Velocity control strategy based on a cloud model for unmanned agricultural vehicle during obstacle crossing
-
摘要:目的
提高遥控操作农业车辆的智能性与安全性。
方法提出一种新的无人农业车辆遇障后的速度控制方法。建立动态环境中无人车辆的碰撞预测模型,确定实时碰撞位置,依据专家经验与农业作业环境制定的云推理规则,建立速度控制策略,实现速度控制。
结果算法预测判断平均耗时0.170 1 s,无人车辆速度控制过程没有受到无威胁障碍物影响,且符合速度云推理规则。
结论该算法能够实现实时碰撞预测,具备抗干扰能力,满足实时性要求。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo improve the intelligence and safety of remote-operated agricultural vehicles.
MethodA new method for unmanned agricultural vehicles during obstacle crossing was proposed. The collision prediction model of unmanned vehicles in dynamic environment was established, and the real-time collision location was determined. According to the cloud inference principle based on both experience of experts and agricultural operation environment, velocity control strategy was established to realize velocity control.
ResultThe algorithm took 0.170 1 s on average to make a prediction, the velocity control results of unmanned vehicles excluded the impact of non-threatening obstacles and accorded with the velocity cloud inference principle.
ConclusionThe established algorithm is able to realize real-time collision prediction, possesses anti-disturbance ability, and satisfies real-time requirement.
-
随着农业产业的转型与发展,无人农业车辆的研发与应用已经成为趋势。国际上对无人农业机器人的研究与探索已相当深入,尤其在避障控制方面已取得巨大突破。国内研究多侧重于路径规划,对机器人车辆如何模拟驾驶员的遇障反应并没有深入探讨,遇障时的速度控制策略也较为模糊[1-3]。一般情况下农业车辆的作业目标和作业路线确定,将速度控制作为避障控制的先决条件,一方面,在动态变化的农业生产环境中,这有利于环境感知到的传感器信息的及时收集及处理,为路径规划打下基础;另一方面,模拟驾驶员在实际驾驶环境中遇到不同类型障碍物的速度调控反应,可以在尽量减少对作业影响的前提下保障作业的安全性。
周海龙[4]在对小型机器人静态避障的研究中利用超声波传感器检测障碍物位置信息,并在此基础上搭建基于专家决策意见的云模型速度控制模块,以障碍物距离为输入,机器人速度为输出,实现无人机器人的速度控制。徐玉华等[5]使用激光测距仪计算机器人转向夹角,估计机器人参考行驶方向与实时行驶方向的偏差对线速度的影响,建立不同行驶条件下机器人的运动模型,实现机器人在避障前的主动调速。以上研究多考虑静态障碍物对机器人运动的影响,没有进一步提出动态环境中的控制算法。魏连锁等[6]设计出基于云模型的粒子群优化算法,对多个障碍物进行识别、跟踪与预测,自主判断障碍物优先级,根据优先级遥控操作机器人避障速度。Xin等[7]提出1种新的无人驾驶车辆在动态环境中的行为决策和路径规划方法,给出时空障碍物栅格图的定义,建立不同的道路碰撞模型,并以此为依据对无人车辆进行速度调控与路径规划。此类研究考虑了动态障碍物的影响,控制效果良好,但需要依赖道路轨迹等先验性信息。本文拟将人的经验、知识与判断有机融入速度控制策略中,使无人农业车辆在进行路径规划与自主避障时,合理调整行驶速度;针对动态的农业生产环境,建立有效的碰撞预测模型,将预测碰撞位置作为速度控制的参考指标之一;无人农业车辆遇障后速度控制的输出应快速、准确,对无威胁障碍物具备一定的抗干扰能力。
1. 云模型
在一般无人车辆控制中,人的作用基本体现为监督,人的感知、知识与判断没能融入农业机器人的控制中。将人的智慧与机器智能结合起来是农机智能化研究的重点。人的经验和智慧具有模糊性和不确定性,很难定量表现出来。将人的理念转化为定量数据,云模型理论是一个很好的工具。云模型可以通过3个数字特征:期望(Ex),熵(En),超熵(He),完成从模糊概念到具体数据的转换,并以云图表现出来,与模糊概念的传统处理方法相比,这种方法更加具体、直观[8-10]。
1.1 云标尺
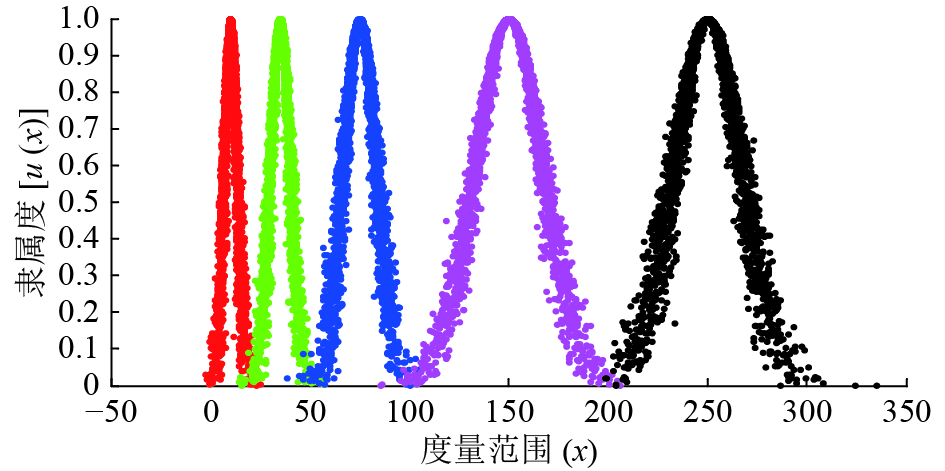
云标尺与速度控制发生器关系的建立是控制策略中至关重要的部分,人的经验与知识借此以模糊数学的方式来表达。上位机将辅助远端操作者,判断障碍物的位置与状态信息,计算相关参数,并在极短的时间内给予速度控制方案。云模型通过期望,熵,超熵,将1个不确定的概念通过以度量范围(x)为横轴、隶属度[u(x)]为纵轴的离散点图形来表示,如图1所示,该离散点图形一般符合正态分布[11]。
结合专家经验与常识,本文将障碍物的预测碰撞位置与障碍物本身的状态作为速度规则推力器制定的指标,将碰撞距离与障碍物的危险度等定性概念转化为定量参数输入,实现无人车辆速度控制输出。本文设定无人农业机械在作业时,行进速度为1 m/s,以试验中传感器准确感知信息的最大距离30 m为界限,专家评估距离参数分为[0,2)、[2,5)、[5,10)、[10,20)、[20,30] 5组,单位为m,定性概念分别为近、较近、一般、较远和远,对应的云参数分别为(1.00,0.33,0.50)、(3.50,0.50,0.70)、(7.50,0.83,0.80)、(15.00,1.67,1.00)和(25.00,1.67,1.50)。
同样,危险度的判断也由多名专家根据实际情况与经验共同评估研讨。危险度评估的关键主要分为3部分:1)是否会威胁人身安全;2)是否会对财产造成较大损失;3)障碍物运动是否增加危险系数。基于以上描述,专家对某作业环境下各障碍物危险度进行评估与云化,将其划分为[0,1)、[1,3)、[3,5)、[5,7)、[7,10] 5个等级,对应危险度分别为低、较低、一般、较高、高这5个概念,对应的云参数分别为(0.50,0.17,0.50)、(2.00,0.33,0.60)、(4.00,0.33,0.80)、(6.00,0.33,1.00)和(8.50,0.50,1.50)。
距离与危险度作为决策参数,是速度控制的主要依据。因此,距离与危险度参数为前件云,速度控制参数为后件云。本文试验车辆作业时行驶速度为1 m/s,以cm/s为量级划定速度控制域为[0,10)、[10,20)、[20,40)、[40,70)和[70,100],定性概念分别为静止、较慢、一般、较快和快,对应的云参数分别为(5.00,1.67,0.80)、(15.00,1.67,1.00)、(30.00,3.30,1.50)、(55.00,5.00,2.00)和(85.00,5.00,2.50)。
1.2 云规则处理器
云模型中表达人知识的典型推理规则为“If X1 and X2 and X3 and …, then Y”这一形式[12],对应本研究,X1、X2、Y分别表示决策参数距离、危险度和速度。例如,某一推理规则为:如果预测碰撞位置的距离是远的,且危险程度是一般的,则其作业速度控制为较快的。该规则为基于人类专家的经验与知识形成的一个知识库。
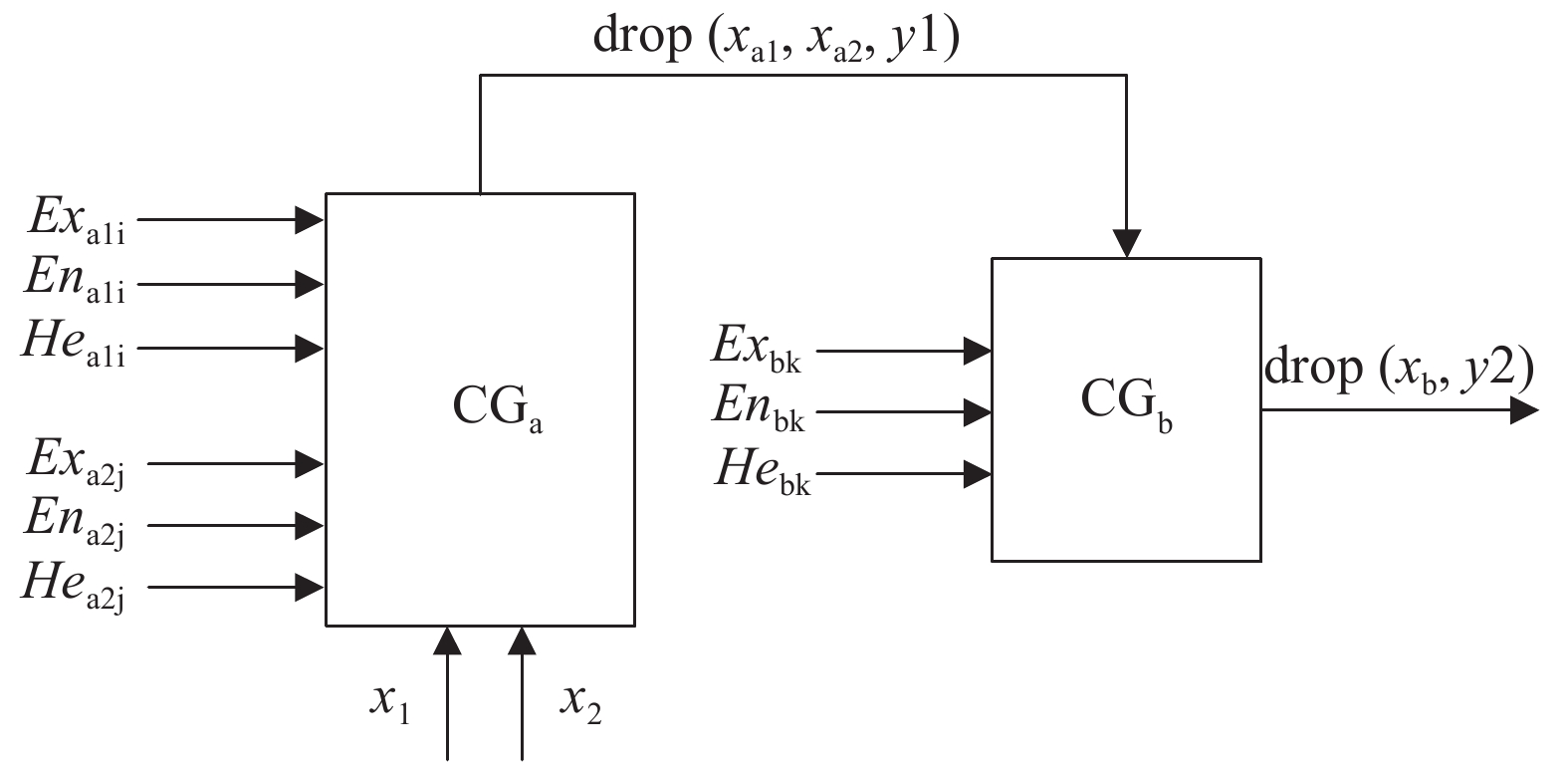
本研究使用双条件多规则处理器,对应于某一规则的双条件处理器如图2所示。该处理器由前件云发生器CGa与后件云发生器CGb两部分组成,其输入:前件距离与危险度定性概念的数字特征(Exa1i,Ena1i,Hea1i)、(Exa2j,Ena2j,Hea2j),i/j分别对应不同的距离/危险度等级;后件速度定性概念的数字特征(Exbk,Enbk,Hebk),k对应不同的速度等级。其输出:满足确定度y2的速度定量值Xb。X1、X2为实时的距离与危险度,用以激活处理器。
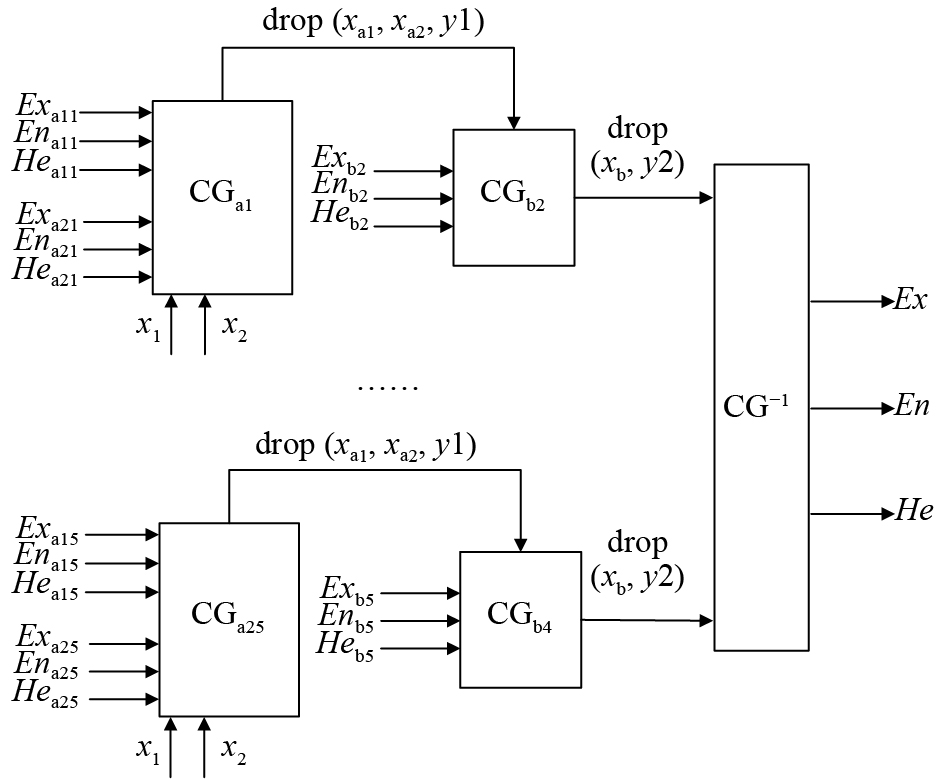
本研究速度推理规则见表1,该规则处理器共25条规则,即形成25个正向云发生器,其中,i、j、k分别对应距离、危险度和速度等级,均取值1、2、3、4、5,表示由低到高5个定性等级。所有规则共同构建的速度规则处理器如图3所示。
表 1 速度推理规则Table 1. Velocity inference principle危险等级(j) 距离等级(i) 近(1) 较近(2) 一般(3) 较远(4) 远(5) 低(1) 速度较慢 速度一般 速度一般 速度较快 速度快 较低(2) 速度较慢 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 速度快 一般(3) 速度零 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 速度较快 较高(4) 速度零 速度较慢 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 高(5) 速度零 速度零 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 规则发生器处理流程:1)根据定性输出的处理算法,对于某一时刻输入的距离X1、危险度X2,计算所有CGa的激活强度并确定其在云标尺上的位置。激活后,云发生器CGa输出确定度y1,选择最大y1值对应的规则为最优规则;2)确定后的y1作为条件激活输出平面CGb上的云标尺,计算xb;3)对定量X1、X2进行N轮评判,得到定性变量采样点集[drop(xb,y2)]。将这些云滴作为输入,导入逆向云发生器(CG–1),还原出最终的云数字特征Ex,En,He,并画出云图;4)将云图反馈给评估专家进行检阅,专家再次提出评估意见,形成新的定性规则发生器输入。
2. 碰撞预测
2.1 直线预测模型
对于静态障碍物,速度输出可直接由障碍物所在位置及其危险度决定。但对于动态障碍物,其变化的运动状态,使得云处理器无法简单地依据距离与危险度决定无人农业车辆的速度。因此,本研究在碰撞预测的基础上,以预测碰撞位置和障碍物危险度为输入,输出无人农业车辆的速度控制结果。
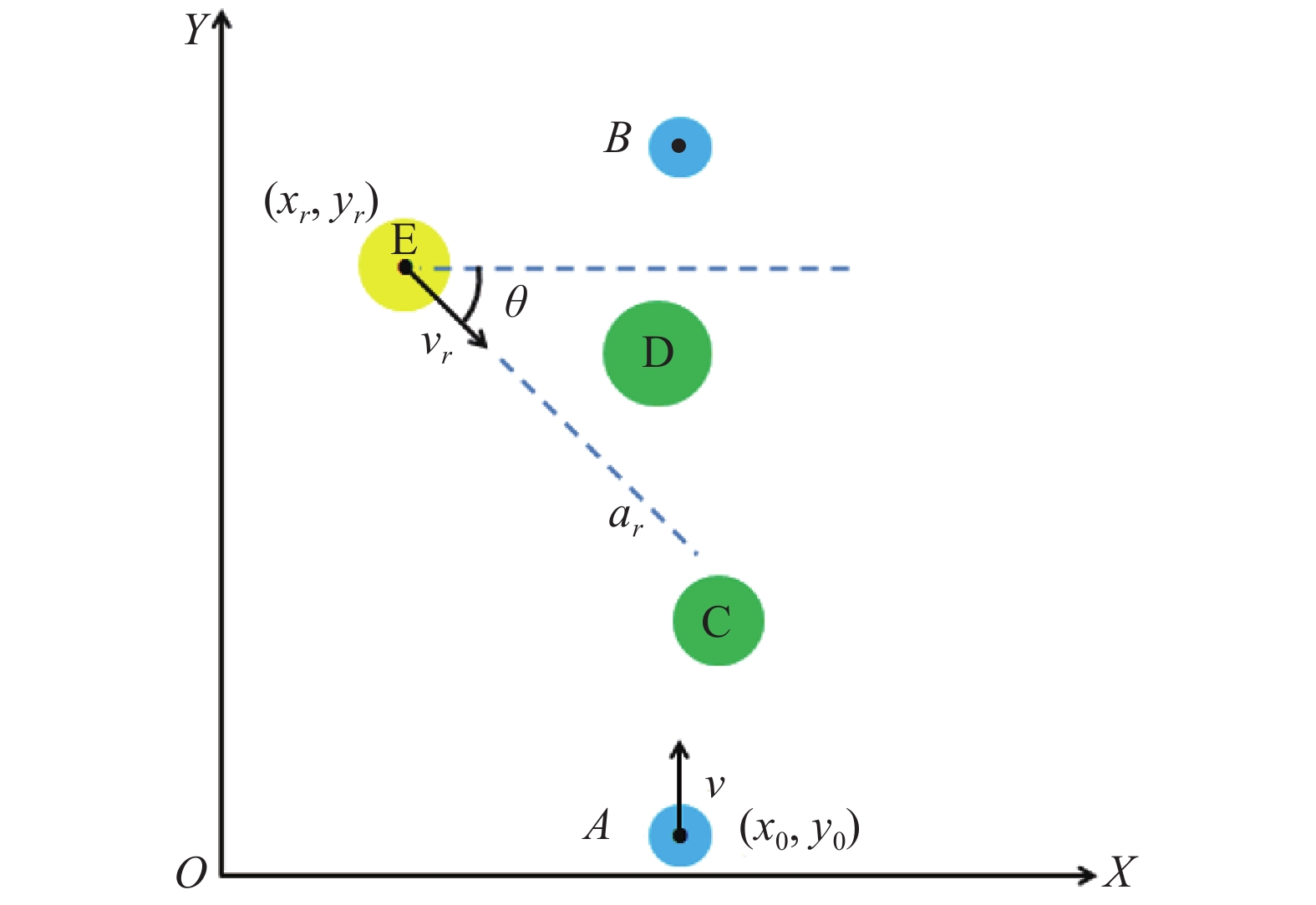
障碍物的运动预测方法有多种,如典型路径模型、保守运动模型等,但这些预测模型都依赖于道路走向或障碍物历史航迹等先验性信息,不适用于道路情况复杂的田间作业环境[13-14]。因此,本研究采用直线预测模型[15],即认为运动障碍物在传感器信息采集间隔时间t′内,仍然按照当前行驶方向近似于直线行驶,如图4所示,设无人农业车辆当前位置为A(x0, y0),向作业目标点B运动。C、D为静态障碍物,E为动态障碍物,(xr, yr)为当前动态障碍物位置。
运动障碍物的预测行驶轨迹方程为:
$$ \left\{ \begin{align} x - {x_r} - {v_r}t\cos \theta - \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}{a_r}{t^2}\cos \theta = 0\\ y - {y_r} - {v_r}t\sin \theta - \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}{a_r}{t^2}\sin \theta = 0 \end{align} \right. \;\;, $$ (1) 式中,vr、ar分别为障碍物行驶速度与加速度,t为运动时间,θ为障碍物运动方向与X轴正向的夹角。
设无人农业车辆是匀速行进作业,则作业时间与行驶路程应成正比,与速度成反比,但无人农业车辆沿作业路线或向目标点行进时并不是完全的直线行驶,需不断调整以约束行进方向,本研究中试验车辆实地作业测试后的修正公式为:
$$ t = p\left( {1 + q\left| {x - {x_{{}_0}}} \right|/\left| {y - {y_{{}_0}}} \right|} \right) \left. \sqrt {{{\left( {x - {x_{{}_0}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {y - {y_{{}_0}}} \right)}^2}} \right/{v_{{}_a}}, $$ (2) 式中,p、q为修正系数,va为农业车辆行驶速度。
假设无人作业车辆的作业路径方程为:
$$ y = kx + b, $$ (3) 式中,k为当前时空坐标下路径方程系数,b为常数。
联立方程(1)、(2)、(3)以及限制条件,即可得碰撞预测方程:
$$ \begin{array}{l} \left\{ \begin{array}{l} x - {x_r} - {v_r}t\cos \theta - \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}{a_r}{t^2}\cos \theta = 0\\ y - {y_r} - {v_r}t\sin \theta - \displaystyle\frac{1}{2} {a_r}{t^2}\sin \theta = 0\\ t = p\left( {1 + q\left| {x - {x_{{}_0}}} \right|/\left| {y - {y_{{}_0}}} \right|} \right) \left. \sqrt {{{\left( {x - {x_{{}_0}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {y - {y_{{}_0}}} \right)}^2}} \right/{v_{{}_a}}\\ y = kx + b \end{array} \right.\\ s.t. \;\;\; t \geqslant 0,{x_{{}_m}} \geqslant x \geqslant 0,{y_{{}_m}}\geqslant y \geqslant 0 \end{array} \text{。} $$ (4) 2.2 动态控制策略
对于动态障碍物,当t0时刻作业车辆以速度v行驶时,若存在预测碰撞点并进行速度调控后,在
${t_{{}_0}} + t'$ 时刻时,预测碰撞点可能会消失,障碍物对作业或已无威胁,此时速度控制模型应为下一步决策提供依据。设t0时刻作业车辆坐标为$\left( {{x_{{}_0}},{y_{{}_0}}} \right)$ ,障碍物坐标为$\left( {{x_{{}_{r0}}},{y_{{}_{r0}}}} \right)$ ,t′后车辆预测位置为$\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ ,障碍物预测位置为$\left( {{x_{{}_{r1}}},{y_{{}_{r1}}}} \right)$ ,则t0时刻车辆与障碍物距离(L)为:$$ L = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_{{}_0}} - {x_{{}_{r0}}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_{{}_0}} - {y_{{}_{r0}}}} \right)}^2}} \;\;, $$ (5) 定义
$$\begin{aligned} L' = & \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_{{}_1}} - {x_{{}_{r1}}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_{{}_1}} - {y_{{}_{r1}}}} \right)}^2}} -\\ & \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_{{}_0}} - {x_{{}_{r0}}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_{{}_0}} - {y_{{}_{r0}}}} \right)}^2}} \;\;, \end{aligned}$$ (6) 由式(6)可知,当L′≥0时,障碍物向远离车辆方向运动;L′<0时的障碍物向靠近作业车辆的方向运动。当动态障碍物远离作业车辆时,无人车辆可恢复正常行驶速度;当障碍物有靠近作业车辆的趋势时,保持调控后的速度不变,直至障碍物远离或产生新的碰撞预测点。
因此,动态环境中的速度控制策略如下:当t0时刻出现障碍物时,若无人车辆与障碍物之间的距离大于设定的安全值,则判断该障碍物是否为运动障碍物,若为运动障碍物,则判断障碍物的运动是否会对作业产生威胁。若无人车辆与障碍物存在预测碰撞位置,则由云发生器输出速度控制结果,若不存在,则保持当前车速不变。时间t′后,若障碍物仍靠近作业车辆,但已无碰撞位置存在,保持当前速度不变,直至障碍物远离作业区域,恢复正常行驶。
3. 试验结果与分析
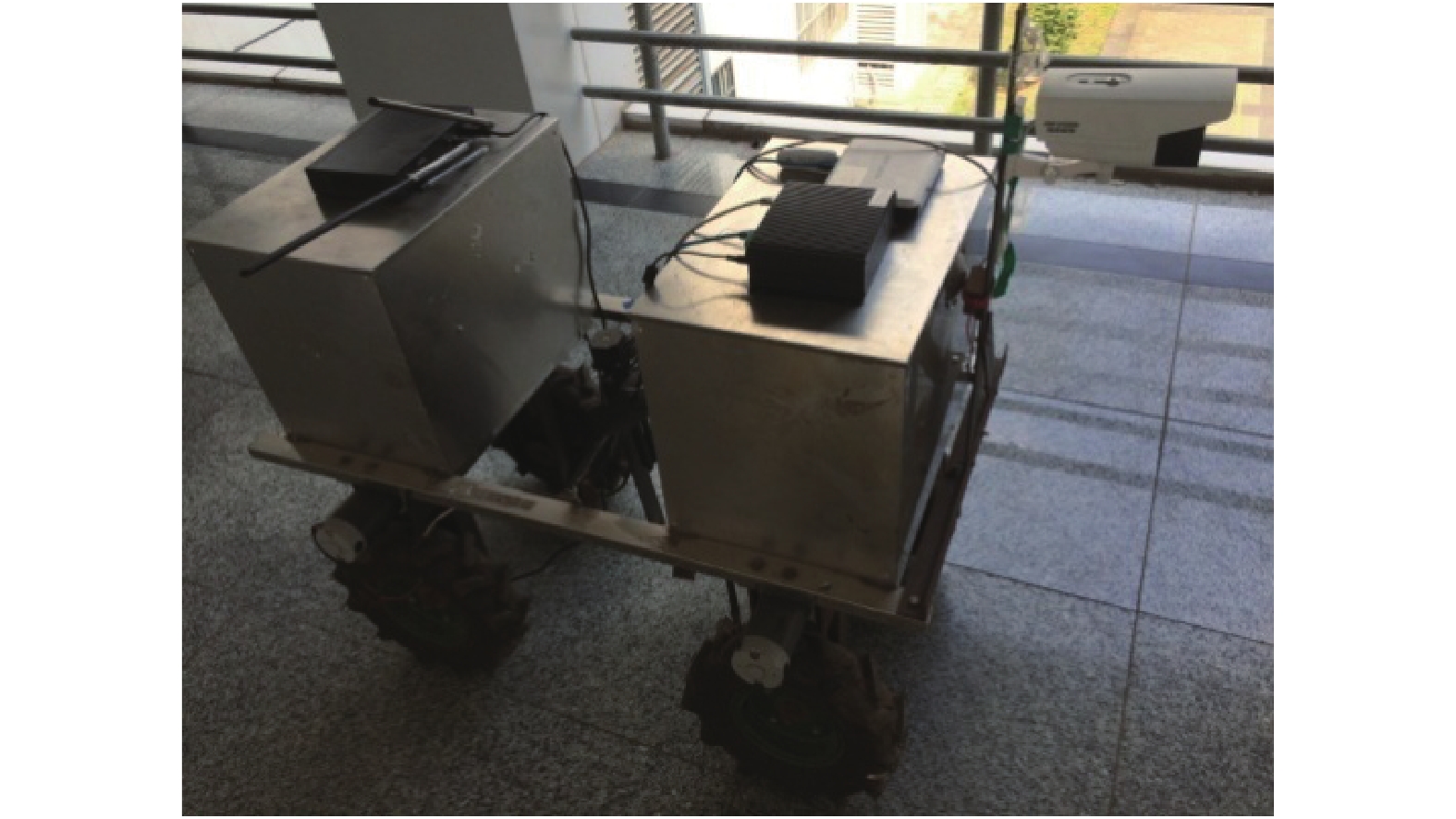
利用Matlab 2012a处理试验数据,并对试验结果进行分析。试验区域空间大小为150 m×40 m,试验载体为1.3 m×0.5 m的无人农业机器人车辆,如图5所示。试验中,将机器人车辆视为质点,车辆装载DS–2CD2T12摄像头,设定分辨率1 280×720;LMS–291单线式激光雷达,扫描半径30 m,扫描范围为0~180°;搭载U–BLOX GPS模块,定位精度0.05 m,速度精度0.01 m·s–1。所设计试验的评价指标如下:安全性高,无人农业车辆遇障后速度控制效果良好;抗干扰能力强,准确排除不会威胁生产作业过程的静、动态障碍物的影响;实时性好,算法耗时短、时延少。
3.1 云处理器试验
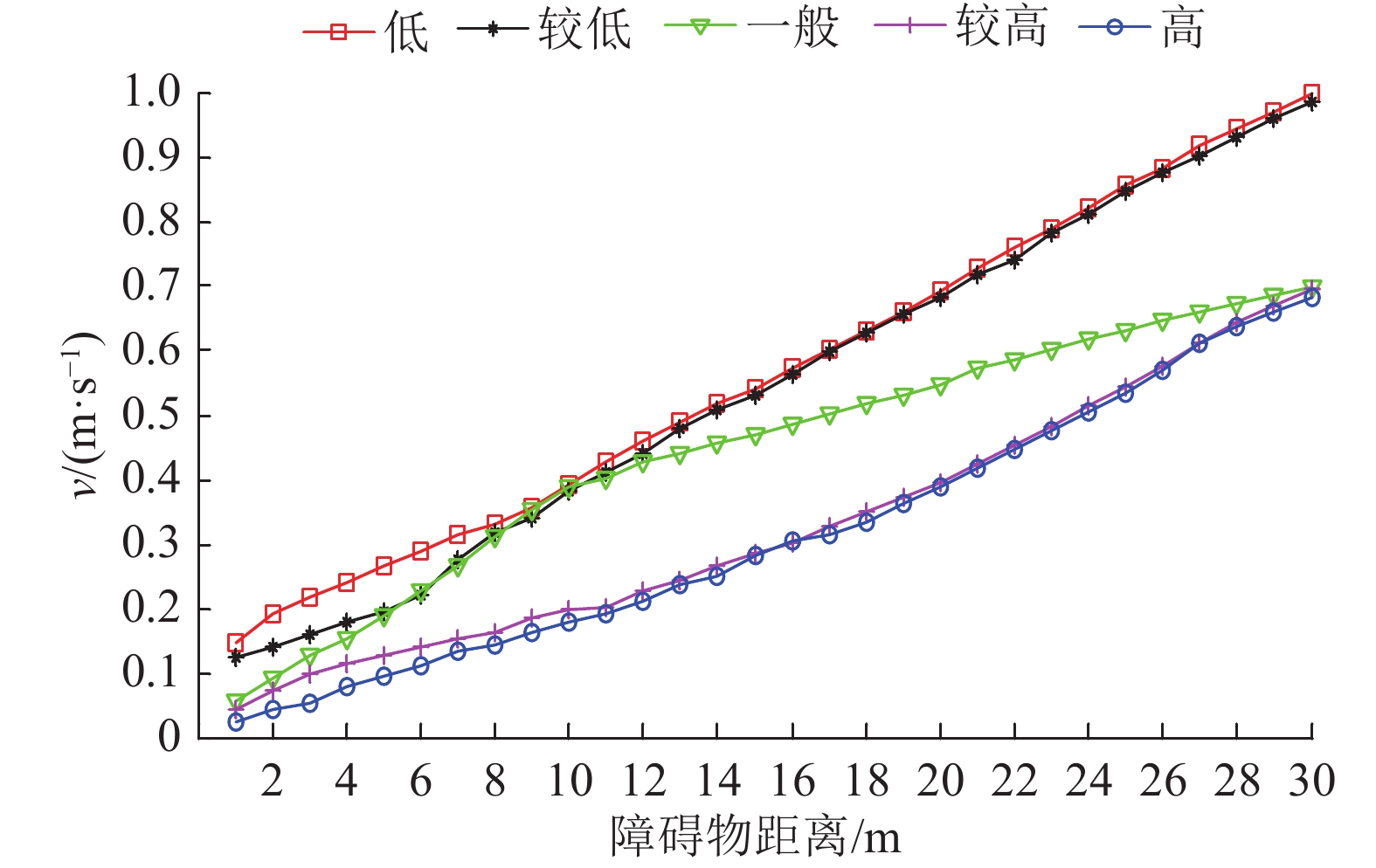
对速度云规则处理器及其输出进行试验,并对结果进行分析。在作业路径中距无人机器人车辆30 m处设置5种不同危险度的障碍物分别进行试验,其危险度分别为0.5、2.0、4.0、6.5和8.0,车辆每向前行驶1 m,记录节点行驶速度,并设定安全距离为1 m。图6为试验速度输出图,在X轴方向,随障碍物距离的接近,云推理器的速度输出逐渐降低,到达安全距离时,避障速度均小于0.15 m·s–1;在Y轴方向,同一障碍物距离下,危险度越高,车辆速度输出越低。各危险度障碍物速度输出均符合专家速度推理规则。
3.2 算法稳定性试验
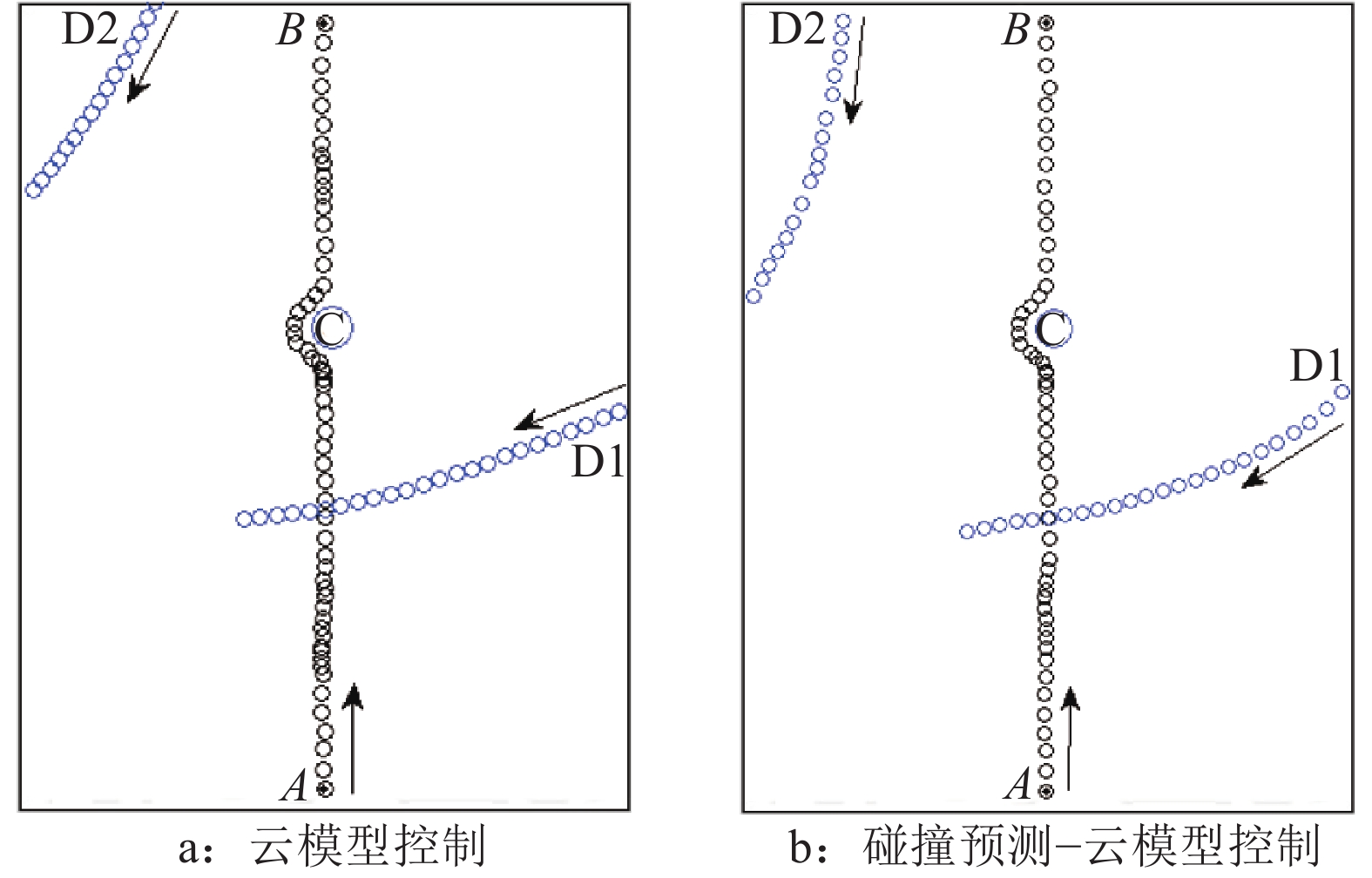
为校验本研究速度控制方法的稳定性,在同一作业环境下,分别对有、无碰撞预测的控制方法进行试验。在作业环境中,无人农业车辆由出发点A向终点B沿直线进行作业。在作业路径中,有1个危险度为3的静态障碍物C,在作业环境中,存在2个危险度为8的动态障碍物D1、D2,分别于车辆行驶后第5和45秒时出现,在同一起点沿相同方向移动。车载传感器每间隔1 s获取农业车辆与障碍物的坐标信息并上传,所有时刻的占用坐标记录在同一空间平面图中,形成空间占用图,如图7所示。图7a为仅以障碍物的距离及危险度为控制标准,不考虑碰撞情况的无人车辆运动占用图;图7b为加入碰撞预测,以静、动态障碍物的危险度及其预测碰撞位置为输入的占用图。
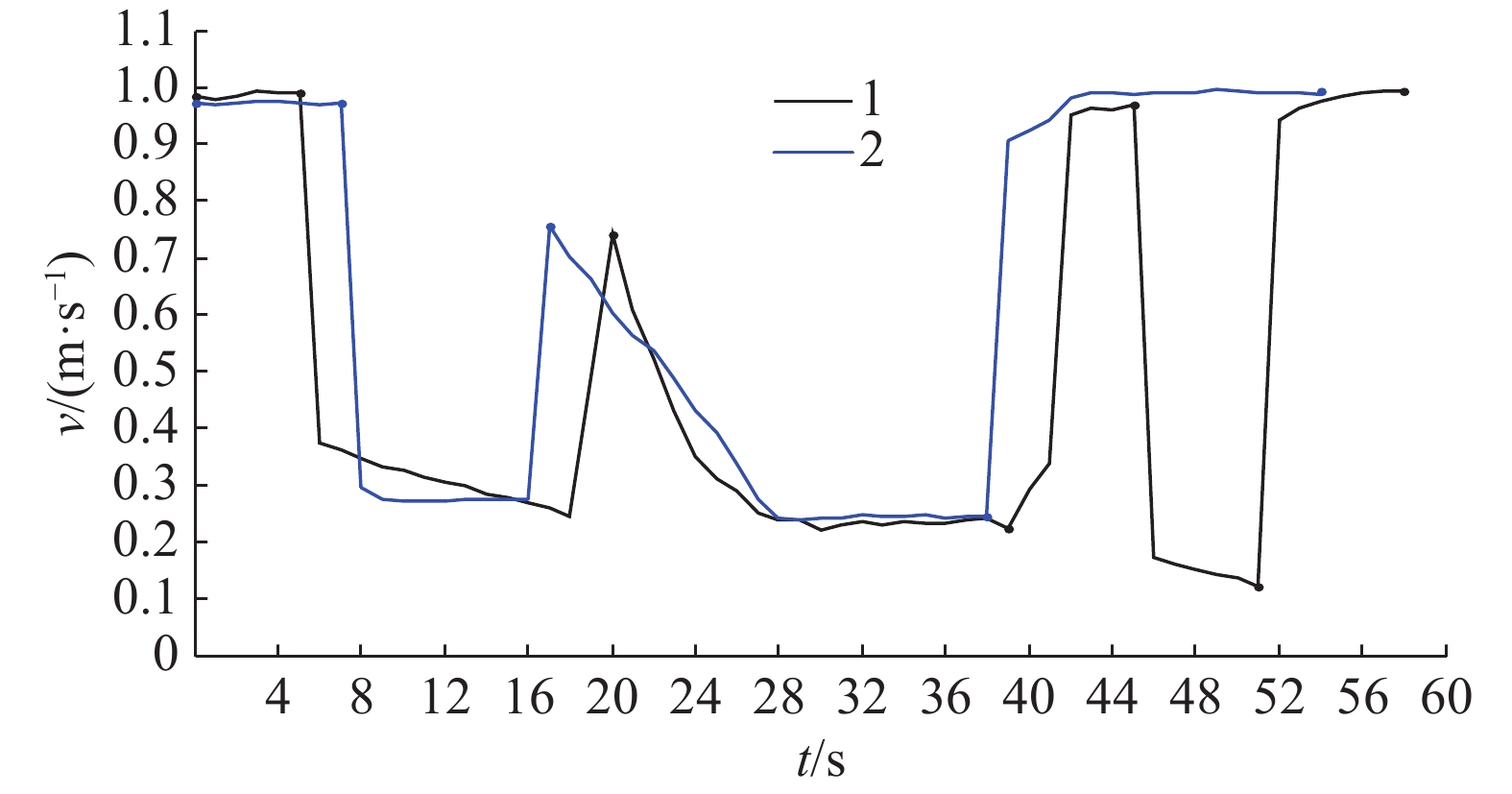
图8为试验所有节点的速度输出图,曲线1为图7a的速度输出,由图8可知,无人农机以接近1 m·s–1的速度由A点向前行驶,行驶后5 s检测到右前方17.9 m处有移动障碍物D1出现,调整当前行驶速度至0.37 m·s–1。第20秒时D1消失,当前速度仅受静态障碍物C影响,并随着与障碍物C的距离缩短而逐渐减小,以0.24 m·s–1的平均速度进行避障,在第41.9秒时避障完成,并恢复正常行驶。第45秒时检测到左前方9.6 m处出现障碍物D2,当即调整速度至1.81 m·s–1,并逐渐减速,直至障碍物D2消失,恢复正常行驶,并于第58.4秒到达目标点B。
图8中曲线2为图7b的速度输出,行驶后第5秒的决策系统判断障碍物D1当前运动趋势不会对作业造成影响,因此无速度变化。第7秒时判断无人农机将在11.8 s后,距当前位置11.2 m处与障碍物D1发生碰撞,平均速度输出为0.27 m·s–1并保持恒定。第16秒时,尽管障碍物D1依然存在于当前作业环境中,但已逐渐远离作业车辆,当前速度仅受静态障碍物C影响。第37.6 秒时避障完成,恢复正常行驶。第45 秒时D2出现,但判断其运动无特殊影响,保持车速不变,第52.6秒时到达目标点B。
由试验结果可知,若无碰撞预测,在第5秒时,不能确定障碍物运动是否会对作业产生影响,在无法保证减速行驶的必要性的情况下,机器人车辆做出减速行为;第45秒时,受到无威胁移动障碍物的干扰,处理器做出减速决策,影响了正常作业进程。而在碰撞预测结果的基础上搭建云速度推理器,在作业过程中,均避免了无威胁障碍物对速度输出结果造成的扰动,保证了正常的作业进程。因此,在碰撞预测基础上搭建的决策系统具有较强的稳定性,不易受到无威胁障碍物的干扰。
3.3 实时性试验
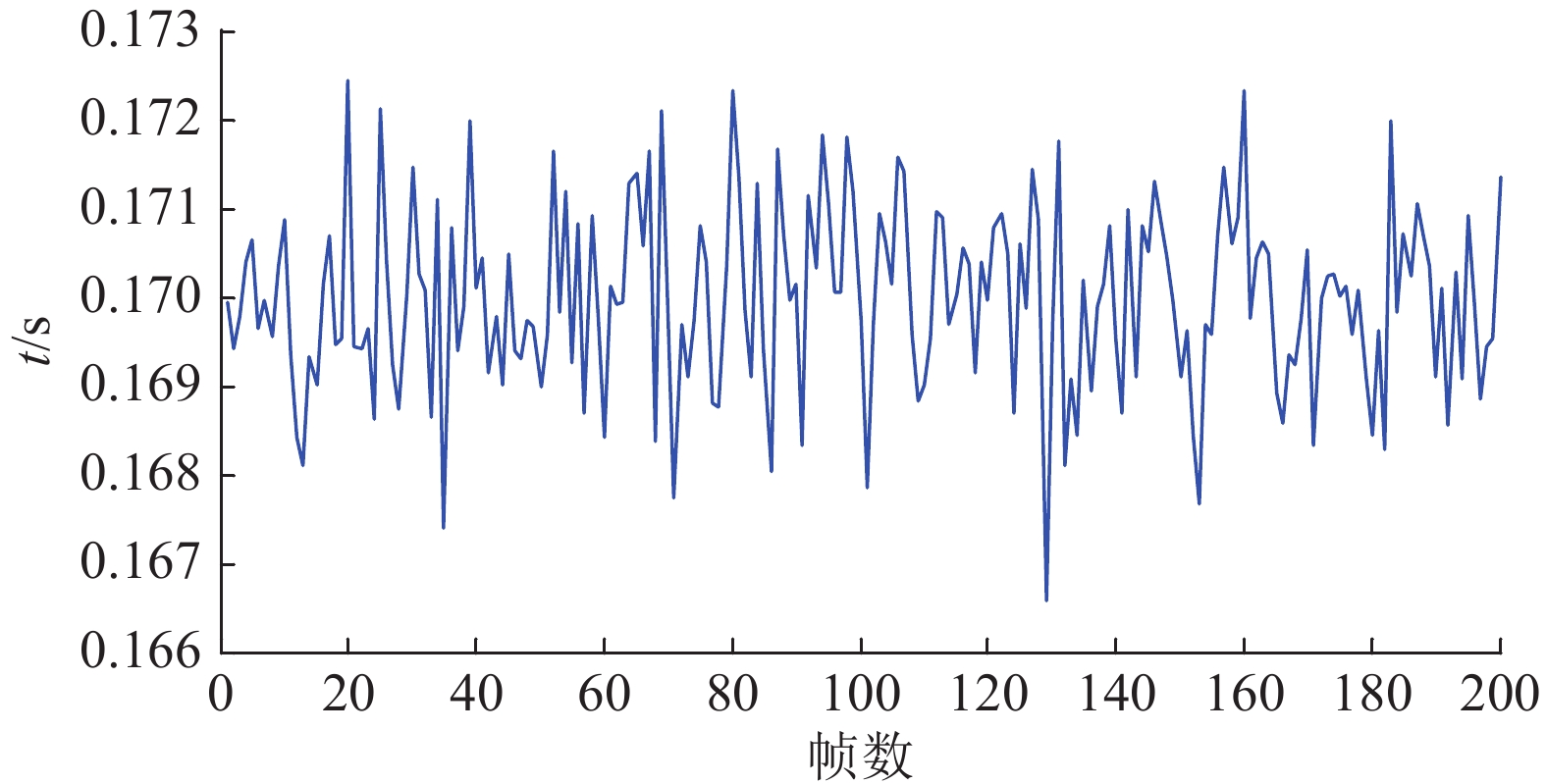
为验证算法的实时性,在一连续作业中,设置不同距离下危险度分别为0.5、2.0、4.0、6.0和9.0的障碍物,以不同障碍物参数为输入对算法耗时进行连续测试,每次速度输出记为1帧,共测试200帧。如图9所示,其平均算法耗时为0.170 1 s,最大耗时为0.172 4 s,理论极限位移为0.172 4 m,小于设定的安全距离值,在算法处理时限内无碰撞危险,因此满足实时性要求。
4. 结论
1) 搭建了速度云规则处理器,以预测碰撞位置和障碍物危险度为输入,无人农业车辆速度为输出,对不同状态的障碍物参数输入有较好的速度控制效果,且满足专家决策意见。
2) 提出了适应道路情况和复杂的动态农业环境的障碍物碰撞预测方法,并以此为依据,建立了速度控制策略。试验结果表明,该方法能有效排除无威胁障碍物的干扰,具有较强的稳定性。
3) 算法平均耗时为每帧0.170 1 s,满足实时性要求。
-
表 1 速度推理规则
Table 1 Velocity inference principle
危险等级(j) 距离等级(i) 近(1) 较近(2) 一般(3) 较远(4) 远(5) 低(1) 速度较慢 速度一般 速度一般 速度较快 速度快 较低(2) 速度较慢 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 速度快 一般(3) 速度零 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 速度较快 较高(4) 速度零 速度较慢 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 高(5) 速度零 速度零 速度较慢 速度一般 速度较快 -
[1] 林佩. 无人驾驶拖拉机研制成功[N]. 中国知识产权报, 2010-01-06. [2] HSU W Y. Brain-computer interface: The next frontier of telemedicine in human-computer interaction[J]. Telemat Inform, 2015, 32(1): 180-192.
[3] ZHONG H, WACHS J P, NOF S Y. Telerobot-enabled HUB-CI model for collaborative lifecycle management of design and prototyping[J]. Comput Ind, 2014, 65(4): 550-562.
[4] 周海龙. 轮式机器人云模型避障控制系统设计与实现[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2011. [5] 徐玉华, 张崇巍, 徐海琴. 基于激光测距仪的移动机器人避障新方法[J]. 机器人, 2010, 32(2): 179-183. [6] 魏连锁, 戴学丰. 基于云模型的粒子群优化算法在路径规划中的应用[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2012, 48(17): 229-232. [7] XIN Y, LIANG H, MEI T, et al. A new occupancy grid of the dynamic environment for autonomous vehicles[C]//IEEE. IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium proceedings. Dearborn: IEEE, 2014: 787-792.
[8] 叶琼, 李绍稳, 张友华, 等. 云模型及应用综述[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2011, 32(12): 4198-4201. [9] 杜湘瑜, 尹全军, 黄柯棣, 等. 基于云模型的定性定量转换方法及其应用[J]. 系统工程与电子术, 2008, 30(4): 772-776. [10] 刘常昱, 冯芒, 戴晓军, 等. 基于云X信息的逆向云新算法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2004, 16(11): 2417-2420. [11] LI D, LIU C, GAN W. A new cognitive model: Cloud model[J]. Int J Intell Syst, 2009, 24(3): 357-375.
[12] SUN X, CAI C, SHEN X. A new cloud model based human-machine cooperative path planning method[J]. J Intell Robot Syst, 2015, 79(1): 3-19.
[13] BALL D, UPCROFT B, WYETH G, et al. Vision-based obstacle detection and navigation for an agricultural robot[J]. J Field Robot, 2016, 33(8): 1107-1130.
[14] ELBANHAWI M, SIMIC M. Randomised kinodynamic motion planning for an autonomous vehicle in semi-structured agricultural areas[J]. Biosyst Eng, 2014, 126: 30-44.
[15] KONOLIGE K. Improved occupancy grids for map building[J]. Auton Robots, 1997, 4(4): 351-367.



 下载:
下载: