Extraction of pig contour based on fully convolutional networks
-
摘要:目的
实现猪舍场景下非接触、低成本的生猪轮廓高效提取。
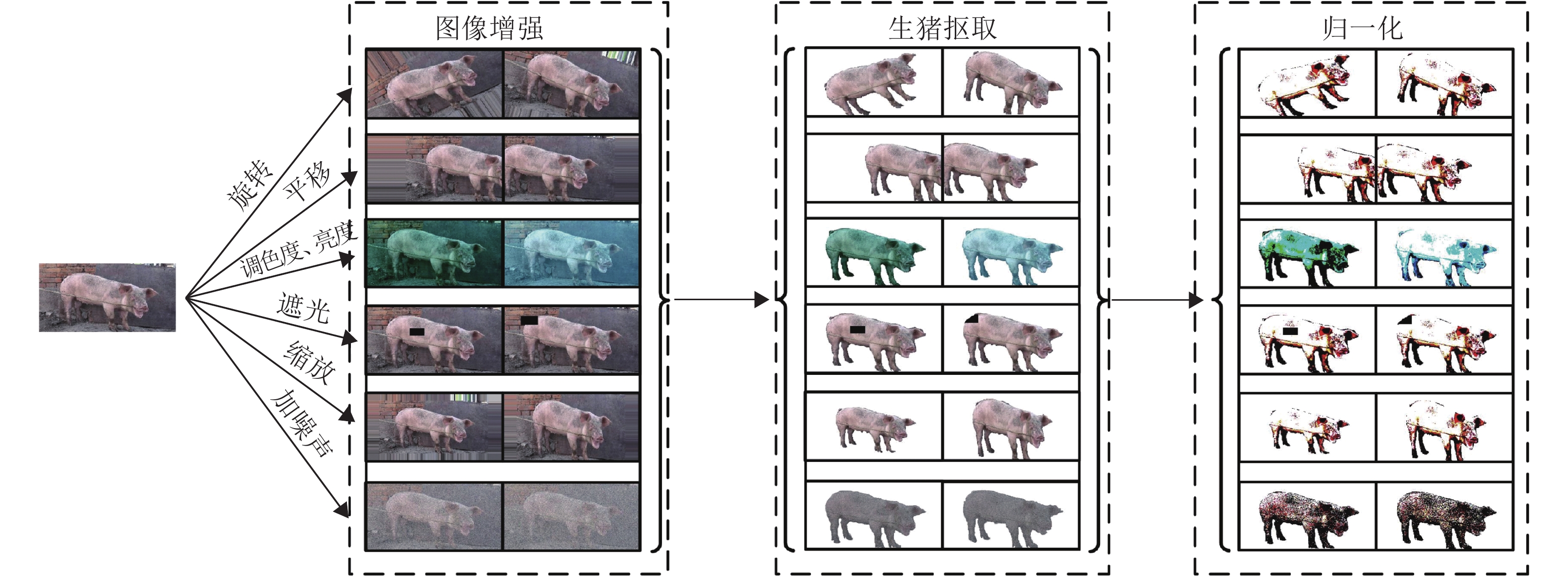
方法以真实养殖环境下的生猪个体为研究对象,提出一种基于VGG16 与UNET相结合的全卷积神经网络模型(VGG-UNET模型)。该模型采用批处理方法,迁移学习VGG16模型参数,通过在模型中构建复制通道深度融合图像深层抽象特征与浅层特征,实现对图像语义级别分割。在30头长白生猪的1 815张数据集上进行模型验证,通过设置不同批大小对比试验,并选取其中具有最佳效果的3组探讨批大小与评价指标值变化趋势间的关系。
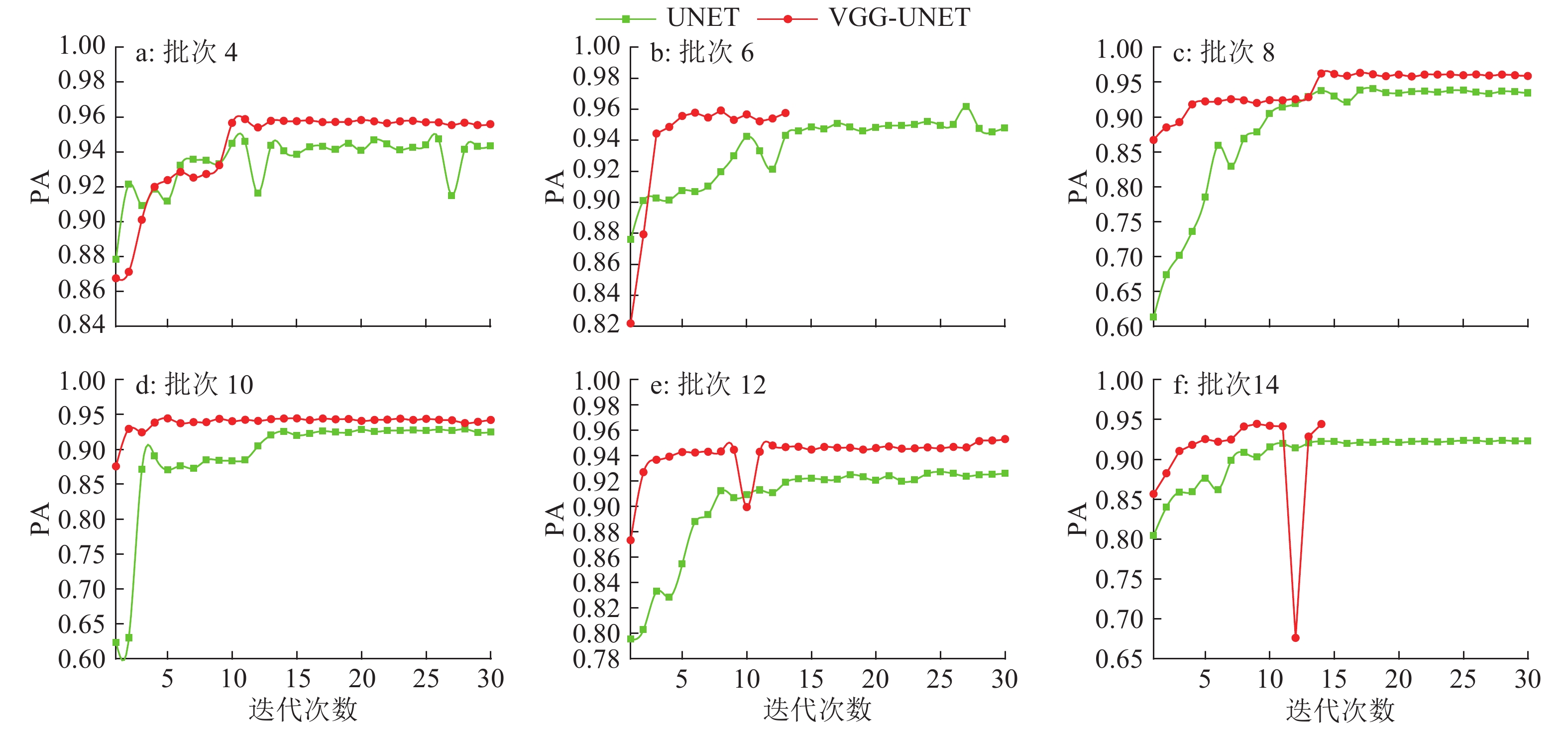
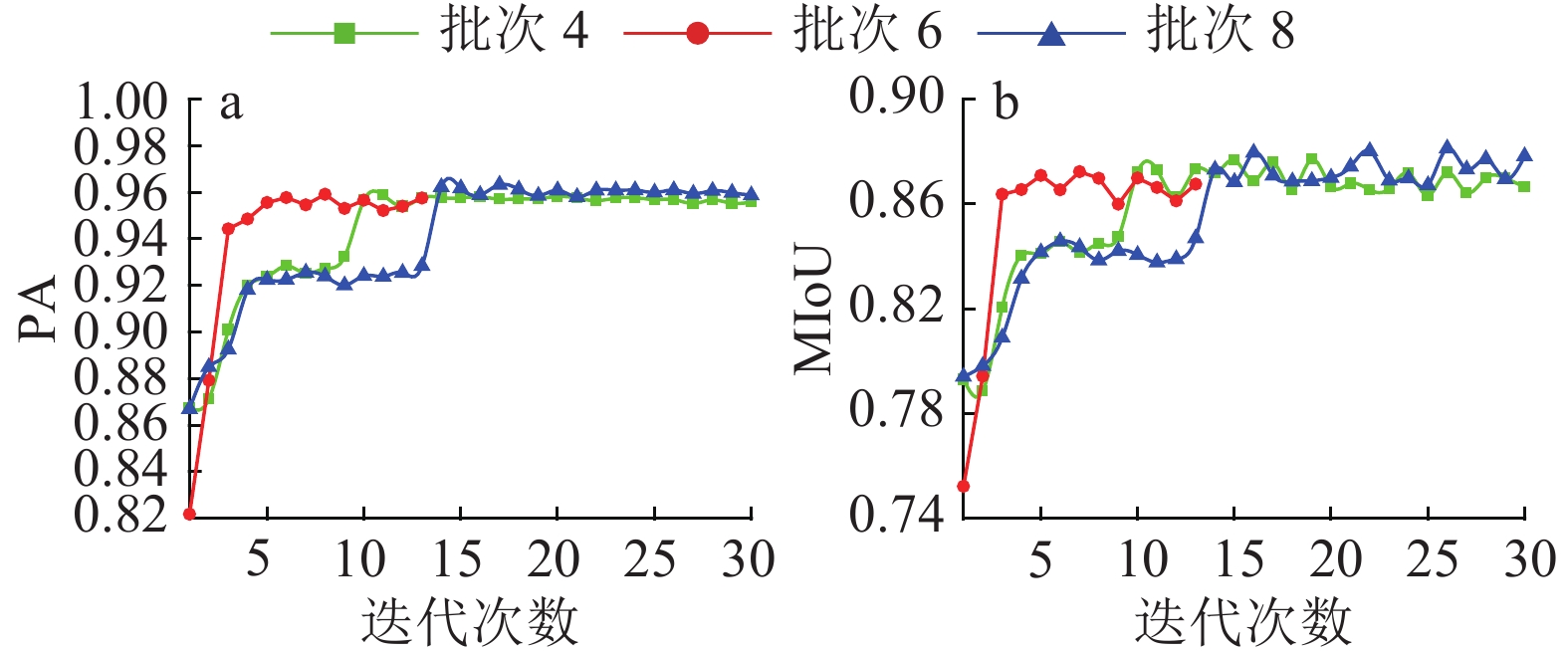
结果测试集上的对比试验结果表明,VGG-UNET模型在像素精度与均交并比方面分别达到94.32% 和86.60%,比单独采用UNET模型分别高出0.89%和1.67%。不同指标值变化情况与批大小间的关系不尽相同。在本文试验环境下,批大小对模型收敛速度的影响不明显。不同批大小条件下PA及MIoU指标值变化综合分析得出,VGG-UNET模型具有较强稳定性和较高鲁棒性;批大小为8 的情况下VGG-UNET模型效果最佳。
结论本文提出的生猪轮廓提取方法(VGG-UNET模型)是有效的,能实现精确、稳定的生猪轮廓提取,且分割结果较为完整,同时模型具有较高鲁棒性,可为后续生猪个体识别研究提供参考。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo realize non-contacting and low-cost pig contour extraction under the piggery scene.
MethodWe took individual pig in the real culture environment as the research object, and proposed a full convolutional neural network model based on the combination of VGG16 and UNET (VGG-UNET model). We adopted the batch processing method in this model to transfer and learn the parameters of VGG16 model. We achieved semantic level segmentation of the image by combining the deep abstract feature and shallow feature in depth via building the duplicate channel. The model was verified on 1 815 datasets of 30 Large White× Landrace pigs. Comparison experiments of different batch sizes were performed, and three groups with the best results were selected to explore the relationship between batch size and the evaluation index.
ResultThrough comparison experiments on datasets, the pixel accuracy and mean intersection-over-union of VGG-UNET model were 94.32% and 86.60% respectively, which were 0.89% and 1.67% higher than those of the UNET model. The experiments showed different relationship between the change of different index values and batch size. Batch size had no obvious impact on the convergence rate of the model under this experimental environment. Through comprehensive analysis of PA and MIoU index values under different batch sizes, the VGG-UNET model showed the highest stability and robustness, and it was found to be the best when the batch size was 8.
ConclusionThe VGG-UNET model is effective for accurate and stable extraction of pig contour. Such segmentation result is relatively complete and the model has higher robustness, which can provide a reference for follow-up identification of individual pigs.
-
-
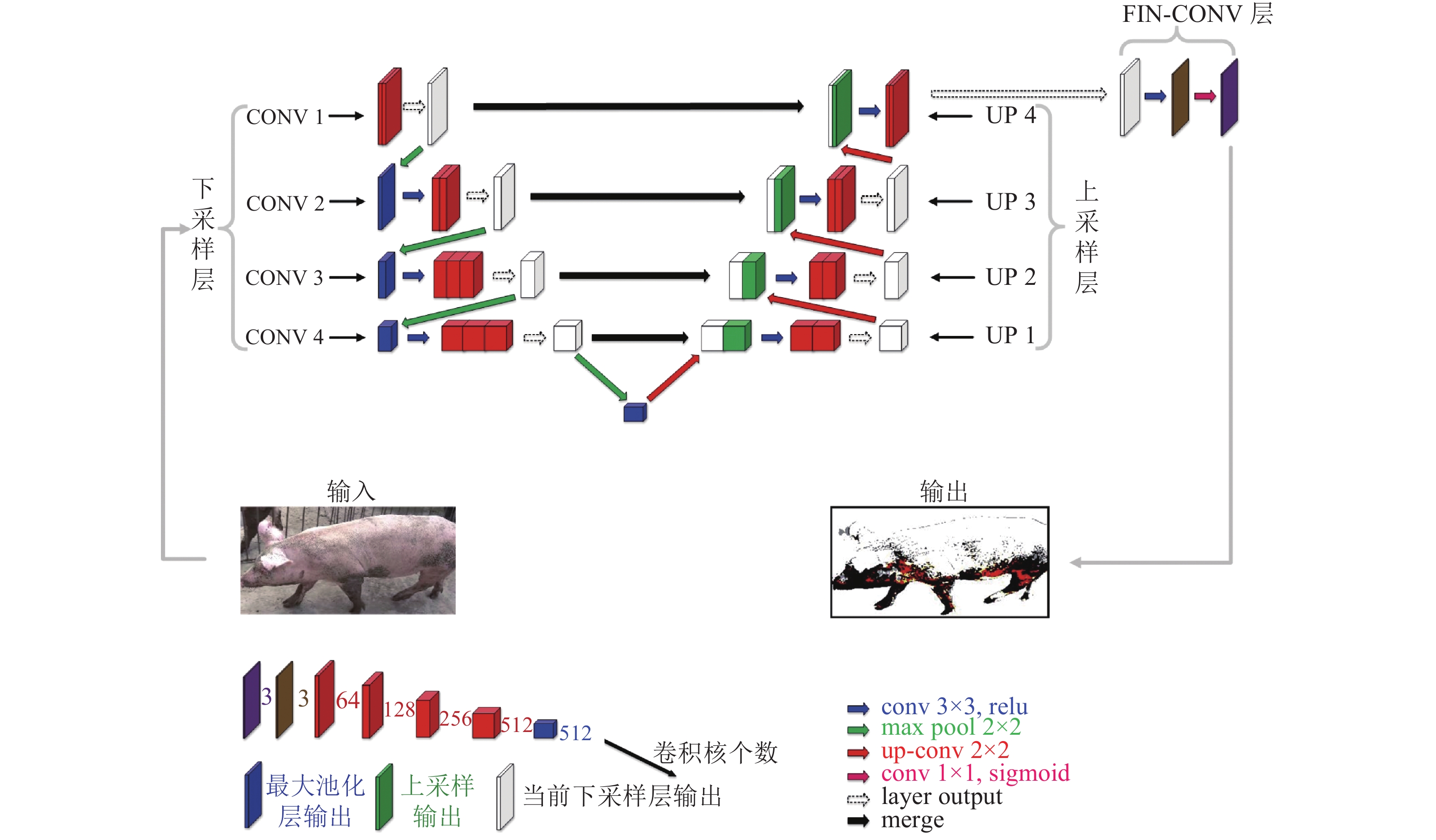
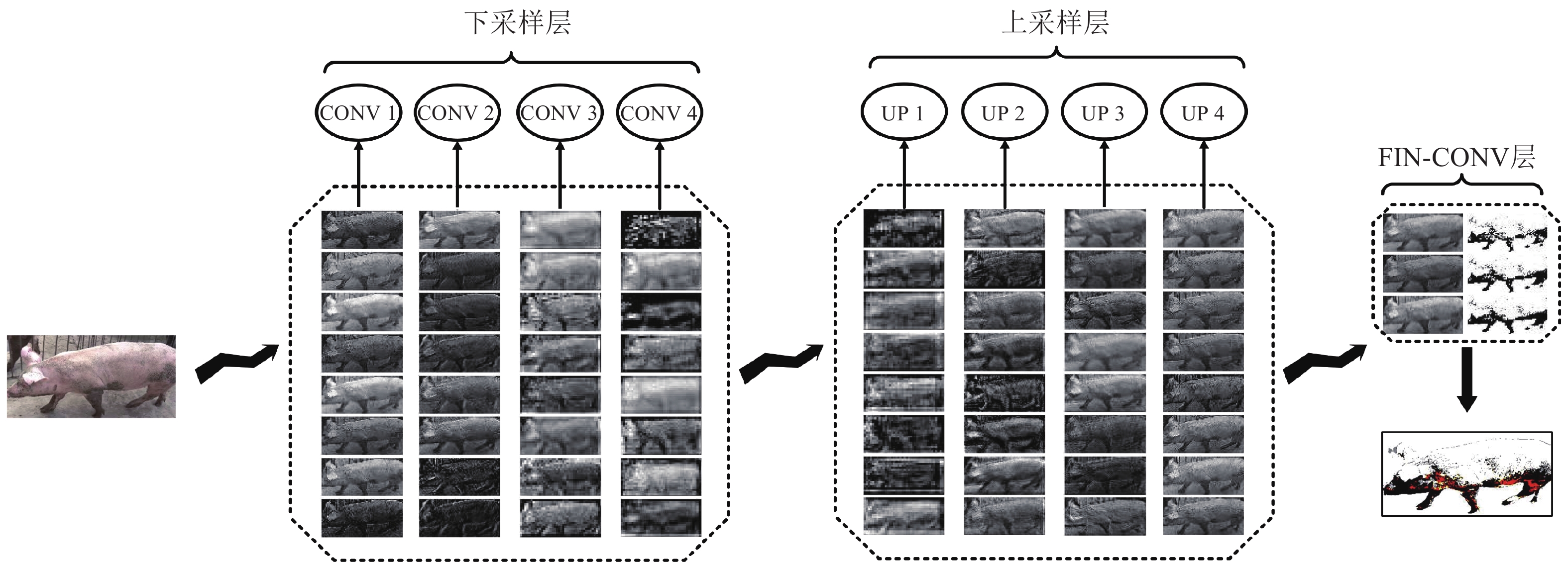
图 2 VGG-UNET网络结构图
图中conv 3×3,relu中conv表示卷积操作,3×3表示卷积核大小,relu表示激活函数;conv 1×1,sigmoid中conv表示卷积操作,1×1表示卷积核大小,sigmoid表示激活函数;up-conv 2×2中up-conv表示反卷积操作,2×2表示反卷积核大小;max pool 2×2中maxpool表示最大池化操作,2×2表示池化核大小;layer output表示当前卷积层级输出;merge表示融合与上采样层处于同一层的下采样层输出操作
Figure 2. Diagram of the VGG-UNET network structure
表 1 不同批大小下模型性能比较
Table 1 The performance comparison of models with different batch sizes
模型 批次 PA MPA MIoU FWIoU UNET 4 0.934 3 0.868 0 0.846 4 0.860 7 6 0.932 7 0.863 8 0.849 3 0.858 1 8 0.883 9 0.857 2 0.817 9 0.838 9 VGG-UNET 4 0.940 3 0.877 6 0.864 2 0.866 5 6 0.941 8 0.874 1 0.864 9 0.864 1 8 0.943 2 0.885 1 0.866 0 0.851 5 -
[1] 杜晓冬, 滕光辉, 李卓, 等. 典型猪舍光环境下机器视觉图像量化评价及筛选[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(2): 213-219. [2] 蔡一欣, 马丽, 刘刚. 奶牛隐性乳房炎便携式计算机视觉快速检测系统设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(增刊1): 63-69. [3] 蔡骋, 宋肖肖, 何进荣. 基于计算机视觉的牛脸轮廓提取算法及实现[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(11): 171-177. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.11.022 [4] 何东健, 刘冬, 赵凯旋. 精准畜牧业中动物信息智能感知与行为检测研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(5): 231-244. [5] 肖德琴, 冯爱晶, 杨秋妹, 等. 基于视频追踪的猪只运动快速检测方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(10): 351-357. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2016.10.045 [6] 刘同海, 李卓, 滕光辉, 等. 基于RBF神经网络的种猪体重预测[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(8): 245-249. [7] 纪滨, 朱伟兴, 刘波, 等. 基于脊腹线波动的猪呼吸急促症状视频分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2011, 27(1): 191-195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2011.01.031 [8] 闫丽, 沈明霞, 谢秋菊, 等. 哺乳母猪高危动作识别方法研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(1): 266-272. [9] 刘龙申, 沈明霞, 柏广宇, 等. 基于机器视觉的母猪分娩检测方法研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(3): 237-242. [10] CAO X, WEI Y, WEN F, et al. Face alignment by explicit shape regression[J]. Int J Comput Vision, 2012, 107(2): 2887-2894.
[11] WU S, KAN M, HE Z, et al. Funnel-structured cascade for multi-view face detection with alignment-awareness[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 221: 138-145. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.09.072
[12] 张志刚, 周明全, 耿国华. 人脸关键特征点自动标定研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2007, 43(21): 197-198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.21.060 [13] 孙龙清, 李玥, 邹远炳, 等. 基于改进Graph Cut算法的生猪图像分割方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(16): 196-202. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.026 [14] 朱伟兴, 纪滨, 秦锋. 基于伪球算子边缘模型的猪前景帧检测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(12): 189-194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.12.031 [15] GUO Y, ZHU W, JIAO P, et al. Foreground detection of group-housed pigs based on the combination of mixture of Gaussians using prediction mechanism and threshold segmentation[J]. Biosyst Eng, 2014, 125(3): 98-104.
[16] 刘波, 朱伟兴, 霍冠英. 生猪轮廓红外与光学图像的融合算法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(17): 113-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.17.015 [17] 马丽, 纪滨, 刘宏申, 等. 单只猪轮廓图的侧视图识别[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(10): 168-174. [18] 王林, 董楠. 基于Gabor特征与卷积神经网络的人体轮廓提取[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2018, 42(1): 89-95. [19] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]// IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco: IEEE, 2015: 3431-3440.
[20] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Commun ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3098997
[21] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. Int J Comput Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y
[22] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco: IEEE, 2015: 1-9.
[23] 杨阿庆, 薛月菊, 黄华盛, 等. 基于全卷积网络的哺乳母猪图像分割[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(23): 219-225. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.23.028 [24] 赵凯旋, 何东健. 基于卷积神经网络的奶牛个体身份识别方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(5): 181-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.05.026 [25] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks forbiomedical image segmentation[C]// MICCAI. International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich: MICCAI, 2015: 234-241.
[26] GARCIA-GARCIA A, ORTS-ESCOLANO S, OPREA S, et al. A survey on deep learning techniques for image and video semantic segmentation[J]. Appl Soft Comput, 2018, 70: 41-65. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.05.018
[27] ISOLA P, ZHU J Y, ZHOU T, et al. Image-to-Image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]//IEEE. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 5967-5976.



 下载:
下载: