Identification of rice sheath blight based on hyperspectral imaging technique
-
摘要:目的
利用高光谱成像技术对水稻纹枯病进行早期的快速无损识别,结合判别分析方法建立相应的鉴别模型。
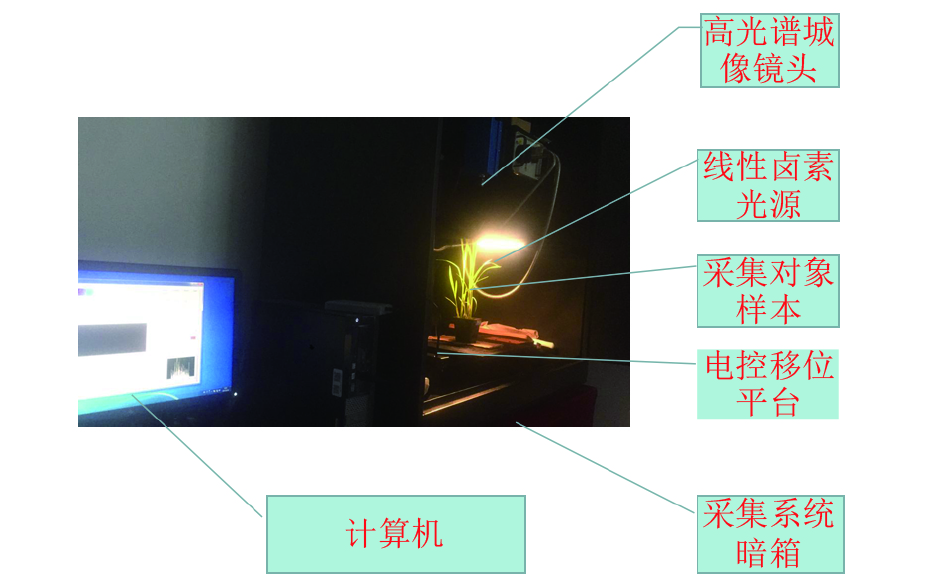
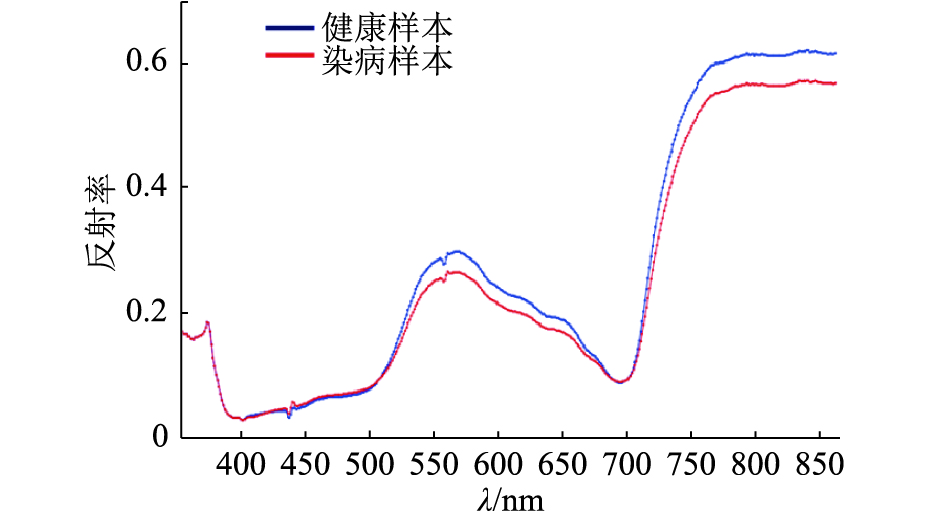
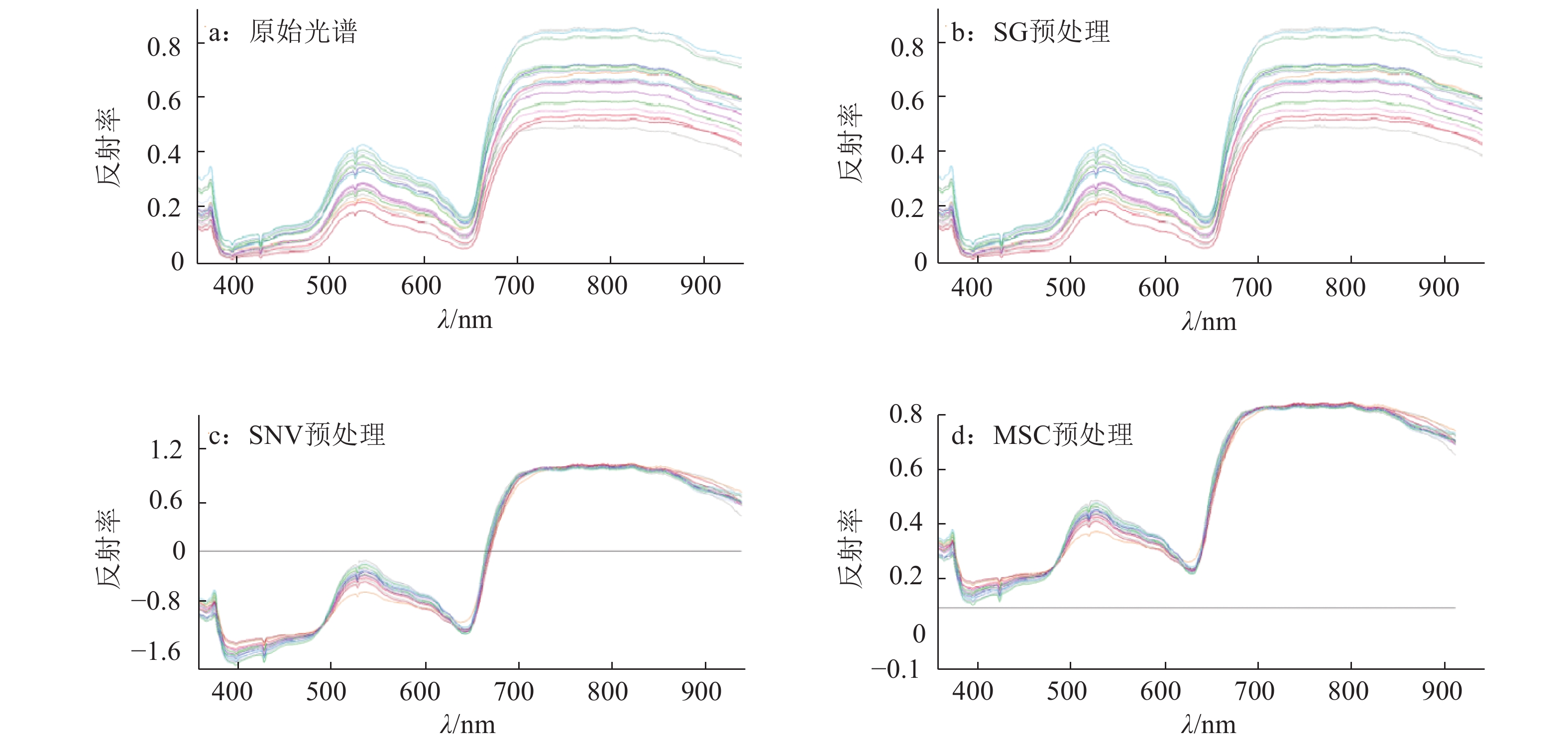
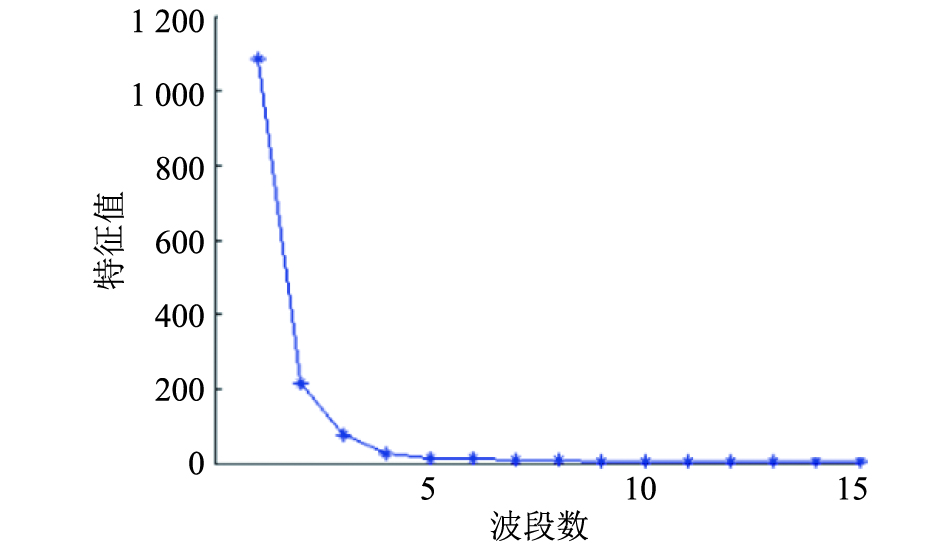
方法以健康和感染纹枯病的水稻幼苗为研究对象,采集叶片和冠层各180个样本的380~1 030 nm波段的360条高光谱图像,剔除明显噪声部分后,以440~943 nm波段作为水稻样本的光谱范围,分别用不同的方法预处理获得水稻叶片的光谱曲线。采用偏最小二乘–判别分析(PLS-DA)对不同预处理的光谱建模。采用MNF算法对冠层的原始光谱数据进行特征信息提取,并基于特征信息建立线性判别分析(LDA)模型和误差反向传播神经网络(BPNN)判别模型。
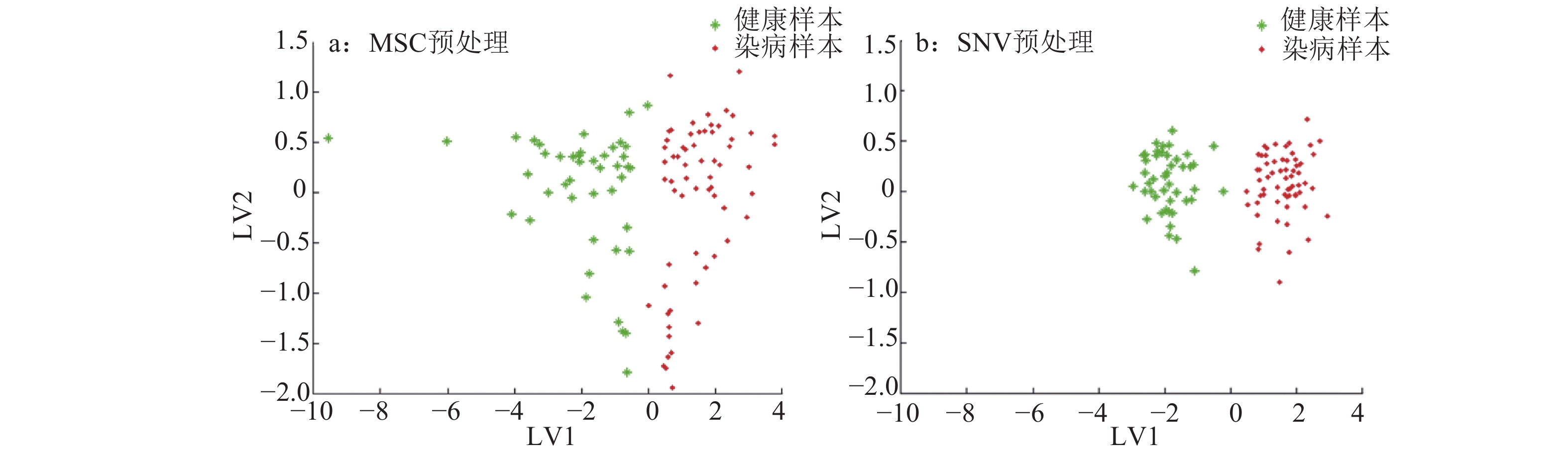
结果标准正态变量变换(SNV)预处理后建立的PLS-DA模型的预测集判别正确率最高,为92.1%。基于特征信息的LAD和BPNN模型的判别结果优于基于全波段的PLS-DA判别模型。基于最小噪声分离变换特征信息提取的BPNN模型取得了最优效果,建模集和预测集正确率分别达99.1%和98.4%。
结论采用高光谱成像技术对水稻纹枯病生理特征进行无损鉴别是可行的,本研究为水稻纹枯病的识别提供了一种新方法。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo realize the rapid and nondestructive identification of rice sheath blight at the early stage using hyperspectral imaging technology, and establish the corresponding identification model.
MethodHealthy rice seedlings and rice seedlings infected with sheath blight were used as the research samples. A total of 360 hyperspectral curves of 180 samples were collected separately from leaves and canopy at the wavelength of 380 to 1 030 nm. After eliminating the obvious noise part, the spectra of rice samples were reserved at the wavelength of 440 to 943 nm, and the spectral curves were preprocessed with different treatments. Partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) was used to model different preprocessed spectra. The feature information was extracted from the original canopy spectral data using the MNF algorithm, and a linear discriminant analysis (LDA) model and a back-propagation neural net-work (BPNN) discriminant model were established based on the feature information.
ResultThe prediction accuracy of PLS-DA model after preprocessing by standard normal variate transformation (SNV) was the highest (92.1%). The discriminant results of LAD and BPNN model based on feature information were superior to the PLS-DA discriminant model based on all bands. The BPNN model based on feature information from minimum noise fraction transformation had optimal results. The accuracies of the model set and prediction set were 99.1% and 98.4% respectively.
ConclusionIt is feasible to identify nondestructively rice sheath blight using hyperspectral imaging technology. Our research provides a new method for identifying rice sheath blight.
-
劳氏黏虫Leucania loreyi (Duponchel)属鳞翅目夜蛾科,在我国分布广泛,是黏虫Mythimna separata (Walker)的近缘种,常与其混杂发生,主要为害玉米Zea mays、水稻Oryza sativa等禾谷类作物[1]。劳氏黏虫幼虫取食禾本科作物叶片、玉米苞叶及籽实,劳氏黏虫发生严重地块的叶片被食成缺刻甚至仅留叶脉,严重影响作物的产量和品质[2]。由于劳氏黏虫与黏虫形态、为害状相似,在田间调查时易将两者混淆。现已有学者对黏虫和劳氏黏虫的形态特征进行了比较[3-5],对黏虫的生物学特性、发生规律、危害特点等进行了较为广泛、系统地研究[6-9],对劳氏黏虫在玉米和水稻上的生物学特性也进行了初步研究[10-11]。
植食性昆虫与寄主植物间存在相互作用的关系[12]。研究表明,植食性昆虫通过视觉、嗅觉、触觉一系列行为来确定寄主植物,寄主植物内存在不同的营养物质和次生代谢产物,这使得植食性昆虫对不同的寄主植物有不同的趋性反应,也影响着昆虫的生长发育和繁殖[13-15]。张勇等[16]研究发现棉铃虫Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner)在取食不同寄主植物后,幼虫发育历期、蛹质量、成虫繁殖力和寿命等都会发生改变。尹娇等[17]研究表明取食不同寄主植物不仅影响草地螟Loxostege sticticalis L.的生长发育,还影响其产卵量和交配率。相似的,斜纹夜蛾Prodenia litura (Fabricius)、小地老虎Agrotis ypsilon (Rottemberg)取食不同的寄主植物对幼虫或成虫的生物学特性都存在或多或少的影响[18-19]。然而,有关劳氏黏虫取食不同寄主植物的生物学特性在国内外鲜见有关报道。本研究以禾本科主要作物玉米、水稻和甘蔗Saccharum officinarum,禾本科杂草稗草Echinochloa crusgalli为食料,系统地研究不同寄主植物对劳氏黏虫生长发育及繁殖的影响,为劳氏黏虫的预测预报及防治提供理论依据。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料
水稻采用感虫水稻品种‘TN1’,由广西农业科学院植物保护研究所提供;甘蔗采用杂交品种‘桂糖29号’,由广西农业科学院甘蔗研究所提供;玉米采用杂交玉米品种‘桂单0810’,由广西农业科学院玉米研究所提供。稗草采自广西农业科学院田间。
劳氏黏虫幼虫采自广西农业科学院水稻田,室内饲养条件为温度(24±1)℃,湿度(75±5)%,光周期为12 h光∶12 h暗。劳氏黏虫幼虫用玉米叶饲养繁殖1代后,将初孵化的幼虫分别用供试寄主植物饲养,以建立各个寄主植物上的试验种群。各寄主植物上的劳氏黏虫试验种群在繁殖1代后,分别取出一定量的初孵幼虫作为供试虫源。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 劳氏黏虫生长发育试验
取生长发育状况一致的劳氏黏虫初孵幼虫,分别用4种寄主植物新鲜叶片单头饲养于养虫杯中(直径4.5 cm、高4 cm),用纸巾和纱布封口,于人工气候箱内饲养,温度为(24±1)℃,湿度为(75±5)%,光照周期为12 h光∶12 h暗,每天更换足量新鲜叶片,每组(1种寄生植物即1组)接虫40头,重复3次。每天09:00和15:00观察记录各养虫杯内幼虫蜕皮情况和存活情况。幼虫化蛹后第2天辨别雌、雄并称取蛹质量。
1.2.2 劳氏黏虫繁殖力试验
取不同寄主植物上初羽化的雌、雄虫各1头置于塑料杯中(直径7.5 cm、高9 cm),杯中放蘸有φ为10%蜂蜜水的棉花球供成虫取食,聚丙烯塑料绳供其产卵,用纱布及皮筋封口,每组重复10次,每天更换新鲜蜂蜜水及产卵绳,观察并记录其产卵前期、产卵量及成虫寿命,期间若雄虫死亡补充雄虫,直至雌虫死亡。同时,在产卵期间取出一定量的卵块,以观察卵的发育历期与孵化率。
1.2.3 生命表组建
取“1.2.1”和“1.2.2”中寄主植物上雌成虫所产的卵,每株寄主植物取200粒左右,参照“1.2.1”记录卵历期及存活率,待卵孵化后每天记录各个虫期的发育历期和存活率,成虫期交配后参照“1.2.2”每天记录雌成虫产卵量和成虫寿命,通过以上资料参照张孝羲[20]的方法,组建劳氏黏虫在各个寄主植物上的试验种群生命表。
1.3 数据处理
数据处理和分析参照文献[21]的方法,用Microsoft Office Excel 2007和DPS 7.05软件处理数据,百分数数据先反正弦平方根后再进行比较,各处理平均数经过方差分析后采用Duncan’s法进行多重比较。
生命表参数种群净增殖率(R0)、平均世代周期(T)、内禀增长率(rm)、周限增长率(λ)、种群加倍时间(td)的计算公式分别为:
$${R_{_0}} = \sum {l_x}{m_x}\text{,}$$ (1) $$T = \sum {l_x}{m_x}x/{R_{_0}}\text{,}$$ (2) $${r_{\rm m}} = \ln {R_{_0}}/T\text{,}$$ (3) $$\lambda = {{\rm e}^{r_{\rm m}}}\text{,}$$ (4) $${t_{\rm d}} = \ln 2/{r_m} = 0.693\;1/{r_{\rm m}}\text{,}$$ (5) 式中,lx是在x期开始时的存活概率,mx表示x期间平均每雌产雌数。
采用Weibull方程[22]描述雌成虫特定年龄存活率,方程公式为:
$${S_{\rm p}}\left(t \right) = {{\rm e}^{ - \left({t/b} \right)c}}\text{,}$$ (6) 式中,Sp (t)为年龄t时的存活率,b为尺度参数,c为形状参数,b和c均大于0。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同寄主植物对劳氏黏虫发育历期的影响
劳氏黏虫取食4种寄主植物均能完成整个生活史(表1)。不同寄主植物对劳氏黏虫的幼虫发育历期有明显影响(F=39.25,df=3、103,P=0.000),幼虫发育历期为取食玉米(20.18 d)<取食水稻(21.29 d)<取食稗草(24.84 d)<取食甘蔗(25.24 d),除取食稗草和甘蔗之间差异不显著外(P>0.05),其他两两之间均存在显著差异(P<0.05)。劳氏黏虫幼虫期取食不同寄主植物对其预蛹期、蛹期、雌成虫寿命和雄成虫寿命影响不显著(P>0.05),但取食不同寄主植物后劳氏黏虫育出的卵的发育历期存在差异(F=4.67,df=3、800,P=0.034),其中以取食玉米所育出的劳氏黏虫卵历期最短,为3.92 d,取食甘蔗的卵历期最长,为5.09 d。因劳氏黏虫在取食不同寄主植物后,卵历期和幼虫历期的差异,导致该虫在全世代周期存在差异(F=6.34,df=3、96,P=0.000 6),在玉米和水稻上的全世代周期无显著差异(P>0.05),但显著短于取食甘蔗和稗草(P<0.05),且在甘蔗组和稗草组之间差异不显著(P >0.05)。
表 1 劳氏黏虫在4种寄主植物上的发育历期1)Table 1. Development durations of Leucania loreyi on four host plants发育期 玉米 水稻 甘蔗 稗草 卵期 3.92±0.19b 4.27±0.27ab 5.09±0.37a 4.40±0.27ab 1龄幼虫 4.68±0.13b 4.89±0.14b 5.61±0.15a 5.41±0.15a 2龄幼虫 2.37±0.08b 2.67±0.12b 3.26±0.12a 3.25±0.13a 3龄幼虫 2.62±0.13b 2.72±0.13b 3.17±0.15a 3.26±0.17a 4龄幼虫 2.47±0.09b 2.58±0.11b 3.34±0.17a 3.07±0.17a 5龄幼虫 2.58±0.11c 3.00±0.17bc 3.50±0.15a 3.39±0.19ab 6龄幼虫 5.33±0.19b 5.28±0.24b 6.15±0.28a 5.81±0.25ab 全幼虫期 20.18±0.24c 21.29±0.45b 25.24±0.28a 24.84±0.32a 预蛹期 2.07±0.05a 2.11±0.06a 2.20±0.08a 2.08±0.06a 蛹期 11.59±0.22a 11.62±0.25a 12.08±0.35a 11.83±0.32a 产卵前期 3.83±0.32b 4.18±0.35ab 5.00±0.30a 4.90±0.35a 雌成虫寿命 11.42±0.78a 11.18±0.30a 10.55±0.39a 10.10±0.43a 雄成虫寿命 12.27±0.36a 12.33±0.51a 11.46±0.57a 11.08±0.50a 全世代 45.67±0.59b 46.85±0.70b 50.58±0.44a 51.35±2.13a 1)同行数据后凡具有一个相同字母者,表示不同寄主植物间差异不显著(P>0.05,Duncan’s 法) 2.2 寄主植物对劳氏黏虫卵、幼虫、蛹、雌成虫存活率的影响
劳氏黏虫整个卵期、幼虫期和蛹期的存活率以在稗草和甘蔗上的较低(图1),但仍分别有58%和60%的卵能发育成成虫,在玉米和水稻上分别有68%和65%的卵能发育为成虫。并且从图1中还可看出,在各寄主植物上从卵到发育成成虫期间的死亡主要发生在卵期和低龄幼虫期。
对雌成虫的存活率采用Weibull模型进行拟合(图2),各寄主植物上雌成虫实际存活率均能与Weibull模型较好拟合,且其形状参数(c)均大于1,这表明雌成虫在4种寄主植物上大多能实现平均寿命。
2.3 寄主植物对劳氏黏虫产卵量、卵孵化率及蛹质量的影响
从雌成虫特定年龄产雌率曲线可以看出每日平均产雌数的动态变化(图2),以玉米为寄主的劳氏黏虫雌虫mx曲线高峰来的最早,在第5天达到高峰,而在其余3种寄主植物上的mx曲线都会出现1个以上的高峰,这表明雌虫在产卵时间分布上存在较大的个体差异。并且,以稗草和甘蔗为寄主时,雌成虫的产卵历期较以玉米和水稻为寄主的短。
从表2可知,幼虫期食物对雌成虫产卵量(F=5.53,df=3、40,P=0.003)和卵孵化率(F=12.46,df=3、962,P=0.000)有显著影响。幼虫期取食玉米的雌虫,其单雌产卵量最多(1019.42粒),卵孵化率最高(93.59%),均显著高于甘蔗组和稗草组(P<0.05),但与水稻组差异不显著(P>0.05)。取食不同寄主植物的幼虫化蛹后,其雌、雄虫蛹质量均表现为玉米>水稻>甘蔗>稗草,并且存在显著差异(P<0.05),其中在稗草上雌成虫蛹质量最低,为22.61 mg。
表 2 劳氏黏虫取食4种寄主植物对产卵量、孵化率及蛹质量的影响Table 2. Effects of four host plants on the fecundity, hatching rate and pupal weight of Leucania loreyi寄主植物 单雌产卵量/粒 孵化率/% m蛹/mg 雌虫 雄虫 玉米 1 019.42±95.22a 93.59±0.93a 32.43±0.36a 35.49±0.39a 水稻 999.73±52.01ab 92.54±0.85a 28.82±0.67b 31.84±0.82b 甘蔗 665.27±60.71c 86.98±1.61b 25.40±0.84c 28.14±0.62c 稗草 790.50±71.03bc 87.56±1.56b 22.61±0.69d 24.46±0.62d 1)同列数据后凡具有一个相同字母者,表示差异不显著(P>0.05,Duncan’s 法) 2.4 寄主植物对劳氏黏虫种群增长的影响
在温度为(24±1)℃,湿度为75%±5%,光照周期为12 h光∶12 h暗的饲养条件下,劳氏黏虫分别取食玉米、水稻、甘蔗和稗草后,得到表3的生命表参数。从表3中可以看出,劳氏黏虫取食玉米叶时,净增殖率(R0)、内禀增长率(rm)和周限增长率(λ)最高,分别为226.54、0.13和1.13,世代平均周期和种群加倍时间最短(td),分别为43.14和5.51,取食水稻叶次之,接下来是稗草,最后是甘蔗。劳氏黏虫在4种寄主植物上的内禀增长率(rm)都大于0,表明种群均能够快速增长。在甘蔗上的净增殖率(R0)最低,但每经过1个世代种群仍能增殖153.71倍。
表 3 不同寄主植物上劳氏黏虫的生命表参数Table 3. The life table parameters of Leucania loreyi on different host plants寄主植物 净增殖率(R0) 世代平均周期(T) 内禀增长率(rm) 周限增长率(λ) 种群加倍时间(td) 玉米 226.54 43.14 0.13 1.13 5.51 水稻 211.48 46.30 0.12 1.12 5.99 甘蔗 153.71 52.83 0.10 1.10 7.27 稗草 171.83 49.20 0.10 1.11 6.63 3. 讨论与结论
田间调查发现劳氏黏虫在广西地区分布广泛。姜玉英等[23]研究认为黏虫的发生面积与黏虫优异寄主小麦、玉米、水稻3种作物的种植面积有直接关系。从广西作物的种植情况来看,2016年禾本科作物种植面积居前3位的分别是水稻(198.39×104 hm2)、甘蔗(97.37×104 hm2)和玉米(62.26×104 hm2)[24]。因此,本研究选取水稻、甘蔗和玉米以及田间常见的禾本科杂草稗草作为劳氏黏虫的食料,研究劳氏黏虫在这4种寄主植物上的生长发育及繁殖能力。
食物营养对昆虫的生长发育及生殖能力产生很大影响[25-26]。本试验结果表明,劳氏黏虫取食不同寄主植物后其幼虫历期和成虫繁殖力均表现出一定的差异。在3种禾本科作物之间,劳氏黏虫取食玉米后,其幼虫发育历期最短,非成虫期存活率最高、雌成虫寿命最长、单雌产卵量最大,其次是取食水稻,最后是甘蔗,这一结果与吴荣宗[27]研究基本一致。田间调查时也发现,当有玉米和水稻种植的季节,劳氏黏虫常见于玉米和水稻上,偶尔危害甘蔗,与本试验结果相吻合。郭松景等[11]研究报道,劳氏黏虫取食玉米后雌成虫寿命为7 d,平均产卵量为266粒。而本试验中雌成虫平均寿命为11.42 d,单雌平均产卵量1 019.42粒,结果出现较大差异可能是由于采用的劳氏黏虫种群不同,郭松景等[11]试验中采用的劳氏黏虫为田间种群,而本试验中采用的是田间采集的幼虫经过室内繁殖饲养1代后的种群。以稗草为寄主植物时,劳氏黏虫除了雌、雄虫蛹质量低于甘蔗组外,其幼虫发育历期、雌成虫寿命、单雌产卵量等与甘蔗组差异均不显著,并且在稗草上的单雌平均产卵量为790.50粒,高于甘蔗组(665.27粒),可见劳氏黏虫取食稗草不仅能够正常的生长发育,还具有较强的繁殖能力,稗草是劳氏黏虫合适的中间寄主。吴荣宗[27]认为龄期数目与幼虫食料有关,当劳氏黏虫取食小麦时幼虫期均为6龄,而以高粱饲养时为7龄,本试验中取食4种寄主植物劳氏黏虫幼虫期均以6龄为主,但均有个别幼虫蜕皮至7龄却不能顺利化蛹的现象,具体原因还有待进一步分析。从研究结果可以看出,与取食稗草和甘蔗相比,取食玉米和水稻的劳氏黏虫不仅在幼虫期发育较快、存活率较高,在蛹质量及产卵量上也相对较重(高),可见,劳氏黏虫幼虫期的食物不仅对幼虫期生长发育有一定影响,对其种群的增殖也有重要影响。
在昆虫生命表参数中,内禀增长率反映了种群在特定环境下的数量增长能力[28]。劳氏黏虫在玉米、水稻、甘蔗和稗草上的内禀增长率分别为0.13、0.12、0.10和0.10,净增殖率分别为226.54、211.48、153.71和171.83,因此在适宜的条件下劳氏黏虫种群均能够在4种寄主植物上增殖,其中在玉米上增长最快,其次是水稻。田间调查发现,在冬季,劳氏黏虫常发现于禾本科杂草、稻桩上,待早春宿根蔗发芽开始为害并繁殖,这势必给翌年的农业生产造成威胁。可见,虽然相比之下取食水稻、甘蔗和稗草的种群增长潜能不如玉米,但它们却为劳氏黏虫越冬提供了丰富的食料。因此,建议在收割农作物的同时应及时清理秸秆并清除田边杂草,冬季时深耕勤耙,在春耕时节再翻耕整畦可有效消除越冬的幼虫和蛹,并在宿根蔗萌芽发苗时注意防治劳氏黏虫。
-
表 1 不同预处理方法建立的水稻纹枯病PLS-DA模型预测结果
Table 1 Results of PLS-DA models for identifying rice sheath blight using the spectra pretreated by different methods
预处理 最优隐含变量 建模集 预测集 样本总数 正确数 正确率/% 样本总数 正确数 正确率/% RAW 6 116 100 86.2 64 55 85.9 SG 6 116 99 85.3 64 53 82.8 SNV 6 116 108 93.1 64 59 92.1 MSC 5 116 105 90.5 64 57 89.1 表 2 基于MNF特征信息提取的LDA和BPNN判别分析模型结果
Table 2 Discriminant analysis results of LDA and BPNN models based on MNF feature information
模型 变量数 建模集 预测集 样本总数 正确数 正确率/% 样本总数 正确数 正确率/% LDA 11 116 112 96.6 64 61 95.3 BPNN 11 116 115 99.1 64 63 98.4 -
[1] 黄玉祥, 杨青. 精细农业的环境效应[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(S2): 250-254. [2] 王大帅, 张俊雄, 李伟. 植保无人机动态变量施药系统设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(5): 86-93. [3] 刘飞, 王莉, 何勇, 等. 应用可见/近红外光谱进行黄酒品种的判别[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2008, 28(3): 586-589. [4] 鲍一丹. 番茄病害早期快速诊断与生理信息快速检测方法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2012. [5] 杨燕. 基于高光谱成像技术的水稻稻瘟病诊断关键技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2012. [6] 赵芸. 基于高光谱和图像处理技术的油菜病虫害早期监测方法和机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. [7] 张初, 刘飞, 孙汶汶, 等. 利用近红外高光谱图像技术快速鉴别西瓜种子品种[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(20): 270-277. [8] PONTIUS J, HALLETT R, MARTIN M. Assessing hemlock decline using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy: Indices comparison and algorithm development[J]. Appl Spectrosc, 2005, 59(6): 836-843.
[9] GRAEFF S, LINK J, CLAUPEIN W. Identification of powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis sp. tritici) and take-all disease (Gaeumannomyces graminis sp. tritici) in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by means of leaf reflectance measurements[J]. Cent Eur J Biol, 2006, 1(2): 275-288.
[10] HUANG W J, LAMB D W, NIU Z, et al. Identification of yellow rust in wheat using in-situ spectral reflectance measurements and airborne hyperspectral imaging[J]. Precis Agric, 2007, 8(4/5): 187-197.
[11] BELASQUE J J, MARCASSA L G, GASPAROTO M C G. Detection of mechanical and disease stresses in citrus plants by fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Appl Opt, 2008, 47(11): 1922-1926.
[12] MARCASSA L G, GASPAROTO M C G, BELASQUE J J, et al. Fluorescence spectroscopy applied to orange trees[J]. Laser Phys, 2006, 16(5): 884-888.
[13] LINS E C, BELASQUE J, MARCASSA L G, et al. Detection of citrus canker in citrus plants using laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Precis Agric, 2009, 10(4): 319-330.
[14] KOBAYASHI T. Detection of rice panicle blast with multispectral radiometer and the potential of using airborne multispectral scanners[J]. Phytopathology, 2001, 91(3): 316-323.
[15] SASAKI Y, OKAMOTO T, IMOU K, et al. Automatic diagnosis of plant disease[J]. J Jap Soc Agr Mach, 1999, 61(2): 119-126.
[16] 朱大洲, 王坤, 周光华. 单粒大豆的近红外光谱特征及品种鉴别研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2010, 30(12): 3217-3221. [17] 刘天玲, 苏琪雅, 孙群, 等. 基于NIR分析和模式识别技术的玉米种子识别系统[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(6): 1550-1553. [18] 张初, 刘飞, 孙汶汶, 等. 近地高光谱成像技术对黑豆品种无损鉴别[J]. 光谱与光谱学分析, 2014, 31(3): 746-750. [19] 张初, 刘飞, 孙汶汶, 等. 近红外光谱技术用于豆浆粉品牌与假冒豆浆粉的鉴别[J]. 光谱与光谱学分析, 2014, 34(7): 1830-1836. [20] 周竹, 李小昱, 陶海龙, 等. 基于高光谱成像技术的马铃薯外部缺陷检测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(21): 221-228. [21] 邹伟, 方慧, 刘飞, 等. 基于高光谱图像技术的油菜籽品种鉴别方法研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2011, 37(2): 175-180. [22] 黄敏, 朱晓, 朱启兵, 等. 基于高光谱图像的玉米种子特征提取与识别[J]. 光子学报, 2012, 41(7): 868-873. [23] 宋海燕, 秦刚, 韩小平, 等. 基于近红外光谱和正交信号–偏最小二乘法对土壤的分类[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(7): 168-171. [24] LUNA A S, DA SILVA A P, PINHO J S, et al. Rapid characterization of transgenic and non-transgenic soybean oils by chemometric methods using NIR spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimi Acta A, 2013, 100(12): 115-119.
[25] CANAZA-CAYO A W, COZZOLINO D, ALOMAR D, et al. A feasibility study of the classification of Alpaca (Lama pacos) wool samples from different ages, sex and color by means of visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Comput Electron Agr, 2012, 88: 141-147.
[26] 宋海燕, 何勇. 基于OSC和PLS的土壤有机质近红外光谱测定[J]. 农业机械学报, 2007, 38(12): 113-115. [27] 张娴, 袁洪福, 郭峥, 等. 正交信号校正应用于多元线性回归建模的研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(12): 3228-3231. [28] GONG A P, QIU Z J, HE Y, et al. A non-destructive method for quantification the irradiation doses of irradiated sucrose using Vis/NIR spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimic Acta A, 2012, 99(99C): 7-11.
[29] 白璘, 惠萌. 基于改进最小噪声分离变换的特征提取与分类[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2015, 37(7): 1344-1348.









 下载:
下载: