Analysis of agronomic traits in recombinant inbred line population of tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrm tataricum)
-
摘要:目的
研究苦荞Fagopyrm tataricum主要农艺性状的遗传变异,揭示影响苦荞单株粒质量的主要因素,筛选综合性状优良的株系,为高产苦荞品种的选育提供理论基础和推荐材料。
方法以小米荞与晋荞2号构建的重组自交系(Recombinant inbred line, RIL)群体399个家系为材料,对株高、主茎分枝数、主花序二分叉花枝数、顶三花枝粒数、单株粒数、单株粒质量、千粒质量、籽粒产量这8个农艺性状进行了遗传变异和相关性分析,利用逐步回归和通径分析挖掘影响单株粒质量的主要因子,基于农艺性状表型值将RIL群体进行聚类分析,通过群组间方差分析筛选优良单株。
结果各性状变异系数为13.1%~42.4%。除了主茎分枝数外,其他性状均存在双向超亲分离现象。株高、主花序二分叉花枝数、单株粒数与单株粒质量、籽粒产量均呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。单株粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数和千粒质量是影响单株粒质量的主要因素,其中单株粒数对单株粒质量的直接作用和总体效应最大。在欧式距离为22.0处,RIL群体可划分为10类,C5类群籽粒产量最高,C1类群在单株粒质量、单株粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数和籽粒产量等方面表现良好。
结论单株粒数可作为高产苦荞品种选育的重要参考指标,C1和C5类群的株系可作为高产苦荞育种的推荐材料。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo study the genetic variation in major agronomic traits of tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrm tataricum), reveal the major factors influencing grain weight per plant, select excellent lines, and provide a theoretical basis and materials for high-yield tartary buckwheat breeding.
MethodUsing 399 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from the cross of ‘Xiaomiqiao’ and ‘Jinqiao2’, we studied the genetic variations of eight agronomic traits including plant height (PH), branch number of main stem (BN), branch number with double-bifurcation on main inflorescence (BND), grain number of the top-three-branch (GNT), grain number per plant (GN), grain weight per plant (GW), 1 000-grain weight (TGW) and grain yield (GY) and did correlation analysis. Multiple regression and path analysis were conducted to detect the traits mostly affected GW. Cluster analysis for the RIL population was carried out based on the phenotypic data of invested traits, and the excellent lines were selected by variance analysis among groups.
ResultThe coefficient variation of the traits ranged from 13.1% to 42.4%. Excepting BN, tremendous transgressive segregation for all traits was observed. PH, BND and GN were significantly positively correlated with GW and GY, respectively (P<0.01). GN, BND and TGW were the traits mostly affected GW. GN had the most direct and overall effects on GW. The RIL population could be divided into ten groups at the Euclidean distance of 22.0. Group C5 had the highest GY and group C1 had fine performance in GW, GN, BND and GY.
ConclusionGN can be used as a reference index for high-yield tartary buckwheat breeding, and lines from group C1 and C5 are recommended as materials for breeding.
-
苦荞[Fagopyrm tataricum (L.) Gaertn],又名鞑靼荞麦,是荞麦属植物中仅次于甜荞的第2大栽培种。苦荞籽粒含有大量的黄酮类化合物和丰富的无机元素[1],具有较高的营养价值和保健功能。随着人们生活质量和健康意识的提高,苦荞产品越来越受人们青睐。研究苦荞产量以及产量相关农艺性状的遗传规律,对加快高产苦荞品种的选育进程具有重要的现实意义。
目前,已有不少学者对苦荞种质资源的各种农艺性状进行了分析。杨玉霞等[2]对来自5个国家的55份苦荞种质主要农艺性状的相关和通径分析表明,有效花序数和千粒质量对单株籽粒产量的直接效应较大。高金锋等[3]对西藏80份苦荞资源农艺性状的主成分分析表明,株型矮和大粒是高产苦荞的育种目标。潘凡等[4]利用来自我国11个省份的180份苦荞种质进行了农艺性状与单株粒质量的通径分析认为,单株粒数与千粒质量是影响单株粒质量的主要因素。苦荞籽粒产量与其构成因子的相关与多元回归分析表明,增加株高、主茎节数、单株粒质量、单株粒数是提高籽粒产量的主要途径[5-6]。此外,也有研究表明,海拔、生育期、生育期均温等生态因子也是苦荞高产的最重要影响因素[7]。上述研究由于调查的种质资源数目、分布地域和农艺性状的不同、得出影响苦荞籽粒产量的主要因子也不同。
苦荞的花朵小,杂交难度大,遗传群体构建相对困难,目前利用遗传群体研究农艺性状变异的报道较少。唐链等[8]和梁龙兵等[9]对小米荞×晋荞2号的F2和F3家系农艺性状的研究发现,株高、主茎分枝数、主花序二分叉花枝数、顶三花枝粒数与单株粒质量和单株粒数呈极显著正相关,可作为苦荞高产杂交育种的重要目标。杜晓磊等[10]以滇宁1号×野苦荞的119个F4家系为作图群体,构建了首张苦荞SSR遗传连锁图谱,并对株高、分枝数、叶长、叶宽、千粒质量等农艺性状进行了QTL分析[11]。闫玉莹[12]以小米荞×晋荞2号的F3群体为作图群体,构建了苦荞高密度单核苷酸多态性 (Single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP)遗传图谱,并对株高、单株粒质量和百粒质量进行QTL定位。然而,上述群体均是非稳定性的分离群体,难以进行多年多点的表型鉴定,不能全面、准确地挖掘影响产量的主要因素及解析农艺性状的遗传变异。重组自交系(Recombinant inbred line, RIL)群体作为一个稳定的永久性分离群体,具有重组程度高、个体基因纯合、可长期重复试验等优点,是理想的遗传作图群体,目前已广泛应用于农作物数量性状的遗传解析和QTL定位研究[13-15]。
本研究以小米荞×晋荞2号的399个RIL群体为材料,分析了株高、主茎分枝数、主花序二分叉花枝数、顶三花枝粒数、单株粒数、单株粒质量、千粒质量、籽粒产量这8个主要农艺性状的遗传变异,通过相关性分析、逐步回归分析、通径分析和聚类分析,挖掘影响单株粒质量的重要因子,筛选综合性状表现良好的株系,为高产苦荞的选育提供指导,也为开展重要农艺性状的QTL定位奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
以苦荞审定品种晋荞2号为父本,云南地方苦荞品种小米荞为母本构建的RIL群体399个F6株系为供试材料。小米荞迟熟、种壳极薄、无刺、无沟槽或者沟槽浅、易脱壳成荞米、出粉率高;晋荞2号为山西省选育的高产优质品种,早熟、种壳厚有沟槽不易脱壳[16-17]。
1.2 农艺性状的考察
试验于2016年8月播种,每个株系种植1个小区,每小区种3行,小区面积为1.0 m2,中等肥力,常规田间管理。收获时期选取有代表性的10个单株进行农艺性状考察。株高:单株基部到主茎尖的高度;主茎分枝数:单株主茎有效分枝个数;主花序二分叉花枝数:主花序上着生的二分叉花枝的个数;顶三花枝粒数:主花序最顶端3个花枝的种子数目;单株粒质量:单株脱粒风干后的籽粒质量;单株粒数:单株所结饱满籽粒个数;千粒质量:根据小区产量中3次抽样100粒饱满籽粒的称量换算成千粒质量;籽粒产量:按小区收获、脱粒后,根据风干后小区的籽粒质量换算成每公顷的籽粒产量。
1.3 数据分析
各性状的平均值、标准差、变异系数等描述统计量分析采用Excel 2010。用SAS8.1软件 (SAS Institutie,美国) 的ANOVA程序进行数据方差分析,用F测验进行亲本间各农艺性状的差异比较,用Duncan’s法进行各类群间农艺性状差异的显著性检验和多重比较分析。农艺性状之间的Pearson相关性分析、主要农艺性状对单株粒质量的逐步多元回归、通径分析在SPSS16.0中完成。分别用R3.2.2统计软件( https://www.R-project.org/)的scale、dist和hclust函数完成群体农艺性状的标准化和中心化、基于欧氏距离的相似性矩阵构建和基于离差平方和法(Ward)的聚类分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 亲本及RIL群体主要农艺性状的评价
亲本主要农艺性状的方差分析表明(表1),小米荞的株高和主花序二分叉花枝数极显著高于晋荞2号(P<0.01),主茎分枝数和千粒质量极显著低于晋荞2号,单株粒质量和籽粒产量显著低于晋荞2号(P<0.05),两亲本的顶三花枝粒数和单株粒数差异不显著(P>0.05)。
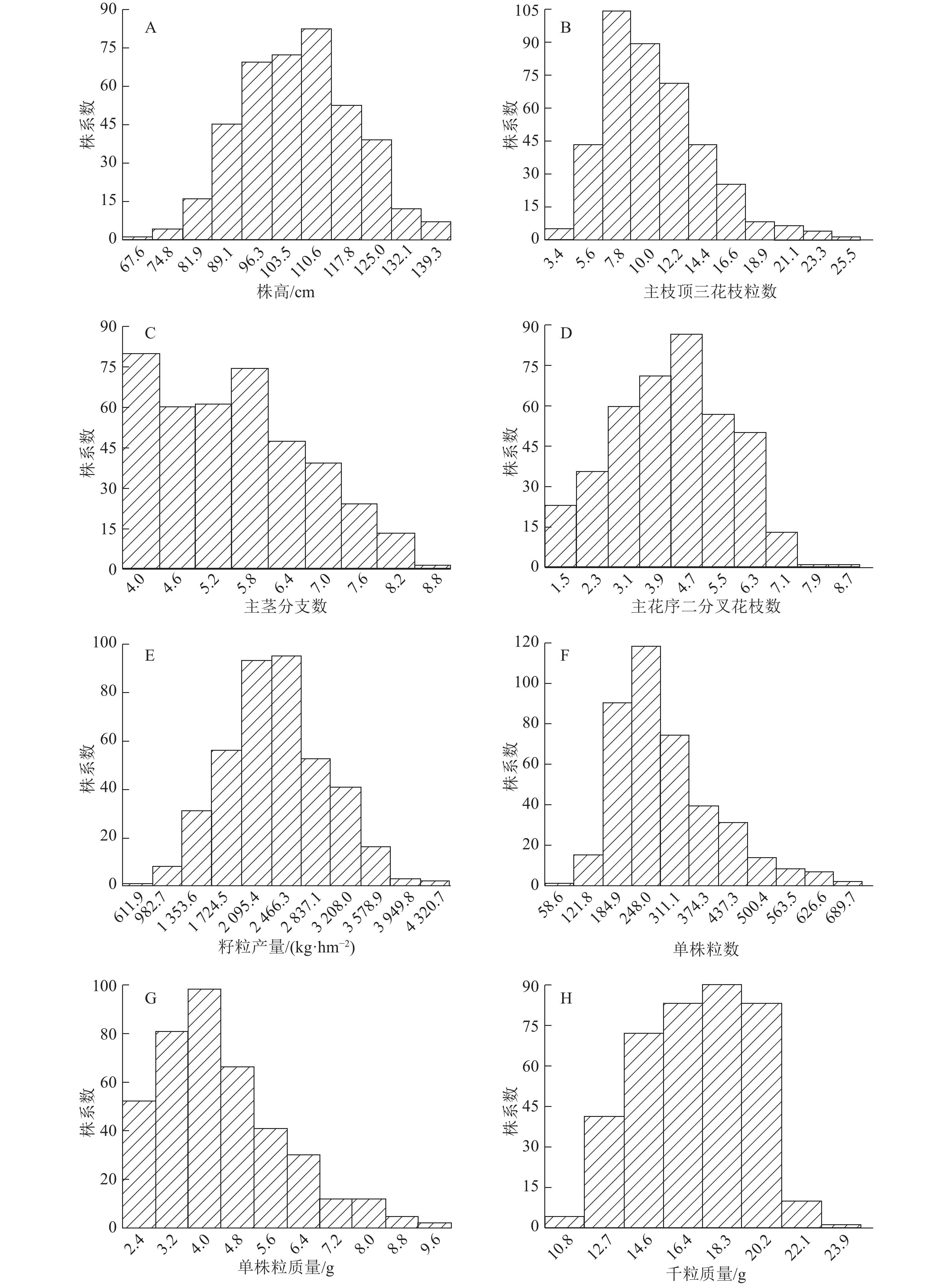
表 1 亲本和重组自交系群体主要农艺性状的表型变异Table 1. Phenotype variation of agronomic traits in the RIL population and their parents性状 亲本 重组自交系群体 小米荞 晋荞2号 F1) 平均值 范围 变异系数/% 偏度 峰度 株高/cm 100.8±7.9 74.3±7.3 91.2** 102.8 66.1~137.8 13.1 0.08 –0.40 主茎分枝数 7.9±1.2 9.9±2.0 11.1** 5.2 2.5~8.5 24.0 0.19 –0.62 单株粒质量/g 2.6±1.1 3.7±1.4 5.8* 4.0 0.9~8.9 37.2 0.83 0.52 顶三花枝粒数 6.5±3.7 6.8±3.1 0.1 9.5 1.9~24.0 40.7 0.80 0.66 主花序二分叉花枝数 3.7±1.2 1.5±0.9 30.7** 3.9 0~8.0 37.9 –0.20 –0.39 单株粒数 190.2±74.5 176.4±53.6 0.3 258.4 57.1~688.2 42.4 1.16 1.31 千粒质量/g 13.5±1.2 20.6±2.0 143.9** 16.1 8.9~23.9 15.9 –0.21 –0.60 籽粒产量/(kg·hm–2) 1 272.1±254.0 1 806.0±188.1 8.6* 2 167.9 610.4~4 319.2 36.8 0.24 0.06 1) “*”和“**”分别表示亲本间同一性状差异达到 0.05 和 0.01 的显著水平(F 测验) RIL群体中主要农艺性状存在较大差异(表1)。变异系数最大的是单株粒数(42.4%),其次是顶三花枝粒数(40.7%),最小的是株高(13.1%)。各性状均呈连续变异,分布频率呈近似正态分布(图1),表明所调查的性状均为多基因控制的数量性状。除了主茎分枝数外,其他7个性状均存在明显的超亲分离现象。千粒质量在RIL群体中的平均值介于双亲之间,主茎分枝数在RIL群体中的平均值低于双亲,株高、顶三花枝粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数、单株粒数和籽粒产量在RIL群体中的平均值均大于双亲。
2.2 RIL群体主要性状的相关性分析
由RIL群体各农艺性状的Pearson相关性系数可知,籽粒产量与单株粒质量、千粒质量、株高、单株粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数均呈极显著正相关;单株粒质量与株高、单株粒数、主茎分枝数、顶三花枝粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数均呈极显著正相关。单株粒数与株高、主茎分枝数、顶三花枝粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数均呈极显著正相关。千粒质量与单株粒数、顶三花枝粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数均呈极显著负相关(表2)。
表 2 苦荞RIL群体各农艺性状的相关分析1)Table 2. Correlation analysis of agronomic traits in the RIL population of tartary buckwheat性状 单株粒质量 千粒质量 株高 单株粒数 主茎分枝数 顶三花枝粒数 主花序二分叉花枝数 千粒质量 –0.067 株高 0.551** –0.002 单株粒数 0.907** –0.443** 0.493** 主茎分枝数 0.390** –0.084 –0.085 0.387** 顶三花枝粒数 0.300** –0.167** –0.047 0.334** 0.315* 主花序二分叉花枝数 0.441** –0.160** 0.635** 0.443** –0.082 –0.163** 籽粒产量 0.354** 0.180** 0.340** 0.236** 0.074 –0.008 0.265** 1) “*”和“**”分别表示相关性达到 0.05 和 0.01 的显著水平 (Pearson 法) 2.3 单株粒质量对农艺性状的逐步回归分析
以籽粒产量(y)为因变量,以单株粒质量、千粒质量、株高、株粒数、主茎分枝数、顶三花枝粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数为自变量进行多元逐步回归分析,建立的回归方程的拟合度R2 仅为0.194。以单株粒质量(y)为因变量,以千粒质量、株高、株粒数、主茎分枝数、顶三花枝粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数为自变量进行多元逐步回归分析,剔除偏回归参数不显著的自变量,根据回归系数输出结果(表3)获得的最优的线性回归方程: y = –3.820+0.243x1+0.015x3+0.030x6。该方程拟合度R2为0.964,即该方程可解释单株粒质量96.4%的表型变异,说明x1(千粒质量)、x3(单株粒数)和x6(主花序二分叉花枝数)是影响单株籽粒产量的主要因素,千粒质量、单株粒数和主花序二分叉花枝数每增加1个单位,单株粒质量平均分别增加0.243、0.010 g和0.030 g。
表 3 苦荞单株粒质量对农艺性状的多元回归分析Table 3. Multiple stepwise regression analysis of grain weight per plant attributable to major agronomic traits of tartary buckwheat模型 自变量1) 偏回归
系数标准
误差通径
系数t P 1 常量 0.824 0.081 10.160 0.000 x3 0.012 0 0.907 42.938 0.000 2 常量 –3.763 0.124 –30.237 0.000 x3 0.015 0 1.092 101.042 0.000 x1 0.244 0.006 0.417 38.620 0.000 3 常量 –3.820 0.125 –30.553 0.000 x3 0.015 0 1.078 91.314 0.000 x1 0.243 0.006 0.416 38.792 0.000 x6 0.030 0.011 0.030 2.818 0.005 1) x1:千粒质量;x3:单株粒数;x6:主花序二分叉花枝数 2.4 主要农艺性状对单株粒质量的通径分析
结合逐步多元回归分析结果,对千粒质量、单株粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数与单株粒质量进行通径分析。结果表明(表4),这3个性状对单株粒质量的直接贡献的大小依次为:单株粒数、千粒质量和主花序二分叉花枝数。
表 4 苦荞单株粒质量与主要农艺性状的通径分析1)Table 4. Path analysis of grain weight per plant attributable to major agronomic traits of tartary buckwheat自变量 简单相
关系数直接通
径系数间接通径系数 合计 x1 x3 x6 x1 –0.067 0.416 –0.478 –0.005 –0.067 x3 0.907 1.078 –0.185 0.013 0.907 x6 0.441 0.030 –0.067 0.477 0.441 1) y:单株粒质量;x1:千粒质量;x3:单株粒数;x6:主花序二分叉花枝数 千粒质量x1对单株粒质量的直接作用较大,直接通径系数为0.416,但通过单株粒数对单株粒质量的间接负向作用也比较大,间接通径系数达–0.478。最终使得千粒质量的对单株粒数的总体效应较小,二者的简单相关系数仅为–0.067。
主花序二分叉花枝数x6对单株粒质量的直接作用较小,直接通径系数仅为0.030。它主要通过单株粒数较大的正向效应间接作用于单株粒质量,使主花序二分叉花枝数对单株粒质量的总体效应值达到了0.441。
单株粒数x3对单株粒质量的直接作用最大,直接通径系数达1.078,它通过千粒质量对单株粒质量的负向间接效应、通过主花序二分叉花枝数对单株粒质量的正向间接效应都比较小,且对单株产量和籽粒产量的总体效应也较大,分别达到0.907和0.236。因此在选育高产品种时,应重视单株粒数的提高。
2.5 RIL群体农艺性状的聚类分析及综合性状优良株系的初步筛选
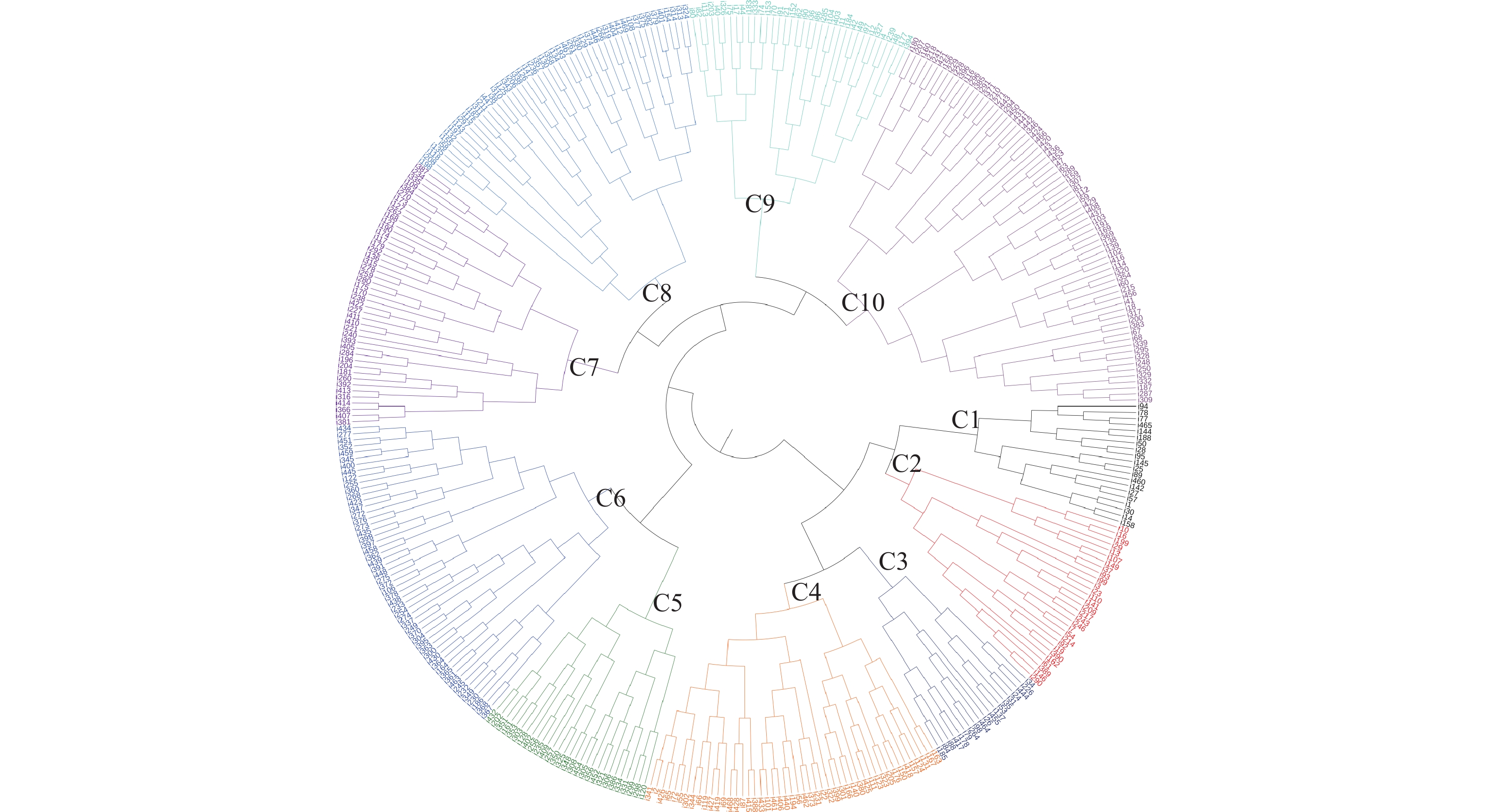
基于8个农艺性状的表型值对RIL群体的聚类分析显示,在欧式距离为45.5处可将399个株系体划分为5类,在欧式距离为22.0处可划分为10类(图2)。为了筛选到性状优良的株系,对10个类群间的农艺性状进行了方差分析(各性状平均值见表5),结果表明,C1类群的单株粒质量和单株粒数、C5和C6类群的千粒质量,C1和C2类群的主茎分枝数,C1、C3和C4类群的主花序二分叉花枝数以及C5类群的籽粒产量显著高于其他类群。C1类群综合性状良好,20个株系的单株粒质量为6.1~8.8 g,单株粒数为396.0~688.2,千粒质量为12.1~16.6 g,主花序二分叉花枝数为3.0~7.0,籽粒产量为1 687.6~3 406.1 kg·hm–2;C5类群的27个株系平均籽粒产量和千粒质量最高,籽粒产量在2 483.9~3 781.7 kg·hm–2之间,千粒质量在11.8~16.6 g之间。
表 5 苦荞RIL群体10个类群间农艺性状的差异1)Table 5. Agronomic trait differences of ten cluster groups in RIL population of tartary buckwheat类群 株系数 单株粒质量/
g千粒质量/
g株高/
cm单株
粒数主茎分
枝数顶三花
枝粒数主花序二分叉
花枝数籽粒产量/
(kg·hm–2)C1 20 7.4a 13.8d 117.2a 541.7a 6.7a 11.2b 5.6a 2 400.6c C2 29 5.9b 14.5d 107.2cd 406.2b 6.6a 16.3a 4.2cd 2 309.1cd C3 19 4.2c 12.0f 111.1bc 349.6c 5.3bc 8.1de 5.2a 1 666.0gh C4 48 5.5b 16.3c 115.0ab 338.1c 5.5b 8.6cd 5.1ab 2 722.3b C5 28 3.8c 18.6a 105.7d 201.8d 4.1e 8.7cd 3.8d 2 984.8a C6 53 3.7c 17.5b 113.6ab 216.7d 4.0e 6.7e 4.6bc 2 125.1de C7 36 3.1d 12.9e 90.3f 238.5d 5.5b 10.8b 2.7e 1 861.7fg C8 72 3.2d 15.6c 98.4e 210.5d 4.7d 8.9cd 4.3cd 1 996.3ef C9 44 2.4e 17.3b 84.7g 140.1e 5.0cd 9.3cd 1.9f 1 622.6h C10 50 4.0c 18.8a 98.7e 216.0d 6.4a 9.8bc 2.9e 2 216.8cde 1)同列数据后凡具有一个相同小写字母者,表示差异不显著(P>0.05, Duncan’s 法) 3. 讨论与结论
已有研究表明,苦荞籽粒产量及相关性状属于多基因控制的数量性状,受环境影响较大[8-9, 11-12],构建稳定的遗传群体,在多个环境下鉴定产量相关性状,有助于准确解析苦荞籽粒产量的遗传基础。作图群体双亲性状差异越显著,定位到主效QTL的可能性就越大[14-15, 18-19]。本研究结果显示,RIL群体亲本小米荞和晋荞2号的株高、主花序二分叉花枝数、主茎分枝数、千粒质量、单株粒质量和籽粒产量存在显著或极显著的差异,RIL群体8个主要农艺性状变异丰富,分布频率呈近似正态分布,多数性状表现为明显的双向超亲分离,表明所调查性状均是受微效多基因控制的数量性状。利用SSR分子标记对RIL群体的基因型分析也表明每个株系基本趋于纯合[20]。
农艺性状相关性分析表明,除千粒质量外,单株粒质量与其他产量构成因素均表现显著正相关,相关程度由大到小依次为单株粒数、株高、主花序二分叉花枝数、主茎分枝数、顶三花种子数,这与潘凡等[4]、李月等[7]和罗燕等[21]利用苦荞种质资源分析农艺性状相关性的结论基本一致,与杨玉霞等[2]和高金锋等[3]单株粒质量与株高、分枝数不相关,与千粒质量极显著正相关的研究结论不符。籽粒产量与单株粒质量、千粒质量、株高、单株粒数、主花序二分叉花枝数极显著正相关,这与李月等[7]和罗燕等[21]的研究结果一致,与汪灿等[6]籽粒产量与分枝数负相关的研究结果不一致,这可能与各研究的考察性状、供试材料数量以及种植地理环境等因素有关。
产量构成因子之间遗传关系复杂,不能仅凭相关系数的大小判断影响产量的主要因素。本研究中,籽粒产量与农艺性状的多元回归分析给出的决定系数R2仅为0.194,剩余因子为0.898,该值较大,说明还需进一步考察其他影响籽粒产量的重要性状(如密度、生育期等)。单株粒质量与农艺性状的多元回归分析表现出良好的拟合度(R2=0.964),表明本研究调查的性状基本上涵盖了影响单株粒质量的主要性状。进一步通径分析表明,单株粒数、千粒质量和主花序二分叉花枝数是影响单株粒质量的主要因素,其中单株粒数对单株粒质量的正向直接作用最大,而千粒质量和主花序二分叉花枝数则分别通过对单株粒数的负向和正向作用间接影响单株粒质量,说明多粒、多二分叉花枝数,千粒质量适中是高产苦荞的育种目标。
遗传分离群体中易于获得超亲和具有良好综合性状的株系,是筛选有较高育种价值株系的有效资源。本研究基于农艺性状的表型值,在欧式距离为22.0处将RIL群体的399个株系聚类为10类,方差分析结果表明,C5类群的27个株系的平均千粒质量和籽粒产量最高,其中25个株系是偏向高产亲本晋荞2号的厚果壳类型,且籽粒产量均超过晋荞2号,可用于高产苦荞的育种实践。C1类群20个株系的单株粒质量、单株粒数、主茎分枝数、主花序二分叉花枝数等性状综合表现良好,其中17个株系的果壳均是偏向母本小米荞的薄壳类型,且籽粒产量均高于小米荞,接近甚至超过高产亲本晋荞2号,可以应用于苦荞厚壳特性的遗传改良[17]。
-
表 1 亲本和重组自交系群体主要农艺性状的表型变异
Table 1 Phenotype variation of agronomic traits in the RIL population and their parents
性状 亲本 重组自交系群体 小米荞 晋荞2号 F1) 平均值 范围 变异系数/% 偏度 峰度 株高/cm 100.8±7.9 74.3±7.3 91.2** 102.8 66.1~137.8 13.1 0.08 –0.40 主茎分枝数 7.9±1.2 9.9±2.0 11.1** 5.2 2.5~8.5 24.0 0.19 –0.62 单株粒质量/g 2.6±1.1 3.7±1.4 5.8* 4.0 0.9~8.9 37.2 0.83 0.52 顶三花枝粒数 6.5±3.7 6.8±3.1 0.1 9.5 1.9~24.0 40.7 0.80 0.66 主花序二分叉花枝数 3.7±1.2 1.5±0.9 30.7** 3.9 0~8.0 37.9 –0.20 –0.39 单株粒数 190.2±74.5 176.4±53.6 0.3 258.4 57.1~688.2 42.4 1.16 1.31 千粒质量/g 13.5±1.2 20.6±2.0 143.9** 16.1 8.9~23.9 15.9 –0.21 –0.60 籽粒产量/(kg·hm–2) 1 272.1±254.0 1 806.0±188.1 8.6* 2 167.9 610.4~4 319.2 36.8 0.24 0.06 1) “*”和“**”分别表示亲本间同一性状差异达到 0.05 和 0.01 的显著水平(F 测验) 表 2 苦荞RIL群体各农艺性状的相关分析1)
Table 2 Correlation analysis of agronomic traits in the RIL population of tartary buckwheat
性状 单株粒质量 千粒质量 株高 单株粒数 主茎分枝数 顶三花枝粒数 主花序二分叉花枝数 千粒质量 –0.067 株高 0.551** –0.002 单株粒数 0.907** –0.443** 0.493** 主茎分枝数 0.390** –0.084 –0.085 0.387** 顶三花枝粒数 0.300** –0.167** –0.047 0.334** 0.315* 主花序二分叉花枝数 0.441** –0.160** 0.635** 0.443** –0.082 –0.163** 籽粒产量 0.354** 0.180** 0.340** 0.236** 0.074 –0.008 0.265** 1) “*”和“**”分别表示相关性达到 0.05 和 0.01 的显著水平 (Pearson 法) 表 3 苦荞单株粒质量对农艺性状的多元回归分析
Table 3 Multiple stepwise regression analysis of grain weight per plant attributable to major agronomic traits of tartary buckwheat
模型 自变量1) 偏回归
系数标准
误差通径
系数t P 1 常量 0.824 0.081 10.160 0.000 x3 0.012 0 0.907 42.938 0.000 2 常量 –3.763 0.124 –30.237 0.000 x3 0.015 0 1.092 101.042 0.000 x1 0.244 0.006 0.417 38.620 0.000 3 常量 –3.820 0.125 –30.553 0.000 x3 0.015 0 1.078 91.314 0.000 x1 0.243 0.006 0.416 38.792 0.000 x6 0.030 0.011 0.030 2.818 0.005 1) x1:千粒质量;x3:单株粒数;x6:主花序二分叉花枝数 表 4 苦荞单株粒质量与主要农艺性状的通径分析1)
Table 4 Path analysis of grain weight per plant attributable to major agronomic traits of tartary buckwheat
自变量 简单相
关系数直接通
径系数间接通径系数 合计 x1 x3 x6 x1 –0.067 0.416 –0.478 –0.005 –0.067 x3 0.907 1.078 –0.185 0.013 0.907 x6 0.441 0.030 –0.067 0.477 0.441 1) y:单株粒质量;x1:千粒质量;x3:单株粒数;x6:主花序二分叉花枝数 表 5 苦荞RIL群体10个类群间农艺性状的差异1)
Table 5 Agronomic trait differences of ten cluster groups in RIL population of tartary buckwheat
类群 株系数 单株粒质量/
g千粒质量/
g株高/
cm单株
粒数主茎分
枝数顶三花
枝粒数主花序二分叉
花枝数籽粒产量/
(kg·hm–2)C1 20 7.4a 13.8d 117.2a 541.7a 6.7a 11.2b 5.6a 2 400.6c C2 29 5.9b 14.5d 107.2cd 406.2b 6.6a 16.3a 4.2cd 2 309.1cd C3 19 4.2c 12.0f 111.1bc 349.6c 5.3bc 8.1de 5.2a 1 666.0gh C4 48 5.5b 16.3c 115.0ab 338.1c 5.5b 8.6cd 5.1ab 2 722.3b C5 28 3.8c 18.6a 105.7d 201.8d 4.1e 8.7cd 3.8d 2 984.8a C6 53 3.7c 17.5b 113.6ab 216.7d 4.0e 6.7e 4.6bc 2 125.1de C7 36 3.1d 12.9e 90.3f 238.5d 5.5b 10.8b 2.7e 1 861.7fg C8 72 3.2d 15.6c 98.4e 210.5d 4.7d 8.9cd 4.3cd 1 996.3ef C9 44 2.4e 17.3b 84.7g 140.1e 5.0cd 9.3cd 1.9f 1 622.6h C10 50 4.0c 18.8a 98.7e 216.0d 6.4a 9.8bc 2.9e 2 216.8cde 1)同列数据后凡具有一个相同小写字母者,表示差异不显著(P>0.05, Duncan’s 法) -
[1] PRZYBYLSKI R, GRUCZYNSKA E. A review of nutritional and nutraceutical components of buckwheat[J]. Eur J Plant Sci Biotechnol, 2009, 3: 10-22.
[2] 杨玉霞, 吴卫, 郑有良, 等. 苦荞主要农艺性状与单株籽粒产量的相关和通径分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, 36(16): 6719-6721. [3] 高金锋, 张慧成, 高小丽, 等. 西藏苦荞种质资源主要农艺性状分析[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2008, 2(31): 1-5. [4] 潘凡, 石桃雄, 陈其皎, 等. 苦荞种质主要农艺性状的变异及其对单株粒质量的贡献研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 2015, 33(6): 829-893. [5] 杨明君, 杨媛, 郭忠贤, 等. 旱作苦荞麦籽粒产量与主要性状的相关分析[J]. 内蒙古农业科技, 2010(2): 49-50. [6] 汪灿, 胡丹, 杨浩, 等. 苦荞主要农艺性状与产量关系的多重分析[J]. 作物杂志, 2013(6): 18-22. [7] 李月, 石桃雄, 黄凯丰, 等. 苦荞生态因子及农艺性状与产量的相关性分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2013, 26(1): 35-41. [8] 唐链, 梁成刚, 梁龙兵, 等. 苦荞株高及主茎分枝数的遗传相关分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(9): 129-132. [9] 梁龙兵, 陈其皎, 石桃雄, 等. 小米荞和晋荞2号杂交后代苦荞主花序特征的遗传研究[J]. 河南农业科学, 2016, 45(5): 13-17. [10] 杜晓磊, 张宗文, 吴斌, 等. 苦荞SSR分子遗传图谱的构建及分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(21): 61-65. [11] 杜晓磊. 来源苦荞SSR和AFLP遗传图谱构建及其重要农艺性状的QTL分析[D]. 太原: 山西大学, 2013. [12] 闫玉莹. 利用SNP标记构建苦荞高密度遗传图谱及重要农艺性状的QTL分析[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2015. [13] 陈燕华, 黄大辉, 邱永福, 等. 水稻主要农艺性状的QTL分析[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2014, 35(6): 42-51. [14] CUI F, ZHAO C, DING A, et al. Construction of an integrative linkage map and QTL mapping of grain yield-related traits using three related wheat RIL populati-ons[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 127(3): 659-675.
[15] XING G, ZHOU B, WANG Y, et al. Genetic components and major QTL confer resistance to bean pyralid (Lamprosema indicata Fabricius) under multiple environments in four RIL populations of soybean[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2012, 125(5): 859-875.
[16] 李秀莲, 史兴海, 朱慧珺. 国鉴苦荞新品种晋荞麦2号的选育及制种技术[J]. 作物杂志, 2011(5): 128-129. [17] 陈庆富, 陈其皎, 石桃雄, 等. 苦荞厚果壳性状的遗传及其与产量因素的相关性研究[J]. 作物杂志, 2015(2): 27-31. [18] ECHEVERRY-SOLARTE M, KUMAR A, KIANIAN S, et al. New QTL alleles for quality-related traits in spring wheat revealed by RIL population derived from supernumerary × non-supernumerary spikelet genotypes[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2015, 128(5): 893-912.
[19] LONG Y, SHI J, QIU D, et al. Flowering time quantitative trait loci analysis with multi-environments in oilseed Brassica and genome-wide alignment with Arabidopsis[J]. Genetics, 2007, 177(4): 2433-2444.
[20] 梁龙兵. 苦荞主要农艺性状的遗传及其SSR分子标记研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2016. [21] 罗燕, 敖学成. 秋播苦荞麦单株性状与株产种量的相关通径分析[J]. 牧草与饲料, 2012, 6(2): 31-34.



 下载:
下载: