Comprehensive evaluation of soil fertility of five typical forest stands in South China
-
摘要:目的
利用多种评价方法综合评价不同林分类型的林下土壤肥力状况,分析这些评价方法对土壤肥力综合评价的影响及其异同,以期为华南地区森林土壤养分管理和森林可持续经营提供理论依据。
方法以华南地区相思Acacia spp.林、杉木Cunninghamia lanceolata林、桉树Eucalyptus urophylla林、马尾松Pinus massoniana林和阔叶混交林的0~20 cm土壤为研究对象,测定了容重、pH、有机质、速效磷、速效钾、碱解氮和全氮含量,通过隶属度函数和偏相关分析进行单项指标评价,并结合相关关系法、主成分分析法、灰色关联分析法和内梅罗指数法对5种林分类型土壤肥力进行综合评价。
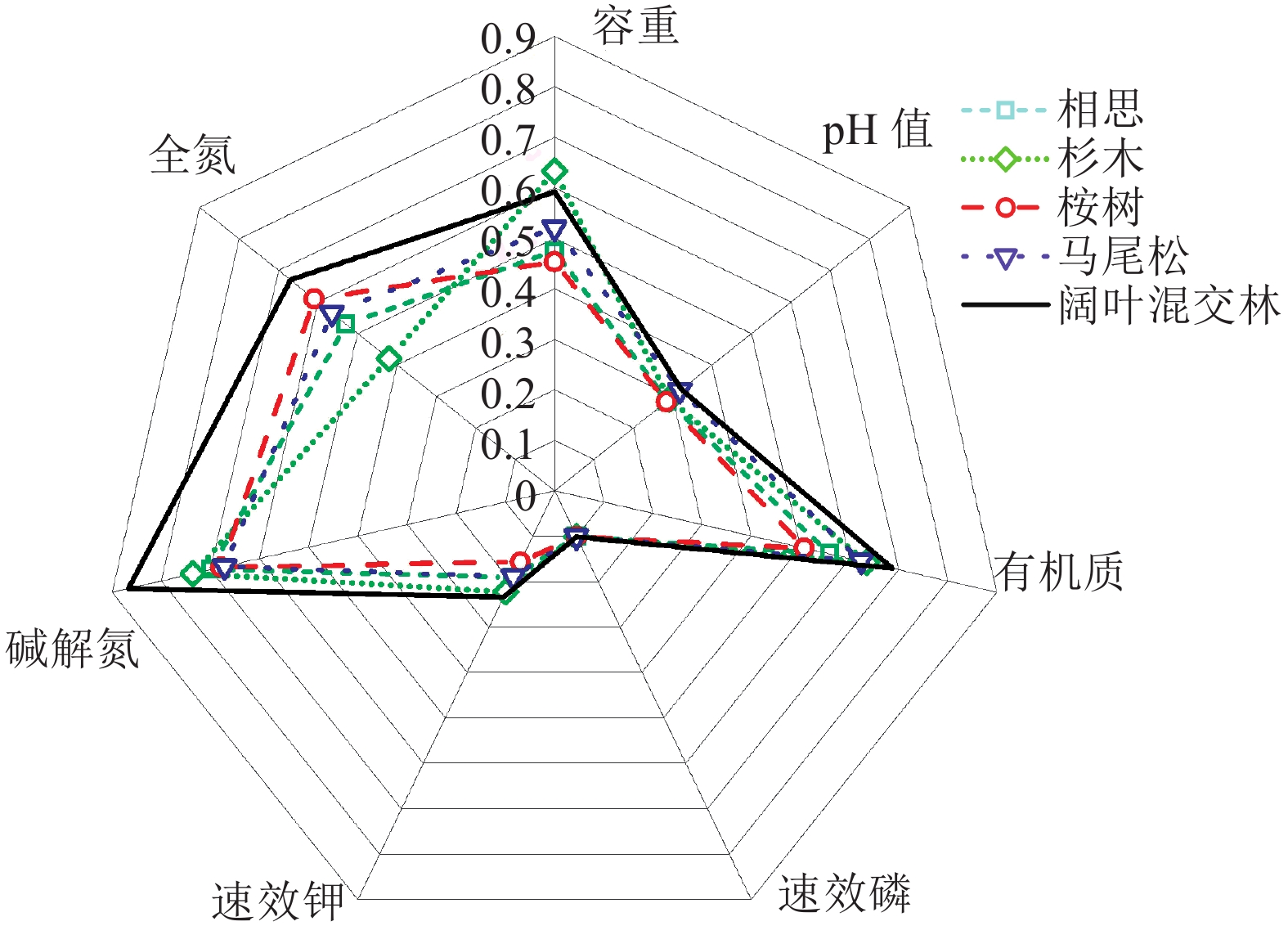
结果5种林分土壤容重变幅为1.24~1.29 g·cm–3,pH变幅为4.11~4.24,有机质含量为21.43~28.18 g·kg–1,速效磷含量为1.12~1.42 mg·kg–1,速效钾含量为40.62~55.20 mg·kg–1,碱解氮含量为106.12~132.28 mg·kg–1,全氮含量为1.03~1.45 g·kg–1;依据全国第2次土壤普查分类标准,有机质和全氮含量均属于中上水平,速效磷含量属于很低水平,速效钾含量为低至中下水平,碱解氮含量为中上至高水平。阔叶混交林的有机质、速效钾、碱解氮和全氮含量均显著高于部分人工林。有机质在土壤肥力中起最重要的作用,速效磷是影响土壤肥力的限制性因子。4种评价方法的综合评价结果一致,土壤肥力大小均表现为阔叶混交林>杉木林>马尾松林>相思林>桉树林。
结论阔叶混交林可以更好地积蓄土壤肥力,桉树林的土壤肥力较低,华南地区森林土壤养分管理时应注重磷钾肥的施用和土壤酸度调节。
Abstract:ObjectiveEvaluating the soil fertility of different forests by a variety of evaluation methods, analyzing the influences as well as differences and similarities of these evaluation methods on soil fertility comprehensive evaluation and providing a theoretical basis for forest soil nutrient management and sustainable development in South China.
MethodFive kinds of forests, including Acacia spp. plantation, Cunninghamia lanceolate plantation, Eucalyptus urophylla plantation, Pinus massoniana plantation and broad-leaved mixed forest were chosen to measure and analyze bulk density, pH, organic matter, available phosphorus, available potassium, alkaline nitrogen and total nitrogen in soil at a depth of 0-20 cm. Single index evaluation was carried out by membership function and partial correlation analysis. Combined with correlation coefficient method, principal component analysis, grey correlation analysis and Nemerow index method, comprehensive evaluation of soil fertility was conducted for five forest stands.
ResultThe soil bulk density of five stands were ranged from 1.24 to 1.29 g·cm–3, and the values of pH were ranged from 4.11 to 4.24. The contents of organic matter were ranged from 21.43 to 28.18 g·kg–1, the contents of available phosphorus were ranged from 1.12 to 1.42 mg·kg–1, the contents of available potassium were ranged from 40.62 to 55.20 mg·kg–1, the contents of alkaline nitrogen were ranged from 106.12 to 132.28 mg·kg–1 and the contents of total nitrogen were ranged from 1.03 to 1.45 g·kg–1. According to the second national soil classification standards, the levels of organic matter and total nitrogen contents were above average values, while the level of available phosphorus content was low, the content of available potassium were ranged from low to below average level, and the content of alkaline nitrogen were ranged from above average to high level. The contents of organic matter, available potassium, available nitrogen and total nitrogen in broad-leaved mixed forest were significantly higher than those in some plantations. Organic matter played the most important role in soil fertility, while available phosphorus was a limiting factor affecting soil fertility. The results of comprehensive evaluation of four kinds of evaluation methods were consistent. The range of soil fertility from high to low was broad-leaved mixed forest > C. lanceolate plantation > P. massoniana plantation > A. spp. plantation > E. urophylla plantation.
ConclusionThe soil fertility accumulation of broad-leaved mixed forest is better than those of other plantations, while the soil of E. urophylla plantation have low fertility. The applications of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer and the adjustment of soil acidity should be emphasized in the management of forest soil nutrients in South China.
-
-
表 1 样地基本情况1)
Table 1 Basic status of sampling plots
林分类型 坡度/(°) 凋落物厚度/cm 郁闭度 树高/m 胸径/cm 相思林 25.7±1.0 5.1±0.7 0.5±0.0 13.5±0.9 14.0±1.0 杉木林 28.7±2.1 5.4±0.6 0.7±0.0 11.3±0.6 12.4±1.3 桉树林 22.2±1.1 5.0±0.4 0.5±0.0 13.8±1.1 12.8±0.9 马尾松林 25.5±1.1 5.1±0.4 0.5±0.0 13.2±0.5 13.4±0.9 阔叶混交林 25.6±1.7 5.7±0.6 0.7±0.0 14.3±1.0 15.9±1.8 1) 表中数据为平均值±标准误 表 2 隶属度函数的转折点取值
Table 2 Values of turning points in membership function
转折点 容重/(g·cm–3) pH w(有机质)/(g·kg–1) w/(mg·kg–1) w(全氮)/(g·kg–1) 速效磷 速效钾 碱解氮 xa 1.00 3.5 6 3 30 30 0.5 xb 1.15 6.5 40 40 200 150 2.0 xc 1.25 xd 1.35 表 3 土壤指标描述性统计
Table 3 Descriptive statistics of soil indicators
n=150 项目 容重/(g·cm–3) pH w(有机质)/
(g·kg–1)w/(mg·kg–1) w(全氮)/
(g·kg–1)速效磷 速效钾 碱解氮 最小值 0.99 3.76 17.92 0.74 20.67 100.20 0.45 最大值 1.56 5.02 31.38 2.44 64.90 140.88 2.83 平均值 1.26 4.17 24.52 1.31 48.30 117.47 1.27 标准差 0.22 0.39 11.08 0.70 17.36 33.85 0.66 变异系数/% 17.88 9.45 44.13 53.79 35.78 29.72 51.59 分布类型 正态 正态 正态 对数正态 对数正态 对数正态 对数正态 表 4 不同林分类型的土壤肥力指标1)
Table 4 Soil fertility indicators of different forest stands
林分类型 容重/
(g·cm–3)pH w(有机质)/
(g·kg–1)w/(mg·kg–1) w(全氮)/
(g·kg–1)速效磷 速效钾 碱解氮 相思林 1.29±0.11a 4.12±0.12a 23.39±5.70ab 1.25±0.65a 46.98±14.32ab 109.83±14.39b 1.22±0.25ab 杉木林 1.24±0.08a 4.14±0.29a 26.22±6.08ab 1.40±0.40a 53.06±11.24a 114.70±13.58b 1.03±0.31b 桉树林 1.27±0.18a 4.11±0.13a 21.43±3.79b 1.12±0.50a 40.62±5.35b 107.16±29.54b 1.35±0.23ab 马尾松林 1.25±0.14a 4.23±0.22a 25.82±9.49ab 1.34±0.27a 46.71±6.7ab 106.12±14.52b 1.28±0.62ab 阔叶混交林 1.25±0.13a 4.24±0.31a 28.18±2.41a 1.42±0.05a 55.20±5.39a 132.28±9.02a 1.45±0.08a 平均值 1.26±0.02 4.17±0.03 25.10±0.90 1.31±0.06 48.50±1.42 113.87±2.76 1.27±0.05 1) 表中数据为平均值±标准误,同列数据后凡是有一个相同字母者表示不同林分类型间差异不显著(P>0.05, Duncan’s 法) 表 5 土壤肥力指标的主成分分析
Table 5 Principal component analysis of soil fertility indicators
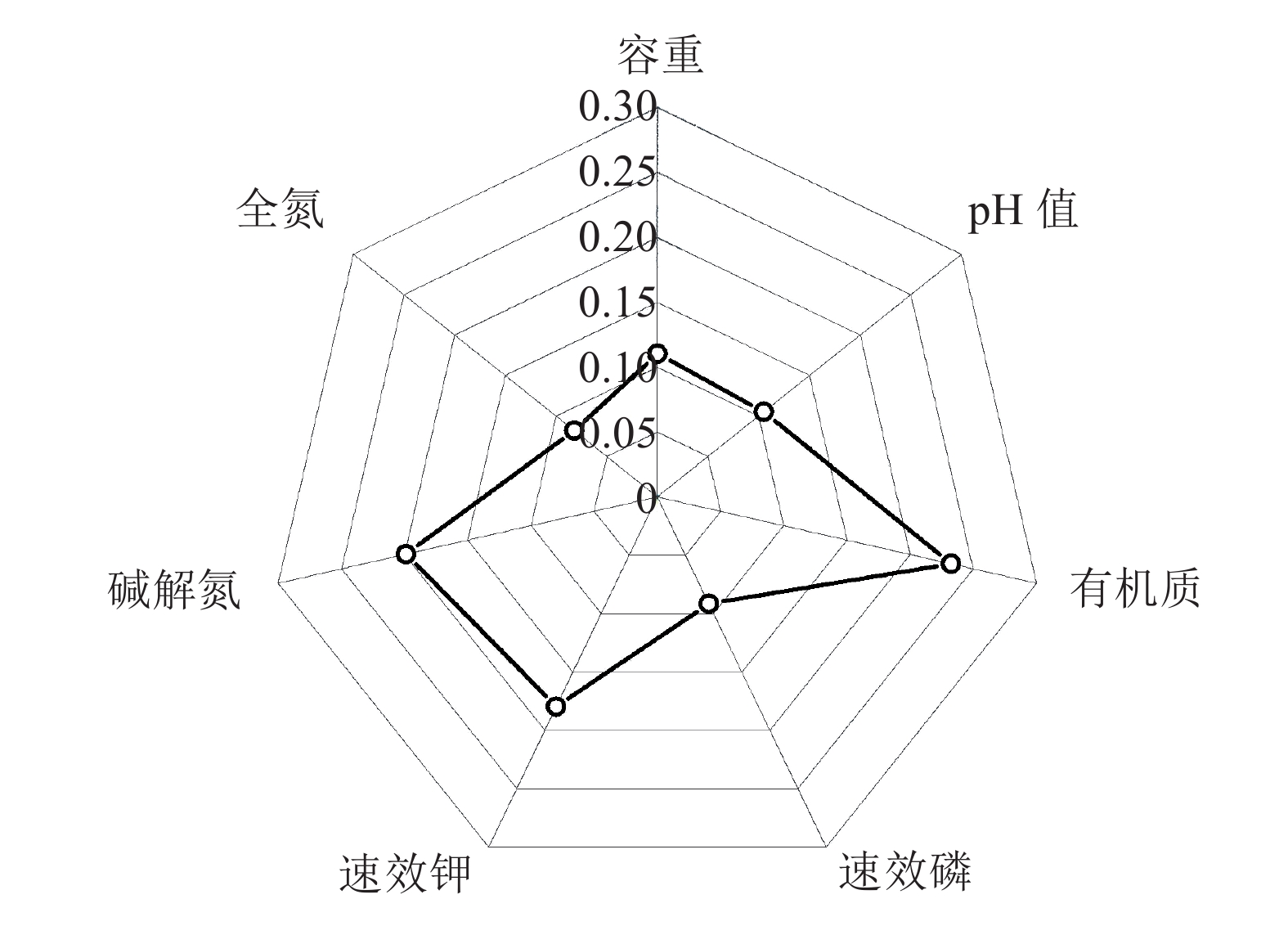
土壤指标 主成分特征向量 公因子方差 权重(ai) PC-1 PC-2 PC-3 容重 0.502 –0.175 –0.441 0.419 0.105 pH –0.175 0.707 0.137 0.567 0.141 有机质 0.801 –0.102 –0.009 0.720 0.180 速效磷 0.072 0.734 –0.056 0.531 0.132 速效钾 0.523 0.502 –0.258 0.605 0.151 碱解氮 0.712 0.094 0.235 0.598 0.149 全氮 0.134 –0.046 0.866 0.568 0.142 特征值 1.727 1.344 1.089 方差贡献率/% 24.671 19.198 15.552 累计方差贡献率/% 24.671 43.869 59.421 表 6 不同林分类型的土壤肥力综合评价
Table 6 Comprehensive evaluation of soil fertility of different forest stands
林分类型 主成分分析法 灰色关联分析法 相关关系法 内梅罗指数法 综合得分(S) 排序 灰色关联度(Ck) 排序 综合指数(IFI) 排序 内梅罗指数(P) 排序 相思林 0.402 4 0.622 4 0.446 4 0.294 4 杉木林 0.428 2 0.749 2 0.489 2 0.314 2 桉树林 0.380 5 0.611 5 0.420 5 0.290 5 马尾松林 0.414 3 0.691 3 0.457 3 0.309 3 阔叶混交林 0.439 1 0.965 1 0.519 1 0.357 1 表 7 单项土壤肥力指标的关联系数ξ(k, i)
Table 7 Correlation coefficients of individual soil fertility indicators
林分类型 容重 pH 有机质 速效磷 速效钾 碱解氮 全氮 相思林 0.442 0.778 0.496 0.997 0.742 0.426 0.470 杉木林 1.000 0.803 0.706 0.999 0.917 0.487 0.333 桉树林 0.410 0.765 0.412 0.999 0.618 0.399 0.673 马尾松林 0.528 0.977 0.666 0.996 0.736 0.389 0.544 阔叶混交林 0.753 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 -
[1] 全国土壤普查办公室. 中国土壤[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998. [2] GARAY I, PELLENS R, KINDEL A, et al. Evaluation of soil conditions in fast-growing plantations of Eucalyptus grandis and Acacia mangium in Brazil: A contribution to the study of sustainable land use[J]. Appl Soil Ecol, 2004, 27(2): 177-187.
[3] RODRIGUES DE LIMA A C, HOOGMOED W, BRUSSAARD L. Soil quality assessment in rice production systems: Establishing a minimum data set[J]. J Environ Qual, 2008, 37(2): 623-630.
[4] FISHER R F, BINKLEY D. Ecology and management of forest soils[J]. Eur J Soil Sci, 2001, 52(1): 169-170.
[5] BAUTISTA-CRUZ A, DEL CASTILLO R F, ETCHEVERS-BARRA J D, et al. Selection and interpretation of soil quality indicators for forest recovery after clearing of a tropical montane cloud forest in Mexico[J]. Forest Ecol Manag, 2012, 277: 74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.04.013
[6] 刘永贤, 熊柳梅, 韦彩会, 等. 广西典型土壤上不同林分的土壤肥力分析与综合评价[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(18): 5229-5233. [7] 杨晓娟, 王海燕, 刘玲, 等. 东北过伐林区不同林分类型土壤肥力质量评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2012, 21(9): 1553-1560. [8] 李萍, 王兵, 戴伟, 等. 亚热带几种林分类型的土壤肥力评价研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 2010, 32(3): 52-58. [9] GARRIGUES E, CORSON M S, ANGERS D A, et al. Soil quality in life cycle assessment: Towards development of an indicator[J]. Ecol Indic, 2012, 18: 434-442. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.12.014
[10] 安康, 谢小平, 张海珍, 等. 西湖风景区土壤肥力的空间格局及其影响因子[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(4): 1091-1096. [11] 周伟, 王文杰, 张波, 等. 长春城市森林绿地土壤肥力评价[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(4): 1211-1220. [12] MASTO R E, CHHONKAR P K, SINGH D, et al. Alternative soil quality indices for evaluating the effect of intensive cropping, fertilisation and manuring for 31 years in the semi-arid soils of India[J]. Environ Monit Assess, 2008, 136(1/2/3): 419-435.
[13] 骆伯胜, 钟继洪, 陈俊坚. 土壤肥力数值化综合评价研究[J]. 土壤, 2004, 36(1): 104-106. [14] 张凯旋, 商侃侃, 达良俊. 上海环城林带不同植物群落土壤质量综合评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(3): 71-77. [15] 金晶炜, 许岳飞, 熊俊芬, 等. 应用灰色关联度法评价砷污染土壤修复效果[J]. 水土保持通报, 2009, 29(6): 213-216. [16] 邓南荣, 吴志峰, 刘平, 等. 城市园林绿化用地土壤肥力诊断与综合评价:以广州市长虹苗圃为例[J]. 土壤与环境, 2000, 9(4): 287-289. [17] 吴玉红, 田霄鸿, 同延安, 等. 基于主成分分析的土壤肥力综合指数评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2010, 29(1): 173-180. [18] 周王子, 董斌, 刘俊杰, 等. 基于权重分析的土壤综合肥力评价方法[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2016, 35(6): 81-86. [19] 王大鹏, 王文斌, 郑亮, 等. 中国主要人工林土壤有机碳的比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(4): 698-704. [20] 李梅, 张学雷. 基于GIS的农田土壤肥力评价及其与土体构型的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(1): 129-136. [21] 叶回春, 张世文, 黄元仿, 等. 北京延庆盆地农田表层土壤肥力评价及其空间变异[J]. 中国农业科学, 2013, 46(15): 3151-3160. [22] 许仙菊, 马洪波, 陈杰, 等. 基于养分丰缺诊断和主成分分析相结合的桑园土壤肥力评价[J]. 土壤, 2013, 45(3): 470-476. [23] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. [24] 张同娟, 杨劲松, 刘广明, 等. 长江河口地区土壤肥力质量综合评价研究:以启东市为例[J]. 土壤通报, 2011, 42(3): 513-517. [25] 唐柄哲, 何丙辉, 闫建梅. 川中丘陵区土地利用方式对土壤理化性质影响的灰色关联分析[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(5): 1445-1452. [26] 赵串串, 安若兰, 赵巧玉, 等. 物元模型在玉树地区林地土壤养分评价中的应用[J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(6): 984-988. [27] 范海荣, 常连生, 王洪海, 等. 城市草坪土壤肥力综合评价[J]. 草业科学, 2010, 27(10): 17-22. [28] 温远光, 刘世荣, 陈放. 连栽对桉树人工林下物种多样性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(9): 1667-1671. [29] 刘飞鹏, 储双双, 裴向阳, 等. 华南3种人工林土壤有机质和养分含量及其综合评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(2): 81-85. [30] 冼干标, 薛立, 梁丽丽, 等. 佛山云勇林场3种人工幼林的生长和土壤养分特征[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2007, 28(4): 119-121. [31] 李静鹏, 徐明锋, 苏志尧, 等. 不同植被恢复类型的土壤肥力质量评价[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(9): 2297-2307. [32] 郝瑞军. 上海城市绿地土壤肥力特征分析与评价[J]. 上海农业学报, 2014, 30(1): 79-84. [33] 许松葵, 薛立. 6种阔叶树幼林的林地土壤特性[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2010, 31(4): 76-81. [34] 戎宇, 刘成刚, 薛建辉. 喀斯特山地不同人工林土壤特性差异与综合评价[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(2): 108-112.



 下载:
下载: