Effects of different levels of phosphorus availability on growth and phosphorus absorption of "Chinese Long" sequenced cucumber genotype
-
摘要:目的
了解黄瓜测序品种“中国龙”对不同磷浓度供应的反应,寻找在水培条件下进行黄瓜磷效率种质筛选的适宜低磷处理浓度.
方法采用营养液水培试验,研究了不同磷浓度供应对黄瓜测序品种“中国龙”生长及其磷吸收的影响.
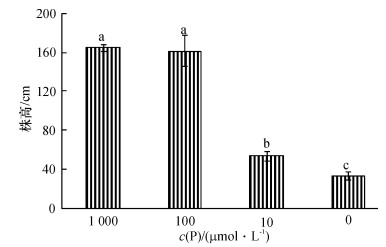
结果和结论随着供磷浓度的降低,“中国龙”的生长受到抑制,植株变矮,老叶黄化.在严重低磷(10和1 μmol·L-1)胁迫时,植株生长受到严重抑制,甚至不能正常结瓜.低磷降低了“中国龙”的生物量、磷吸收效率,但增加了根冠比,促进了碳水化合物向根部的分配.此外,在低磷胁迫下,“中国龙”还通过降低根平均直径,即根变细,来增加与养分的接触面积. 10~100 μmol·L-1之间的磷浓度(如50 μmol·L-1)可作为黄瓜磷效率种质资源筛选的低磷处理浓度.
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the responses of "Chinese long" sequenced cucumber genotype to different phosphorus (P) availability, and to screen an optimal low-P-treatment concentration for cucumber germplasms screening for P efficiency under a hydropoic condition.
MethodHydroponic culture was used to test effects of different P availability on the growth and P absorption of "Chinese Long".
Result and conclusionThe results showed that with the decrease in P availability, cucumber plants became shorter and smaller, and new leaves became smaller and old leaves became yellow. Severe P deficiency (10 and 1 μmol·L-1) significantly inhibited the cucumber plant growth, even resulting in abnormal fruits. Low P availability decreased the biomass and P uptake efficiency of "Chinese Long", but increased its ratio of root to shoot, which preferably allocated carbonhydrate to root. Furthermore, under P deficiency, "Chinese Long" also formed finer roots with a small root diameter, thus increasing the contact area with nutrients in the growth medium. The P concentration of 10-100 μmol·L-1, for example 50 μmol·L-1, can be used to screen the cucumber germplasms for P efficiency.
-
Keywords:
- cucumber /
- phosphorus absorption /
- phosphorus efficiency /
- low P concentration
-
-
表 1 不同磷浓度下黄瓜生物量1)
Table 1 Plant biomass at different levels of P availability

表 2 不同磷浓度下黄瓜根形态参数1)
Table 2 Cucumber root morphological parameters at different levels of P availability

表 3 不同磷浓度下黄瓜植物磷效率1)
Table 3 Cucumber plant P efficiency at different levels of P availability

-
[1] RAGHOTHAMA K G. Phosphate acquisition[J]. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 1999, 50(1):665-693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.665
[2] VANCE C P, UHDE-STONE C, ALLAN D L. Phosphorus acquisition and use:Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource[J]. New Phytol, 2003, 157(3):423-447. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
[3] 刘建中, 李振声, 李继云.利用植物自身潜力提高土壤中磷的生物有效性[J].农业生态研究, 1994, 2(5):16-23. http://qikan.cqvip.com/article/detail.aspx?id=1469400 [4] CORDELL D, DRANGBERT J O, WHITE S. The story of phosphorus:Global food security and food for thought[J]. Glob Environ Change, 2009, 19(2):292-305. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.10.009
[5] 李振声.我国粮食生产的潜力和存在的问题[J].生命科学, 1992, 4(1):1-3. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000002817270 [6] 严小龙, 张福锁.植物营养遗传学[M], 北京:农业出版社, 1997. [7] CHIOU T J, LIN S I. Signaling network in sensing phos- phate availability in plants[J]. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2011, 62:185-206. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103849
[8] ZHANG Z L, LIAO H, LUCAS W J. Molecular mecha- nisms underlying phosphate sensing, signaling and adapta- tion in plants[J]. J Integr Plant Biol, 2014, 56(3):192-220. doi: 10.1111/jipb.v56.3
[9] 孙军利, 赵宝龙, 蒋卫杰, 等.氮、磷和钾肥施用量对有机生态型无土栽培温室黄瓜产量影响的研究[J].北方园艺, 2006(6):10-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0009.2006.06.004 [10] 刘军, 曹之富, 黄延楠, 等.日光温室黄瓜冬春茬栽培氮磷钾吸收特性研究[J].中国农业科学, 2007, 49(9):2109-2113. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2007.09.036 [11] 王合理.黄瓜营养液育苗不同磷营养水平的效果研究[J].新疆农垦科技, 2000(1):23-24. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjnkkj200001011 [12] CIERESZKO I, JANONIS A, KOCIAKOWSKA M. Growth and metabolism of cucumber in phosphorus-defi- cient conditions[J]. J Plant Nutr, 2002, 25(5):1115- 1127.
[13] 徐雷, 梁林洲, 董晓英, 等.高磷胁迫对黄瓜幼苗生长及养分吸收和分配的影响[J].湖北农业科学, 2013, 52(1):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0439-8114.2013.01.015 [14] 庞欣, 张福锁, 李春俭.部分根系供磷对黄瓜根系和幼苗生长及根系酸性磷酸酶活性的影响[J].植物生理学报, 2000, 26(2):153-158. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-3877.2000.02.014 [15] RUIZ J M, ROMERO L. Nitrogen metabolism and yield response of cucumber(Cucumis sativus L. cv. Brunex)plants to phosphorus fertilization[J]. J Sci Food Agr, 2000, 80(14):2069-2073. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0010
[16] HUANG S W, LI R Q, ZHANG Z H, et al. The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L.[J]. Nat Genet, 2009, 41(12):1275-1281. doi: 10.1038/ng.475
[17] 劳家柽.土壤农化分析手册[M].北京:农业出版社, 1988:229-299. [18] ABEL S, TICCONI C A, DELATORRE C A. Phosphate sensing in higher plants[J]. Physiol Plantarum, 2002, 115(1):1-8. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1150101.x
[19] 吴楚, 谢裕春, 甘彩霞.磷胁迫对黄瓜幼苗生长·光合作用·生物量及其分配的影响[J].安徽农业科学, 2005, 33(10):47-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ahnykx200510030 [20] 齐海季, 林洲, 赵学强, 等.土壤磷含量对黄瓜幼苗生长和磷素吸收的影响[J].江苏农业科学, 2012, 40(1):152-154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2012.01.056 [21] 邢宏燕, 王二明, 李滨, 等.有效利用土壤磷的小麦种质筛选方法研究[J].作物学报, 2000, 26(6):839-844. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2000.06.031 [22] 高方远, 陆贤军, 康海岐, 等.水稻耐低磷种质的苗期筛选与鉴定[J].作物学报, 2006, 32(8):1151-1155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2006.08.008




 下载:
下载: