度(RH)和光合有效辐射(PAR).每次测定30片叶, 重复记录5次数据, 取其平均值进行统计分析; 其中, 日变化值为当天测定时间点的平均值, 季节变化值为测定月份的平均值.
1.3.4 光响应曲线测定
选择晴天10:00-11:30进行, 将红蓝光源LED设定光合有效辐射(PAR)12个梯度, 分别为0、20、50、100、200、400、600、800、1 000、1 200、1 500、1 800 μmol·m-2·s-1, 自动测定该条件下叶片的净光合速率, 最长等待时间为200 s, 最短为120 s, △CO2为15, 测定时样室CO2摩尔分数为(400 ± 1) μmol·mol-1, 叶片温度为(30.0 ± 0.5) ℃.测定3株, 每株重复3次, 取其平均值统计分析.光饱和点和光补偿点等特征值计算参见文献[5].
1.3.5 水分和光能利用效率
水分利用效率(WUE)为净光合速率与蒸腾速率的比值(WUE = Pn /Tr); 光能利用效率(QUE)为净光合速率与光合有效辐射的比值(QUE = Pn /PAR).
1.4 试验数据处理
利用LI-6400仪器自带软件进行生理指标数据采集与分析; 采用Microsoft Excel 2003进行图表绘制, 用SPSS17.0进行回归方程拟合及统计分析.
2. 结果与分析
2.1 净光合速率变化特征
2.1.1 净光合速率日变化
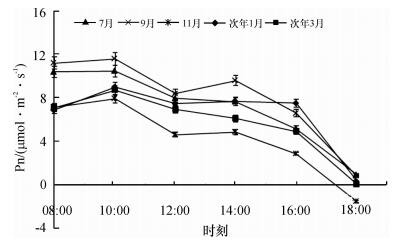
由图 1可看出, 在不同月份高州油茶Pn的日变化曲线均呈“双峰型”, 第1峰值在10:00, 第2峰值在14:00;在当天的12:00-13:00出现“光合午休”现象; 测定期内, 日Pn的最大值出现在9月的10:00, 为11.56 μmol·m-2·s-1, 最小值出现在11月的18:00, 为-1.60 μmol·m-2·s-1.
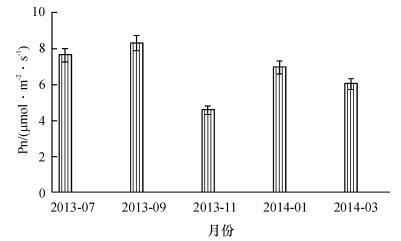
2.1.2 净光合速率季节变化
如图 2所示, 高州油茶Pn季节变化趋势为:9月>7月>次年1月>次年3月>11月, 其中9月份Pn的平均值最大(7.70 μmol· m-2· s-1), 11月份为全年最低值(4.27 μmol·m-2·s-1).
2.2 蒸腾速率变化特征
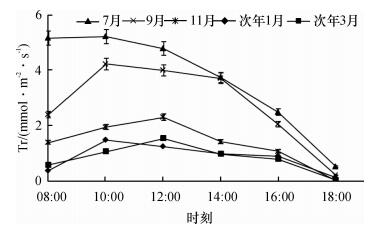
2.2.1 蒸腾速率日变化
高州油茶蒸腾速率在不同月份的日变化趋势均呈“单峰型”(图 3).由图 3可见, 7、9月和次年1月, Tr均在10:00左右达到峰值, 分别为5.21、4.22和1.49 mmol · m-2· s-1, 10:00以后逐渐下降, 直至18:00左右降为最低值; 11月和次年3月份, 早晨随光照的增强和温度的升高高州油茶Tr逐渐升高, 于12:00达到最高峰, 峰值分别为2.31和1.54 mmol·m-2·s-1, 随后逐渐下降, 18:00左右达到当天最低值.
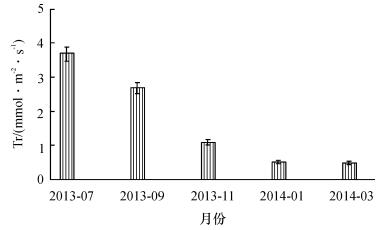
2.2.2 蒸腾速率季节变化
如图 4所示, 高州油茶Tr的季节变化趋势为:7月>9月>11月>次年3月>次年1月.7月的Tr平均值为全年最高值(3.65 mmol·m-2·s-1), 因此可确认7月是其蒸腾耗水的旺盛期; 9月和11月也保持较高的蒸腾速率, 1月和3月蒸腾速率较低, 全年Tr的最低值(0.84 mmol·m-2·s-1)出现在3月份.
2.3 气孔导度变化特征
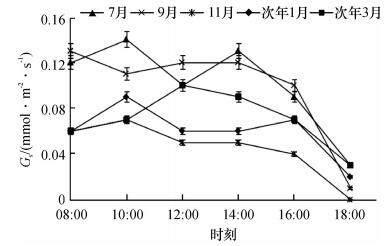
2.3.1 气孔导度日变化
从图 5可以看到, 高州油茶Gs的日变化趋势有“单峰型”和“双峰型”2种.7、9、11月和次年1月的Gs日变化均呈“双峰型”, 其中7和11月份变化趋势相似, 首高峰出现时间都在10:00, 峰值分别为0.07和0.14 mmol·m-2·s-1; 次高峰出现在14:00, 峰值分别为0.055和0.13 mmol·m-2·s-1; 9月份Gs的首高峰提前, 出现在08:00, 峰值为0.13 mmol·m-2·s-1, 次高峰依然出现在14:00, 峰值为0.12 mmol·m-2·s-1.次年1月份Gs双峰值则出现在10:00和16:00, 分别为0.09和0.07 mmol·m-2·s-1.3月份Gs呈“单峰型”变化, 峰值出现在12:00, 随后Gs逐渐降低直至18:00降至0.03 mmol·m-2·s-1左右, 因此整体上Gs上午高于下午.
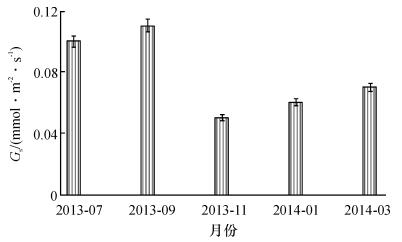
2.3.2 气孔导度季节变化
如图 6所示, 高州油茶Gs的季节变化呈现“升-降-升”的趋势, Gs 9月最高, 11月最低, 这可能与该月温度和湿度都较低, 叶片细胞水分不足有关.
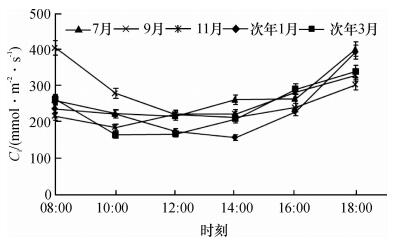
2.4 胞间CO2浓度变化特征
2.4.1 胞间CO2浓度日变化
如图 7所示, 高州油茶Ci日变化趋势均呈“ U”型, 早晚较高, 其他时段均较低, 且基本平稳.7、9、11月份Ci在12:00达到最低值, 随后慢慢上升, 到18:00在光照强度极弱的情况下, 叶片主要进行呼吸作用释放CO2, Ci达到最大值.次年1和3月份则分别在14:00和10:00达到最低值.
2.4.2 胞间CO2浓度季节变化
如图 8所示, 高州油茶7和9月份Ci维持较高值, 分别为270.48和275.98 mmol·m-2·s-1; 11月和次年1、3月份的Ci比较稳定, 分别为234.44、238.02和242.35 mmol·m-2·s-1.这与高州油茶光合速率的进程和生长节律相吻合.
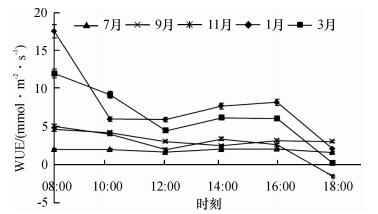
2.5 水分利用效率变化特征
2.5.1 水分利用效率日变化
由图 9可知, 高州油茶WUE日变化呈“降-升-降”的变化趋势.从总体来看, 10:00前由于光照强度、大气相对湿度高, 气孔开度较大, 净光合速率较快, 而蒸腾速率处于较低水平, 因此WUE较高.随后, 由于气温和光照的继续增强、大气相对湿度的降低, 蒸腾作用急剧增强, 水分散失多, 气孔关闭, 出现“光合午休”, 在一定程度上调节了树体水分运输和水分供需的平衡, 此时WUE较低, 随后慢慢回升, 不同月份WUE出现次高峰的时间有所差异.16:00以后, 随着温度降低, 光照减弱, 湿度回升, 气孔导度减小, 净光合速率下降, 蒸腾速率也缓慢下降, WUE也下降, 18:00降到最低.
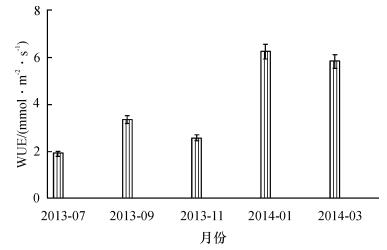
2.5.2 水分利用效率季节变化
如图 10所示, 高州油茶在不同月份和不同测定时期, 水分利用效率相差很大, 7、9和11月份WUE较低.次年1和3月份WUE较高.总体趋势为:次年1月>次年3月>9月>11月>7月.
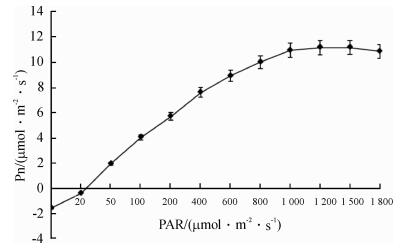
2.6 光响应曲线特征
如图 11所示:在光强极弱的情况下(0 ~ 200 μmol·m-2·s-1), 光合速率低于呼吸速率, Pn为负值; 在中强光照下(400 ~ 1000 μmol·m-2·s-1), 随着光照强度的逐渐升高, Pn也上升, Pn与光照强度呈线性关系; 但在强光照下(1 000 μmol·m-2·s-1以上), 随着光照强度的增加, 光合速率增加缓慢, 并最后趋于平缓.说明当光照强度达到一定值时, Pn达到最大, 之后随着光照强度的继续增加, Pn反而有所下降, 从而达其光饱和点.
本文采用二项式拟合[5, 7], 得到光响应曲线的回归方程为Y = - 6 × 10-6X2 + 0.017X + 0.536(R2 =0.953 2, P = 0.01), 最大净光合速率(Pnmax)为12.58 μmol · m-2· s-1; 光饱和点为1 417 μmol·m-2·s-1; 将0 ~ 200 μmol·m-2·s-1之间数值通过直线回归方程Y = 0.032 3X-0.611 (R2=0.923 1, P = 0.01)进行拟合, 得到表观量子效率为0.032 3;光补偿点为18.92 μmol·m-2·s-1; 暗呼吸速率为- 0.611 μmol·m-2·s-1.
2.7 光合生理主要参数与生态因子的相关分析
表 1为高州油茶光合生理主要参数与生态因子的相关分析.从表 1可看出, 其净光合速率(Pn)与光合有效辐射(PAR)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)呈极显著相关, 与空气温度(θa)呈显著相关, 与大气CO2浓度(Ca)呈显著负相关.说明PAR、Tr、Gs的变化均能对植物的Pn产生很大影响, 与上文所分析的净光合速率日变化结果相一致.Tr与PAR呈极显著相关, 与Gs、θa、θl呈显著相关, 这表明PAR、Gs、θa、θl的升高, 在一定程度上能促进植物叶片的蒸腾速率.
表 1 光合生理主要参数与生态因子的相关分析1)Table 1. Photosynthesis-related parameters and related analyses of ecological factors
3. 讨论与结论
高州油茶净光合速率的日变化进程为“双峰型”, 在12:00-13:00时段存在不同程度的“午休”现象.蒸腾速率、气孔导度与净光合速率的变化趋势基本相似, 并与之存在极显著的相关关系; 在7-9月份期间, 其光合、蒸腾和气孔导度处于高峰期.这些光合生理特征与本区域环境因子具有良好的适应机制, 即在各指标达到一定峰值后, 由于蒸腾耗水加剧导致树体水分亏缺时, 树体驱动回避机制, 出现“午休”现象, 进而起到调节水分及适应逆境的作用.研究结果对制订该树种生产管理技术时具有指导作用, 特别是7-9月份外界温度高, 光合有效辐射强, 蒸腾强度大, 为保证树体正常生长, 应注重补充水分.
高州油茶最大净光合速率和光饱和点比其他普通油茶物种高[8-9], 其最大蒸腾速率、光补偿点和暗呼吸速率却比其他普通油茶物种低[8-9].这说明该物种在高光、高温、高湿环境中表现出较强的生理适应性, 具高光效率和有效调节环境胁迫的能力.目前该树种虽然在华南区域已得到一定程度的应用推广, 但由于各种原因, 至今未能开展良种选育工作.因此, 建议加强其种质资源收集保存和评价利用工作.
华南热带亚热带区域油茶物种资源丰富, 长期选择和演化蕴藏着大量的高光效基因[10].因此今后在该区域油茶资源评价利用时, 应增加其光合生理指标的评价, 并将高光效的功能特性挖掘融合到油茶品种选育与创制工作中, 选育出区域内高光效低消耗或经济产量转化率高的油茶品种及无性系.
-
表 1 光合生理主要参数与生态因子的相关分析1)
Table 1 Photosynthesis-related parameters and related analyses of ecological factors

-
[1] ISEBRANDS J C, CEULEMANS R, WIARD B. Genetic variation in photosynthetic traits among Populous clones in relation to yield[J]. Plant Physiol Biochem, 1988, 26 (4):427-437.
[2] 奚如春, 邓小梅, 龚春, 等.高亚油酸含量油茶优良无性系的选育[J].林业科学研究, 2006, 19(2):158-164. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2006.02.006 [3] 林中弘, 张国.高州油茶的选育与丰产试验[J].经济林研究, 1985, 3(1):84-86. [4] 王瑞, 陈永忠, 杨小胡, 等.油茶光合作用及其影响因素研究进展[J].经济林研究, 2007, 25(2):78-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8981.2007.02.019 [5] 高雪, 莫宝盈, 奚如春, 等.盆栽条件下三个油茶栽培种的光合蒸腾特性比较[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 2012, 32(4):89-94. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/znlxyxb201204019 [6] 王瑞, 陈永忠, 王湘南.油茶优良无性系光合作用的日变化[J].中国农学通报, 2009, 25(24):236-239. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgnxtb200924047 [7] 佘诚棋, 程鹏, 季琳琳, 等.油茶光合作用光响应曲线的拟合[J].经济林研究, 2012, 30(1):118-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8981.2012.01.023 [8] 李建安, 何志祥, 孙颖, 等.油茶林分光合特性的研究[J].中南林业科技大学学报, 2010, 30(10):56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2010.10.010 [9] 孔文娟, 刘学录, 姚小华, 等. 4个油茶物种的光合特性研究[J].西南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 35(1):16-22. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xnnydxxb201301003 [10] 王瑞, 陈永忠.油茶高光效育种及其栽培技术探讨[J].林业科技开发, 2011, 25(3):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8101.2011.03.001



 下载:
下载: