Changes of vigor, physiological characteristics and genetic diversities of artificially aged sweet corn seeds
-
摘要:目的
研究人工老化处理对甜玉米 Zea mays L. saccharata Sturt. 种子活力、生理特性和遗传多样性的影响,为甜玉米种子贮藏及大田生产提供参考。
方法以甜玉米品种‘农甜88’和‘农甜99’为试验材料,采用人工老化的方法处理玉米种子,沙床发芽法检测种子的发芽势、发芽率、发芽指数和活力指数。测定了种子的脱氢酶(Dehydrogenase,DHA)活性、过氧化物酶(Peroxidase,POD)活性、相对电导率(Relative electrical conductivity, REC)和丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)含量,采用SRAP标记检测不同处理时间种子的遗传多样性,分析种子生理指标和遗传多样性与种子活力的关系。
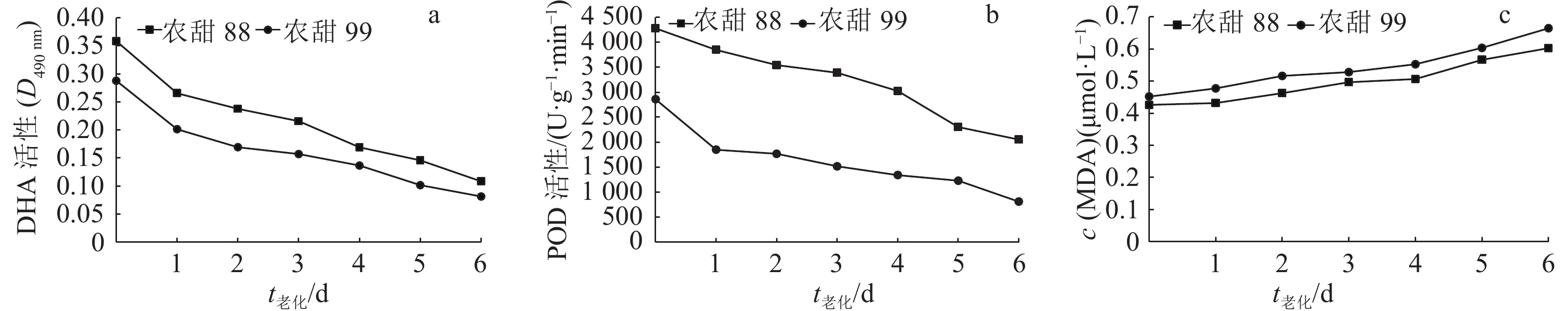
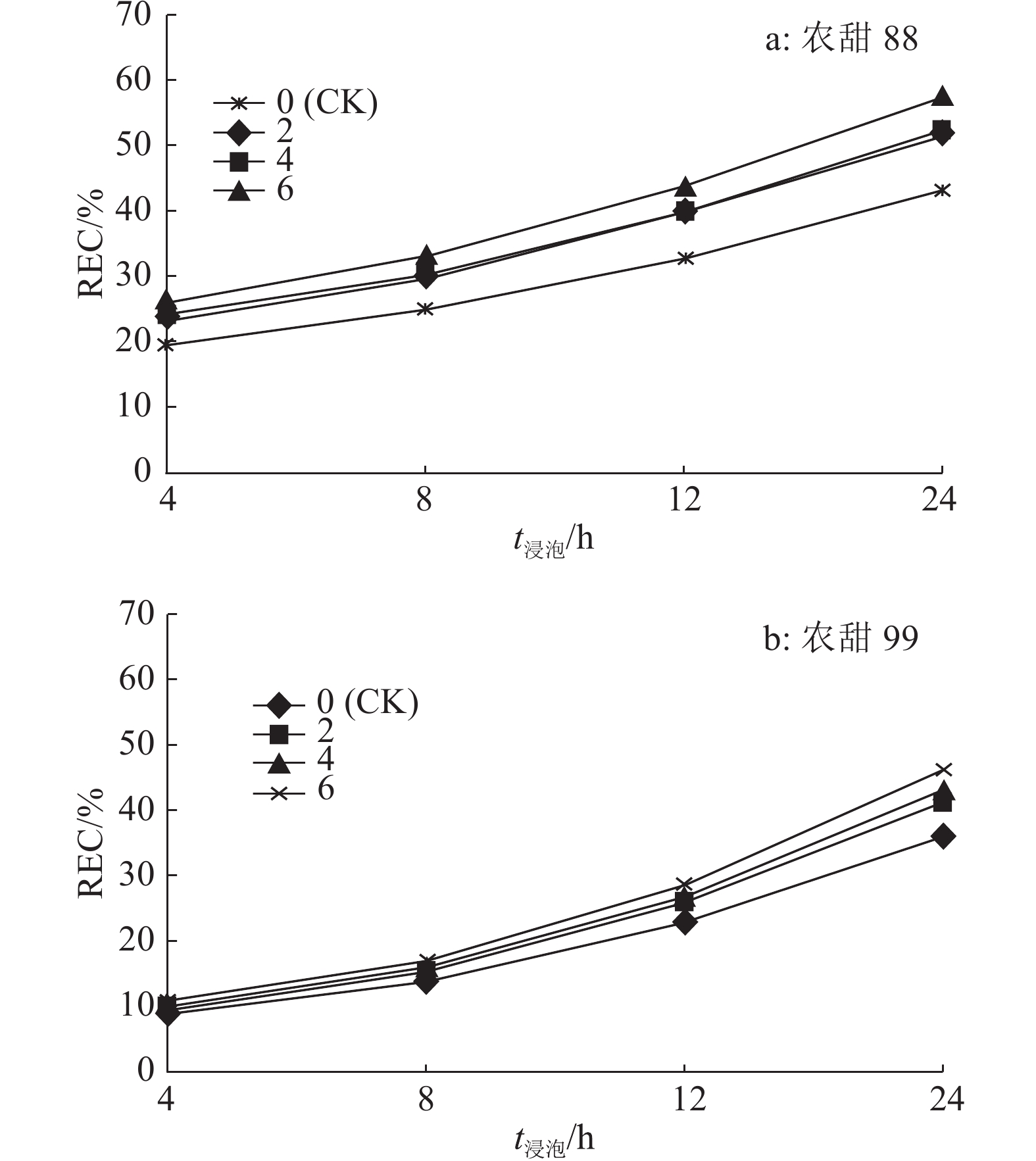
结果随老化时间的增加,2个品种种子的发芽势、发芽率、发芽指数、活力指数、DHA活性和POD活性逐渐降低,而REC和MDA含量则逐渐升高。老化处理6 d后,‘农甜88’和‘农甜99’种子的发芽势、发芽率、发芽指数、活力指数、DHA活性、POD活性分别比对照下降18.32%和43.15%、10.73%和15.38%、19.43%和23.60%、41.85%和45.70%、69.78%和71.74%、52.02%和71.60%;浸泡24 h的REC分别比对照提高了33.68%和27.68%,MDA含量分别比对照提高了41.50%和47.08%。老化处理使种子的遗传多样性下降,老化处理6 d后,‘农甜88’和‘农甜99’等位基因数、有效等位基因数、基因多样性分别比对照下降29.35%和23.58%、25.00%和20.00%、96.99%和83.35%。相关性分析发现, 2个品种老化种子浸出液的REC和MDA含量均与种子活力各性状呈显著或极显著负相关,DHA和POD活性均与种子活力各性状呈显著或极显著正相关。
结论随老化时间的增加,2个甜玉米品种种子的活力以及DHA、POD活性逐渐降低、REC和MDA含量逐渐升高;种子老化处理降低了种子遗传物质的多样性;‘农甜88’种子耐老化能力强于‘农甜99’。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo identify the effects of artificial aging on vigor, physiological characteristics and genetic diversities of sweet corn (Zea mays L. saccharata Sturt.) seeds, and provide a reference for sweet corn seed storage and field production.
Method‘Nongtian88’ and ‘Nongtian99’ were selected as experimental materials and their seeds were treated using the method of artificial aging. The germination potential, germination rate, germination index and vigor index were measured using the method of germination in sand bed. The dehydrogenase (DHA) activity, peroxidase (POD) activity, relative electrical conductivity (REC) and malondialdehyde (MDA) content of artificially aged seeds were measured. The genetic diversity of artificially aged seeds was detected using SRAP, and the relationships between physiological characteristics, genetic diversities and seed vigor were analyzed.
ResultWith the increase of aging time, seed germination potentials, germination rates, germination indexes, vigor indexes, DHA activities and POD activities of two cultivars decreased gradually, while the RECs and MDA contents increased gradually. Compared to the control (CK), the germination potentials, germination rates, germination indexes, vigor indexes, DHA activities and POD activities of ‘Nongtian88’ and ‘Nongtian99’ seeds decreased by 18.32% and 43.15%, 10.73% and 15.38%, 19.43% and 23.60%, 41.85% and 45.70%, 69.78% and 71.74%, 52.02% and 71.60% respectively after aging treatment for six days. The RECs of ‘Nongtian88’ and ‘Nongtian99’ seeds after soaking for 24 hours increased by 33.68% and 27.68% respectively than that of CK, and MDA contents increased by 41.50% and 47.08% respectively than that of CK. Compared to CK, the seed genetic diversities decreased after artificial aging treatment, the allele numbers, effective allele numbers and gene diversities of ‘Nongtian88’ and ‘Nongtian99’ seeds decreased by 29.35% and 23.58%, 25.00% and 20.00%, 96.99% and 83.35% respectively after aging treatment for six days. The correlation analysis showed that the RECs and MDA contents of aged seeds of two cultivars were significantly or highly significantly negatively correlated with vigor indexes, while DHA and POD activities were significantly or highly significantly positively correlated with seed vigor indexes.
ConclusionWith the increase of artificially aging time, the seed vigor indexes, DHA and POD activities of two sweet corn cultivars decrease gradually, while the RECs and MDA contents increase gradually. Artificial aging results in the decrease of seed genetic diversity. ‘Nongtian88’ seed has stronger aging resistant ability than ‘Nongtian99’.
-
Keywords:
- sweet corn /
- artificial aging /
- seed vigor /
- physiological characteristic /
- genetic diversity
-
-
表 1 多样性分析采用的SRAP引物名称及序列
Table 1 The SRAP primers and sequences for genetic diversity analyses
引物名称 正向引物序列 引物名称 反向引物序列 M1 TGAGTCCAAACCGGATA E1 GACTGCGTACGAATTAAT M2 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAGC E2 GACTGCGTACGAATTTGC M3 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAT E3 GACTGCGTACGAATTGAC M4 TGAGTCCAAACCGGACC E4 GACTGCGTACGAATTTGA M5 TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAG E5 GACTGCGTACGAATTAAC 表 2 ‘农甜88’和‘农甜99’经不同老化处理时间后种子活力指标比较1)
Table 2 Comparisons of vigor indexes of ‘Nongtian88’ and ‘Nongtian99’ seeds after different aging time
品种 t老化/d 发芽势/% 发芽率/% 发芽指数 活力指数 农甜88 0(对照) 94.67±0.04a 99.33±0.03a 4.58±0.12a 64.78±5.31a 1 91.33±0.02ab 95.33±0.03ab 4.42±0.16ab 61.50±5.32a 2 85.33±0.03bcd 92.00±0.02abc 4.08±0.09bc 49.05±1.59b 3 87.00±0.01abc 92.00±0.00abc 4.07±0.05bc 48.73±0.32b 4 84.67±0.01bcd 91.33±0.01abc 4.05±0.04bc 44.48±0.76bc 5 82.00±0.02cd 86.00±0.02c 3.77±0.09c 43.63±1.80bc 6 77.33±0.02d 88.67±0.02bc 3.69±0.11c 37.67±0.83c 农甜99 0(对照) 63.33±0.02a 95.33±0.01a 3.39±0.02a 59.28±2.39a 1 59.33±0.04a 93.33±0.02a 3.29±0.06a 53.58±2.55ab 2 56.67±0.01a 83.33±0.01b 3.05±0.05ab 45.88±3.74abc 3 52.67±0.09a 83.33±0.05b 2.90±0.22bc 44.92±8.13bc 4 52.67±0.01a 82.00±0.04b 2.89±0.12bc 40.39±4.48bc 5 46.67±0.07ab 82.67±0.02b 2.75±0.12bc 39.33±2.24c 6 36.00±0.03b 80.67±0.02b 2.59±0.04c 32.19±0.95c 1) 同一品种、同列数据后凡是有一个相同小写字母者,表示不同处理间差异不显著(P>0.05,Duncan’s 法) 表 3 老化处理后甜玉米种子发芽指标与生理指标的相关性1)
Table 3 Correlations between germination indexes and physiological indexes of sweet corn seeds after aging treatment
发芽指标 品种 不同浸泡时间的 REC DHA活性 POD活性 MDA含量 4 h 8 h 12 h 24 h 发芽势 农甜88 –0.990 11** –0.993 55** –0.992 41** –0.995 62** 0.951 64** 0.956 29** –0.937 54** 农甜99 –0.931 71 –0.923 28 –0.918 10 –0.917 32 0.899 76** 0.891 85** –0.987 84** 发芽率 农甜88 –0.993 74** –0.992 91** –0.995 00** –0.992 03** 0.938 93** 0.927 39** –0.877 18** 农甜99 –0.933 01 –0.943 27 –0.947 99 –0.946 30 0.898 27** 0.865 46* –0.811 89* 发芽指数 农甜88 –0.993 04** –0.996 02** –0.995 56** –0.997 84** 0.955 65** 0.963 71** –0.948 29** 农甜99 –0.996 02** –0.993 06** –0.991 23** –0.991 78** 0.956 06** 0.929 07** –0.963 55** 活力指数 农甜88 –0.998 38** –0.996 20** –0.990 86** –0.992 77** 0.952 10** 0.922 16** –0.911 62** 农甜99 –0.999 88** –0.999 46** –0.999 02** –0.999 61** 0.970 92** 0.955 26** –0.960 40** 1) “*” 和 “**” 分别表示相关性达到 0.05 和 0.01 的显著水平 表 4 不同老化时间甜玉米种子的遗传多样性分析
Table 4 The genetic diversity analyses of sweet corn seeds after different aging time
品种 t老化/d 等位基因数 有效等位基因数 基因多样性 农甜88 1 1.434 2 1.347 4 0.193 0 2 1.421 1 1.336 8 0.187 1 3 1.118 4 1.094 7 0.052 6 4 1.065 8 1.052 6 0.029 2 5 1.039 5 1.031 6 0.017 5 6 1.013 2 1.010 5 0.005 8 农甜99 1 1.394 7 1.315 8 0.175 4 2 1.289 5 1.231 6 0.128 7 3 1.236 8 1.189 5 0.105 3 4 1.223 7 1.178 9 0.099 4 5 1.157 9 1.126 3 0.070 2 6 1.065 8 1.052 6 0.029 2 -
[1] 李小琴, 王青峰. 广东省甜玉米发展现状与对策探讨[J]. 作物杂志, 2007(3): 32-34. [2] 罗军, 万忠, 谭俊, 等. 2013年广东甜玉米产业发展形势与对策建议[J]. 广东农业科学, 2014, 41(5): 42-45. [3] 胡晋. 种子学[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2014. [4] 樊龙江, 颜启传. 甜玉米种子活力低下原因及其种子处理技术研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 1996(6): 24-26. [5] 徐秀兰, 吴学宏, 张国珍, 等. 甜玉米种子携带真菌与种子活力关系分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2006, 39(8): 1565-1570. [6] 王青峰, 宫庆友, 沈凌云, 等. 超甜玉米种子活力研究[J]. 种子, 2007, 26(6): 4-7. [7] STYER R C, CANTLIFFE D J. Dependence of seed vigor during germination on carbohydrate source in endosperm mutants of maize[J]. Plant Physiol, 1984, 76(1): 196-200.
[8] 欧阳西荣, 徐辉, 李丽. 种子老化对玉米幼苗生长和植株发育的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2002, 18(6): 31-35. [9] 张海艳. 低温对鲜食玉米种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 2013, 49(4): 347-350. [10] 胡晋. 对种子活力测定方法: TTC定量法的改进[J]. 种子, 1986(Z1): 71-72. [11] 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000. [12] LI G, QUIROS C F. Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: Its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2001, 103(2): 455-461.
[13] 赵炜, 刘冠明, 王晓明, 等. 应用SRAP标记分析甜玉米自交系的遗传差异[J]. 玉米科学, 2007, 15(S1): 154-156. [14] YEH F, YANG R, BOYLE T, et al. POPGENE, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis [M]. Edmonton: Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Centre, University of Alberta, Canada, 1997.
[15] 乔燕祥, 高平平, 马俊华, 等. 两个玉米自交系在种子老化过程中的生理特性和种子活力变化的研究[J]. 作物学报, 2003, 29(1): 123-127. [16] 张海艳. 糯玉米种子老化过程中种子活力和生理特性的变化[J]. 玉米科学, 2015, 23(1): 92-96. [17] 汪晓峰, 丛滋金. 膜质变等生化变化与玉米种子老化[J]. 种子, 1993(1): 68-69. [18] 刘建军, 马俊华, 孟俊文, 等. 玉米种子老化过程中抗氧化酶活性的变化[J]. 山西农业科学, 2013, 41(9): 907-910. [19] 乔燕祥, 高平平, 王果萍, 等. 玉米种子老化过程中EST同工酶变化与染色体畸变的研究[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2003, 4(2): 114-118. [20] 张晗, 卢新雄, 张志娥, 等. 种子老化对玉米种质资源遗传完整性变化的影响[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2005, 6(3): 271-275. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张逸风,赵瑜君,苏平,吴晓毅,夏梦,高伟,黄璐琦. 比较蛋白质组学揭示茉莉酸甲酯诱导的雷公藤甲素生物合成. 中国现代中药. 2024(02): 316-327 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王婷,来欢欢,赵微,崔美林,张秀红. 基于蛋白质组学技术对植物乳杆菌YP36细菌素的抑菌机制研究. 中国酿造. 2024(04): 98-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: