Cloning of resistance gene analogs from Lagenaria siceraria based on conserved domains of NBS -LRR type R gene
-
摘要:目的
分离鉴定瓠瓜Lagenaria siceraria抗病种质的抗病基因同源序列(Resistance gene analogs, RGAs), 为瓠瓜功能性抗病基因的克隆及分子标记辅助育种奠定基础.
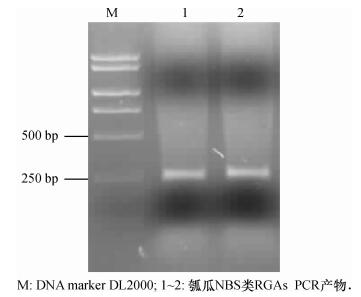
方法根据已知核苷酸结合位点和富亮氨酸重复(Nucleotide binding site and leucine rich repeat, NBS-LRR)类抗病基因保守区设计简并引物, 从“大籽瓠”抗性材料基因组DNA中分离抗病基因同源序列, 并利用生物信息学软件进行长度变异、保守结构域、同源比对与系统进化分析.
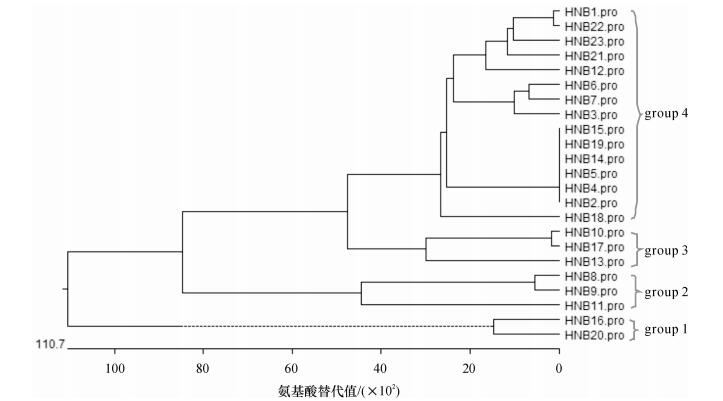
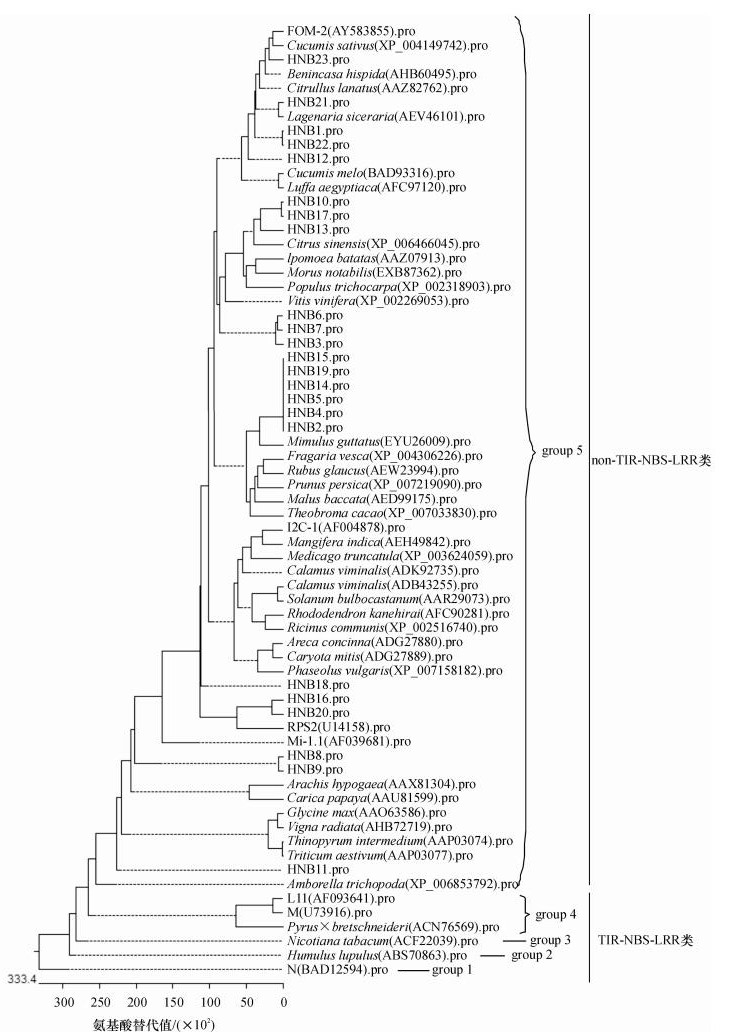
结果和结论基于同源克隆策略, 获得23条瓠瓜NBS抗病同源序列, 命名为HNB1 ~ HNB23, GenBank登录号为KJ908192 ~ KJ908214.序列分析及同源比对结果表明, 这些RGAs长度变异在242 ~ 261 nt之间, 18条序列具有连续开放阅读框(Open reading frame, ORF), 推导氨基酸序列具有P-loop、Kinase-2a典型NBS类R基因保守结构域;核苷酸序列相似性为41.5% ~ 98.8%, 氨基酸序列相似性为21.5% ~ 100.0%;利用NCBI Blast同源搜索发现, 与其他植物尤其是冬瓜、黄瓜、葫芦及丝瓜的已知R基因具有40% ~ 100%相似性;氨基酸序列聚类分析将其分为5个组;同源进化分析表明, 23条瓠瓜RGAs均为non-TIR-NBS-LRR类R基因, 与推导氨基酸序列多重比较结果一致.
Abstract:ObjectiveIsolation and identification of resistance gene analogs (RGAs) of Lagenaria siceraria would lay the foundation for a further cloning of disease resistance genes and marker-assisted selection (MAS) of resistance breeding.
MethodAccording to the conserved domains of nucleotide binding site and leucine rich repeat (NBS-LRR) type of disease-resistance genes in most known plants, degenerate primers were designed and synthesized to isolate resistance gene analogs from genomic DNA of bottle gourd resistant variety " Dazihu", with length variation, conservative domain, homology alignment and phylogenetics analyzed by various bioinformatics softwares.
Result and conclusionTwenty three RGAs were obtained and named as HNB1 - HNB23, and the GenBank accession numbers were KJ908192 - KJ908214.Sequences analyses and alignment results indicated that the full-length of RGAs varied from 242 nt to 261 nt, and the deduced amino acids sequences contained typical conserved domains of NBS R genes, such as P-loop and Kinase-2a.Eighteen sequences had continuous open reading frames (ORFs).These RGAs showed a great homologous differences with the similarity ranging from 41. 5% to 98.8%, and the amino acid sequence similarity varied from 21.5% to 100.0%.At the nucleotide level, the sequence identity of 23 RGAs ranged from 40% to 100% with the cloned NBS R genes from other plants, especially cucumber, wax gourd, luffa and calabash.The result of clustering analyses showed that all RGAs were divided into 5 groups.These RGAs were ranked into non-TIR-NBS-LRR type by homology and evolution analyses, which was consistent with the classification result based on multiple alignment of deduced amino acid sequences.
-
Keywords:
- Lagenaria siceraria /
- NBS-LRR type /
- resistance gene analogs /
- degenerate primer /
- sequence analysis
-
-
-
[1] HEISER C B. Variation in the bottle gourd[M] //MEGGERS B J, AYENSU E S, DUCKWORTH W D. Tropical forest ecosystems in Africa and South America: A comparative review. Washington D C: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1973: 121-128.
[2] 彭庆务, 何晓明, 谢大森, 等.瓠瓜的特征特性及育种对策[J].广东农业科学, 2003, 30(1): 18-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2003.01.007 [3] 陈孟强, 牛玉, 林鉴荣, 等.瓠瓜部分种质资源主要性状的初步评价[J].广东农业科学, 2012, 39(23): 22-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2012.23.008 [4] 李开银, 石伟平, 胡宇舟, 等.湖北部分瓠瓜种质资源初步研究及利用[J].中国蔬菜, 2003(3): 33-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6346.2003.03.015 [5] 高山, 许端祥, 林碧英, 等. 38份瓠瓜种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2007, 8 (4): 396-400. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1810.2007.04.004 [6] 高山, 许端祥, 林碧英, 等.瓠瓜种质资源遗传多样性的RAPD分析[J].分子植物育种, 2007, 5(4):502-506. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-416X.2007.04.010 [7] 周先治, 陈阳, 陈最, 等.基于5.8S rDNA和ITS序列探讨亚洲瓠瓜的地理分化[J].中国蔬菜, 2011(6): 49-53. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94878X/201106/1001575128.html [8] 谷昊, 陈绍宁, 竺锡武, 等.复合侵染瓠瓜的两种病毒的互作研究[J].科技通报, 2009, 25(4): 419-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7119.2009.04.007 [9] 王玲平, 吴晓花, 汪宝根, 等.与瓠瓜品系J083白粉病抗性基因连锁的SCAR分子标记[J].浙江大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 2011, 37(2): 119-124. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zjdxxb-nyysm201102001 [10] 肖光辉.瓠瓜DNA直接导入西瓜抗枯萎病育种研究进展[J].中国西瓜甜瓜, 2002(2): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2002.02.021 [11] 阙友雄, 许莉萍, 林剑伟, 等.斑茅NBS-LRR类抗病基因同源序列的克隆与分析[J].热带作物学报, 2009, 30(2): 192-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2009.02.015 [12] KANAZIN V, MAREK L F, SHOEMAKER R C. Resistance gene analogs are conserved and clustered in soybean [J]. PNAS, 1996, 93(21): 11746-11750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.21.11746
[13] 李峰, 张颖, 樊秀彩, 等.植物NBS-LRR类抗病基因的研究进展[J].分子植物育种, 2011, 9(108): 1784-1780. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10389-1014322642.htm [14] 贺超英, 张志永, 陈受宜.大豆中NBS类抗病基因同源序列的分离与鉴定[J].科学通报, 2001, 46(12): 1017-1021. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.12.013 [15] GURURANI M A, VENKATESH J, UPADHYAYA C P, et al. Plant disease resistance genes: Current status and future directions[J]. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol, 2012, 78: 51-65. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2012.01.002
[16] SHI A, KANTARTZI S K, MMBAGA M, et al. Isolation of resistance gene analogues from flowering dogwood (Cornus f lorida L.)[J]. J Phytopathol, 2008, 156(11 /12): 742-746.
[17] XU Q, WEN X, DENG X. Isolation of TIR and nonTIR NBS-LRR resistance gene analogues and identification of molecular markers linked to a powdery mildew resistance locus in chestnut rose (Rosa roxburghii Tratt)[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2005, 111(5): 819-830. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-0002-7
[18] MEYERS B C, DICKERMAN A W, MICHELMORE R W, et al. Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide binding superfamily[J]. Plant J, 1999, 20 (3): 317-332. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.t01-1-00606.x
[19] 阙友雄, 许莉萍, 林剑伟, 等.甘蔗NBS-LRR类抗病基因同源序列的分离与鉴定[J].作物学报, 2009, 35 (4): 631-639. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zuowxb200904009 [20] 丁国华, 池春玉, 周秀艳, 等.黄瓜抗病基因类似序列(RGA)的同源性分析和Southern鉴定[J].园艺学报, 2007, 34(2): 355-360. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2007.02.017 [21] SUN D Q, HU Y L, ZHANG L B, et al. Cloning and analysis of fusarium wilt resistance gene analogs in " Goldfinger"banana[J]. Mol Plant Breed, 2009, 7(6): 1215-1222.
[22] 王彦华, 侯喜林, 申书兴, 等.不结球白菜抗病基因同源序列的克隆及分析[J].中国农业科学, 2006, 39 (12): 2621-2626. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2006.12.032 [23] 丁海, 宛煜嵩, 朱美霞, 等.大豆抗病基因同源序列的克隆与分析[J].分子植物育种, 2003, 1 (2):217-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-416X.2003.02.009 [24] DOYLE J J, DOYLE J L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf material[J]. Phytochem Bull, 1987, 19(1): 11-15.
[25] 丁国华, 秦智伟, 刘宏宇, 等.黄瓜NBS类型抗病基因同源序列的克隆与分析[J].园艺学报, 2005, 32 (4): 638-642. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0513-353X.2005.04.014 [26] 刘洋, 姚全胜, 苏俊波, 等.芒果NBS类抗病基因同源序列克隆与分析[J].植物遗传资源学报, 2013, 14 (3): 571-576. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zwyczyxb201303031 [27] 王铎, 刘长远, 赵奎华, 等.辣椒NBS-LRR类抗病基因同源序列的克隆与分析[J].沈阳农业大学学报, 2011, 2 (42): 98-101. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10307-1013283110.htm [28] 高丽华, 周以飞, 郑伟文, 等.南瓜NBS类抗病基因同源序列的克隆与分析[J].长江蔬菜, 2007(8): 40-43. doi: 10.3865/j.issn.1001-3547.2007.08.029 [29] 陈玲, 张颢, 邱显钦, 等.云南悬钩子蔷薇NBS-LRR类抗病基因同源克隆与分析[J].植物分类与资源学报, 2012, 34 (1): 56-62. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ynzwyj201201009 [30] QILIN P, JONATHAN W, KOBERT F. Divergent evolution of plant NBS-LRR resistance gene homologous in dicot and cereal genomes[J]. J Mol Evol, 2000, 50: 203-213. doi: 10.1007/s002399910023
[31] 王贤磊, 高兴旺, 张铁钢, 等.甜瓜抗病基因同源序列的克隆与分析[J].新疆大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 28(2): 136-144. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjdxxb201102003 [32] ELLIS J, DODDS P, PRYORT. Structure, function and evolution of plant disease resistance genes[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2000, 3(4): 278-284. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00080-7
[33] BELKHADIR Y R, SUBR A M, DANGL L J. Plant disease resistance protein signaling: NBS-LRR protein and their partners[J]. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 2004, 7 (4): 391-399. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.05.009
[34] GOFF S A, RICKE D, LAN T H, et al. A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica)[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5565): 92-100. doi: 10.1126/science.1068275
[35] TRAUL F W. The functions and consensus motifs of nine types of peptide segments that form different types of nucleotide binding sites[J]. Eur J Biochem, 1994, 222 (1): 9-19. doi: 10.1111/ejb.1994.222.issue-1



 下载:
下载: