Cloning surface protective antigen A gene from Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae and its expression in Pichia pastoris
-
摘要:目的
以毕赤酵母Pichia pastoris X-33为宿主表达猪丹毒丝菌Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae SpaA基因氨基端的免疫保护区蛋白.
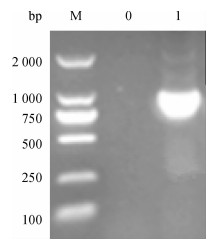
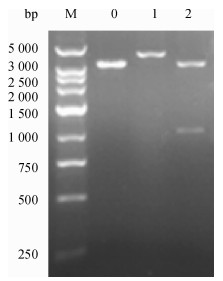
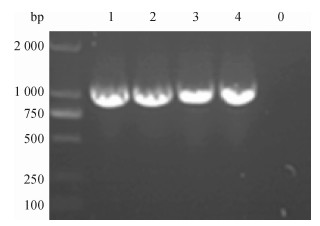
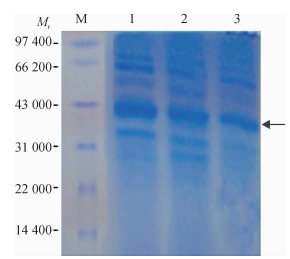
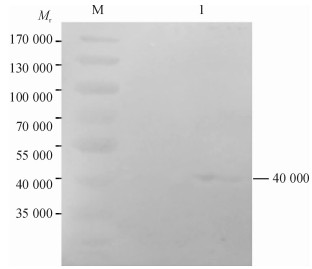
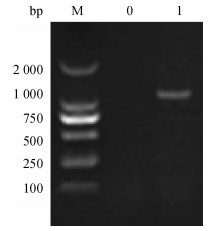
方法以采集于广东某猪场的猪丹毒丝菌为模板, 根据NCBI中已发表的Spa基因cDNA序列设计1对引物, 通过PCR扩增得到SpaA-N, 并将其连接到表达载体pPICZαC上, 得到重组表达质粒pPICZαC-SpaA-N; 用Sac Ⅰ酶将重组表达质粒pPICZαC-SpaA-N线性化后电转化入毕赤酵母X-33, 经含博来霉素ZencinTM抗性的YPDS平板筛选和PCR鉴定的阳性转化子, 用含不同浓度博来霉素抗性的YPDS平板筛选出高拷贝子并进行甲醇诱导培养, 分别于诱导48、72、96 h后离心收集上清液, 立即做SDS-PAGE, 并进行SDS-PAGE及Western-blot试验.
结果和结论成功克隆并表达了SpaA-N基因, 构建了重组表达质粒pPICZαC-SpaA-N, 并以毕赤酵母X-33为宿主成功表达了猪丹毒丝菌SpaA基因氨基端的免疫保护区蛋白.丹毒丝菌SpaA-N作为免疫保护区在酵母宿主中得以成功表达.
Abstract:ObjectiveImmunization protection area protein, which lies in the N-terminal protective domain of surface protective antigen A(SpaA) of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, was expressed in Pichia pastoris X-33.
MethodUsing the swine erysipelas, which was isolated from a pig farm in Guangdong as template, a pair of primers was designed according to the cDNA sequence of Spa gene from NCBI.The amino terminal sequence was achieved by PCR amplification, after being inserted into the expression vector pPICZαC to get the recombinant plasmid of pPICZαC-SpaA-N.Recombinant plasmid of pPICZαC-SpaA-N by Sac Ⅰ enzyme was linearized, and electro transformed it into P.pastoris X-33.The positive transformant, screened by YPDS tablet with ZencinTM and identified by PCR at different concentrations of ZencinTM, achieved the high number of copies which were induced and cultured by methanol.Supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 48, 72, 96 h respectively after induction, and SDS-PAGE and Western-blot tests were carried out.
Result and conclusionThe SpaA gene was successfully cloned and expressed, and the recombinant plasmid of pPICZαC-SpaA-N was constructed.The immunization protection area protein, which lies in SpaA gene amino terminal of swine E.rhusiopathiae in P.pastoris X-33, was successfully expressed.SpaA gene of swine E.rhusiopathiae has been successfully expressed asimmunization protection area protein in yeast host, which will lay a foundation for the development and the mass production of subunit vaccine of swine E.rhusiopathiae.
-
致谢: 感谢兽医学院传染病教研室的老师和同学给予的支持和帮助!
-
-
[1] BROOKE C J, RILEY T V.Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: Bacteriology, epidemiology and clinical manifestations of an occupational pathogen[J].J Med Microbiol, 1999, 48 (9): 789-799. doi: 10.1099/00222615-48-9-789
[2] BOO T W, HONE R, HURLEY J.Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis: A preventable zoonosis[J]. Ir J Med Sci, 2003, 172(2): 81-82. doi: 10.1007/BF02915253
[3] SITT T, BOWEN L, MYRA T, et al.Cellular immune responses in cetaceans immunized with a porcine erysipelas vaccine[J ]. Vet Immunol Immunopathol, 2010, 137 (3/4): 181-189.
[4] GARTRELL B D, ALLEY M R, MACK H, et al.Erysipelas in the critically endangered kakapo (Strigops habroptilus)[J]. Avian Pathol, 2005, 34(5): 383-387. doi: 10.1080/03079450500268583
[5] HASSANEIN R, SAWADA T, KATAOKA Y, et al.Serovars of Erysipelothrix species isolated from the tonsils of healthy cattle in Japan[J ]. Vet Microbiol, 2001, 82 (1): 97-100. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(01)00379-0
[6] BOERNER L, NEVIS K R, HINCKLEY L S, et al.Erysipelothrix septicemia in a little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor)[J]. J Vet Diagn Invest, 2004, 16(2): 145-149. doi: 10.1177/104063870401600209
[7] HOLTIFIELD J L, COOPER G L, CHARLTON B R.An outbreak of erysipelas in 2-day-old poultry[J ]. Avian Pathol, 2000, 44(33): 721-724.
[8] CHEUN H I, KAWAMOTO K, HIRAMATSU M, et al. Protective immunity of SpaA-antigen producing lactococcus lactis against Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae intfection[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2004, 96(6): 1347-1353. doi: 10.1111/jam.2004.96.issue-6
[9] HASSANEIN R, SAWADA T, KATAOKA Y, et al. Pathogenicity for mice and swine of Erysipelothrix isolates from the tonsils of healthy cattle[J ]. Vet Microbiol, 2003, 91(2/3): 231-238. doi: 10.1016-S0378-1135(02)00293-6/
[10] 朱凤琼, 陈达燕, 夏英杰, 等.猪丹毒杆菌的分离及鉴定[J].现代农业科技, 2012(4): 316-317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2012.04.200 [11] 邱美珍, 杜丽飞, 杨爱梅, 等.猪丹毒杆菌临床分离鉴定与药敏试验[J].养猪, 2011(6): 111-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1957.2011.06.065 [12] 郭良兴, 陈克研, 赵魁, 等.猪丹毒杆菌的分离鉴定及耐药性试验[J].中国畜牧兽医, 2011, 38(4): 199-202. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgxmsy201104051 [13] 车勇良, 陈如敬, 王隆柏, 等.猪丹毒杆菌的分离鉴定及其SpaA基因的遗传变异分析[J].中国兽医学报, 2011, 31(11): 1591-1593. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsyxb201111012 [14] 万莉, 韩国全, 郭万柱, 等.猪丹毒疫苗研究进展[J].猪业科学, 2010(6): 32-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5358.2010.06.008 [15] 周绪斌, 丹尼, 李聪, 等.猪丹毒---古老的传染病是否从中国规模化猪场消失了[J].农业新技术, 2009 (5): 22-24. [16] FREDDY H, FRANK P, KOEN C, et al.Efficacy of vaccines against bacterial diseases in swine: What can we expect[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2004, 100(3/4): 255-268.
[17] SILVA A J, HORTA A C, IEMMA M, et al.Production of potential subunit vaccine against swine erysipelas in fedbatch cultures of E.coli BL21(DE3)[J]. New Biotechnol, 2009, 255(6): 187-188.
[18] MAKINO S, YAMAMOTO K, MURAKAMI S, et al. Properties of repeat domain found in a novel protective antigen, SpaA, of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae[J]. Microb Pathog, 1998, 25(2): 101-109. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1998.0216
[19] IMADA Y, GOJI N, ISHIKAWA H, et al.Truncated surface protective antigen (SpaA) of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae serotypes 1a and 2b in pigs[J]. Infect Immun, 1999, 67(9): 4376-4382. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_96755
[20] ALAINA L I, JAMES A R, PAUL J H.Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: Association of Spa-type with serotype and role in protective immunity[J]. Vaccine, 2010, 28 (13): 2490-2496. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.01.041
[21] 曹文尧. 丹毒丝菌表面保护抗原A作为重组亚单位疫苗和核酸疫苗的初步研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2007. [22] 谭侃侃. 丹毒丝菌的分离鉴定及其SpaA-N蛋白和lipo蛋白的免疫原性分析[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2011. [23] 吾鲁木汗·那孜尔别克, 张磊, 何翠, 等.猪丹毒丝菌天然SpaA和重组SpaA-N免疫保护效果的评价[J].微生物学报, 2010, 50 (3): 367-372. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wswxb201003012 [24] 李伟杰, 赵耘, 康凯, 等.红斑丹毒丝菌SpaA抗原基因的克隆、序列分析及蛋白结构预测[J].中国兽医学报, 2011, 31(11): 1591-1594. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7645853 [25] DA A J, SILVA M R, IEMMA A C, et al.Cloning, autoinduction expression, and purification of rSpaA swine erysipelas antigen[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2012, 65 (4): 369374.
[26] OPRIESSNIG T L, HOFFMAN J, HARRIS D L, et al. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: Genetic charact erization of Midwest US isolates and live commercial vaccines using pulsed field gel electrophoresis[J]. J Vet Diagn Invest, 2004, 16(2) : 101-107. doi: 10.1177/104063870401600202
[27] JIN F L, XU X X, YU X Q, et al.High-level expression of active recombinant ubiquitin carboxyl terminal hydrolase of drosophila melanogaster in Pichia pastoris[J]. Protein Expr Purif, 2009, 65(2): 115-121. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2008.08.010
[28] 杨梅, 温真, 林丽玉.毕赤酵母蛋白表达系统研究进展[J].生物技术通报, 2011(4): 46-51. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swjstb201104009 [29] DALY R, HEARN M T W.Expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris: A useful experimental tool in protein engineering and production[J]. J Mol Recognit, 2005, 18(2): 119-138. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1352



 下载:
下载: