Fast and nondestructive gender detection of Bombyx mori chrysalis in the cocoon based on near infrared transmission spectroscopy
-
摘要:目的
利用近红外漫透射光谱快速无损鉴别家蚕Bombyx mori种茧茧壳内蚕蛹的雌雄,以提高育种效率、降低人工成本。
方法以芙9、9芙、湘7和7湘4个蚕品种为研究对象,采集比较了样本在可见和近红外区间的漫透射光谱,建立比较了各品种偏最小二乘判别分析(PLSDA)、后向传播神经网络(BPNN)以及支持向量机分类(SVM)判别模型,通过分类器特性(ROC)曲线研究了各模型的鲁棒性,采用差值法和遗传算法提取了特征波长。
结果芙9、9芙、湘7和7湘品种利用450~900 nm光谱建模的雌雄鉴别准确率分别为95.20%、95.65%、88.80%和87.50%,利用900~1 700 nm 光谱建模的准确率分别为100%、96.00%、92.22%和94.21%;采用PLSDA、BPNN和SVM模型都能够对蚕蛹雌雄做出较好的无损鉴别,3种模型真雌性率分别为95.96%、95.83%和100%,真雄性率分别为98.98%、96.04%和82.18%,准确率分别为97.46%、95.94%和90.86%,进一步通过ROC曲线分析,PLSDA模型效果最优,BPNN模型次之;手动提取20个波段建立PLSDA模型,鉴别真雌性率为93.75%,真雄性率为95.45%,准确率为94.57%。
结论近红外波段900~1 700 nm的漫透射光谱比可见–近红外波段450~950 nm含有更丰富的蚕蛹雌雄分类信息;3种鉴别模型中,PLSDA模型效果最优;提取特征波段后,准确率能达到生产需要。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo identify the gender of Bombyx mori chrysalis in the cocoon by rapid and non-destructive method based on near infrared transmission spectroscopy, improve breeding efficiency and reduce labor cost.
MethodWe used four silkworm varieties including Fu 9, 9 Fu, Xiang 7 and 7 Xiang, and compared their diffuse transmission spectra between 450-950 nm and 900-1700 nm. Partial least squares discrimination analysis (PLSDA), back propagation neural network (BPNN) and support vector machine (SVM) discrimination models were established and compared among different varieties. The robustness of the models was studied through the receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve. Characteristic wavelengths were extracted by difference method and genetic algorithm.
ResultThe identification accuracy rates for Fu 9, 9 Fu, Xiang 7 and 7 Xiang varieties were 95.20%, 95.65%, 88.80% and 87.50% respectively using 450-950 nm spectra, and were 100%, 96.00%, 92.22% and 94.21% respectively using 900-1 700 nm spectra. Using PLSDA, BPNN and SVM models resulted in good identification of male and female silkworm pupae, the true female rates were 95.96%, 95.83% and 100%, the true male rates were 98.98%, 96.04% and 82.18%, and the accuracy rates were 97.46%, 95.94% and 90.86%, respectively. Based on the analysis of ROC curve, the PLSDA model was the optimal, followed by the BPNN model. Twenty bands were extracted manually as the equipment input, and the true female rate, true male rate and accuracy rate were 93.75%, 95.45% and 94.57% respectively based on the PLSDA model.
ConclusionDiffuse transmission spectra in the near infrared (900-1 700 nm) contains more classification information of male and female pupae compared with the visible-near infrared (450-950 nm). The PLSDA model is the optimal one among three models. After extracting the characristic bands, the accuracy rate can meet the requirements of actual production.
-
Keywords:
- Bombyx mori /
- silkworm chrysalis /
- gender /
- near infrared spectroscopy /
- diffuse transmission /
- band /
- nondestructive detection
-
中国是世界蚕丝业的发源地,我国已有5 000多年的植桑养蚕的历史,蚕桑产业是我国最具特色的传统优势产业之一,为中华民族经济的发展做出了巨大的贡献,而且对民族文化的传播与弘扬也起了极为重要的作用[1-3]。根据农业部种植业管理司的统计,2015年,我国桑园面积8.218×105 hm2,发种量1 585.58万张,蚕茧产量6.379×105 t[2],是世界上最大的蚕丝生产国和出口国[4-5]。
蚕丝产业是一个包括品种选育、蚕种制造、栽桑养蚕、鲜茧收烘、干茧流通、缫丝织绸、印染加工、外贸出口和多元利用在内的完整产业链,良种繁育是其中的重要环节。目前我国茧丝生产中使用的都是1代杂交种,蚕种场需要在蚕蛾羽化之前把蚕茧削开倒出蚕蛹进行雌雄辨别,以便对交品种羽化时间的调节和保证杂交彻底[6-8]。蚕上蔟后,经过1周进行茧质调查后削茧鉴蛹,削茧过早,容易发生伤蛹而感染病原,增加死蛹机会;时间太晚,雌雄蛹鉴别时间紧张,且准确率降低,影响杂交率,因此常常要在短短4~5 d内完成削茧鉴蛹。由于蚕种场的制种量大,时间紧迫,工人的劳动强度很大,往往需要聘请大量临时工,劳动力成本很高。在发蛾之前能预先快速无损识别蚕茧内蚕蛹的雌雄,对降低种场工人的劳动强度,提高制种效率和企业经济效益,有着重要的作用。目前不削茧辨性的方法有荧光蚕茧辨性(Fluorescent cocoon sex identification, FCSI)、磁共振成像(Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI)、X射线成像技术等,但存在只适用于特定的FCSI蚕品种、检测费用高、检测时间长或者检测精度不高等问题。
近红外光(Near infrared, NIR)是介于可见光谱区和中红外光谱区之间的电磁波,波长范围约为780~2 526 nm[9-10]。蚕茧中茧丝的化学构成主要有丝素和丝胶2种蛋白质,还含有极少量的蜡物质、碳水化合物、色素和无机物,蚕蛹的主要成分是脂肪、蛋白质和水。使用近红外光谱无损检测完整的蚕茧样本时,茧丝中的丝素蛋白、丝胶蛋白及蚕蛹蛋白中含有的C-H、O-H、N-H等含氢基团会对近红外光谱产生特征吸收, 茧壳内蚕蛹雌雄组分的比例和构成不同(例如雌性蚕蛹中包含大量的蚕卵,雄性没有),完整蚕茧样本的近红外光谱能够反映雌雄蚕蛹之间的不同[6-8]。本文从样本选择、光谱仪波段选择、光路构建、分析建模、特征波段提取等方面进行了研究,并设计了用于蚕茧快速无损性别鉴别的样机,以期为蚕桑行业专用的光谱检测设备提供理论基础和实践依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 蚕蛹雌雄检测样机系统构成
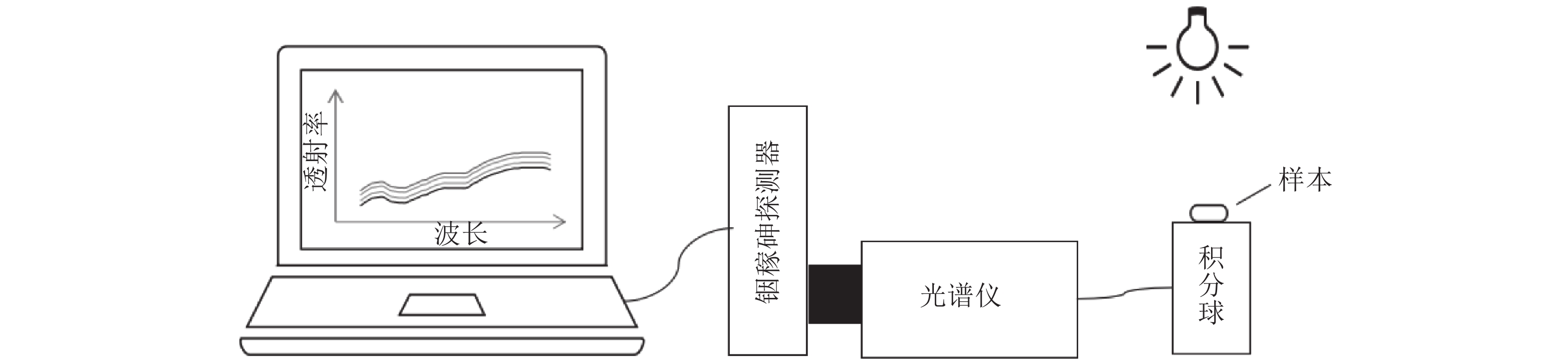
将完整的蚕茧样本逐个放到采集系统的检测工位进行检测。采集系统的构成采用100 W的卤素灯作为光源(出射光通过隔热片照射样本),漫透射光通过积分球收集,然后通过600 μm光纤连接到光谱仪。为了比较不同波段的建模效果,分别选用2种不同光谱仪进行采集:Maya2000pro型便携式光纤光谱仪(检测范围:175~1 100 nm;内置探测器:Hamamatsu S10420;信噪比:450:1;Ocean optics, 美国)和NirQuest512型便携式光纤光谱仪(检测范围:850~1 700 nm;探测器:Hamamatsu G9204-512,InGaAs线性阵列;Ocean optics, 美国)。光谱仪设置积分时间均为200 ms, 平均次数为4以提高数据的稳定性,平滑宽度为4以匹配系统的分辨率,系统构成如图1所示。
1.2 蚕蛹样本和雌雄检测
广东省蚕种生产中主要使用的原种品种有芙9、9芙、湘7和7湘共4个品种。在2016年9月、10月和11月,分批次从广东丝源集团的蚕种场取得这4个品种样本,每次样本数量在97~600枚之间。根据蚕蛹的腹部第8、9腹节外部特征,削茧取蛹进行雌雄辨别,对难以判别的则解剖蚕蛹的腹部,以是否有卵来判别雌雄[11-12]。
1.3 光谱预处理
采集到的原始光谱数据X使用Savitzky-Golay卷积平滑求导以消除光谱数据的噪声以及基线平移(滤波器宽度:15,多项式阶数:2,求导阶数:1)。用于表征样本雌雄的Y矩阵采用平均中值方法预处理,从各变量中扣除没有信息含量的均值部分。
1.4 建模方法及评价标准
本文主要采用了偏最小二乘判别分析(Partial least squares discrimination analysis,PLSDA)来建立判别模型。在本文中PLSDA模型所产生的结果如非特别说明,均以留一法交叉验证的方式进行无偏验证,即在验证过程中取出1个样本,用剩下的样本重新建立PLSDA模型,并用该模型对取出的样本进行分类预测,不断重复这个过程,直到所有的样本都被预测完成。计算潜变量(Latent variable,LV)数量的选择基于验证均方根误差(Root mean square error of cross validation,RMSECV)最小的原则。后向传播神经网络(BPNN)和支持向量机分类(SVM)算法也被用来进行分类器效果的比较。分类器的评价指标采用真雌性率、真雄性率和准确率来评价, 其计算公式如下:
真雌性率=雌性正确鉴定数/雌性样本数×100%,
真雄性率=雄性正确鉴定数/雄性样本数×100%,
准确率=雌雄正确鉴定数/雌雄样品总数×100%。
分类器特性(ROC)曲线以及曲线下的面积(Area under curve,AUC)也被用来进一步评价各个分类算法的鲁棒性,其AUC值越大,表征分类器的效果越好[13]。
1.5 光谱数据的特征波长选择方法
为了简化模型,本文采用了自行设计的差值法和遗传算法[14](Genetic algorithm,GA)进行特征波长选择。差值法是利用PLSDA算法的系数矩阵和光谱数据的分布特征对光谱数据进行了变量选择,具体是对光谱数据进行预处理后,求取雌性光谱均值与雄性光谱均值的差,再乘以PLSDA算法的系数矩阵B,可得到蚕蛹雌雄光谱的差值,即:Δy=B(x雌–x雄),Δy数值较大时则反映对应的波长点对分辨雌雄比较重要。通过设置合理的Δy阈值与结合各个单点的建模效果,最终可以提取建模用特征波长。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同光谱波段间的漫透射光谱比较
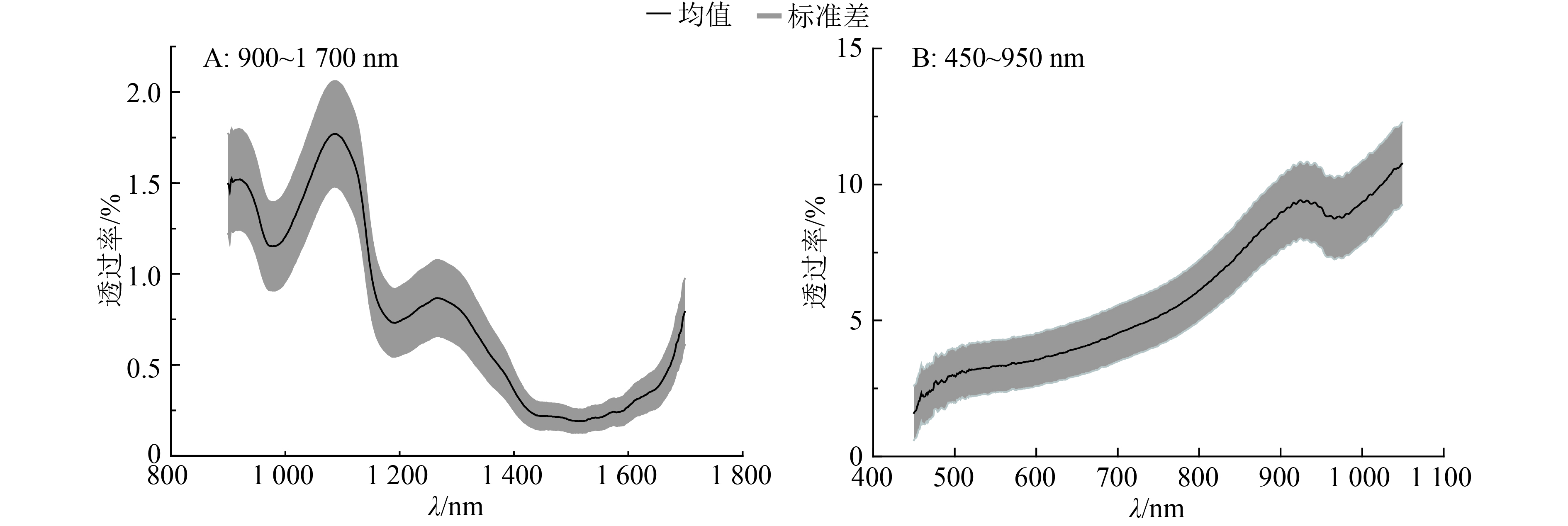
为了寻找合适鉴别的光谱波段,试验采集比较了97枚芙9样本在可见–近红外450~950 nm以及在近红外900~1 700 nm之间的漫透射光谱,如图2所示,在近红外900~1 700 nm之间的波峰波谷信息比在可见–近红外450~950 nm范围内要丰富。
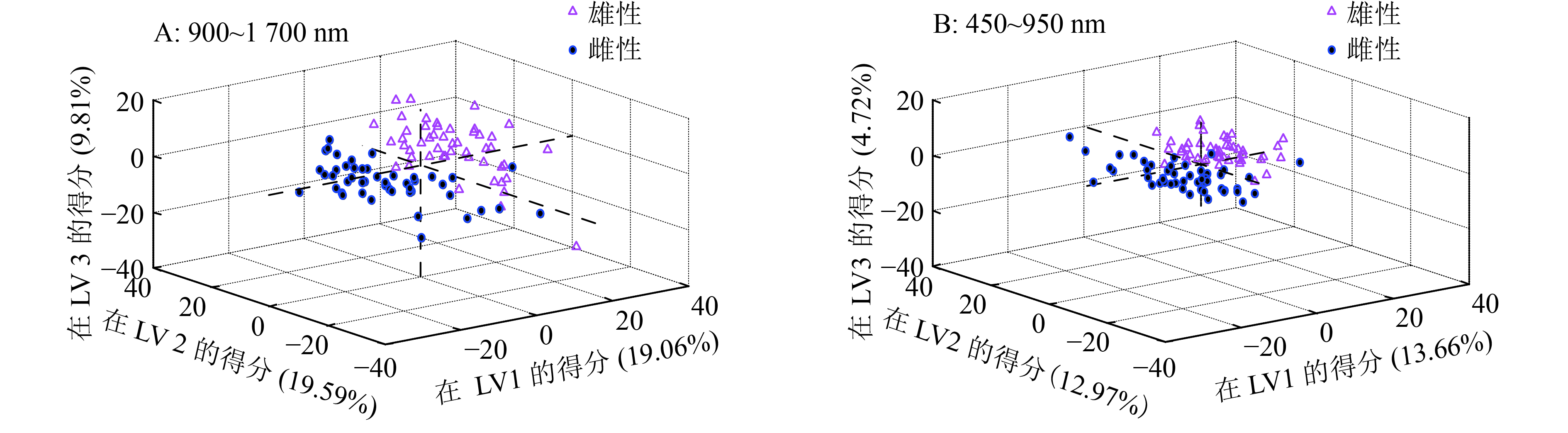
进一步通过PLSDA判别分析,以芙9品种的97枚样本为例,将采集到的近红外900~1 700 nm和可见–近红外450~950 nm 2个波段范围的光谱数据分别作为输入变量,建立PLSDA判别模型。为了减少光谱数据的维数,通常会使用主成分分析(Principal component analysis,PCA)提取1组正交的主成分(Principal components,PCs)来描述原来的光谱矩阵[15-17]。在分类问题中,PLSDA采用了PCA的基本原理,通过使光谱变量x和分类矩阵y之间的协方差最大,得到LV,LV能更好解释光谱变量中与分类相关的信息,而不是像PCs主要描述的是在光谱变量中起主宰作用的信息[18]。97枚样本在LV1, LV2和LV3上的三维得分图如图3所示。以近红外900~1 700 nm光谱作为输入变量时,LV1、LV2和LV3对光谱变量的信息描述分别达到19.06%、19.59%和9.81%,累计达到48.49%,是最重要的前3个潜变量,由图3A中可见,LV1具有很好的分辨能力,雌雄样本在LV1上的得分基本以0为分水岭,分别处于正或负的一边。以可见近红外450~950 nm光谱作为输入变量时,LV1、LV2和LV3对光谱变量的信息描述分别达到13.66%、12.97%和4.72%,累计达到31.35%,由图3B可见,仍然是LV1的区分能力最强。在2种情况下,雌雄个体都可以做出较好的分类,相比较而言,以近红外900~1 700 nm光谱作为输入变量时,LV1具有更好的分辨能力,雌雄样本可以得到很好的分辨。
2.2 不同蚕种的建模效果比较
将芙9、9芙、湘7和7湘家蚕原种分别采集可见–近红外450~950 nm以及在近红外900~1 700 nm的漫透射光谱。最后建立PLSDA模型进行雌雄鉴别,当PLSDA模型的分类阈值是0.5时准确率结果如表1所示, 对于同品种的种茧,利用近红外900~1 700 nm光谱建模的准确率要高于用可见–近红外450~950 nm光谱的建模准确率,即前者的鉴别效果优于后者,这与“2.1”中的结果一致。当使用450~950 nm光谱建模时,芙9和9芙、湘7和7湘这4个品种的鉴别准确率分别达到95.20%、95.65%、88.80%和87.50%。当使用900~1 700 nm光谱建模时,芙9和9芙这2个品种的鉴别准确率较高,分别达到100%和96.00%,而湘7和7湘这2个品种的鉴别准确率相对较低,分别为92.22%和94.21%。主要是由于芙9和9芙蚕茧呈椭圆形,个体较大,入射光充分进入到蚕蛹体内,出射光携带信息量较丰富,而湘7和7湘蚕是日本系统品种,茧呈浅束腰型 ,蚕茧个体较小,部分入射光并没有充分进入蚕蛹内部,直接进入到收光的积分球中,导致采集的漫透射光谱携带的信息量不够充分。
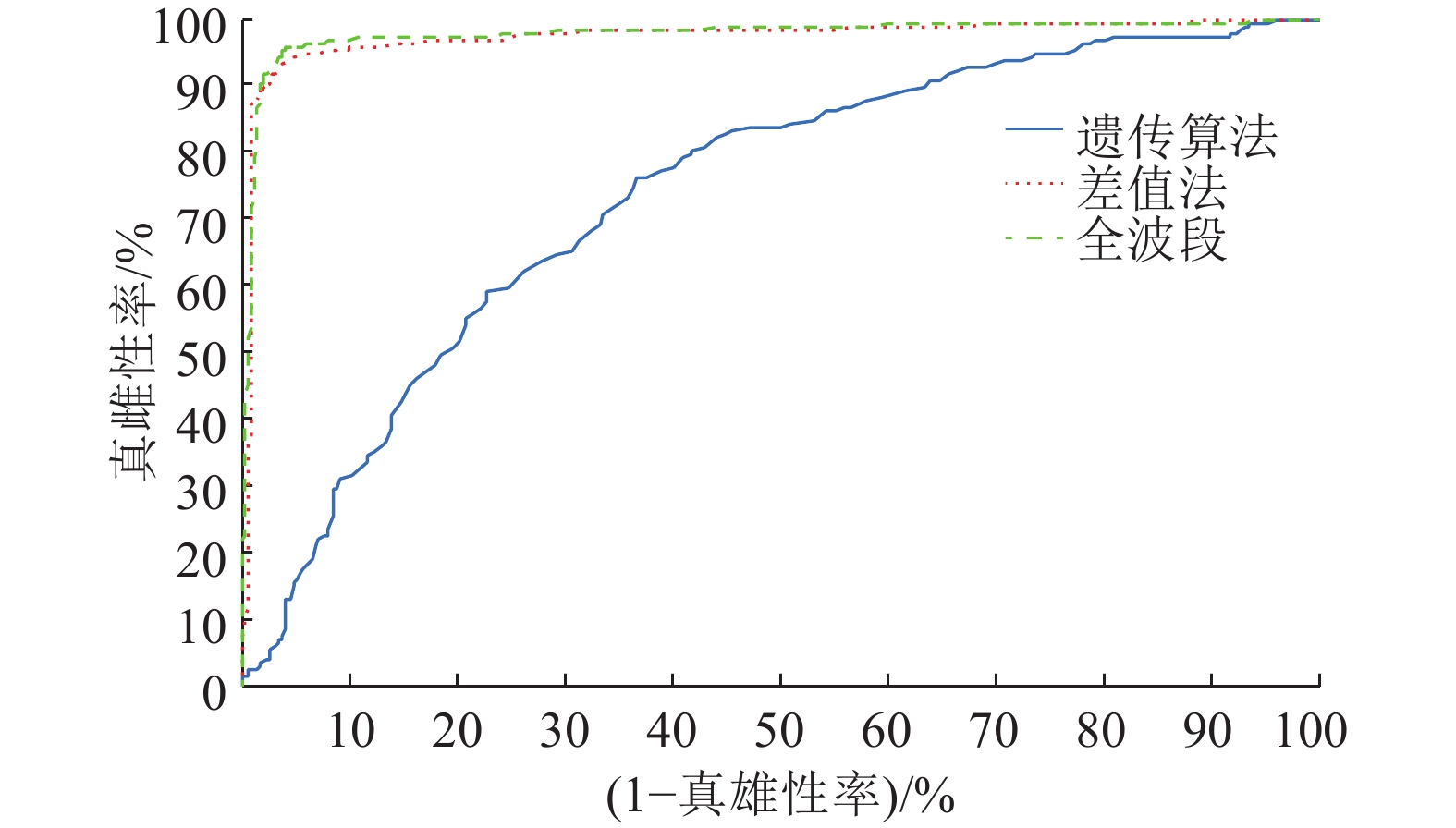
表 1 PLSDA、BPNN和SVM建模方法的效果比较Table 1. Effect comparison of PLSDA,BPNN and SVM models模型 样本数 真实值 预测值 真雌性率/% 真雄性率/% 准确率/% AUC1) 雌性 雄性 雌性 雄性 正确 错误 正确 错误 PLSDA 197 96 101 95 4 97 1 95.96 98.98 97.46 0.975 BPNN 197 96 101 92 4 97 4 95.83 96.04 95.94 0.959 SVM 197 96 101 96 18 83 0 100 82.18 90.86 0.910 1) AUC表示分类器特征曲线下的积分面积 2.3 基于不同建模方法的蚕蛹雌雄判别以及模型评价
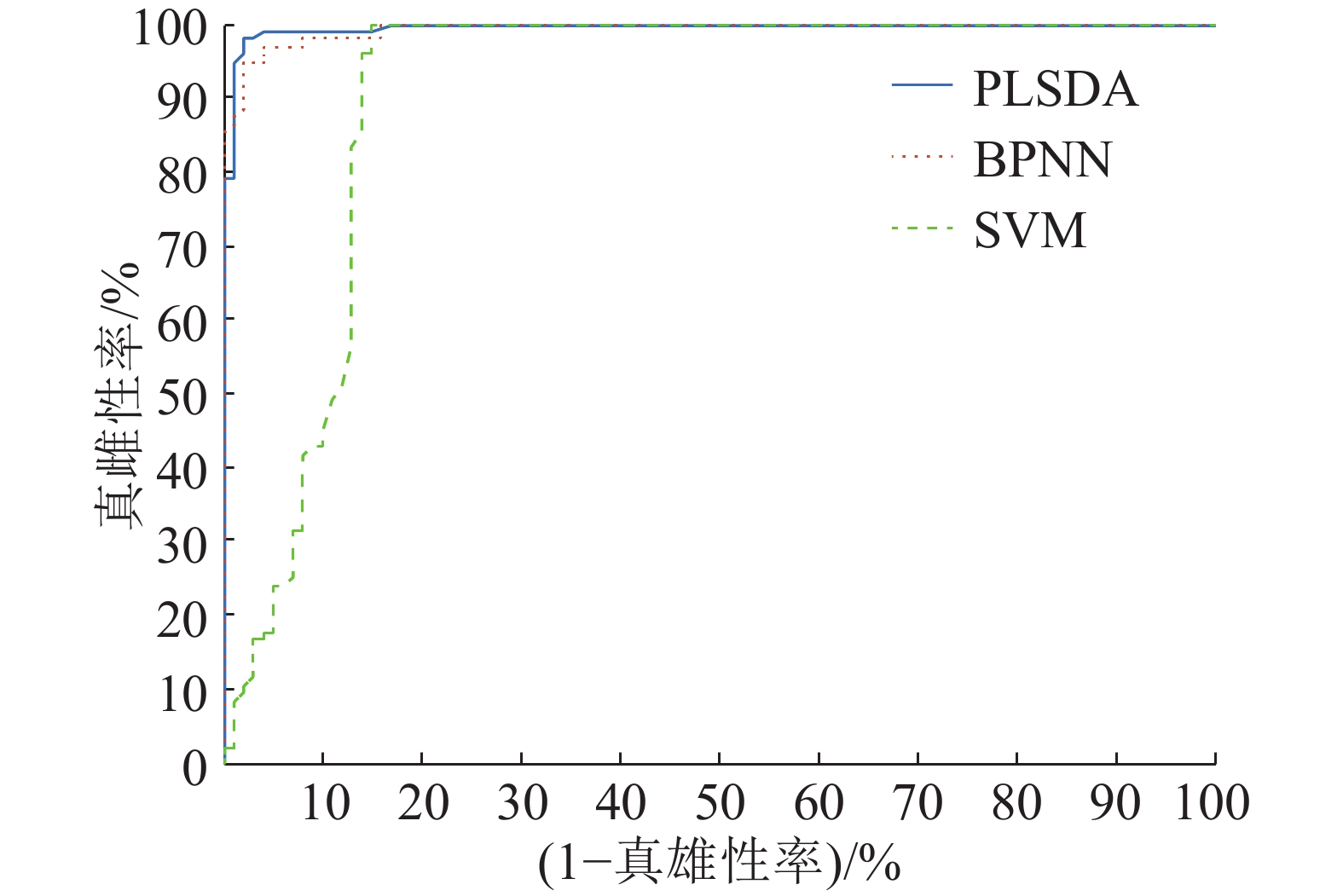
为了评价不同建模方法的建模效果,分别采用PLSDA、BPNN以及SVM建立蚕茧内蚕蛹的雌雄无损鉴别模型。采用混合品种共736个样本(芙9品种365个、湘7品种190个、7湘品种191个)作为样本集,并随机分成校正集(288个雌性、251个雄性,共539个样本)与预测集(96个雌性,101个雄性,共197个样本),此小节所有模型均采用外部验证的方式。采用近红外900~1 700nm透射光谱作为模型的输入变量。当分类模型采用的分类阈值是0.5时,各模型的鉴别结果如表1所示,PLSDA模型的真雌性率、真雄性率以及鉴别准确率分别达到95.96%、98.98%和97.46%,真雄性率和准确率都是3类模型中最高的,真雌性率仅次于SVM模型,其分类性能能够达到业界的要求。而SVM模型的真雌性率、真雄性率以及鉴别准确率分别达到100%、82.18%和90.86%,真雄性率和准确率是3类模型中最低的,特别是真雄性率不能达到业内的分类要求,但真雌性率最高。BPNN模型的真雌性率、真雄性率以及鉴别准确率分别达到95.83%、96.04%和95.94%,各项指标都在3类模型中居中,也能达到业界的分类要求。为了进一步评价各种分类模型的性能,分别作出了3类模型的分类器特征曲线(Receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线,如图4所示。PLSDA、BPNN以及SVM模型的ROC曲线下的积分面积(Area under the cure, AUC)分别是0.975、0.959以及0.910,这显示相对BPNN与SVM模型,PLSDA模型在本项目中有更好的分类性能。
2.4 光谱变量选择压缩后的建模效果
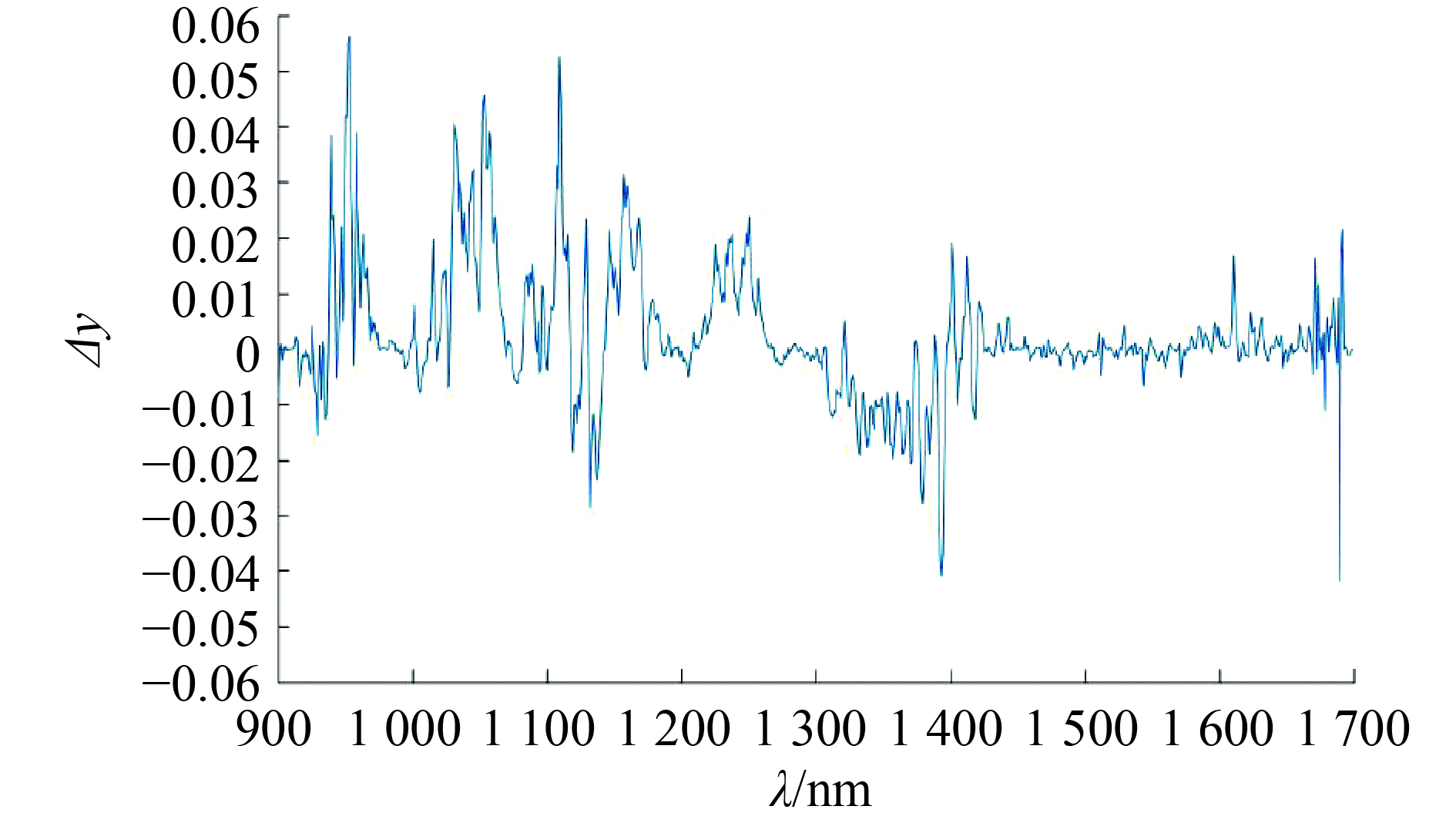
基于光谱信息的检测设备,检测光谱范围宽,光谱仪和CCD探测器要求高,设备成本较高,这会妨碍其在基层蚕种生产中的广泛应用。为了简化设备构造,降低设备成本,进而指导设计应用于蚕种生产的专用光谱设备,有必要探索根据少量蚕蛹的特征波段构建模型的途径。本项目采用差值法和遗传算法对特征波段进行了提取。在差值法中,Δy(雌、雄蚕茧光谱数据各波段的差值)与波长关系如图5所示,主要依据Δy的大小(Δy>0.029)并结合单个波长的建模效果进行选择,筛选出来的波长共有20个,分别为:940、953、954、958、959、1 031、1 032、1 036、1 044、1 045、1 056、1 057、1 058、1 109、1 110、1 132、1 157、1 158、1 394和1 689 nm。采用遗传算法筛选出来的波长也共有20个,分别为:1 188、1 439、1 450、1 461、1 471、1 472、1 491、1 496、1 501、1 509、1 516、1 518、1 524、1 551、1 554、1 570、1 573、1 574、1 587和1 631 nm。
采用混合品种共736枚样本(芙9品种365个、湘7品种190个、7湘品种191个)做为样本集,分别采用基于差值法手动筛选的20个波长、遗传算法筛选的20个波长以及全波段800个波长作为输入,采用留一法交叉内部验证,建立PLSDA模型,得到模型的判别结果如表2所示。结果显示,通过基于差值法手动筛选出来的20个波长建模,得到的模型的真雌性率、真雄性率和判别准确率为93.75%、95.45%和94.57%,全波段800个波长建模达到的真雌性率、真雄性率和判别准确率为95.57%、96.02%和95.79%,两相比较,前者准确率降低1.22%,但仍然处于业界可以接受的水平,但其模型输入光谱变量只有后者的2.5%,模型复杂度大大减小。采用遗传算法筛选出来的20个波长建模,真雌性率、真雄性率和判别准确率为76.04%、63.35%和69.97%,效果最差,不能为业界所接受。进一步通过各模型的ROC曲线下的面积AUC进行分析(图6),差值法筛选的20个波长模型的ROC曲线下AUC为0.972 7,全波段800个波长模型的ROC曲线下AUC为0.978 2,前者少0.004 5,但仍是可以接受的水平。
表 2 差值法、遗传算法和全波段建模的比较Table 2. Effect comparison of difference method, genetic algorithm and full-waveband models方法 样本数 真实值 预测值 真雌性率/% 真雄性率/% 准确率/% AUC1) 雌性 雄性 雌性 雄性 正确 错误 正确 错误 差值法 736 384 352 360 24 336 16 93.75 95.45 94.57 0.972 7 遗传算法 736 384 352 292 92 223 129 76.04 63.35 69.97 0.738 2 全波段 736 384 352 367 17 338 14 95.57 96.02 95.79 0.978 2 1) AUC表示分类器特征曲线下的积分面积 3. 结论
本文选用广东省蚕种生产中最常使用的蚕品种,以完整的蚕茧为研究对象,采用光谱技术和化学计量学的方法,研究了蚕茧中蚕蛹雌雄的无损快速鉴别方法。通过试验分析得出以下结论:
1)近红外波段900~1 700 nm的漫透射光谱比可见–近红外波段450~950 nm中含有更丰富的蚕蛹雌雄分类信息;
2)芙9、9芙品种的雌雄鉴别效果优于湘7和7湘品种,原因在于芙9、9芙蚕品种的茧型是椭圆形,而湘7和7湘是浅束腰型,浅束腰型影响了光谱信息含量;
3)采用PLSDA、BPNN以及SVM方法都能够对蚕蛹雌雄做出较好的无损鉴别(PLSDA模型真雌性率为95.96%,真雄性率为98.98%,准确率为97.46%;BPNN模型真雌性率为95.83%,真雄性率为96.04%,准确率为95.94%;SVM模型模型真雌性率为100%,真雄性率为82.18%,准确率为90.86%),进一步通过ROC曲线分析,PLSDA方法的效果最优,BPNN方法次之, 都能为业界所接受;
4)考虑到进一步生产蚕业专用光谱检测设备的成本需要,可以尝试提取部分波段940、953、954、958、959、1 031、1 032、1 036、1 044、1 045、1 056、1 057、1 058、1 109、1 110、1 132、1 157、1 158、1 394和1 689 nm作为设备输入,此时鉴别真雌性率为93.75%,真雄性率为 95.45%,准确率为94.57%,可以达到实际生产的需要。
-
表 1 PLSDA、BPNN和SVM建模方法的效果比较
Table 1 Effect comparison of PLSDA,BPNN and SVM models
模型 样本数 真实值 预测值 真雌性率/% 真雄性率/% 准确率/% AUC1) 雌性 雄性 雌性 雄性 正确 错误 正确 错误 PLSDA 197 96 101 95 4 97 1 95.96 98.98 97.46 0.975 BPNN 197 96 101 92 4 97 4 95.83 96.04 95.94 0.959 SVM 197 96 101 96 18 83 0 100 82.18 90.86 0.910 1) AUC表示分类器特征曲线下的积分面积 表 2 差值法、遗传算法和全波段建模的比较
Table 2 Effect comparison of difference method, genetic algorithm and full-waveband models
方法 样本数 真实值 预测值 真雌性率/% 真雄性率/% 准确率/% AUC1) 雌性 雄性 雌性 雄性 正确 错误 正确 错误 差值法 736 384 352 360 24 336 16 93.75 95.45 94.57 0.972 7 遗传算法 736 384 352 292 92 223 129 76.04 63.35 69.97 0.738 2 全波段 736 384 352 367 17 338 14 95.57 96.02 95.79 0.978 2 1) AUC表示分类器特征曲线下的积分面积 -
[1] 代芬, 吴玲, 叶观燕, 等. 基于近红外漫透射光谱信息的蚕茧雌雄检测[J]. 农业机械学报, 2015, 46(12): 280-283. [2] 封槐松, 李建琴. 我国蚕桑产业发展 “十二五” 回顾与 “十三五” 展望[J]. 中国蚕业, 2016, 37(1): 4-10. [3] 顾国达, 徐俊良. 论我国蚕丝业的多中心起源[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2003, 33(3): 42-47. [4] 顾国达, 李建琴. 2012年蚕桑产业发展趋势与建议[J]. 中国蚕业, 2012, 33(1): 1-4. [5] 李建琴, 顾国达. “一带一路” 对中国蚕丝业发展的战略意义[J]. 中国蚕业, 2015, 36(4): 1-7. [6] 潘沈元, 金同铭, 陆国权, 等. 蚕茧近红外反射光谱的模式识别[J]. 生物物理学报, 1995, 11(1): 53-59. [7] 潘沈元. 蚕茧近红外反射光谱的模式识别II. 光谱识别中特征值选取方法的探讨[J]. 生物物理学报, 1998, 14(2): 252-256. [8] 潘沈元, 陶鸣, 孙爱群, 等. 雌雄蚕蛹近红外反射光谱的差异及其模式识别[J]. 昆虫学报, 1996, 39(4): 360-365. [9] MARTEL A, BURGHAMMER M, DAVIES R J, et al. Silk fiber assembly studied by synchrotron radiation SAXS/WAXS and raman spectroscopy[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130(50): 17070-17074.
[10] 刘桂花, 张中湖. 拉曼与近红外、中红外光谱在药品掺杂筛选应用中的前景分析[J]. 齐鲁药事, 2012, 31(11): 634-635. [11] LEFEVRE T, PAQUET-MERCIER F, LESAGE S, et al. Study by raman spectromicroscopy of the effect of tensile deformation on the molecular structure of Bombyx mori silk[J]. Vib Spectrosc, 2009, 51(1): 136-141.
[12] 金航峰. 基于光谱和高光谱图像技术的蚕茧品质无损检测研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013. [13] 颜辉, 陈斌, 金尚忠. 基于NIR的主成分结合支持向量机鉴别蚕茧雌雄的研究[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2008, 25(10): 1261-1264. [14] SHAFFER R E, SMALL G W, ARNOLD M A. Genetic algorithm-based protocol for coupling digital filtering and partial least-squares regression: Application to the near-infrared analysis of glucose in biological matrices[J]. Anal Chem, 1996, 68(15): 2663-2675.
[15] DELWICHE S R, HARELAND G A. Detection of scab-damaged red spring wheat kernels by near-infrared reflectance[J]. Cereal Chem, 2004, 81(5): 643-649.
[16] CHRISTY A A, KASEMSUMRAN S, DU Y, et al. The detection and quantification of adulteration in olive oil by near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics[J]. Anal Sci, 2004, 20(6): 935-940.
[17] BERARDO N, PISACANE V, BATTILANI P, et al. Rapid detection of kernel rots and mycotoxins in maize by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy[J]. J Agr Food Chem, 2005, 53(21): 8128-8134.
[18] BERGHOLT M S, ZHENG W, LIN K, et al. Raman endoscopy for in vivo differentiation between benign and malignant ulcers in the stomach[J]. Analyst, 2010, 135(12): 3162-3168.



 下载:
下载: