Genetic analysis and mapping of a rice purple leaf gene pl41
-
摘要:目的
对水稻材料pl41的紫叶性状进行遗传分析和基因定位,为pl41基因的图位克隆、功能研究及其育种利用奠定基础。
方法在紫叶籼稻品种‘Z3474’与绿叶粳稻品种‘日本晴’的杂交后代中,获得1个紫叶性状稳定遗传的材料pl41。观察pl41表型特征;配制pl41/日本晴杂交组合,利用F1及F2分离群体进行紫叶基因的遗传分析和基因定位研究。
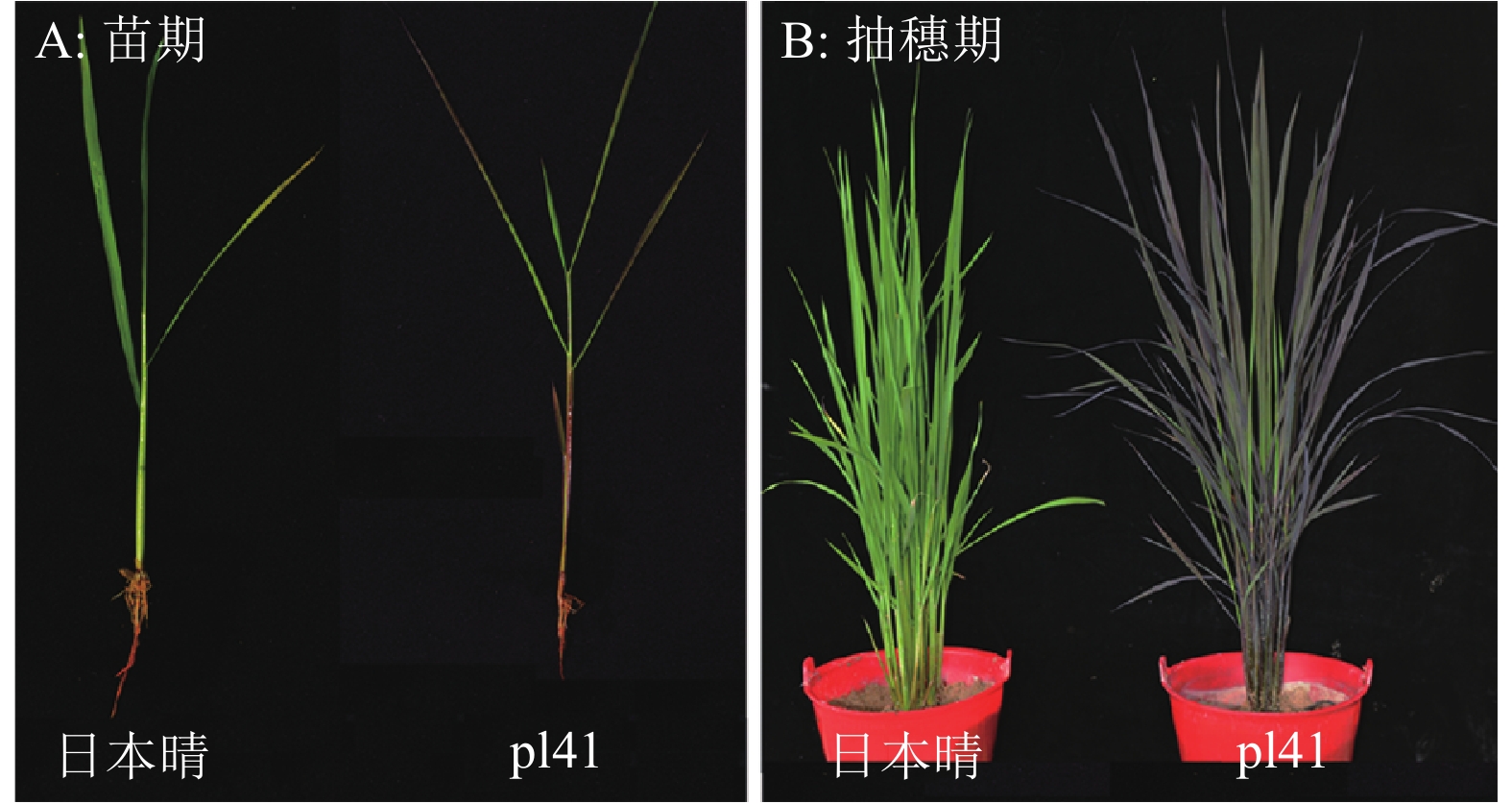
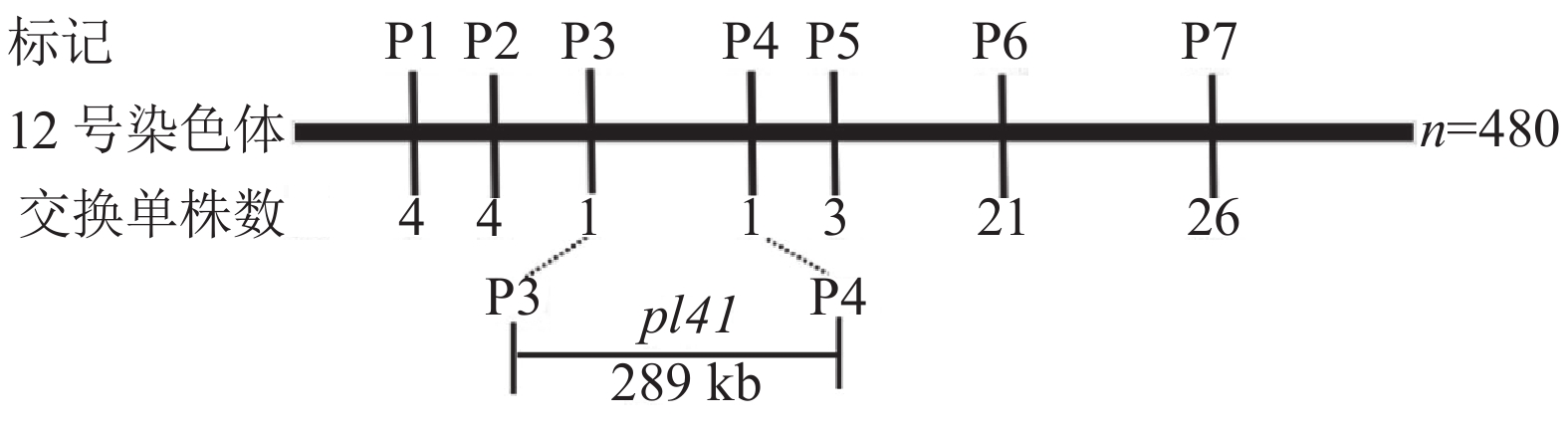
结果pl41紫色性状首先出现在苗期的叶鞘、叶尖和叶缘处,在抽穗期,pl41植株地上部分组织均呈现较深的紫色。与‘日本晴’相比,pl41叶绿素含量在苗期显著高于‘日本晴’,在抽穗期显著低于‘日本晴’,在灌浆期无显著差异;pl41花青素含量在苗期、抽穗期和灌浆期均极显著高于‘日本晴’。pl41紫叶性状受1对隐性核基因控制,定位在第12号染色体短臂289 kb范围内,对该区域5个预测基因的编码区序列进行了测序比对分析,发现其编码区序列在pl41与‘日本晴’之间无差异。
结论初步定位了水稻pl41紫叶基因的范围,其最终确定还需要候选基因的精细定位、序列比对分析和转录水平分析。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo carry out genetic analysis and gene mapping of purple leaf character in the rice material pl41, and provide a foundation for pl41 gene map-based cloning, function research and application in rice breeding.
MethodThe genetically stable purple leaf germplasm pl41 was derived from the hybrids of a purple leaf indica cultivar ‘Z3474’ and a green leaf japonica cultivar ‘Nipponbare’. The phenotypic characteristics of pl41 were surveyed. pl41 was crossed with ‘Nipponbare’, then F1 and F2 segregation progenies were used for genetic analysis and preliminary mapping of pl41 gene.
ResultThe purple character of pl41 firstly appeared in leaf sheath, leaf apex and leaf margin at seedling stage, then the aboveground parts of pl41 plant presented dark purple at heading stage. Compared to ‘Nipponbare’, chlorophyll content of pl41 was significantly higher at seedling stage, significantly lower at heading stage and there was no significant difference at filling stage. Anthocyanin contents of pl41 were all significantly higher than those of ‘Nipponbare’ at seedling, heading and filling stages. The purple leaf character of pl41 was controlled by a pair of recessive nuclear genes, which was mapped to a 289 kb region on the short arm of chromosome 12. By sequencing for coding sequences of five genes within this mapped region, no difference was found in coding sequences of these genes between Pl41 and ‘Nipponbare’.
ConclusionThe region of rice purple leaf gene pl41 is mapped preliminarily. The exact determination of pl41 depends on fine mapping, sequence alignment analysis and transcription analysis of candidate genes.
-
Keywords:
- rice (Oryza sativa L.) /
- purple leaf trait /
- genetic analysis /
- gene mapping /
- pl41 gene
-
随着人们生活水平的提高,消费者对牛奶质量和安全的要求也越来越高.酰胺类除草剂为触杀型除草剂,广泛用于大豆、玉米、以及谷物田中杂草的防治[1].至2007年,全球酰胺类除草剂的销售额占全球除草剂市场的7.9%[2].然而,乙草胺、异丙甲草胺和丁草胺等酰胺类除草剂在动物体内可以转化为致癌的代谢产物二烷基醌亚胺[3],致使动物发生癌症的风险提高.奶牛摄入被污染的饲料和水后,农药在奶牛体内积累[4],在生物富集放大的作用下,对人类的健康造成极大的威胁.因此,加强对牛奶中酰胺类除草剂的监测十分必要.
酰胺类除草剂常用的检测方法有气相色谱法[5]、液相色谱法[6]、气质联用法(GC-MS)[7]等.常用的样品前处理方法有液液萃取[8]、固相萃取等,因这些传统的样品前处理方法有机溶剂耗量大,提取过程繁琐、耗时,越来越多的科研人员致力于小型化和微型化前处理方法的研究.2006年,Rezaee等[9]提出了一种新型的样品前处理技术,分散液液微萃取技术(Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction, DLLME),在此技术中,微量的萃取剂(密度大于水)和分散剂分别加入到待测样品中,振荡混匀,使其形成一个萃取剂/分散剂/样品的乳浊液体系,此时,萃取剂以极小的液滴分散于样品溶液中,增大了萃取剂与目标分析物的接触面积,使目标分析物快速浓缩溶解在萃取剂液滴中,经过离心,包含目标分析物的有机相沉于底部.该技术极大地减少了有机溶剂的使用量,缩短了提取时间,是一个简单、高效、环境友好的前处理方法.
目前,分散液液微萃取技术已经广泛地应用于水[10]、果汁、蔬菜等样品中农药残留的检测,白沙沙等[11]运用磁性石墨烯固相萃取-分散液液微萃取法测定了水和绿茶中5种酰胺类除草剂残留,王鹤等[12]运用液液微萃取技术检测了水中4种酰胺类除草剂;用分散液液微萃取技术对牛奶中农药残留的检测也有少许报道,如Natalia等[13]运用该技术检测了牛奶中阿维菌素等大内环酯类农药.Farajzadeh等[14]和Gao等[15]分别测定了牛奶中三唑类农药和磺酰类药物的残留.本文建立了分散液液微萃取技术测定牛奶中4种酰胺类农药的方法,并对影响试验效率的因素如萃取剂种类和体积的选择,分散剂种类和体积的选择,提取时间等进行了讨论和优化,在最优试验条件下,对实际牛奶样品进行了检测.
1. 材料与方法
1.1 主要仪器和试剂
Agilent 6890N-5975气相色谱质谱联用仪(Agilent,USA); SZ-93自动双重纯水蒸馏器(上海亚荣生化仪器厂);Anke TDL-4离心机(上海安亭科学仪器厂);移液枪(德国艾本德公司);微型进样器(上海亿圣仪器仪表有限公司);BS124S电子分析天平(赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司).
农药标准品:甲草胺质量浓度100 mg·L-1、乙草胺质量浓度100 mg·L-1、丙草胺质量浓度100 mg·L-1、异丙甲草胺质量浓度100 mg·L-1,均在农业部环境保护科研监测所购买.用色谱纯乙腈将其配制成适当质量浓度的混合标准储备液,将此储备液逐级稀释配制成质量浓度分别为0.05、0.10、0.50、1.00和5.00 mg·L-1的混合标准系列溶液,储存于冰箱中.
甲醇、乙腈、丙酮、二氯甲烷、三氯甲烷、四氯化碳、氯苯均为分析纯,体积分数均大于99%,为天津市富宇精细化工有限公司产品;色谱纯乙腈为美国Fisher公司产品.纯牛奶样品从附近大型超市购得.
1.2 色谱条件
气相色谱(Gas chromatography)分析条件:Rtx-5MS石英毛细管色谱柱(30 m×0.32 mm×0.25 μm);He载气(体积分数为99.999%),载气流速1.00 mL·min-1;不分流进样,进样体积1.0 μL.进样口温度270 ℃;柱温采用程序升温:初始温度150 ℃,以10 ℃·min-1升温至250 ℃,保持2 min.
质谱(Mass spectrum)分析条件:接口温度280 ℃;离子源为电子轰击源(EI),电子能量70 eV;离子源温度230 ℃;四级杆温度150 ℃;采用选择离子方式(SIM)监测,所选择的质量碎片信息见表 1.在最优的色谱条件下,对质量浓度为1.00 mg·L-1的4种酰胺类农药混合标准液进行了上机测定,结果见图 1,此时,目标峰峰形良好,且分离度高.
表 1 4种酰胺类除草剂的保留时间和特征离子Table 1. The retention time and characteristic ions of four amide herbicides
1.3 样品预处理
1.3.1 提取
准确量取牛奶5.0 mL于10.0 mL离心管中,加入乙腈2.0 mL和NaCl 1.0 g,涡旋振荡1.0 min,然后在4 000 r·min-1的转速下离心10.0 min,离心后,蛋白质等大分子物质沉于底部,取0.5 mL上层提取液于尖底玻璃管中,用氮气流将乙腈吹干.
1.3.2 分散液相微萃取(DLLME)过程
在尖底玻璃管中加入去离子水5.0 mL,目标化合物溶解于离子水中形成样品溶液.将含有0.80 mL分散剂和40 μL提取剂的混合液快速注入样品溶液中,涡旋振荡提取1.0 min,提取剂以极细小的液滴的形式均匀分散在样品溶液中,样品溶液形成一个乳浊液体系,样品溶液中的目标待测物被浓缩至提取剂液滴中,然后以3 500 r·min-1的转速离心3.0 min,因提取剂密度大于水,故离心后会沉积至离心管底部,将上层水相移去,用微量进样针取1.0 μL有机相进行色谱分析.
1.3.3 计算方法
为了评价该方法的萃取效率,本文使用提取回收率(Extraction recovery)作为评价指标,并通过公式(1)计算获得.

(1) 其中,norg为萃取溶剂中目标分析物的量,n0为牛奶样品中目标分析物的量,ρorg和Vorg分别为萃取溶剂中目标分析物的质量浓度以及萃取结束后萃取溶剂的体积,ρ0为牛奶中目标分析物的质量浓度,Vaq为牛奶样品的体积.
2. 结果与分析
为获得最优试验条件,本文对影响萃取效率的因素,如萃取剂的种类和体积,分散剂的种类和体积,萃取时间以及盐浓度等进行了讨论和优化.
2.1 影响因素
2.1.1 萃取剂种类的选择
萃取剂是影响萃取效率的重要因素之一,首先萃取剂对目标分析物要有良好的萃取效果,萃取效率常遵循“相似相容原则”;其次萃取剂在水中要有较小的溶解度并且密度要大于水.基于以上条件,本试验分别选择相同体积(50 μL)的二氯甲烷、氯苯、三氯甲烷和四氯化碳作为萃取溶剂,用单因子变量的方法对4种萃取剂的萃取效果进行了评价,结果如图 2所示,四氯化碳对4种酰胺类萃取剂的萃取效率最高,萃取回收率为68%~75%;三氯甲烷次之,萃取回收率为50%~53%;氯苯和二氯甲烷最差,萃取回收率只有34%~48%,根据上述结果,本试验选择四氯化碳作为萃取剂.
2.1.2 萃取剂体积的选择
萃取剂体积影响试验的萃取效率,当萃取剂体积过大时,虽然样品中分析物的提取会更完全,但是,稀释效应会导致目标分析物在萃取剂中的浓度降低,从而使富集效果变差.萃取剂体积过小时,首先,会导致对目标分析物萃取不完全,萃取回收率降低;其次,体积过小不便于后续试验过程中萃取剂的收集.综合以上因素,本试验选择5种不同体积的四氯化碳(40、50、60、70和80 μL)对样品进行萃取,结果如图 3所示,各目标分析物的萃取效率均随着萃取剂体积的增大而变小,这可能是由于萃取剂体积的增大对目标分析物起到稀释效应,目标分析物浓度降低,进而萃取效率降低.故本试验选择的萃取剂体积为40 μL.
2.1.3 分散剂种类的选择
分散剂影响萃取剂在水相中的分散效果,在分散剂的作用下,萃取剂以极小的液滴分散在样品中,增大了样品与萃取剂的接触面积,从而使样品中的目标分析物被快速地萃取至有机相中.分散剂既要溶于萃取剂,又要溶于水相,本研究比较了甲醇、乙腈和丙酮3种分散剂对萃取效果的影响,结果(图 4)表明,甲醇做分散剂时,取得了相对较好的萃取效果.故本试验选择甲醇作为分散剂.
2.1.4 分散剂体积的选择
分散剂体积影响分散效果和沉积相体积大小,本文讨论了400、600、800、1 000和1 200 μL 5种不同体积的甲醇作为分散剂时对萃取效率的影响,结果(图 5)表明,当分散剂体积从400 μL增至1 000 μL时,萃取效率逐渐增加,并在1 000 μL时达最大值,当分散剂体积大于1 000 μL时,萃取效率反而减小.这可能是由于分散剂体积过小时,萃取剂在水相中分散程度较低,导致萃取效率较低,随着分散剂体积的增大,分散效果逐渐提高,进而逐步提高了萃取效率;当分散剂体积过大时,目标分析物在水相中的溶解度增大,致使萃取效率减小.因此,本试验选择1 000 μL的甲醇为分散剂.
2.1.5 涡旋时间对萃取效率的影响
涡旋振荡提取的目的是使萃取剂-分散剂-水相三相形成一个乳化体系,并在乳化状态下保持一定的时间.因此,涡旋转速和涡旋时间都可以影响萃取效率,Yiantzi等[16]报道,涡旋转速越大,萃取效率越高.本试验所用涡旋振荡仪的工作效率为2 000 rad·min-1,故本研究只讨论涡旋时间对萃取效率的影响.在其他萃取条件相同的情况下,本试验设定了5组不同的涡旋时间(0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0和2.5 min),结果见图 6,涡旋时间由0.5 min升至1.0 min时,目标分析物的萃取效率也随之升高,当涡旋时间大于1.0 min时,萃取效率变化不大.说明萃取剂在1.0 min内已经完成了对目标分析物的萃取,故本试验选择的涡旋时间为1.0 min.
2.1.6 盐质量浓度对试验萃取效率的影响
盐析效应被普遍应用于液液萃取和固相微萃取中,通常,盐的加入能够降低目标分析物在水相中的溶解度,促进目标分析物进入有机相.此外,盐还能够促进水相和有机相的分层,Farajzadeh等[14]发现,随着水相中盐质量浓度的增加,能够收集到的有机相的体积也在增加.本试验考察了水相中不同质量浓度NaCl(0.01、0.02、0.03、0.04和0.05 g·mL-1)对试验效率的影响,结果见图 7,随着盐质量浓度的增加,甲草胺、丙草胺和异丙甲草胺的萃取效率都随之增加,然而乙草胺的萃取效率却有下降趋势,这是因为盐析效应对不同化合物的影响不同,综合考虑,本试验选择0.05 g·mL-1的NaCl作为试验条件,此时,甲草胺、丙草胺和异丙甲草胺的萃取效率达到最大,而乙草胺的萃取效率下降不明显.
2.2 方法的线性、准确度、检出限
用色谱乙腈将农药标准储备液分别稀释为0.05、0.10、0.50、1.00和5.00 mg·L-1系列质量浓度梯度,在最优色谱条件下上机测定,以各农药标准液的质量浓度(ρ)为横坐标,峰面积(A)为纵坐标,作标准曲线.结果见表 2,4种酰胺类农药在0.05~5.00 mg·L-1范围内均具有良好的线性关系,线性相关系数≥0.997 8.检出限(LOD)是根据信噪比(S/N)为3时获得,结果在0.8~1.4 μg·L-1之间.
表 2 方法的线性、相关系数、检出限Table 2. Linearity, correlation coefficients, and limit of detection of the method
2.3 样品分析
在牛奶样品中分别设置0.01、0.05和0.10 mg·L-1 3个质量浓度水平进行添加回收试验,每个添加质量浓度重复5次,按照上述最优的样品前处理方法萃取并上机分析,结果见表 3,4种酰胺类农药的添加回收率为67.00~105.7%,相对标准偏差(RSD)为1.6%~8.3%.此外,样品中的基质没有对目标峰造成干扰,结果见图 8和图 9.
表 3 4种酰胺类除草剂在牛奶样品中的添加回收率和相对标准偏差Table 3. Recoveries and relative standard deviations of four amide herbicides in milk samples
2.4 与其他前处理方法的比较
分散液液微萃取技术与其他前处理技术比较结果见表 4.在酰胺类农药的分析测定中,分散液液微萃取技术消耗的有机溶剂量明显比分散固相微萃取和固相萃取少, 比固相微萃取更为省时, 重复性和检出限也均优于其他方法.
表 4 不同方法对酰胺类除草剂分析测定的比较Table 4. Comparisons of DLLME-GC-MS with other methods for the extraction and determination of amide herbicides
3. 结论
本研究经过一系列试验,优化了试验条件,使得本试验的回收率达到67.0%~105.7%,相对标准偏差小于8.3%.本方法运用分散液液微萃取技术分析测定了牛奶中的酰胺类除草剂,与原有文献研究相比,实现了酰胺类除草剂的小型化分析,也为以后牛奶中的农药残留研究打下了基础.另外,萃取剂种类是分散液相微萃取技术的关键,由于萃取剂密度必须大于水,所以目前供选择的萃取剂大多都是含氯的溶剂,如氯苯、二氯甲烷、三氯甲烷和四氯化碳.这些溶剂大都毒性较高,因此,寻找更加高效、环保的萃取剂是分散液相微萃取技术有待进一步解决的问题.本方法属于新型化和小型化前处理方法,符合市场上大批量样品的监督和检测的需求,所以有继续优化和研究的必要.综上所述,分散液液微萃取技术在农药残留分析领域的应用具有极大的潜力,需要针对该方法的某些不足进行进一步的改进,以实现对食品安全更好的监督.
-
表 1 pl41和‘日本晴’在3个不同发育时期叶绿素、类胡萝卜素及花青素含量比较1)
Table 1 Comparisons of chlorophyll, carotenoid and anthocyanin contents between pl41 and ‘Nipponbare’ at three different developmental stages
生长期 材料 w(mg·g–1) 花青素相对含量 叶绿素a 叶绿素b 总叶绿素 类胡萝卜素 苗期 pl41 5.37±0.52** 1.13±0.10** 6.50±0.62** 2.07±0.19** 2.73±0.07*** 日本晴 4.05±0.06 0.82±0.01 4.87±0.07 1.54±0.02 0.07±0.01 抽穗期 pl41 2.68±0.18** 0.47±0.07** 3.15±0.24** 1.03±0.04** 17.00±0.35*** 日本晴 4.78±0.33 1.30±0.14 6.08±0.47 1.94±0.12 0.08±0.44 灌浆期 pl41 3.20±0.18 0.65±0.04 3.85±0.22 1.65±0.08 10.88±0.43*** 日本晴 3.44±0.19 0.65±0.04 4.09±0.23 1.66±0.08 0.02±0.01 1) “**”和“***”分别表示pl41和‘日本晴’相同时期的相同指标在 0.01 和 0.001 水平差异显著(t 检验法) 表 2 pl41初步定位所用引物
Table 2 Primers used in preliminary mapping of pl41
名称 分子标记类型 正向序列(5′→3′) 反向序列(5′→3′) P1 SSR GCTTCCCTTGTATACTCTATCT CCTCTTATCAGACGCACAA P2 SSR CTTCTTCCCGTTGTTCCCAA GTTTGGAGGTGAGCTGGACA P3 STS TGGTAACTAGTACTCTCCCTT CTTCTGTAACTCCATTCTGA P4 STS TTTTAACATCTCCATTCTCG GACGAATAGTCAAACAGTGC P5 STS TGTTGAATATGCACAAAGAG TGGTTCATTGGCTTAGGA P6 STS TTATTCCCCGACCAATCAAC CAAATTCCGCTTGGTATTGAC P7 STS TCCCAATCATGGAAATACTT TTGTTTCTTAGAAGCAGAGG 表 3 定位区间内的基因注释
Table 3 Gene annotation in the preliminary mapped region
编号 基因功能注释 基因 ID 编号 基因功能注释 基因 ID 1 DUF567 结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g02720 28 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g03000 2 组氨酸三聚体家族蛋白 LOC_Os12g02730 29 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g03010 3 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g02750 30 转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g03020 4 DUF567 结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g02760 31 保守的假定蛋白 LOC_Os12g03030 5 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g02770 32 无顶端分生组织蛋白 LOC_Os12g03040 6 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g02780 33 无顶端分生组织蛋白 LOC_Os12g03050 7 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g02790 34 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g03060 8 CRP11–富含半胱氨酸蛋白前体 LOC_Os12g02800 35 FHA 结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g03070 9 蛋白激酶结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g02810 36 rp3 蛋白 LOC_Os12g03080 10 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g02814 37 核糖体蛋白 LOC_Os12g03090 11 胞苷酰基转移酶结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g02820 38 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g03094 12 SNF7 结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g02830 39 结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g03100 13 ATCHX 蛋白 LOC_Os12g02840 40 ZF–HD 蛋白二聚化结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g03110 14 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g02850 41 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g03120 15 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g02860 42 CDC45A–假定的DNA复制起始蛋白 LOC_Os12g03130 16 GRAS 家族转录因子结构域包含蛋白 LOC_Os12g02870 43 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g03140 17 E2F 相关蛋白 LOC_Os12g02880 44 MYB 类转录因子蛋白 LOC_Os12g03150 18 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g02890 45 转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g03160 19 反转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g02900 46 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g03170 20 糖基转移酶 LOC_Os12g02910 47 Mad3/BUB1 同源蛋白 LOC_Os12g03180 21 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g02920 48 高丝氨酸脱氢酶 LOC_Os12g03190 22 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g02930 49 MATE 转运蛋白 LOC_Os12g03200 23 EMB2748 蛋白 LOC_Os12g02950 50 转座子蛋白 LOC_Os12g03210 24 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g02940 51 表达蛋白 LOC_Os12g03220 25 谷胱甘肽–S–转移酶 LOC_Os12g02960 52 MATE 转运蛋白 LOC_Os12g03230 26 RNA 结合蛋白 LOC_Os12g02970 53 MATE 转运蛋白 LOC_Os12g03240 27 核苷三磷酸酶 LOC_Os12g02980 -
[1] WU D, SHU Q, XIA Y. In vitro mutagenesis induced novel thermo/photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterile indica rice with green-revertible xanthan leaf color marker[J]. Euphytica, 2002, 123(2): 195-202.
[2] 曹立勇, 钱前, 朱旭东, 等. 紫色标记籼型光–温敏核不育系中紫S的选育及其配组的杂种优势[J]. 作物学报, 1999, 25(l): 44-49. [3] 杨腾帮, 许旭明, 张受刚. 具有隐性紫叶标记性状的籼型光敏核不育系明紫02S的选育[J]. 福建农业科技, 2005(l): 3-5. [4] 杨腾帮, 许旭明, 张受刚, 等. 隐性紫叶光温敏核不育水稻明紫03S的选育[J]. 福建农业科技, 2005(5): 54-56. [5] 余显权, 吴平理, 赵福胜, 等. 隐性紫叶水稻的改良及其应用探讨[J]. 贵州农业科学, 2003, 31(3): 3-6. [6] 向关伦, 黄宗洪, 杨占烈, 等. 水稻不育系紫IIA的选育[J]. 种子, 2007, 26(1): 93-95. [7] 邓国富, 梁世荣, 周萌, 等. 水稻紫红叶标记不育系先红A的选育及应用[J]. 中国稻米, 2008(5): 26-28. [8] XIE D Y, SHARMA S B, WRIGHT E, et al. Metabolic engineering of proanthocyanidins through co-expression of anthocyanidin reductase and the PAP1 MYB transcription factor[J]. Plant J, 2006, 45(6): 895-907.
[9] MARRS K A, ALFENITO M R, LLOYD A M, et al. A glutathione S-transferase involved in vacuolar transfer encoded by the maize gene Bronze-2[J]. Nature, 1995, 375(6530): 397-400.
[10] GOODMAN C D, CASATI P, WALBOT V. A multidrug resistance-associated protein involved in anthocyanin transport in Zea mays[J]. Plant Cell, 2004, 16(7): 1812-1826.
[11] SAITOH K, ONISHI K, MIKAMI I, et al. Allelic diversification at the C (OsC1) locus of wild and cultivated rice: Nucleotide changes associated with phenotypes[J]. Genetics, 2004, 168(2): 997-1007.
[12] SAKAMOTO W, OHMORI T, KAGEYAMA K, et al. The purple leaf (pl) locus of rice: pl w allele has a complex organization and includes two genes encoding basic helix-loop-helix proteins involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis[J]. Plant Cell Physiol, 2001, 42(9): 982-991.
[13] MONNA L, LIN H, KOJIMA S, et al. Genetic dissection of a genomic region for a quantitative trait locus, Hd3, into two loci, Hd3a and Hd3b, controlling heading date in rice[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2002, 104(5): 772-778.
[14] WANG W Y, DING H F, LI G X, et al. Delimitation of the PSH1(t) gene for rice purple leaf sheath to a 23.5 kb DNA fragment[J]. Genome, 2009, 52: 268-274.
[15] KITAMURA S, SHIKAZONO N, TANAKA A. TRANSPARENT TESTA 19 is involved in the accumulation of both anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant J, 2004, 37(1): 104-114.
[16] DEBEAUJON I, PEETERS A J M, LÉON-KLOOSTERZIEL K M, et al. The TRANSPARENT TESTA12 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a multidrug secondary transporter-like protein required for flavonoid sequestration in vacuoles of the seed coat endothelium[J]. Plant Cell, 2001, 13: 853-871.



 下载:
下载: