Morphological recognition of rice seedlings based on GoogLeNet and UAV image
-
摘要:目的
针对目前国内评价插秧质量主要以人工观察和随机抽样的现状,提出一种基于卷积神经网络GoogLeNet 对水稻秧苗图像进行形态识别的方法。
方法首先,利用无人机超低空航拍获取清晰、完整的稻田秧苗图像,通过裁剪标记制作漂秧、伤秧和合格秧苗数据集;然后,基于GoogLeNet结构训练数据,得到最佳网络识别模型;最后,对单穴秧苗图像进行分类试验,并与传统图像分类算法(SVM、BP神经网络)进行对比。
结果在相同样本的条件下,基于GoogLeNet的秧苗形态识别方法更快、更准确地完成了判断分类,秧苗形态识别的平均正确率为91.17%,平均耗时0.27 s;与SVM和BP神经网络相比,分类平均精度分别提高了21和13个百分点,检测时间分别缩短了1.09 和0.58 s。
结论本研究可为水稻插秧质量评价提供相关支持。
Abstract:ObjectiveIn view of the current situation that the quality of transplanting is mainly based on manual observation and random sampling in China, it is proposed to use the convolutional neural network GoogLeNet to recognize the morphology of rice seedlings.
MethodFirstly, clear and intact images of rice seedlings were obtained by UAV aerial photography at low altitude. Data sets of floating seedlings, damaged seedlings and qualified seedlings were made by cutting and marking. Then, based on the GoogLeNet structure training data, the optimal network recognition model was obtained. Finally, the image classification experiment of seedlings per hole was carried out, and compared with traditional image classification algorithms (SVM, BP neural network).
ResultUnder the condition of using the same samples, the seedling morphology recognition method based on GoogLeNet completed the judgment and classification was faster and more accurately. The average accuracy of seedling morphology recognition was 91.17%, and the average detection time was 0.27 s. Compared with SVM and BP neural network, the average classification accuracy increased by 21 and 13 percentage points respectively, and the detection time was shortened by 1.09 and 0.58 s respectively.
ConclusionThis study can provide the relevant support for evaluation of rice transplanting quality.
-
Keywords:
- Rice /
- Transplanting quality /
- Seedling morphology /
- GoogLeNet /
- UAV; Image classification
-
-
表 1 研究区域的试验信息
Table 1 Test information of research areas
试验地点
Test location试验时间
Test time插秧机
Rice transplanter型号
Model水稻品种
Rice variety南京市溧水区 Lishui of Nanjing 2020−05 星月神 Seeyes 2ZG-6S 宁3828 Ning 3828 张家港市南丰镇 Nanfeng of Zhangjiagang 2020−06 久保田 Kubota 2ZGQ-6D5 南粳505 Nanjing 505 常州市新北区 Xinbei of Changzhou 2020−06 丰疆 Fengjiang 2ZG-4A 软玉2号 Ruanyu 2 靖江市东兴镇 Dongxing of Jingjiang 2020−07 富尔代 Fuerdai 2ZG-8A 南粳5055 Nanjing 5055 丹阳市章村 Zhangcun of Danyang 2021−06 沃得 World 2ZGF-8E 淮稻5号 Huaidao 5 表 2 无人机分辨率及有效距离
Table 2 UAV resolution and effective range
试验序号
Test batch飞行相对高度/m
Relative flight height分辨率/mm
Resolution图片有效距离(长×宽)/m
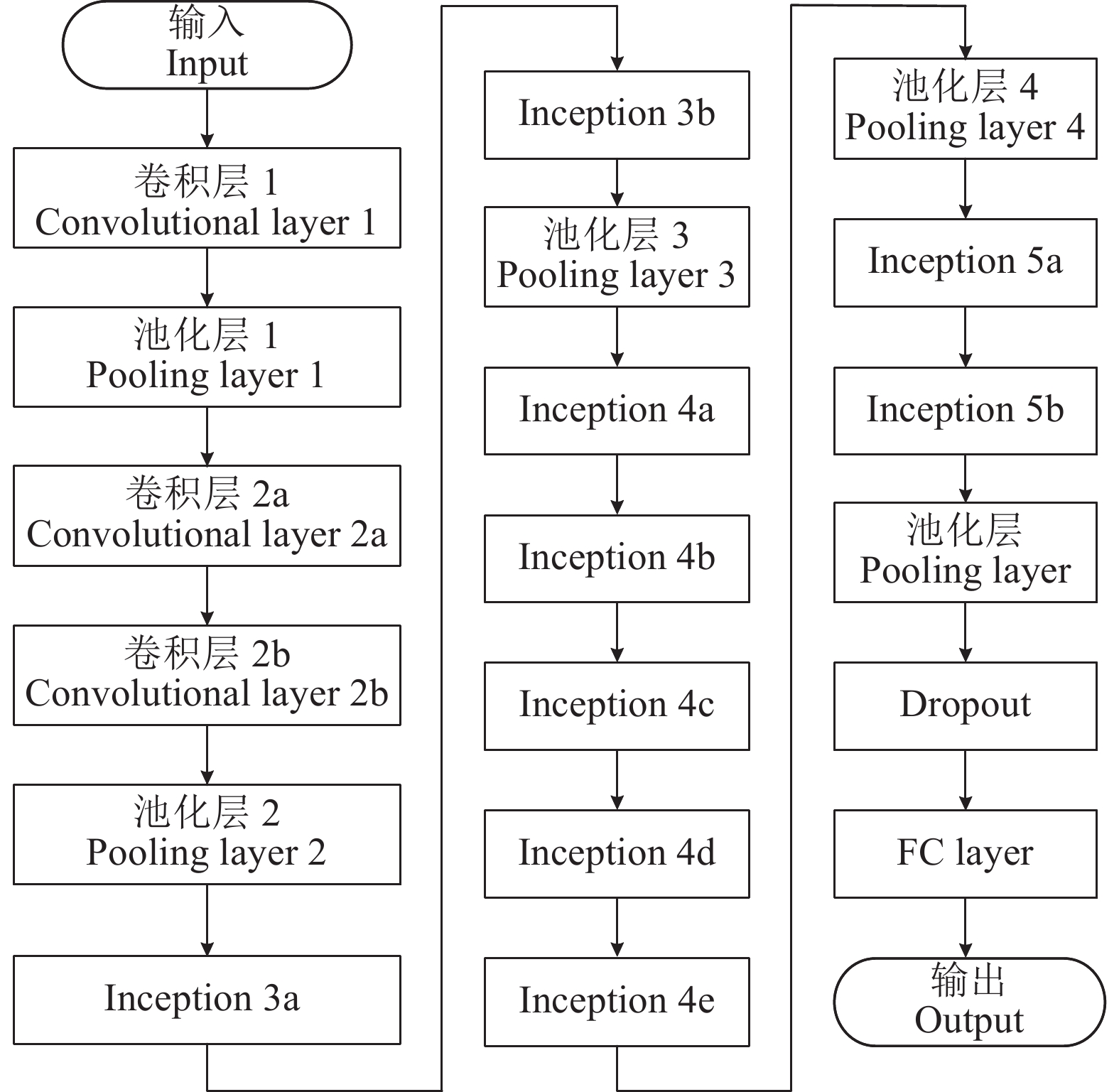
The effective distance of picture (Length×Width)1 2 0.55 3.0×2 2 3 0.82 4.5×3 3 5 1.40 7.5×5 4 10 2.80 15.0×10 表 3 GoogLeNet结构参数1)
Table 3 The structural parameters of GoogLeNet
结构
Structure核尺寸
Patch size步长
Stride填充数
PaddingC1×1 #3×3 C3×3 #5×5 C5×5 P3×3 数据维度
Data dimension输入 Input 224×224×3 卷积层1
Convolutional layer 17×7 2 3 112×112×64 池化层1 Pooling layer 1 3×3 2 1 56×56×64 卷积层2a
Convolutional layer 2a1×1 1 0 56×56×64 卷积层2b
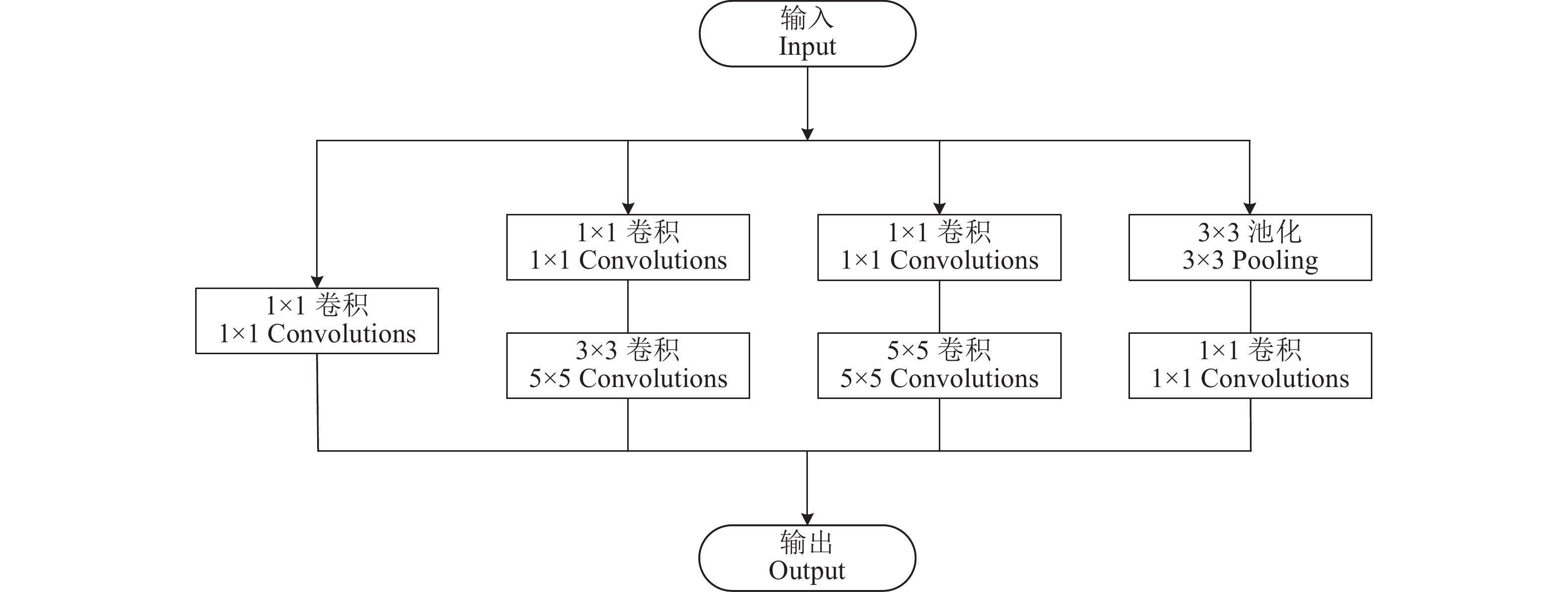
Convolutional layer 2b3×3 1 1 56×56×192 池化层2 Pooling layer 2 3×3 2 1 28×28×192 Inception 3a 64 96 128 16 32 32 28×28×256 Inception 3b 128 128 192 32 96 64 28×28×480 池化层3 Pooling layer 3 3×3 2 1 14×14×480 Inception 4a 192 96 208 16 48 64 14×14×512 Inception 4b 160 112 224 24 64 64 14×14×512 Inception 4c 128 128 256 24 64 64 14×14×512 Inception 4d 112 144 288 32 64 64 14×14×528 Inception 4e 256 160 320 32 128 128 14×14×832 池化层4 Pooling layer 4 3×3 2 1 7×7×832 Inception 5a 256 160 320 32 128 128 7×7×832 Inception 5b 384 192 384 48 128 128 7×7×1024 池化层 Pooling layer 7×7 1 0 1×1×1024 Dropout 1×1×1024 FC layer 1×1×3 输出 Output 1×1×3 1) “C1×1” “C3×3”和“C5×5”表示在Inception module结构中相对应的卷积核数量,“#3×3”和“#5×5”表示在对应卷积之前,使用的1×1的卷积核数量,“P3×3”表示经过最大池化后,使用的1×1的卷积核数量
1) “C1×1” ,“C3×3” and “C5×5” indicate the corresponding number of convolution kernels in the inception module structure, and “#3×3” and “#5×5” indicate the number of 1×1 convolution kernels used before the corresponding convolution, and “P3×3” indicates the number of 1×1 convolution kernels used after max pooling表 4 水稻秧苗轮廓特征参数信息
Table 4 Parameter information of rice seedling outline feature
图像类别 Image type 狭长度 Aspect ratio 矩形度 Rectangularity 紧凑度 Compactness M1 M2 漂秧
Floating
seedling1.837 0.445 0.150 1.181 3.492 伤秧
Damaged
seedling1.440 0.457 0.119 1.361 4.735 合格秧苗
Qualified
seedling2.554 0.477 0.134 1.075 2.626 表 5 3种算法的秧苗形态识别试验结果
Table 5 The experimental results of three algorithms for recognition of seedling morphology
算法
Algorithm
识别正确率/% Recognition accuracy 平均识别时间/s
Average
recognition time漂秧
Floating seedling伤秧
Damaged seedling合格秧苗
Qualified seedlingGoogLeNet 91.6 85.5 96.4 0.27 SVM 69.6 64.2 76.3 1.36 BP神经网络 BP neural network 76.9 72.7 86.9 0.85 -
[1] 李鸣钰, 高西宁, 潘婕, 等. 未来升温1.5 ℃与2.0 ℃背景下中国水稻产量可能变化趋势[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(3): 567-581. [2] 李忠华, 刘欣. 影响高速插秧机作业质量的因素分析[J]. 现代化农业, 2014(4): 56-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0254.2014.04.032 [3] 辛明金, 邬立岩, 宋玉秋, 等. VP6型水稻插秧机作业质量试验研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2016, 37(4): 19-23. [4] 潘海珠, 陈仲新. 无人机高光谱遥感数据在冬小麦叶面积指数反演中的应用[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2018, 39(3): 32-37. [5] 胡琪, 武红旗, 轩俊伟, 等. 基于无人机DSM的小麦倒伏信息提取[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2020, 48(16): 227-231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2020.16.064 [6] 赵春霞. 基于ResNet18的图像分类在农作物病虫害诊断中的应用[J]. 农业与技术, 2021, 41(19): 10-13. [7] 程千, 徐洪刚, 曹引波, 等. 基于无人机多时相植被指数的冬小麦产量估测[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(03): 160-167. [8] 王林惠, 甘海明, 岳学军, 等. 基于图像识别的无人机精准喷雾控制系统的研究[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2016, 37(6): 23-30. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.2016.06.004 [9] ASHOURLOO D, AGHIGHI H, MATKAN A A, et al. An investigation into machinelearning regression techniques for the leaf rust disease detection using hyperspectral measurement[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(9): 4344-4351.
[10] HAQ M A, RAHAMAN G, BARAL P, et al. Deep learning based supervised image classification using UAV images for forest areas classification[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2020, 49(3): 601-606.
[11] 王丽君, 淮永建, 彭月橙. 基于叶片图像多特征融合的观叶植物种类识别[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2015, 37(1): 55-61. [12] 陶惠林, 徐良骥, 冯海宽, 等. 基于无人机高光谱遥感数据的冬小麦产量估算[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(7): 146-155. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2020.07.017 [13] 赵静, 潘方江, 兰玉彬, 等. 无人机可见光遥感和特征融合的小麦倒伏面积提取[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(3): 73-80. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.03.009 [14] 刘嘉政, 王雪峰, 王甜. 基于深度学习的5种树皮纹理图像识别研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2019, 41(4): 146-154. [15] ZHANG Q, CHEN MESJ, LI B. A visual navigation algorithm for paddy field weeding robot based on image understanding[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2017, 143: 66-78. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2017.09.008
[16] 李静, 陈桂芬, 安宇. 基于优化卷积神经网络的玉米螟虫害图像识别[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2020, 41(3): 110-116. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.201907017 [17] WEI D, HUANG Y B, ZHAO C J, et al. Identification of seedling cabbages and weeds using hyperspectral imaging[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2015, 8(5): 65-72.
[18] 林相泽, 朱赛华, 张俊媛, 等. 基于迁移学习和Mask R-CNN的稻飞虱图像分类方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(7): 201-207. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2019.07.021 [19] 陈进, 韩梦娜, 练毅, 等. 基于U-Net模型的含杂水稻籽粒图像分割[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(10): 174-180. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.10.021 [20] 杨万里, 段凌凤, 杨万能. 基于深度学习的水稻表型特征提取和穗质量预测研究[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2021, 40(1): 227-235. [21] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 水稻插秧机试验方法: GB/T 6243—2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [22] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 水稻插秧机: DG/T 008—2019[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2019.




 下载:
下载: